Optimization of Graphene Oxide Incorporated in Fly Ash-Based Self-Compacting Concrete
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mix Proportioning
2.3. Mix Proportioning and Construction of RSM Model
2.4. Sample Preparations and Casting
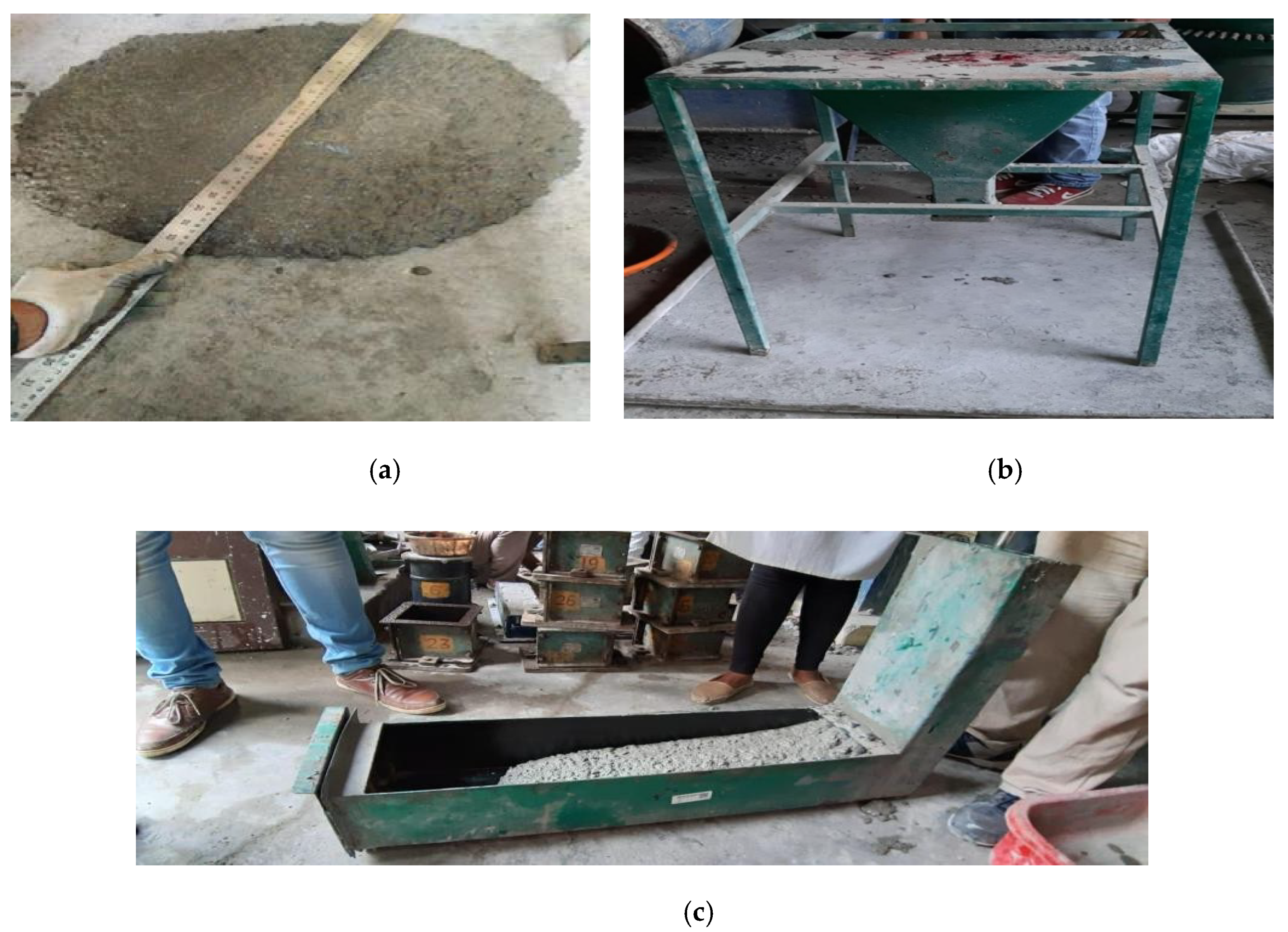
2.5. Test Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Fresh Properties of Self-Compacting Concrete
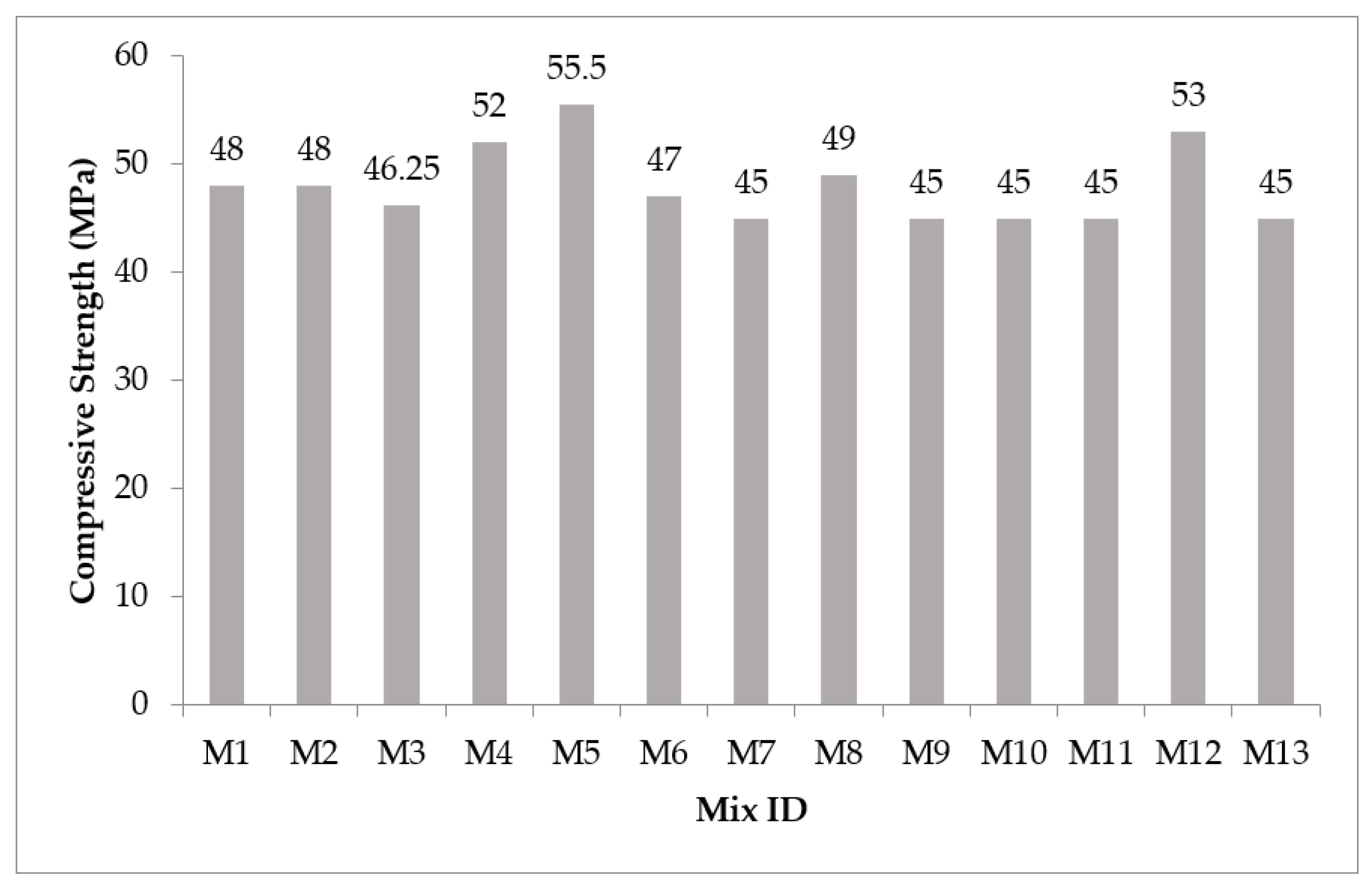
3.2. Compressive Strength
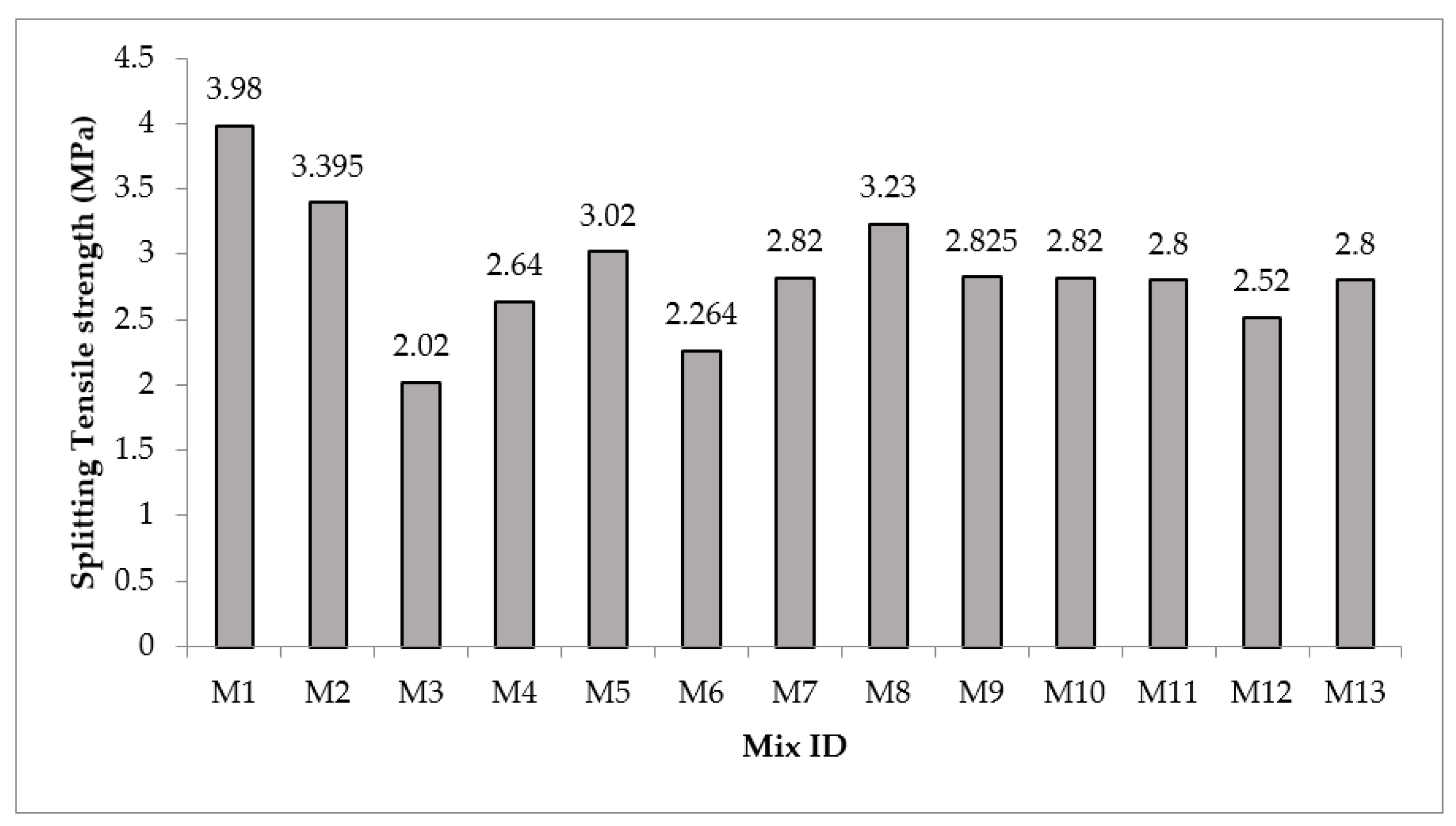
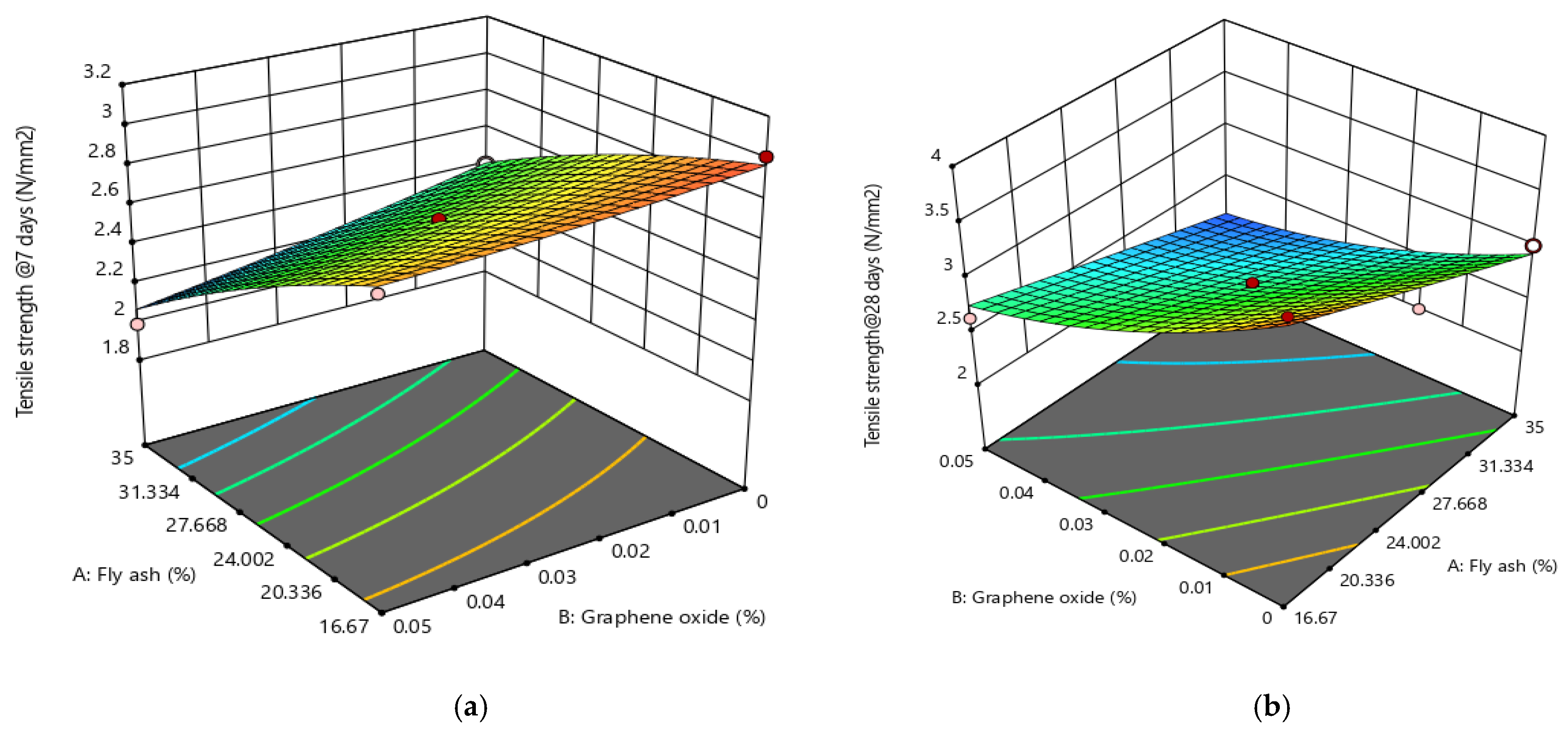
3.3. Splitting Tensile Strength
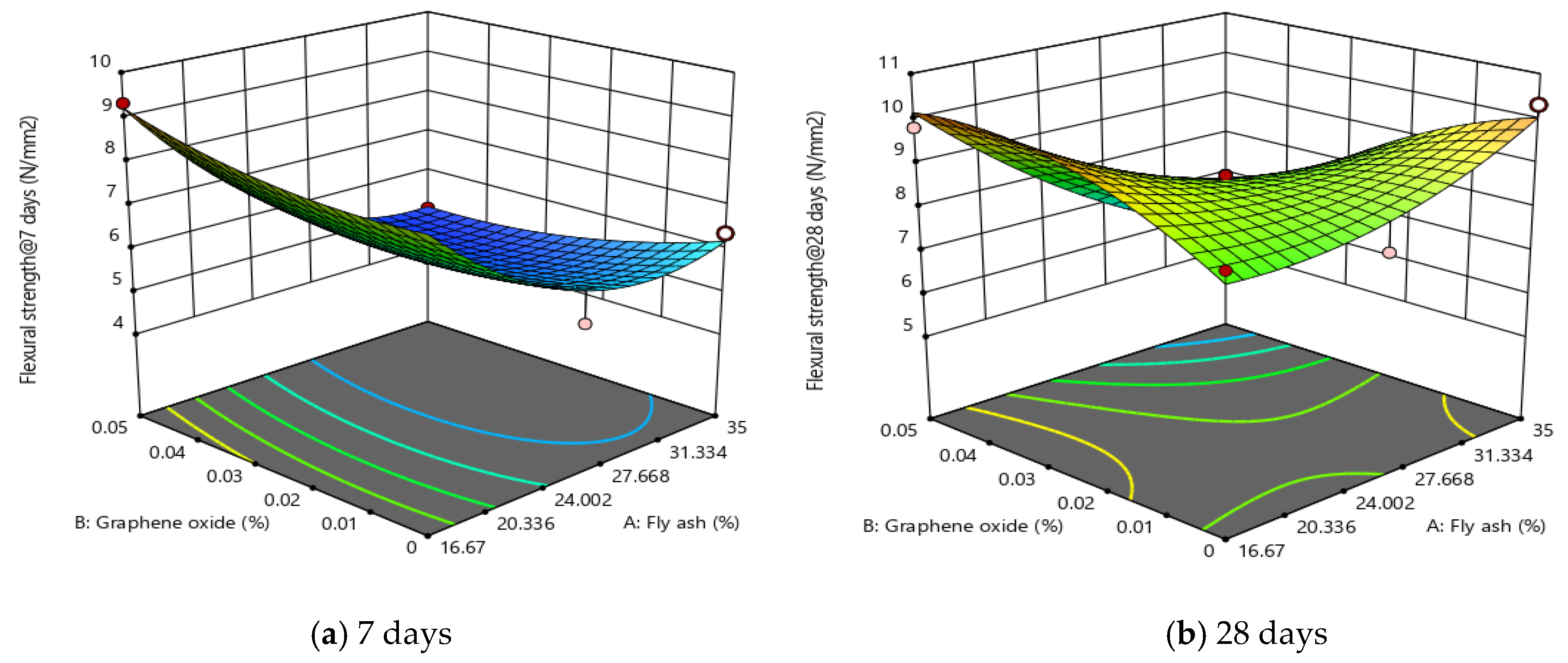
3.4. Flexural Strength
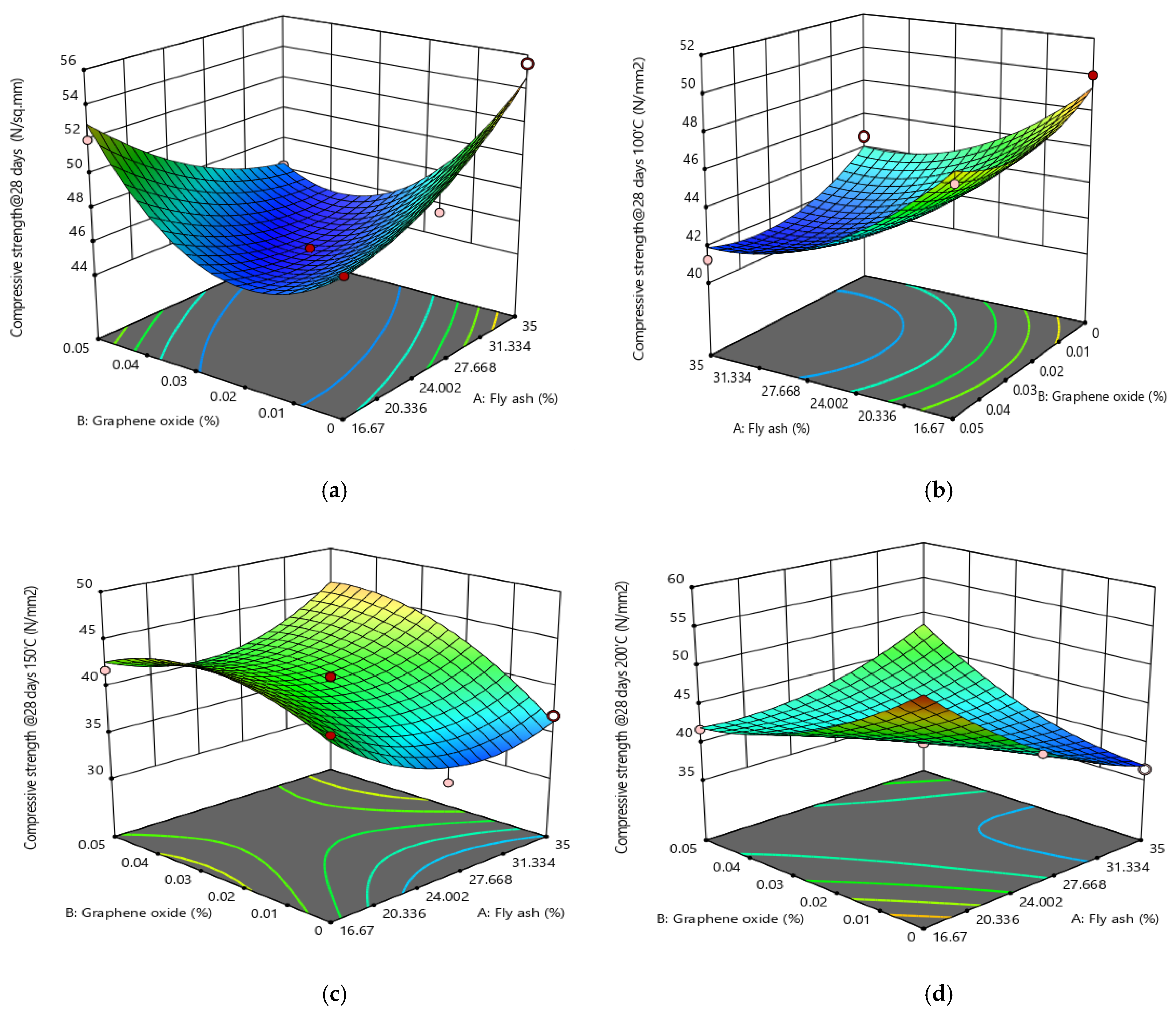
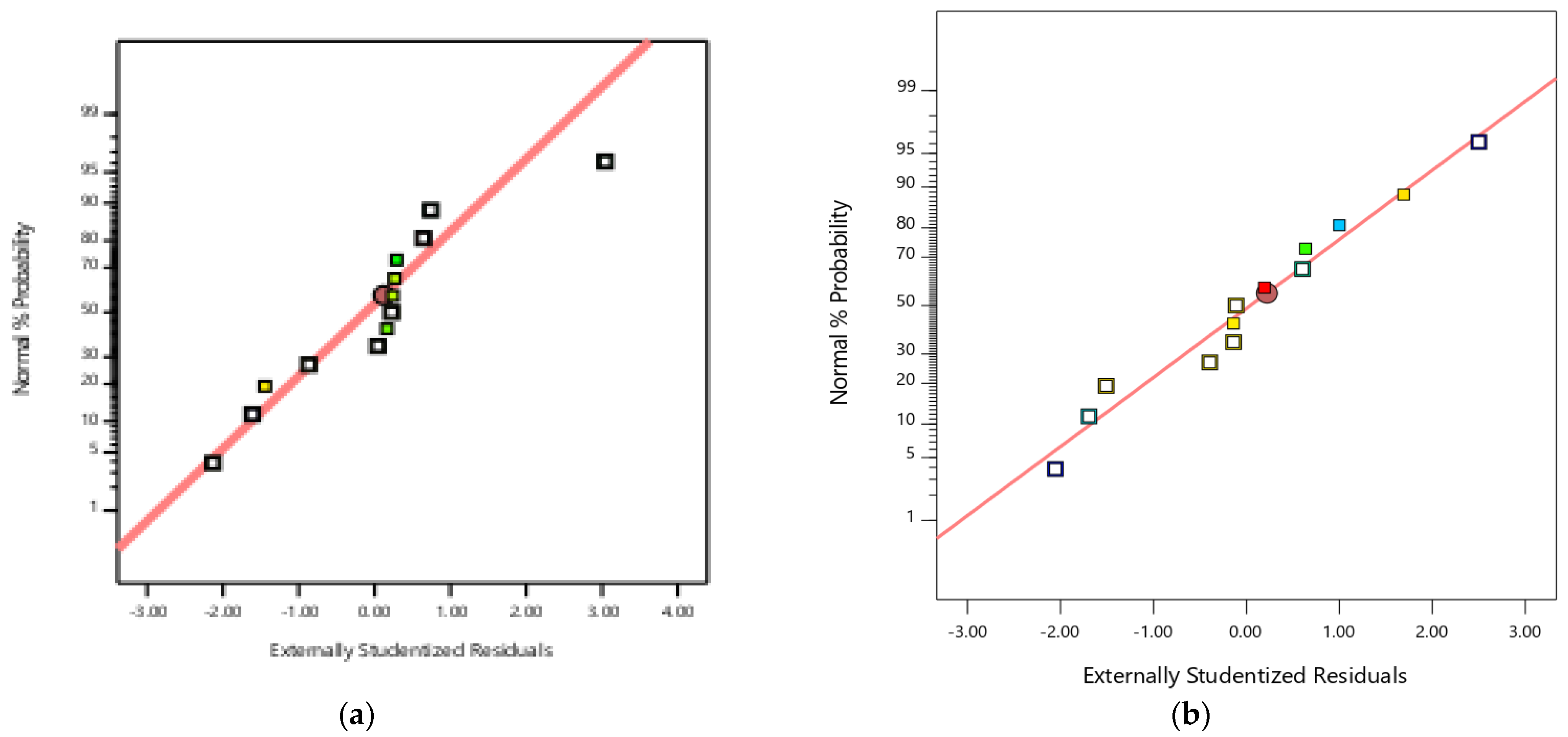
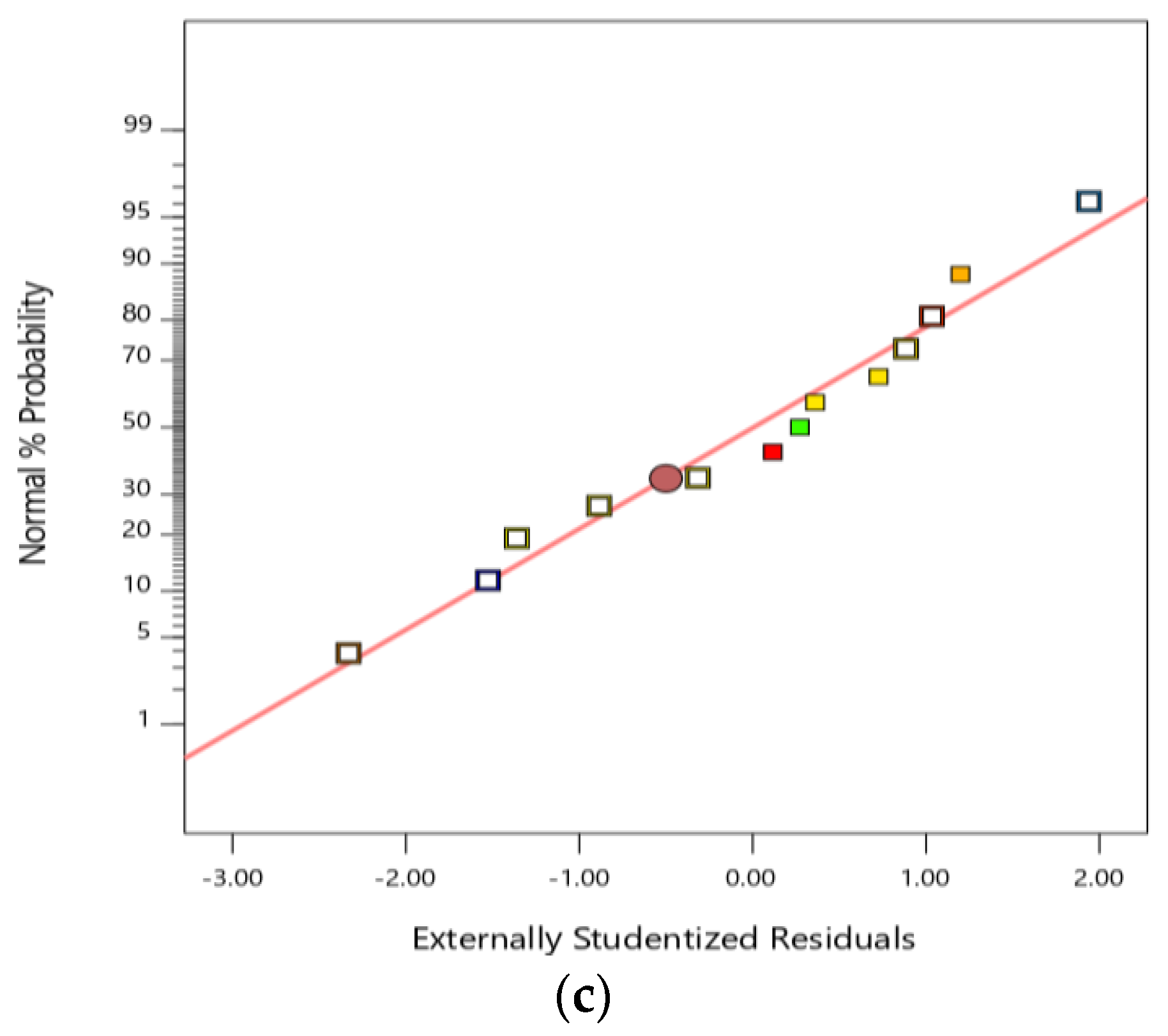
3.5. Analysis of Variance for RSM Models
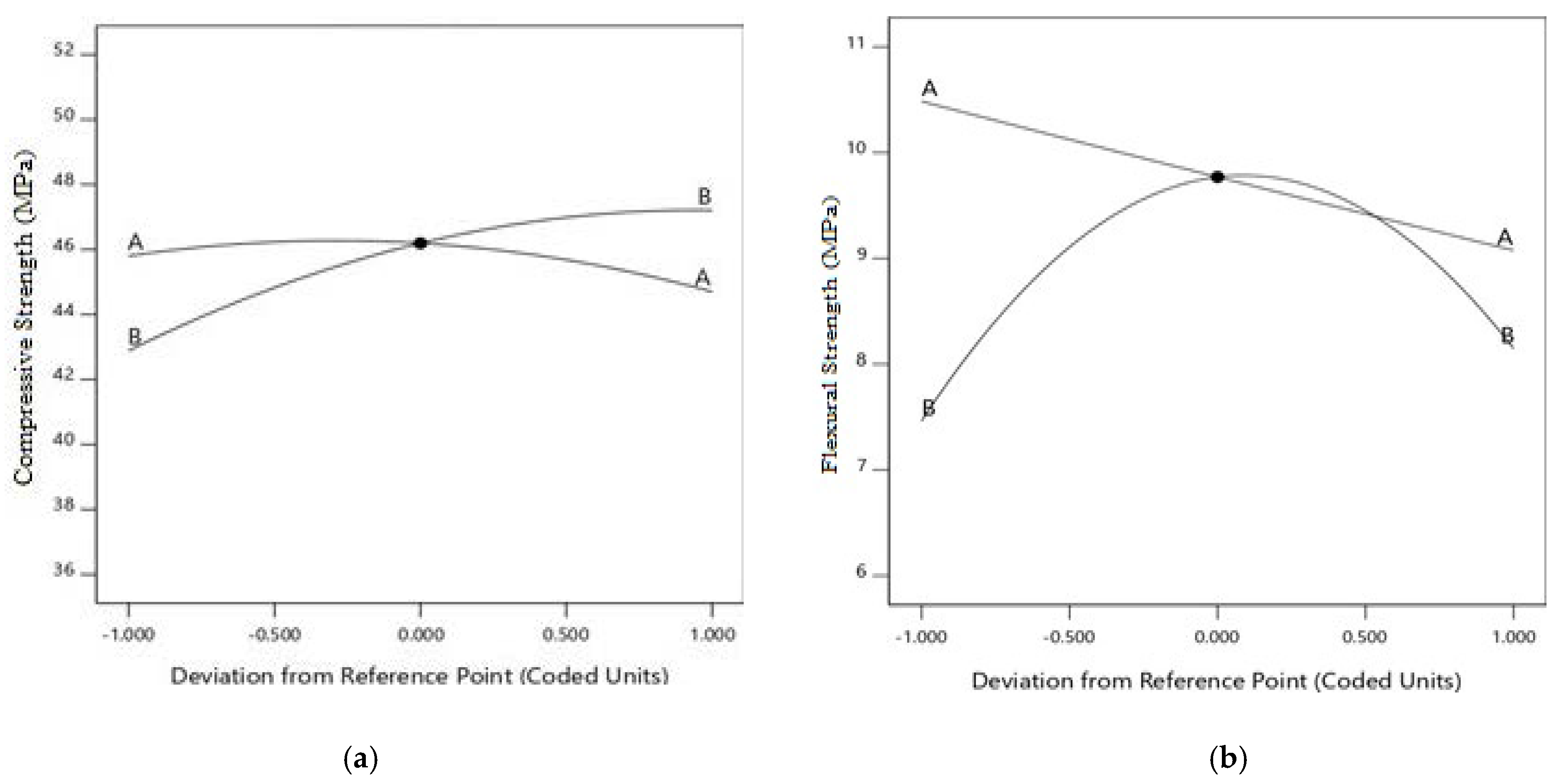
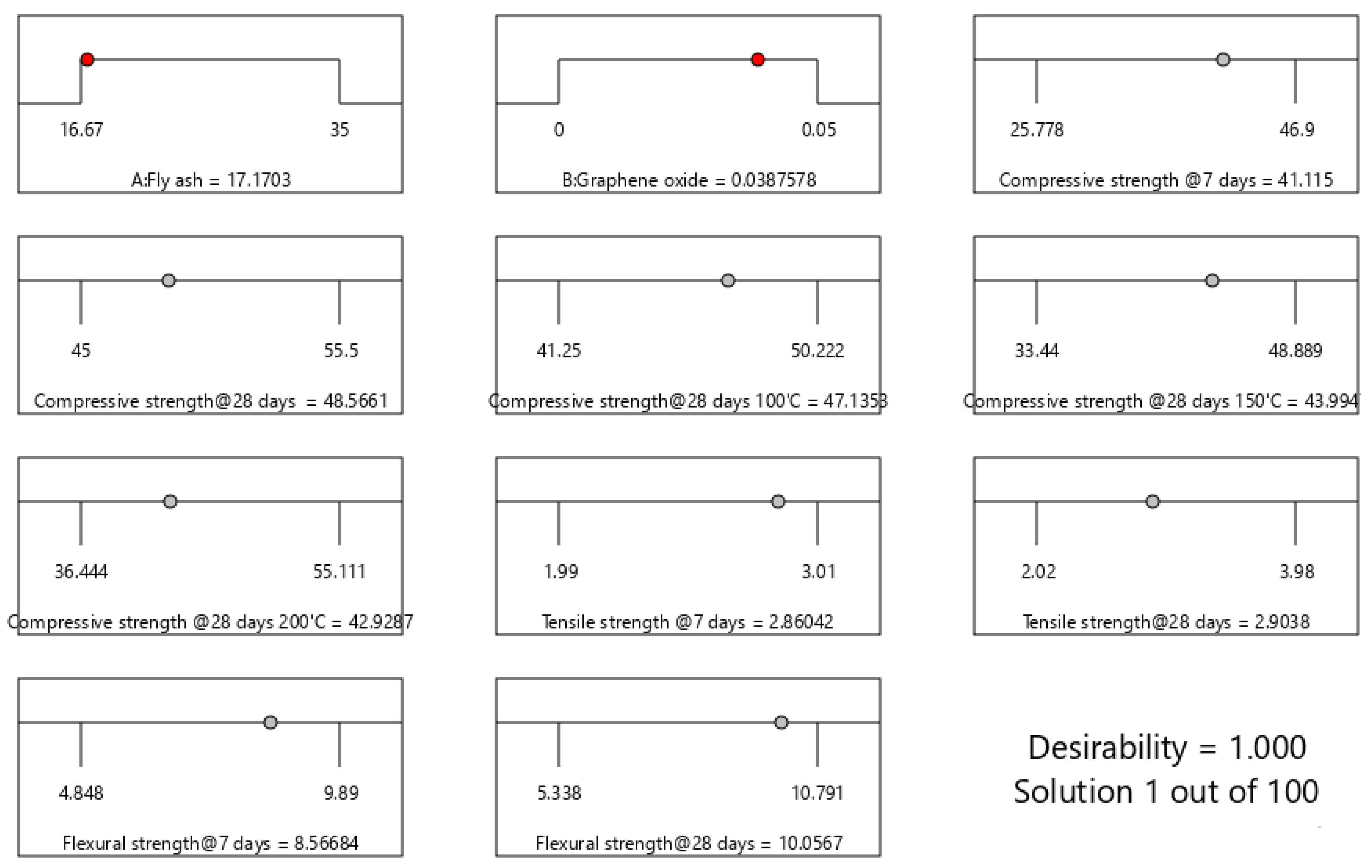
3.6. Optimization and Experimental Validation
4. Conclusions
- GO reduced the fresh properties of SCC such as slump, flowability, and compaction. Therefore, for GO to be used effectively in SCC, more superplasticizer is required.
- GO improved the mechanical strengths of fly ash-based SCC, where for CS of the optimum GO content was 0.03%, while for FS and STS, the optimum GO content was 0.05%.
- The optimum content of fly ash was 35%, that satisfies the both flowability and deformabilty property of self-compacting concrete.
- The addition of GO enhances the heat resistance of fly ash-based SCC, where the reduction in CS of the SCC when subjected to even higher temperature is almost due to the inclusion of grapheme oxide.
- The FS of fly ash-based SCC improved significantly at an early age with the addition of GO; this gives the SCC an advantage to be used in pavement applications.
- The developed models for estimating the 28-day CS, flexural strength, and STS using RSM were statistically significant with very high accuracy.
- Multi-objective optimization results showed that the optimum combinations of fly ash (as cement replacement material) and GO (as additive) were 17.17% and 0.039%, respectively, to reach optimal performance of the SCC mix as both normal and elevated temperature, with a desirability of 100%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sobuz, M.H.R.; Saha, A.; Anamika, J.F.; Houda, M.; Azab, M.; Akid, A.S.M.; Rana, M.J. Development of Self-Compacting Concrete Incorporating Rice Husk Ash with Waste Galvanized Copper Wire Fiber. Buildings 2022, 12, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokulnath, V.; Ramesh, B.; Reddy, S.S. Addition