Anchor Force Monitoring Using Impedance Technique with Single-Point Mount Lead-Zirconate-Titanate Interface: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
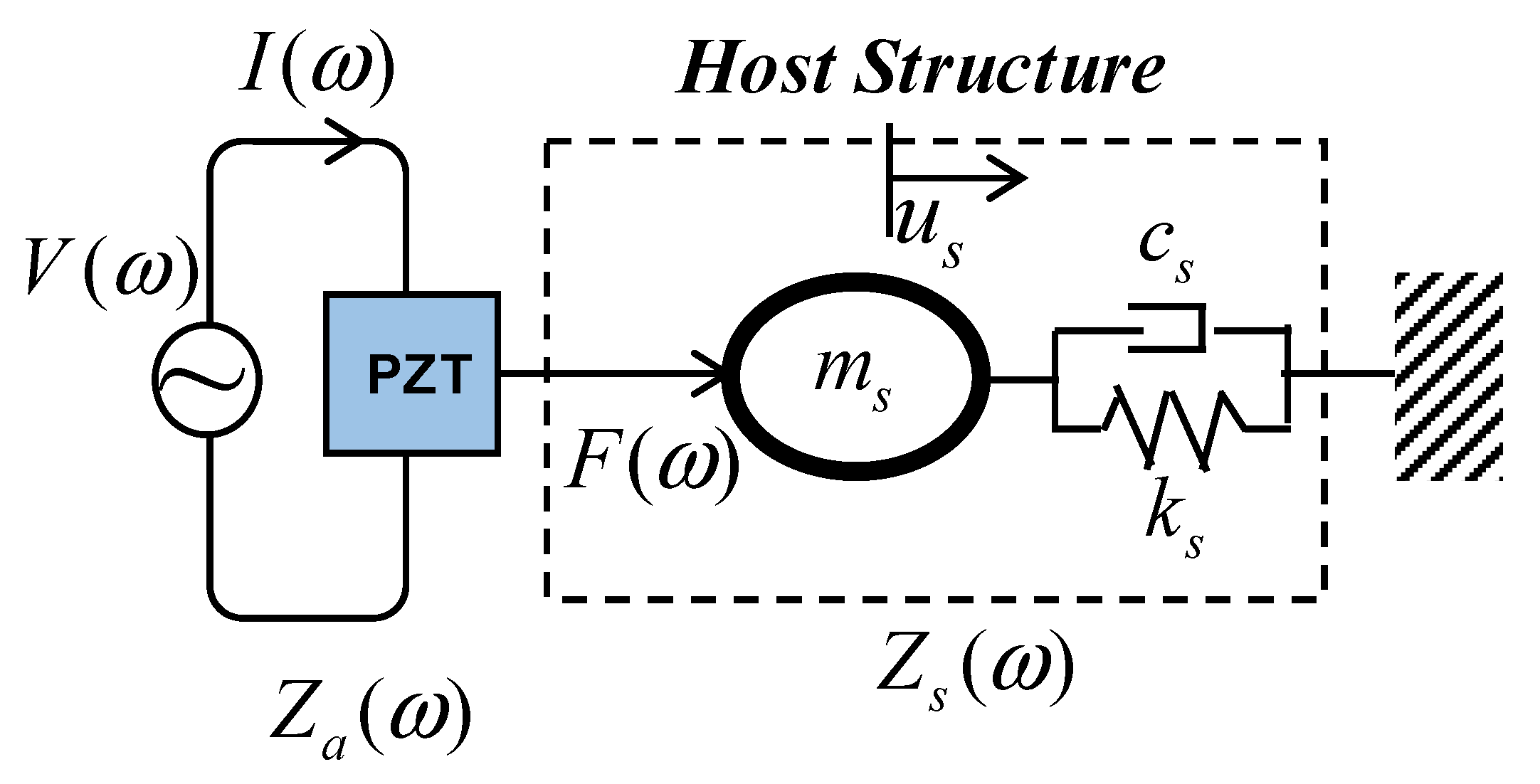
2. The Fundamental of Electromechanical Impedance Technique
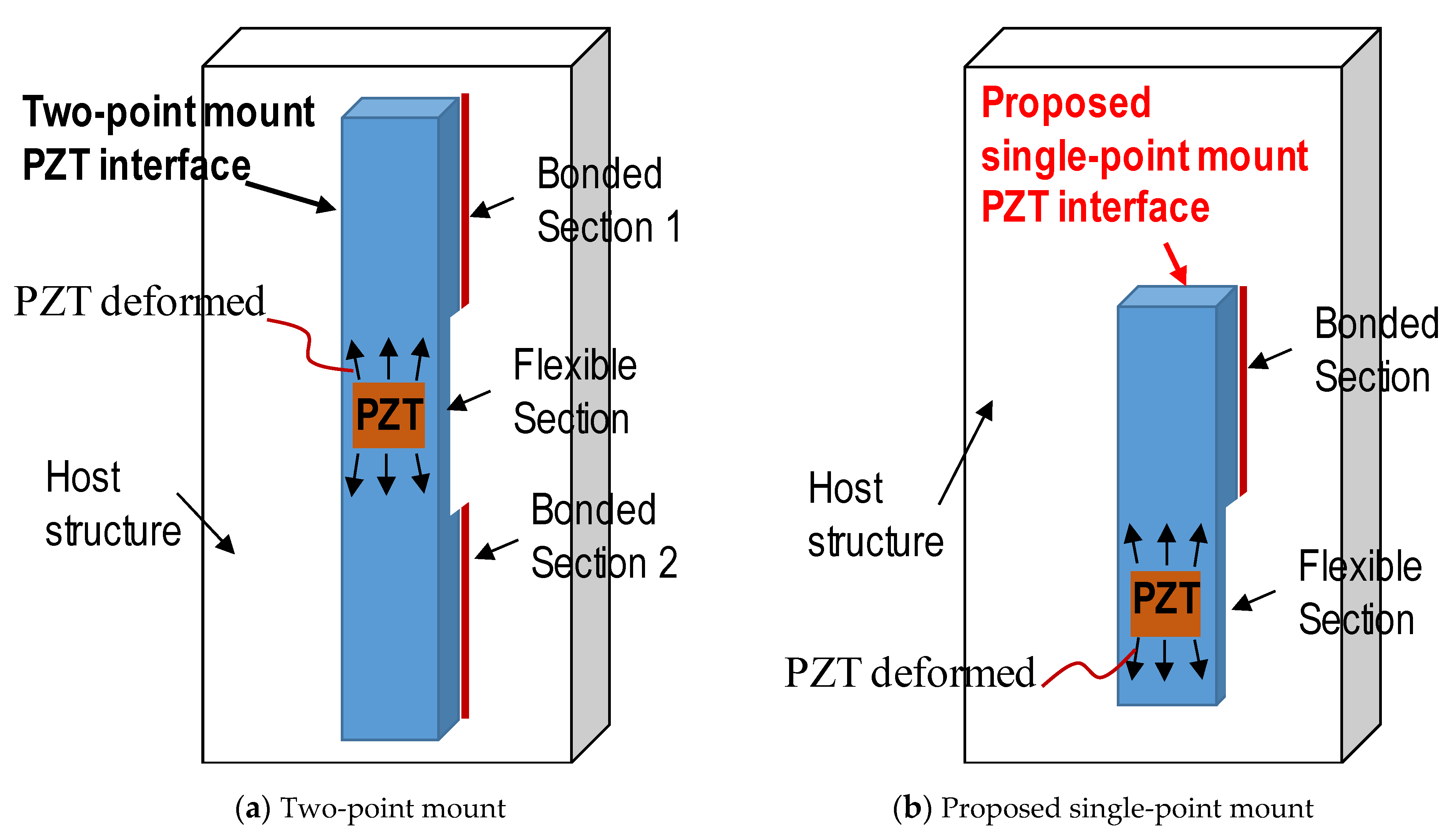
3. Design of Single-Point Mount PZT Interface and Its Numerical Feasibility
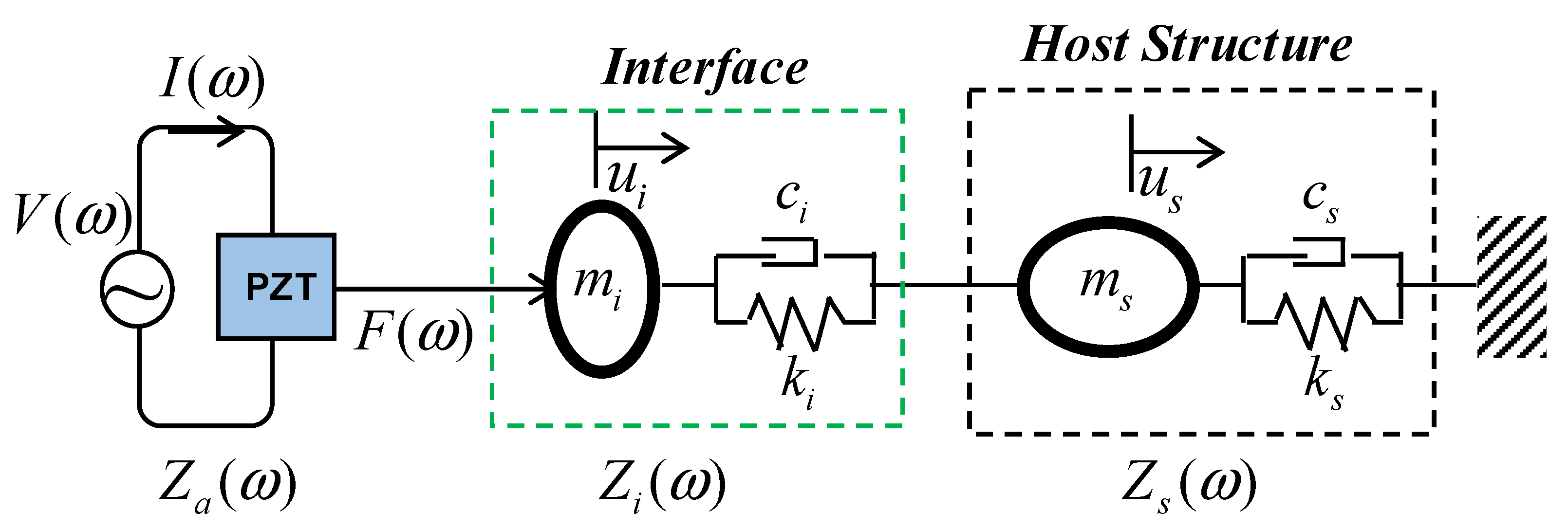
3.1. Conceptual Design of Single-Point Mount PZT Interface and Its Electromechanical Impedance
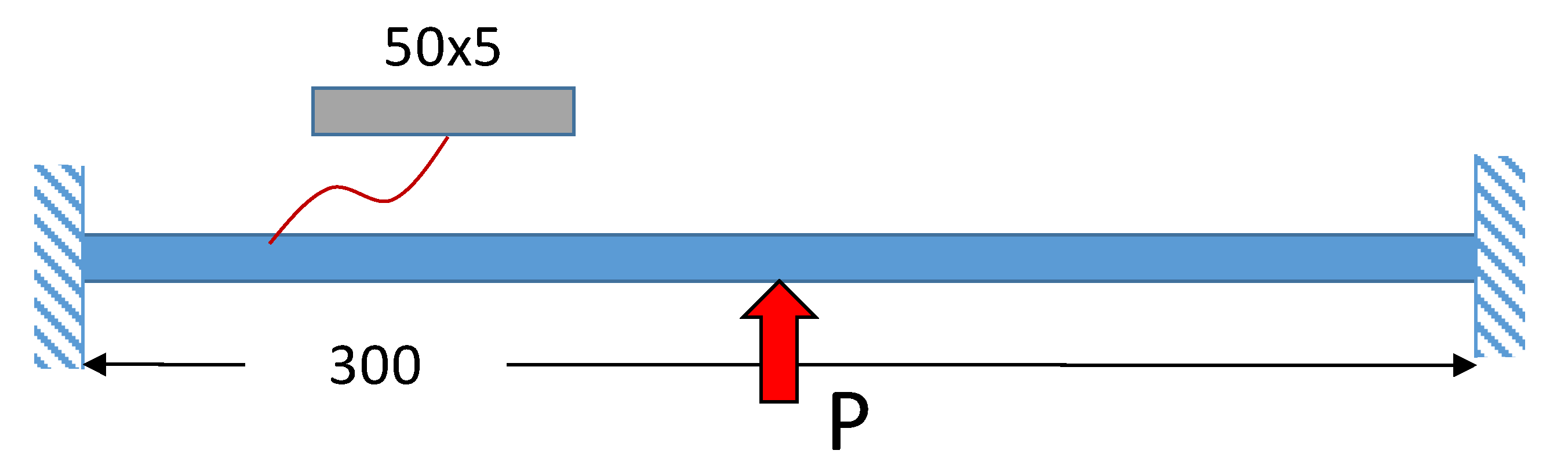
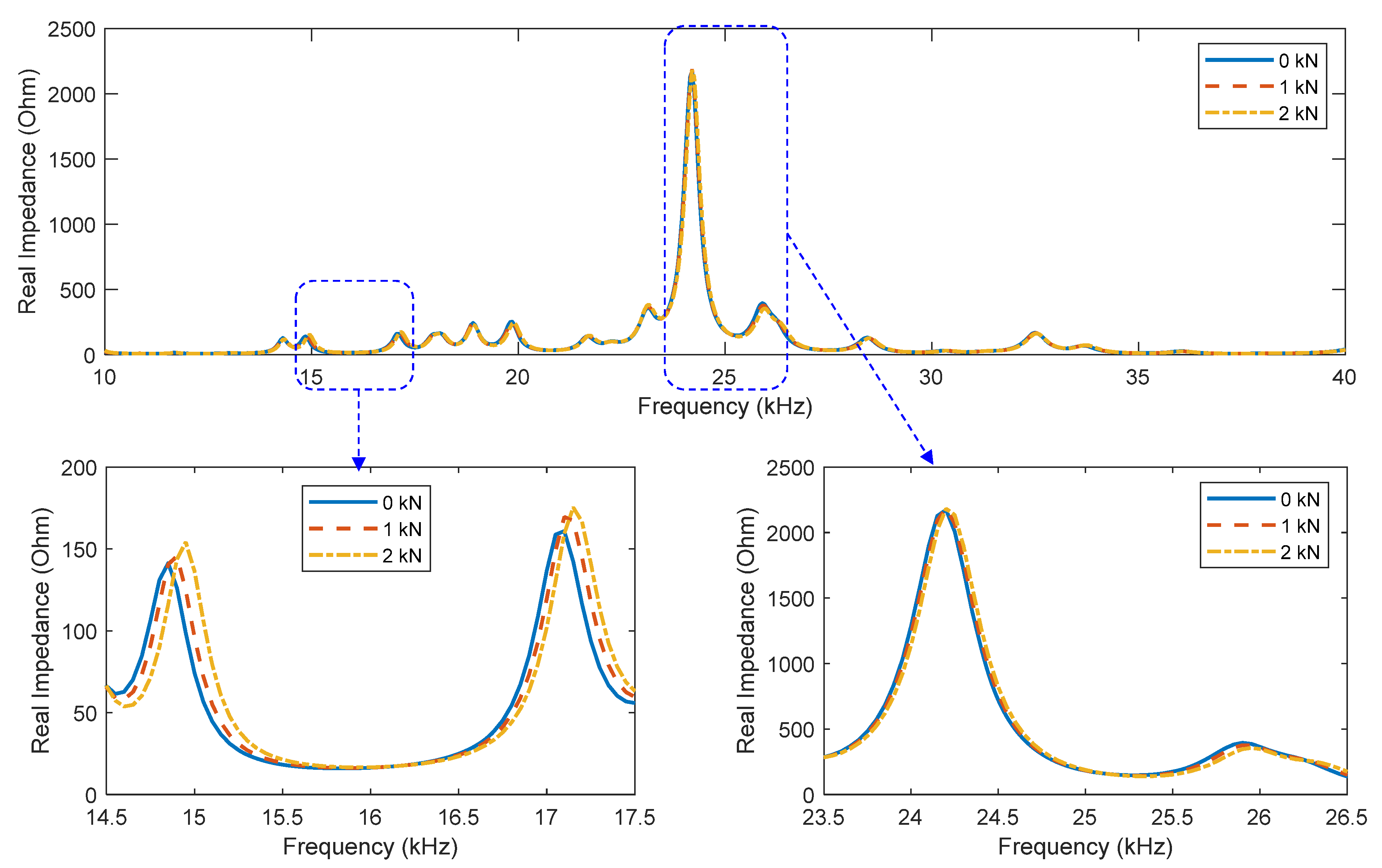
3.2. Numerical Feasibility of Single-Point Mount PZT Interface
4. Experimental Feasibility Study
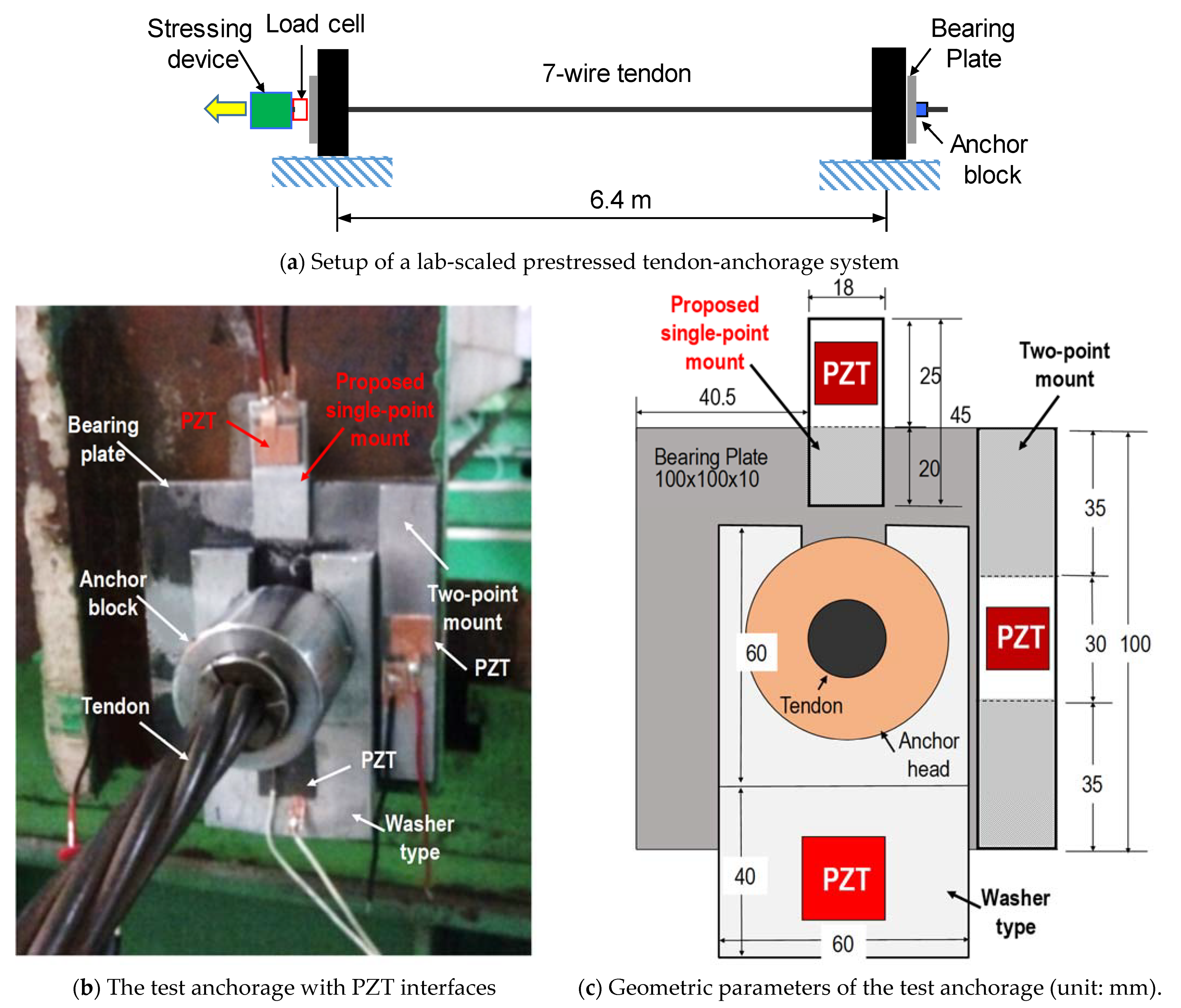
4.1. Experimental Setup
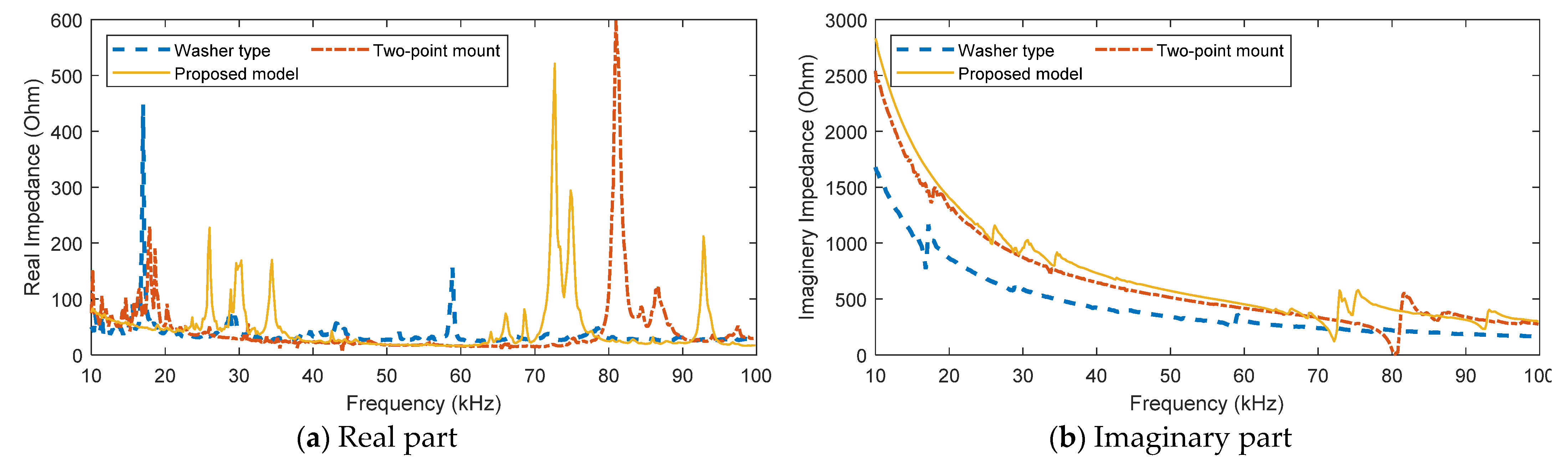
4.2. Electromechanical Impedance Responses
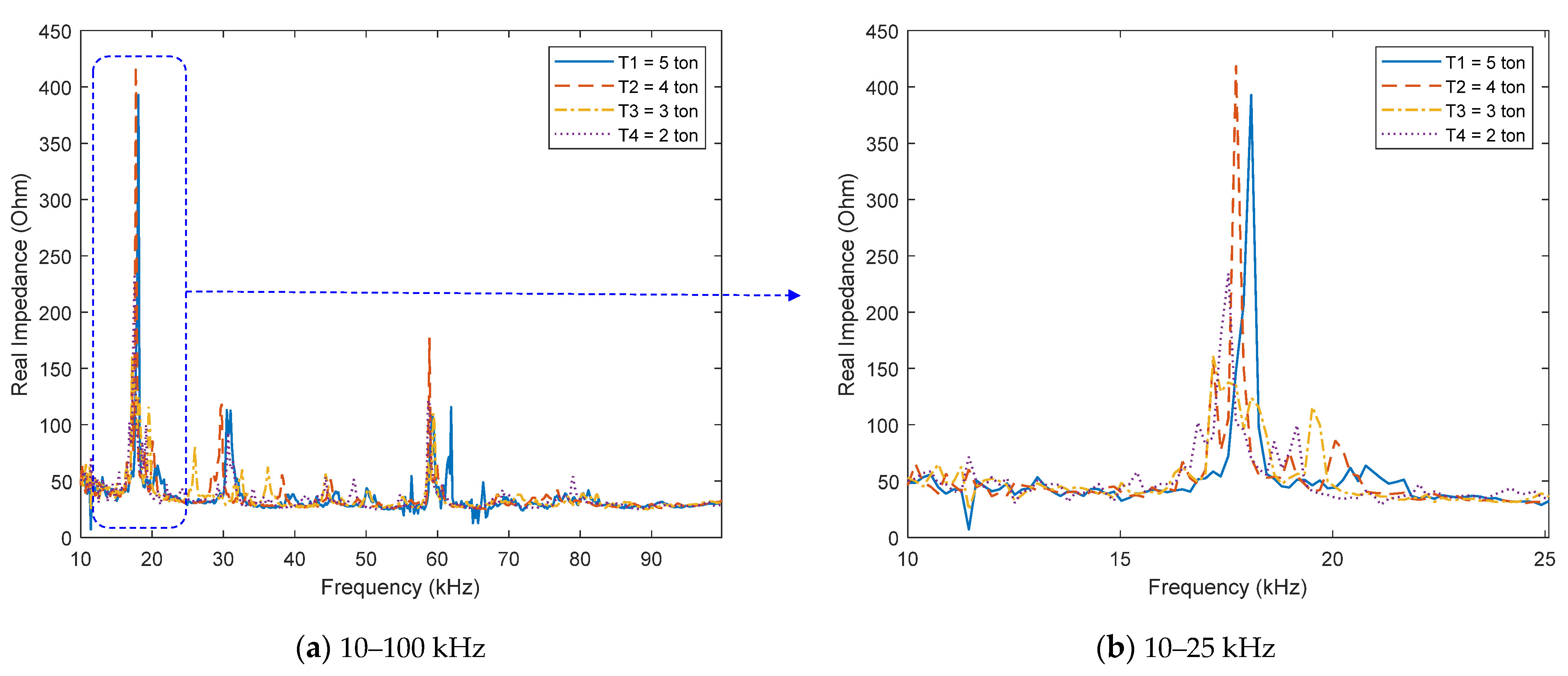
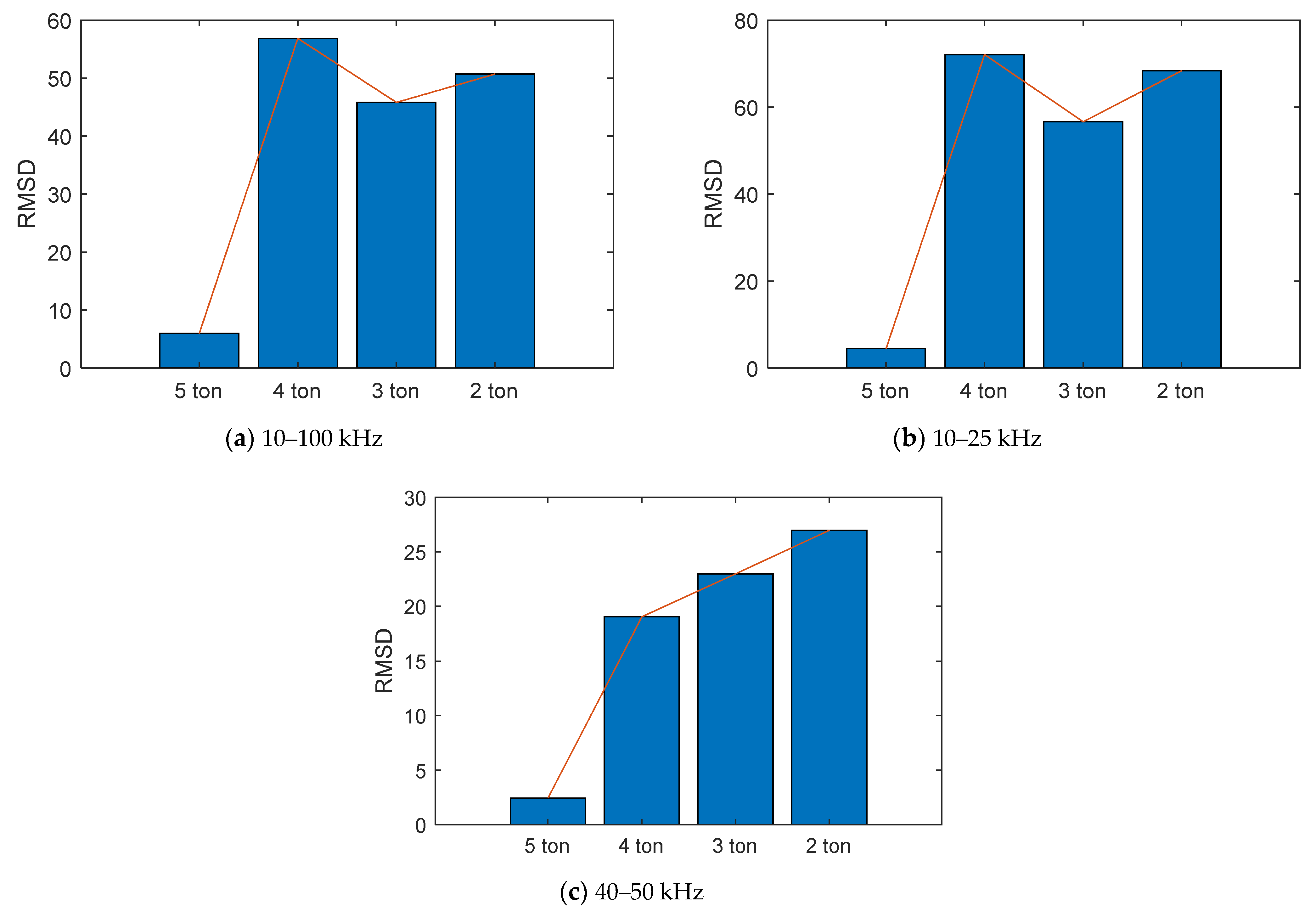
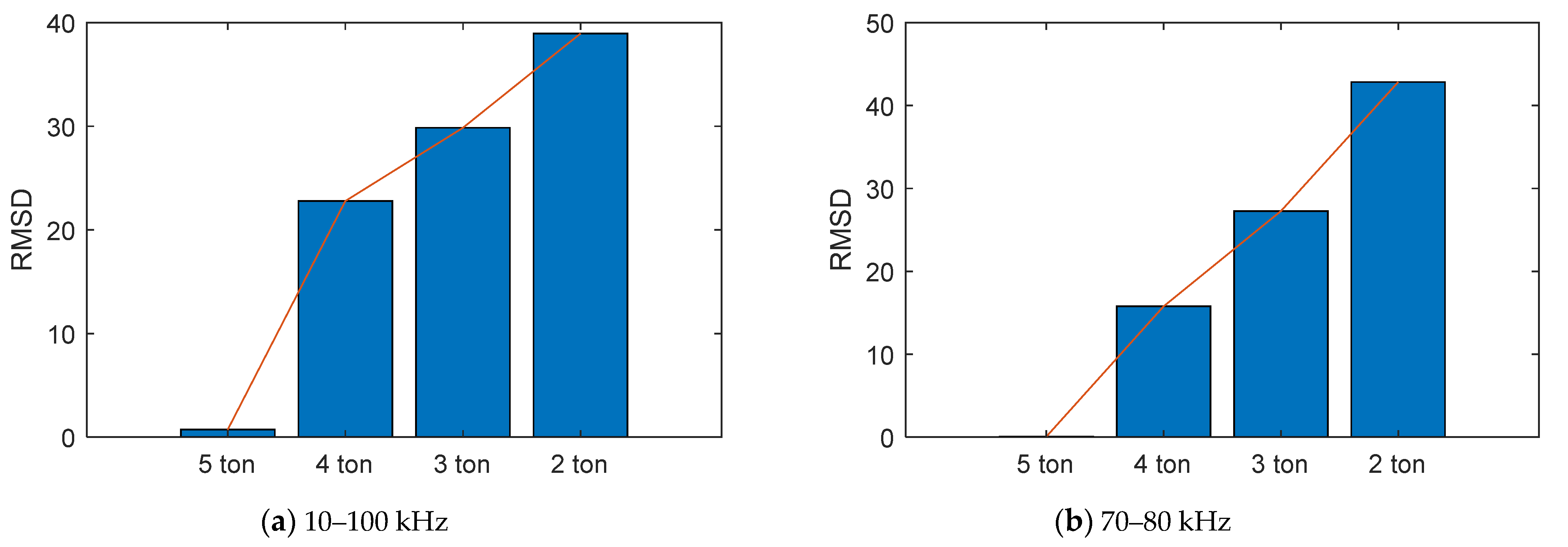
4.3. Monitoring of Anchor Force Reduction Using Electromechanical Impedance Responses
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandrasekar, P.; Dayaratnam, P. Analysis of probability of failure of prestressed concrete beams. Build. Sci. 1975, 10, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuyama, S.; Yokoyama, K.; Niitani, K.; Ohtsu, M.; Uomoto, T. Detection and evaluation of failures in high-strength tendon of prestressed concrete bridges by acoustic emission. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyemelukwe, O.; Kunnath, S. Field Measurement and Evaluation of Time-Dependent Losses in Prestressed Concrete Bridges; Final Report, Project Number: WPI-0510735; Florida Department of Transportation: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Yao, R. Monitoring and analysis of long-term prestress losses in post-tensioned concrete beams. Measurement 2018, 122, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, J.; Nowak, W.; Slowik, V.; Klink, T. Strain Monitoring at a Prestressed Concrete Bridge. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Optical Fiber Sensors, Williamsburg, VA, USA, 28 October 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Nellen, P.; Broennimann, R.; Frank, A.; Mauron, P.; Sennhauser, U. Structurally Embedded Fiber Bragg Gratings: Civil Engineering Applications; SPIE: Boston, MA, USA, 1999; Volume 3860. [Google Scholar]
- Suhartomo, A.; Simatupang, J.W.; Widjaja, B.; Gapsari, F. Feasibility Study on Structural Health Monitoring Systems Using Fiber-Optic Sensors (FOS) Technology for Transportation Infrastructures in Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 494, 012054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Park, Y.; Park, S.Y.; Cho, K.; Cho, J.R. A sensor-type PC strand with an embedded FBG sensor for monitoring prestress forces. Sensors 2015, 15, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, T.-C.; Kim, J.-T. FOS-Based Prestress Force Monitoring and Temperature Effect Estimation in Unbonded Tendons of PSC Girders. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2017, 30, B4016005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Sung, H.-J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.