Abstract
Due to health and pollution concerns of aquatic environments related to the presence of heavy metal toxic ions, the necessity of developing devices able to detect and to monitor such kinds of species has recently gained importance. Carbon paste electrodes (CPEs) a starting approach to obtain new ion-selective devices by supporting materials like bentonite and/or clay; which become sensitive to lead(II) when they are suitably modified by chemical treatments to obtain different hybrid materials. In this work, two natural clays and three different hybrid materials were produced and then were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to assess their physico-chemical properties. After this stage, the electrochemical characterization of the modified CPEs using hybrid materials was performed by cyclic voltammetry, using the standard Fe(CN)64−/Fe(CN)63− redox couple. Subsequently, this study performed electrochemical experiments on lead(II) containing solutions, to test the ability of the examined CPEs to detect this toxic ion present in very low amounts. Lead(II) exhibited a reversible two electron oxidation/reduction behaviour in the cyclic voltammetry analyses and a reasonably good linear behaviour of the current associated with the oxidation peak as a function of its concentration (5.0–40.0 μg/L). The detection limit was found to vary in the range of 3–5 μg/L for the different modified CPEs. The presence of several co-existing ions showed that an interference variation had occurred. These results, therefore, show a restriction of the selectivity of the electrode up to a certain extent in the lead(II) detection. Finally, tap water with spiked lead(II) was analyzed to verify the suitability of the electrodes in the low level detection of lead(II) from real matrix samples.
1. Introduction
Contamination of aquatic environments with heavy metal toxic ions is one of most serious environmental concerns in recent years. Enhanced industrial activities pose further environmental threats to our water bodies [1]. Industrial effluents that are incompletely treated or untreated are often discharged to the aquatic environment causing detrimental water quality. This ultimately causes adverse effects to human health as well as the aquatic ecosystem. Heavy metals such as lead(II) are highly toxic to human health and an excessive intake of lead(II) causes several severe health problems. Lead poisoning in human being is reflected by neurological, hematological, and renal side effects, viz., genitive and behavioral impairment of infants and children [2], restraint of the formation of hemoglobin [3], and chronic kidney dysfunction or hyperuricemia [4]. Lead enters into the biosystem through all means i.e., air, water, and soil. It was reported previously that a large number of deaths had occurred during the period of 2001 to 2003 in Washington, DC because of the leakage of lead into the drinking water system [5]. Furthermore, the high biological half-life of lead tends to lead to long term effects in biological systems, e.g., lead persists in bone for more than 20 years [6]. It is interesting to note that about 20% of lead exposure to human beings is through contaminated drinking water [7]. Therefore, an efficient, selective, inexpensive, and in situ detection system is needed and is important to protect the environment/ecosystem and in particular human health.
Recently, colorimetric [8,9] or surface-enhanced Raman scattering [10] methods have been developed using advanced materials for the trace detection of lead(II) from aqueous solutions. Similarly, the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technique was introduced with the multi-metallic layers of Au-Ag-Au nanostructures in chitosan-graphene oxide (CS-GO). The proposed tri-metallic nanostructure was able to boost the shift in the SPR angle, where it is increased up to 3.5° for 1 ppm of lead(II) [11].
Electrochemical devices have shown promise as alternatives in the detection of several heavy metal toxic ions with achievable selectivity coupled with the lower detection limit down to sub-trace levels. These are found to be useful in the electro-Fenton process, employing an advanced double hydroxide modified carbon-felt cathode [12]. The greatest drawback of utilizing the electrochemical methods are with its poor selectivity since the interference of co-existing ions hampers the detection of target ion(s) and limited its practical implacability in real matrix samples [13,14,15]. However, the modifications of the working electrodes with the nano- or hybrid materials or nano-composites pave the way for the efficient and selective detection of several target ions from aqueous solutions [13,14,16]. In one study, a micro/nano crystalline boron-doped diamond electrode was optimized for the detection of lead using square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry. The detection limit was found to be 1 μg/L of lead(II) [6]. Reduced graphene oxide (RGO) was modified with gold to obtain the graphene-Au nano-composite. The nano-composite was electrochemically coated onto the surface of a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) and the modified GCE (G-Au/GCE) was introduced for the detection of lead(II) in 0.1 mol/L acetate buffer (pH 5.3) under the square wave anodic stripping voltammetric (SWASV) measurements. The electroanalytical method provides a detection limit of lead(II) of 0.8 nM [17]. Indeed, the G-Au/GCE exhibited fairly good selectivity for lead(II) detection even in the presence of Cu2+. Similarly, mesoporous MnFe2O4 nanocrystalline clusters (NC) are synthesized and utilized in the modification of GCE [18]. Furthermore, the modified GCE is utilized in the selective detection of lead(II) using square wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SWASV) that indicated that the electrode is highly sensitive for lead(II) with the LOD (limit of detection) of 0.054 μM. Moreover, the presence of several cations Cd2+, Zn2+, and Hg2+ did not affect the lead(II) detection. Lead(II) and cadmium(II) are detected using NiO (nickel oxide nano-structures i.e., rods, balls, and flakes) modified glassy carbon electrodes [19]. Results indicate that the GCE modified with NiO balls possesses an enhanced redox ability having a fairly high electron transferability, which enables its suitable electrochemical detection of lead(II) and cadmium(II). Furthermore, the detection ability for its highest detection sensitivity to lead(II) (13.46 A/M) and cadmium(II) (5.10 A/M) with the lowest detection limit (DL) of 0.08 μM for lead(II) and 0.07 μM for cadmium(II) is obtained for the NiO ball modified GCE. The cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticle-decorated graphene hybrid is synthesized hydrothermally and the GCE is modified with the hybrid material [20]. The modified GCE is used for the simultaneous detection of cadmium(II), lead(II), copper(II), and mercury(II) from aqueous solutions under the differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetric (DPASV) technique. The oxidation peaks of cadmium(II), lead(II), copper(II), and mercury(II) onto the CeO2/Graphene GCE is obtained at the applied potentials of ca. −0.76, −0.54, −0.06, and 0.31 V versus the Hg/Hg2Cl2 reference electrode that enables the detection of these cations simultaneously. A dual electrochemical and colorimetric technique is introduced for the simultaneous detection of lead(II), cadmium(II), and copper(II). The lead and cadmium are detected electrochemically using a bismuth modified boron doped diamond electrode whereas the copper(II) is detected by the catalytic etching of silver nanoplates (AgNPls) by thiosulfate (S2O32−). This is performed using a new microfluidic paper-based analytical device (μPAD) [21]. The carbon paste electrode (CPE) is suitably modified with the poly(1,8-diaminonaphthalene) and bismuth film (Bi-Poly1,8-DAN/CPE) and employed in the detection of lead(II) using square wave voltammetry in acidic medium [22]. The analytical method provided a detection limit of 0.3 μg/L for lead(II) with required reproducibility of the results. Therefore, the present communication aims to describe the efficacy of indigenous hybrid materials by exploiting natural clay samples, bentonite (BC) and local clay (LC), as precursor materials. The carbon paste electrode is suitably modified using the hybrid materials (BCH, LCH, and LCAH) to obtain the modified CPEs. The modified CPEs are found to be reliable and cost effective devices for the trace level detection of lead(II) from aqueous solutions. The applicability of the device is further appealing for its in situ detection of lead(II), and interfering ions and tap water samples are tested for its application in real matrix analysis.
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Reagents and Apparatus
Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (HDTMA), carbon powder (Glassy Spherical Powder 2–12 micron), and titanium wire (0.81 mm) were procured from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA. Paraffin oil, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA), and glycine were purchased from HiMedia Chemicals, Mumbai, India. Cadmium nitrate, copper sulphate, lead nitrate, and potassium chloride were procured from Merck, Mumbai, India. Ferric nitrate was obtained from Loba Chemie, Kolkata, India and aluminium trichloride was obtained from Fisher Scientific, Mumbai, India. Bentonite (BC) and local clay (LC) were collected from the Bhuj, Gujarat and Phullen, Champhai district, Mizoram, India, respectively. Cation exchange capacities (CEC) of bentonite and local clay were found to be 69.35 and 46.38 meq/100 g of bentonite and local clay, respectively [23]. The deionized water was further purified (18 MΩ-cm) using a Millipore water purification system (Milli-Q+).
A Potentiostat/Galvanostat (BioLogic Science Instruments, Seyssinet-Pariset, France, Model: SP 50) was used for electrochemical measurements. The electrochemical data obtained by the potentiostat/galvanostat was then analyzed using the ECLab® computer software (Biologic, Seyssinet-Pariset, France). Ag|AgCl (saturated) and platinum electrodes were used as reference and supporting electrodes in a cell assembly. CPE was further modified with the hybrid material and was used as the working electrode.
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Synthesis of Hybrid Materials
BC and LC were loaded with HDTMA by the wet cation exchange process and named as BCH and LCH, respectively [24]. Local clay was also pillared with aluminium and then loaded with the HDTMA to obtain the inorgano-organo-clay sample (LCAH) [25]. The hybrid materials along with the pristine clay samples were characterized by FT-IR using a FT-IR spectrometer (Bruker, Tensor 27, Billerica, MA, USA) by the KBr disk method and by X-ray diffraction analysis using the X-ray diffractometer (PANalytical, Almelo, The Netherland). Cu Kα radiation with wavelength 1.5418 Å was employed for the X-ray diffraction study. The specific surface area, pore volume, and pore size of the solids were obtained by the nitrogen adsorption and desorption method using the BET (Brunauer, Emmett and Teller) Analyzer (Macsorb HM-1201, Mountech, Tokyo, Japan). The surface morphology of the hybrid materials along with the pristine clay was obtained by taking SEM images of these solids. For this purpose, a Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (S-4700, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) was employed. The elemental composition of pristine clay was obtained by XRF analysis (X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer Model: ZSX 100e, Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan).
2.2.2. Fabrication of the Working Electrode
The carbon paste electrode was modified with the hybrid materials. The detailed description of the modification is described elsewhere [23]. The carbon paste electrodes were modified with pristine BC, pristine LC, BCH, LCH and LCAH and named as CPE-BC, CPE-LC, CPE-BCH, CPE-LCH, and CPE-LCAH, respectively. The surface of the working electrode was polished with a glassy paper prior to its electrochemical use. At the completion of each experiment, the open end of the tube was also cut by a sharp knife to obtain an unexposed active surface.