of reinforcing materials in self compacting concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, A.; Savva, P.; Petrou, M.F.; Ioannou, I.; Pantazopoulou, S. Assessing the quality of concrete–reinforcement interface in Self Compacting Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 240, 117933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turuallo, G.; Soutsos, M.N. Supplementary cementitious materials: Strength development of self-compacting concrete under different curing temperature. Procedia Eng. 2015, 125, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, H.; Ge, Y.; Cai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Mechanical properties and microstructure of graphene oxide cement-based composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 194, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, S.; Li, W.; Chen, S.J.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Duan, W.H. Investigation on dispersion of graphene oxide in cement composite using different surfactant treatments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concrete, S.-C. The European guidelines for self-compacting concrete. BIBM 2005, 22, 1040. [Google Scholar]
- De Schutter, G.; Bartos, P.J.; Domone, P.; Gibbs, J. Self-Compacting Concrete; Whittles Publishing Caithness: Dunbeath, UK, 2008; Volume 288. [Google Scholar]
- Okamura, H.; Ozawa, K.; Ouchi, M. Self-compacting concrete. Struct. Concr. 2000, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Hughes, P.; Niu, H.; Fan, Y. A new method to improve the properties of recycled aggregate concrete: Composite addition of basalt fiber and nano-silica. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saorin, F.J.B.; Belmonte, I.M.; Costa, C.P.; Lopez, C.R.; Paya, M.V. QSI methods for determining the quality of the surface finish of concrete. Sustainability 2018, 10, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, R.; Gupta, R.; Nagar, R. Impact on fresh, mechanical, and microstructural properties of high strength self-compacting concrete by marble cutting slurry waste, fly ash, and silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 117888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sudalaimani, K.; Shanmugasundaram, M. An investigation on self-compacting concrete using ultrafine natural steatite powder as replacement to cement. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 8949041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Song, L.; Song, Y.; Dai, G.; Liu, J. An intensive review on the role of graphene oxide in cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 241, 117939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, G.; Wu, J.; Lei, T.; Wang, S.; Strokova, V.; Nelyubova, V.; Wang, M.; Ye, Z. From graphene oxide to reduced graphene oxide: Enhanced hydration and compressive strength of cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 118699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Hua, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Zhou, X. Mechanical properties and shrinkage behavior of concrete-containing graphene-oxide nanosheets. Materials 2020, 13, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adamu, M.; Trabanpruek, P.; Jongvivatsakul, P.; Likitlersuang, S.; Iwanami, M. Mechanical performance and optimization of high-volume fly ash concrete containing plastic wastes and graphene nanoplatelets using response surface methodology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 308, 125085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Khan, R. Effect of graphene oxide on mechanical and durability performance of concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 27, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, M.; Trabanpruek, P.; Limwibul, V.; Jongvivatsakul, P.; Iwanami, M.; Likitlersuang, S. Compressive Behavior and Durability Performance of High-Volume Fly-Ash Concrete with Plastic Waste and Graphene Nanoplatelets by Using Response-Surface Methodology. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 04022222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, B.; Leung, C.Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, G. Aggregation size effect of graphene oxide on its reinforcing efficiency to cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 100, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhini, S.; Padmanaban, I. Experimental investigation on graphene oxide composites with fly ash concrete. Int. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 2016, 9, 515–519. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, S.; Ma, Y.; Qiu, C.; Zhou, Q. Regulation of GO on cement hydration crystals and its toughening effect. Mag. Concr. Res. 2013, 65, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Ma, Y.; Qiu, C.; Sun, T.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q. Effect of graphene oxide nanosheets of microstructure and mechanical properties of cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horszczaruk, E.; Mijowska, E.; Kalenczuk, R.J.; Aleksandrzak, M.; Mijowska, S. Nanocomposite of cement/graphene oxide–Impact on hydration kinetics and Young’s modulus. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 78, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Sanjayan, J.; Nazari, A.; Al-Saadi, N. Effects of graphene oxide in enhancing the performance of concrete exposed to high-temperature. Aust. J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 15, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babak, F.; Abolfazl, H.; Alimorad, R.; Parviz, G. Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Graphene Oxide: Cement Nanocomposites. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 276323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chuah, S.; Pan, Z.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Wang, C.M.; Duan, W.H. Nano reinforced cement and concrete composites and new perspective from graphene oxide. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Yao, J.; Leung, C.K. Using graphene oxide to strengthen the bond between PE fiber and matrix to improve the strain hardening behavior of SHCC. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 126, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, H.; Siddique, R.M.A.; Shah, S.A.R.; Azab, M.; Qadeer, R.; Ullah, M.K.; Iqbal, F. Mechanical Performance of Polymeric ARGF-Based Fly Ash-Concrete Composites: A Study for Eco-Friendly Circular Economy Application. Polymers 2022, 14, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, M.; Ayeni, K.O.; Haruna, S.I.; Mansour, Y.E.-H.I.; Haruna, S. Durability performance of pervious concrete containing rice husk ash and calcium carbide: A response surface methodology approach. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 14, e00547. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khed, V.C.; Mohammed, B.S.; Liew, M.; Zawawi, N.A.W.A. Development of response surface models for self-compacting hybrid fibre reinforced rubberized cementitious composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, M.; Haruna, S.I.; Ibrahim, Y.E.; Alanazi, H. Evaluation of the mechanical performance of concrete containing calcium carbide residue and nano silica using response surface methodology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 67076–67102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IS 516; Methods of Tests for Strength of Concrete. Tests for Compressive Strength of Concrete Specimen. Bureau of Indian Standards: Delhi, India, 2006.
