UHPC-Filled Rectangular Steel Tubular Beam–Column: Numerical Study and Design
Abstract
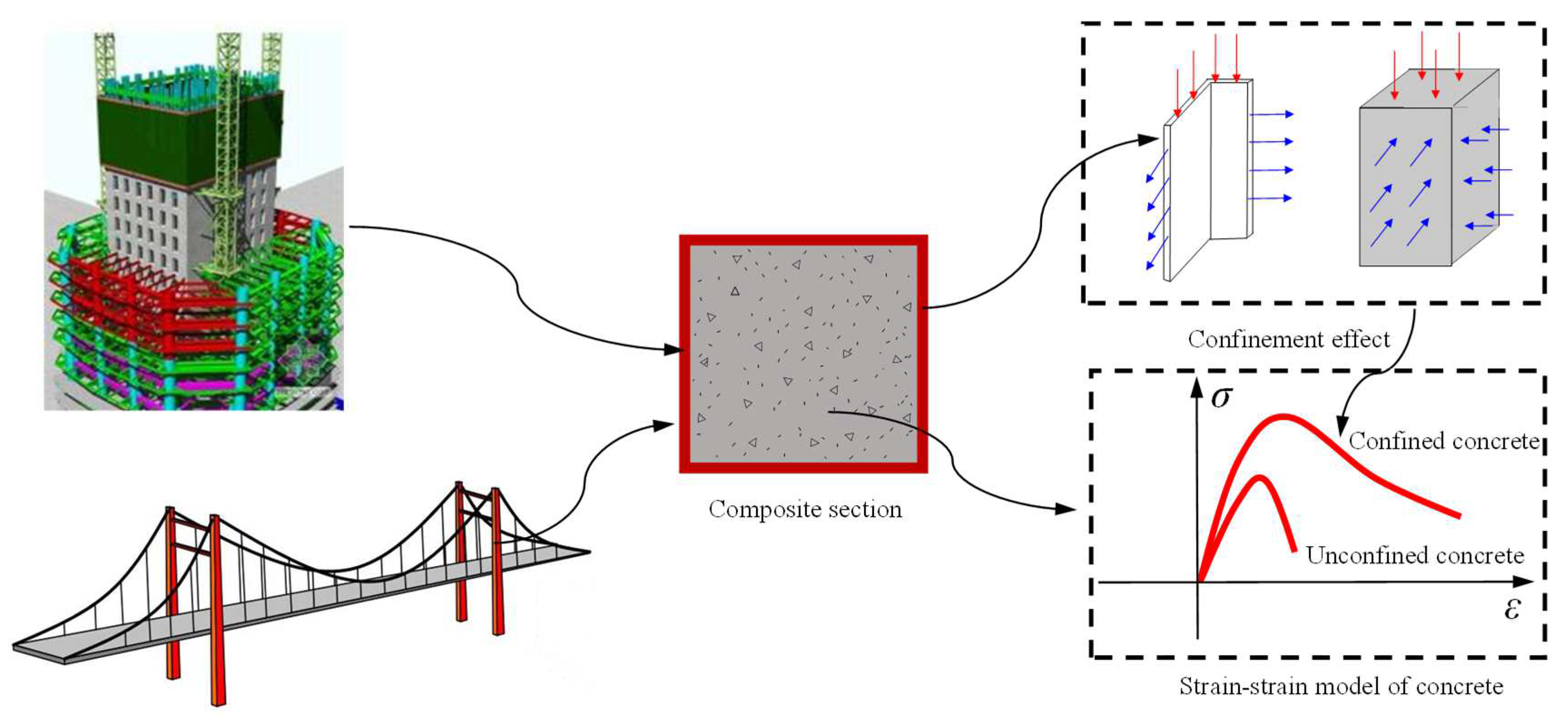
1. Introduction
2. Modeling Framework for UHPCFST Beam–Column
- (1)
- Plain section assumption.
- (2)
- The bond-slip in the interface between the UHPC and the steel tube was neglected.
