Experimental Study on Self-Compacting Concrete-Filled Thin-Walled Steel Tube Columns
Abstract
1. Introduction
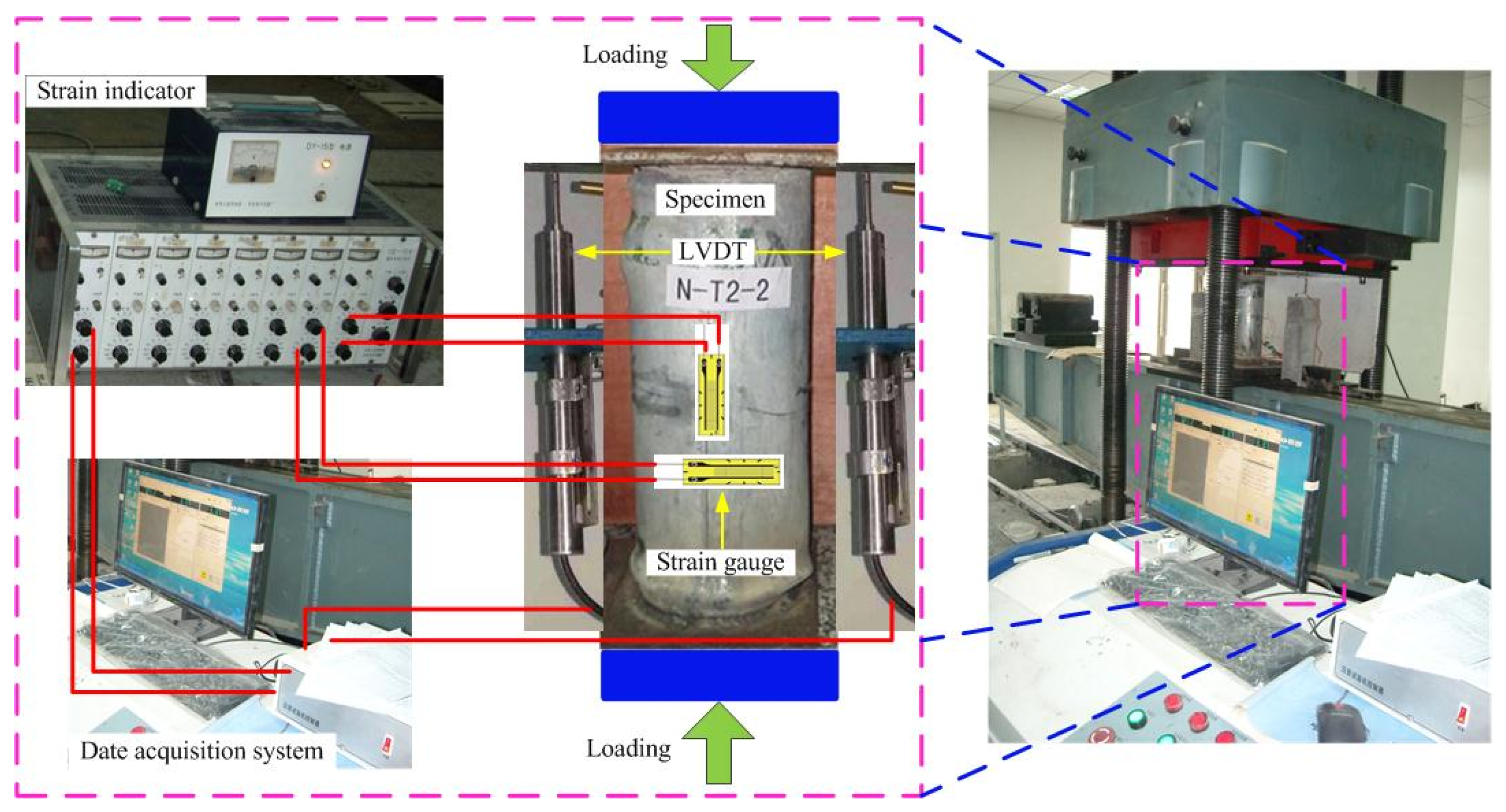
2. Experimental Programs
