What Drives Construction Practitioners’ Acceptance of Intelligent Surveillance Systems? An Extended Technology Acceptance Model
Abstract
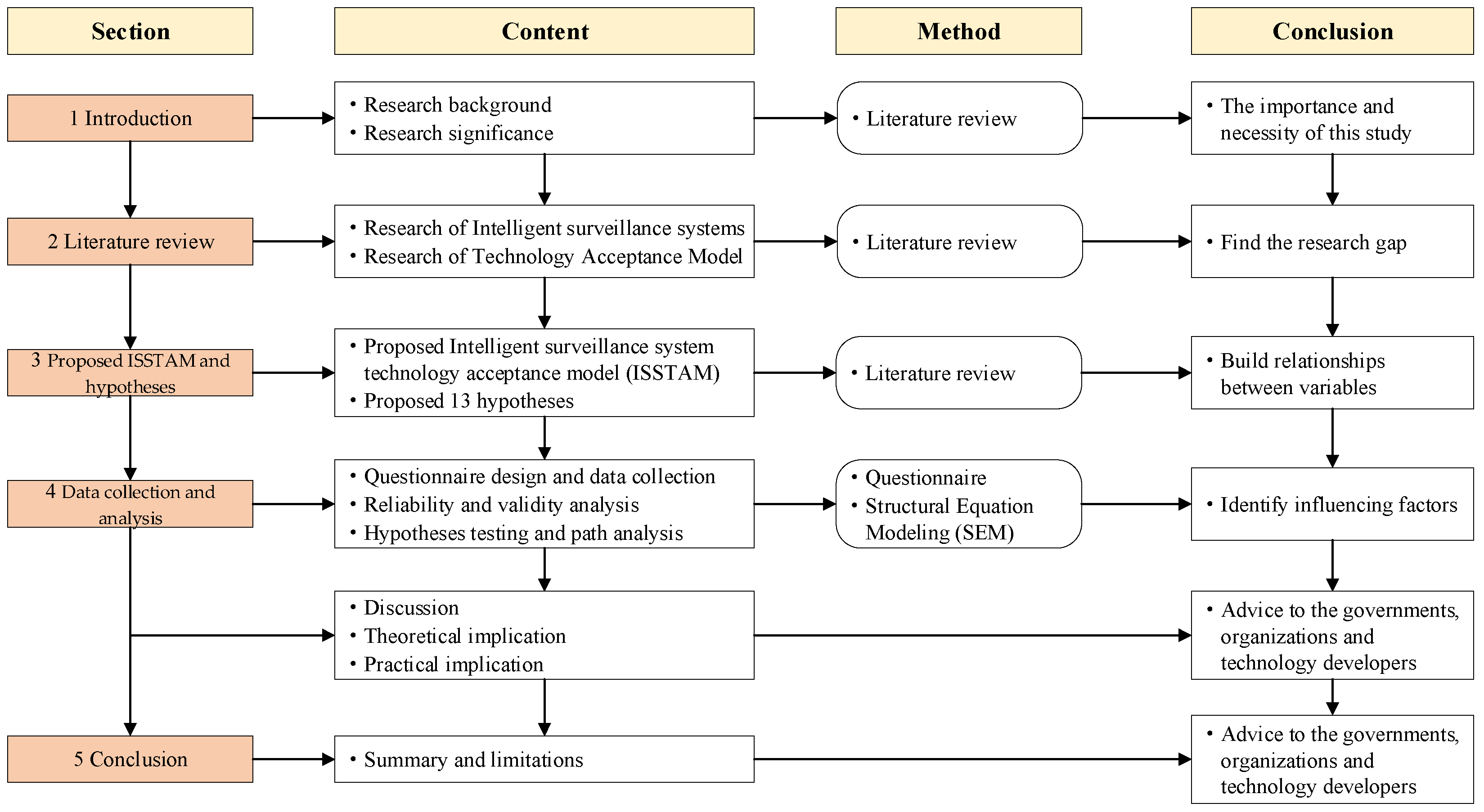
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Intelligent Surveillance System for Construction Safety Management
2.2. Technology Acceptance Model
2.3. Summary of the Review
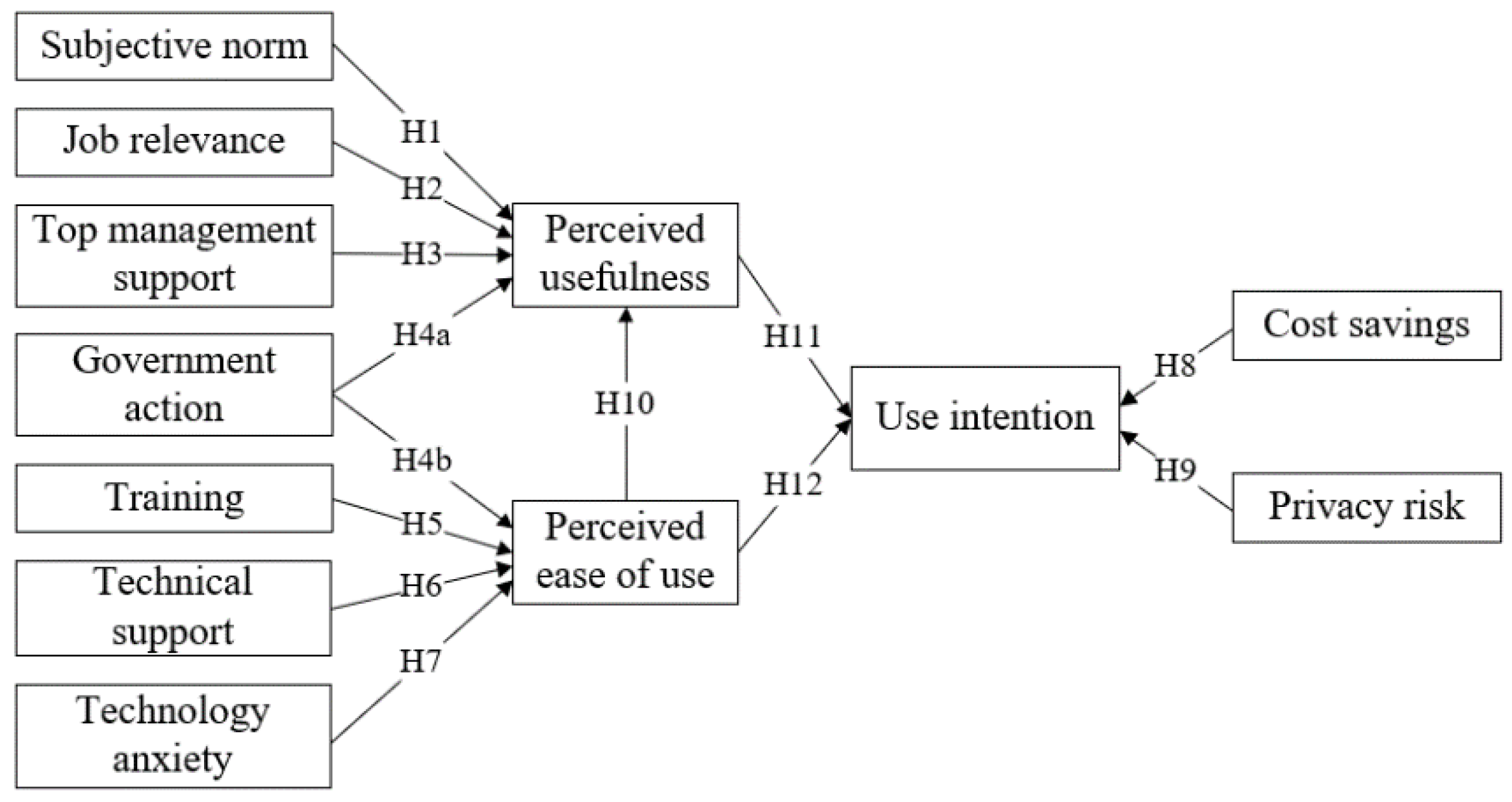
3. Proposed ISSTAM and Hypotheses
3.1. Research Model
3.2. Hypotheses of External Variables
3.2.1. Subjective Norm
3.2.2. Job Relevance
3.2.3. Top Management Support
3.2.4. Government Action
3.2.5. Training
3.2.6. Technical Support
3.2.7. Technology Anxiety
3.2.8. Cost Savings
3.2.9. Privacy Risk
3.3. Hypotheses of Original TAM Variables
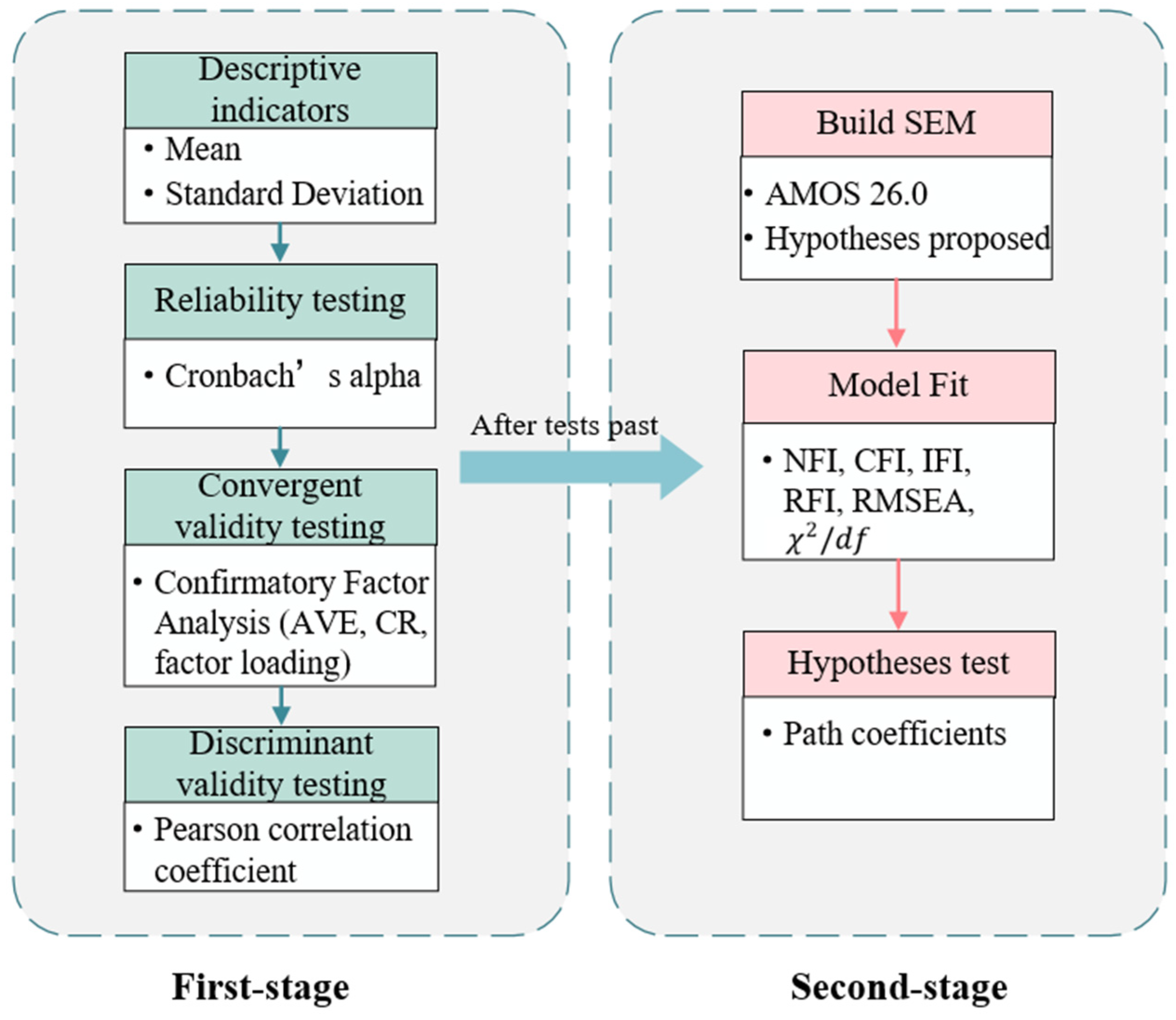
4. Data Collection and Analysis
4.1. Questionnaire Design and Data Collection
4.2. Evaluation of ISSTAM
4.2.1. Reliability Testing
4.2.2. Convergent Validity Testing
4.2.3. Discriminant Validity Testing
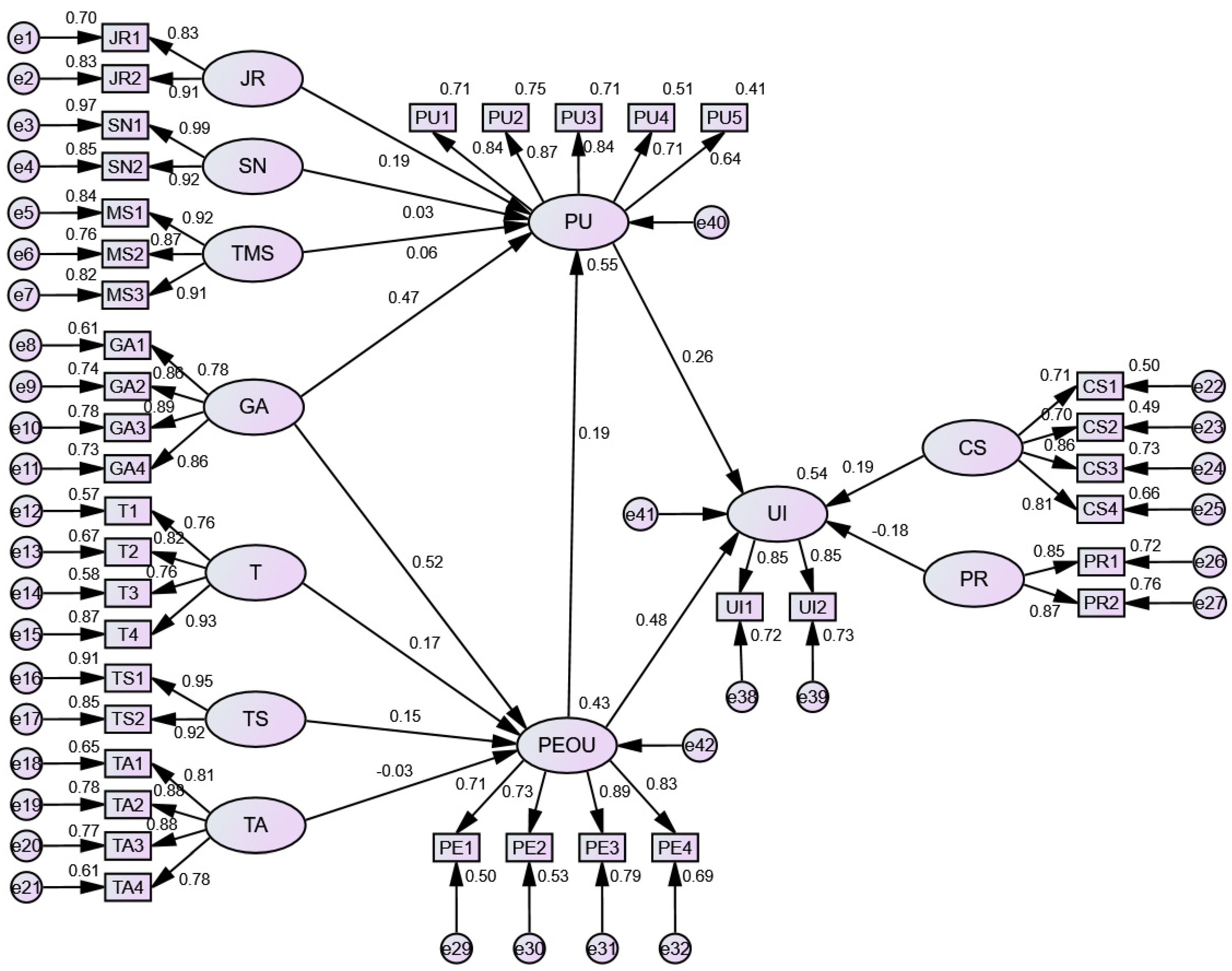
4.3. Analysis of the Structural Model
4.3.1. Model Fit
4.3.2. Hypothesis Tests
4.4. Discussion and Implication
4.4.1. Discussion
4.4.2. Theoretical Implications
4.4.3. Practical Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. List of Measurement Items for Each Variable
| Variable | Item | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job relevance | JR1 | Usage of ISS is closely related to my daily work. | [24,28,55] |
