Data-Driven Prediction Model for High-Strength Bolts in Composite Beams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Finite Element Modeling
2.1. Material Constitutive
2.1.1. Concrete
- In the case of concrete under compression, the following definitions apply: represents the ratio of the compressive stress () to the uniaxial compressive strength (), x denotes the ratio of the compressive strain () to the corresponding compressive strain at the uniaxial tensile strength (), and is set to 1. The variables and stand for the uniaxial compressive and tensile strengths of concrete, respectively, while and are the associated compressive and tensile strains. Additionally, represents the compressive cubic strength of concrete, with the variables and defined as and , respectively. For overall concrete, is given as , while is used for locally confined concrete in the nonlinear finite element analysis.
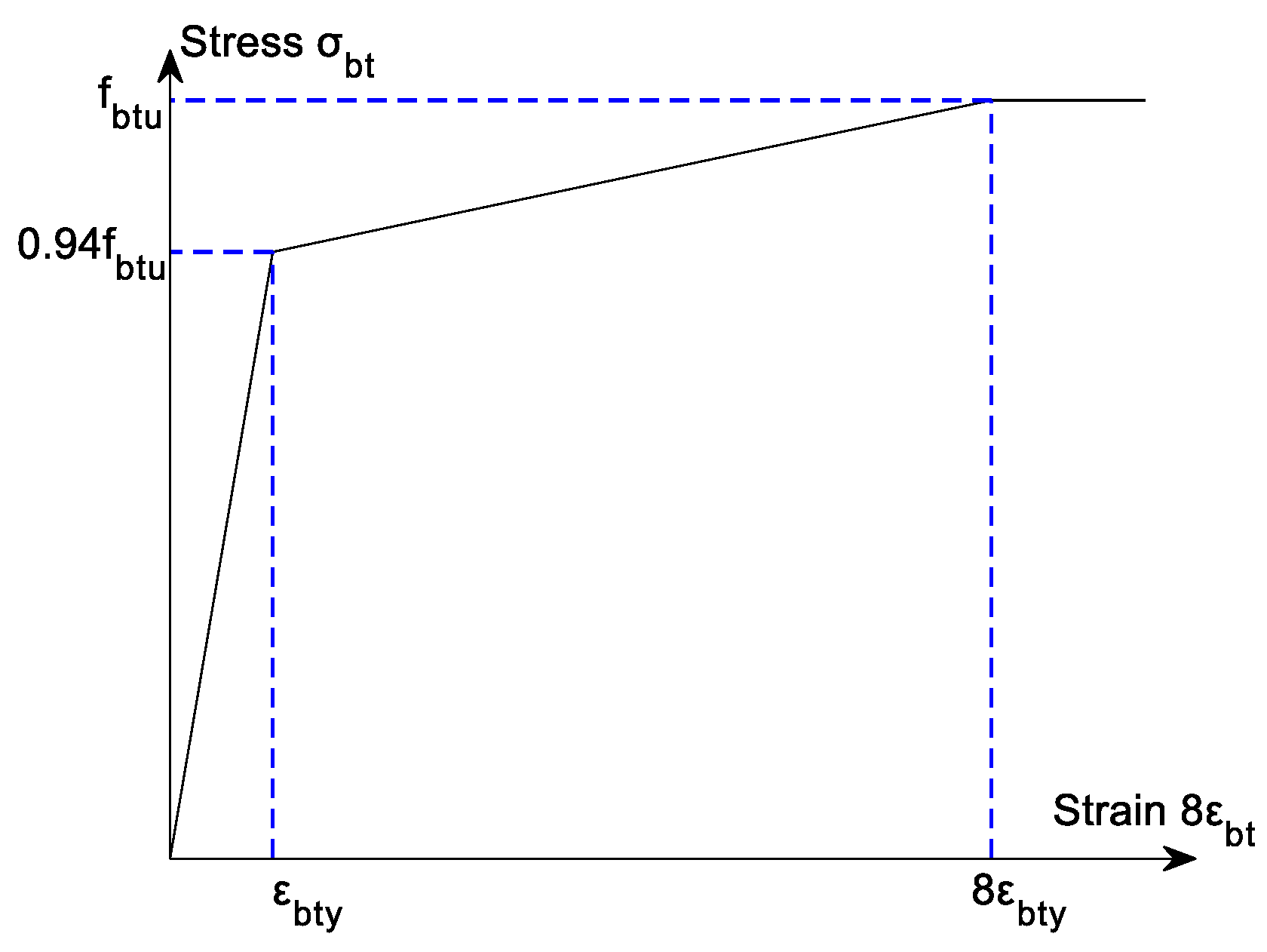
- For concrete in tension, the following relationships are established: y is the ratio of the tensile stress () to the uniaxial tensile strength (), x represents the ratio of the tensile strain () to the corresponding tensile strain at the uniaxial tensile strength (), and is set to 2. The variable is assigned a value of 0.8 for the nonlinear finite element analysis of reinforced concrete structures, while is calculated as . Additionally, equals .