-M. Monitoring of tension force and load transfer of groundanchor by using optical FBG sensors embedded tendon. Smart Struct. Syst. 2011, 7, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, D.; Zhu, H.; Luo, H.; Yang, J. An effective electromechanical impedance technique for steel structural health monitoring. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, S.; Soh, C.K. Electro-Mechanical Impedance Technique. In Smart Materials in Structural Health Monitoring, Control and Biomechanics; Soh, C.-K., Yang, Y., Bhalla, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 17–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Sohn, H.; Farrar, C.R.; Inman, D.J. Overview of piezoelectric impedance-based health monitoring and path forward. Shock Vib. Dig. 2003, 35, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, J.; Park, S.; Yun, C.-B. Impedance-based structural health monitoring using neural networks for autonomous frequency range selection. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 125011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.J.; Kim, M.K.; Sohn, H.; Park, C.Y. Impedance based damage detection under varying temperature and loading conditions. NDT E Int. 2011, 44, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.D.; Lee, P.Y.; Nguyen, K.D.; Hong, D.S.; Kim, J.T.; Shin, S.W.; Yun, C.B.; Shinozuka, M. Solar-powered multi-scale sensor node on Imote2 platform for hybrid SHM in cable-stayed bridge. Smart Struct. Syst. 2012, 9, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campeiro, L.M.; da Silveira, R.Z.; Baptista, F.G. Impedance-based damage detection under noise and vibration effects. Struct. Health Monit. 