| JR2 | Usage of ISS is very important to my work. | ||
| Subjective norm | SN1 | People who are important to me think I should use ISS. | [24,28,72] |
| SN2 | People who influence my behavior think I should use ISS. | ||
| Top management support | MS1 | Top management encouraged me to use ISS. | [28,37] |
| MS2 | Top management understands the benefits of ISS. | ||
| MS3 | Top management recognizes my efforts in using ISS. | ||
| Cost savings | CS1 | The price of ISS is reasonable. | [59] |
| CS2 | The cost of ISS would not become a financial burden. | ||
| CS3 | ISS is cheaper than other safety supervision equipment. | [53] | |
| CS4 | ISS has lower maintenance costs than other safety regulations. | ||
| Training | T1 | After training, my understanding of ISS has been greatly improved. | [28] |
| T2 | After training, I am confident in using ISS. | ||
| T3 | The training content is comprehensive and the training time is long enough. | ||
| T4 | There are experienced and knowledgeable trainers to help me understand and use ISS. | ||
| Technical support | TS1 | When I encounter difficulties in using ISS, it is easy to contact technicians and get help. | [28,37] |
| TS2 | When I encounter difficulties in using ISS, technicians can provide effective help. | ||
| Technology anxiety | TA1 | I feel nervous in the face of new technology. | [53,54,72] |
