Properties Evolution of Some Hydraulic Mortars Incorporating Graphene Oxides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.2.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (FT-IR)
2.2.2. Mechanical Tests
2.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.4. Experimental Studies for the Evaluation of Mortars Exposed to Corrosive Attacks
3. Results and Discussions
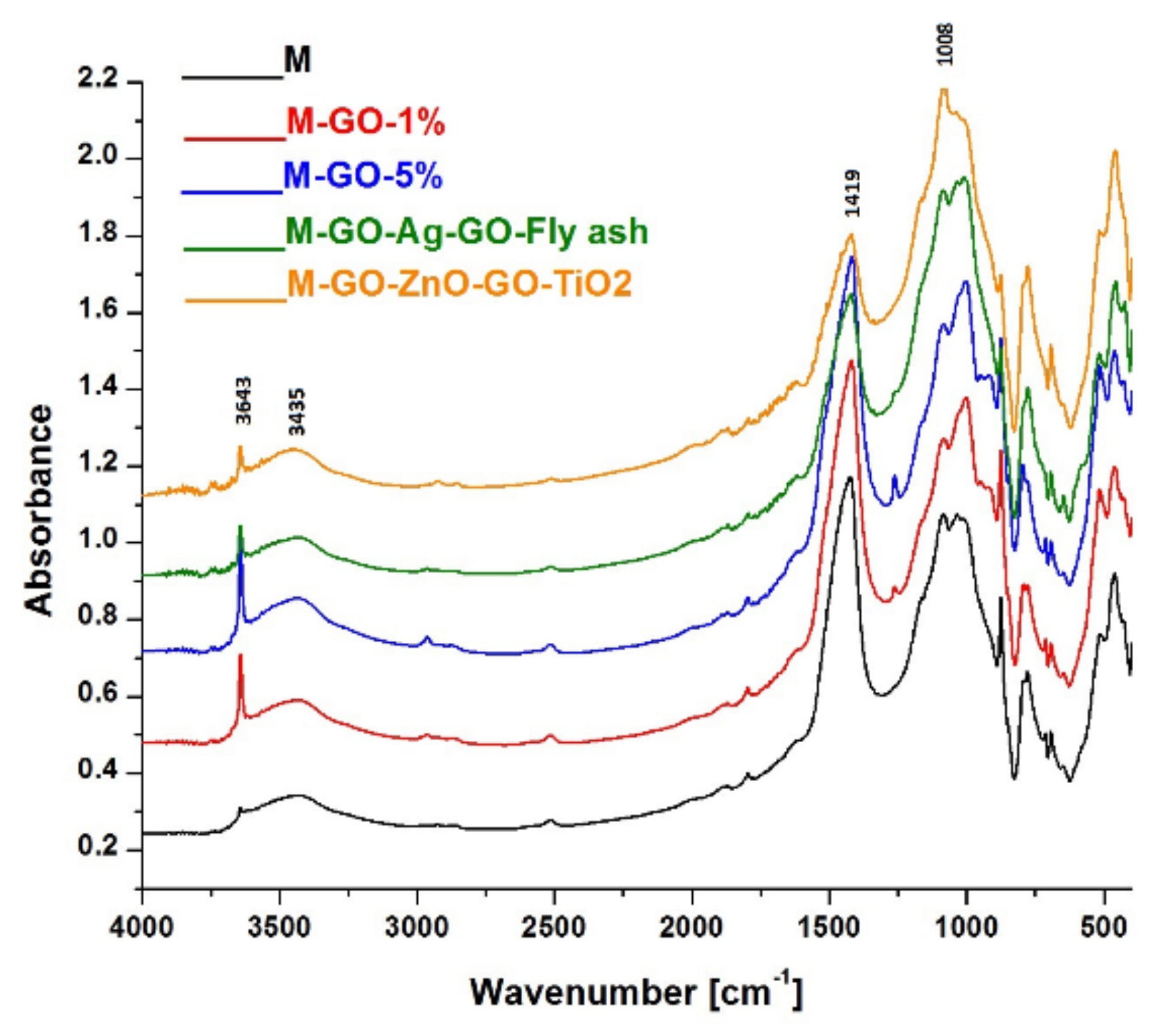
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (FT-IR)
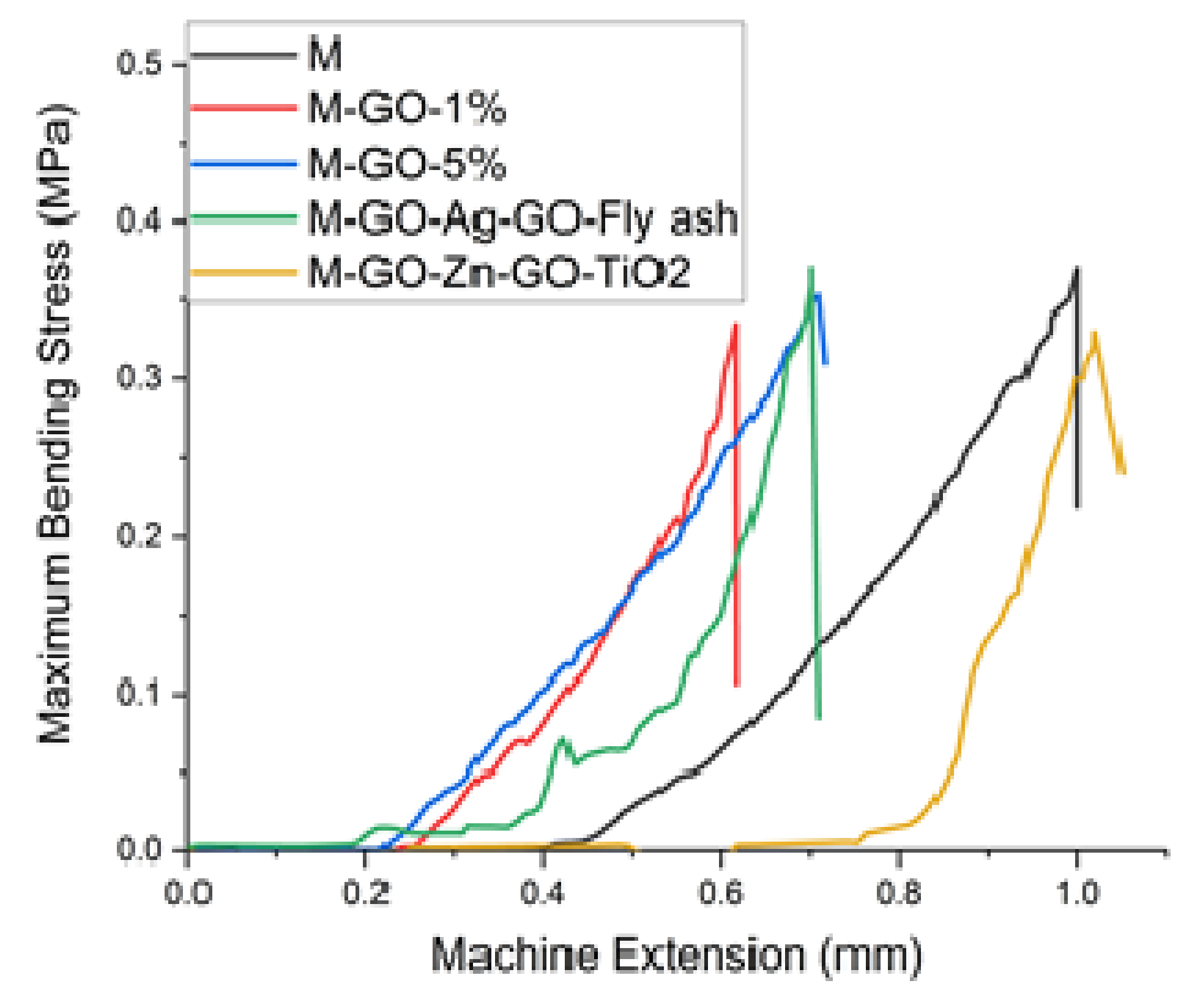
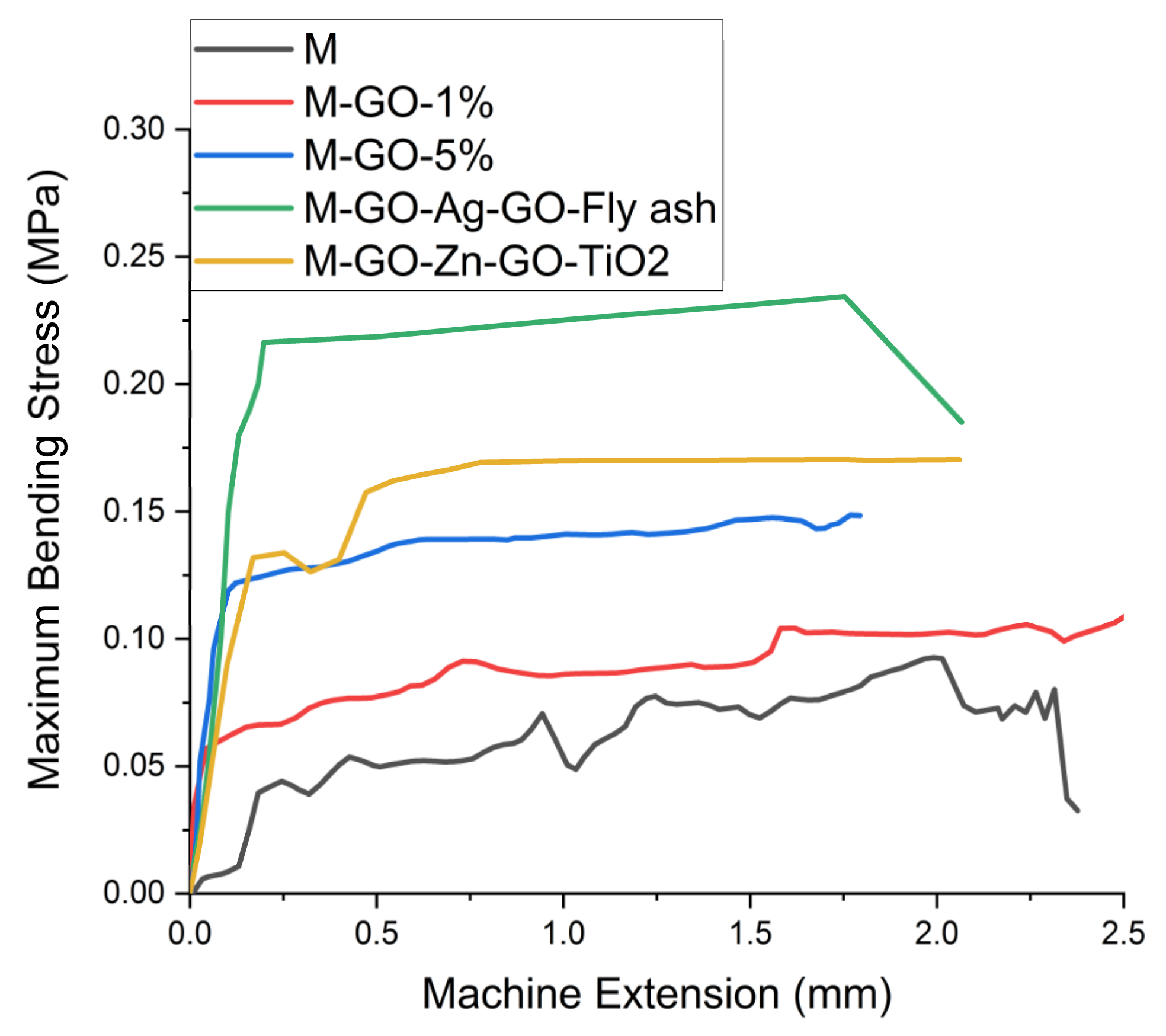
3.2. Mechanical Properties
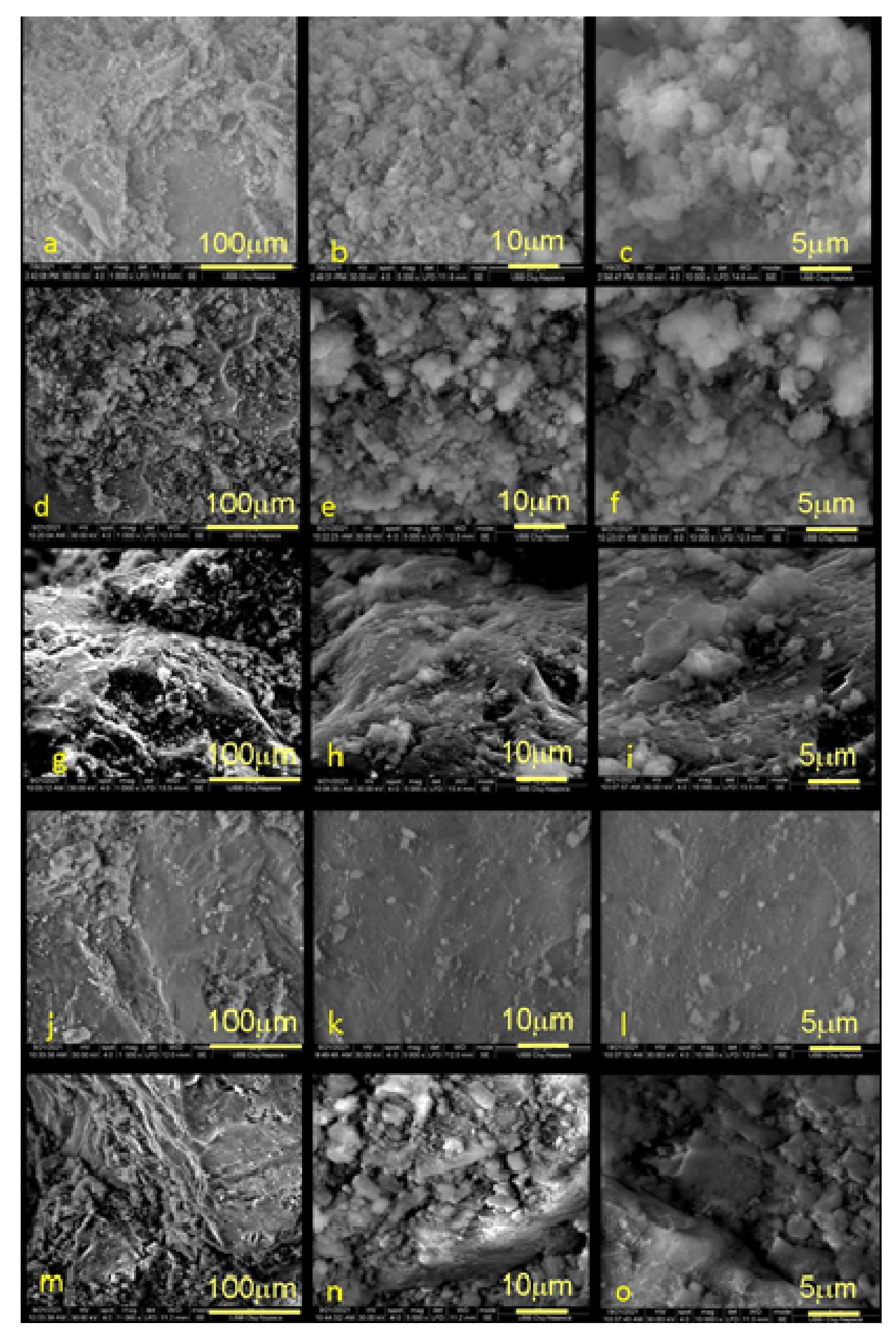
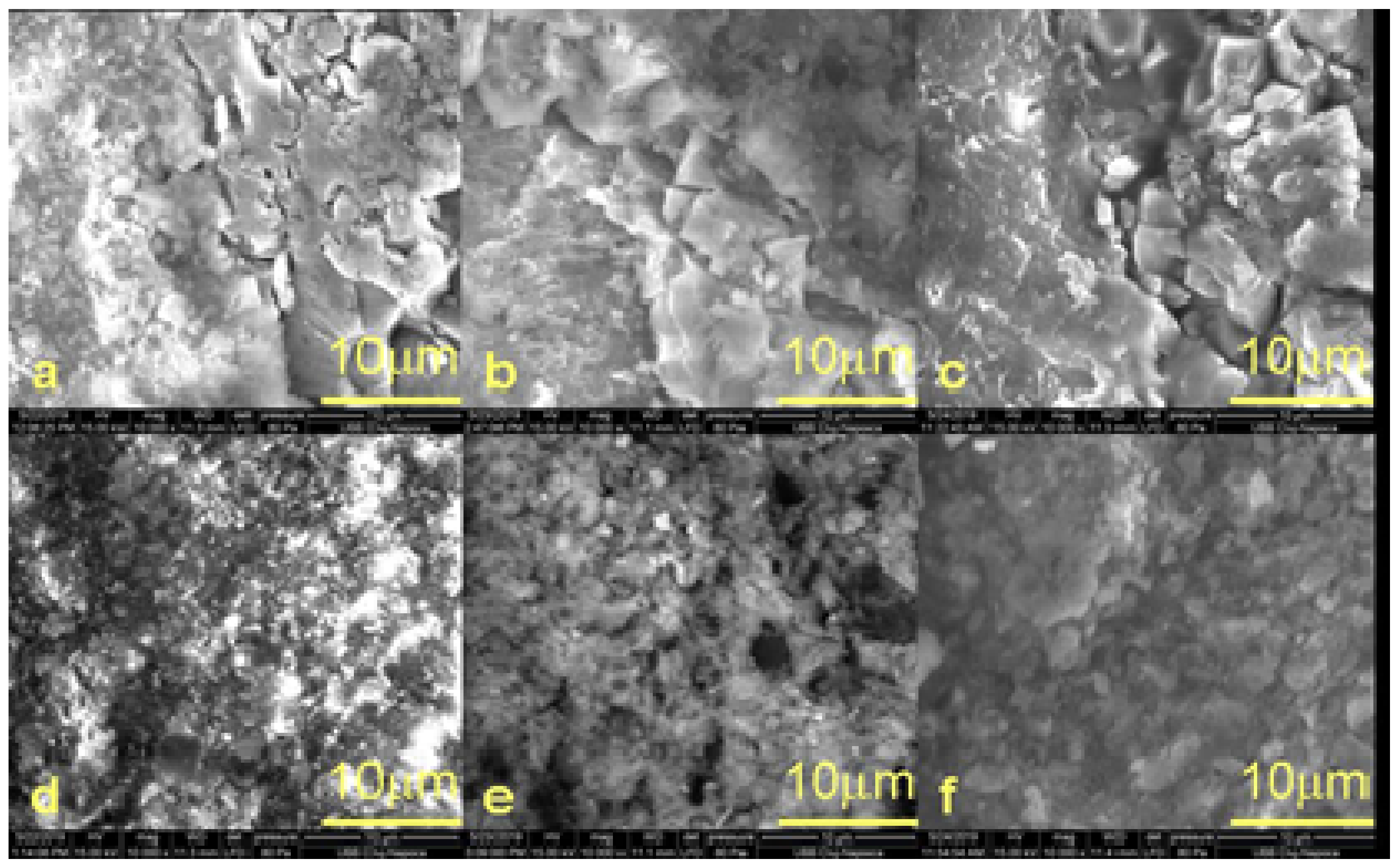
3.3. Morphological and Structural Characterization
3.4. Surface Deterioration of the Mortars Exposed to Chemical Attack
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haach, V.G.; Vasconcelos, G.; Lourenco, P.B. Influence of aggregates grading and water/cement ratio in workability and hardened properties of mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2980–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, L.; Coffetti, D.; Crotti, E. Plain and ultrafine fly ashes mortars for environmentally friendly construction materials. Sustainability 2018, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkatarama Reddy, B.V.; Gupta, A. Influence of sand grading on the characteristics of mortars and soil–cement block masonry. