Diffusion Bonding of Ti2AlNb Alloy and High-Nb-Containing TiAl Alloy: Interfacial Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
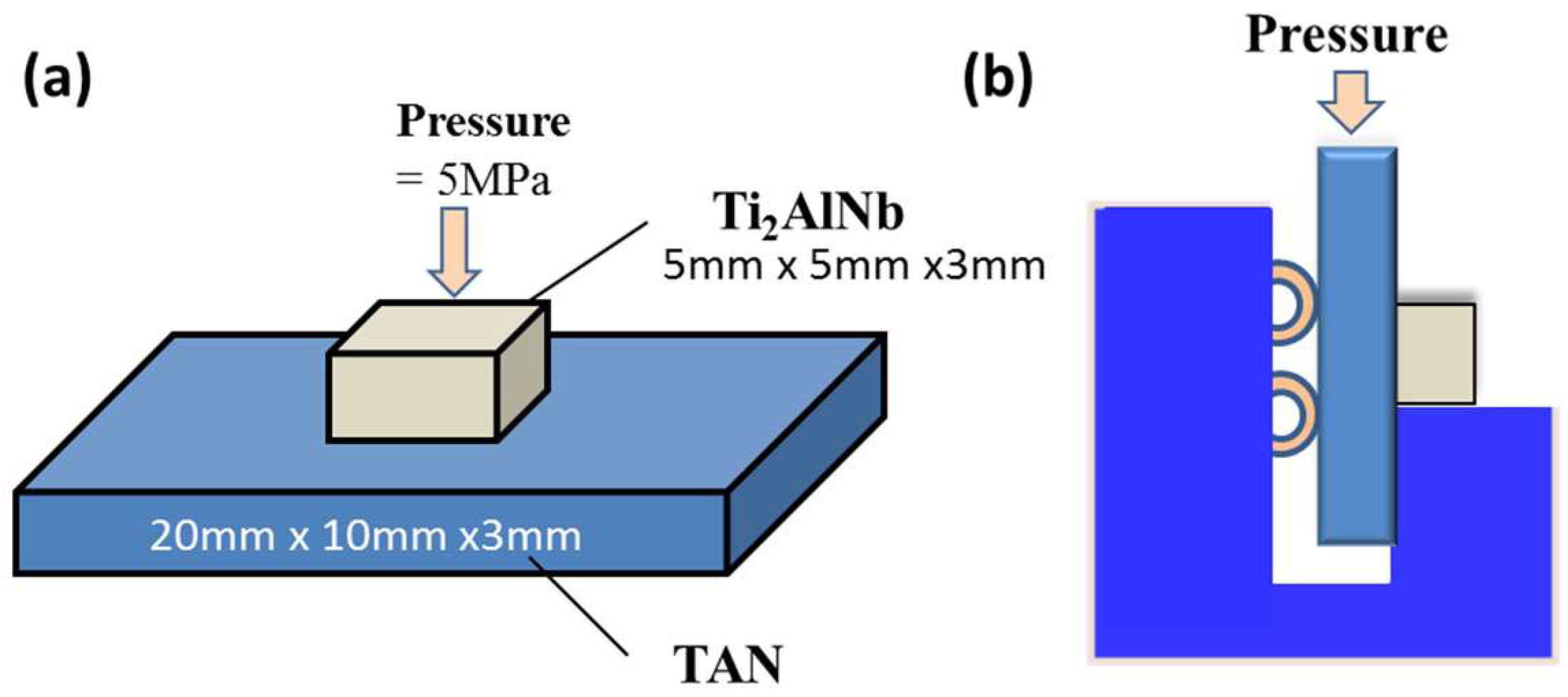
2. Experimental Section
3. Results and Discussion
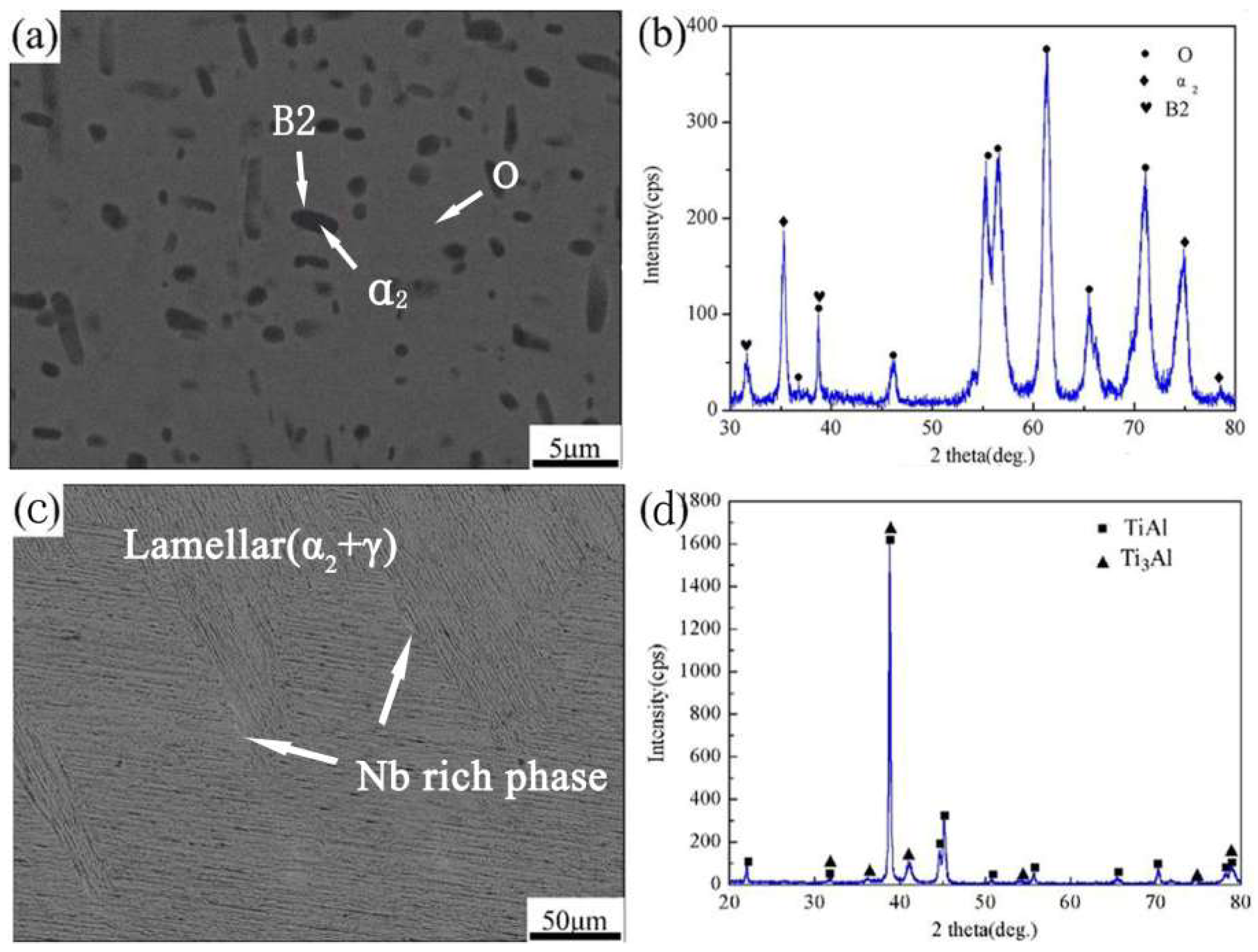
3.1. Typical Interfacial Microstructure of Ti2AlNb/TAN Bonded Joints
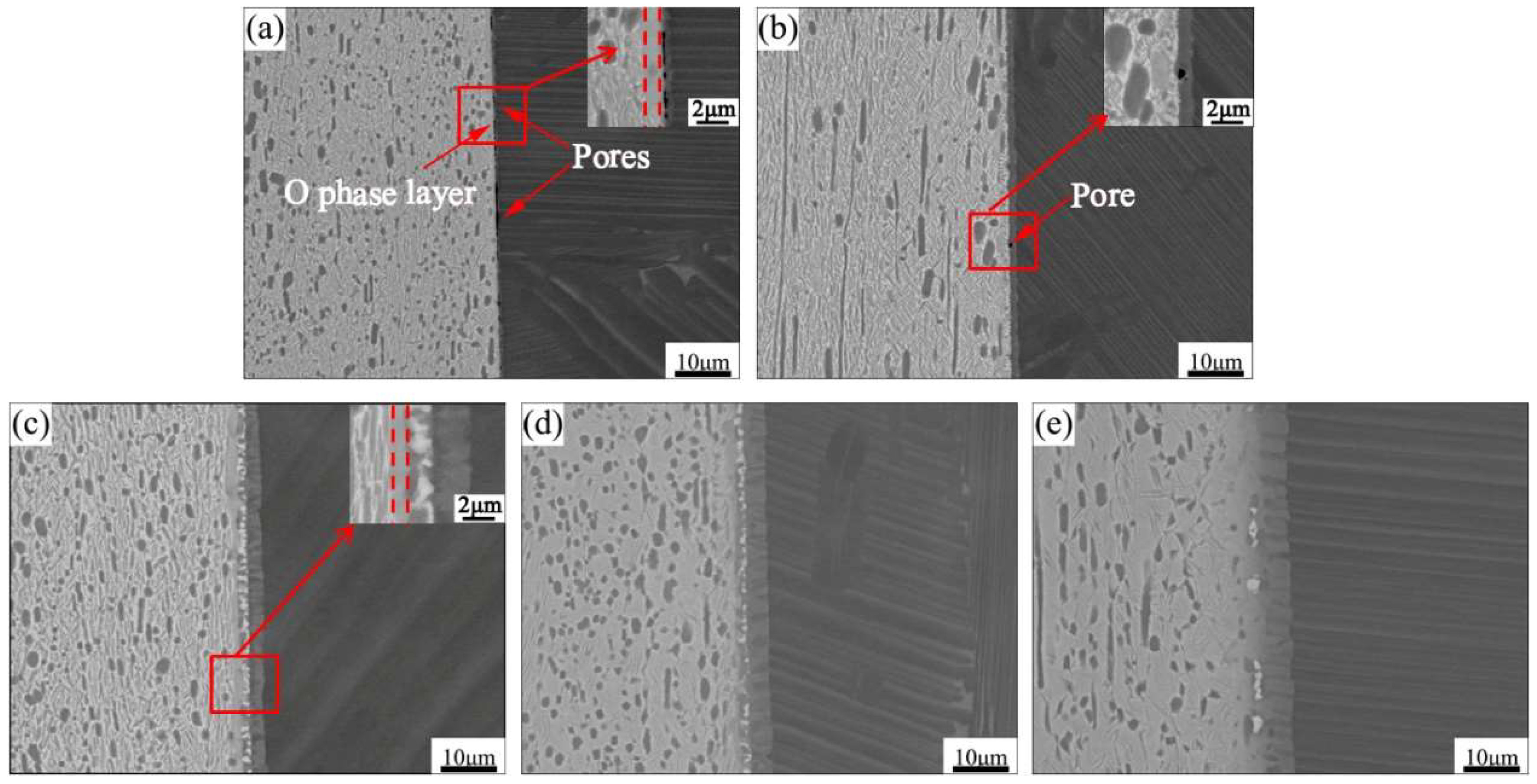