| TA2 | I am worried that it is difficult to learn new technology. | ||
| TA3 | I am reluctant to use new technology because I am worried about making big mistakes. | ||
| TA4 | When using a new technology, I worry that it might be broken in some way. | ||
| Privacy risk | PR1 | I am worried that my privacy will be threatened. | [62] |
| PR2 | I am worried that the video captured by surveillance would be abused. | ||
| Government action | GA1 | Government issues relevant guidance or compulsory policies. | [30,46] |
| GA2 | Government grants subsidies or bonuses. | ||
| GA3 | Government promulgates relevant laws and regulations. | ||
| GA4 | Government launches a pilot project using ISS. | ||
| Perceived usefulness | PU1 | Using ISS can increase the speed of work. | [24,28,72] |
| PU2 | Using ISS can improve the quality of work. | ||
| PU3 | Compared with other equipment, more work can be done with ISS. | ||
| PU4 | Using ISS can improve safety of work. | [75] | |
| PU5 | Using ISS can increase safety awareness. | ||
| Perceived ease of use | PE1 | Using ISS would be easy for me. | [24,28,75] |
| PE2 | Using ISS would not consume a lot of my energy. | ||
| PE3 | ISS is very easy to control for me. | ||
| PE4 | I clearly know how to use ISS. | ||
| Use intention | UI1 | Assuming I have access to the system, I intend to use it. | [24] |
| UI2 | Given that I have access to the system, I predict that I would use it. | ||