- BIS, I. 5816; Indian Standard Splitting Tensile Strength of Concrete-Method of Test. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 1999.
- IS 516; Methods of Tests for Strength of Concrete. Test for Flexural Strength of Moulded Flexure Test Specimens. Bureau of Indian Standards: Delhi, India, 2006.
- Efnarc, S. EFNARC Guidelines for Self-Compacting Concrete; EFNARC: Farnham, UK, 2002; pp. 1–32. Available online: www.Efnarc.org (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Pesaralanka, V.; Khed, V.C. Flowability and compressive strength test on self compacting mortar using graphene oxide. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsh, P.; Marathe, S.; Bhat, A.K. Influence of graphene oxide on properties of concrete in the presence of silica fumes and M-sand. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, H. Mechanical and perceptual characterization of ultra-high-performance cement-based composites with silane-treated graphene nano-platelets. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 240, 117926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.H.; Montgomery, D.C.; Anderson-Cook, C.M. Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Adamu, M.; Mohammed, B.S.; Liew, M.S. Mechanical properties and performance of high volume fly ash roller compacted concrete containing crumb rubber and nano silica. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, B.S.; Khed, V.C.; Liew, M.S. Optimization of hybrid fibres in engineered cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.H.; Khuri, A.I.; Carter, W.H. Response surface methodology: 1966–l988. Technometrics 1989, 31, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achara, B.E.; Mohammed, B.S.; Liew, M. Bond behaviour of nano-silica-modified self-compacting engineered cementitious composite using response surface methodology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 796–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Oxide/Property | Cement | Fly Ash | Silica Fume |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 21.77 | 58.26 | 95.85 |
| Fe2O3 | 4.14 | 5.76 | 0.05 |
| Al2O3 | 6.56 | 31.74 | 0.26 |
| CaO | 60.13 | 1.96 | 0.21 |
| MgO | 2.09 | 0.15 | 0.45 |
| Na2O | 0.38 | 0.78 | - |
| K2O | 0.43 | 0.73 | - |
| SO3 | 2.17 | 0.17 | 1.00 |
| LOI | 2.39 | 0.31 | 2.80 |
| Specific gravity | 3.16 | 2.25 | 2.07 |
| Consistency (%) | 33 | - | - |
| Fineness (m2/Kg) | 307 | 350 | - |
| Properties | Values |
|---|---|
| Surface area | 110–250 m2/g |
| Bulk density | 0.121 g/cm3 |
| Physical form | Fluffy, very light powder |
