Ottoman Mosques in Albania: Building Acoustic Exploration inside Five Case Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
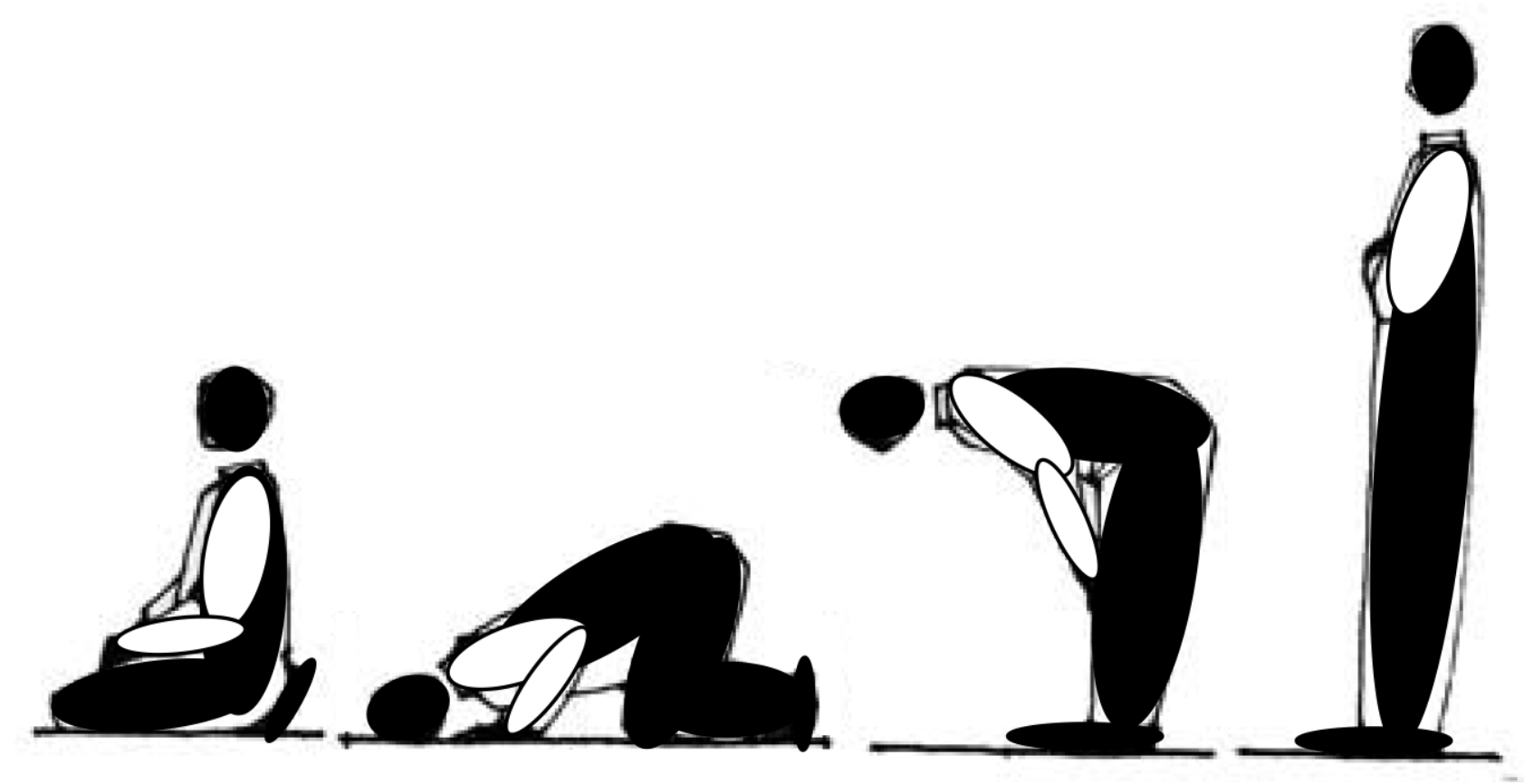
Holy Meaning of a Mosque
- Arabesque design, deriving from North Africa and evoking plant configurations;
- Arabic calligraphy;
- Repetition in modules of a specific geometric pattern.