2.2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
The cyclic voltammetric measurements were conducted for the detection of lead(II). The cyclic voltammograms were recorded with an exciting potential of ±2.0 V against an Ag|AgCl (satd.) reference electrode. The electrochemical cell contained a lead(II) solution (50.0 mL) having a known concentration and pH in 1.0 mol/L KCl. Prior to recording the cyclic voltammograms, the experimental lead(II) solution was deoxygenated using a stream of high purity nitrogen gas (99.99%) for 10 min. The modified CPE performance was assessed with the standard Fe(CN)64−/Fe(CN)63− solutions (2.0 mmol/L of each). The presence of 5 fold excess of interfering ions (cations Cd(II), Cu(II), Mn(II), and Fe(III), and anions EDTA, phosphate, and glycine) was studied, independently, in the detection of lead(II) with a concentration of 30.0 μg/L in 1.0 mol/L KCl at pH 6.0 and with a scan rate 100 mV/s. Moreover, the stability of the carbon paste electrode or dissolution of carbon paste was also observed by monitoring the dissolution of carbon in the bulk solution by simple filtration, which indicated that almost a negligible amount of carbon deposition occurred on the 0.25 µm filter paper. The electrochemical data was obtained for six replicate samples and the error was indicated as ±3σ values. Additionally, some trials were conducted using a different electrode as well.
2.2.4. Real Tap Water Analysis
The tap water sample was collected from the laboratory tap. It was analyzed by AAS (Fast Sequential Atomic Absorption Spectrometer, Model AA240FS, Varian, Palo Alto, CA, USA) for various metal ions. It was also subjected to TOC (total organic carbon) analysis using the TOC analyzer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan; Model: TOC-VCPH/CPN). The tap water was used in the lead(II) solution preparation and spiked with various concentrations of lead(II), i.e., 5.0 to 40.0 μg/L having 1.0 mol/L KCl and pH 6.0.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Hybrid Materials
The XRF results for the pristine bentonite and local clay are given in Table 1. It is evident from Table 1 that both clay samples contain silicon, aluminium, and iron oxides. In addition, a notable amount of Na, Mg, and K are also present, which are likely to be the exchangeable cations lying within the interspace of the clay. Moreover, it is noted that the composition of metal oxides for both clay materials is found to be almost identical.

Table 1.
Various components present in bentonite and local clay samples as estimated by the XRF (X-ray Fluorescence) analysis.
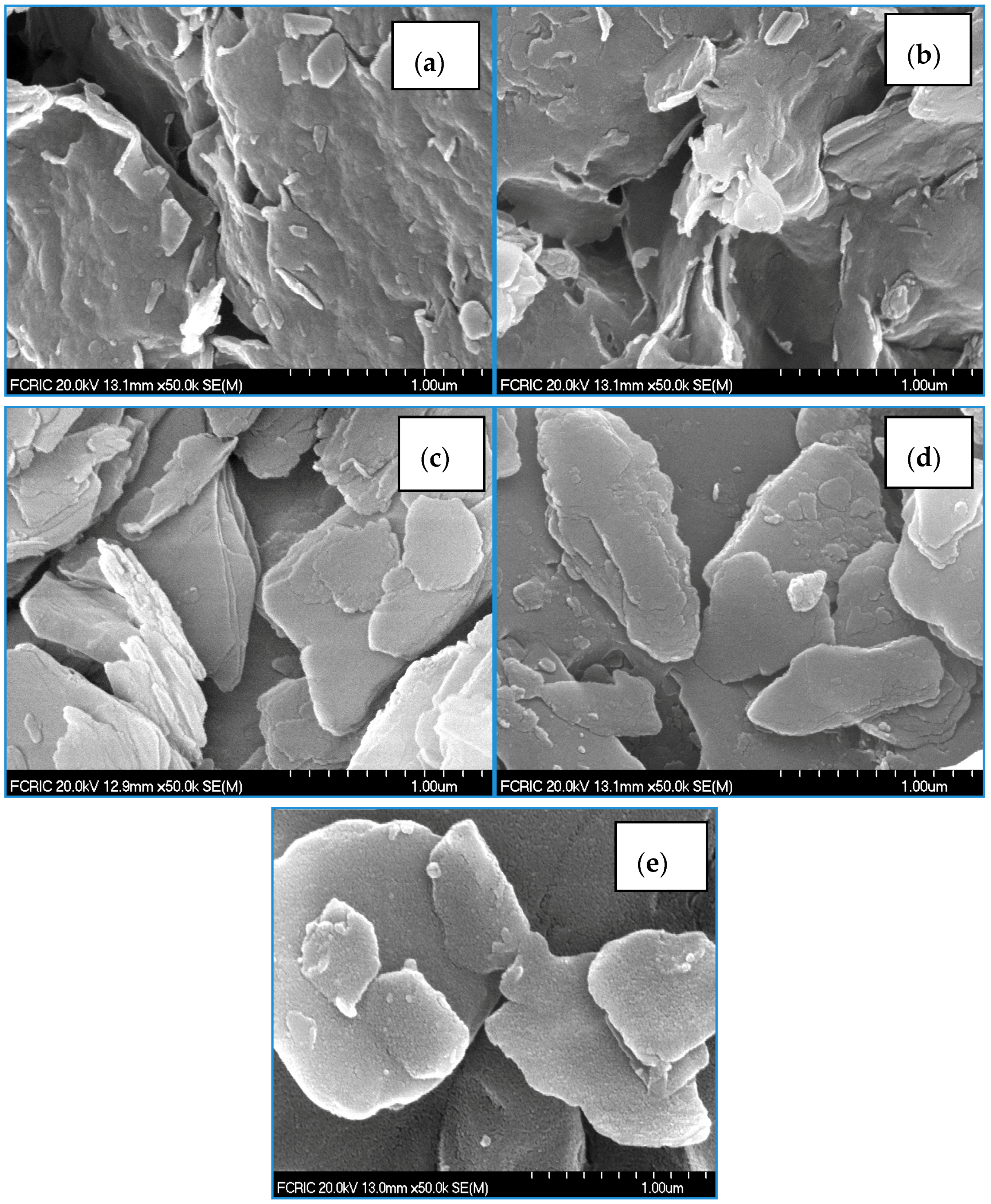
The surface morphology of the pristine clays and their hybrid materials is illustrated in Figure 1a–e. The FE-SEM images clearly revealed that the BC and LC possess relatively compact and ordered surface structures, while the modified solids show more heterogeneous and disordered surface structures. It is assumed that the water molecules or the exchangeable cations present within the interspace of clay are exchanged with the HDTMA cations, and consequently are firmly anchored within the interspace of clay. It is important to note that the surface structure of the modified solids seems to be more porous in nature. In addition, the microtopography of LCAH is distinct with very fine particles on the surface, and aluminium is possibly aggregated/immobilized as aluminium oxide on the surface (Figure 1e).
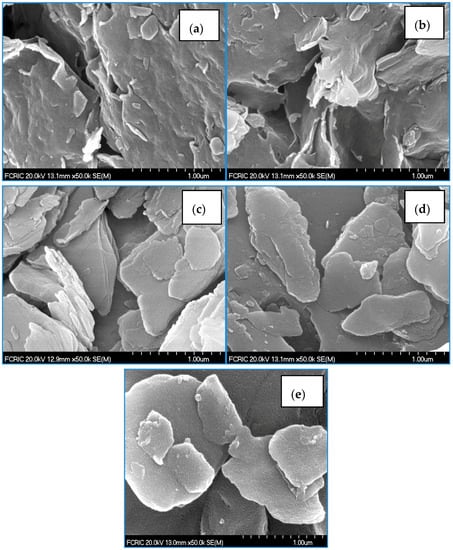
Figure 1.
Scanning electron microcopy (SEM) images of (a) BC; (b) BCH; (c) LC; (d) LCH and (e) LCAH. Reproduced with permission from [24], Copyright Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015.
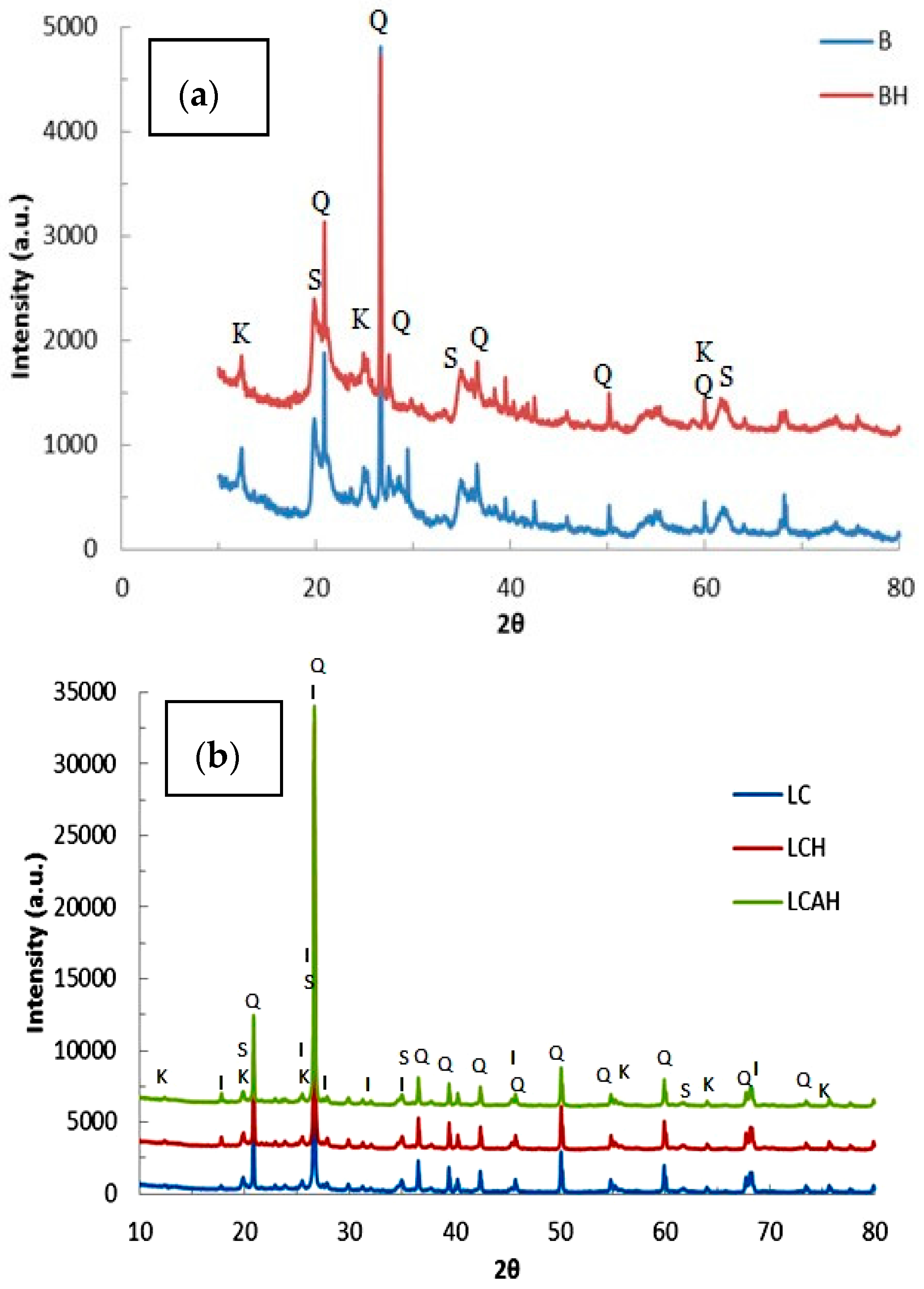
X-ray diffraction data for the solids, viz., BC, BCH, LC, LCH, and LCAH are shown in Figure 2a,b for the bentonite and local clay based solids, respectively. Sharp X-ray diffraction peaks are observed for these solids with well-defined d-spacings. The XRD data of bentonite and local clays are matched with the standard ICDD (International Centre for Diffraction Data) reference pattern. It is also seen that both clay samples contain varying proportions of quartz, smectite, illite, and kaolinite minerals, observed as the characteristic peaks in the XRD diffraction pattern. Furthermore, quantitatively, it is seen that bentonite has 43.71%, 23.17%, 1.73%, and 31.39% of quartz, smectite, kaolinite, and illite, respectively. Similarly, the local clay is composed of 79.35%, 6.20%, 0.45%, and 14.01% of quartz, smectite, kaolinite, and illite, respectively. Other visible diffraction peaks are, perhaps, due to the presence of some impurity. The XRD pattern of the modified clay samples is almost similar to its pristine clay form, with modest alterations in d-values and intensities of peaks. It is further observed that bentonite is comprised of a relatively higher percentage of smectite and illite mineral phases in comparison with the local clay sample, whereas the local clay possessed a high content of silica compared to bentonite. The variation in the content of the mineral phases ultimately affects the specific properties of the clay materials. The specific surface area and pore sizes are, apparently, also controlled by the presence of specific mineral phases.