2018, 17, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Soman, R.; Wandowski, T.; Malinowski, P. A Variable Data Fusion Approach for Electromechanical Impedance-Based Damage Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xue, X. Advances in the Structural Health Monitoring of Bridges Using Piezoelectric Transducers. Sensors 2018, 18, 4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-T.; Park, J.-H.; Hong, D.-S.; Park, W.-S. Hybrid health monitoring of prestressed concrete girder bridges by sequential vibration-impedance approaches. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Jaber, H.; Glisic, B. Monitoring of prestressing forces in prestressed concrete structures—An overview. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, T.C.; Kim, J.T. RBFN-based temperature compensation method for impedance monitoring in prestressed tendon anchorage. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2018, 25, e2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-T.; Park, J.-H.; Hong, D.-S.; Cho, H.-M.; Na, W.-B.; Yi, J.-H. Vibration and impedance monitoring for prestress-loss prediction in PSC girder bridges. Smart Struct. Syst. 2009, 5, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.-C.; Lee, S.-Y.; Dang, N.-L.; Kim, J.-T. Sensing region characteristics of smart piezoelectric interface for damage monitoring in plate-like structures. Sensors 2019, 19, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, T.-C.; Dang, N.-L.; Kim, J.-T. Advances and challenges in impedance-based structural health monitoring. Struct. Monit. Maint. 