2.1.2. Steel Components
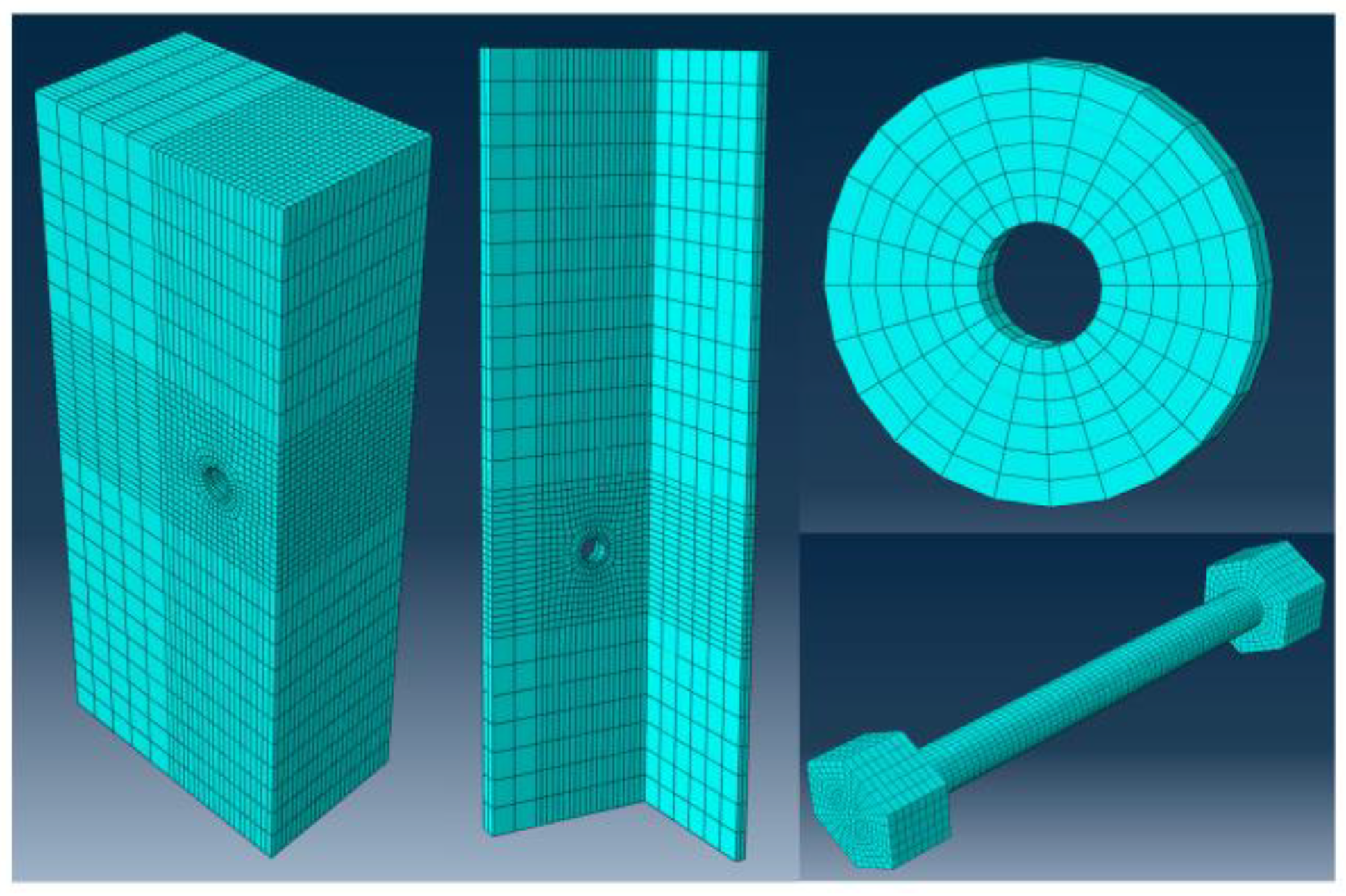
2.2. Geometric Model, Element Type, and Mesh
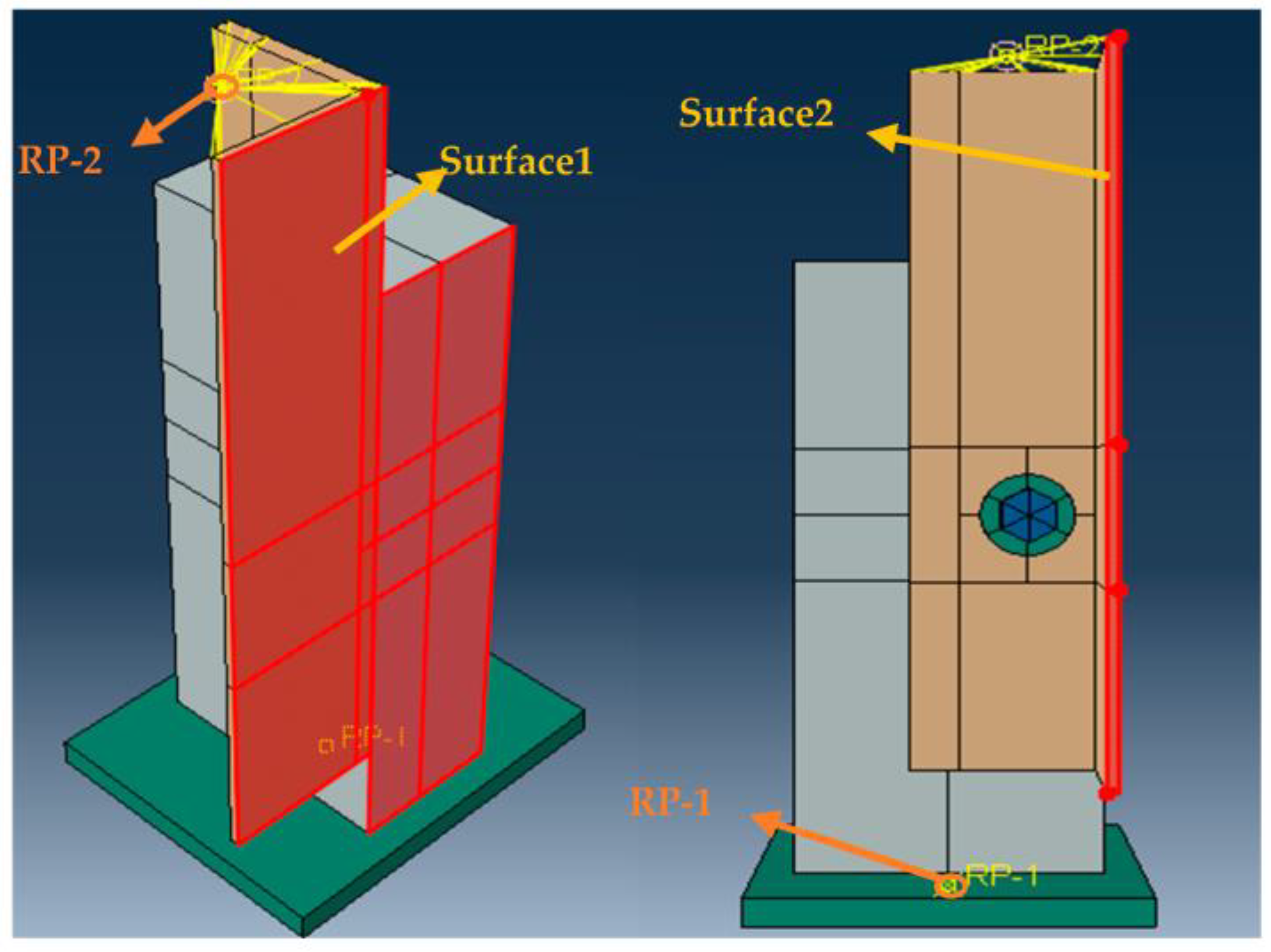
2.3. Interaction Conditions
2.4. Boundary Conditions
2.5. Loading, Analysis Method, and Failure Criteria
2.6. Finite Element Model Verification
3. Establishment of a Database