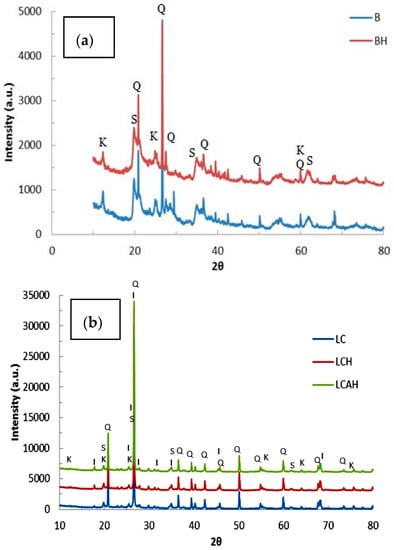
Figure 2.
X-ray diffraction pattern of (a) bentonite based and (b) local clay based samples [S: Smectite; K: Kaolinite; Q: Quartz; and I: Illite] [24], Copyright Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015.
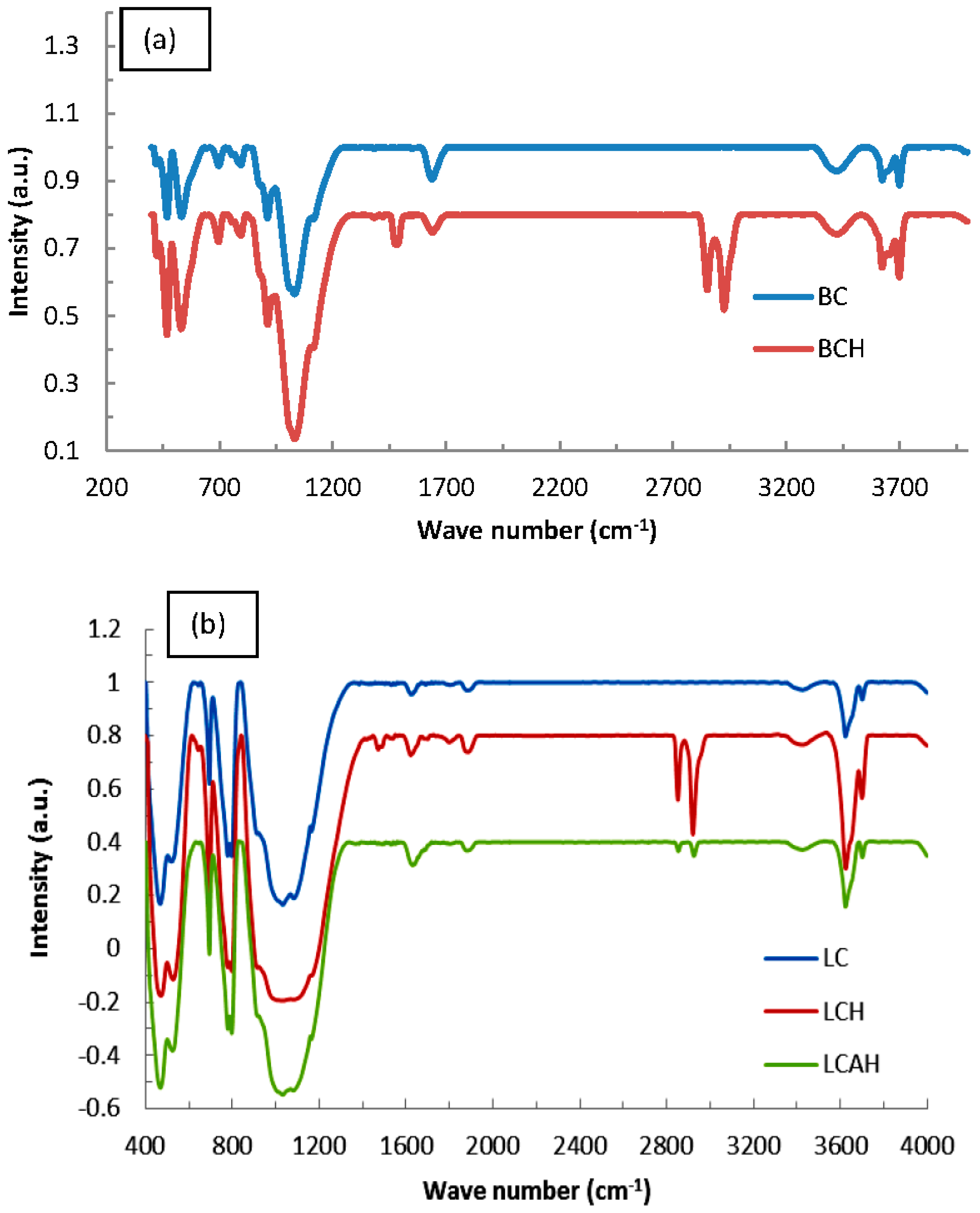
FT-IR spectra of bentonite and local clay based samples are illustrated in Figure 3a,b, respectively. Bands at 1110 and 1030 cm−1 are due to the Si–O stretching vibrations. Similarly, a pair of IR bands centred around 695 cm−1 and 795 cm−1 is due to the quartz Si–O vibrations. Similarly, a vibration peak at 753 cm−1 corresponds to Si–O deformation [26,27]. A broad peak at 3420 cm−1 belongs to the OH stretching of H-bonded water molecule(s). A vibration peak at 1640 cm−1 belongs to the OH deformational mode of water [28,29]. This clearly indicates the presence of hydroxyl groups within the clay sheets, while water molecules are present within the interlayer space of the clay. It is interesting to note that the modified samples, i.e., BCH, LCH, or LCAH possess two distinct vibration bands at 2925 and 2850 cm−1 that are associated with the asymmetric and symmetric C–H stretching vibrations of the –CH2 group, respectively. A band at 1480 cm−1 is assigned to the bending mode of the CH2 group [26,29,30]. This confirms the introduction of the HDTMA molecule within the clay network of all these modified solids.
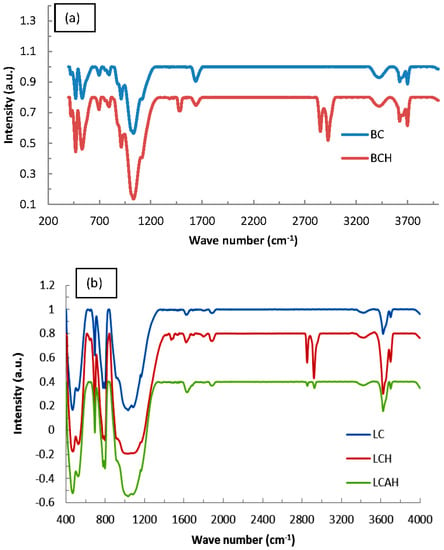
Figure 3.
FT-IR spectra of (a) bentonite and (b) local clay based materials [24], Copyright Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015.
The BET specific surface area along with the pore size of these solids, viz., BC, BCH, LC, LCH, and LCAH are obtained by the nitrogen adsorption and desorption method. The results are illustrated in Table 2. Table 2 reveals that pristine bentonite possessed a relatively high BET specific surface area with a low pore size value. The high specific surface area of BC is due to the presence of a higher percentage of mineral phases, viz., smectite, kaolinite, and illite compared to the quartz/silica content. However, the HDTMA-modified bentonite shows a remarkable decrease in the specific surface area and an increase in pore size (diameter). This is due to the fact that the HDTMA occupies the interspace, leading to a decrease in the specific surface area, whereas the propping up of the interlayer caused an enhancement of the pore size of the solid. On the other hand, the unmodified local clay (LC) shows very low specific surface area, i.e., 2.94 m2/g. This is due to the high silica/quartz content of the local clay sample. However, the presence of HDTMA or Al-HDTMA caused a relative increase in the specific surface area as well as a decrease in the pore size of the modified solids.

Table 2.
BET pore size and specific surface area of the pristine clay and hybrid materials.