3.2. Effect of Bonding Parameters on the Interfacial Microstructure of Ti2AlNb/TAN Joints
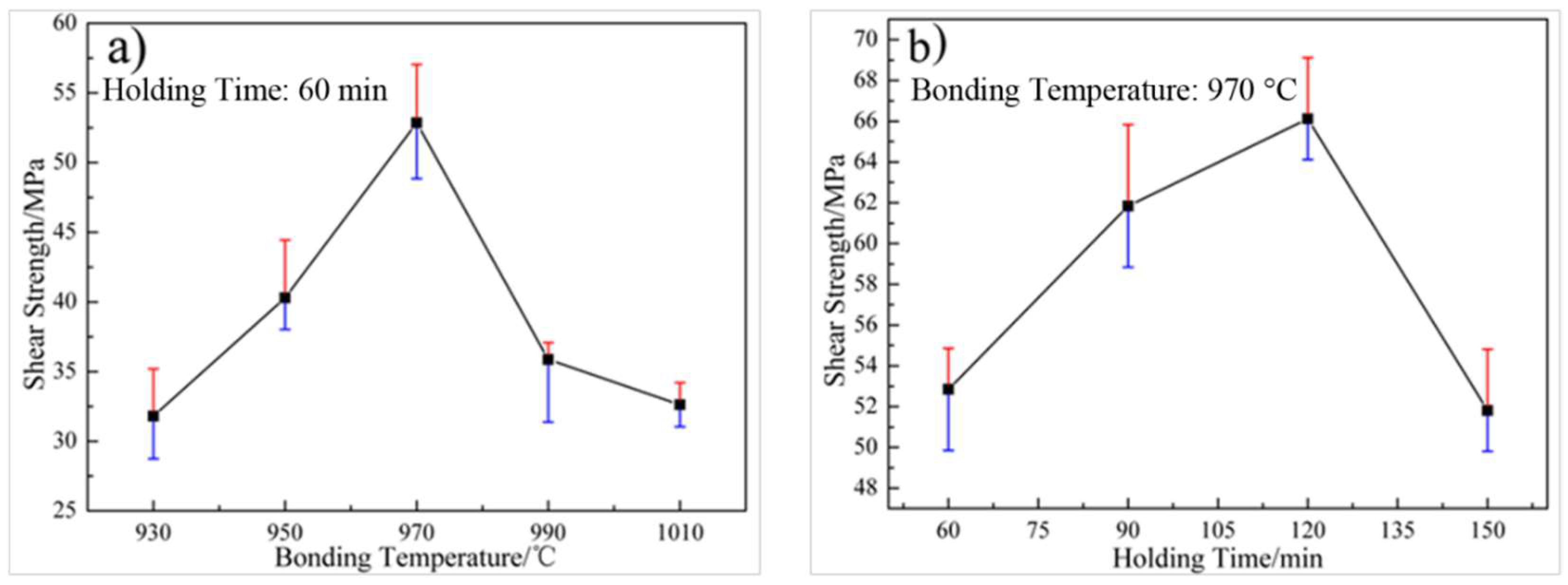
3.3. Bonding Properties and Fracture Morphology of Bonded Ti2AlNb/TAN Joints
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The typical interfacial microstructure of the Ti2AlNb/TAN joints bonded at 970 °C for 15 min under a pressure of 5 MPa was Ti2AlNb substrate/O phase/Al(Nb,Ti)2 + Ti3Al/Ti3Al/TAN substrate.
- (2)
- Bonding temperature had a great influence on the priority of the formation of O phase and Al(Nb,Ti)2 phase. When bonding temperature was low, Al atoms diffused to the Ti2AlNb substrate directly, which caused the formation of O phase without Al(Nb,Ti)2 phase. When the bonding temperature was high enough, Nb atoms reached the desired concentration quickly. In this condition, Al atoms first reacted with B2 phase to generate Al(Nb,Ti)2 phase. Then, excess Al atoms passed though the mixed layer to the Ti2AlNb substrate and promoted the formation of O phase. As bonding temperature or holding time were further increased, Al(Nb,Ti)2 phase gradually decomposed into Ti3Al phase and a Ti3Al transition layer formed. Meanwhile, the O phase layer changed from a continuous state to a discontinuous one.