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopouloua, M.; Armaghanib, D.J.; Bakolasa, A.; Douvikac, M.G.; Moropouloua, A.; Asteris, P.G. Compressive strength of natural hydraulic lime mortars using soft computing techniques. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2019, 17, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, E.; Silva, E.F.; Sousa, J.G.G.; Salomao, M.C.F. Friction influence between particles in the behavior of flow of lime-rendering mortars. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2015, 27, 04014136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Yu, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhan, S.; Qian, K. Effect of nano-TiO2 on the mechanical properties of cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, C.A.; Jochem, L.F.; Repette, W.L.; Hotza, D. Evaluation of nano-TiO2 on properties of cementitious mortars. Matéria 2020, 25, 12883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodan, D.; Moldovan, M.; Furtos, G.; Saroși, C.; Filip, M.; Perhaița, I.; Carpa, R.; Popa, M.; Cuc, S.; Varvara, S.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of some graphene oxide powders intended to improve the quality of hydraulic mortars. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emiru, T.F.; Ayele, D.W. Controlled synthesis, characterization and reduction of graphene oxide: A convenient method for large scale production. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2017, 4, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.Y.; Lu, C.; Leung, C.K.Y.; Li, Z. Graphene oxide modified Strain Hardening Cementitious Composites with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties by incorporating ultra-fine phase change materials. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2019, 98, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indukuri, C.S.R.; Nerella, R.; Madduru, S.R.C. Effect of graphene oxide on microstructure and strengthened properties of fly ash and silica fume based cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, X.; Wu, Y.Y.; Deng, X.; Zheng, Z. The effect of graphene oxide on the mechanical properties, impermeability and corrosion resistance of cement mortar containing mineral admixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 288, 123059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulos, G.; Katsioti, M.; Fardis, M.; Karatasios, I.; Alhassan, S.; Karagianni, M.; Papavassiliou, G.; Hassan, J. The