3.2. Electrochemical Response of Modified CPE
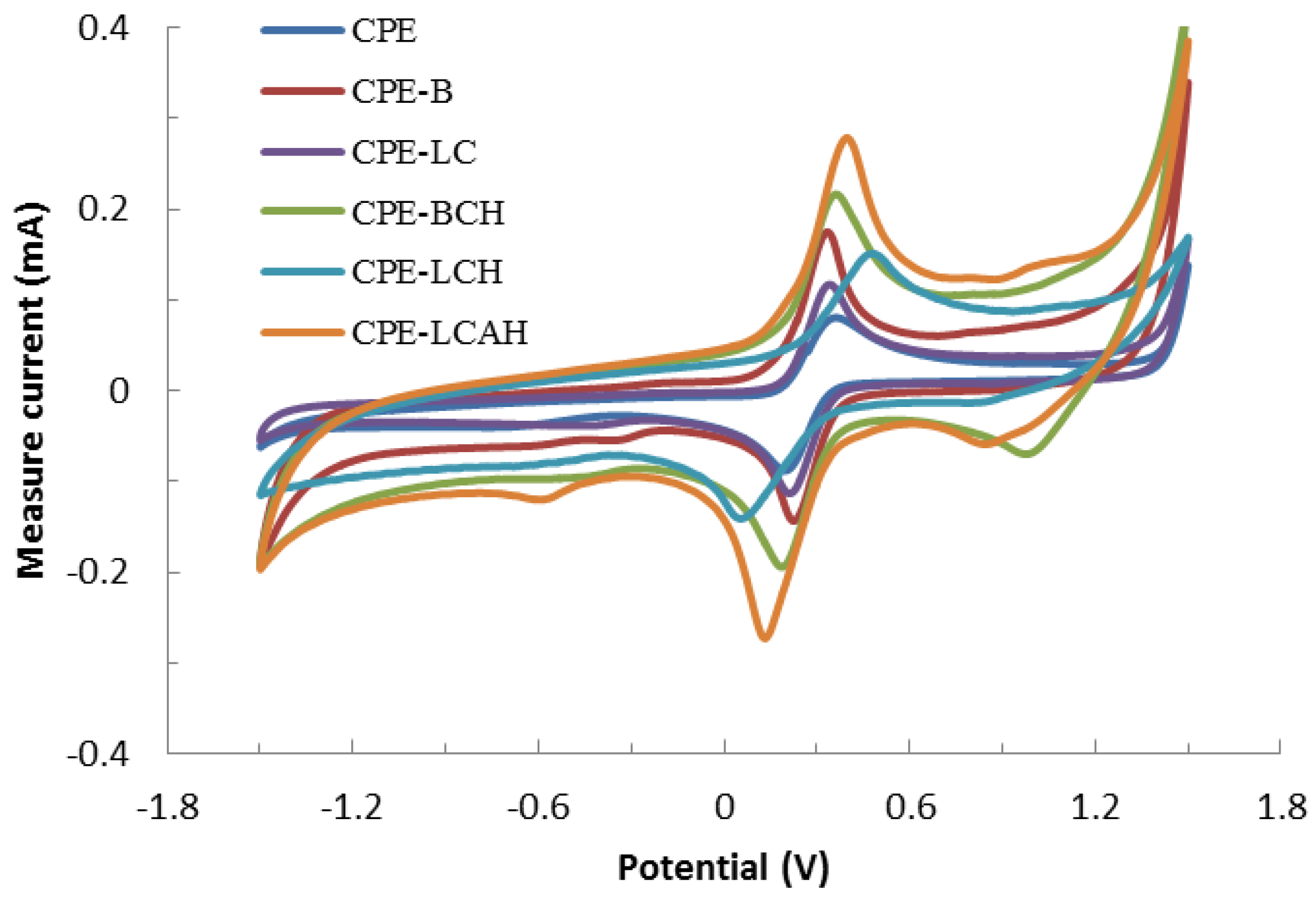
The electrochemical response of various carbon paste electrodes are obtained for the 2.0 mmol/L solution of the Fe(CN)64−/Fe(CN)63− redox couple to analyze the performance of the modified CPEs along with the bare CPE. The corresponding cyclic voltammograms are shown in Figure 4. Figure 4 indicates that a fairly good electrochemical response was obtained using the modified carbon paste electrodes since well-defined cathodic and anodic peaks were obtained in the voltammograms. It was further evident that when the electrodes are modified with hybrid materials, BCH, LCH, and LCAH exhibited relatively enhanced electrochemical signals as the concomitant cathodic or anodic currents also increased significantly for the hybrid material modified CPEs compared to the bare CPE of the BC or LC modified CPEs. This indicated that the hybrid materials have rendered an enhanced electrical conductivity which eventually results in the enhanced electrochemical signals. It also implied that the hybrid materials introduced with the carbon paste electrodes eventually enhanced the electron transfer kinetics with an enhanced surface sensitivity [17,31]. Therefore, the CPE modified with hybrid materials showed an enhanced sensitivity of detection and could be useful materials in the development of electrochemical sensors [18].
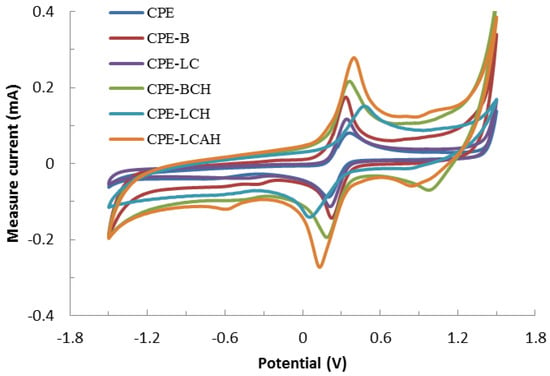
Figure 4.
Electrochemical behavior of various carbon paste electrodes modified with hybrid materials using the 2.0 mmol/L Fe(CN)64−/Fe(CN)63− at the scan rate of 100 mV/s.
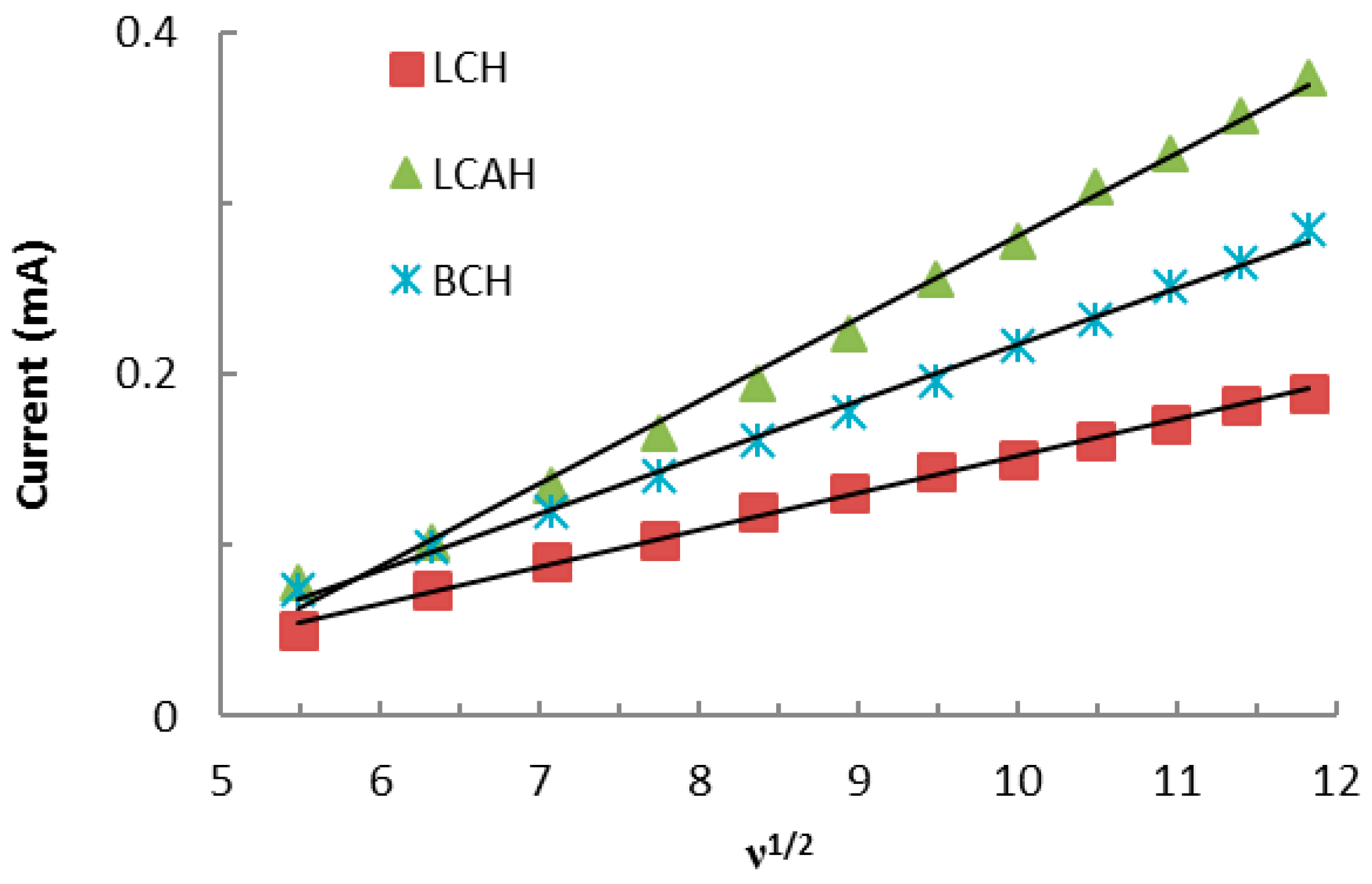
Furthermore, the Fe(CN)64−/Fe(CN)63− redox couple was utilized for the scan rate studies. The scan rates were varied from 30 to 140 mV/s using a constant concentration of Fe(CN)63−/Fe(CN)64− 2.0 mmol/L solution while employing various hybrid material modified carbon paste electrodes, i.e., BCH, LCH, and LCAH at neutral pH conditions. The results are shown in Supplementary Materials Figure S1. It is evident that an identical CV (cyclic voltammogram) pattern is obtained for these modified CPEs (Figure S1), however, the anodic/cathodic peak current is proportional to the scan rate. Moreover, the scan rate studies are also commensurate with the electroactive surface area of the modified CPEs [32]. Therefore, the mass transfer study using the hybrid material modified carbon paste electrode was performed (Figure 5). It is clear from Figure 5 that the anodic (or cathodic, not shown in the figure) current responses were directly proportional to the square root of the scan rate (ν1/2). Therefore, it followed the Randle-Sevick Equation (1) [23]:
where Im is the peak cathodic current (A); n is the number of electrons involved in reduction; D is the diffusion coefficient of Fe(CN)64−/Fe(CN)63− (cm2/s) in aqueous media and equal to 6.70 × 10−7 cm2/s; ν is the scan rate (V/s); C is the concentration of electroactive species (mol/cm3); and A is the electroactive surface area of the working electrode (cm2). The slope of the straight lines (cf. Figure 5) could help in deducing the electroactive surface area of the employed electrodes (A). The electroactive surface area of the modified electrodes was then calculated using the slope of these straight lines (cf. Figure 5) and the results are shown in Table 3. These results serve as a quantitative measure of the active surface area of the electrode modified with the hybrid materials. Furthermore, the LCAH apparently showed an almost 2.2 times higher surface area compared to the LCH-modified CPE. The electroactive surface area of modified CPEs is perhaps proportional to the amount of electroactive sites available on the electrode surface and thus enables it for electron transfer reactions [33].
Im = 2.69 × 105 × n2/3 × ν1/2 × D1/2 × C × A
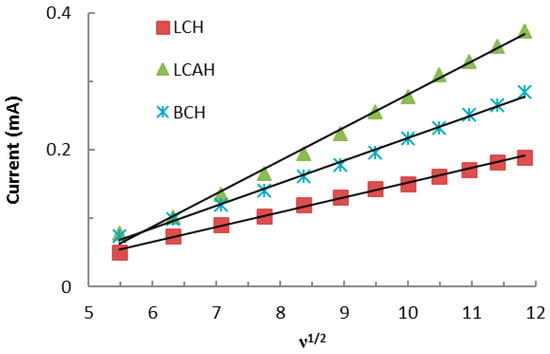
Figure 5.