- (3)
- The Al(Nb,Ti)2 phase was hard and brittle, so the initial fracture location mainly occurred in the mixed layer. With the decomposition of Al(Nb,Ti)2 phase and the formation of transition layer, the shear strength was improved, and the average value reached 66.1 MPa when Ti2AlNb alloy and TAN alloy were bonded at 970 °C for 120 min. The fracture location mainly occurred in the Ti3Al transition layer and the fracture mode was brittle fracture.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Z.-G.; Wu, J.; Guo, R.-P.; Xu, L.; Yang, R. Hot deformation mechanism and ring rolling behavior of powder metallurgy Ti2AlNb intermetallics. Acta Metall. Sin. 2017, 30, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.; Tang, B.; Kou, H. Microstructure evolution of a high Nb containing TiAl alloy with (α2 + γ) microstructure during elevated temperature deformation. Metals 2018, 8, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, W.; Zong, Y.; Zhong, X.; Shan, D. Effect of initial microstructures on hot deformation behavior and workability of Ti2AlNb-based alloy. Metals 2018, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-R.; Liu, G.-H.; Xu, M.; Fu, T.-L.; Tian, Y.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, Z.-D. Hot deformation behavior and microstructural characteristics of Ti–46Al–8Nb alloy. Acta Metall. Sin. 2018, 31, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.; Bin, L.; Rui, Y.; Xiaodong, H.; Ping, R. Local deformation and processing maps of Ti-24Al-17Nb-0.5 Mo alloy. Acta Metall. Sin. 2012, 25, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Yang, F.; Xu, W.; Wang, Z.; Qu, X. Metal Injection moulding of high Nb-containing TiAl alloy and its oxidation behaviour at 900 °C. Metals 2018, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoguo, S.; Jian, C.; Jiakun, L.; Liyan, Z.; Jicai, F. Reaction-diffusion bonding of high Nb containing TiAl alloy. Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 2014, 43, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.-J.; Li, Z.-R.; Liu, R.-H.; Feng, S.