Improvement of Heat-Affected Zone Toughness of Steel Plates for High Heat Input Welding by Inclusion Control with Ca Deoxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Experimental Steel Preparation
2.2. Welding Thermal Simulation Experiments
2.3. Characterization of Inclusions and Microstructures
3. Results
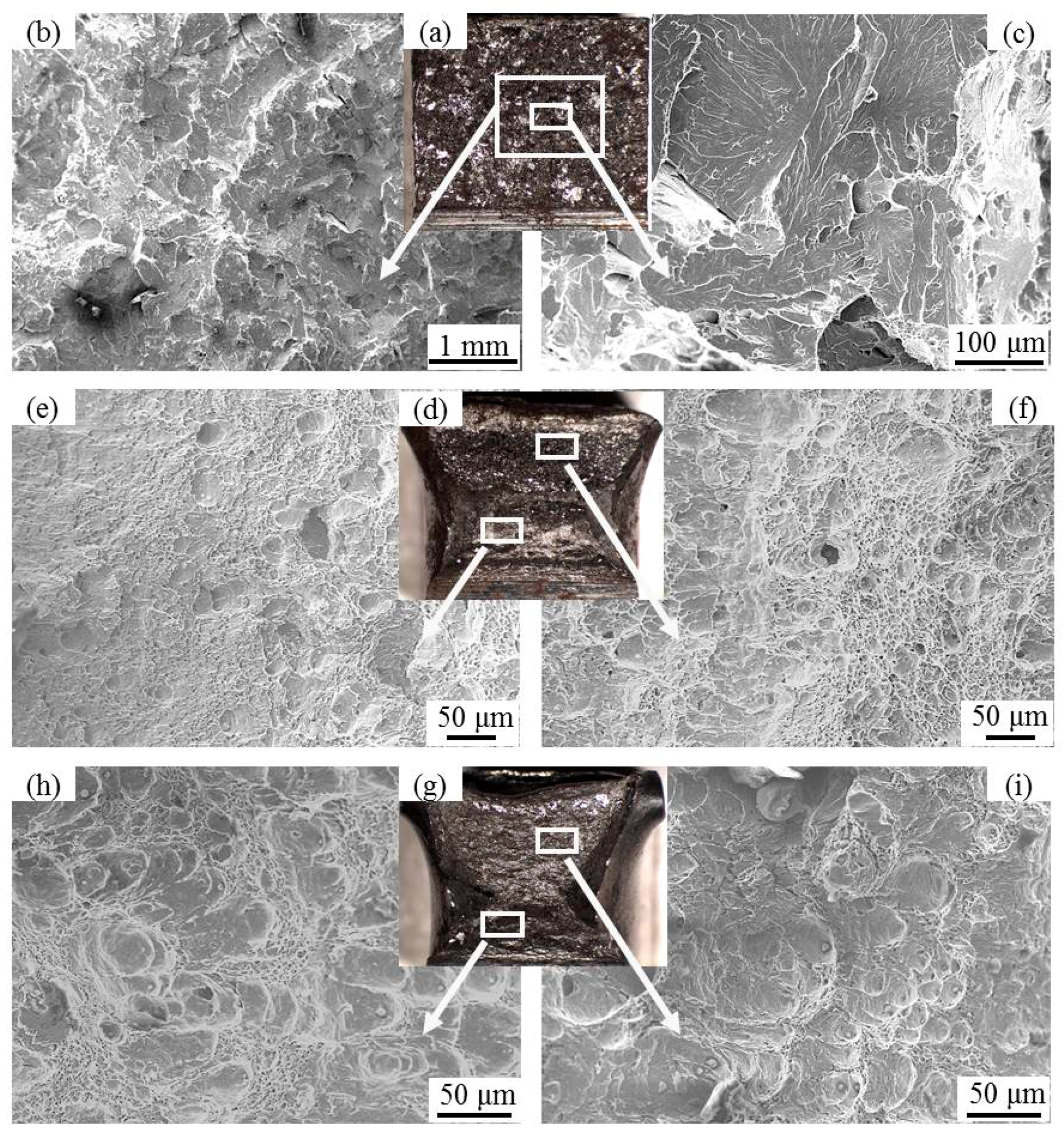
3.1. HAZ Toughness
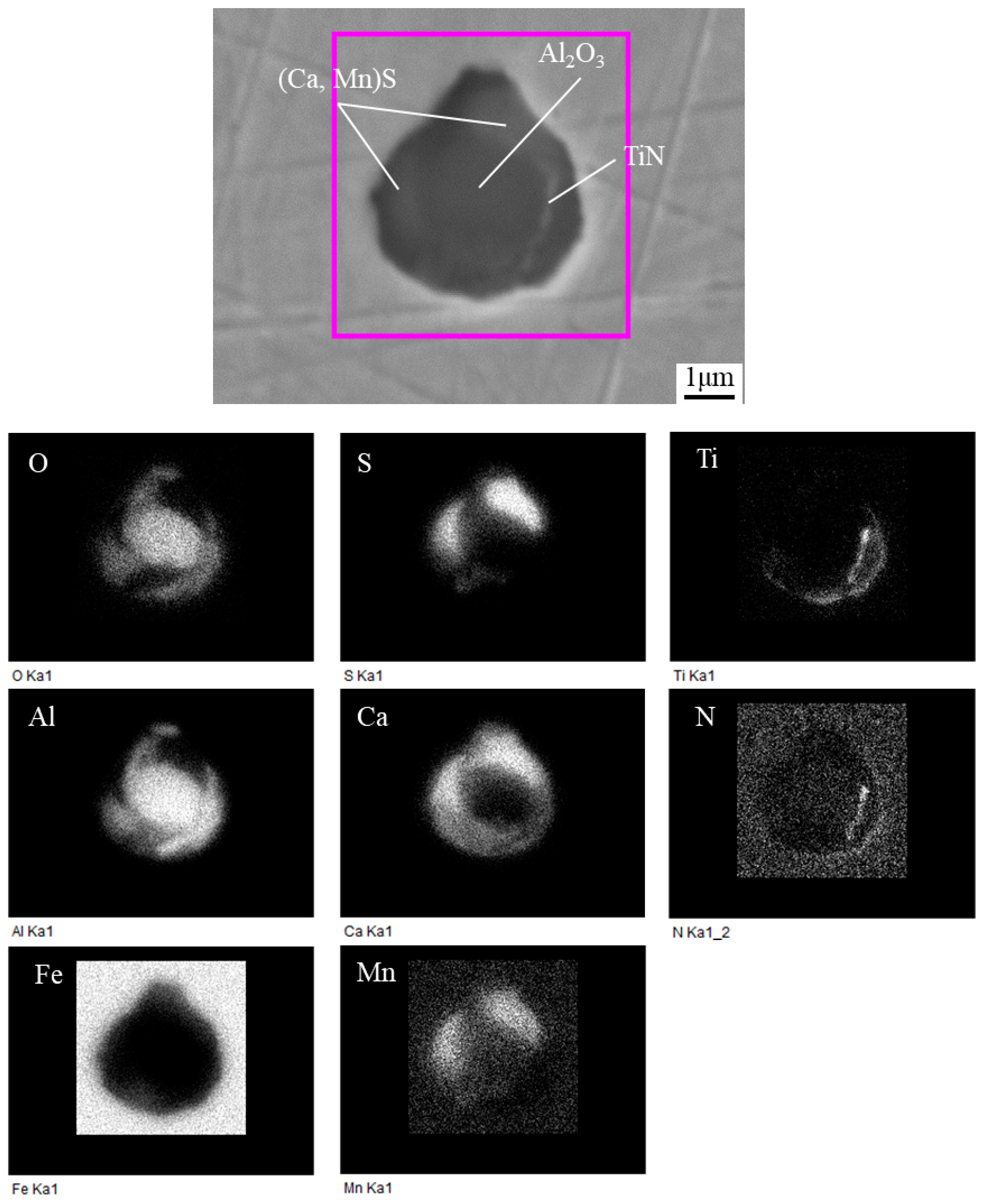
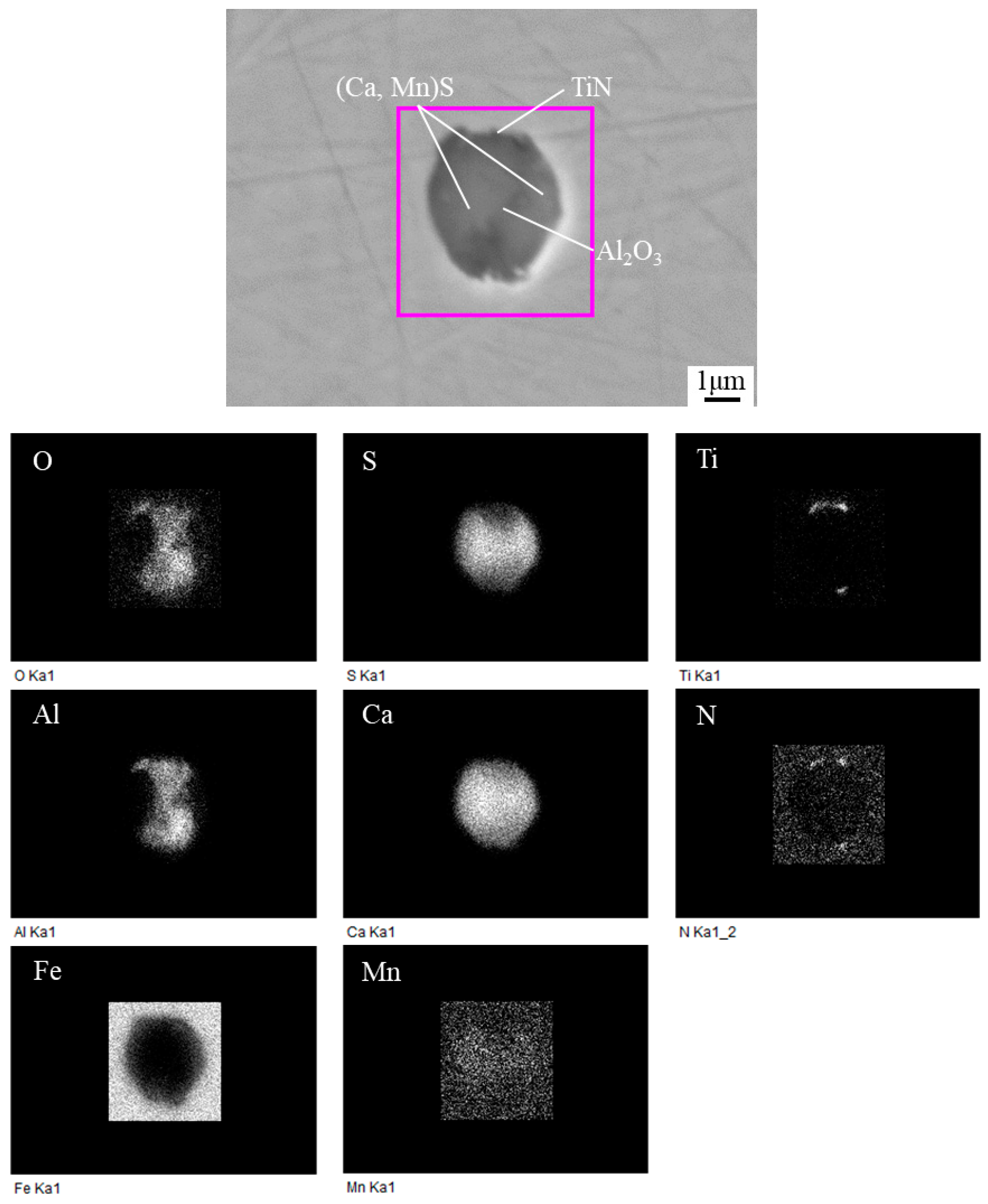
3.2. Typical Inclusions
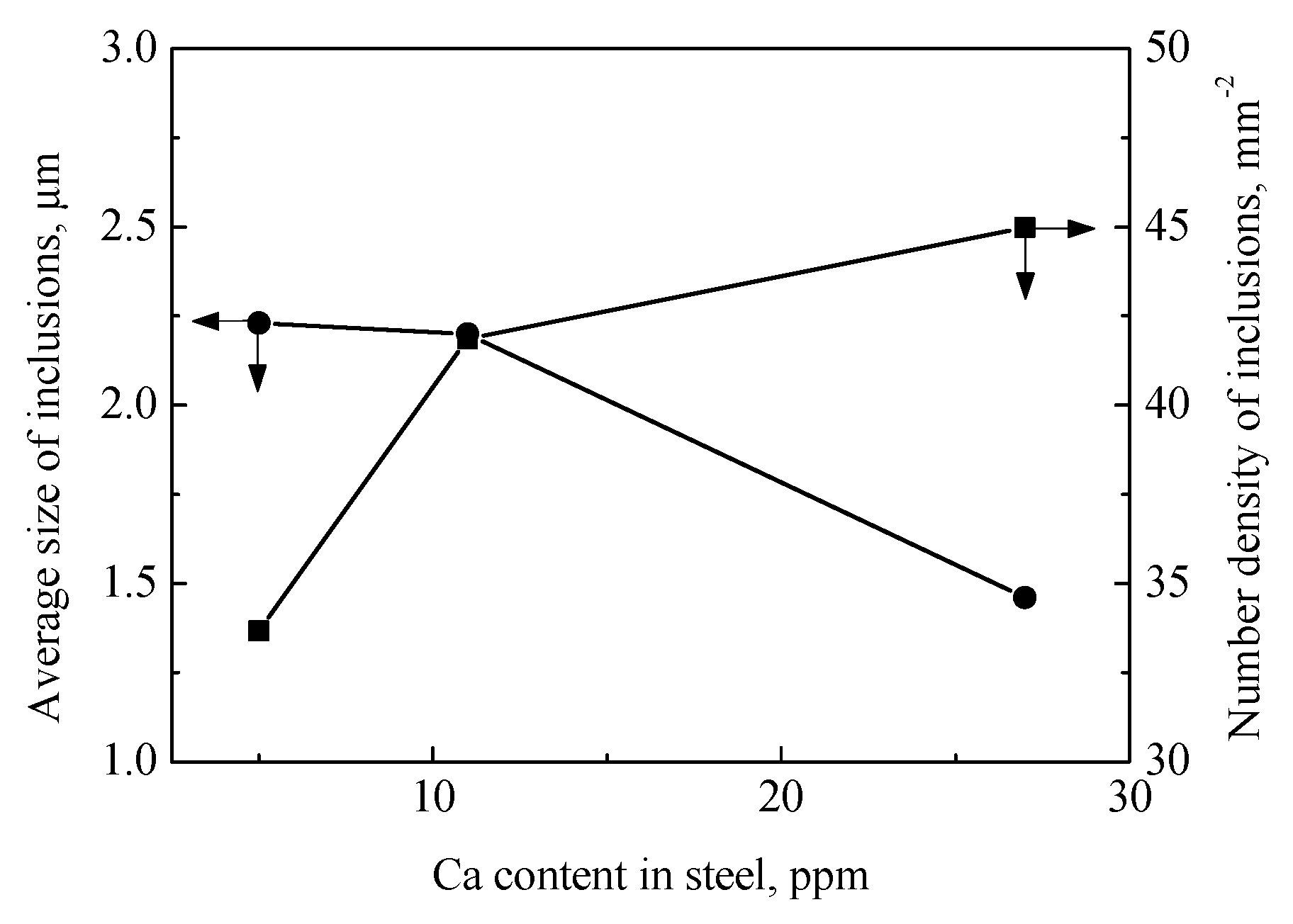
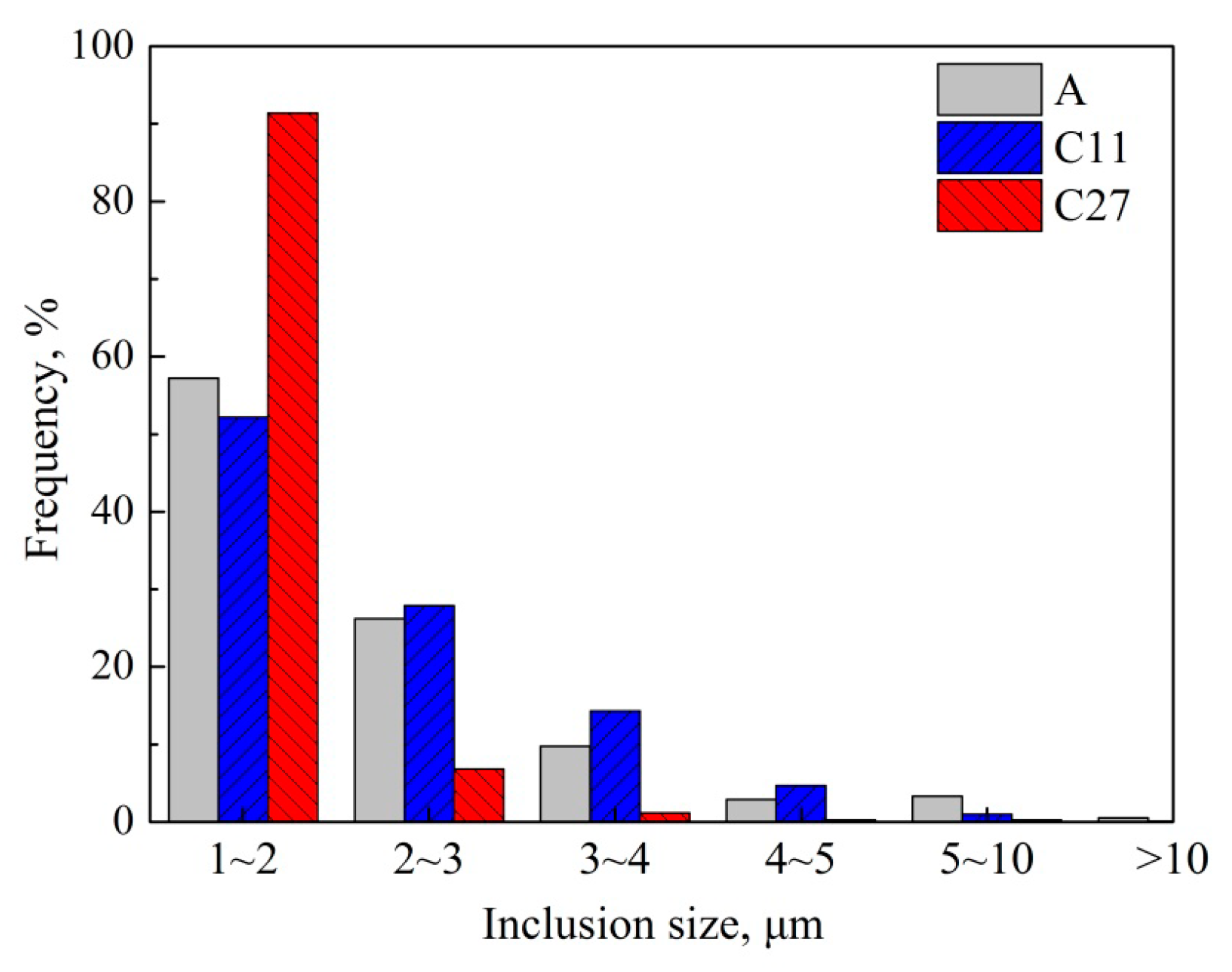
3.3. Number Density and Size of Inclusions
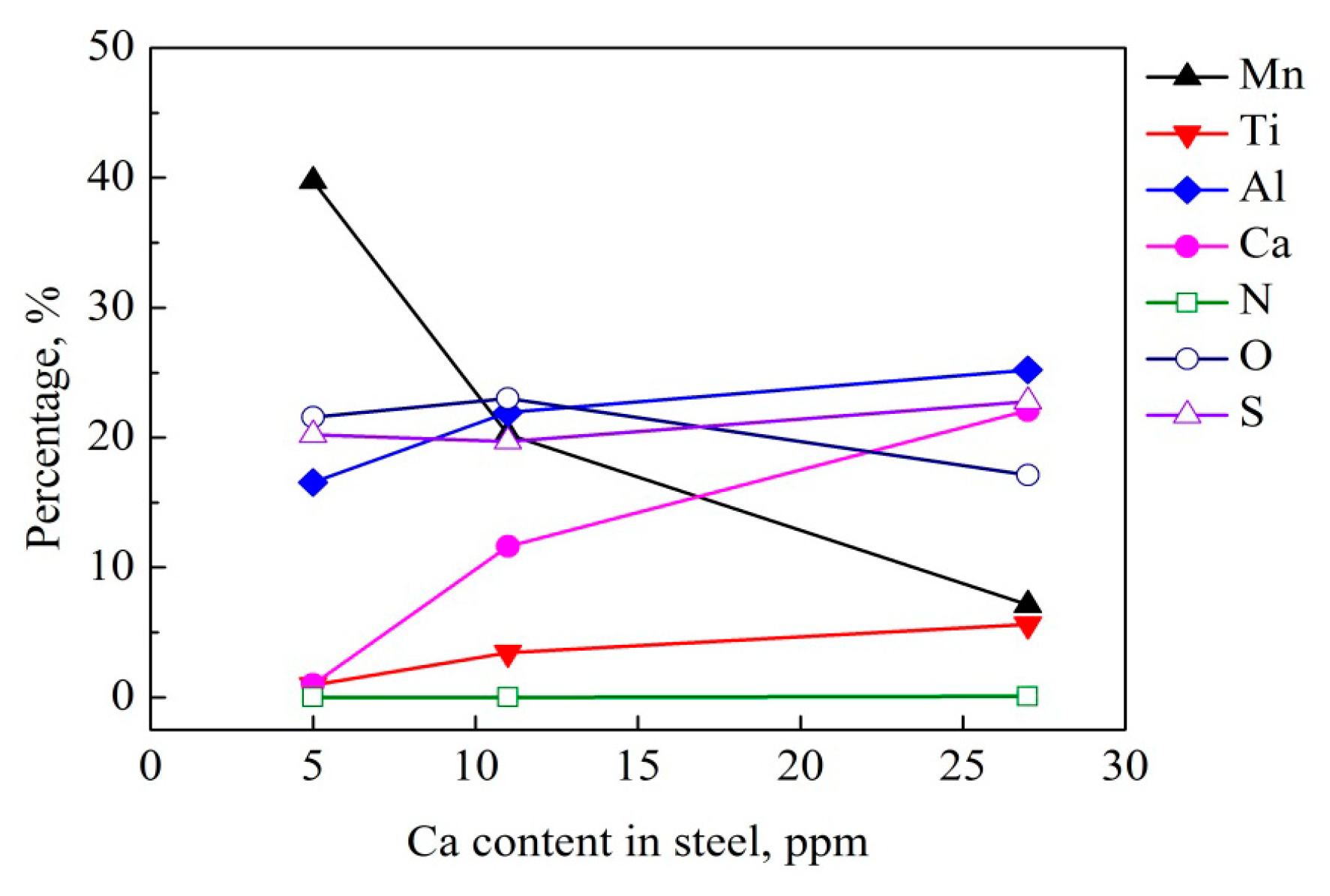
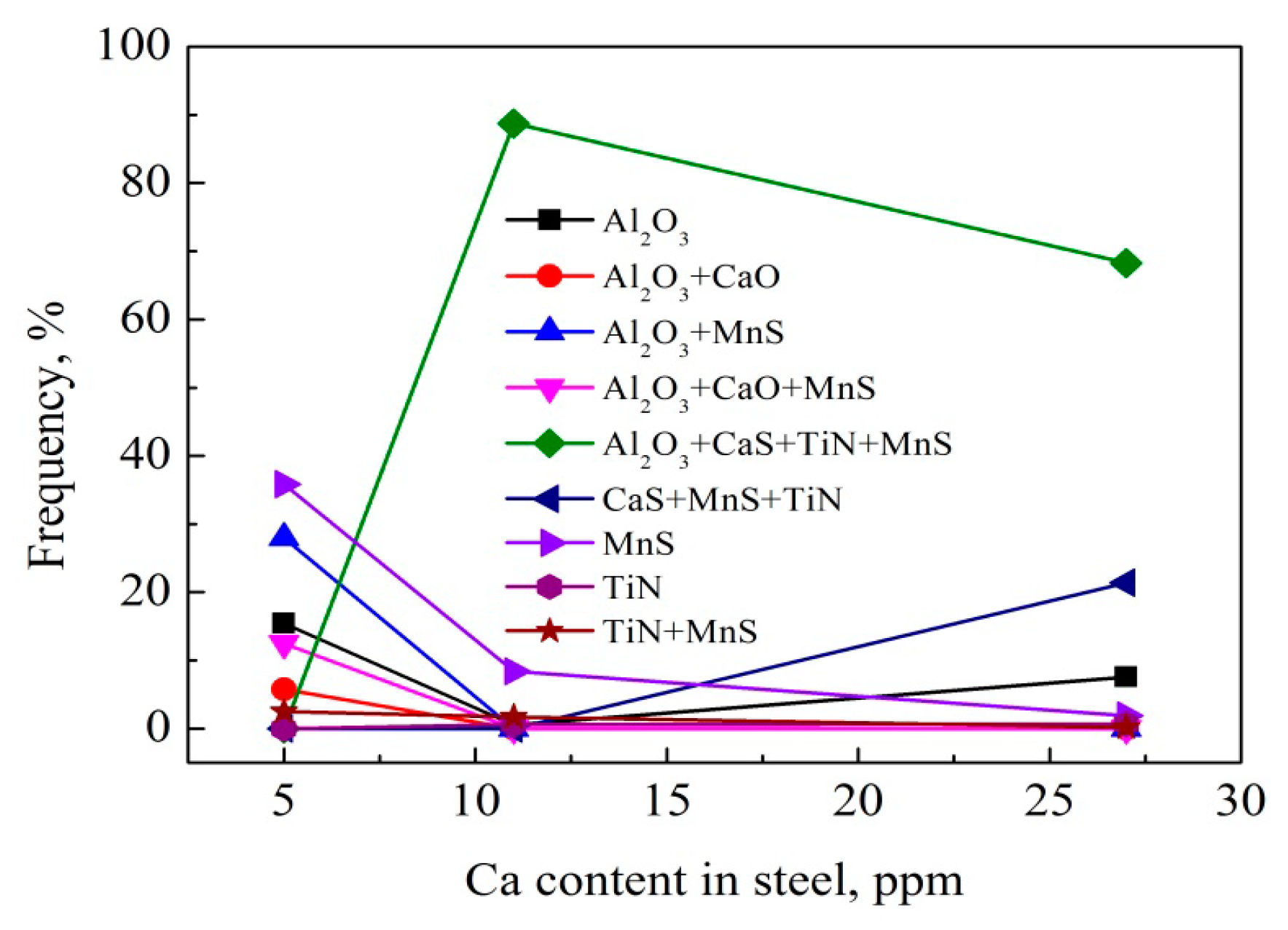
3.4. Composition of Inclusions
3.5. Characteristics of HAZ Microstructures
4. Discussion
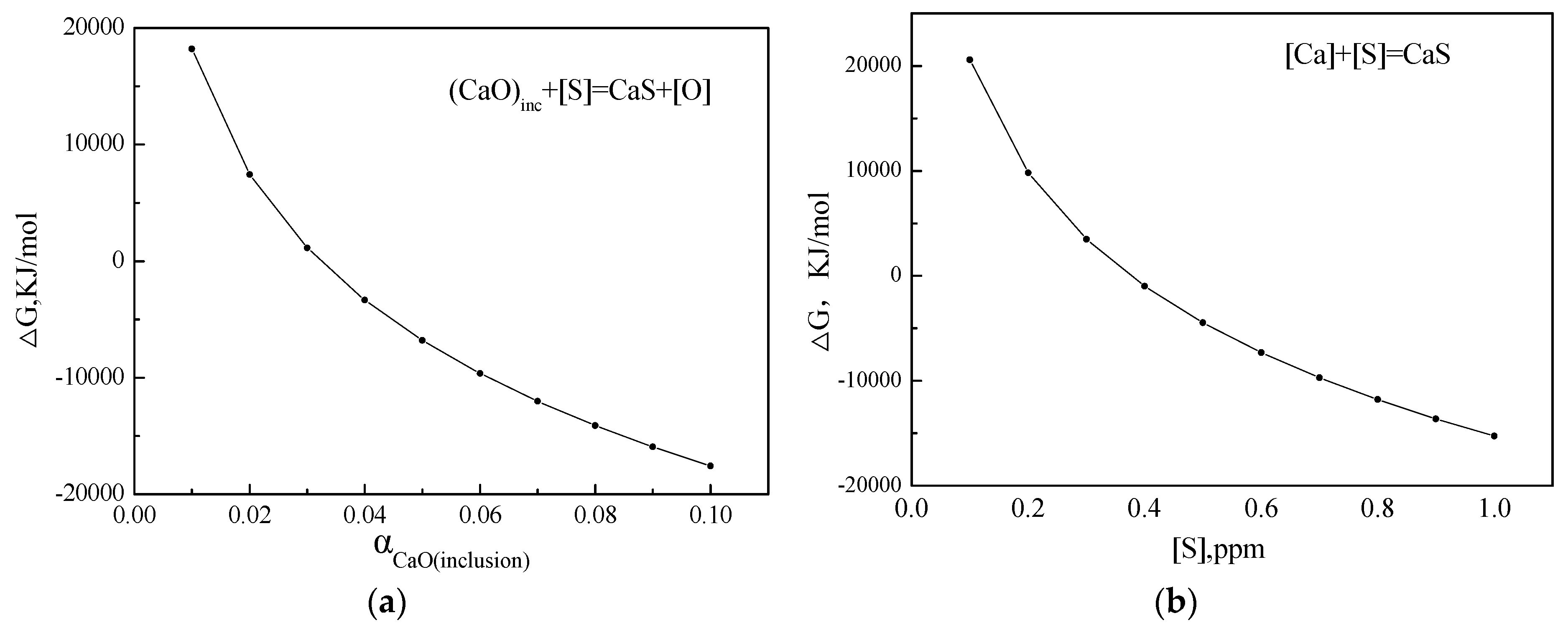
4.1. Behavior of Ca Element in Oxide Metallurgy Technology
4.2. Mechanism of HAZ Toughness Improved by Ca Deoxidation
5. Conclusions
- The typical inclusions found in the HAZs of steel samples with Ca deoxidation containing 11 and 27 ppm Ca were Al2O3 + CaS + MnS + TiN complex inclusions with the size in the range of 1~3 μm, together with TiN formed at the edge of this type of inclusions.