2.1. Material Properties
2.2. Specimens Design and Preparation
2.3. Test Programs
3. Results and Discussions
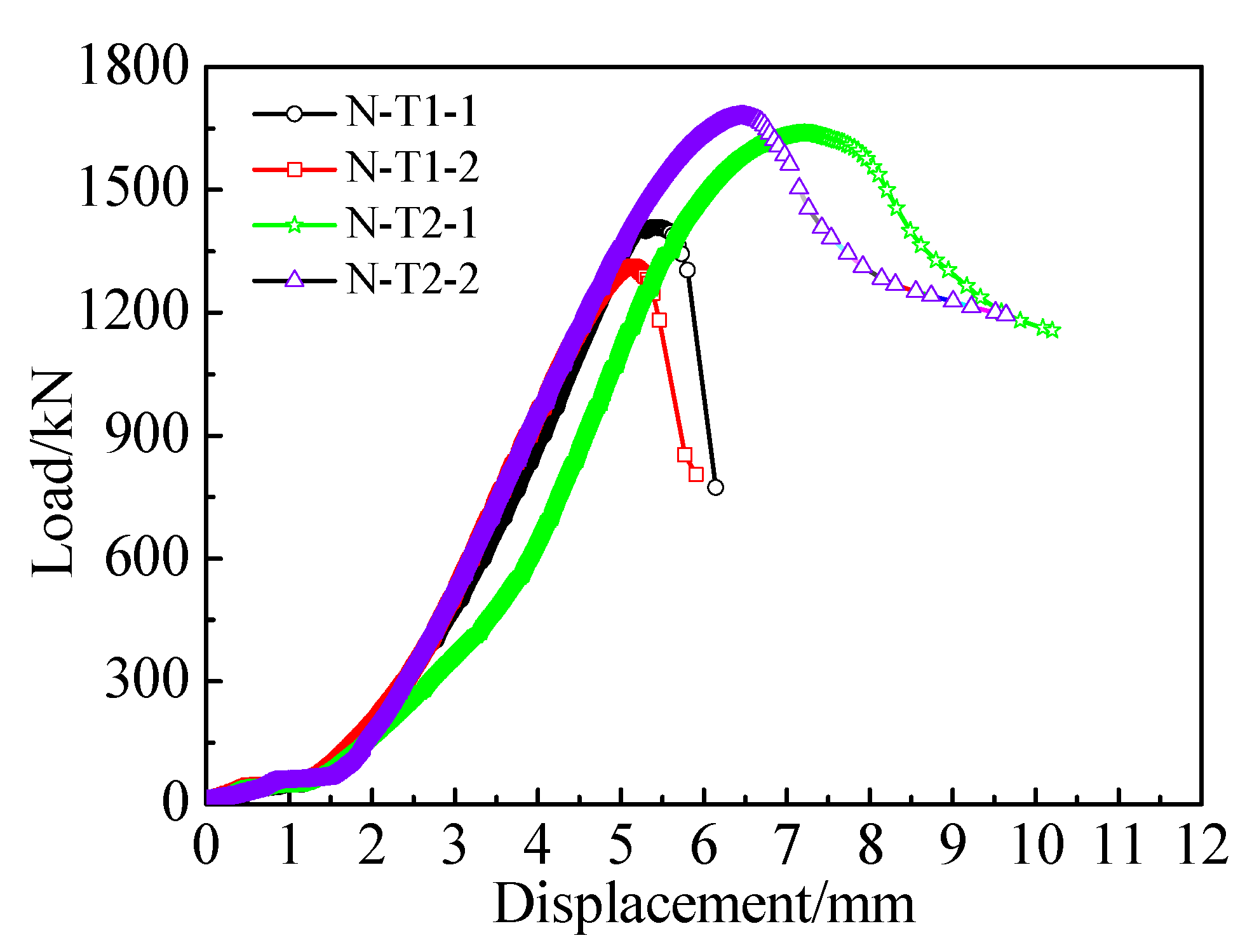
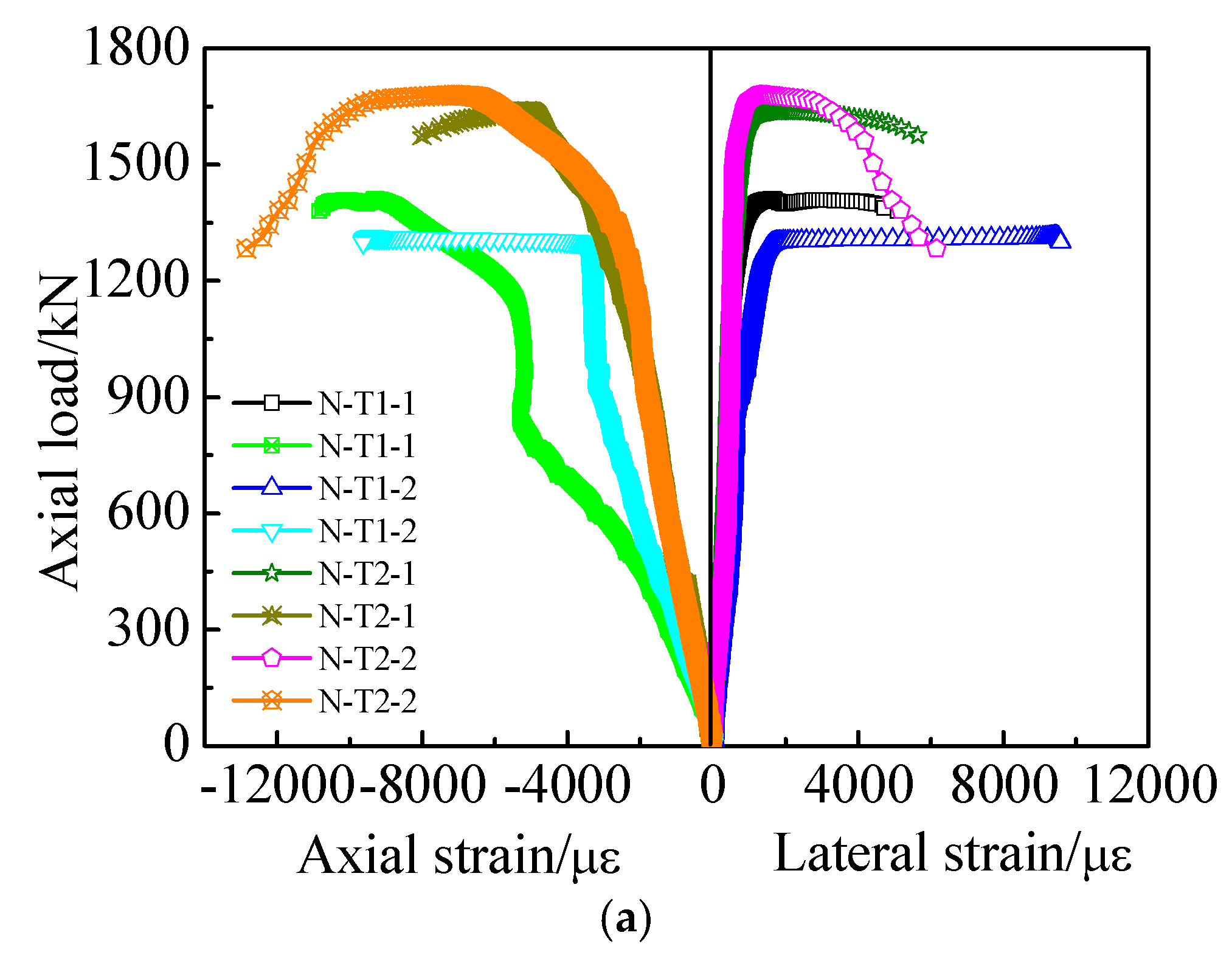