| Odour | Odour less |
| Colour | Black powder |
| Thickness | 0.8–2 nm |
| Carbon content | 60–80% |
| Mixes | Cement (Kg/m3) | Fly Ash (Kg/m3) | Graphene Oxide (Kg/m3) | Silica Fume (Kg/m3) | Powder Content (Kg/m3) | M Sand (Kg/m3) | Coarse Aggregate (Kg/m3) | Super Plasticizer (VMA) (Kg/m3) | Super Plasticizer (PCE) (Kg/m3) | Water (Kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSC mix | 425 | 100 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| Factors | Units | Minimum Level (−1) | Maximum Level (+1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | Kg/m3 | 210 | 425 |
| Graphene oxide | % | 0 | 0.05 |
| Fly ash | % | 16.67 | 35 |
| Silica powder | Kg/m3 | 25 | 25 |
| Powder content | Kg/m3 | 50 | 50 |
| Mix ID | Mix Details | Run in RSM | Fly Ash (%) | Graphene Oxide (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 35 FA + 0.05 GO Mix | 1 | 35 | 0.05 |
| M2 | 25.835 FA + 0.025 GO Mix | 2 | 25.835 | 0.025 |
| M3 | 35 FA + 0 GO Mix | 3 | 35 | 0 |
| M4 | 16.67 FA + 0.05 GO Mix | 4 | 16.67 | 0.05 |
| M5 | 25.835FA + 0 GO Mix | 5 | 25.835 | 0 |
| M6 | 38.7963 FA + 0.025 GO Mix | 6 | 38.7963 | 0.025 |
| M7 | 16.67 FA + 0 GO Mix | 7 | 16.67 | 0 |
| M8 | 25.835 FA + 0.025 GO Mix | 8 | 25.835 | 0.025 |
| M9 | 12.8737 FA + 0.025 GO Mix | 9 | 12.8737 | 0.025 |
| M10 | 25.835 FA + 0.025 GO Mix | 10 | 25.835 | 0.025 |
| M11 | 25.835 FA + 0.025 GO Mix | 11 | 25.835 | 0.025 |
| M12 | 25.835 FA + 0.025 GO Mix | 12 | 25.835 | 0.025 |
| M13 | 25.835 FA + 0.0604 GO Mix | 13 | 25.835 | 0.0604 |
| Mixes | Quantities of Materials per Kg/m3 (Kg/m3) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | Fly Ash | GO | Silica Fume | Powder Content | M-Sand | Coarse Agg | Super Plasticizer (VMA) | Super Plasticizer (PCE) | Water | |
| M1 | 315 | 210 | 0.3 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M2 | 370 | 155 | 0.15 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M3 | 405 | 210 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M4 | 425 | 100 | 0.3 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M5 | 370 | 155 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M6 | 293 | 232 | 0.15 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M7 | 425 | 100 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M8 | 370 | 155 | 0.15 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M9 | 448 | 77 | 0.15 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M10 | 370 | 155 | 0.15 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M11 | 370 | 155 | 0.15 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M12 | 370 | 155 | 0.15 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| M13 | 370 | 155 | 0.384 | 25 | 50 | 875 | 675 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 160 |