role of titanium dioxide on the hydration of portland cement: A combined NMR and Ultrasonic Study Molecules. Molecules 2020, 25, 5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, F.; Sobolev, K. Nanotechnology in concrete-A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2060–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, C.S.; Wititanun, N.; Nuntawong, N.; Chindaudom, P.; Oaew, S.; Kedkeaw, C.; Limsuwan, P. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide nanosheets. Procedia Eng. 2012, 32, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Jing, H.; Fu, G.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, X. Studies on combined effects of graphene oxide-fly ash hybrid on the workability, mechanical performance and pore structures of cementitious grouting under high W/C ratio. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 281, 122578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Ouyang, D. Effect of graphene oxide on mechanical properties of cement mortar and its strengthening mechanism. Materials 2019, 12, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, D.; Wei, H.; Zuo, X.; Zheng, K.; Wang, Q. Use of graphene oxide to improve the durability and mechanical properties of mortar immersed in flowing river for three years. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Lee, J.C.; Qian, B. Mechanical properties and microstructure of high-strength lightweight concrete incorporating graphene oxide. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qi, G.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Shan, S.; Lu, C. Research progress on the effect of graphene oxide on the properties of cement-based composites. New Carbon Mater. 2021, 36, 729–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.H.; Jeong, H.K. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2015, 630, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafai, N.; El-Khouly, M.E.; El-Kemary, M.; Ramadan, M.; Eldesoukey, I.; Masoud, M. Graphene oxide decorated with zinc oxide nanoflower, silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Fabrication, characterization, DNA interaction, and antibacterial activity. RSC Adv. 2019, 7, 3704–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khorrami, S.; Abdollahi, Z.; Eshaghi, G.; Khosravi, A.; Bidram, E.; Zarrabi, A. An improved method for fabrication of Ag-GO nanocomposite with controlled anticancer and antibacterial behavior; A comparative study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baboo, R.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S. Effect of fly ash on mortat mixes with quarry dust as fine aggregate. Mat. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 626425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Sinsiri, T. Effect of fly ash fineness on compressive strength and pore size of blended cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltulu, M.; Şahin, R. Effect of nano-SiO2, nano-Al2O3 and nano-Fe2O3 powders on compressive strengths and capillary water absorption of cement mortar containing fly ash: A comparative study. Energ. Buil. 2013, 58, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavia, S.; Treacy, E. A comparative study of the durability and behaviour of fat lime and feebly-hydraulic lime mortars. Mater. Struct. 2006, 39, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, M.d.R.; Fragata, A.; Velosa, A.L.; Magalhães, A.C.; Margalha, G. Lime-based mortars: Viability for use as substitution renders in historical buildings. Inter. J. Archit. Herit. 2010, 4, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SR EN 1015-11:2002; Methods of Test for Mortar for Masonry-Part 11: Determination of Flexural and Compressive Strength of Hardened Mortar. Slovenian Institute for Standardization: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2002.