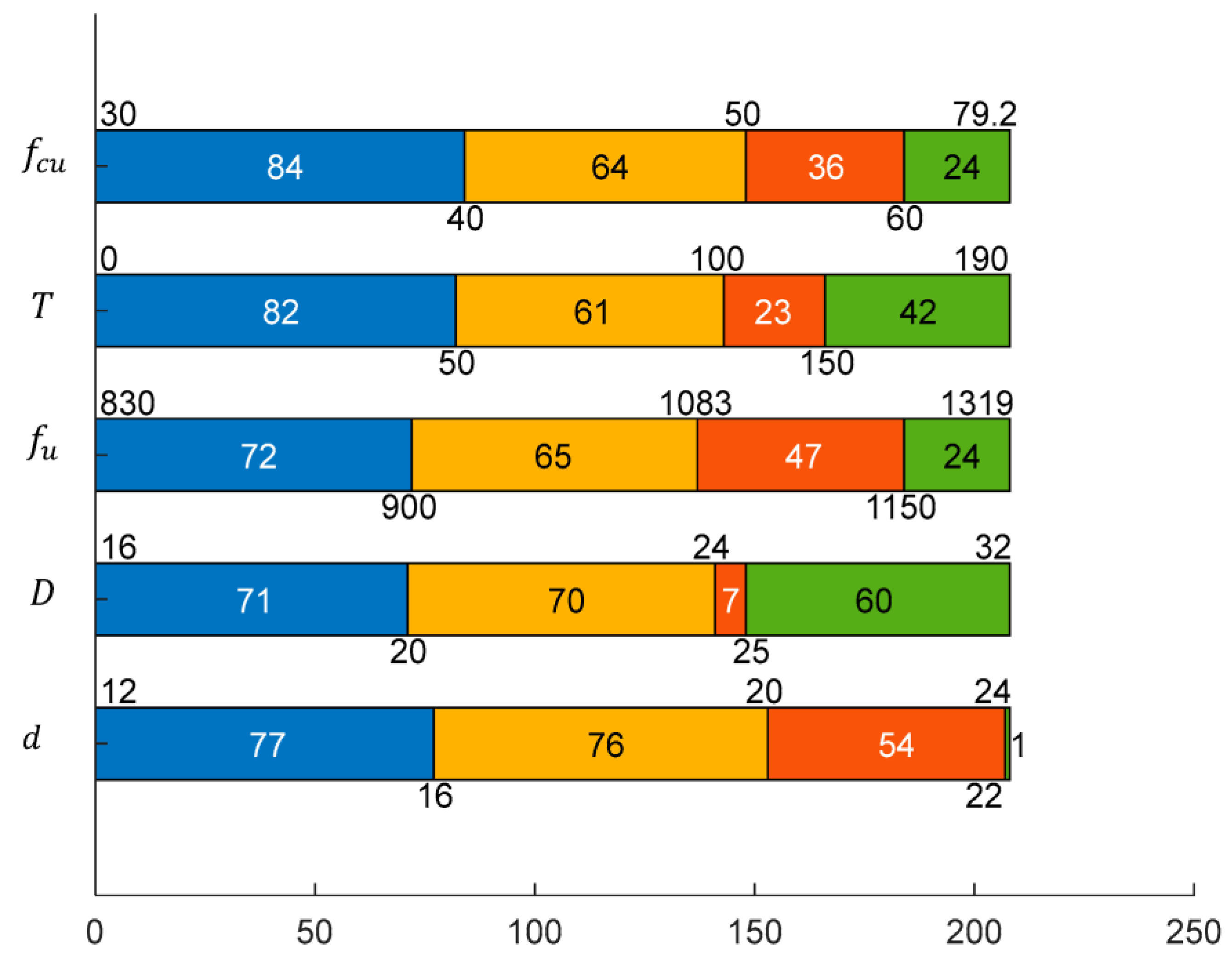
3.1. Choosing Research Variables
- = 1.25 is the partial factor.
- d is the diameter of the shank of the stud.
- is the overall nominal height of the stud.
- for ; for .
- is the specified ultimate tensile strength of the material of the stud.
- is the characteristic cylinder compressive strength of the concrete at the age considered.
3.2. Data Collection Standards and Guidelines
- To apply forces, all specimens are loaded using the method of “inserting a steel beam between two concrete slabs”.
- The geometric dimensions and material properties of the concrete slabs, steel beams, and high-strength bolts in all samples were defined.