Linear curves obtained between the ν1/2 against the current for the redox behavior of Fe(CN)64−/Fe(CN)63− using various hybrid material modified electrodes.

Table 3.
Randle–Sevick linear equation and electroactive surface area obtained for the redox behavior of the Fe(CN)64−/Fe(CN)63− couple, for the hybrid material modified carbon paste electrodes.
3.3. Electroanalytical Response of Various Modified Carbon Paste Electrodes
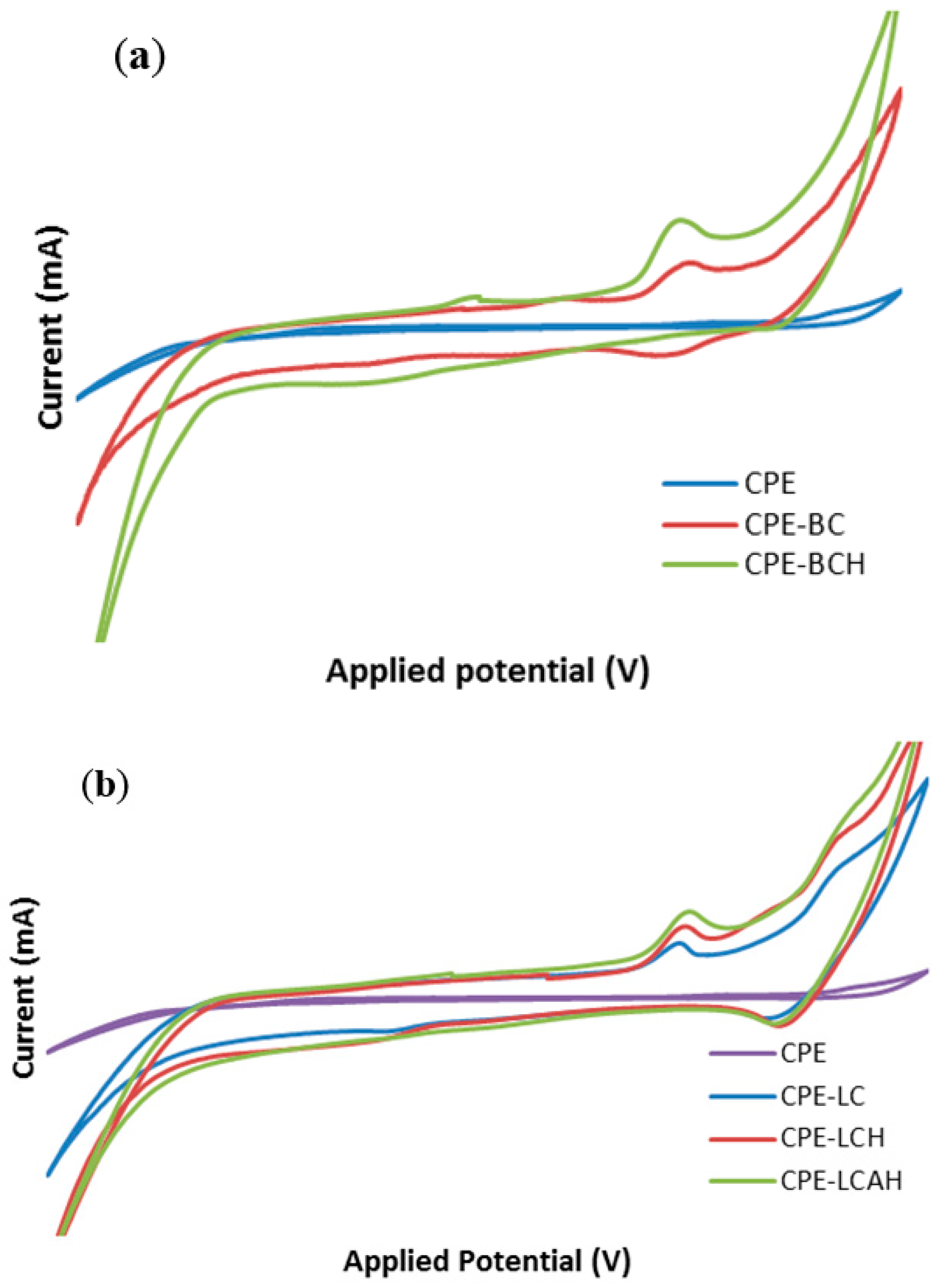
The comparative electrochemical response of various modified and bare carbon paste electrodes was studied for lead(II) at pH 5.0. The results are shown in Figure 6. It was interesting to observe that the lead(II) showed almost no electrochemical signal with the bare CPE, however, the response is significantly increased with the modified CPEs. This could be ascribed to the fact that the lead(II) was not adsorbed efficiently onto the bare CPE surface and hence, it provided no or negligible electrochemical signal. However, the modified CPEs exhibited a significantly high electrochemical response indicative of an effective adsorption of lead(II) on the electrode surface and thus results in an enhanced signal. The enhanced electrical current was also attributed to the enhanced specific electro active surface area of the modified electrodes, as corroborated by the scan rate studies (vide supra). The other studies demonstrated that the CPEs modified with hybrid materials achieved significantly high electro active surface areas, which results in an enhanced electrochemical response of the modified electrode [13]. Moreover, it was also noted that the peak current was relatively higher for the hybrid materials BCH, LCH, or LCAH modified CPEs compared to their respective pristine clay modified CPEs. Previously, it was reported that RGO/GCE and G-Au/GCE had shown significantly higher current compared to the bare GCE for lead(II) detection. In addition, it was suggested that it was difficult for lead(II) to adsorb onto the bare GCE, whereas it strongly adsorbed onto the modified GCE [17].
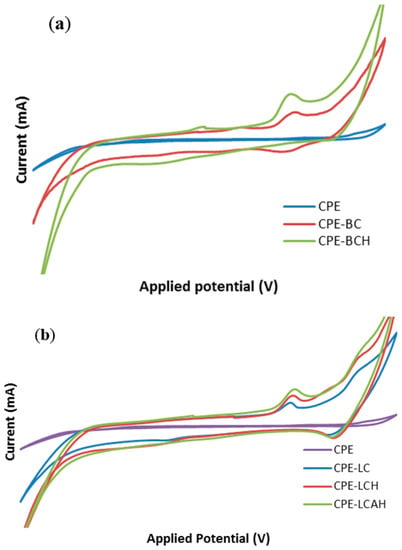
Figure 6.
Electroanalytical response of lead(II) using various modified and bare carbon paste electrodes (a) bentonite based modified CPEs and (b) local clay based modified CPEs [Initial concentration of lead(II): 50.0 μg/L; pH: 5.0 in 1.0 mol/L KCl solution].
Lead(II) showed an oxidation peak at an applied potential of around ca. 0.85 V, whereas the reduction peak was found to be distorted, or mostly a broadened peak was observed around an applied potential of ca. −0.50 using the hybrid material modified CPEs. Therefore, a two electron redox process was proposed for lead(II). This could be ascribed as Equation (2):
Pb2+ + 2e ↔ Pb (0)
Similar, the redox behavior was reported previously for the cyclic voltammetric studies of cadmium(II) using the modified carbon paste electrodes [13].
3.4. Effect of pH
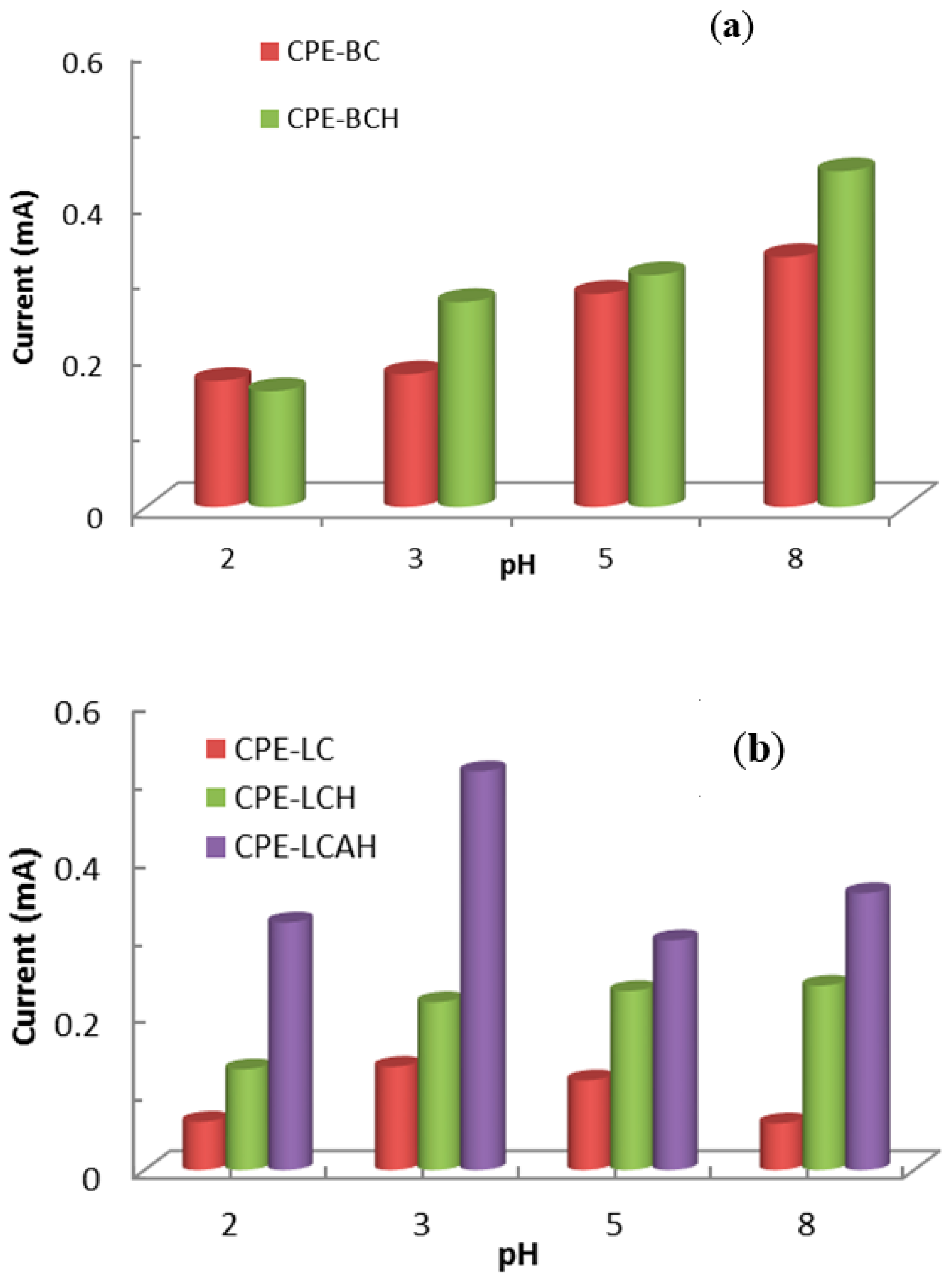
The pH dependent electrochemical response of lead(II) is presented in Figure 7. The peak oxidative current was recorded as a function of the solution pH. It was observed that at relatively lower pH values, i.e., pH 2.0, the peak current was significantly lower which was due to the fact that there could be strong competition between the H+ and Pb2+ ions towards the electrode surface. Moreover, it was also likely that at this low pH, the materials were not stable at the electrode surface. Therefore, collectively it resulted in a low electrochemical response of lead(II) detection against the modified CPEs. Previously, it was reported that extremely low adsorption of lead(II) occurred on the sericite solid at low pH values [34] or on porous magnesium oxide nanoflowers [35]. Furthermore, the current was increased with the increase in pH which was due to the fact that the increase in pH favoured the significantly high adsorption of lead(II) onto the electrode surface, and subsequently favoured the redox process taking place on the electrode surface. The voltammetric signals were directly correlated with the collection and stability of lead(II) against the electrode materials [36].