- (3)
- The sine curve with a half wave for the lateral deflection curve of the beam–column.
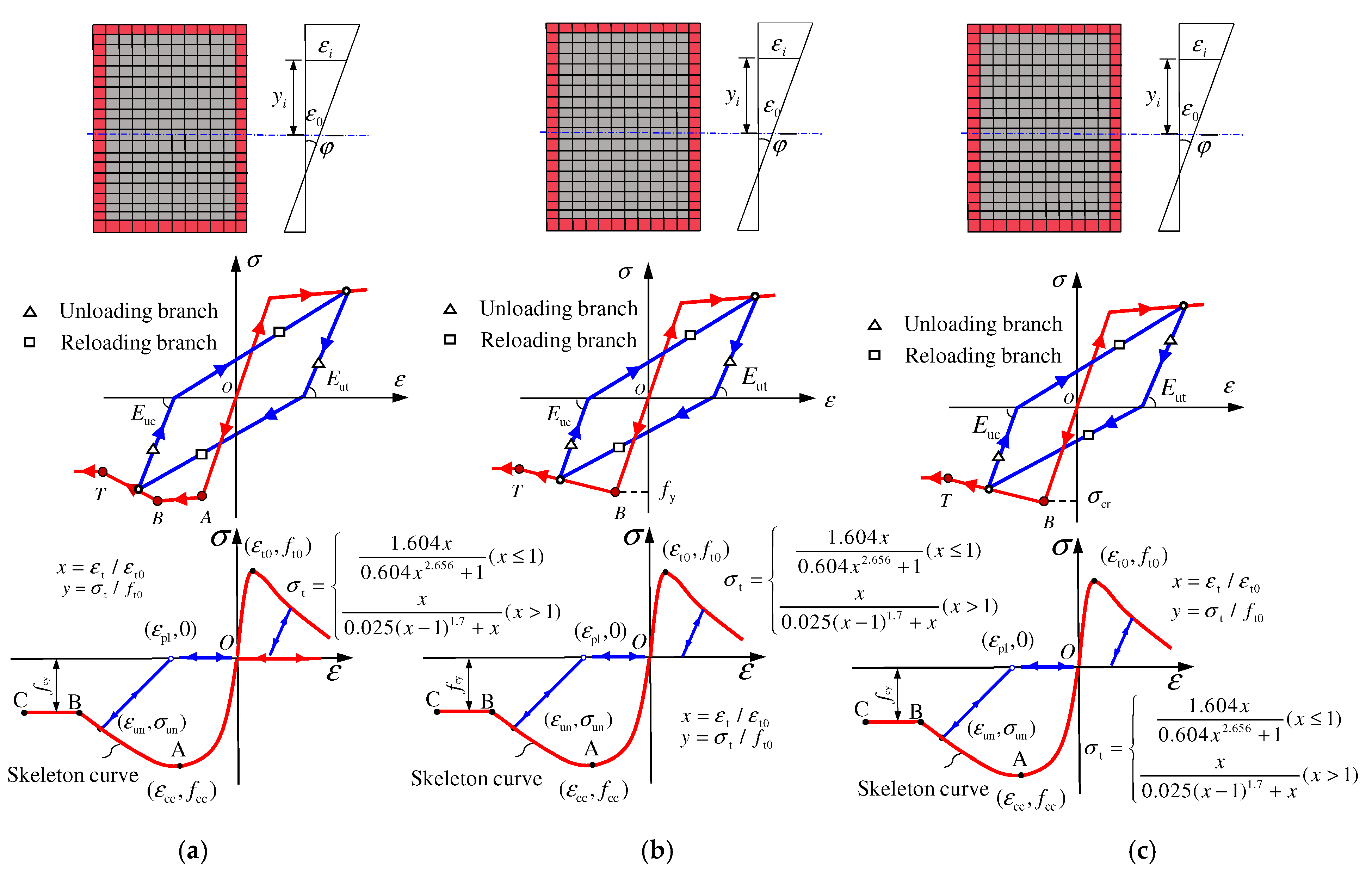
2.1. Constitutive Model of Materials
2.1.1. UHPC
2.1.2. Structural Steel
3. Model Verification
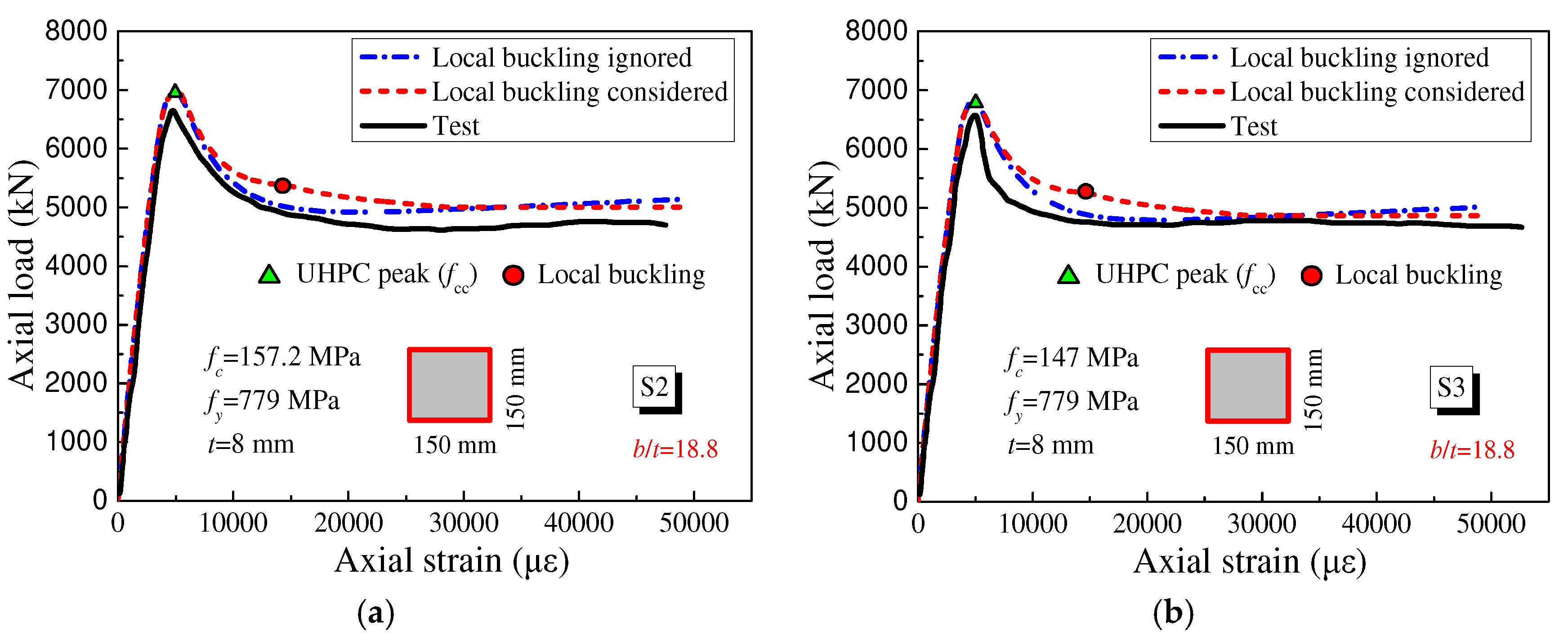