4. Model Evaluation
4.1. Existing Evaluation Models
| Concrete Failure | Connector Fracture | Unit | Model Sequence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN 1994-1-1 (2004) [25] | N, mm, MPa | (6) | ||
| AISC 360-16 (2016) [31] | (7) | |||
| GB 50017 (2017) [32] | (8) | |||
| Zhang et al. (2019 [4] | (9) |
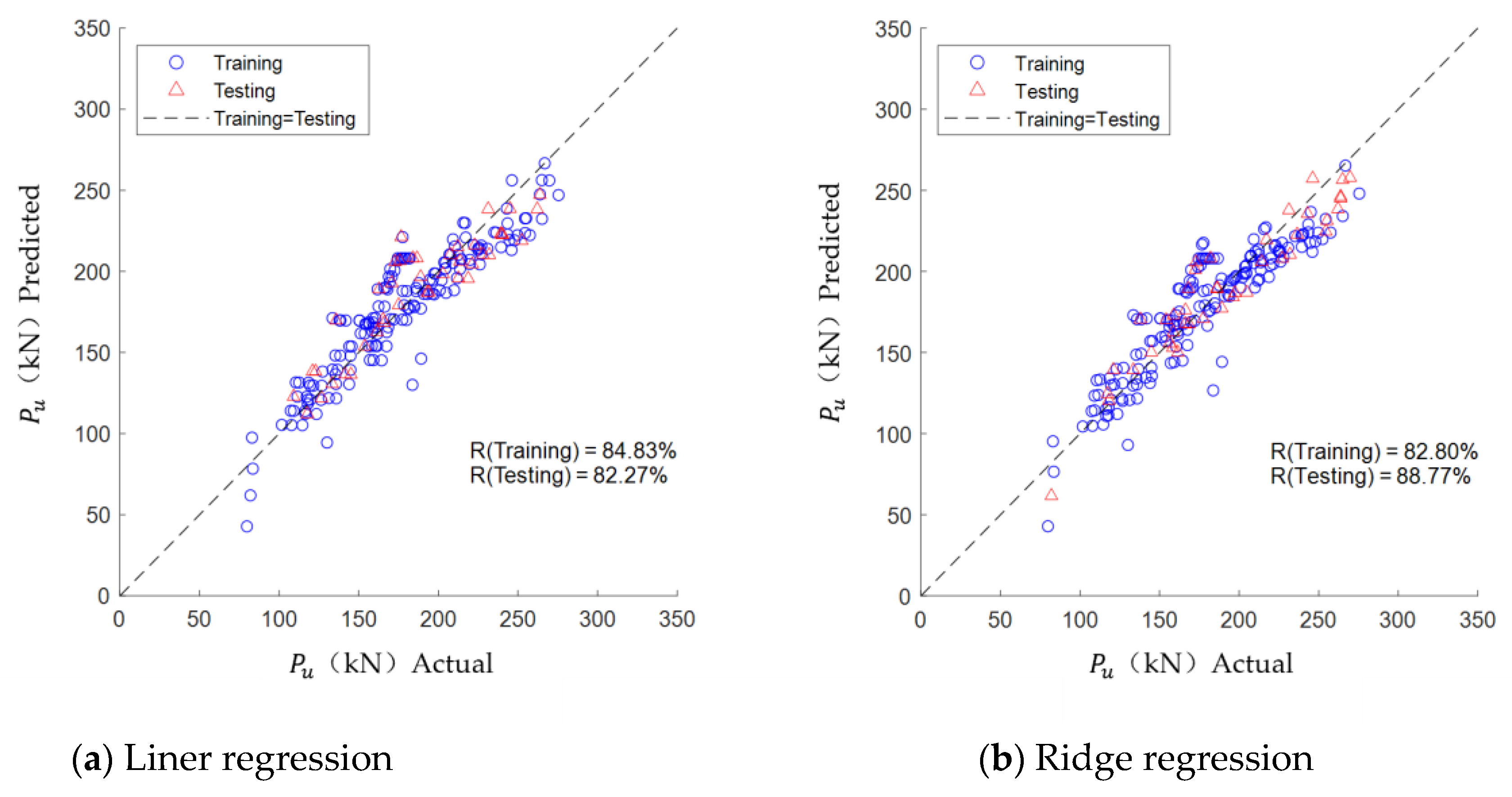
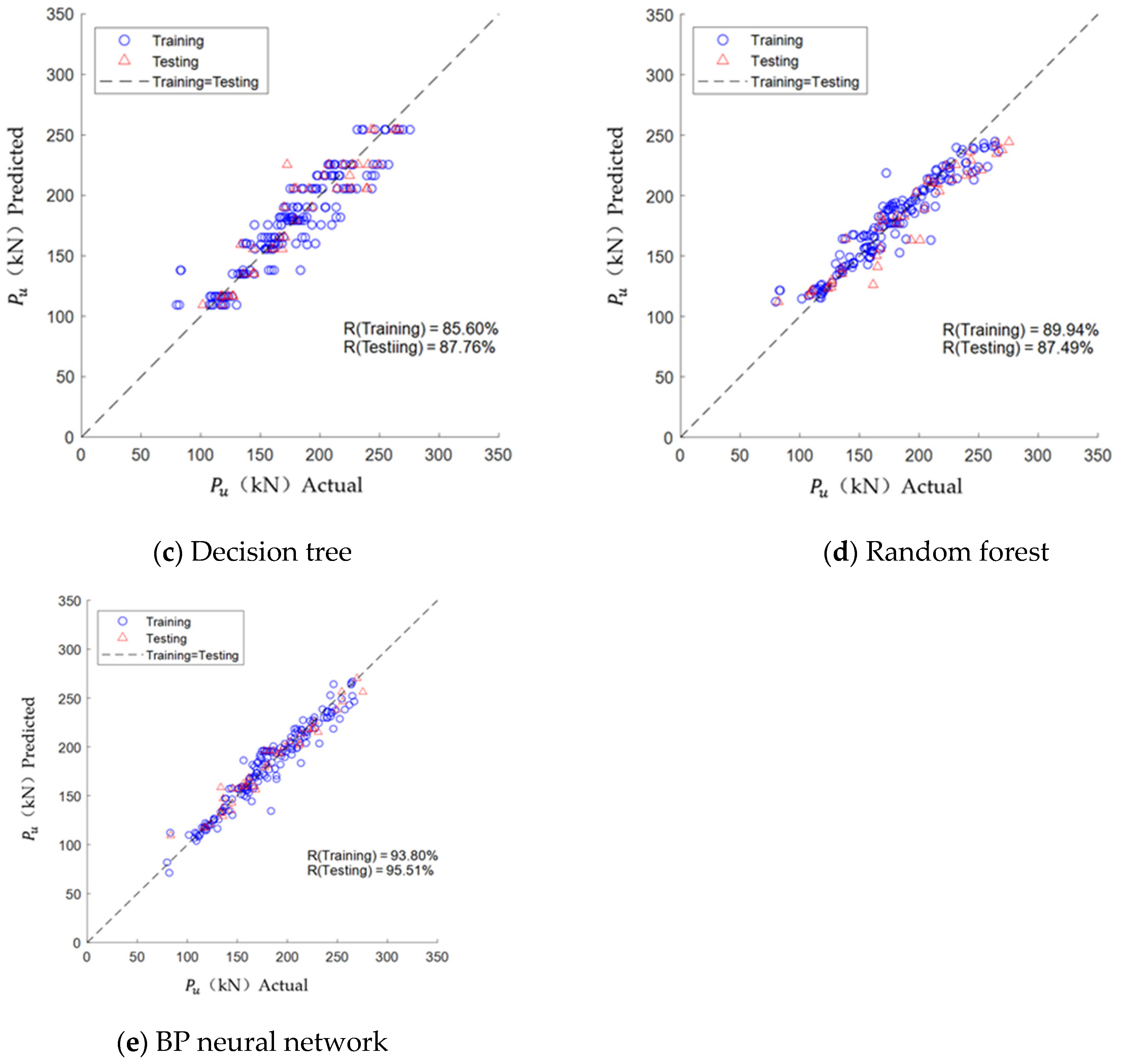
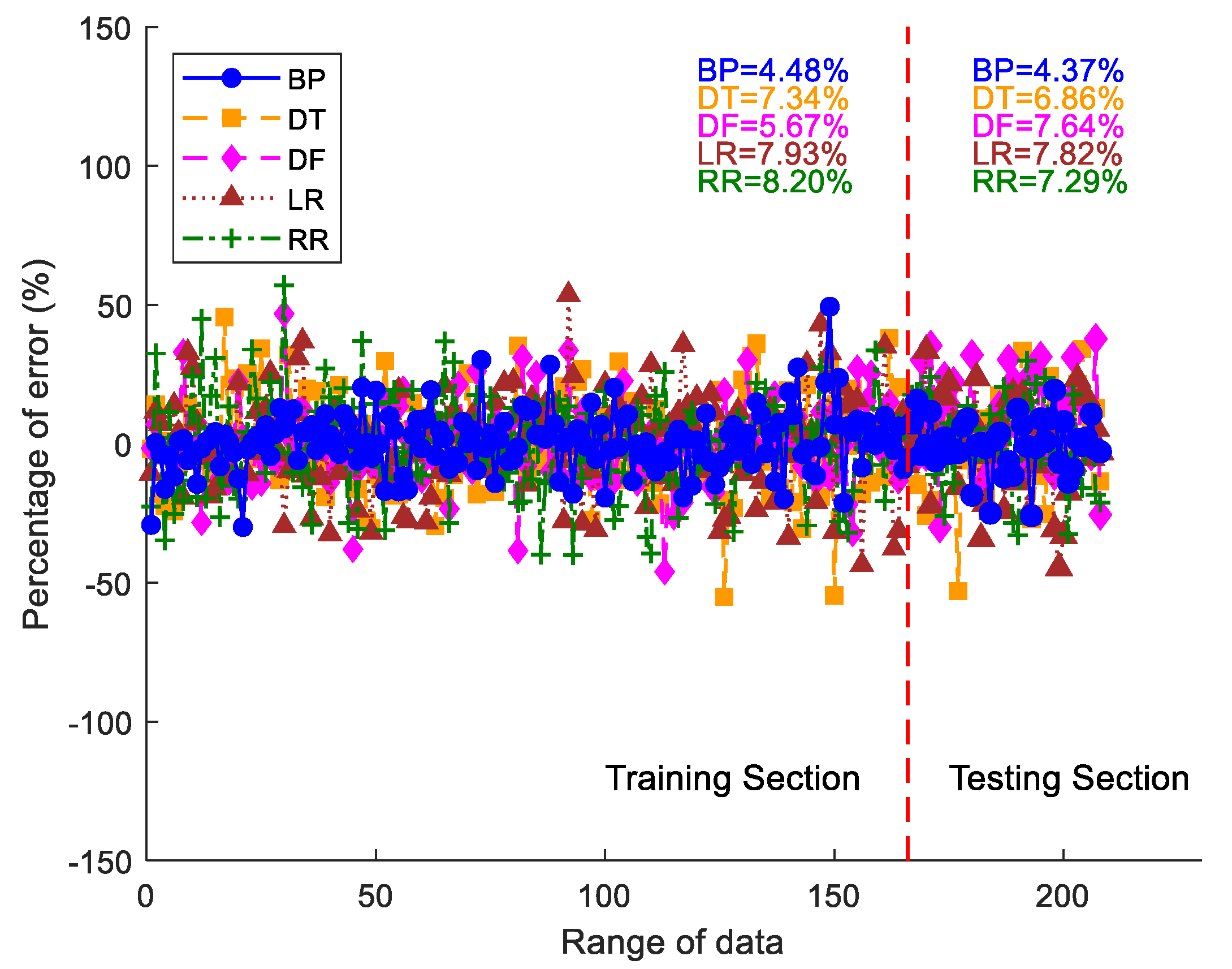
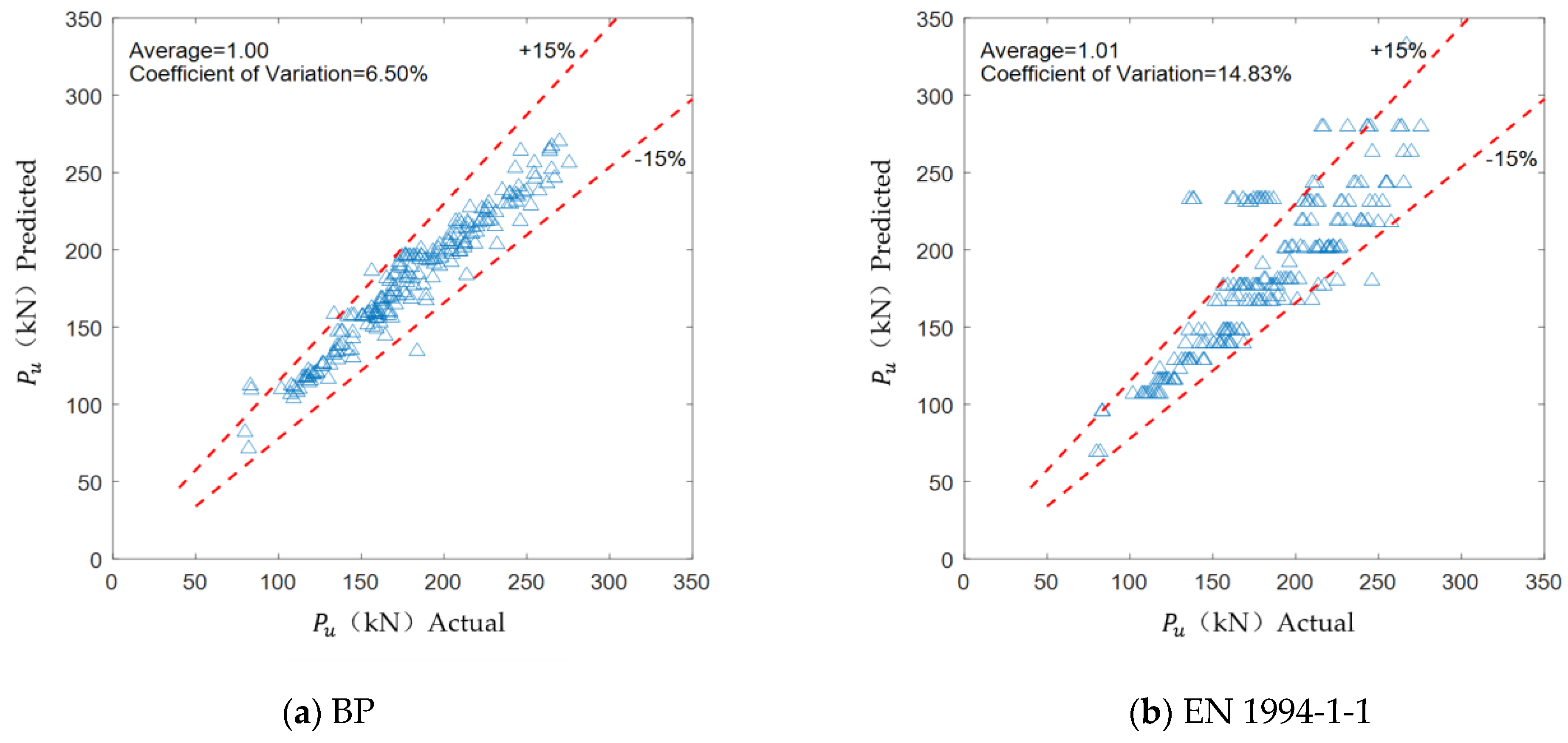