- EN 1607:1996/1607:1997; Thermal Insulating Products for Building Applications. Determination of Tensile Strength Perpendicular to Faces. Serbian Institute for Standardization: Belgrade, Serbia, 1997.
- ASTM C348-14; Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Hydraulic-Cement Motars. ASTEM: New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- SR EN 1015-12:2001; Methods of Test for Mortar for Masonry-Part 12: Determination of Adhesive Strength of Hardened Rendering and Plastering Mortars on Substrates. Slovenian Institute for Standardization: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2001.
- Brunello, V.; Corti, C.; Sansonetti, A.; Tedeschi, C.; Rampazzi, L. Non-invasive FTIR study of mortar model samples: Comparison among innovative and traditional techniques. Europ. Physic. J. Plus 2019, 134, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, P.; Duarte, P.; Barbosa, D.; Ferreira, I. New composite of natural hydraulic lime mortar with graphene oxide. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diekamp, A.; Stalder, R.; Konzett, J.; Mirwald, P.W. Lime mortar with natural hydraulic components: Characterisation of reaction rims with FTIR Imaging in ATR-mode. Hist. Mort. 2012, 7, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.J.; Gong, L.X.; Tang, L.C.; Wu, L.B.; Jiang, J.X. Mechanical properties of epoxy composites filled with silane-functionalized graphene oxide. Comp. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 64, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Official Monitor of Romania, PART I, Nr. 389 bis/11.VI.2010, Acts of the Specialized Bodies of the Central Public Administration of Regional Development and Tourism, ORDER to Complete the Technical Regulation “Design Code for Masonry Structures”, Indicative CR 6-2006, Approved by Transport Order, Constructions and Tourism no. 1.712/2006 *). 2010, p. 36. Available online: https://www.mdlpa.ro/userfiles/reglementari/Domeniul_V/V_9_2_CR_6_2006_COMPLETARE.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2021).
- Amrhein, J.E. Reinforced Masonry Engineering Handbook, 5th ed.; Updated; Masonry Institute of America: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Hermida, M.I.; Borrero-López, A.M.; Flores-Alés, V.; Alejandre, F.J.; Franco, J.M.; Santos, A.; Esquivias, L. Characterization and analysis of the carbonation process of a lime mortar obtained from phosphogypsum waste. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, M.; Santhanam, M. Effect of reduced graphene oxide, alumina and silica nanoparticles on the deterioration characteristics of Portland cement paste exposed to acidic environment. Cem. Conc. Compos. 2018, 91, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, R.; Yao, H.; Farhan, S.; Zheng, S.; Du, C. Study on the three dimensional mechanism of graphene oxide nanosheets modified cement. Construct. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mortar Code | NHL 3.5/Sand * [v/v] | Water/NHL 3.5 [wt%] | Graphene Oxide Powders/NHL 3.5 [wt%] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO | GO-Ag | GO-Fly Ash | GO-ZnO | GO-TiO2 | |||