3.1. Axial Behavior of UHPCFST Stub Columns
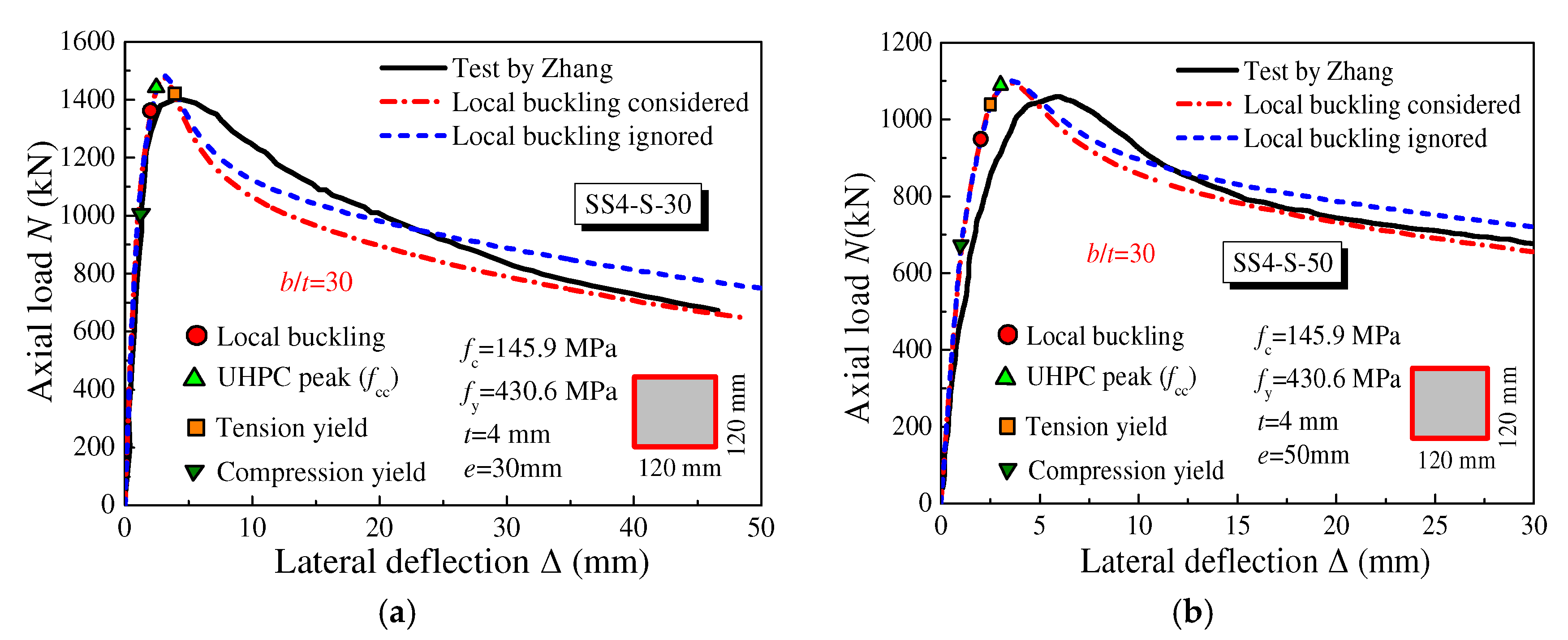
3.2. Eccentric Behavior of UHPCFST Columns
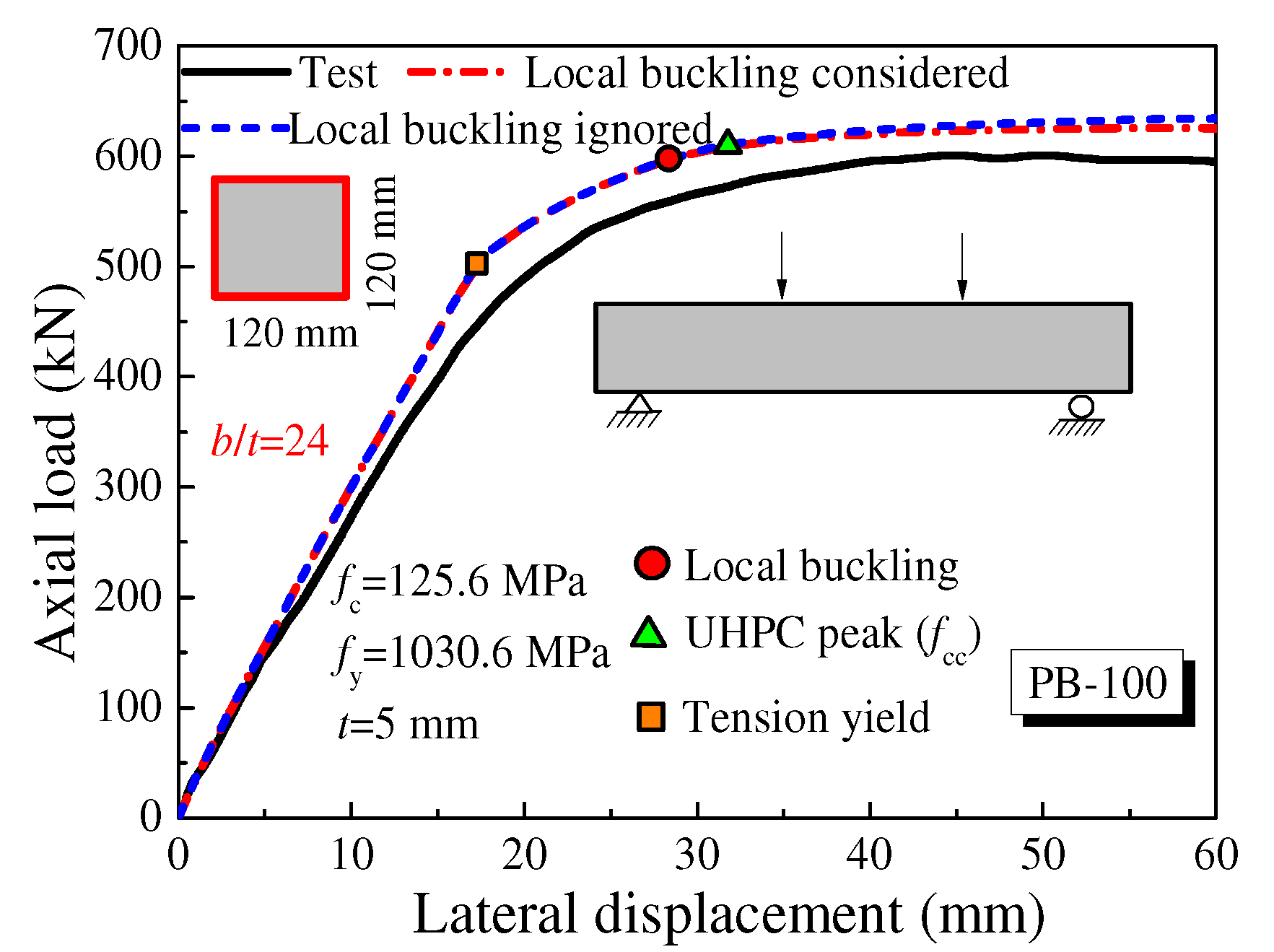
3.3. UHPCFST Beams Subjected to Bending
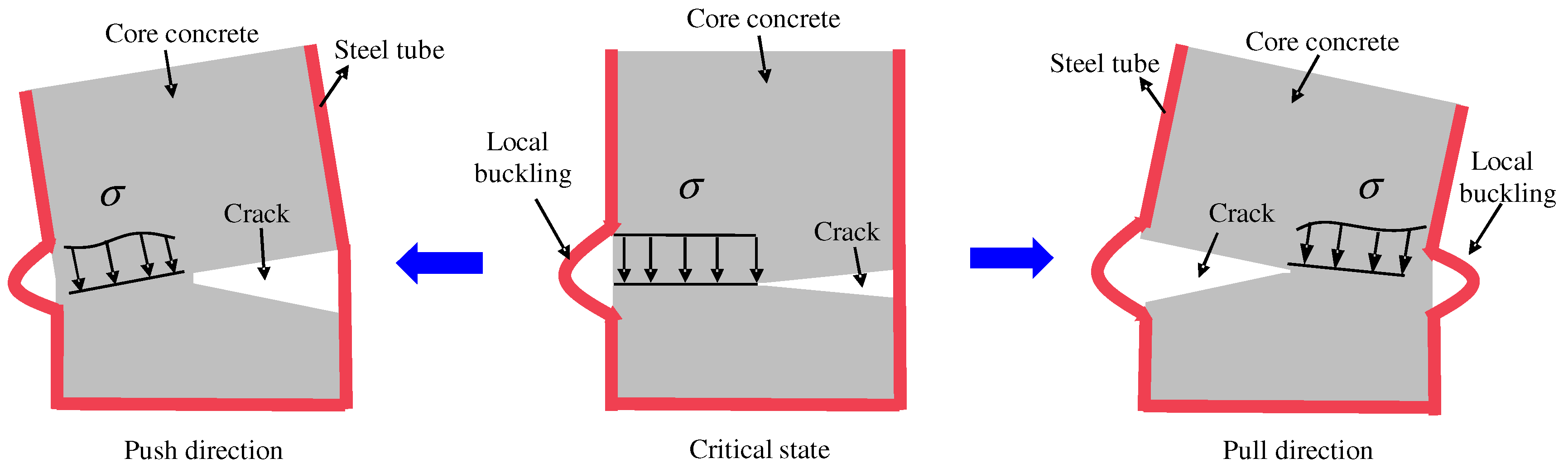
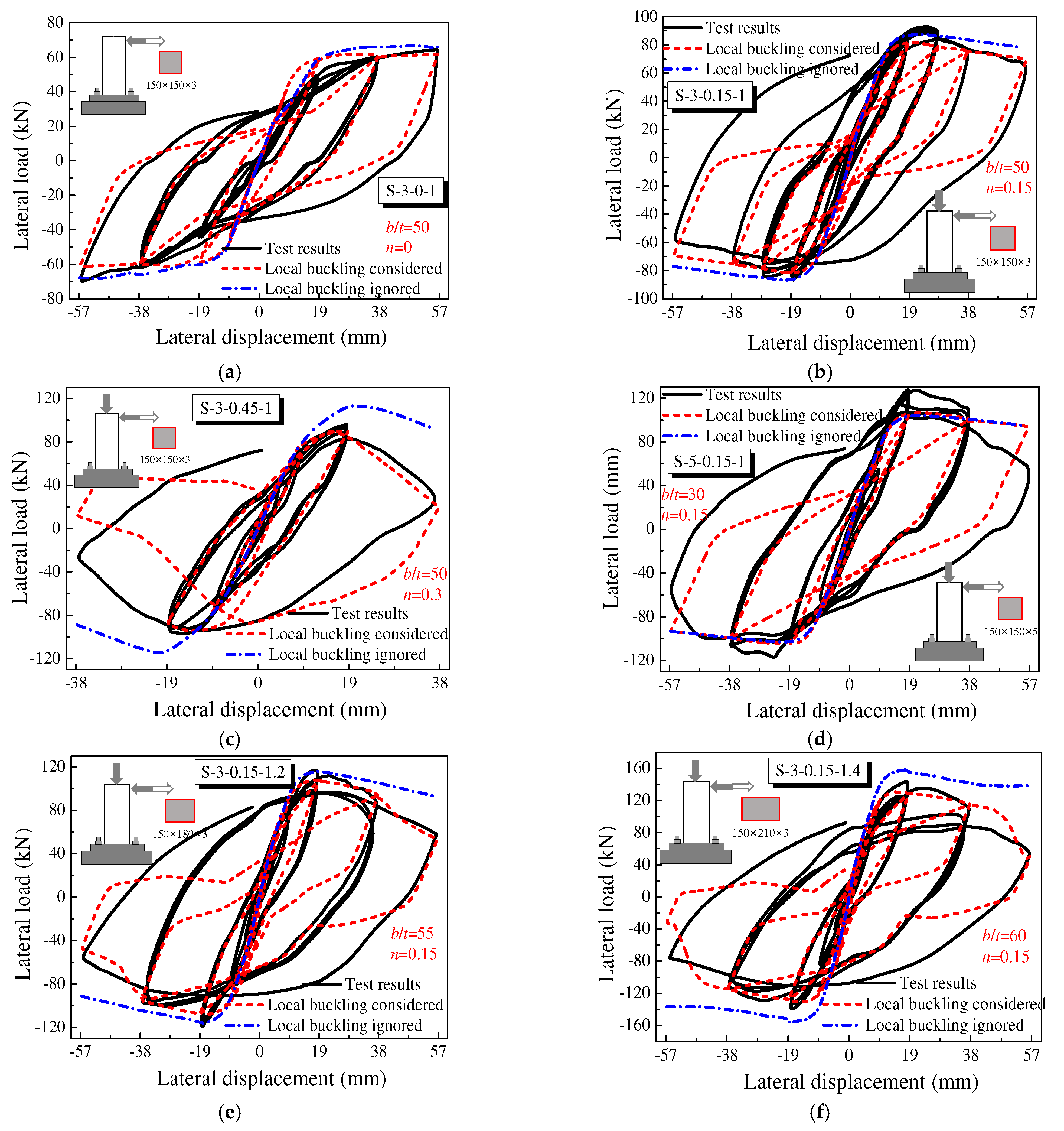
