Confined Spaces in Buildings with High Indoor Radon Concentration: A Case Study Analysis with the Application of Constructive Remediation Measures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
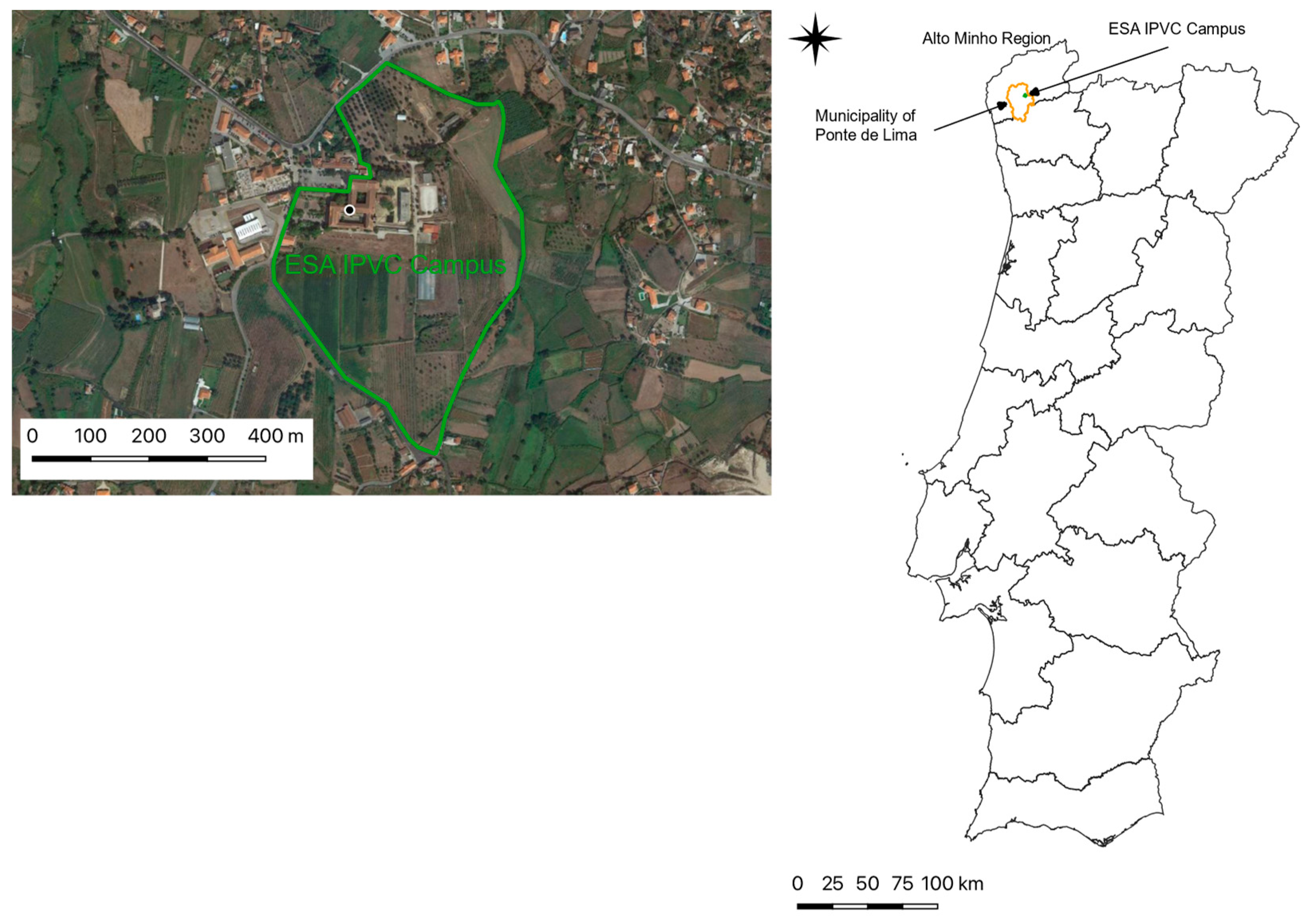
2.1. Framework
2.2. Monitoring and Data Acquisition
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNSCEAR. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation UNSCEAR 2008—Report to the General Assembly with Scientific Annexes: Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation; United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Stoulos, S.; Manolopoulou, M.; Papastefanou, C. Assessment of Natural Radiation Exposure and Radon Exhalation from Building Materials in Greece. J. Environ. Radioact. 2003, 69, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protection against Radon-222 at Home and at Work. A Report of a Task Group of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. Ann. ICRP 1993, 23, 1–45.
