Sound Insulation of Façade Element with Triple IGU
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Analyses of Sound Reduction Index Dependence from Frequency
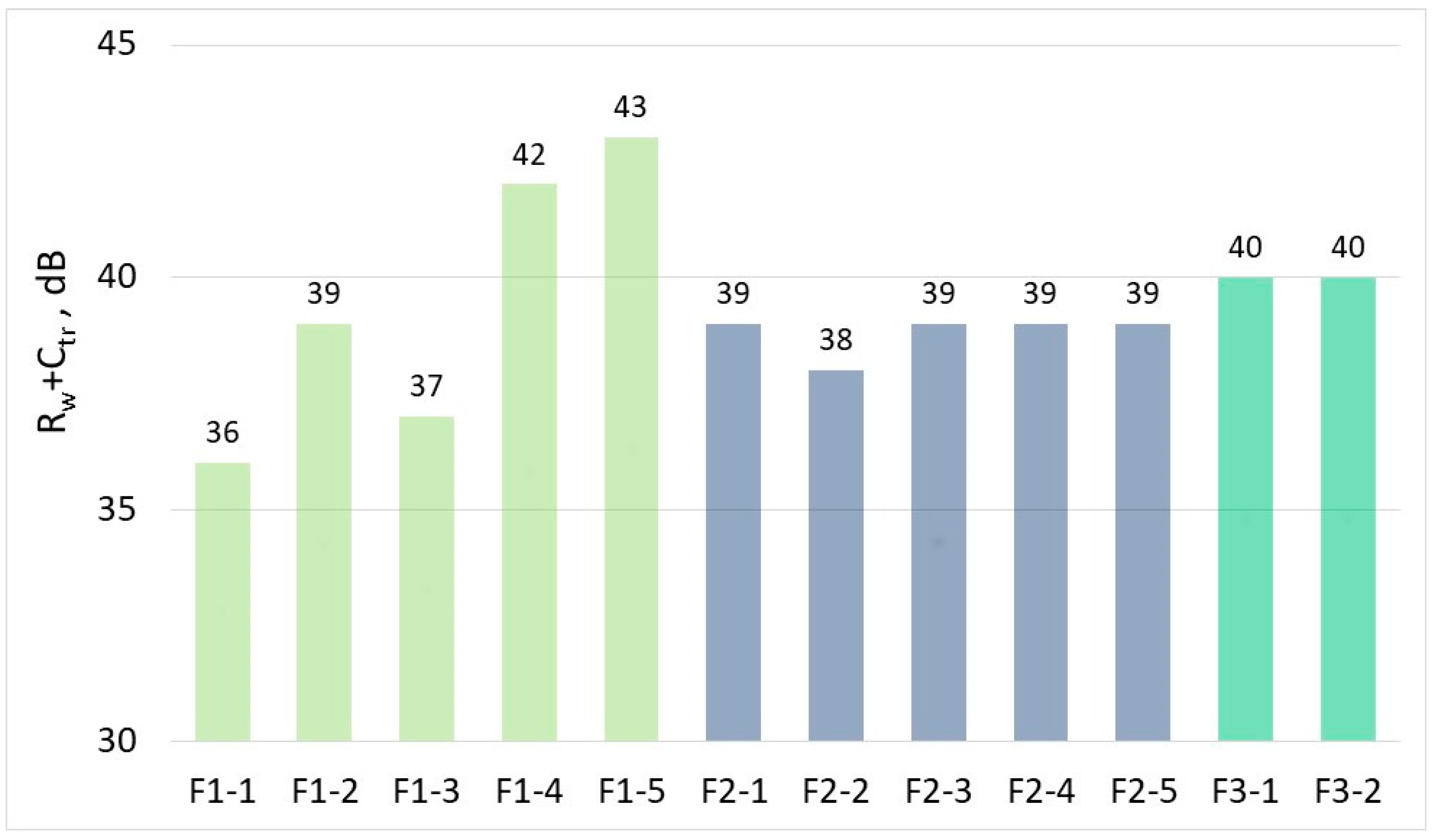
3.2. Weighted Sound Reduction Index
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- When triple insulating glass units (IGUs) with inner laminated glass are used for energy efficient and safety structural glazing, the highest values of sound insulation indicators are achieved not by using more laminated glass sheets, but by increasing the thickness of the external ordinary glass and gas cavities;
- When structural glazing has safety requirements on both sides and external and internal laminated glasses should be installed, the use of a second sound reduction film does not improve the sound insulation properties of the structural glazing;
- Use of inner laminated glass sheet in triple-glazed units has the least effect on the sound insulation level of structural glazing, so it is not to be used;
- Increasing the mass of the structural glazing frame by filling the frame cavities with a material of any density does not have a significant effect on the sound insulation of the glazed façade since most of the noise passes through the IGU;
- The sound insulation of the structural glazing depends on the range of noise frequencies, so when choosing the glazing unit, the dominant noise source must be considered.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, L.; Oliveira, M.; Silva, J. Urban form indicators as proxy on the noise exposure of buildings. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 76, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenchine, V.V. Assessment of amplitude modulation in environmental noise measurements. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 104, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaporozhets, O.; Fiks, B.; Jagniatinskis, A.; Tokarev, V.; Karpenko, S.; Mickaitis, M. Indoor noise A-level assessment related to the environmental noise spectrum on the building facade. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 185, 108380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keränen, J.; Hakala, J.; Hongisto, V. The sound insulation of façades at frequencies 5–5000 Hz. Build. Environ. 2019, 156, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombolato, A.; Bonomini, F.; Di Bella, A. Methodology for the evaluation of low-frequency environmental noise: A case-study. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 187, 108517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Song, H. Effect of building façade on indoor transportation noise annoyance in terms of frequency spectrum and expectation for sound insulation. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 152, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussi, C.; Aucejo, M.; Larbi, W.; Deü, J.-F. Numerical analyses of the sound transmission at low frequencies of a calibrated Insulating Glazing Unit. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 179, 108065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Martino, E.; Mansour, A.; Bentley, R. Environmental Noise Exposure and Mental Health: Evidence From a Population-Based Longitudinal Study. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2022, 63, e39–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EEA Report. Environmental Noise in Europe—2020; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019; ISSN 1977–8449. [Google Scholar]
- Kurra, S.; Dal, L. Sound insulation design by using noise maps. Build. Environ. 2012, 49, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caniato, M. Sound insulation of complex façades: A complete study combining different numerical approaches. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 169, 107484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naticchia, B.; Carbonari, A. Feasibility analysis of an active technology to improve acoustic comfort in buildings. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2785–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadeu, A.J.; Mateus, D. Sound transmission through single, double and triple glazing. Experimental evaluation. Appl. Acoust. 2001, 62, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia, P.; Gupta, A. Sound attenuation in triple panel using locally resonant sonic crystal and porous material. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 156, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LST EN ISO 10140-1:2010; Acoustics—Laboratory Measurement of Sound Insulation of Building Elements—Part 1: Application Rules for Specific Products. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- LST EN ISO 10140-2:2010; Acoustics—Laboratory Measurement of Sound Insulation of Building Elements—Part 2: Measurement of Airborne Sound Insulation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- LST EN ISO 10140-4:2010; Acoustics—Laboratory Measurement of Sound Insulation of Building Elements—Part 4: Measurement Procedures and Requirements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- LST EN ISO 10140-5:2010; Acoustics—Laboratory Measurement of Sound Insulation of Building Elements—Part 5: Requirements for Test Facilities and Equipment. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- LST EN ISO 717–1:2013; Acoustics—Rating of Sound Insulation in Buildings and of Building Elements—Part 1: Airborne Sound Insulation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Larson Davis Noise Spectra Meter–Generator Parameters. Available online: http://granat-e.ru/larson_davis_2800_2900.html (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Larson Davis Microphone with Initial Microphone Preamplifier Parameters. Available online: https://cdn.thomasnet.com/ccp/10052672/109083.pdf. (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Nordic Metrology Science, Dariaus and Girėno Str. 23, Vilnius, Lithuania. Available online: https://nordicmetrology.com/ (accessed on 1 August 2021).
