Appendix B. List of Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| HSE | Health and Safety Executive |
| MEPs | Members of the European Parliament |
| TAM | Technology acceptance model |
| ISSTAM | Intelligent surveillance system technology acceptance model |
| PPE | Personal protective equipment |
| IT | Information technology |
| TOE | Technology–organization–environment |
| PU | Perceived usefulness |
| PEOU | Perceived ease of use |
| UI | Use intention |
| SN | Subjective norm |
| JB | Job relevance |
| TMS | Top management support |
| GA | Government action |
| T | Training |
| TS | Technical support |
| TA | Technology anxiety |
| CS | Cost savings |
| PR | Privacy risk |
| CFA | Confirmatory factor analysis |
| CR | Composite reliability |
| AVE | Average variance extracted |
| SEM | Structural equation model |
References
- Kang, Y.; Siddiqui, S.; Suk Sung, J.; Chi, S.; Kim, C. Trends of Fall Accidents in the U.S. Construction Industry. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Skibniewski, M.J. Perceiving interactions and dynamics of safety leadership in construction projects. Saf. Sci. 2018, 106, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Department of the People’s Republic of China. Notification of Production Safety Accidents in Housing and Municipal Engineering. Available online: http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/202006/t20200624_246031.html (accessed on 19 June 2020).