- Nazaroff, W.W. Radon Transport from Soil to Air. Rev. Geophys. 1992, 30, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samet, J.M.; Eradze, G.R. Radon and Lung Cancer Risk: Taking Stock at the Millenium. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zoughool, M.; Krewski, D. Health Effects of Radon: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, S.; Hill, D.; Auvinen, A.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Baysson, H.; Bochicchio, F.; Deo, H.; Falk, R.; Forastiere, F.; Hakama, M.; et al. Radon in Homes and Risk of Lung Cancer: Collaborative Analysis of Individual Data from 13 European Case-Control Studies. BMJ 2005, 330, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, E.J.; Rademacher, K.; Wiggins, A.; Rayens, M.K. Personalized Report-Back to Renters on Radon and Tobacco Smoke Exposure. J. Environ. Health 2018, 80, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lemjabbar-Alaoui, H.; Hassan, O.U.I.; Yang, Y.W.; Buchanan, P. Lung Cancer: Biology and Treatment Options. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2015, 1856, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krewski, D.; Lubin, J.H.; Zielinski, J.M.; Alavanja, M.; Catalan, V.S.; Field, R.W.; Klotz, J.B.; Létourneau, E.G.; Lynch, C.F.; Lyon, J.I.; et al. Residential Radon and Risk of Lung Cancer: A Combined Analysis of 7 North American Case-Control Studies. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberg, A.J.; Ford, J.G.; Samet, J.M. Epidemiology of Lung Cancer: ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (2nd Edition). Chest 2007, 132, 29S–55S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, J.; Govindan, R. Lung Cancer in Never Smokers: A Review. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltrenas, P.; Grubliauskas, R.; Danila, V. Seasonal Variation of Indoor Radon Concentration Levels in Different Premises of a University Building. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Singh, J.; Kaur, B. Performance Study of Some Reverse Osmosis Systems for Removal of Uranium and Total Dissolved Solids in Underground Waters of Punjab State, India. J. Adv. Phys. 2014, 4, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Pernot, J.G.; Jörin, C.H.; Niculita-Hirzel, H.; Perret, V.; Licina, D. Energy, Indoor Air Quality, Occupant Behavior, Self-Reported Symptoms and Satisfaction in Energy-Efficient Dwellings in Switzerland. Build. Environ. 2020, 171, 106618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Handbook on Indoor Radon: A Public Health Perspective; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Bossew, P.; Cinelli, G.; Ciotoli, G.; Crowley, Q.G.; de Cort, M.; Medina, J.E.; Gruber, V.; Petermann, E.; Tollefsen, T. Development of a Geogenic Radon Hazard Index—Concept, History, Experiences. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, B.L.; Krewski, D.; Chen, J.; Zielinski, J.M.; Brand, K.P.; Meyerhof, D. Assessment and management of residential radon health risks: A report from the health Canada radon workshop. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2006, 69, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.; Ferreira, C.; Ulisses, P.; Márquez-Medina, D. Lung Cancer Overview. In Fighting Lung Cancer with Conventional Therapies; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lugg, A.; Probert, D. Indoor Radon Gas: A Potential Health Hazard Resulting from Implementing Energy-Efficiency Measures. Appl. Energy 1997, 56, 93–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Uddin, Z.; Rehman, J.U.; Bakhsh, M.; Ullah, H. Evaluation of Radon Concentration and Heavy Metals in Drinking Water and Their Health Implications to the Population of Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 100, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royse, K.R. The Handling of Hazard Data on a National Scale: A Case Study from the British Geological Survey. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 32, 753–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisk, W.J.; Singer, B.C.; Chan, W.R. Association of Residential Energy Efficiency Retrofits with Indoor Environmental Quality, Comfort, and Health: A Review of Empirical Data. Build. Environ. 2020, 180, 107067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. Fifteen Years Experience in Measuring 224Ra and 223Ra by Delayed-Coincidence Counting. Mar. Chem. 2008, 109, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelikhah, M.; Shahrokhi, A.; Imani, M.; Chalupnik, S.; Kovács, T. Radiological Assessment of Indoor Radon and Thoron Concentrations and Indoor Radon Map of Dwellings in Mashhad, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelsson, C. Retrospective Determination of Radon in Houses. Nature 1988, 334, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbarese, C.; Ambrosino, F.; D’Onofrio, A. Development of Radon Transport Model in Different Types of Dwellings to Assess Indoor Activity Concentration. J. Environ. Radioact. 2021, 227, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paridaens, J.; de Saint-Georges, L.; Vanmarcke, H. Mitigation of a Radon-Rich Belgian Dwelling Using Active Subslab Depressurization. J. Environ. Radioact. 