3.1. Load-Deformation Characteristics
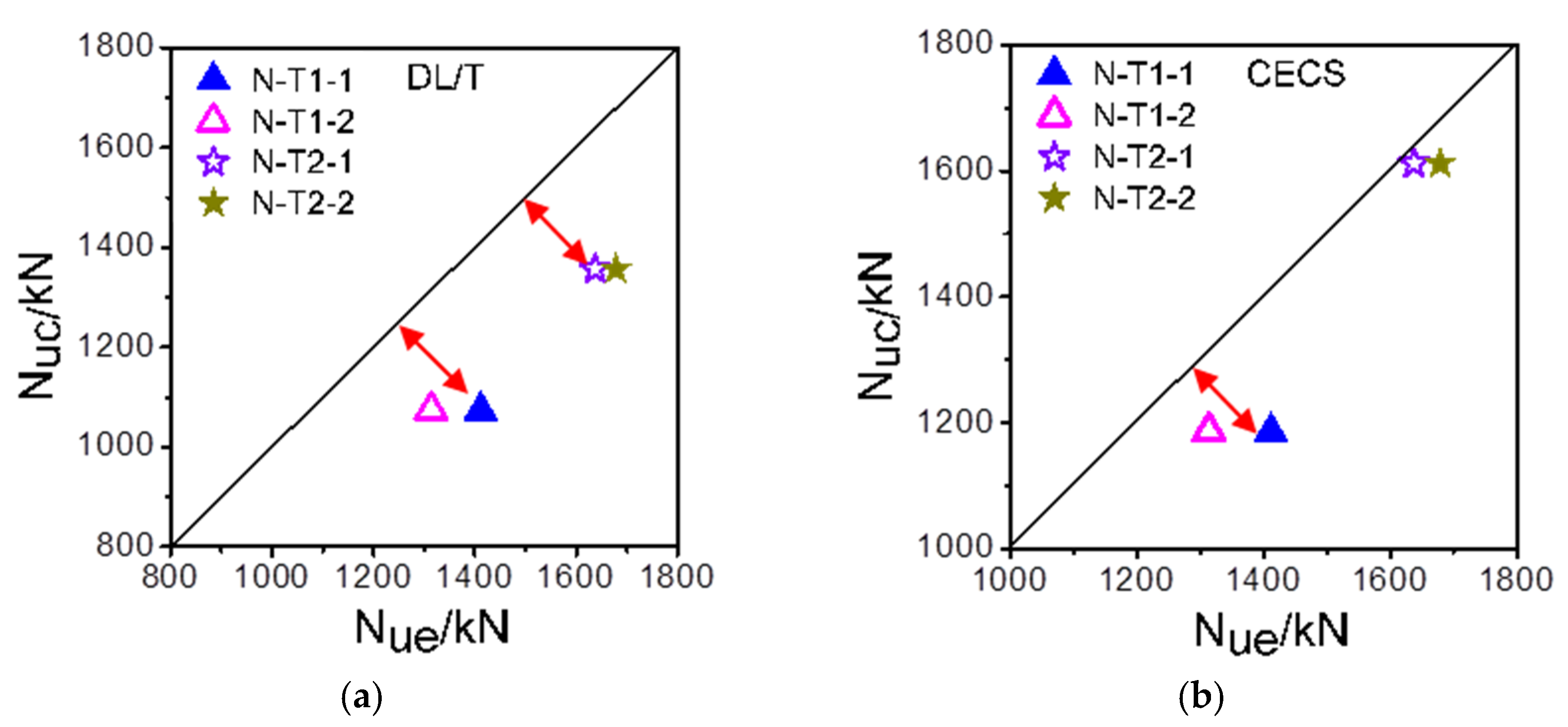
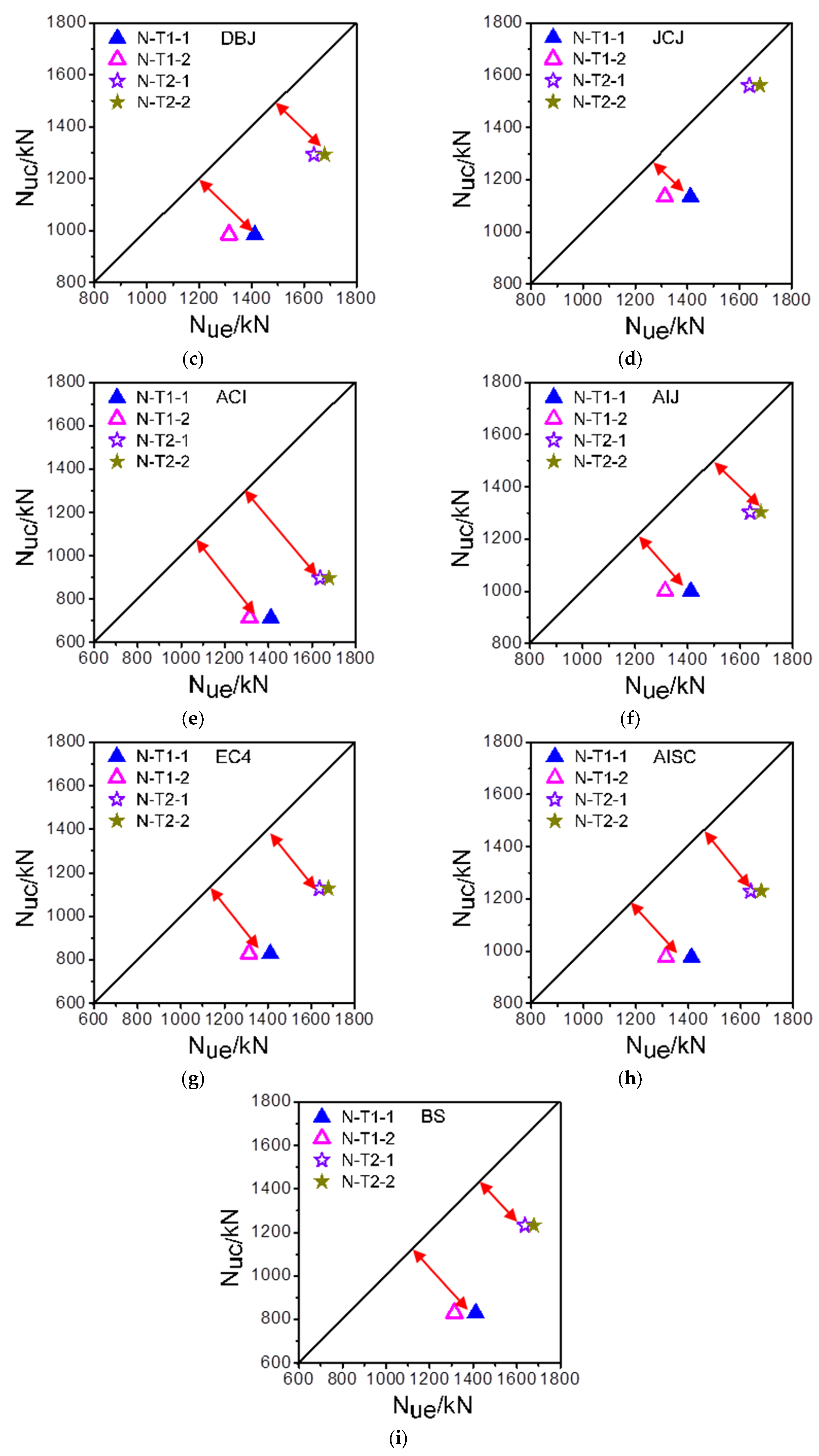
3.2. Formulas in Different Design Codes on the Ultimate Load