2017, 4, 301–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.-D.; Kim, J.-T. Smart PZT-interface for wireless impedance-based prestress-loss monitoring in tendon-anchorage connection. Smart Struct. Syst. 2012, 9, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.-C.; Kim, J.-T. Impedance-Based Cable Force Monitoring in Tendon-Anchorage Using Portable PZT-Interface Technique. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.-C.; Park, Y.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, J.-T. Feasibility verification of mountable PZT-interface for impedance monitoring in tendon-anchorage. Shock Vib. 2015, 2015, 262975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryu, J.-Y.; Huynh, T.-C.; Kim, J.-T. Tension force estimation in axially loaded members using wearable piezoelectric interface technique. Sensors 2019, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tawie, R.; Park, H.B.; Baek, J.; Na, W.S. Damage Detection Performance of the Electromechanical Impedance (EMI) Technique with Various Attachment Methods on Glass Fibre Composite Plates. Sensors 2019, 19, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, T.-C.; Kim, J.-T. Quantitative damage identification in tendon anchorage via PZT interface-based impedance monitoring technique. Smart Struct. Syst. 2017, 20, 181–195. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, N.L.; Huynh, T.C.; Pham, Q.Q.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.T. Damage-sensitive impedance sensor placement on multi-strand anchorage based on local stress variation analysis. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2020, 27, e2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.