3.4. UHPCFST Columns Subjected to Cyclic Loading
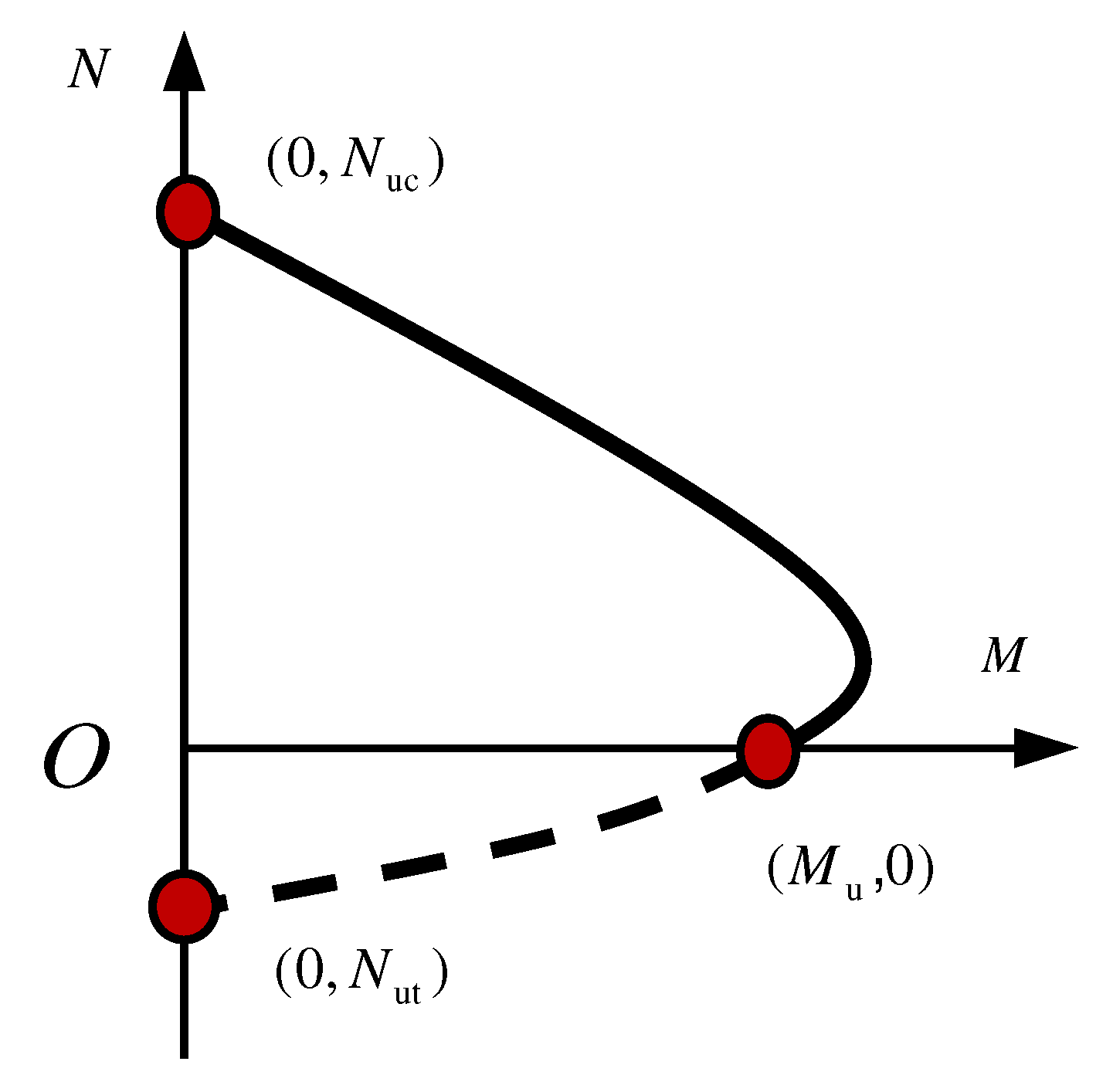
4. Proposed Practical Method for Moment Bearing Capacity
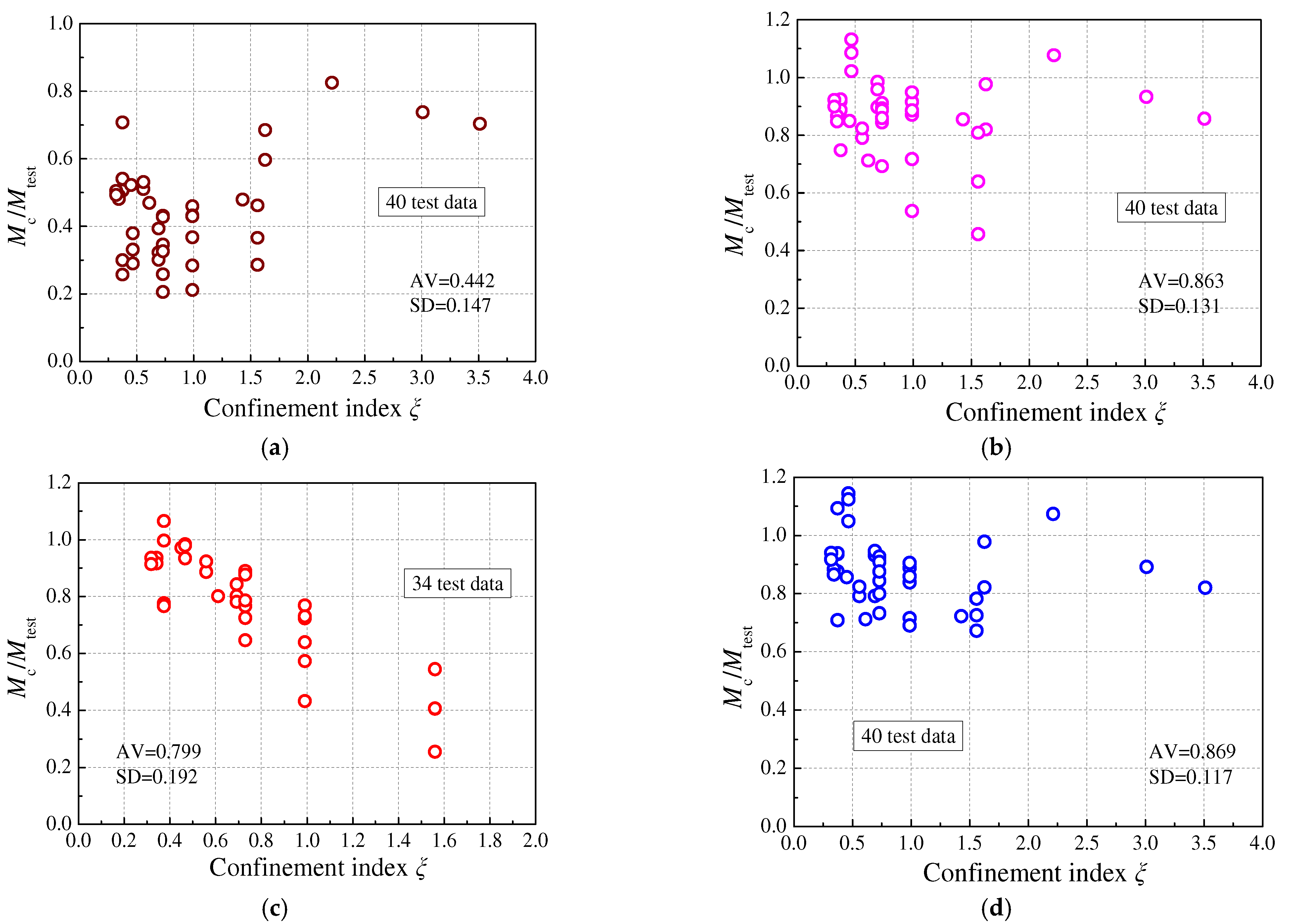
4.1. Comparisons with Current Provisions Codes
4.2. Proposed Calculation Method
- (1)
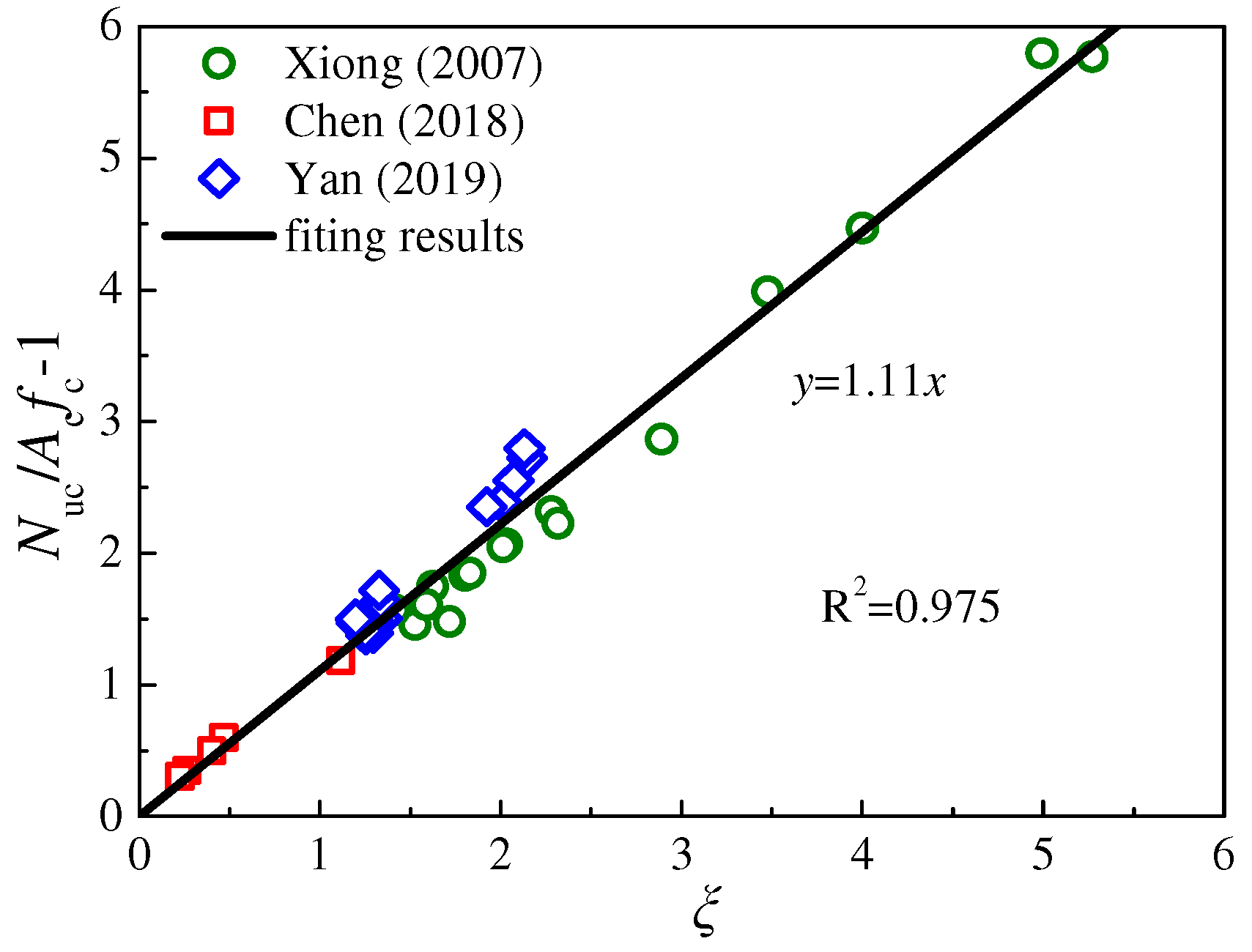