3.3. Comparison on the Ultimate Loads between Experiments and Theoretical Values
4. Conclusions
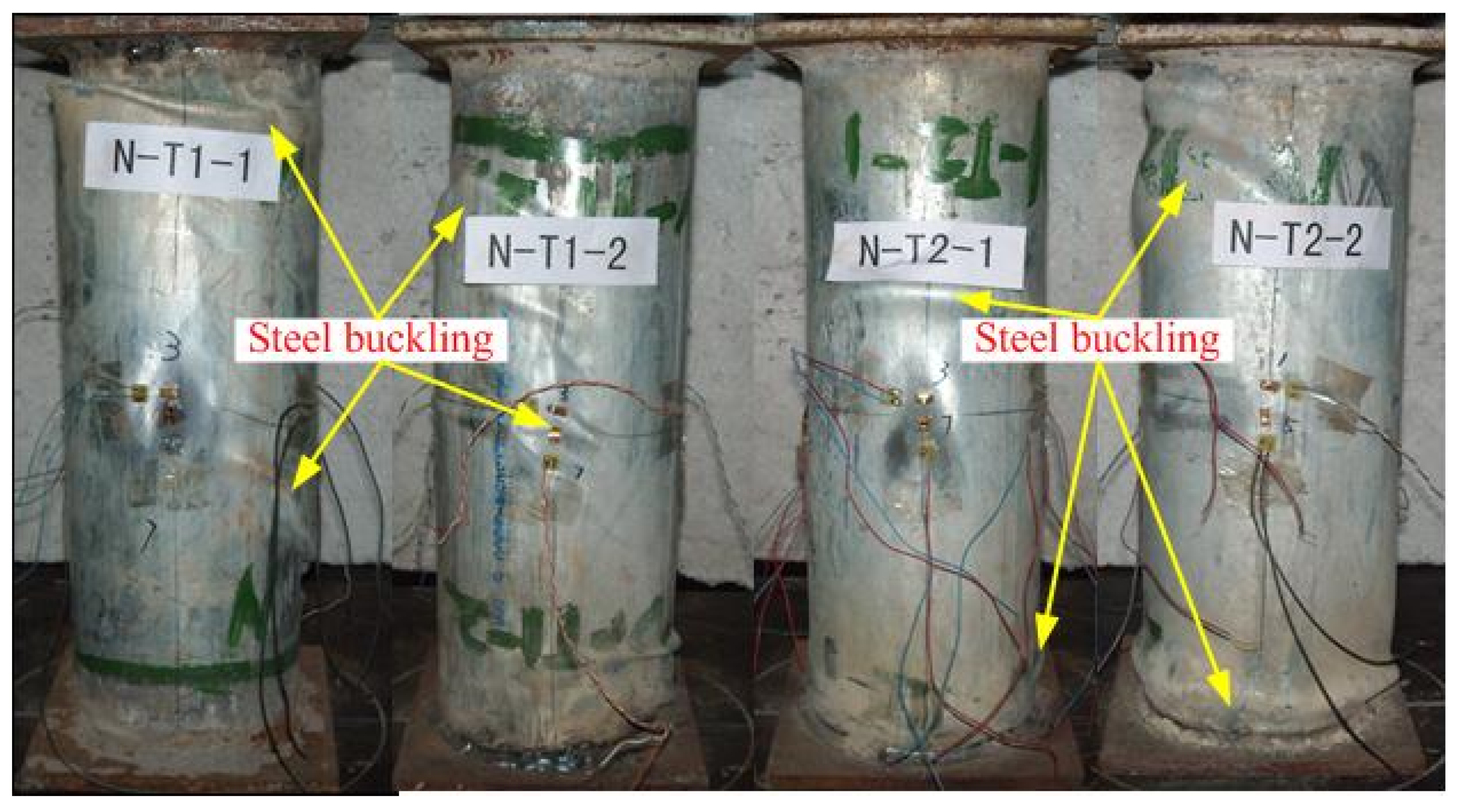
- Typical failure modes of SCCFTST columns with different wall thickness of thin-walled steel tubes present outward buckling. The amount of outward local buckling increased with decreasing wall thicknesses and increasing D/t ratios, respectively.