-L.; Huynh, T.-C.; Kim, J.-T. Local strand-breakage detection in multi-strand anchorage system using an impedance-based stress monitoring method—Feasibility study. Sensors 2019, 19, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, T.-C.; Kim, J.-T. Quantification of temperature effect on impedance monitoring via PZT interface for prestressed tendon anchorage. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 125004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.-C.; Lee, K.-S.; Kim, J.-T. Local dynamic characteristics of PZT impedance interface on tendon anchorage under prestress force variation. Smart Struct. Syst. 2015, 15, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Sun, F.P.; Rogers, C.A. Coupled Electro-Mechanical Analysis of Adaptive Material Systems—Determination of the Actuator Power Consumption and System Energy Transfer. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1994, 5, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Farrar, C.R.; di Scalea, F.L.; Coccia, S. Performance assessment and validation of piezoelectric active-sensors in structural health monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.-P.; Tran, Q.H.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Pradhan, A.M.S.; Huynh, T.-C. Understanding Impedance Response Characteristics of a Piezoelectric-Based Smart Interface Subjected to Functional Degradations. Complexity 2021, 2021, 5728679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Farrar, C.R.; Rutherford, A.C.; Robertson, A.N. Piezoelectric Active Sensor Self-Diagnostics Using Electrical Admittance Measurements. J. Vib. Acoust. 