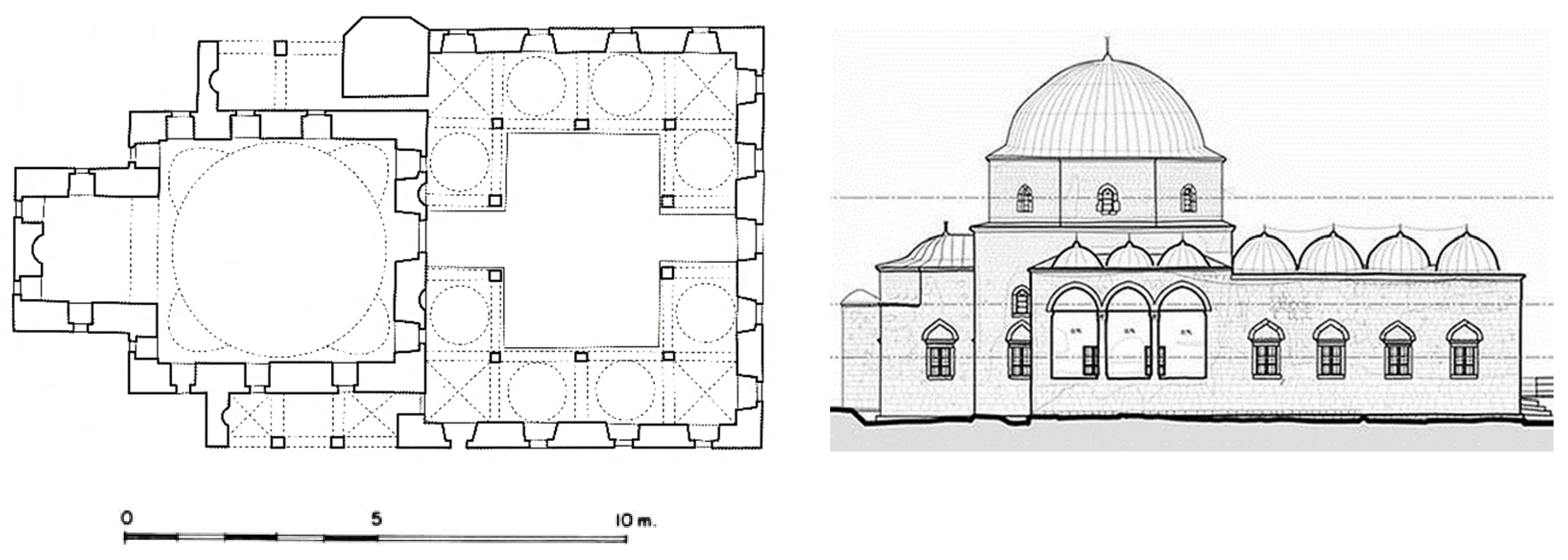
2. The Architectural Features of a Single-Unit Mosque
3. Historical Background and Architectural Characteristics
3.1. Mosque of Naziresha in Elbasan
3.2. Lead Mosque in Berat
3.3. Kubelie Mosque in Kavaja
3.4. Et’hem Bey Mosque in Tirana
3.5. Lead Mosque in Shkodra
3.6. Summary of the Architectural Features
4. Measurements
- Early decay time (EDT), measured in seconds, is the time corresponding to 10 dB from the decay curve of the sound pressure level measured after the interruption of the noise source. The EDT is particularly sensitive to the microphone position.
- Similar to EDT, the reverberation time (T20) is defined as the time required for the sound pressure level to drop by 60 dB after the noise source has been switched off. The value of this parameter is in function of the room volume and absorption of the surface area. Since the absorption of materials varies with frequency, the reverberation time varies according to the considered frequency bands.
- Clarity index (C50) is a characteristic parameter of speech goodness in a hall. It is a descriptor obtained from the correlation of the emitted energy that reaches the listener within the first 50 milliseconds (including the early reflections) and the energy that arrives in the following instants.
- Definition (D50) is a parameter related to the goodness of speech understanding in a room. It is obtained from the correlation of energy that reaches the receiver in the first 50 milliseconds and entire signal energy built up in the room until its total dissipation. The early reflection energy added to the direct sound gives a positive contribution to speech understanding.
- Speech transmission index (STI) represents the degree of amplitude modulation in a speech signal and refers to the distortion of a speech caused by reverberation, echoes and/or background noise. STI values can be comprised between 0 and 1: if the result is >0.5, favorable speech conditions occur.