- The decreasing rate of the load-deformation curves in the descending branch decreased with increasing wall thickness. However, the ultimate loads of SCCFTST columns increase with increasing wall thickness.
- The ultimate loads are conservatively estimated by the design codes, including DL/T, CECS, DBJ, JCJ, ACI, AIJ, EC4, AISC, and BS. Compared with the ultimate loads from the experiments, the corresponding decrease rates of the predicted ultimate loads using different design codes are 20%, 8%, 25%, 11%, 47%, 24%, 36%, 27%, and 32%, respectively. Additionally, ACI and CECS are the most conservative and accurate design codes for predicting the ultimate loads of the SCCFTST columns, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schneider, S.P. Axially loaded concrete-filled steel tubes. J. Struct. Eng. 1998, 124, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, F.; Lai, J. Strength behavior of circular concrete-filled steel tube stub columns under axial compression: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 322, 126144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Luo, X.; Zhu, C.; Tang, C. Analysis of circular concrete-filled steel tube (CFT) support in high ground stress conditions. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 43, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Cao, J.; Yan, X.; Zhang, F. Mechanism and application of concrete-filled steel tubular support in deep and high stress roadway. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Chen, J.; Jin, W. Experimental investigation of thin-walled concrete-filled steel tube columns with reinforced lattice angle. Thin-Walled Struct. 2014, 84, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, M.F.; Elchalakani, M.; Karrech, A.; Patel, V.I.; Yang, B. Behaviour of Concrete-Filled Double-Skin Short Columns under Compression through Finite Element Modelling: SHS Outer and SHS Inner Tubes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, J.S.; Yang, Y. Cyclic testing of thin-walled circular steel tubular columns filled with demolished concrete blocks and fresh concrete. Thin-Walled Struct. 2013, 66, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouzi, R.A.; Almasaeid, H.H.; Salman, D.G.; Abendeh, R.M.; Rabayah, H.S. Prediction of bond-slip behavior of circular/squared concrete-filled steel tubes. Buildings 2022, 12, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.L.; Ibañez, C.; Espinós, A.; Portolés, J.M.; Hospitaler, A. Influence of Ultra-High Strength Concrete on Circular Concrete-Filled Dual Steel Columns; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Zhu, C.; Miao, K.; Zheng, K.; Tang, Y. Compressive performance of concrete-filled steel tube columns with in-built seawater and sea sand concrete-filled FRP tubes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 317, 125933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Visintin, P. Structural performance of geopolymer-concrete-filled steel tube members subjected to compression and bending. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 188, 107026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, B.; Liu, X.; Sun, Z. Seismic behavior of a novel beam to reinforced concrete-filled steel tube column joint. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 187, 106931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, Z.; Naghipour, M.; Nematzadeh, M. Structural behavior of prestressed self-compacting concrete-encased concrete-filled steel tubes beams. Struct. Concr. 2021, 22, 2011–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekyapar, T. Experimental performance of concrete filled welded steel tube columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2016, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, C.W.; Lehman, D.E.; Bishop, E. Strength and stiffness of circular concrete-filled tubes. J. Struct. Eng. 2010, 136, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Han, L.; Zhuang, J. Axial loading behavior of CFRP strengthened concrete-filled steel tubular stub columns. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2007, 10, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Gho, W. Axial load behaviour of high-strength rectangular concrete-filled steel tubular stub columns. Thin-Walled Struct. 2005, 43, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Qu, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L.; Huang, Z. A comparative study on mechanical and environmental performance of concrete-filled steel tubes using molybdenum tailing aggregate. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 189, 107100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, B.Z.; Wang, J.T. Experimental and Analytical Research on Flexural Behavior of Concrete-Filled High-Strength Steel Tubular Members. Materials 2022, 15, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, A.E.; Rangan, B.V. Tests on high-strength concrete-filled steel tubular columns. Struct. J. 1999, 96, 268–274. [Google Scholar]