2006, 128, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, G.; Yun, C.-B.; Farrar, C.R. Sensor Self-diagnosis Using a Modified Impedance Model for Active Sensing-based Structural Health Monitoring. Struct. Health Monit. 2009, 8, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.P.; Chaudhry, Z.; Liang, C.; Rogers, C.A. Truss Structure Integrity Identification Using PZT Sensor-Actuator. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1995, 6, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, T.J.; Balamonica, K.; Priya, C.B.; Gopalakrishnan, N.; Murthy, S.G.N. Piezoelectric EMI–Based Monitoring of Early Strength Gain in Concrete and Damage Detection in Structural Components. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2017, 23, 04017029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Kim, J.T.; Ta, Q.B.; Ho, D.D.; Phan, T.T.V.; Huynh, T.C. Deep learning-based functional assessment of piezoelectric-based smart interface under various degradations. Smart Struct. Syst. 2021, 28, 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Qu, W.; Xiao, L.; Lu, Y. Removal of temperature effect in impedance-based damage detection using the cointegration method. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2019, 30, 2189–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, K.; Lalande, F.; Rogers, C.A. Effects of temperature on the electrical impedance of piezoelectric sensors. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures and Materials 1996: Smart Structures and Integrated Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 25 February 1996. [Google Scholar]