| Mix ID | Slump | V-Funnel (s) | L-Box | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d1 | d1 | s | T500 | H1 | H2 | H1/H2 | ||
| M1 | 750 | 755 | 753 | 3 | 9 | 75 | 70 | 0.93 |
| M2 | 730 | 735 | 733 | 3 | 8 | 74 | 69 | 0.92 |
| M3 | 740 | 735 | 740 | 2 | 7 | 75 | 74 | 1 |
| M4 | 670 | 672 | 670 | 2 | 7 | 75 | 71 | 0.94 |
| M5 | 735 | 733 | 735 | 2 | 6 | 75 | 74 | 1 |
| M6 | 758 | 755 | 756 | 4 | 10 | 75 | 74 | 1 |
| M7 | 730 | 725 | 728 | 2 | 6 | 75 | 72 | 0.96 |
| M8 | 700 | 695 | 698 | 3 | 8 | 74 | 68 | 0.92 |
| M9 | 785 | 782 | 783 | 2 | 6 | 72 | 65 | 0.90 |
| M10 | 743 | 745 | 744 | 3 | 8 | 73 | 67 | 0.92 |
| M12 | 745 | 748 | 746 | 3 | 8 | 72 | 66 | 0.92 |
| M13 | 640 | 650 | 645 | 5 | 12 | 75 | 67 | 0.89 |
| Responses | Source | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28-day Compressive Strength (MPa) | Model | 136.55 | 27.31 | 1589.50 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A-Fly ash | 2.40 | 2.40 | 139.94 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| B-GO | 30.31 | 30.31 | 1764.22 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| AB | 95.96 | 95.96 | 5585.01 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| A² | 6.26 | 6.26 | 364.17 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| B² | 6.38 | 6.38 | 371.44 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| Residual | 0.1203 | 0.0172 | ||||
| Lack of Fit | 0.0778 | 0.0259 | 2.44 | 0.2039 | not significant | |
| Pure Error | 0.0424 | 0.0106 | ||||
| 28-day Flexural Strength (MPa) | Model | 22.40 | 4.48 | 31.09 | 0.0001 | significant |
| A-Fly ash | 4.12 | 4.12 | 28.56 | 0.0011 | significant | |
| B-GO | 2.81 | 2.81 | 19.53 | 0.0031 | significant | |
| AB | 9.34 | 9.34 | 64.80 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| A2 | 2.04 | 2.04 | 14.14 | 0.0071 | significant | |
| B2 | 1.95 | 1.95 | 13.56 | 0.0078 | significant | |
| Residual | 1.01 | 0.1441 | ||||
| Lack of Fit | 0.0069 | 0.0023 | 3.47 | 0.1304 | not significant | |
| Pure Error | 0.0027 | 0.0007 | ||||
| 28-day Splitting Tensile Strength (MPa) | Model | 6.69 | 1.34 | 1452.54 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A-Fly ash | 1.29 | 1.29 | 1395.83 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| B-GO | 2.58 | 2.58 | 2803.38 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| AB | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1327.72 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| A² | 0.0005 | 0.0005 | 0.5041 | 0.5006 | significant | |