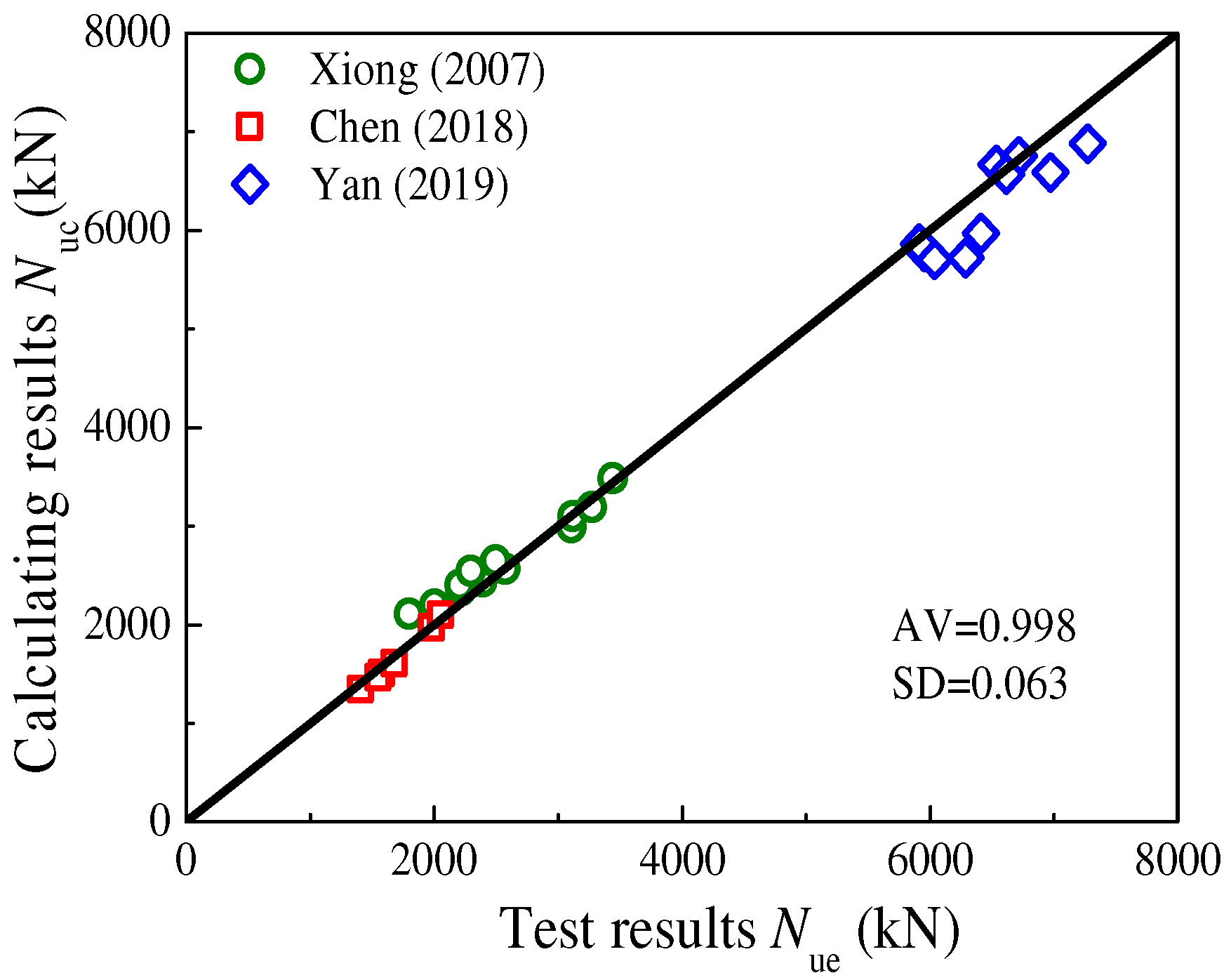
- Axial compression bearing capacity Nuc
- (2)
- Pure bending bearing capacity Mu
- (3)
- Axial tensile bearing capacity Nut
5. Conclusions
- 1.
- The axial compression ratio (n) and width-to-thickness ratio (b/t) are two significant factors that affect the local buckling of steel tubes. Neglecting the local buckling of thin-walled steel tubes overestimates the post-peak ductility of the UHPCFST beam–column; the overestimation of the peak load is up to 17%. However, when b/t is less than 30, the local buckling can be neglected.
- 2.