5. Measured Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdou, A. Measurement of acoustical characteristics of mosques in Saudi Arabia. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammad, R.N.S. RASTI Measurements in Mosques in Amman, Jordan. Appl. Acoust. 1990, 30, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhateeb, A.; Adas, A.; Attia, M.; Balila, Y. The acoustics of Masjids, why they differ from the classical speech rooms. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Congress for Sound and Vibration (ICSV), Florence, Italy, 15–16 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kassim, D.; Putra, A.; Nor, M.J. The acoustical characteristics of the Sayyidina Abu Barak Mosque, UTeM. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 10, 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H.U. The Mosque: History, Architectural Development & Regional Diversity, Paperback ed.; Thames & Hudson Ltd.: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kahera, A.; Abdumalik, L.; Anz, C. Design Criteria for Mosques and Islamic Centers, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kuran, A. The Mosque in Early Ottoman Architecture; The University of Chicago Press Ltd.: Chicago, IL, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Kuban, D.A. Symbol of Ottoman Architecture: The Süleymaniye in Ottoman Architecture; Antique Collectors′ Club: Suffolk, UK, 2010; pp. 277–294. [Google Scholar]
- Wikimedia. Available online: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/a6/Elbasan_-_Naziresha_Mosque_%28by_Pudelek%29.JPG (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Wikimedia. Available online: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/71/Xhamia_e_Plumbit_Berat.jpg (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Wikimedia. Available online: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/89/Kavaja_Mosque.jpg (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Wikimedia. Available online: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/4b/Et%27hem_Bey_Mosque_%26_Clock_tower.jpg (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Wikimedia. Available online: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6e/Albania_Lead_Mosque_02.JPG (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Pätynen, J.; Katz, B.F.G. Investigation on the balloon as an impulse source. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, EL27–EL33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fausti, P.; Farina, A. Acoustic measurements in opera houses: Comparison between different techniques and equipment. J. Sound Vib. 2000, 232, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farina, A. Brahma Microphones—Ambisonics microphone. Available online: www.brahmamic.com (accessed on 8 July 2021).
- Available online: http://pcfarina.eng.unipr.it/Public/Brahma/Brahmavolver/ (accessed on 26 June 2021).
- Gomez-Agustina, L.; Bernard, J. Practical and technical suitability perceptions of sound sources and test signals used in room acoustic testing. In Proceedings of the 48th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering Noise Control Engineering Inter-Noise, Madrid, Spain, 16–19 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Agustina, L.; Vazquez-Barrera, P. Repeatability of the balloon pop as a sound source in a room. In Proceedings of the Institute of Acoustics, London, UK, 5–9 October 2020; Volume 42. [Google Scholar]
- Part 1: Performance Spaces. ISO 3382-1: Acoustics—Measurement of Room Acoustic Parameters; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Abdou, A.A. Assessment of mosque acoustics for speech intelligibility employing impulse response measurements. In Proceedings of the 15th International Congress Sound Vibration, Daejeon, South Korea, 6–10 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, V.L. Acoustical criteria for auditoriums and their relation to model techniques. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1970, 47, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zühre, S.G.; Mehmet, Ç. Impact of design decisions on acoustical comfort parameters: Case study of Doğramacızade Ali Paşa Mosque. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 834–844. [Google Scholar]