- In conventional Al-killed steel sample containing 5 ppm Ca, the existence form of Ca element was CaO in the Al2O3 + CaO or Al2O3 + CaO + MnS complex inclusions. On the other hand, the Ca element in the inclusions of the steels with Ca deoxidation mainly existed in the form of (Ca, Mn)S covering the central Al2O3.
- With increasing Ca content in the steels from 5 to 11 and 27 ppm, the size of inclusions increased from 2.23 to 2.20 and then to 1.46 μm, and the number density of inclusions increased steadily from 33.7 to 41.9, and then to 45.0 mm−2.
- The average size of prior-austenite grains in HAZs of conventional Al-killed deoxidation and developed steel with Ca deoxidation were all larger than 200 μm. In the steel sample with Ca deoxidation, Al2O3 + CaS + MnS + TiN complex inclusions were potent to induce the formation of intragranular acicular ferrite (IAF) so that well-developed IAF formed in the HAZ microstructures. Therefore, excellent HAZ toughness of steel plates after welding with heat input of 400 kJ·cm−1 was obtained by utilizing oxide metallurgy technology with Ca deoxidation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Zhu, K.; Wang, R.; Shen, J.G. Improving the toughness of heat affected zone of steel plate by use of fine inclusion particles. Steel Res. Int. 2011, 82, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, K.; Wang, G.D. Progress in the technological development of oxide metallurgy for manufacturing steel plates with excellent HAZ toughness. Baosteel Tech. Res. 2008, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ogibayashi, S. Advances in technology of oxide metallurgy. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 1994, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, R.Z.; Wang, Y.N.; Wang, W.L. Effect of Mg content on the microstructure and toughness of heat-affected zone of steel plate after high heat input welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Yang, Z.G. Effect of magnesium on the austenite grain growth of the heat-affected zone in low-carbon high-strength steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 2207–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, R.Z.; Wang, W.L.; Wang, Y.N. Effect of Mg addition on formation of intragranular acicular ferrite in heat-affected zone of steel plate after high-heat-input welding. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2018, 25, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.H.; Zhang, P.Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, F.X. Effect of high heat input on toughness and microstructure of coarse grain heat affected zone in Zr bearing low varbon steel. ISIJ Int. 2014, 54, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, A.; Kiyose, A.; Uemori, R.; Minagawa, M.; Hoshino, M.; Nakashima, T.; Ishida, K.; Yasui, H. Super high HAZ toughness technology with fine microstructure imparted by fine particles. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 2004, 90, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, S.; Bodnar, R.; Raines, J.; Wang, Y.F. Inclusion engineering and metallurgy of calcium treatment. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2018, 25, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.F.; Li, J.S.; Wang, Z.F.; Li, J.; Lin, L. Modification of MgO·Al2O3 spinel inclusions in Al-killed steel by Ca-treatment. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2011, 18, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, X.H.; Yang, G.W.; Wei, P.Y.; He, J.P. Inclusion evolution and estimation during secondary refining in calcium treated aluminum killed steels. Steel Res. Int. 2014, 85, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. A kinetic model for Ca treatment of Al-killed steels using FactSage macro processing. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2017, 44, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, H.J.; Ren, Y.; Yang, W. Effect of sulfur in steel on transient evolution of inclusions during calcium treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 610–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Yang, J.; Xin, X.L.; Wang, R.Z.; Xu, L.Y. The effect of cooling conditions on the evolution of