- EC4 and AIJ design codes predict relatively accurate bending capacities of UHPCFSTs with AV values of 0.863 and 0.869; even ξ is within the suitable range of 0.5~2.0, and the AV value provided by the GB50936 is only 0.799.
- 3.
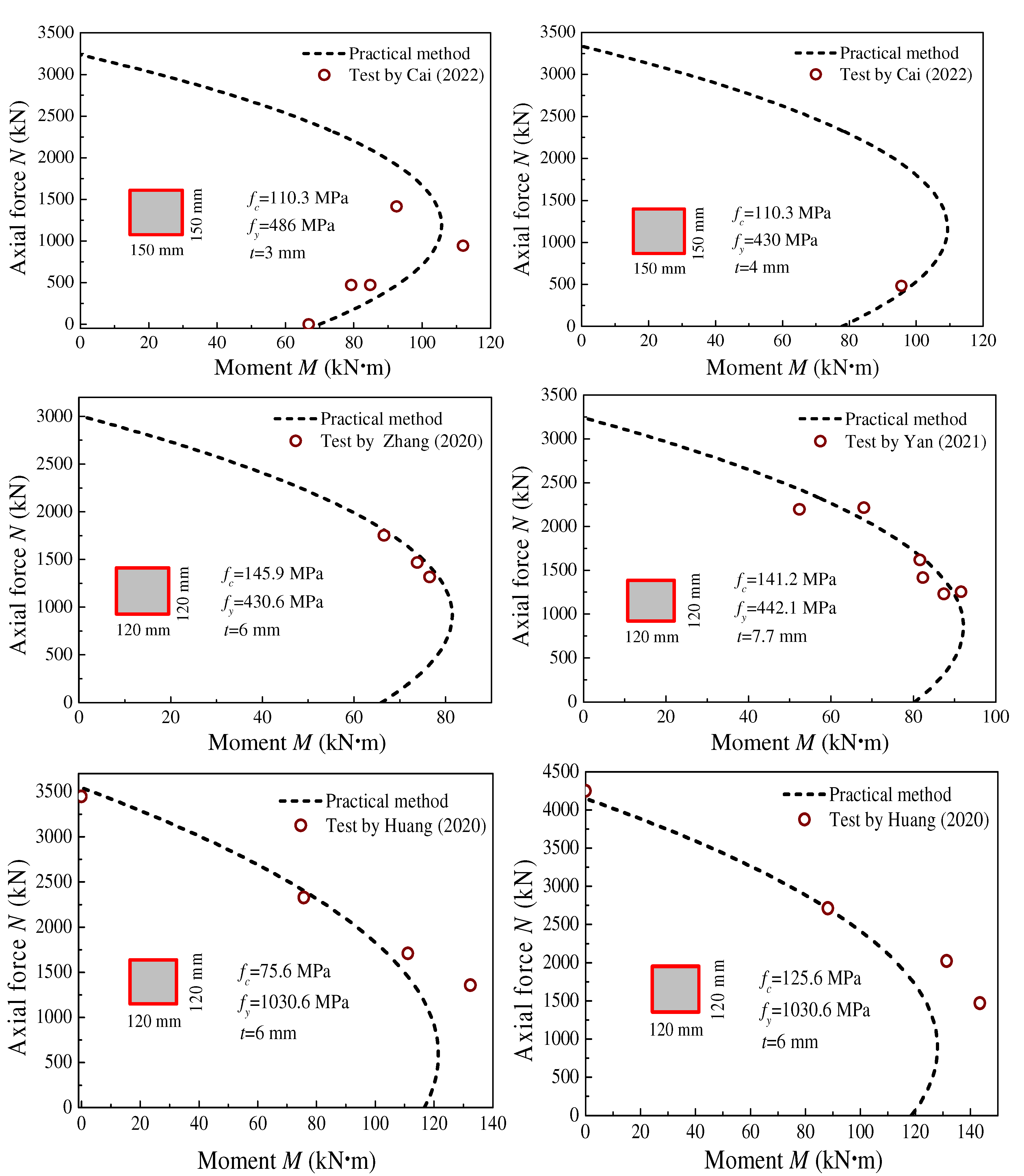
- A practical method was proposed in this work to calculate the bending moment capacities of UHPCFSTs by constructing a quadratic parabola. Compared with the experimental results in the published literature, the proposed method possesses high precision with an AV value of 1.04.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, L.H. Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Structures: From Theory to Practices; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A.M.T.; Jones, S.W.; Mahmud, G.H. Experimental test methods to determine the uniaxial tensile and compressive behaviour of ultra high performance fibre reinforced concrete (UHPFRC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.H.; Wu, F.H.; Chi, Y. Effects of coarse aggregate and steel fibre contents on mechanical properties of high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 206, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannawi, K.; Bian, H.; Prince-Agbodjan, W. Effect of different types of fibers on the microstructure and the mechanical behavior of ultra-high performance fiber-reinforced concretes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 86, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohrevand, P.; Mirmiran, A. Behavior of ultrahighperformance concrete confined by fiber reinforced polymers. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 2011, 23, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temsah, Y.; Jahami, A.; Aouad, C. Silos structural response to blast loading. Eng. Struct. 2021, 243, 112671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Xu, L.H.; Chi, Y. Seismic performance of rectangular ultra-high performance concrete filled steel tube (UHPCFST) columns. Compos. Struct. 2021, 259, 113242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.H.; Lu, Q.R.; Chi, Y. Axial compressive performance of UHPC filled steel tube stub columns containing steel-polypropylene hybrid fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 754–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AISC 360-10; Specification for Structural Steel Buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction: Chicago, IL, USA, 2010.
- EC4; Design of Composite Steel and Concrete Structures. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- GB50936-2014; Technical Code for Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Structures. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- AIJ; Recommendations for Design and Construction of Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Structures. Architectural Institute of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2001.