- Uy, B. Strength of short concrete filled high strength steel box columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2001, 57, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yang, Y. Analysis of thin-walled steel RHS columns filled with concrete under long-term sustained loads. Thin-Walled Struct. 2003, 41, 849–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.F. Axial stress-strain behavior of high-strength concrete confined by circular thin-walled steel tubes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 177, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, G.M. Compressive behavior of thin-walled circular steel tubular columns filled with steel stirrup-reinforced compound concrete. Eng. Struct. 2018, 170, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Nematzadeh, M. Bond behavior of lightweight concrete-filled steel tubes containing rock wool waste after exposure to high temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 124039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Qi, A.; Chen, Y. Study on the hysteretic behavior of recycled aggregate concrete-filled steel tube columns containing ferronickel slag. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 46, 103695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayough, P.; Ibrahim, Z.; Sulong, N.R.; Hsiao, P.C. The effects of cross-sectional shapes on the axial performance of concrete-filled steel tube columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 176, 106424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, M.F.; Kharoob, O.F. Analysis of circular concrete-filled double skin tubular slender columns with external stainless steel tubes. Thin-Walled Struct. 2014, 79, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Han, L.; Wang, Z. Experimental behaviour of stiffened concrete-filled thin-walled hollow steel structural (HSS) stub columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2005, 61, 962–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ding, F.; Lu, D.; Lyu, F.; Huang, S.; Cao, Z.; Wang, H. Finite Element Analysis of the Mechanical Properties of Axially Compressed Square High-Strength Concrete-Filled Steel Tube Stub Columns Based on a Constitutive Model for High-Strength Materials. Materials 2022, 15, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Han, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, W. Shear behavior of high-strength square concrete filled steel tube members. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 196, 107423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Uy, B.; Han, L.H.; Wang, Z.B. Analysis and design of concrete-filled stiffened thin-walled steel tubular columns under axial compression. Thin-Walled Struct. 2009, 47, 1544–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Xu, L.; Chi, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yu, C.; He, C. Seismic performance of rectangular ultra-high performance concrete filled steel tube (UHPCFST) columns. Compos. Struct. 2021, 259, 113242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Han, L. Experimental behaviour of recycled aggregate concrete filled steel tubular columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2006, 62, 1310–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehnaz, S.M.; Shah, S.M.I.; Ganesh, G.M. Experimental and theoretical study on rectangular concrete filled steel tube columns subjected to axial compression. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Su, Y.; Wei, J.; Lu, J.; Li, X. The Eccentric Compression Performance of Spirally Stiffened Thin-Walled Square Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Laminated Composite Members. Buildings 2022, 12, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeghiche, J.; Chaoui, K. An experimental behaviour of concrete-filled steel tubular columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2005, 61, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Xue, Z.; Cao, M. Surface Cracking and Fractal Characteristics of Cement Paste after Exposure to High Temperatures. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Yu, Y. Axial compression performance of square thin walled concrete-Filled steel tube stub columns with reinforcement stiffener under constant high-Temperature. Materials 2019, 12, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, H.; Radix, H.J. Self-compacting concrete: Theoretical and experimental study. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 2116–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-Cuesta, V.; Skaf, M.; Faleschini, F.; Manso, J.M.; Ortega-López, V. Self-compacting concrete manufactured with recycled concrete aggregate: An overview. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yao, G. Experimental behaviour of thin-walled hollow structural steel (HSS) columns filled with self-consolidating concrete (SCC). Thin-Walled Struct. 2004, 42, 1357–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Jiang, C.; Jia, Y.; Yang, G.; Li, M.; Tang, X.; Chen, D. Axial Loading Behaviour of Self-Compacting Concrete-Filled Thin-Walled Steel Tubular Stub Columns. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 228-2010; Metallic Materials Tensile Testing-Method of Test at Room Temperature. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
- GB 50081-2002; Standard for Test Method of Mechanical Properties on Ordinary Concrete. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Tao, Z.; Han, L.; Zhao, X. Behaviour of concrete-filled double skin (CHS inner and CHS outer) steel tubular stub columns and beam-columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2004, 60, 1129–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Han, L. Behaviour of concrete-encased CFST columns under combined compression and bending. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2014, 101, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayalan, P.; Aly, T.; Patnaikuni, I. Behaviour of concrete-filled steel tubes under static and variable repeated loading. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2009, 65, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DL/T 5085-1999; Code for Design of Steel-Concrete Composite Structure. China Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 1999.