non-metallic inclusions in high manganese TWIP steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Terasaki, H.; Komizo, Y. In situ observation of the formation of intragranular acicular ferrite at non-metallic inclusions in C-Mn steel. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.W.; Wang, X.H. Inclusion evolution after calcium addition in low carbon Al-killed steel with ultra low sulfur content. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Byun, J.S.; Shim, J.H.; Cho, Y.W. Non-metallic inclusions and acicular ferrite in low carbon steel. Mater. Trans. 2000, 41, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricks, R.A.; Howell, P.R.; Barritte, G.S. The nature of acicular ferrite in HSLA steel weld metals. J. Mater. Sci. 1982, 17, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, J.M.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Titanium-rich mineral phases and the nucleation of bainite. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1994, 25, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, M. Nucleation of phase transformations at intragranular inclusions in steel. Met. Mater. 1998, 4, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Terasaki, H.; Komizo, Y. Relation between inclusion surface and acicular ferrite in low carbon low alloy steel weld. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nako, H.; Okazaki, Y.; Speer, J.G. Acicular ferrite formation on Ti-rare earth metal-Zr complex oxides. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.H.; Cho, Y.W.; Chung, S.H.; Shim, J.D.; Lee, D.N. Nucleation of intragranular ferrite at Ti2O3 particle in low carbon steel. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 2751–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, S.; Nakashima, A.; Okamoto, K.; Kanaya, K. Improved toughness of weld fussion zone by fine TiN particles and development of a steel for large heat input welding. Tetsu-to-Hagané 1975, 11, 2589–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.Z.; Jönsson, P.G.; Shibata, H.; Nakajima, K. Inclusion and microstructure characteristics in steels with TiN additions. Steel Res. Int. 2016, 87, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramfitt, B.I. The effect of carbide and nitride additions on the heterogeneous nucleation behavior of liquid iron. Metall. Trans. 1970, 1, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkita, S.; Horii, Y. Recent development in controlling the microstructure and properties of low alloy steel weld metals. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, H.; Uemori, R.; Fujioka, M. The role of Mn depletion in intra-granular ferrite transformation in the heat affected zone of welded joints with large heat input in structural steels. ISIJ Int. 1996, 36, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Yang, C.F.; Su, H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Xu, Z. Effect of magnesium on inclusion formation in Ti-killed steels and microstructural evolution in welding induced coarse-grained heat affected zone. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2009, 16, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Song, B.; Pan, N.; Hu, Q.Y.; Mao, J.H. Effect of SiMg alloy on inclusions and microstructhres of 16Mn steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2011, 38, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.C.; Wang, X.M.; Li, S.R.; Shang, C.J.; He, X.L. Effects of inclusions on microstructure and properties of heat-affected-zone for low-carbon steels. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2012, 55, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Steel | C | Mn | P | S | Ca | Al | Ti | O | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.078 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.0005 | 0.026 | 0.012 | 0.0022 | 0.0014 |
| C11 | 0.078 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.0011 | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.0012 | 0.0029 |
| C27 | 0.078 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.0027 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.0013 | 0.0030 |
| Specimen | Individual Value (J) | Mean Value (J) | FA (%) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 14, 33, 34 | 27 | 0, 5, 5 | 127 |
| C11 | 180, 189, 192 | 187 | 70, 70, 70 | 39 |
| C27 | 88, 136, 144 | 123 | 35, 45, 50 | 917 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Yang, J.; Xu, L. Improvement of Heat-Affected Zone Toughness of Steel Plates for High Heat Input Welding by Inclusion Control with Ca Deoxidation. Metals 2018, 8, 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110946
Wang R, Yang J, Xu L. Improvement of Heat-Affected Zone Toughness of Steel Plates for High Heat Input Welding by Inclusion Control with Ca Deoxidation. Metals. 2018; 8(11):946. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110946
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ruizhi, Jian Yang, and Longyun Xu. 2018. "Improvement of Heat-Affected Zone Toughness of Steel Plates for High Heat Input Welding by Inclusion Control with Ca Deoxidation" Metals 8, no. 11: 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110946
APA StyleWang, R., Yang, J., & Xu, L. (2018). Improvement of Heat-Affected Zone Toughness of Steel Plates for High Heat Input Welding by Inclusion Control with Ca Deoxidation. Metals, 8(11), 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110946