| Parameters | The Interface and the Beam |
|---|---|
| Young’s modulus, E (GPa) | 70 |
| Poisson’s ratio, υ | 0.33 |
| Mass density, ρ (kg/m3) | 2700 |
| Damping loss factor, η | 0.02 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Elastic compliance, (m2/N) | |
| Dielectric coupling constant, (C/N) | |
| Permittivity, (Farad/m) | |
| Mass density, ρ (kg/m3) | 7750 |
| Damping loss factor, η | 0.005 |
| Dielectric loss factor, δ | 0.015 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, T.-C.; Ho, D.-D.; Huynh, T.-C. Anchor Force Monitoring Using Impedance Technique with Single-Point Mount Lead-Zirconate-Titanate Interface: A Feasibility Study. Buildings 2021, 11, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11090382
Le T-C, Ho D-D, Huynh T-C. Anchor Force Monitoring Using Impedance Technique with Single-Point Mount Lead-Zirconate-Titanate Interface: A Feasibility Study. Buildings. 2021; 11(9):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11090382
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Thanh-Cao, Duc-Duy Ho, and Thanh-Canh Huynh. 2021. "Anchor Force Monitoring Using Impedance Technique with Single-Point Mount Lead-Zirconate-Titanate Interface: A Feasibility Study" Buildings 11, no. 9: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11090382
APA StyleLe, T.-C., Ho, D.-D., & Huynh, T.-C. (2021). Anchor Force Monitoring Using Impedance Technique with Single-Point Mount Lead-Zirconate-Titanate Interface: A Feasibility Study. Buildings, 11(9), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11090382