- CECS 28-2012; Technical Specification for Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Structures. China Planning Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012.
- DBJ T13-51-2010; Technical Specification for Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Structures. Fuzhou University Press: Fuzhou, China, 2010.
- JCJ 01-89; Design and Construction Specification for Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Structures. Tongji University Press: Shanghai, China, 1989.
- ACI 318-1999; Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary. American Concrete Institut: Farmingtion Hills, MI, USA, 1999.
- AIJ 1997; Recommendations for Design and Construction of Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Structures. Architectural Institute of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 1997.
- EC4 1994; Design of Composite Steel and Concrete Structures, Part1: General Rules and Rules for Building. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1994.
- AISC 1999; Specification for Structural Steel Buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction: Chicago, IL, USA, 1999.
- BS 5400 1979; Steel Concrete and Composite Bridges, Part 5: Code of Practice for Design Composite Bridges. British Standards Institution: British, UK, 1979.

| D×t×L | L/D | D/t | Yield Strength fy | Ultimate Strength | Modulus of Elasticity Es | Poisson’ Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm3 | MPa | MPa | MPa | |||
| 140 × 1.2 × 420 | 3.0 | 116.7 | 345.0 | 415.0 | 1.8 × 105 | 0.30 |
| 140 × 3 × 420 | 3.0 | 46.7 | 358.3 | 456.7 | 2.0 × 105 | 0.28 |
| Water | Cement | Fine Aggregate | Coarse Aggregate | Fly Ash | Superplasticizer | fcu | fck | Ec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg/m3 | kg/m3 | kg/m3 | kg/m3 | kg/m3 | % | MPa | MPa | MPa |
| 199.0 | 401.5 | 836.5 | 768.5 | 122.1 | 0.4 | 84.0 | 65.8 | 3.0 × 104 |
| Numbers | Nue/kN | Nuc/kN | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL/T | CECS | DBJ | JCJ | ACI | AIJ | EC4 | AISC | BS | ||
| N-T1-1 | 1411.6 | 1073.8 | 1186.7 | 985.1 | 1134.5 | 713.9 | 1000.6 | 829.0 | 976.8 | 830.1 |
| N-T1-2 | 1314.0 | 1073.8 | 1186.7 | 985.1 | 1134.5 | 713.9 | 1000.6 | 829.0 | 976.8 | 830.1 |
| N-T2-1 | 1637.6 | 1356.7 | 1611.3 | 1293.0 | 1560.8 | 896.7 | 1302.7 | 1127.0 | 1229.7 | 1231.6 |
| N-T2-2 | 1678.6 | 1356.7 | 1611.3 | 1293.0 | 1560.8 | 896.7 | 1302.7 | 1127.0 | 1229.7 | 1231.6 |
| Numbers | Nuc/Nue | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL/T | CECS | DBJ | JCJ | ACI | AIJ | EC4 | AISC | BS | |
| N-T1-1 | 0.761 | 0.841 | 0.698 | 0.804 | 0.506 | 0.709 | 0.587 | 0.692 | 0.588 |
| N-T1-2 | 0.817 | 0.903 | 0.750 | 0.863 | 0.543 | 0.761 | 0.631 | 0.743 | 0.632 |
| N-T2-1 | 0.828 | 0.984 | 0.790 | 0.953 | 0.548 | 0.795 | 0.688 | 0.751 | 0.752 |
| N-T2-2 | 0.808 | 0.960 | 0.770 | 0.930 | 0.534 | 0.776 | 0.671 | 0.733 | 0.734 |
| Average value | 0.804 | 0.922 | 0.752 | 0.888 | 0.533 | 0.760 | 0.644 | 0.730 | 0.677 |
| COV | 0.037 | 0.069 | 0.053 | 0.076 | 0.035 | 0.049 | 0.070 | 0.036 | 0.117 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jia, Y.; Li, L. Experimental Study on Self-Compacting Concrete-Filled Thin-Walled Steel Tube Columns. Buildings 2022, 12, 2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122134
Wang Y, Zhang L, Jia Y, Li L. Experimental Study on Self-Compacting Concrete-Filled Thin-Walled Steel Tube Columns. Buildings. 2022; 12(12):2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122134
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yunyang, Liqing Zhang, Yandong Jia, and Li Li. 2022. "Experimental Study on Self-Compacting Concrete-Filled Thin-Walled Steel Tube Columns" Buildings 12, no. 12: 2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122134
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, L., Jia, Y., & Li, L. (2022). Experimental Study on Self-Compacting Concrete-Filled Thin-Walled Steel Tube Columns. Buildings, 12(12), 2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122134








