Simultaneous Increase of Electrical Conductivity and Hardness of Al–1.5 wt.% Mn Alloy by Addition of 1.5 wt.% Cu and 0.5 wt.% Zr
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
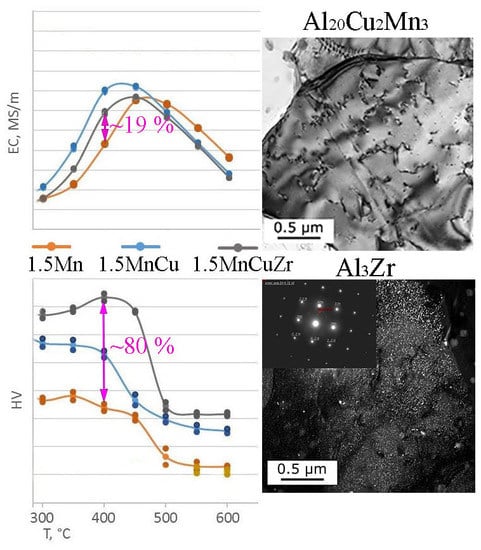
3.1. Computational and Experimental Analysis of The Evolution of The Microstructure
3.2. Hardness and Electrical Conductivity Analysis
4. Discussion
- Q(Al)—volume fraction of (Al) in alloy;
- CMn, CCu and CZr—concentrations of Mn, Cu and Zr in (Al) correspondingly, wt.%;
- KMn, KCu and KZr—coefficients of EC decrease per 1 wt.% of Mn, Cu and Zr in (Al) correspondingly;
- K0—empirical constant.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hatch, J.E. (Ed.) Aluminum: Properties and Physical Metallurgy; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1984; pp. 48–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, Q.C. Strain-induced precipitation kinetics during non-isothermal annealing of Al-Mn alloys. J. Alloy Compd. 2018, 735, 2275–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Arnberg, L. Quantitative study on the precipitation behavior of dispersoids in DC-cast AA3003 alloy during heating and homogenization. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 3415–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.G. Effect of magnesium on dispersoid strengthening of Al−Mn−Mg−Si (3xxx) alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 2793–2799. [Google Scholar]
- Belov, N.A.; Alabin, A.N.; Yakovev, A.A. Influence of copper on the formation of cast microstructure of aluminum alloys containing 1% (wt.) Mn. Tsvetnyye Met. 2014, 7, 66–72. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tadeusz, A.K.; Piwowarska, M.; Uliasz, P. Studies on the process of heat treatment of conductive AlZr alloys obtained in various productive processes. Arch. Metal. Mater. 2011, 56, 687–692. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Q.; Poole, W.J.; Wells, M.A.; Parson, N.C. Microstructure evolution during homogenization of Al–Mn–Fe–Si alloys: Modeling and experimental results. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4961–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.D.; Hill, T.; Kamp, N. The Effect of hot deformation on dispersoid evolution in a model 3xxx alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2014, 794, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.P.; Kuijpers, N.C.W.; van der Zwaag, S. Effect of microsegregation and dislocations on the nucleation kinetics of precipitation in aluminium alloy AA3003. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 341, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.G. Improvement in the mechanical properties and creep resistance of Al-Mn-Mg 3004 alloy with Sc and Zr addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 729, 196–207. [Google Scholar]
- Polmear, I.J. Light Alloys. From Traditional Alloys to Nanocrystals, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 129–130. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM B941-16. Standard Specification for Heat Resistant Aluminum-Zirconium Alloy Wire for Electrical Purposes; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Osuch, P.; Walkowicz, M.; Knych, T.; Dymek, S. Impact of the direct ageing procedure on the age hardening response of Al-Mg-Si 6101 alloy. Materials 2018, 11, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Sesin, J.M.; Arita, M.; Horita, Z. High strength and electrical conductivity of Al-Fe alloys produced by synergistic combination of high-pressure torsion and aging. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogucheva, A.A.; Zyabkin, D.V.; Kaibyshev, R.O. Effect of annealing on the structure and properties of aluminum alloy Al-8% MM. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2012, 53, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard specification. International Alloy Designations and Chemical Composition Limits for Wrought Aluminum and Wrought Aluminum Alloys; The Aluminum Association Publications: Arlington, VA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Liang, Z. Effect of Zr addition on properties of Al-Mg-Si aluminum alloy used for all aluminum alloy conductor. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4195–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, T.S.; Mavlyutov, A.M.; Latynina, T.A.; Ubyivovk, E.V.; Murashkin, M.Y.; Schneider, R.; Gerthsen, D.; Valiev, R.Z. Influence of severe plastic deformation on microstructure strength and electrical conductivity of aged Al-0.4Zr (wt.%) alloy. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2018, 55, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipling, K.E.; Karnesky, R.A.; Lee, C.P.; Dunand, D.C.; Seidman, D.N. Precipitation evolution in Al–0.1Sc, Al–0.1Zr and Al–0.1Sc–0.1Zr (at.%) alloys during isochronal aging. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 5184–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çadırl, E.; Tecer, H.; Sahin, M.; Yılmaz, E.; Kırındı, T.; Gündüz, M. Effect of heat treatments on the microhardness and tensile strength of Al–0.25 wt.% Zr alloy. J. Alloy Compd. 2015, 632, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, W.; Danoix, F.; Hallem, H.; Forbord, B.; Bostel, A.; Marthinsen, K. Precipitation kinetic of Al3(Sc,Zr) dispersoids in aluminium. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 470, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, N.A.; Korotkova, N.O.; Akopyan, T.K.; Pesin, A.M. Phase composition and mechanical properties of Al–1.5%Cu–1.5%Mn–0.35%Zr(Fe,Si) wire alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 782, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Q.; Yang, Y.Q.; Huang, B.; Li, M.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Ru, J.G. Crystal substructures of the rotation-twinned T (Al20Cu2Mn3) phase in 2024 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 583, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondolfo, L.F. Aluminum Alloys: Structure and Properties; Butterworths: London, UK, 1976; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, P.; Li, S. Effect of Ce addition on microstructure of Al20Cu2Mn3 twin phase in an Al–Cu–Mn casting alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 532, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Pei, C.; Ma, C. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Mn alloy with La and Sm addition. Rare Metals 2012, 31, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, N.A.; Alabin, A.N.; Matveeva, I.A.; Eskin, D.G. Effect of Zr additions and annealing temperature on electrical conductivity and hardness of hot rolled Al sheets. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo-Calc Software–Computational Materials Engineering. Available online: http://www.thermocalc.com (accessed on 7 October 2019).
- Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, W.; Zhang, W. Effect of applied pressure and ultrasonic vibration on microstructure and microhardness of Al—5.0Cu alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 2296–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoeller, T.L.; Sanders, T.H., Jr. The rate of solidification and the effects of local composition on the subsequent nucleation of Al20Cu2Mn3 dispersoid phase in Al-4Cu-0.3Fe-0.4Mn-0.2Si alloys. J. Phys. IV Fr. 2004, 120, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Murashkin, M.Y.; Sabirov, I. A nanostructural design to produce high-strength Al alloys with enhanced electrical conductivity. Scripta Mater. 2014, 76, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlach, M.; Stulikova, I.; Smola, B.; Kekule, T.; Kudrnova, H.; Kodetova, V.; Ocenasek, V.; Malek, J.; Neubert, V. Annealing effects in hot-deformed Al-Mn-Sc-Zr alloys. Metal. Mater. 