| B² | 0.6193 | 0.6193 | 672.20 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| Residual | 0.0064 | 0.0009 | ||||
| Lack of Fit | 0.0047 | 0.0016 | 3.66 | 0.1209 | not significant | |
| Pure Error | 0.0017 | 0.0004 |
| Response | R2 | Adj. R2 | Pred. R2 | SD | Adeq. Pre | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compressive strength (MPa) | 0.9786 | 0.9633 | 0.8538 | 0.9172 | 28.2375 | 43.51 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 0.9663 | 0.9423 | 0.7880 | 0.1189 | 21.9103 | 2.86 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 0.9569 | 0.9231 | 0.7387 | 0.3796 | 19.7592 | 8.63 |
| Variables/Responses | Goal | Lower Limit | Upper Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fly ash (%) | In range | 16.67 | 35 |
| Graphene oxide (%) | In range | 0 | 0.05 |
| Temperature (°C) | In range | 23 | 200 |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | Maximize | 45 | 55.5 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | Maximize | 2.02 | 3.98 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | Maximize | 5.338 | 10.791 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khed, V.C.; Pesaralanka, V.; Adamu, M.; Ibrahim, Y.E.; Azab, M.; Reddy, M.A.K.; Hakamy, A.; Deifalla, A.F. Optimization of Graphene Oxide Incorporated in Fly Ash-Based Self-Compacting Concrete. Buildings 2022, 12, 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12112002
Khed VC, Pesaralanka V, Adamu M, Ibrahim YE, Azab M, Reddy MAK, Hakamy A, Deifalla AF. Optimization of Graphene Oxide Incorporated in Fly Ash-Based Self-Compacting Concrete. Buildings. 2022; 12(11):2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12112002
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhed, Veerendrakumar C., Vyshnavi Pesaralanka, Musa Adamu, Yasser E. Ibrahim, Marc Azab, M. Achyutha Kumar Reddy, Ahmad Hakamy, and Ahmed Farouk Deifalla. 2022. "Optimization of Graphene Oxide Incorporated in Fly Ash-Based Self-Compacting Concrete" Buildings 12, no. 11: 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12112002
APA StyleKhed, V. C., Pesaralanka, V., Adamu, M., Ibrahim, Y. E., Azab, M., Reddy, M. A. K., Hakamy, A., & Deifalla, A. F. (2022). Optimization of Graphene Oxide Incorporated in Fly Ash-Based Self-Compacting Concrete. Buildings, 12(11), 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12112002