- Alic, E.; Ozcevik Bilen, A. Determination of the characteristics of contemporary Turkish mosque and its acoustic properties. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Congress Acoustics, Aachen, Germany, 9–13 September 2019; pp. 3983–3990. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelazeez, M.K.; Hammad, R.N.; Mustafa, A. Acoustics of King Abdullah Mosque. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 90, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhateeb, A.; Eldakdoky, S. The acoustics of Mumluk masjids: A case study of Iwan-type masjids in Cairo. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 178, 107988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peer, I.; Rafaely, B.; Zigel, Y. Room acoustics parameters affecting speaker recognition degradation under reverberation. In Proceedings of the 2008 Hands-Free Speech Communication and Microphone Arrays (HSCMA), Trento, Italy, 6–8 May 2008; pp. 136–139. [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt, W.; Abel Alim, O.; Schmidt, W. Definition and basis of making an objective evaluation to distinguish between useful and useless clarity defining musical performances. Acta Acust. 1975, 3, 126–137. [Google Scholar]
- Thiele, R. Richtungsverteilungs und zeitfolge del schallruckewurfe in raumen. Acta Acust. 1953, 3, 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Aleshkin, V.; Schirjetsky, C.; Subbotkin, A. Estimating sound absorption coefficient of prayers in mosques. Akustika 2019, 32, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaburro, G.; Iannace, G.; Lombardi, I.; Trematerra, A. Acoustic design of ancient buildings: The odea of Pompeii and Posillipo. Buildings 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronchin, L.; Merli, F.; Manfren, M.; Nastasi, B. The sound diffusion in Italian Opera Houses: Some examples. Build. Acoust. 2020, 27, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukaj, S.; Ciaburro, G.; Iannace, G.; Lombardi, I.; Trematerra, A. The Acoustics of the Benevento Roman Theatre. Buildings 2021, 11, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, G.; Ciaburro, G.; Trematerra, A.; Foglia, C. Acoustic correction of a renaissance period hall. Can. Acoust. —Acoust. Can. 2019, 47, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Iannace, G.; Berardi, U.; De Rossi, F.; Mazza, S.; Trematerra, A.; Ciaburro, G. Acoustic enhancement of a modern church. Buildings 2019, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oldham, D.J.; Elkhateeb, A.E. The absorption characteristics of Muslim worshippers. Build. Acoust. 