| M | 1/2.5 | 1.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| M-GO-1% | 1/2.5 | 1.05 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| M-GO-5% | 1/2.5 | 1.05 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| M-GO-Ag-GO-Fly ash | 1/2.5 | 1.05 | 0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 |
| M-GO-ZnO-GO-TiO2 | 1/2.5 | 1.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Mortar Sample | FT-IR Maximum [cm−1] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 3644 | 3422 | 1423 | 1083 |
| M-GO-1% | 3642 | 3427 | 1419 | 1000 |
| M-GO-5% | 3642 | 3446 | 1419 | 1006 |
| M-GO-Ag-GO-Fly ash | 3643 | 3436 | 1419 | 1008 |
| M-GO-ZnO-GO-TiO2 | 3643 | 3435 | 1419 | 1008 |
| Mortar Sample | Load at Break (N) ± SD | Tensile Strength (MPa) ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| M | 124.53 ± 45.88 a | 0.59212 ± 0.17312 a |
| M-GO-1% | 193.82 ± 38.99 b | 0.49614 ± 0.12067 b |
| M-GO-5% | 162.28 ± 35.04 c | 0.40569 ± 0.10982 c |
| M-GO-Ag-GO-Fly ash | 164.03 ± 29.44 d | 0.41197 ± 0.05225 c |
| M-GO-ZnO-GO-TiO2 | 138.38 ± 31.85 e | 0.38596 ± 0.12874 c |
| p value | 2.50748 × 10−7 | 2.43666 × 10−9 |
| Mortar Sample | Load at Maximum Load (N) ± SD | Maximum Bending Stress (MPa) ± SD | Load at Break (N)± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| M | 131.41 ± 33.28 a | 0.37098 ± 0.05844 a | 105.12 ± 20.65 a |
| M-GO-1% | 146.14 ± 25.79 b | 0.33599 ± 0.09508 b | 120.91 ± 28.63 b |
| M-GO-5% | 151.59 ± 20.95 b | 0.35528 ± 0.08038 c | 121.27 ± 23.92 b |
| M-GO-Ag-GO-Fly ash | 149.95 ± 23.92 b | 0.37572 ± 0.09558 d | 119.96 ± 30.86 b |
| M-GO-ZnO-GO-TiO2 | 198.29 ± 16.04 c | 0.33238 ± 0.10195 e | 158.64 ± 24.55 c |
| p value | 6.08071 × 10−7 | 6.83773 × 10−6 | 6.57792 × 10−7 |
| Mortar Sample | Load at Maximum Load (N) ± SD | Tensile Strength (MPa) ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| M | 120.10 ± 20.95 a | 0.10388 ± 0.03115 a |
| M-GO-1% | 170.98 ± 18.24 b | 0.11245 ± 0.02877 a |
| M-GO-5% | 143.12 ± 10.66 c | 0.11405 ± 0.01609 a |
| M-GO-Ag-GO-Fly ash | 200.5 ± 25.81 d | 0.23512 ± 0.09959 b |
| M-GO-ZnO-GO-TiO2 | 210.67 ± 19.05 e | 0.17143 ± 0.05132 c |
| p value | 6.65134 × 10−8 | 3.47601 × 10−6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dorin, P.; Doina, P.; Simona, V.; Maria, P.; Stanca, C.; Codruta, S.; Marioara, M.; Raluca, I.; Razvan, E. Properties Evolution of Some Hydraulic Mortars Incorporating Graphene Oxides. Buildings 2022, 12, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12060864
Dorin P, Doina P, Simona V, Maria P, Stanca C, Codruta S, Marioara M, Raluca I, Razvan E. Properties Evolution of Some Hydraulic Mortars Incorporating Graphene Oxides. Buildings. 2022; 12(6):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12060864
Chicago/Turabian StyleDorin, Popa, Prodan Doina, Varvara Simona, Popa Maria, Cuc Stanca, Sarosi Codruta, Moldovan Marioara, Ivan Raluca, and Ene Razvan. 2022. "Properties Evolution of Some Hydraulic Mortars Incorporating Graphene Oxides" Buildings 12, no. 6: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12060864
APA StyleDorin, P., Doina, P., Simona, V., Maria, P., Stanca, C., Codruta, S., Marioara, M., Raluca, I., & Razvan, E. (2022). Properties Evolution of Some Hydraulic Mortars Incorporating Graphene Oxides. Buildings, 12(6), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12060864