| Type of IGU | External Glass | Inner Glass | Internal Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Ordinary | Ordinary | Laminated |
| B | Ordinary | Laminated | Laminated |
| C | Laminated | Ordinary | Laminated |
| No. | Specimen | IGU | Type of IGU * |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F1-1 | 6-18 Ar-6-18 Ar-44.2 lam SR | A |
| 2 | F1-2 | 6-18 Ar-6-18 Ar-55.2 lam | |
| 3 | F1-3 | 6-18 Ar-6-18 Ar-55.2 lam SR | |
| 4 | F1-4 | 8-18 Ar-6-20 Ar-55.2 lam SR | |
| 5 | F1-5 | 8-18 Ar-6-20 Ar-66.2 lam SR | |
| 6 | F2-1 | 6-18 Ar-33.1 lam-18 Ar-55.2 lam SR | B |
| 7 | F2-2 | 6-18 Ar-33.1 lam SR-18 Ar-55.2 lam SR | |
| 8 | F2-3 | 8-16 Ar-44.1 lam-16 Ar-55.2 lam SR | |
| 9 | F2-4 | 8-16 Ar-44.1 lam SR-16 Ar-55.2 lam SR | |
| 10 | F2-5 | 10-14 Ar-44.1 lam-16 Ar-55.2 lam SR | |
| 11 | F3-1 | 44.1 lam-18 Ar-6-16 Ar-55.2 lam SR | C |
| 12 | F3-2 | 44.1 lam SR-18 Ar-6-16 Ar-55.2 lam SR |
| No. | Specimen | IGU | Type of IGU * | Material Inside Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FF2-1 | 6-18 Ar-33.1 lam-18 Ar-55.2 lam SR | B | Gypsum fibreboard |
| 2 | FF2-3 | 8-16 Ar-44.1 lam-16 Ar-55.2 lam SR | B | |
| 3 | FF2-4 | 8-16 Ar-44.1 lam SR-16 Ar-55.2 lam SR | B | |
| 4 | FF2-5 | 10-14 Ar-44.1 lam-16 Ar-55.2 lam SR | B | |
| 5 | FF3-1 | 44.1 lam -18 Ar-6-16 Ar-55.2 lam SR | C | |
| 6 | FF3-2 | 44.1 lam SR-18 Ar-6-16 Ar-55.2 lam SR | C | |
| 7 | FF2-6 | 6-18 Ar-33.1 lam-18 Ar-55.2 lam SR | B | Gypsum plasterboard |
| 8 | FF2-7 | 6-18 Ar-33.1 lam-18 Ar-55.2 lam SR | B | Steel S275 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bliūdžius, R.; Miškinis, K.; Buhagiar, V.; Banionis, K. Sound Insulation of Façade Element with Triple IGU. Buildings 2022, 12, 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12081239
Bliūdžius R, Miškinis K, Buhagiar V, Banionis K. Sound Insulation of Façade Element with Triple IGU. Buildings. 2022; 12(8):1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12081239
Chicago/Turabian StyleBliūdžius, Raimondas, Kęstutis Miškinis, Vincent Buhagiar, and Karolis Banionis. 2022. "Sound Insulation of Façade Element with Triple IGU" Buildings 12, no. 8: 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12081239
APA StyleBliūdžius, R., Miškinis, K., Buhagiar, V., & Banionis, K. (2022). Sound Insulation of Façade Element with Triple IGU. Buildings, 12(8), 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12081239