- Health and Safety Executive. Construction Statistics in Great Britain. 2020. Available online: https://www.hse.gov.uk/statistics/industry/index.htm (accessed on 4 November 2020).
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Construction:NAICS 23. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/iag/tgs/iag23.htm (accessed on 18 January 2019).
- Heinrich, H.W.; Petersen, D.; Roos, N.R.; Brown, J.; Hazlett, S. Industrial Accident Prevention: A Safety Management Approach, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Xiong, C.; Gong, P. A real-time control approach based on intelligent video surveillance for violations by construction workers. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2018, 24, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Department of the People’s Republic of China. Jiangsu Construction Upgraded “Smart Site” Pilot Project. Available online: http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/xinwen/dfxx/202006/20200624_246018.html (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Seo, J.; Han, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, H. Computer vision techniques for construction safety and health monitoring. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, K. Workplace surveillance: An overview. Labor History 2010, 51, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summary, A. Summary: Use of Artificial Intelligence by the Police: MEPs Oppose Mass Surveillance. Available online: https://ai-summary.com/summary-use-of-artificial-intelligence-by-the-police-meps-oppose-mass-surveillan/ (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Mathur, G.; Bundele, M. Research on Intelligent Video Surveillance techniques for suspicious activity detection critical review. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE), Jaipur, India, 23–25 December 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, R.; Yang, Z. A critical review of vision-based occupational health and safety monitoring of construction site workers. Saf. Sci. 2020, 126, 104658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Ding, L.; Luo, H.; Rose, T.M.; An, W. Detecting non-hardhat-use by a deep learning method from far-field surveillance videos. Autom. Constr. 2018, 85, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mneymneh Bahaa, E.; Abbas, M.; Khoury, H. Vision-Based Framework for Intelligent Monitoring of Hardhat Wearing on Construction Sites. J. Comput. Civil. Eng. 2019, 33, 04018066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cai, N.; Chen, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, G. Automatic detection of hardhats worn by construction personnel: A deep learning approach and benchmark dataset. Autom. Constr. 2019, 106, 102894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-W.; Brilakis, I. Construction worker detection in video frames for initializing vision trackers. Autom. Constr. 2012, 28, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.; Son, H.; Kim, C. A Comparative Study of Machine Learning Classification for Color-based Safety Vest Detection on Construction-Site Images. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 4254–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Lee, S. A vision-based motion capture and recognition framework for behavior-based safety management. Autom. Constr. 2013, 35, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Guo, H.; Ding, Q.; Li, H.; Skitmore, M. An experimental study of real-time identification of construction workers’ unsafe behaviors. Autom. Constr. 2017, 82, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konstantinou, E.; Lasenby, J.; Brilakis, I. Adaptive computer vision-based 2D tracking of workers in complex environments. Autom. Constr. 2019, 103, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D. Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Q. 1989, 13, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Igbaria, M.; Zinatelli, N.; Cragg, P.; Cavaye, A.L.M. Personal Computing Acceptance Factors in Small Firms: A Structural Equation Model. MIS Q. 1997, 21, 279–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Davis, F.D. A Theoretical Extension of the Technology Acceptance Model: Four Longitudinal Field Studies. Manag. Sci. 2000, 46, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manis, K.T.; Choi, D. The virtual reality hardware acceptance model (VR-HAM): Extending and individuating the technology acceptance model (TAM) for virtual reality hardware. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 100, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.H.; You, S.C.; Park, R.W.; Lee, S. Using an Extended Technology Acceptance Model to Understand the Factors Influencing Telehealth Utilization After Flattening the COVID-19 Curve in South Korea: Cross-sectional Survey Study. JMIR Med. Inform. 2021, 9, e25435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, A.J.; Sepasgozar, S.M.E. Developing a theoretical framework for intelligent contract acceptance. Constr. Innov. 2020, 20, 421–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.; Park, Y.; Kim, C.; Chou, J.