2005, 79, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Géczi, G.; Benécs, J.; Kristóf, K.; Horváth, M. High Concentrations of Radon and Carbon Dioxide in Energy-Efficient Family Houses without Heat Recovery Ventilation. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2018, 26, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Yuan, H.; Kearfott, K. A Model Comparison of Diffusion-Controlled Radon Exhalation from Solid and Cavity Walls with Application to High Background Radiation Areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 43389–43395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frutos-Puerto, S.; Pinilla-Gil, E.; Andrade, E.; Reis, M.; Madruga, M.J.; Rodríguez, C.M. Radon and Thoron Exhalation Rate, Emanation Factor and Radioactivity Risks of Building Materials of the Iberian Peninsula. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, C.M.; Kang, D.R. A Deterministic Model for Estimating Indoor Radon Concentrations in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ward, I.C. Modelling Multiple Radon Entry and Transport in a Domestic Dwelling. Build. Environ. 1997, 32, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ward, I.C. Multiple Radon Entry Modeling in a House with a Cellar. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1999, 49, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mehdipour, L.A.; Mortazavi, S.M.J.; Saion, E.B.; Mozdarani, H.; Aziz, S.A.; Kamari, H.M.; Faghihi, R.; Mehdizadeh, S.; Kardan, M.R.; Mortazavi, A.; et al. Natural Ventilation Considerations for Radon Prone Areas of Ramsar. Int. J. Radiat. Res. 2014, 12, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Henschel, D.B. Analysis of Radon Mitigation Techniques Used in Existing Us Houses. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 1994, 56, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves-Kirkby, C.J.; Denman, A.R.; Phillips, P.S.; Crockett, R.G.M.; Woolridge, A.C.; Tornberg, R. Radon Mitigation in Domestic Properties and Its Health Implications-a Comparison between during-Construction and Post-Construction Radon Reduction. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.M.; Gomes, J.; Krewski, D.R. Radon Interventions around the Globe: A Systematic Review. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valin, I.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Brito, L. Miguel De Mosteiro a Escola: ESA IPVC 35o Aniversário; Oficina das Edições: Ponte de Lima, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Carta Geológica De Portugal, Escala 1/200000—Notícia Explicativa Da Folha 1; Pereira, E., Ed.; Serviços Geológicos de Portugal: Lisbon, Portugal, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Valdbjørn Rasmussen, T.; Cornelius, T. Use of Radon Barriers to Reach an Acceptable Radon Level. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences, Tallinn, Estonia, 6–9 September 2020; Volume 172. [Google Scholar]
- Jelle, B.P.; Noreng, K.; Erichsen, T.H.; Strand, T. Implementation of Radon Barriers, Model Development and Calculation of Radon Concentration in Indoor Air. J. Build. Phys. 2011, 34, 195–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Rn sampling | Passive diffusion chamber |
| Detection method | Alpha spectrometry |
| Detector | 1 silicon photodiode |
| Diffusion time constant | 25 min |
| Measurement range | 0–50,000 Bq.m−3 |
| Sampling rate | 1 h |
| Operation environment | 4 °C to 40 °C 5% RH to 85% RH non-condensing 50 kPa to 110 kPa |
| Temperature | 0.336 °C resolution, ±1 °C accuracy |
| Humidity | 0.5% RH resolution, ±4.5% accuracy |
| Barometric pressure | 0.01 kPa resolution, ±1 kPa accuracy |
| Monitoring Period | 13 March 2019–13 June 2019 |
| No. of measurements | 2181 |
| Average value | 6479.6 Bq·m−3 |
| Standard deviation | 3900.8 Bq·m−3 |
| Max. value | 18,737.7 Bq·m−3 |
| Min. value | 134.2 Bq·m−3 |
| Elongation | 19% |
| Tear resistance | 405 N |
| Water vapor transmission | 0.03 g·m−2·d−1 |
| Color tone | Red (top side) and black (underside) |
| Thickness | 0.35 mm |
| Monitoring Period | 3 September 2019–3 September 2019 |
| No. of measurements | 2181 |
| Average value | 634.4 Bq·m−3 |
| Standard deviation | 475.0 Bq·m−3 |
| Max. value | 3407.4 Bq·m−3 |
| Min. value | 21.7 Bq·m−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nunes, L.J.R.; Curado, A. Confined Spaces in Buildings with High Indoor Radon Concentration: A Case Study Analysis with the Application of Constructive Remediation Measures. Buildings 2023, 13, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010049
Nunes LJR, Curado A. Confined Spaces in Buildings with High Indoor Radon Concentration: A Case Study Analysis with the Application of Constructive Remediation Measures. Buildings. 2023; 13(1):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010049
Chicago/Turabian StyleNunes, Leonel J. R., and António Curado. 2023. "Confined Spaces in Buildings with High Indoor Radon Concentration: A Case Study Analysis with the Application of Constructive Remediation Measures" Buildings 13, no. 1: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010049
APA StyleNunes, L. J. R., & Curado, A. (2023). Confined Spaces in Buildings with High Indoor Radon Concentration: A Case Study Analysis with the Application of Constructive Remediation Measures. Buildings, 13(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010049