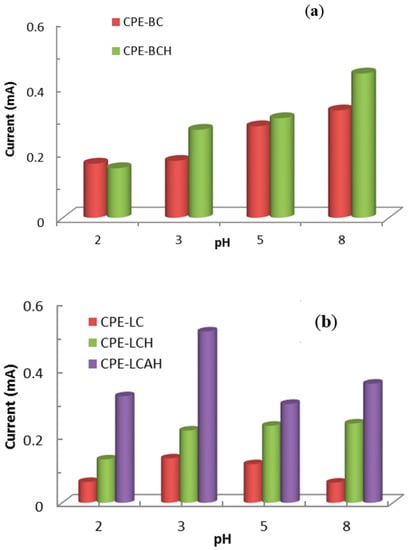
Figure 7.
pH dependent electrochemical response of lead(II) using modified CPEs (a) bentonite based modified CPEs and (b) local clay based modified CPEs [Initial concentration of lead(II): 50.0 μg/L, 1.0 mol/L KCl solution].
Therefore, based on the pH dependence studies, an optimum pH 5.0 was selected for further studies of lead(II) detection. Although a relatively better electrochemical signal was obtained at pH 8.0, at this alkaline pH lead(II) is susceptible to forming insoluble Pb(OH)2 and may lead to poor reproducibility. Moreover, around neutral pH, it is advantageous to detect the lead from the aquatic environment.
3.5. Electroanalysis Performance of Modified CPEs for Lead(II) Detection
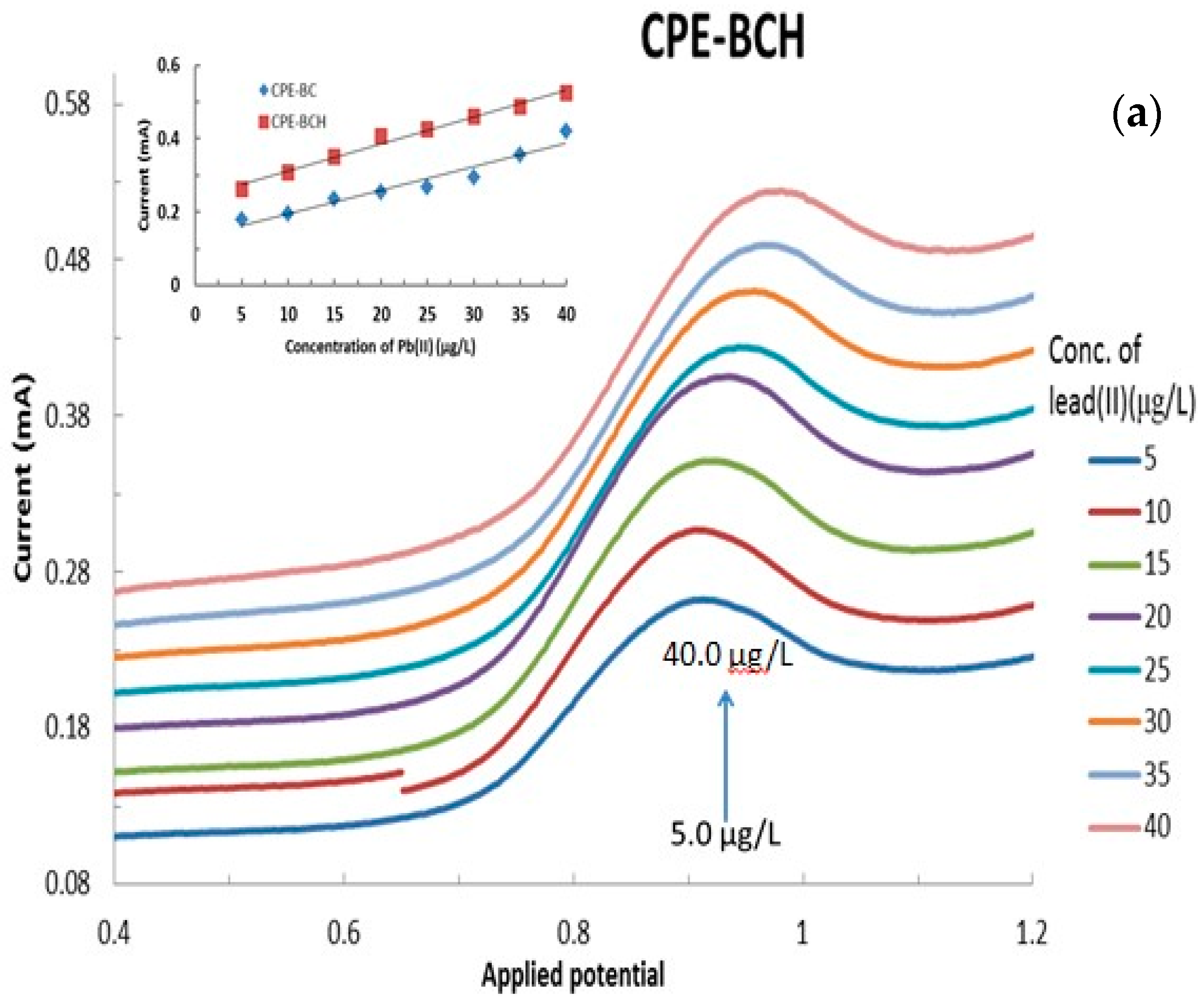
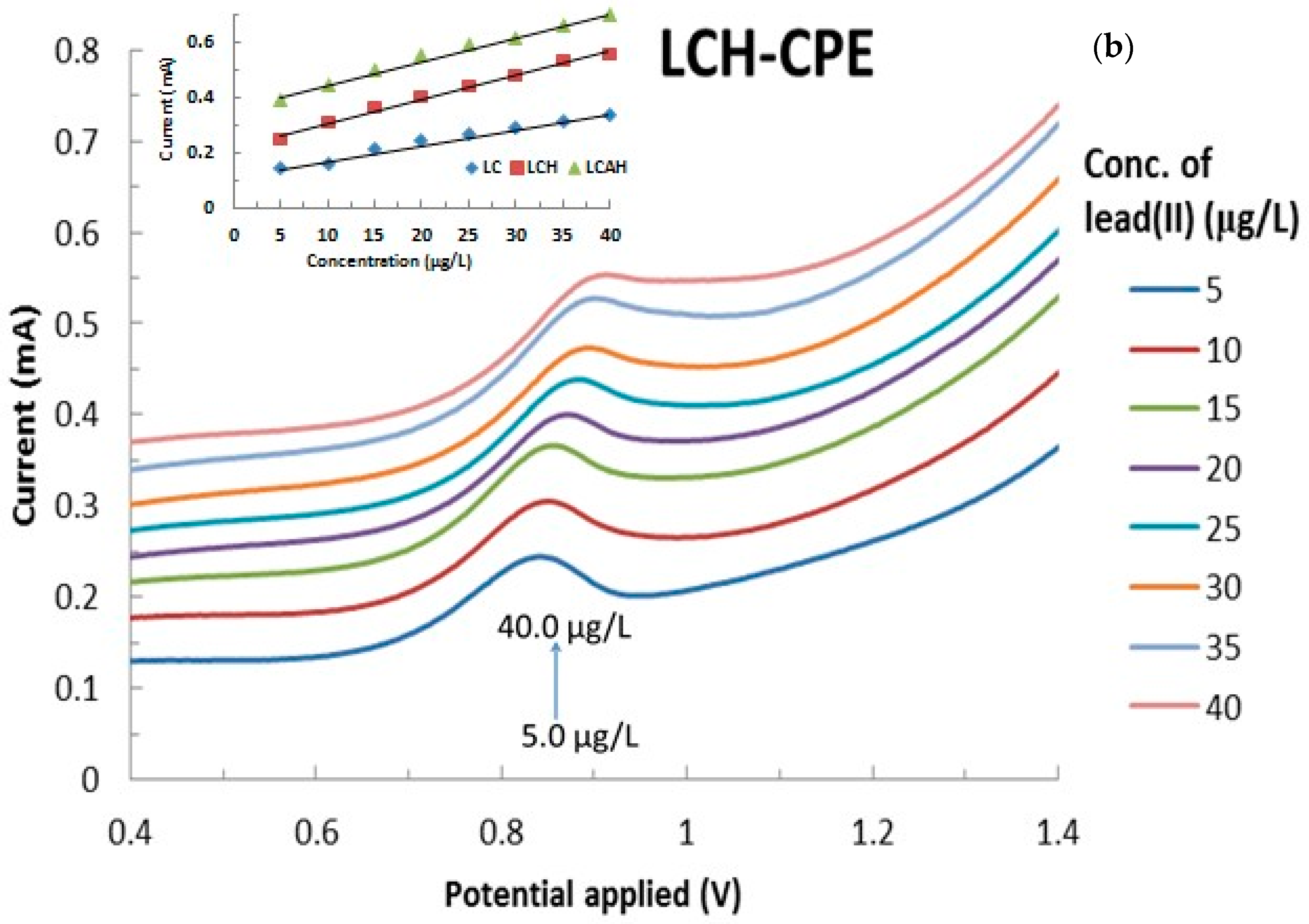
The electroanalysis of lead(II) using various modified CPEs was performed as a function of lead(II) concentration that was varied from 5.0 μg/L to 40.0 μg/L at a constant pH 5.0 with 1.0 mol/L KCl. The results are presented in Figure 8a,b, respectively, for the bentonite and local clay based modified CPEs (The full cyclic voltammograms are shown in Supplementary Materials Figure S2). It is evident from Figure 8 that an increase in the concentration of lead(II) apparently caused a significant increase in the anodic currents as measured by the CVs. This result indicated that the Pb(0) was oxidized to Pb(II) and the concomitant increase in the anodic current. It should be noted that the hybrid material modified CPEs showed relatively better electrochemical response compared to the respective pristine clay modified CPEs (data not shown). This indicated that the hybrid materials are found to be more suitable alternative materials for the modification of carbon paste electrodes for the application of low level detection of lead(II).