-S. Toward an understanding of construction professionals’ acceptance of mobile computing devices in South Korea: An extension of the technology acceptance model. Autom. Constr. 2012, 28, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C. Emerging Information Technology Acceptance Model for the Development of Smart Construction System. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2018, 24, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Yang, Y.; Xue, X. Promoting Owners’ BIM Adoption Behaviors to Achieve Sustainable Project Management. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, T.K.M.; Man, S.S.; Chan, A.H.S. Exploring the acceptance of PPE by construction workers: An extension of the technology acceptance model with safety management practices and safety consciousness. Saf. Sci. 2021, 139, 105239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornatzky, L.G.; Fleischer, M.; Chakrabarti, A.K. The processes of Technological Innovation; D.C. Heath & Company: Lexington, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Nnaji, C.; Gambatese, J.; Karakhan, A.; Eseonu, C. Influential safety technology adoption predictors in construction. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2019, 26, 2655–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.; Flin, R. Unlocking the Potential: Understanding the Psychological Factors That Influence Technology Adoption in the Upstream Oil and Gas Industry. SPE J. 2020, 25, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations, 5th ed.; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.-H.; Ha, N.T.T.; Tai, H.-W.; Chang, C.-A. The Willingness to Adopt the Internet of Things (Iot) Conception in Taiwan’s Construction Industry. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2020, 26, 534–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Son, H.; Kim, C. Investigating the determinants of construction professionals’ acceptance of web-based training: An extension of the technology acceptance model. Autom. Constr. 2012, 22, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafey, A.; Saar, C.C.; Aminudin, E.B.; Gheisari, M.; Usmani, A. Technology acceptance model for Augmented Reality and Building Information Modeling integration in the construction industry. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2020, 25, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wismantoro, Y.; Himawan, H.; Widiyatmoko, K. Measuring the Interest of Smartphone Usage by Using Technology Acceptance Model Approach. J. Asian Finance Econ. Bus. 2020, 7, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Pérez, M.; Martínez Sánchez, A.; de Luis Carnicer, P.; José Vela Jiménez, M. A technology acceptance model of innovation adoption: The case of teleworking. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2004, 7, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latane, B. The psychology of social impact. Am. Psychol. 1981, 36, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, H.C. Empirical Evidence for a Descriptive Model of Implementation. MIS Q. 1978, 2, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igbaria, M. An examination of the factors contributing to microcomputer technology acceptance. Acc. Manag. Inf. Technol. 1994, 4, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Ahn, S.; Rameezdeen, R.; Baroudi, B. Investigation into post-adoption usage of mobile ICTs in Australian construction projects. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2019, 28, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.; Agarwal, R.; Sambamurthy, V. Sources of Influence on Beliefs about Information Technology Use: An Empirical Study of Knowledge Workers. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 657–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Factors Influencing BIM Adoption for Construction Enterprises in China. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolores Gallego, M.; Bueno, S.; José Racero, F.; Noyes, J. Open source software: The effects of training on acceptance. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 49, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, R.A.; Hueros, A.D. Motivational factors that influence the acceptance of Moodle using TAM. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2010, 26, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Igbaria, M. End-user computing effectiveness: A structural equation model. Omega 1990, 18, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardiansah, M.N.; Chariri, A.; Rahardja, S.; Udin, U. The effect of electronic payments security on e-commerce consumer perception: An extended model of technology acceptance. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2020, 10, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servidio, R.; Cronin, M. PerLE: An “Open Source”, ELearning Moodle-Based, Platform. A Study of University Undergraduates’ Acceptance. Behav. Sci. 2018, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Presno, C. Taking the Byte Out of Internet Anxiety: Instructional Techniques That Reduce Computer/Internet Anxiety in the Classroom. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 1998, 18, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberger, C.; Spörrle, M.; Welpe, I.M. Not fearless, but self-enhanced: The effects of anxiety on the willingness to use autonomous cars depend on individual levels of self-enhancement. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2017, 116, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, K.; Sattler, B. Anxiety, crowding, and time pressure in public self-service technology acceptance. J. Serv. Mark. 2014, 28, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Bala, H. Technology Acceptance Model 3 and a Research Agenda on Interventions. Decis. Sci. 2008, 39, 273–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hackbarth, G.; Grover, V.; Yi, M.Y. Computer playfulness and anxiety: Positive and negative mediators of the system experience effect on perceived ease of use. Inf. Manag. 2003, 40, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpala, I.; Nnaji, C.; Karakhan, A.A. Utilizing Emerging Technologies for Construction Safety Risk Mitigation. Pract. Period. Struct. Des. Constr. 2020, 25, 04020002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnaji, C.; Gambatese, J.; Karakhan, A.; Osei-Kyei, R. Development and Application of Safety Technology Adoption Decision-Making Tool. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 04020028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Shin, D.-H. An acceptance model for smart watches. Internet Res. 2015, 25, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, N.; Guo, X.; Peng, J. Understanding the acceptance of mobile health services: A comparison and integration of alternative models. J. Electron. Commer. Res. 2013, 14, 183–200. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Park, N. CCTV-RFID enabled multifactor authentication model for secure differential level video access control. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 23461–23481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.; Soroya, S.H.; Ahmad, S.; Mahmood, K. Antecedents of Self-Disclosure on Social Networking Sites (SNSs): A Study of Facebook Users. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T. The impact of privacy concern on user adoption of location—Based services. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2011, 111, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, P.; Basu, C. Interpreting the Impact of Perceived Privacy and Security Concerns in Patients’ Use of Online Health Information Systems. J. Inf. Priv. Secur. 2012, 8, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albashrawi, M.; Motiwalla, L. Privacy and Personalization in Continued Usage Intention of Mobile Banking: An Integrative Perspective. Inf. Syst. Front. 2017, 21, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rese, A.; Ganster, L.; Baier, D. Chatbots in retailers’ customer communication: How to measure their acceptance? J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2020, 56, 102176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; McCabe, B.; Jia, G.; Sun, J. Effects of Safety Climate and Safety Behavior on Safety Outcomes between Supervisors and Construction Workers. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 04019092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.C.; Gerbing, D.W. Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychol. Bull. 1988, 103, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVellis, R.F. Scale Development: Theory and Applications; Sage Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Yi, Y. On the evaluation of structural equation models. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1988, 16, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Skitmore, M.; Xia, B. A critical review of structural equation modeling applications in construction research. Autom. Constr. 2015, 49, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Li, H. Application of the extended theory of planned behavior to understand individual’s energy saving behavior in workplaces. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberger, R.; Fasolo, P.; Davis-LaMastro, V. Perceived organizational support and employee diligence, commitment, and innovation. J. Appl. Psychol. 1990, 75, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, B.; Hwang, S.; Lee, S. What drives construction workers’ acceptance of wearable technologies in the workplace? Indoor localization and wearable health devices for occupational safety and health. Autom. Constr. 2017, 84, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Category | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 160 | 72.73% |
| Female | 60 | 27.27% | |
| Age | 20–29 | 173 | 78.64% |
| 30–39 | 26 | 11.82% | |
| 40–49 | 13 | 5.91% | |
| ≥50 | 8 | 3.64% | |
| Education | ≤High school | 11 | 5.00% |
| Junior college | 19 | 8.64% | |
| Undergraduate | 172 | 78.18% | |
| ≥Postgraduate | 18 | 8.18% | |
| Job experience | 0–5 years | 177 | 80.45% |
| 5–10 years | 24 | 10.91% | |
| 11–15 years | 8 | 3.64% | |
| ≥16 years | 11 | 5.00% | |
| Position | Worker | 52 | 23.64% |
| Security manager | 6 | 2.73% | |
| Construction engineer | 23 | 10.45% | |