2015, 53, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlach, M.; Cizeka, J.; Smola, B.; Stulikova, I.; Hruska, P.; Kodetova, V.; Danisa, S.; Tanprayoon, D.; Neubert, V. Influence of dislocations on precipitation processes in hot-extruded Al–Mn–Sc–Zr alloy. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 109, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlach, M.; Stulikova, I.; Smola, B.; Piesova, J.; Cisarova, H.; Danis, S.; Plasek, J.; Gemma, R.; Tanprayoon, D.; Neuber, V. Effect of cold rolling on precipitation processes in Al–Mn–Sc–Zr alloy. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 548, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wei, L. Effects of La addition on the mechanical properties and thermal-resistant properties of Al–Mg–Si–Zr alloys based on AA 6201. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Alloy Designation | Concentrations, wt.% (at.) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Mn | Fe | Si | Zr | Al | |
| 1.5Mn | - | 1.57 ± 0.03 (0.78) | 0.04 ± 0.03 (0.03) | 0.00 ± 0.02 (0.00) | - | Balance |
| 1.5Cu | 1.64 ± 0.05 (0.70) | - | 0.03 ± 0.03 (0.01) | 0.00 ± 0.02 (0.00) | - | |
| 1.5MnCu | 1.61 ± 0.05 (0.70) | 1.39 ± 0.03 (0.69) | 0.06 ± 0.03 (0.03) | 0.00 ± 0.02 (0.00) | - | |
| 1.5MnCuZr | 1.61 ± 0.05 (0.70) | 1.37 ± 0.03 (0.69) | 0.17 ± 0.03 (0.08) | 0.00 ± 0.02 (0.00) | 0.55 ± 0.06 (0.17) | |
| Alloy | Concentration in (Al), wt.% (at.) | EC, MS/m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Cu | Zr | Fe | Si | ||
| 1.5Mn | 1.52 ± 0.12 (0.76) | - | - | 0.04 ± 0.10 (0.02) | 0.01 ± 0.08 (0.01) | 13.3 |
| 1.5Cu | - | 1.17 ± 0.16 (0.48) | - | 0.03 ± 0.10 (0.02) | 0.02 ± 0.08 (0.02) | 32.4 |
| 1.5MnCu | 1.39 ± 0.11 (0.69) | 1.30 ± 0.16 (0.57) | - | 0.02 ± 0.10 (0.01) | 0.01 ± 0.08 (0.01) | 13.7 |
| 1.5MnCuZr | 1.18 ± 0.11 (0.56) | 1.04 ± 0.16 (0.43) | 0.39 ± 0.21 (0.11) | 0.05 ± 0.10 (0.03) | 0.01 ± 0.08 (0.01) | 12.2 |
| T, °C | Alloy | The Fraction of Phases, vol.% | Concentrations in (Al), wt.% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al6Mn | Al20Cu2Mn3 | Al2Cu | Mn | Cu | ||
| 200 | 0Cu | 6.19 | - | - | <0.01 | - |
| 1.5Cu | - | 7.01 | 0.82 | <0.01 | 0.10 | |
| 250 | 0Cu | 6.17 | - | - | <0.01 | - |
| 1.5Cu | - | 6.99 | 0.60 | <0.01 | 0.24 | |
| 300 | 0Cu | 6.12 | - | - | 0.02 | - |
| 1.5Cu | - | 6.96 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.47 | |
| 350 | 0Cu | 6.01 | - | - | 0.05 | - |
| 1.5Cu | - | 6.87 | - | 0.03 | 0.60 | |
| 400 | 0Cu | 5.80 | - | - | 0.11 | - |
| 1.5Cu | - | 6.64 | - | 0.07 | 0.64 | |
| 450 | 0Cu | 5.43 | - | - | 0.21 | - |
| 1.5Cu | - | 6.19 | - | 0.17 | 0.71 | |
| 500 | 0Cu | 4.83 | - | - | 0.37 | - |
| 1.5Cu | - | 5.54 | - | 0.33 | 0.82 | |
| 550 | 0Cu | 3.93 | - | - | 0.60 | - |
| 1.5Cu | - | 4.33 | - | 0.56 | 0.99 | |
| 600 | 0Cu | 2.53 | - | - | 0.93 | - |
| 1.5Cu | - | 2.78 | - | 0.86 | 1.22 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belov, N.; Korotkova, N.; Akopyan, T.; Tsydenov, K. Simultaneous Increase of Electrical Conductivity and Hardness of Al–1.5 wt.% Mn Alloy by Addition of 1.5 wt.% Cu and 0.5 wt.% Zr. Metals 2019, 9, 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121246
Belov N, Korotkova N, Akopyan T, Tsydenov K. Simultaneous Increase of Electrical Conductivity and Hardness of Al–1.5 wt.% Mn Alloy by Addition of 1.5 wt.% Cu and 0.5 wt.% Zr. Metals. 2019; 9(12):1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121246
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelov, Nikolay, Natalya Korotkova, Torgom Akopyan, and Kirill Tsydenov. 2019. "Simultaneous Increase of Electrical Conductivity and Hardness of Al–1.5 wt.% Mn Alloy by Addition of 1.5 wt.% Cu and 0.5 wt.% Zr" Metals 9, no. 12: 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121246
APA StyleBelov, N., Korotkova, N., Akopyan, T., & Tsydenov, K. (2019). Simultaneous Increase of Electrical Conductivity and Hardness of Al–1.5 wt.% Mn Alloy by Addition of 1.5 wt.% Cu and 0.5 wt.% Zr. Metals, 9(12), 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121246