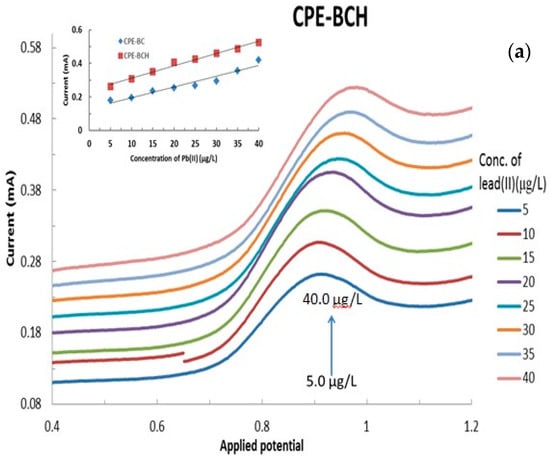
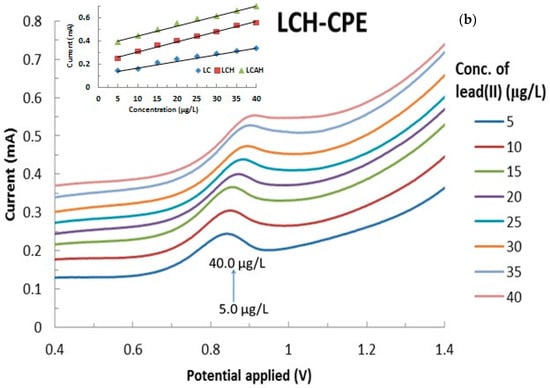
Figure 8.
Effect of lead(II) concentration on the electrochemical behavior of lead(II) using (a) BCH and (b) LCAH modified electrodes. Insets are the calibration curves obtained for the detection of lead(II) using the various modified CPEs.
Furthermore, the peak current was utilized to draw the regression line for these modified CPEs in the detection of lead(II) or even for the development of a lead sensor. The results are shown in Figure 8 (insets). It is evident from the regression line that a reasonably good correlation is obtained for the studied concentration range of lead(II) and its oxidative peak current values. The corresponding electrode sensitivities are found to be 0.0064 (R2 = 0.9385), 0.0057 (R2 = 0.9821), 0.0073 (R2 = 0.9874), 0.0087 (R2 = 0.9904), and 0.0086 mAL/μg (R2 = 0.9876) for the CPE-BC, CPE-LC, CPE-BCH, CPE-LCH, and CPE-LCAH electrodes, respectively. It is again evident that the hybrid materials showed significantly higher sensitivity compared to the pristine clay modified CPEs. Similar high sensitivity (19.9 μA/μM) was obtained for the lead(II) detection using the MnFe2O4 NC (nanocrystalline cluster) modified GCE [18].
The detection limit (DL) and quantification limit (QL) were calculated in the detection of lead(II) using various hybrid material modified CPEs. The DL and QL were estimated using the standard equations, 3 × S.D./m and 10 × S.D./m, respectively (where S.D. stands for sample standard deviation of the blank sample (n = 6) and m is the slope of the calibration line) [13]. The DL values were found to be 4.804, 2.926, and 3.665 μg/L for the CPE-BCH, CPE-LCH, and CPE-LCAH-modified CPEs, respectively. Moreover, the QL values were found to be 16.012, 9.754, and 12.218 μg/L, respectively, for the CPE-BCH, CPE-LCH, and CPE-LCAH modified CPEs, respectively. The determined DL values for these modified-CPEs were much lower compared to the MCL (Maximum Contaminant Level for lead: 15 μg/L) suggested by the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) for lead(II) in drinking water supplies, which showed its practical applicability in the detection of lead(II). Comparatively, among the three hybrid materials employed, the LCH-modified CPE had a minimum DL value. The experimental data were recorded for six replicated experiments and it is interesting to note that a reasonably good reproducibility of the results was obtained since the relative standard deviations (RSD) were below 4%. It was reported previously that using a miniaturized and compact microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) chemical sensor incorporated with a three-dimensional, free-standing micropillar working electrode showed a sensitivity of 32 nA/(μg/L) as well as a favorable detection limit of 0.2 μg/L for lead(II) detection [1]. A CeO2 nanoparticle-decorated graphene hybrid modified glassy carbon electrode had a LOD of 0.1057 nM for lead(II) using the differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetric (DPASV) method [20]. An electrochemically reduced graphene oxide-graphite reinforced carbon (ErGO-GRC) electrode was introduced with SWV (square wave voltammetry) and showed a detection limit of 0.09 nM for lead(II) [16].
3.6. Interferences Studies
The presence of several co-existing cations and anions (50.0 μg/L) were tested at a fixed concentration of lead(II). The results are shown in Table 4. Table 4 clearly reveals that the co-existing ions are interfering, to a varying extent, with the three differently modified CPEs. This is, perhaps, due to the affinity of these interfering ions towards the electrode surface which ultimately affects the detection of lead(II). However, the CPEs modified with the LCH and LCAH showed relatively reproducible results even in the presence of several co-existing ions compared to the BCH modified CPE. The lead(II) detection is highly varied and significant deviation from the blank value of lead(II) was observed for the BCH modified CPE. This is, perhaps, due to the sorption of these interfering ions onto the electrode surface and also taking part in the redox process at the studied electrode potential. These results, therefore, restricted the selectivity of the electrode, up to certain extent, in lead(II) detection. It was previously observed that Na+ and Ca2+ ions did not significantly affect the electrochemical detection of lead(II) ions using the Graphene/CeO2 modified GCE [20].

Table 4.
Concentration of lead(II) calculated from the calibration line of lead(II) (5.0 μg/L to 40.0 μg/L) in the presence of interfering ions [Concentration of co-exiting ion: 50.0 μg/L].
3.7. Detection of Lead in Tap Water Sample
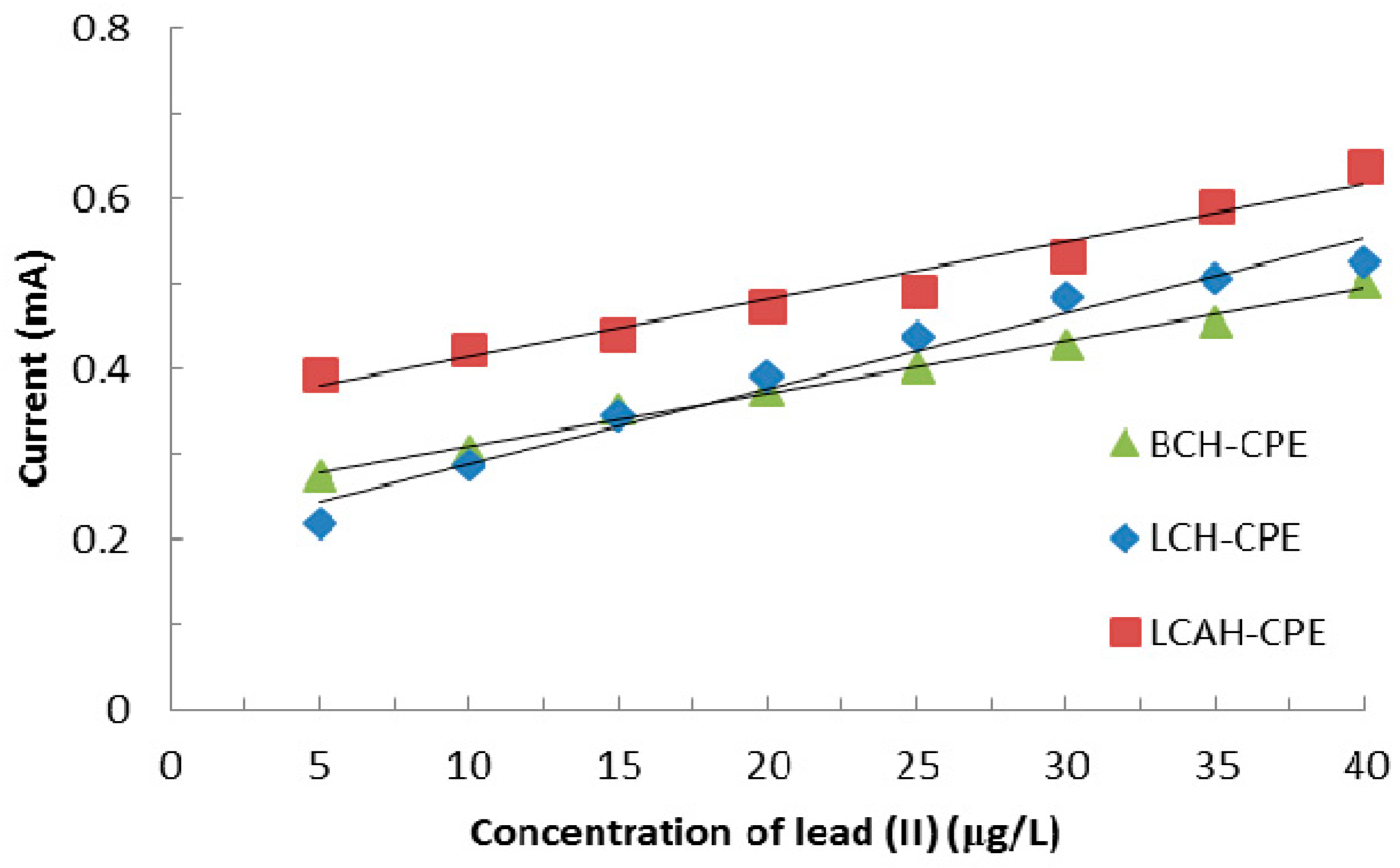
Tap water was analyzed and the analytical results are presented in Table 5. Table 5 indicates that the tap water had a relatively high concentration of calcium and magnesium along with inorganic carbon. This is perhaps due to the presence of carbonates and bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium [37]. The tap water also had some dissolved organic carbon. The tap water was spiked with lead(II) having various concentrations, i.e., from 5.0 to 40.0 μg/L. The regression lines were obtained between the peak anodic current and the concentration of lead(II) using various hybrid material modified CPEs and are depicted in Figure 9. Figure 9 clearly shows that a reasonably good linear relationship between the concentration of lead(II) and oxidative peak current is obtained using the CPE-BCH, CPE-LCH, and CPE-LCAH electrodes. Moreover, reasonably high electrode sensitivity is obtained for these modified electrodes. The sensitivity is measured as 0.0062 (R2 = 0.9905), 0.0088 (R2 = 0.9704), and 0.0067 (R2 = 0.9654) mAL/μg for the CPE-BCH, CPE-LCH, and CPE-LCAH electrodes, respectively. Thus, the electrochemical method described here is a useful analytical method for real matrix analysis, to be employed for lead(II) detection.

Table 5.
Analysis of tap water sample.