| Cost engineer | 37 | 16.82% | |
| Project manager | 8 | 3.64% | |
| Top management | 11 | 5.00% | |
| Construction design institute | 10 | 4.55% | |
| Other managers | 73 | 33.18% |
| Variable | Item | Mean (SD) | Factor Loading | AVE | CR | Cronbach’s Alpha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Job relevance | JR1 | 3.755 (1.13) | 0.834 | 0.765 | 0.866 | 0.864 |
| JR2 | 3.659 (1.17) | 0.913 | ||||
| Subjective norm | SN1 | 4.095 (0.93) | 0.985 | 0.910 | 0.953 | 0.952 |
| SN2 | 4.082 (0.93) | 0.922 | ||||
| Top management support | MS1 | 3.923 (0.94) | 0.916 | 0.807 | 0.926 | 0.926 |
| MS2 | 3.865 (0.96) | 0.872 | ||||
| MS3 | 3.731 (0.96) | 0.907 | ||||
| Cost savings | CS1 | 3.690 (0.96) | 0.710 | 0.596 | 0.854 | 0.855 |
| CS2 | 3.607 (0.96) | 0.701 | ||||
| CS3 | 3.625 (0.99) | 0.855 | ||||
| CS4 | 3.494 (0.93) | 0.811 | ||||
| Training | T1 | 3.909 (0.92) | 0.757 | 0.673 | 0.891 | 0.895 |
| T2 | 3.900 (0.92) | 0.817 | ||||
| T3 | 3.891 (0.93) | 0.764 | ||||
| T4 | 3.977 (0.89) | 0.932 | ||||
| Technical support | TS1 | 4.009 (0.90) | 0.952 | 0.878 | 0.935 | 0.935 |
| TS2 | 4.077 (0.91) | 0.922 | ||||
| Technology anxiety | TA1 | 2.950 (1.16) | 0.809 | 0.704 | 0.905 | 0.903 |
| TA2 | 2.786 (1.21) | 0.880 | ||||
| TA3 | 2.727 (1.19) | 0.880 | ||||
| TA4 | 2.927 (1.19) | 0.782 | ||||
| Privacy risk | PR1 | 3.323 (1.08) | 0.850 | 0.742 | 0.852 | 0.851 |
| PR2 | 3.509 (1.12) | 0.873 | ||||
| Government action | GA1 | 3.841 (0.97) | 0.782 | 0.719 | 0.911 | 0.909 |
| GA2 | 3.964 (0.99) | 0.863 | ||||
| GA3 | 4.077 (0.92) | 0.885 | ||||
| GA4 | 3.914 (0.95) | 0.857 | ||||
| Perceived usefulness | PU1 | 3.977 (0.95) | 0.841 | 0.616 | 0.888 | 0.886 |
| PU2 | 4.064 (0.90) | 0.866 | ||||
| PU3 | 3.923 (0.94) | 0.841 | ||||
| PU4 | 4.018 (0.92) | 0.711 | ||||
| PU5 | 3.859 (0.93) | 0.642 | ||||
| Perceived ease of use | PE1 | 3.850 (0.86) | 0.709 | 0.629 | 0.870 | 0.863 |
| PE2 | 3.555 (0.94) | 0.727 | ||||
| PE3 | 3.655 (0.92) | 0.890 | ||||
| PE4 | 3.668 (0.91) | 0.831 | ||||
| Use intention | UI1 | 3.773 (0.95) | 0.846 | 0.723 | 0.840 | 0.847 |
| UI2 | 3.750 (0.91) | 0.855 |
| Item | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| KMO measure of sampling adequacy | 0.85 | |
| Bartlett’s test of sphericity | Approx. chi-square | 6303.605 |
| df | 703 | |
| Sig. | 0.000 | |
| JR | SN | TMS | T | TS | TA | CS | PR | GA | PU | PEOU | UI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JR | 0.874 | |||||||||||
| SN | 0.257 | 0.954 | ||||||||||
| TMS | 0.309 | 0.184 | 0.899 | |||||||||
| T | 0.275 | 0.810 | 0.213 | 0.820 | ||||||||
| TS | 0.450 | 0.373 | 0.232 | 0.261 | 0.937 | |||||||
| TA | 0.225 | 0.098 | 0.120 | 0.116 | 0.083 | 0.839 | ||||||
| CS | 0.369 | 0.393 | −0.005 | 0.39 | 0.385 | 0.219 | 0.772 | |||||
| PR | 0.149 | 0.066 | −0.036 | 0.112 | 0.266 | 0.437 | 0.219 | 0.862 | ||||
| GA | 0.441 | 0.364 | 0.248 | 0.333 | 0.337 | 0.209 | 0.327 | 0.217 | 0.848 | |||
| PU | 0.489 | 0.280 | 0.275 | 0.340 | 0.321 | 0.172 | 0.292 | 0.161 | 0.695 | 0.785 | ||
| PEOU | 0.334 | 0.325 | 0.195 | 0.362 | 0.372 | 0.111 | 0.285 | 0.157 | 0.617 | 0.569 | 0.793 | |
| UI | 0.335 | 0.295 | 0.172 | 0.291 | 0.322 | 0.062 | 0.370 | −0.021 | 0.506 | 0.566 | 0.660 | 0.851 |
| Model Fitness | GFI | CFI | TLI | IFI | RMSEA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Criteria | <3 | >0.80 | >0.90 | >0.90 | >0.90 | <0.08 |
| Fitness | 1.698 | 0.810 | 0.928 | 0.918 | 0.929 | 0.056 |
| Hypothesis | Path | Path Coefficients | p | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | PU ← JR | 0.191 | 0.004 | Accepted |
| H2 | PU ← SN | 0.035 | 0.544 | Not accepted |
| H3 | PU ← TMS | 0.056 | 0.340 | Not accepted |
| H4a | PU ← GA | 0.468 | *** | Accepted |
| H4b | PEOU ← GA | 0.518 | *** | Accepted |
| H5 | PEOU ← T | 0.168 | 0.010 | Accepted |
| H6 | PEOU ← TS | 0.146 | 0.024 | Accepted |
| H7 | PEOU ← TA | −0.029 | 0.634 | Not accepted |
| H8 | UI ← CS | 0.195 | 0.004 | Accepted |
| H9 | UI ← PR | −0.181 | 0.006 | Accepted |
| H10 | PU ← PEOU | 0.194 | 0.014 | Accepted |
| H11 | UI ← PEOU | 0.484 | *** | Accepted |
| H12 | UI ← PU | 0.263 | 0.003 | Accepted |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Deng, Y. What Drives Construction Practitioners’ Acceptance of Intelligent Surveillance Systems? An Extended Technology Acceptance Model. Buildings 2022, 12, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12020104
Lu Y, Deng Y. What Drives Construction Practitioners’ Acceptance of Intelligent Surveillance Systems? An Extended Technology Acceptance Model. Buildings. 2022; 12(2):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12020104
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Ying, and Yunxuan Deng. 2022. "What Drives Construction Practitioners’ Acceptance of Intelligent Surveillance Systems? An Extended Technology Acceptance Model" Buildings 12, no. 2: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12020104
APA StyleLu, Y., & Deng, Y. (2022). What Drives Construction Practitioners’ Acceptance of Intelligent Surveillance Systems? An Extended Technology Acceptance Model. Buildings, 12(2), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12020104