-C. Effects of joining conditions on microstructure and mechanical properties of Cf/Al composites and TiAl alloy combustion synthesis joints. Acta Metall. Sin. 2015, 28, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wu, P.; He, Q. Microstructure and shear strength of brazing TiAl/Si3N4 joints with Ag-Cu binary alloy as filler metal. Metals 2018, 8, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Zhao, H.; Cao, J.; Song, X.; Tang, D.; Feng, J. Brazing high Nb containing TiAl alloy using Ti-28Ni eutectic brazing alloy: Interfacial microstructure and joining properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 636, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, H.; Kou, H.; Li, J. Microstructure determined fracture behavior of a high Nb containing TiAl alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 666, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, B.; Liu, W.; Feng, J. Crack formation and control upon the electron beam welding of TiAl-based alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1857–1863. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, M.; Lei, Z.; Chen, Y. Microstructure evolution and tensile properties of laser-TIG hybrid welds of Ti2AlNb-based titanium aluminide. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 3778–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, F.; Ma, T.; Li, W.; Wu, X. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of linear friction welded Ti2AlNb alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 646, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Ben, B.; Hu, S.; Feng, J.; Tang, D. Vacuum brazing high Nb-containing TiAl alloy to Ti60 alloy using Ti-28Ni eutectic brazing alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 692, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Dai, X.; Liu, J.; Si, X.; Feng, J. Relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties of TiAl/Ti2AlNb joint brazed using Ti-27Co eutectic filler metal. Mater. Des. 2017, 121, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Qi, X.S.; Kou, H.C.; Li, J.S.; Milenkovic, S. Recrystallization behavior at diffusion bonding interface of high Nb containing TiAl Alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.-S.; Xie, E.-H.; Bai, H.-L.; Wu, A.-P.; Wang, Q.; Ren, J.-L. A study on transient liquid phase diffusion bonding of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 499, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Feng, J.C.; Li, Z.R. Microstructure and fracture properties of reaction-assisted diffusion bonding of TiAl intermetallic with Al/Ni multilayer foils. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 466, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, R.; Li, X. Diffusion bonding technology of a titanium alloy to a stainless steel web with an Ni interlayer. Mater. Charact. 