- Lai, Z.C.; Varma, A.H. Effective stress-strain relationships for analysis of noncompact and slender filled composite (CFT) members. Eng Struct. 2016, 124, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.C.; Varma, A.H.; Griffis, L.G. Analysis and design of noncompact and slender CFT beam-columns. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Deng, F.Q.; Yan, Y.X. Nonlinear analysis on the static and cyclic behaviors of UHPC filled rectangular steel tube columns. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, H.R.; Foster, S.J. Nonlinear static and cyclic analysis of concrete-filled steel columns. J. Constr. Steel. Res. 2010, 66, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.Q.; Uy, B.; Liew, J.Y.R. Local buckling of steel plates in concrete filled thin-walled steel tubular beam-columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2007, 63, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Liang, Q.Q.; Patel, V.I. Nonlinear analysis of rectangular concrete-filled double steel tubular short columns incorporating local buckling. Eng. Struct. 2012, 175, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Liang, Q.Q.; Patel, V.I. Nonlinear analysis of square concrete-filled double steel tubular slender columns incorporating preload effects. Eng. Struct. 2020, 207, 110272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrcelj, Z.; Uy, B. Strength of slender concrete-filled steel box columns incorporating local buckling. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2002, 58, 275–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, B. Strength of concrete filled steel box columns incorporating local buckling. J. Struct. Eng. 2000, 126, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.H.; Ekkehard, F.; Thai, D.K. Simplified stress-strain model for circular steel tube confined UHPC and UHPFRC columns. Steel Compos. Struct. 2018, 29, 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Susantha, K.A.S.; Ge, H.; Usami, T. Uniaxial stress strain relationship of concrete confined by various shaped steel tubes. Eng. Struct. 2001, 23, 1331–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zha, X.X.; Ye, J.Q. A unified formulation for circle and polygon concrete-filled steel tube columns under axial compression. Eng. Struct. 2013, 49, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.L.; Gho, W. Axial load behavior of high-strength rectangular concrete-filled steel tubular stub columns. Thin-Walled Struct. 2005, 43, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar]
- An, L.H.; Fehling, E. Assessment of stress-strain model for UHPC confined by steel tube stub columns. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2017, 63, 371–384. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, A.X.; Liang, X.W.; Yu, J. Experimental study of uniaxial tensile characteristics of ultra-high performance concrete. J. Hunan Univ. 2018, 45, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Mander, J.B.; Priestly, M.N.J.; Park, R. Theoretical stress–strain model for confined concrete. J. Struct. Eng. 1988, 114, 1804–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakino, K.; Nakahara, H.; Morino, S. Behavior of centrally loaded concrete-filled steel-tube short columns. J. Struct. Eng. 2004, 130, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, G.; Nuti, C. Nonlinear cyclic behavior of reinforcing bars including buckling. J. Struct. Eng. 1992, 118, 3268–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, R.P.; Maekawa, K. Path-dependent cyclic stress-strain relationship of reinforcing bar including buckling. Eng. Struct. 2002, 24, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, L.L.; Restrepo-Posada, J.I. Model for predicting cyclic behavior of reinforcing steel. J. Struct. Eng. 1995, 121, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Zhang, R.; Jia, L.J. Structural behavior of UHPC filled steel tube columns under axial loading. Thin Walled Struct. 2018, 130, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.X.; Xiong, D.L.; Richard, J.Y.R. Axial performance of short concrete filled steel tubes with high-and ultra-high- strength materials. Eng. Struct. 2007, 136, 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, S.M.; Gu, P. Structural behavior of UHPC filled steel tubular columns under eccentric loading. Thin Walled Struct. 2020, 156, 106959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.C.; Uy, B.; Li, D.X. Behavior and design of ultra-high-strength CFST members subjected to compression and bending. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 175, 106351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, S.; Copur, A.; Aydogan, M. Flexural behavior of square UHPC-filled hollow steel section beams. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2012, 43, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H. Seismic Behavior and Hysteretic Model Research on the Ultra-High Performance Concrete Filled Rectangular Steel Tube Columns; Wuhan University: Wuhan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.B.; Chen, A.Z.; Zhu, J.S. Behaviours of square UHPFRC-filled steel tubular stub columns under eccentric compression. Thin Walled Struct. 2021, 159, 107222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AISC-LRFD; Load and Resistance Factor Design Specification for Structural Steel Buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction: Chicago, IL, USA, 1999.
- Yan, Y.X.; Xu, L.H.; Li, B. Axial behavior of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) filled stocky steel tubes with square sections. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 158, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Deng, Z.C.; Sun, T. Flexural behavior of ultra-high performance concrete filled high-strength steel tube. Struct. Concrete. 2022, 22, 1688–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.X.; Xiong, D.L.; Richard, L.J.Y. Flexural performance of concrete filled tubes with high tensile steel and ultra-high strength concrete. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2007, 132, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.C.; Yao, P.Y.; Huang, W.J. Reactive powder concrete-filled steel tube (RPCFT) members subjected to axial tension: Experimental study and design. Structures 2020, 28, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| CFST Shape | Design Codes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISC 360 [9] | EC4 [10] | GB 50936 [11] | AIJ [12] | |
| Circle (D/t) | λp = 0.15Es/fy, λr = 0.19Es/fy, λmax = 0.31Es/fy | 90 × 235/fy | 135 × 235/fy | |
| Square (b/t) | ,, | |||
| Key Points | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | ||||
| T | ||||
| Source | b (mm) | L (mm) | t (mm) | fc (MPa) | fy (MPa) | ξ | Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang [35] | 120 | 600~1200 | 4~6 | 145.9 | 430~460 | 0.47~0.69 | 6 |
| Yan [39] | 120 | 600 | 6.6~7 | 141.2 | 435.6~442.1 | 0.73~0.99 | 12 |
| Huang [36] | 120 | 500 | 5 | 125.6 | 1030.6 | 1.56 | 3 |
| Cai [38] | 100~210 | 700~1000 | 3~18 | 110.3~128.1 | 371~486 | 0.37~3.51 | 19 |
| Source | b (mm) | L (mm) | t (mm) | fc (MPa) | fy (MPa) | ξ | Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xiong [34] | 150 | 450 | 8~12.5 | 147~164 | 565~846 | 1.2~2.15 | 15 |
| Chen [33] | 150 | 450 | 2~7.6 | 113~131 | 307~372 | 0.23~1.28 | 6 |
| Yan [41] | 150 | 450 | 4.9~18.5 | 89.2~128.1 | 444.6~668.8 | 1.41~5.27 | 16 |
| Source | b (mm) | L (mm) | t (mm) | fc (MPa) | fy (MPa) | ξ | Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li [42] | 150 | 1600 | 4~8 | 101.3~102.8 | 350~535 | 0.39~1.21 | 4 |
| Xiong [43] | 200 | 2400 | 12~12.5 | 180–183 | 465~756 | 0.79~1.22 | 3 |
| Guler [37] | 80 | 1200 | 2.51~4 | 130.7–134.1 | 268~288 | 0.31~0.47 | 9 |
| Cai [38] | 150 | 950 | 3 | 110.3 | 486 | 0.375 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, H.; Yan, Y. UHPC-Filled Rectangular Steel Tubular Beam–Column: Numerical Study and Design. Buildings 2022, 12, 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12111882
Cai H, Yan Y. UHPC-Filled Rectangular Steel Tubular Beam–Column: Numerical Study and Design. Buildings. 2022; 12(11):1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12111882
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Heng, and Yanxiang Yan. 2022. "UHPC-Filled Rectangular Steel Tubular Beam–Column: Numerical Study and Design" Buildings 12, no. 11: 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12111882
APA StyleCai, H., & Yan, Y. (2022). UHPC-Filled Rectangular Steel Tubular Beam–Column: Numerical Study and Design. Buildings, 12(11), 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12111882