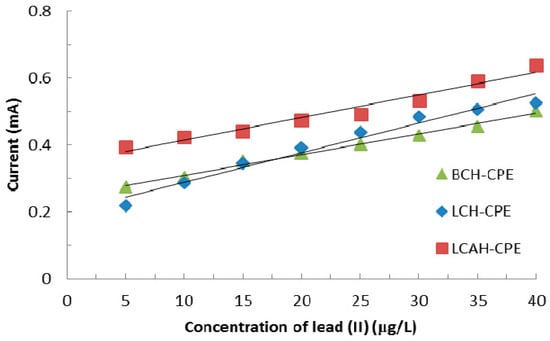
Figure 9.
Regression lines obtained for the real tap water samples in the detection of lead(II) using various hybrid material modified carbon paste electrodes.
4. Conclusions
CPE was modified using hybrid materials. The bentonite (BC) and locally collected clay (LC) were loaded with HDTMA to obtain the BCH and LCH hybrid materials. Similarly, the LCH was pillared with aluminum, and subsequently modified with HDTMA to obtain the LCAH hybrid materials. The surface morphology was obtained by SEM images of these solids. The BET specific surface area of the BC, BCH, LC, LCH, and LCAH was found to be 80.86, 4.68, 2.94, 11.87, and 4.55 m2/g, respectively. XRF analysis of BC and LC indicated that both the clay samples possessed silicon, aluminium, and iron oxides with a varied content of exchangeable cations, viz., Na, K, and Mg. The performance of the modified electrodes was assessed with the standard Fe(CN)64−/Fe(CN)63− redox behavior under cyclic voltammetric studies. The scan rate studies enabled us to determine the electroactive surface area of these modified CPEs, viz., 4.739, 3.088, and 6.937 cm2 for the BCH, LCH, and LCAH modified CPEs, respectively. Furthermore, the hybrid material modified CPEs showed a significantly higher electrical signal compared to the bare CPE or pristine clay modified CPEs for lead(II) detection. The cyclic voltammograms of lead(II) using the modified CPEs showed a reversible redox behavior of lead(II), however, a pronounced anodic peak occurred at an applied potential around ca. 8.5 V. Low anodic peak current was obtained at lower pH values for lead(II) using the modified CPEs, however, a fairly good electrochemical response occurred for a wide pH range, i.e., pH 3–8. The modified CPEs showed a fairly good linearity between the concentration of lead(II) (5.0 to 40.0 μg/L) and the peak anodic current. The sensitivity of these modified electrodes were found to be 0.0064, 0.0057, 0.0073, 0.0087, and 0.0086 mAL/μg for the CPE-BC, CPE-LC, CPE-BCH, CPE-LCH, and CPE-LCAH electrodes, respectively. The presence of several co-existing ions showed interferences up to a certain extent; however CPE-LCH possessed relatively better selectivity in lead(II) detection. Tap water with spiked lead(II) showed reasonably good selectivity of lead(II) detection with the sensitivity calculated as 0.0062, 0.0088, and 0.0067 mAL/μg for the CPE-BCH, CPE-LCH, and CPE-LCAH electrodes, respectively. The modified carbon paste electrode with the hybrid materials could be an inexpensive and potential alternative method for the in situ low level detection of lead(II) from aqueous solutions.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/2075-4701/7/4/124/s1.
Acknowledgment
One of authors D.T. wishes to acknowledge the CSIR, New Delhi, for financial support in the form of a Research Project (vide No.: 01 (2567)/12/EMR-II). The authors are thankful to Muthukumaran R., Department of Chemistry, Mizoram University, for his kind help in modifying the English of this paper.
Author Contributions
D.T. and S.-M.L. conceived and designed the experiments. Z. has conducted mostly the electrochemical experiments. Moreover, the J.-H.H. helped in finalizing the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| BC | Bentonite |
| LC | Local Clay |
| CPE | Carbon paste electrode |
| GCE | Glassy carbon paste electrode |
| HDTMA | hexdadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide |
| BCH | HDTMA loaded bentonite |
| LCH | HDTMA loaded local clay |
| LCAH | Aluminum pillared local clay |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| FT-IR | (Fourier Transform Infra-Red) |
| BET | Brunauer, Emmett and Teller |
| XRF | X-ray fluorescence |
| DL | Detection limit |
| QL | Quantification limit |
References
- Wang, N.; Kanhere, E.; Miao, J.; Triantafyllou, M.S. Miniaturized chemical sensor with bio-inspired micropillar workingelectrode array for lead detection. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 233, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyer, R.A. Lead toxicity: Current concerns. Environ. Health Perspect. 1993, 100, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, R.M.; Raghunath, R.; Mahapatra, S.; Sadasivan, S. Blood lead and its effect on Cd, Cu, Zn, Fe and hemoglobin levels of children. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 277, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, P.A. Increased body lead burden-cause or consequence of chronicrenal insufficiency? N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, M. Fetal death and reduced birth rates associated with exposure tolead-contaminated drinking water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arantes, T.M.; Sardinha, A.; Baldan, M.R.; Cristovan, F.H.; Ferreira, N.G. Lead detection using micro/nanocrystalline boron-doped diamond by square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Talanta 2014, 128, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Barrow, C.J.; Wang, H.; Yang, W. A biomimetic sensor for the detection of lead in water. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wei, L.; Liu, X.; Lei, L.; Li, G. Ultrasensitive detection of lead ion based on target induced assembly of DNAzyme modified gold nanoparticle and graphene oxide. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 831, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Gu, W.; Zhang, C.; Shi, X.; Xian, Y. In situ regulation nanoarchitecture of Au nanoparticles/reduced graphene oxide colloid for sensitive and selective SERS detection of lead ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 465, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaruddin, N.H.; Bakar, A.A.A.; Yaacob, M.H.; Mahdi, M.A.; Zan, M.S.D.; Shaari, S. Enhancement of chitosan-graphene oxide SPR sensor with a multi-metallic layers of Au-Ag-Au nanostructurefor lead(II) ion detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 361, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Le, T.X.H.; Bechelany, M.; Esposito, G.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Oturana, M.A.; Cretin, M. A hierarchical CoFe-layered double hydroxide modified carbon-felt cathode for heterogeneous electro-Fenton process. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3655–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Zirlianngura; Anjudikkal, J.; Tiwari, D. Electrochemical sensor for trace determination of cadmium(II) from aqueous solutions: Use of hybrid materials precursors to natural clays. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2016, 96, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Wildgoose, G.G.; Compton, R.G. Sensitive electrochemical detection of Arsenic(III) using gold nanoparticle modified carbon nanotubes via anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 620, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardegan, A.; Scopece, P.; Lamberti, F.; Meneghetti, M.; Moretto, L.M.; Ugo, P. Electroanalysis of trace inorganic arsenic with gold Nanoelectrode ensembles. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamsawahini, K.; Sathishkumar, P.; Ahamad, R.; Yusoff, A.R.M. PVDF–ErGO–GRC electrode: A single set up electrochemical system for separation, pre-concentration and detection of lead ions in complex aqueous samples. Talanta 2016, 148, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, E. Glassy carbon electrode modified by graphene-gold nanocomposite coating for detection of trace lead ions in acetate buffer solution. Thin Solid Films 2015, 584, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.J.; Zhou, S.F.; Fan, H.L.; Zhang, Q.X.; Liu, Y.Q. Mesoporous MnFe2O4 nanocrystal clusters for electrochemistry detection of lead by stripping voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 755, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wen, H.; Fu, Q.; Peng, D.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X. Morphology-dependent NiO modified glassy carbon electrode surfacefor lead(II) and cadmium(II) detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 363, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.L.; Zhao, S.Q.; Ye, H.L.; Yuan, J.; Song, P.; Hu, S.Q. Graphene/CeO2 hybrid materials for the simultaneous electrochemical detection of cadmium(II), lead(II), copper(II), and mercury(II). J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 757, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyo, S.; Apiluk, A.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakula, O. High sensitivity and specificity simultaneous determination of lead, cadmium and copper using μPAD with dual electrochemical and colorimetric detection. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 233, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, F.E.; Ouarzane, A.; Rhazi, M.E. Electrochemical detection of lead (II) at bismuth/Poly(1,8-diaminonaphthalene) modified carbon paste electrode. Arab. J. Chem. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirlianngura; Jamsheera, A.; Tiwari, D.; Lee, S.M. Efficient use of novel hybrid materials in the ultra-trace determination of arsenic from aqueous solutions: An electrochemical study. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 18730–18738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanhmingliana; Tiwari, D. Efficient use of hybrid materials in the remediation of aquatic environment contaminated with micro-pollutant diclofenac sodium. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanhmingliana; Lee, S.M.; Tiwari, D.; Prasad, S.K. Efficient attenuation of 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE2) and tetracycline using novel hybrid materials: Batch and column reactor studies. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 46834–46842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroke, U.O.; El-Nafaty, U.A. XRF, XRD and FTIR properties and characterization of HDTMA-Br surface modified organo-kaolinite clay. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2014, 4, 817–825. [Google Scholar]
- Eisazadeh, A.; Kassim, K.A.; Nur, H. Solid–state NMR and FTIR studies of lime stabilized montmorillonitic and lateritic clays. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 67–68, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, A.; Yilmaz, N.; Eren, E.; Caglar, B.; Afsin, B.; Sarihan, A. Structural analysis of naproxen–intercalated bentonite (Unye). Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, M.S.; Ahlafi, H.; Moussout, H.; Boukhlifi, F.; Zegaoui, O. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium and phenol onto bentonite modified with hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (HDTMABr). J. Adv. Chem. 2014, 8, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar]
- Jović-Jovičić, N.; Milutinović-Nikolić, A.; Banković, P.; Dojčinović, B.; Nedić, B.; Gržetić, I.; Jovanović, D. Synthesis, characterization and adsorptive properties of organobentonites. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2010, 117, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.H.; Yao, M.G.; Liu, B.; Li, Q.J.; Liu, R.; Lv, H.; Lu, S.C.; Chen, C.; Zou, B.; Cui, T.; et al. Controlled synthesis of CeO2/graphene nanocomposites with highly enhanced optical and catalytic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 11741–11745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndlovu, T.; Mamba, B.B.; Sampath, S.; Krause, R.W.; Arotiba, O.A. Voltammetric detection of arsenic on a bismuth modified exfoliated graphite electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 128, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Torres, D.; Huerta, F.; Montilla, F.; Morallon, E. Study on electroactive and electrocatalytic surfaces of single walled carbon nanotube-modified electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 2464–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Kim, H.U.; Lee, S.M. Removal behavior of sericite for Cu(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions: Batch and column studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 57, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yang, R.; Yu, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, X.J. Stripping voltammetry study of ultra-trace toxic metal ions on highly selectively adsorptive porous magnesium oxide nanoflowers. Analyst 2012, 137, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Yu, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, X.J. O2-plasma oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for Cd(II) and Pb(II) detection: Evidence of adsorption capacity for electrochemical sensing. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 1506–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Zirlianngura; Lee, S.M. Fabrication of efficient and selective total arsenic sensor using the hybrid materials modified carbon paste electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 784, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).