1999, 43, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, L.I.; Ramos, A.S.; Vieira, M.F.; Viana, F.; Vieira, M.T.; Koçak, M. Solid-state diffusion bonding of gamma-TiAl alloys using Ti/Al thin films as interlayers. Intermetallics 2006, 14, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, K.; Lu, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, D. The structural design and superplastic forming/diffusion bonding of Ti 2 AlNb based alloy for four-layer structure. Mater. Des. 2016, 104, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.S.; Bai, H.L.; Xie, E.H.; Wu, S.J.; Wu, A.P.; Wang, Q.; Ren, J.L. Solid diffusion bonding of Ti-22Al-25Nb O phase alloy. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2008, 18, 577–582. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Cui, Y.; Yang, R. Diffusion bonding of dissimilar intermetallic alloys based on Ti2AlNb and TiAl. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2009, 25, 819–824. [Google Scholar]
- Hellwig, A.; Palm, M.; Inden, G. Phase equilibria in the Al-Nb-Ti system at high temperatures. Intermetallics 1998, 6, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraleedharan, K.; Gogia, A.K.; Nandy, T.K.; Banerjee, D.; Lele, S. Transformations in a Ti-24AI-15Nb alloy: Part I. Phase equilibria and microstructure. Metall. Trans. A 1992, 23, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Nam, S.W.; Hagiwara, M. Phase identification and effect of W on the microstructure and micro-hardness of Ti2AlNb-based intermetallic alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 350, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Xiao, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Han, J.; Jia, Y. Phase transformations of the L12-Ti3Al phase in γ-TiAl alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 121, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.W.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Kim, Y.W. Composition change during creep in colonies oriented for easy-slip of Ti-46.5Al-2Cr-3Nb-0.2W. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 291, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

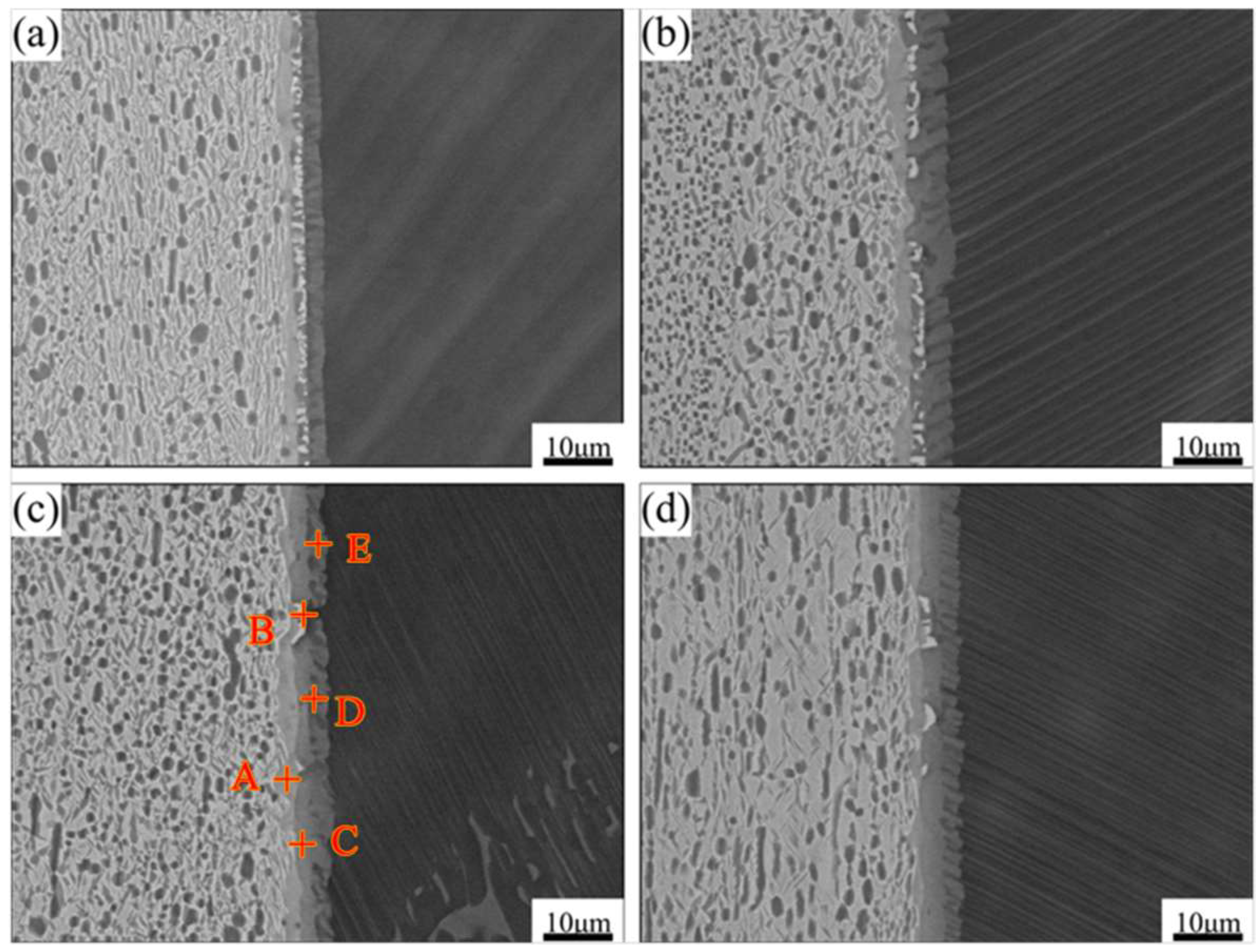
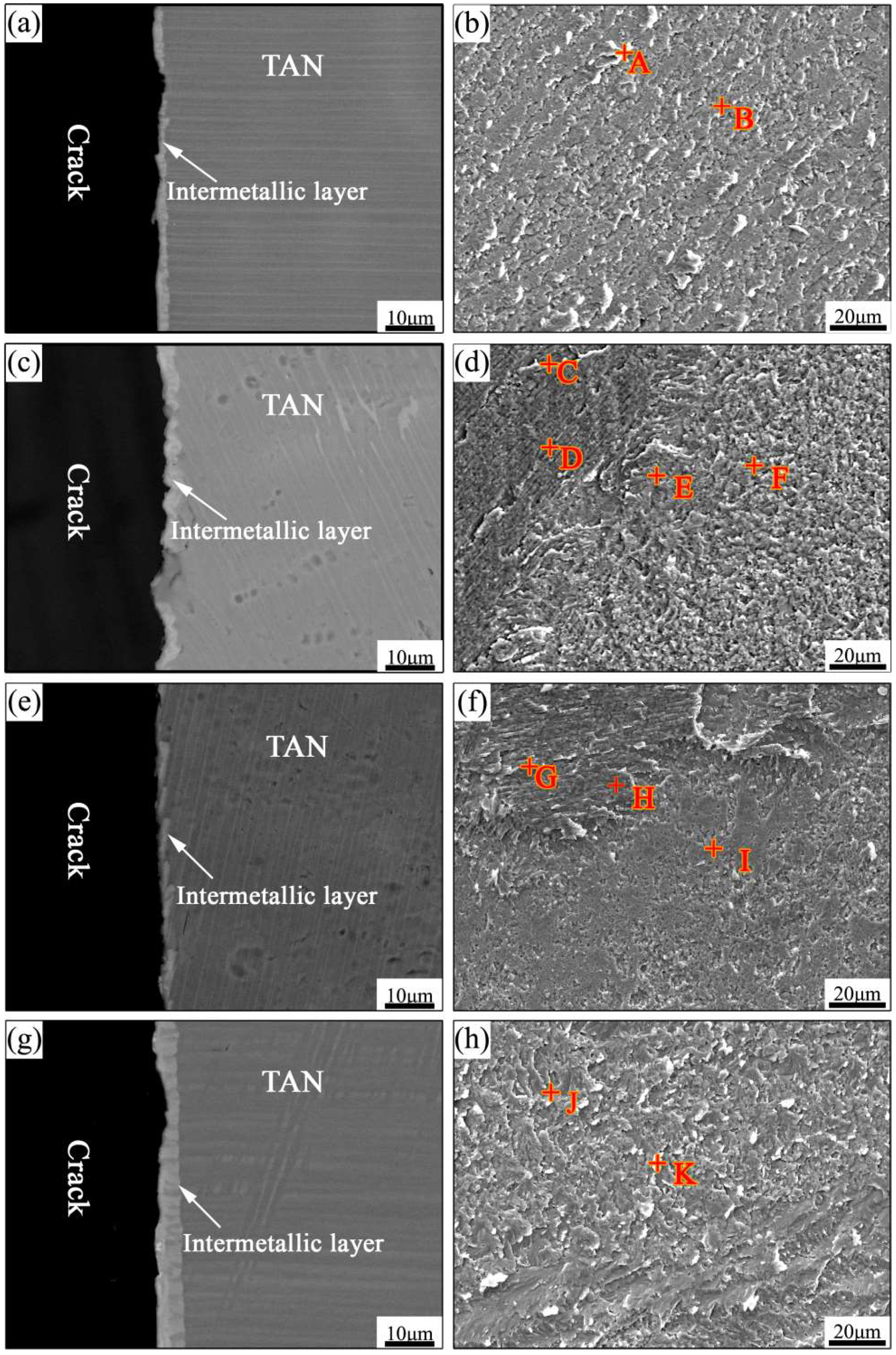

| Spot | Ti | Al | Nb | Possible Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 54.84 | 21.78 | 23.37 | B2 |
| B | 55.24 | 24.09 | 20.67 | O |