2008, 15, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, A.; Hafizah, D.; Yaakob, M.Y.; Nor, M.J.M. Study on the use of micro-perforated panel to improve acoustic performance in mosque. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 393, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.J.; D’Antonio, P. Acoustic Absorbers and Diffusers: Theory, Design and Application, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]



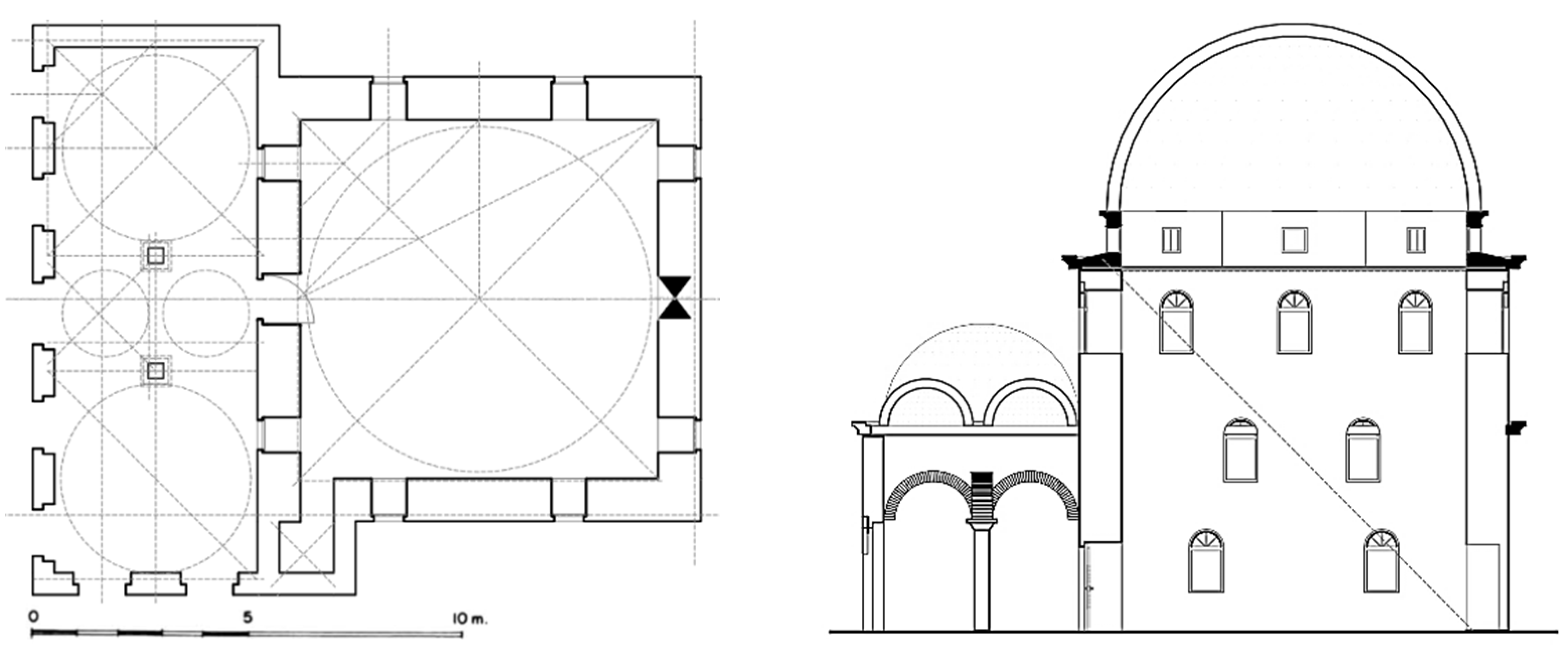

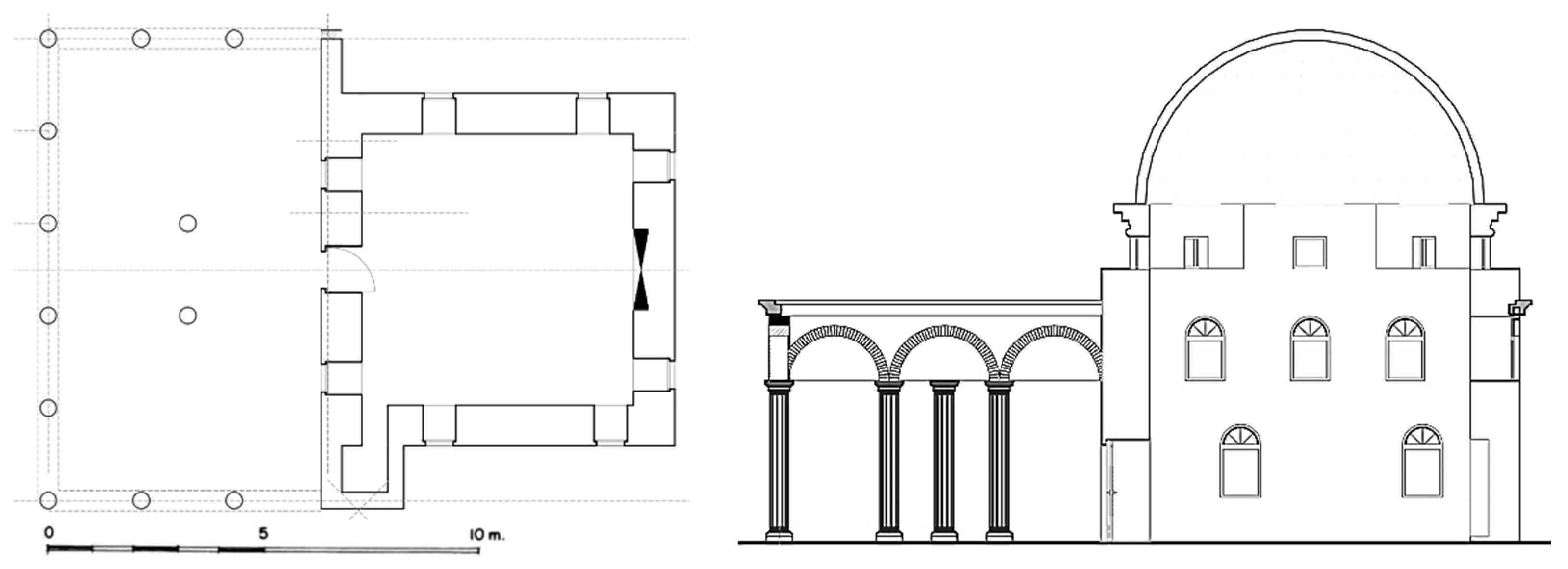

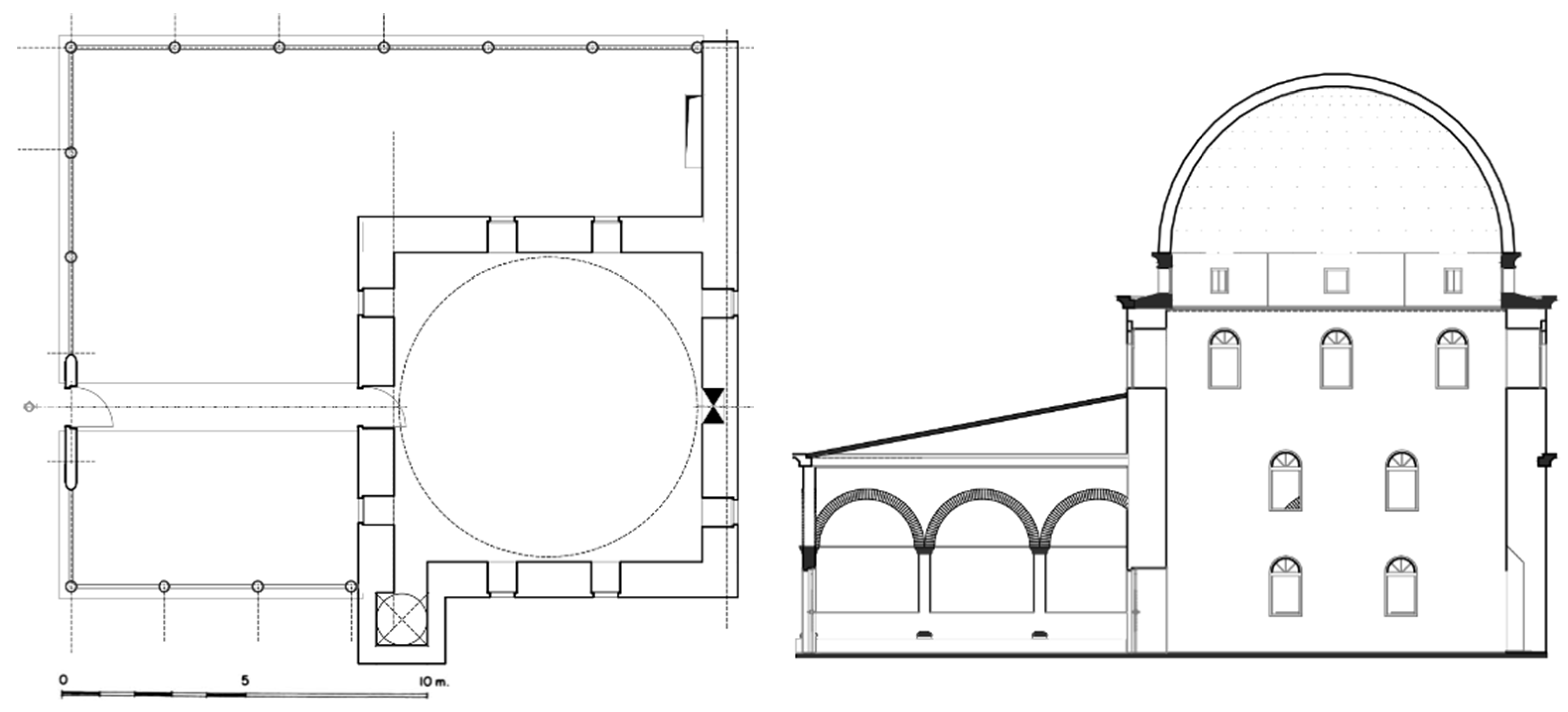









| Description | Elbasan | Berat | Kavaja | Tirana | Shkodra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Musalla dimensions (m) | 9 × 9 | 10.2 × 10.2 | 8.6 × 8.6 | 10.5 × 10.5 | 9.2 × 9.2 |
| Height of dome (m) | 13.9 | 14.4 | 10.5 | 14.4 | 14.7 |
| Total volume (m3) | 954 | 1307 | 691 | 1394 | 1050 |
| Presence of courtyard | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Bad | Poor | Fair | Good | Excellent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–0.3 | 0.3–0.45 | 0.45–0.6 | 0.6–0.75 | 0.75–1.0 |
| A-Weighted Equivalent Sound Pressure Levels LAeq (dB) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elbasan | Berat | Kavaja | Tirana | Shkodra |
| 51 | 49 | 48 | 56 | 43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sukaj, S.; Bevilacqua, A.; Ciaburro, G.; Iannace, G.; Trematerra, A. Ottoman Mosques in Albania: Building Acoustic Exploration inside Five Case Studies. Buildings 2021, 11, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11100430
Sukaj S, Bevilacqua A, Ciaburro G, Iannace G, Trematerra A. Ottoman Mosques in Albania: Building Acoustic Exploration inside Five Case Studies. Buildings. 2021; 11(10):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11100430
Chicago/Turabian StyleSukaj, Silvana, Antonella Bevilacqua, Giuseppe Ciaburro, Gino Iannace, and Amelia Trematerra. 2021. "Ottoman Mosques in Albania: Building Acoustic Exploration inside Five Case Studies" Buildings 11, no. 10: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11100430
APA StyleSukaj, S., Bevilacqua, A., Ciaburro, G., Iannace, G., & Trematerra, A. (2021). Ottoman Mosques in Albania: Building Acoustic Exploration inside Five Case Studies. Buildings, 11(10), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11100430