| C | 59.85 | 24.91 | 15.24 | α2-Ti3Al |
| D | 52.25 | 27.83 | 19.93 | O |
| E | 56.28 | 26.87 | 16.85 | α2-Ti3Al |
| F | 42.55 | 36.69 | 20.75 | Al(Nb,Ti)2 |
| G | 54.53 | 35.25 | 10.22 | α2-Ti3Al |
| H | 55.81 | 27.84 | 16.35 | α2-Ti3Al |
| Spot | Ti | Al | Nb | Possible Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 52.34 | 27.50 | 20.07 | O |
| B | 43.91 | 34.80 | 21.29 | Al(Nb,Ti)2 |
| C | 51.33 | 33.45 | 15.23 | α2-Ti3Al |
| D | 56.78 | 33.78 | 9.43 | α2-Ti3Al |
| E | 53.22 | 35.89 | 10.89 | α2-Ti3Al |
| Spot | Ti | Al | Nb | Possible Phase | Corresponding IMC Layer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 49.77 | 38.29 | 11.44 | Al(Nb,Ti)2 | mixed layer |
| B | 51.91 | 31.88 | 16.22 | α2-Ti3Al | mixed layer |
| C | 44.82 | 38.31 | 16.87 | Al(Nb,Ti)2 | mixed layer |
| D | 52.78 | 33.74 | 13.48 | α2-Ti3Al | Ti3Al phase layer |
| E | 50.09 | 31.37 | 18.54 | α2-Ti3Al | mixed layer |
| F | 50.28 | 31.25 | 18.47 | α2-Ti3Al | mixed layer |
| G | 44.63 | 47.38 | 8.00 | TiAl | TAN substrate |
| H | 58.16 | 33.27 | 8.57 | α2-Ti3Al | transition layer |
| H | 53.09 | 31.47 | 15.44 | α2-Ti3Al | transition layer |
| J | 52.67 | 35.08 | 12.25 | α2-Ti3Al | transition layer |
| K | 51.82 | 30.72 | 17.46 | α2-Ti3Al | transition layer |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bian, H.; Lei, Y.; Fu, W.; Hu, S.; Song, X.; Feng, J. Diffusion Bonding of Ti2AlNb Alloy and High-Nb-Containing TiAl Alloy: Interfacial Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Metals 2018, 8, 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121061
Bian H, Lei Y, Fu W, Hu S, Song X, Feng J. Diffusion Bonding of Ti2AlNb Alloy and High-Nb-Containing TiAl Alloy: Interfacial Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Metals. 2018; 8(12):1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121061
Chicago/Turabian StyleBian, Hong, Yuzhen Lei, Wei Fu, Shengpeng Hu, Xiaoguo Song, and Jicai Feng. 2018. "Diffusion Bonding of Ti2AlNb Alloy and High-Nb-Containing TiAl Alloy: Interfacial Microstructure and Mechanical Properties" Metals 8, no. 12: 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121061
APA StyleBian, H., Lei, Y., Fu, W., Hu, S., Song, X., & Feng, J. (2018). Diffusion Bonding of Ti2AlNb Alloy and High-Nb-Containing TiAl Alloy: Interfacial Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Metals, 8(12), 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121061