4.2. Model Assessment
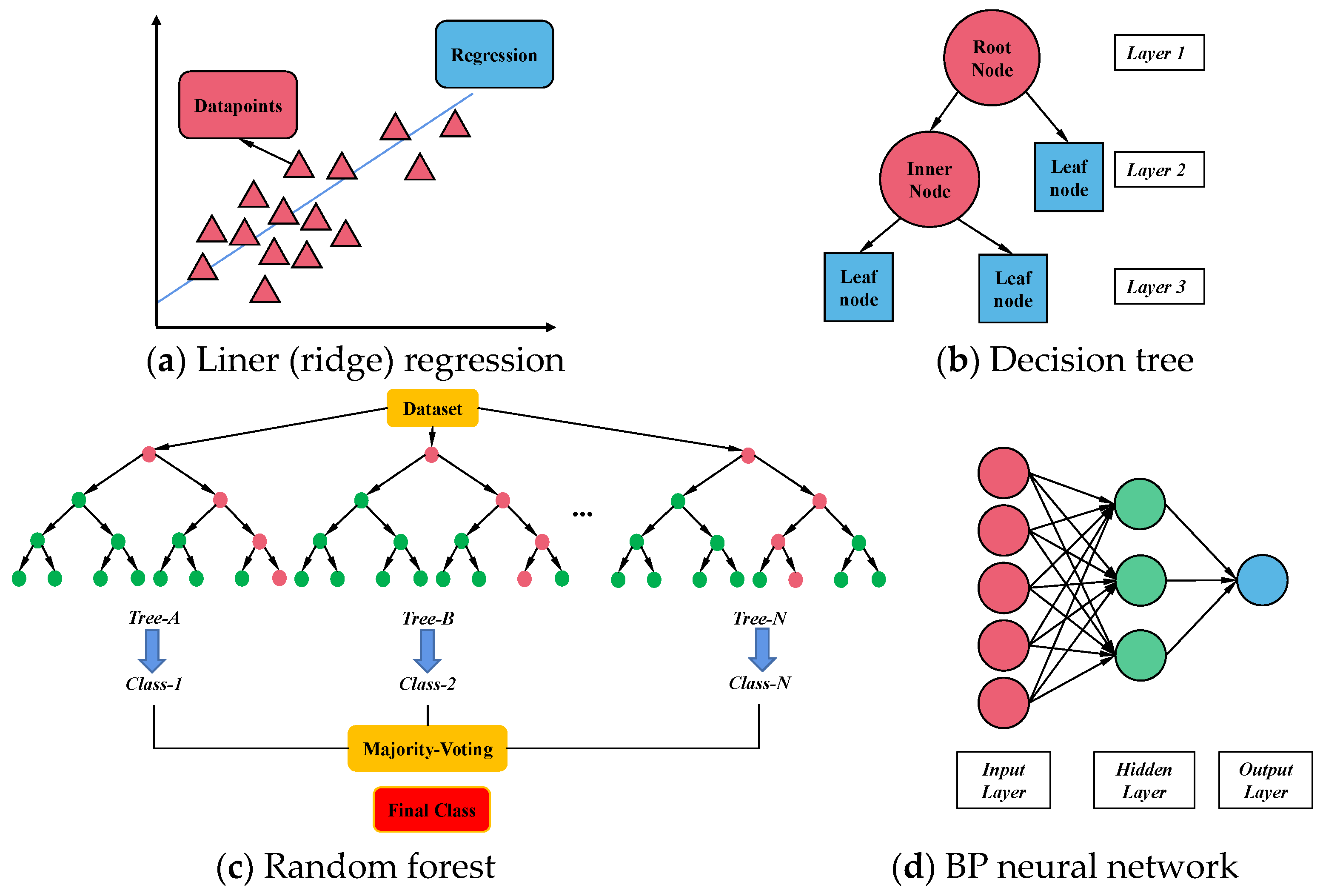
5. Establishment of the Data-Driven Model
5.1. Model Construction and Evaluation
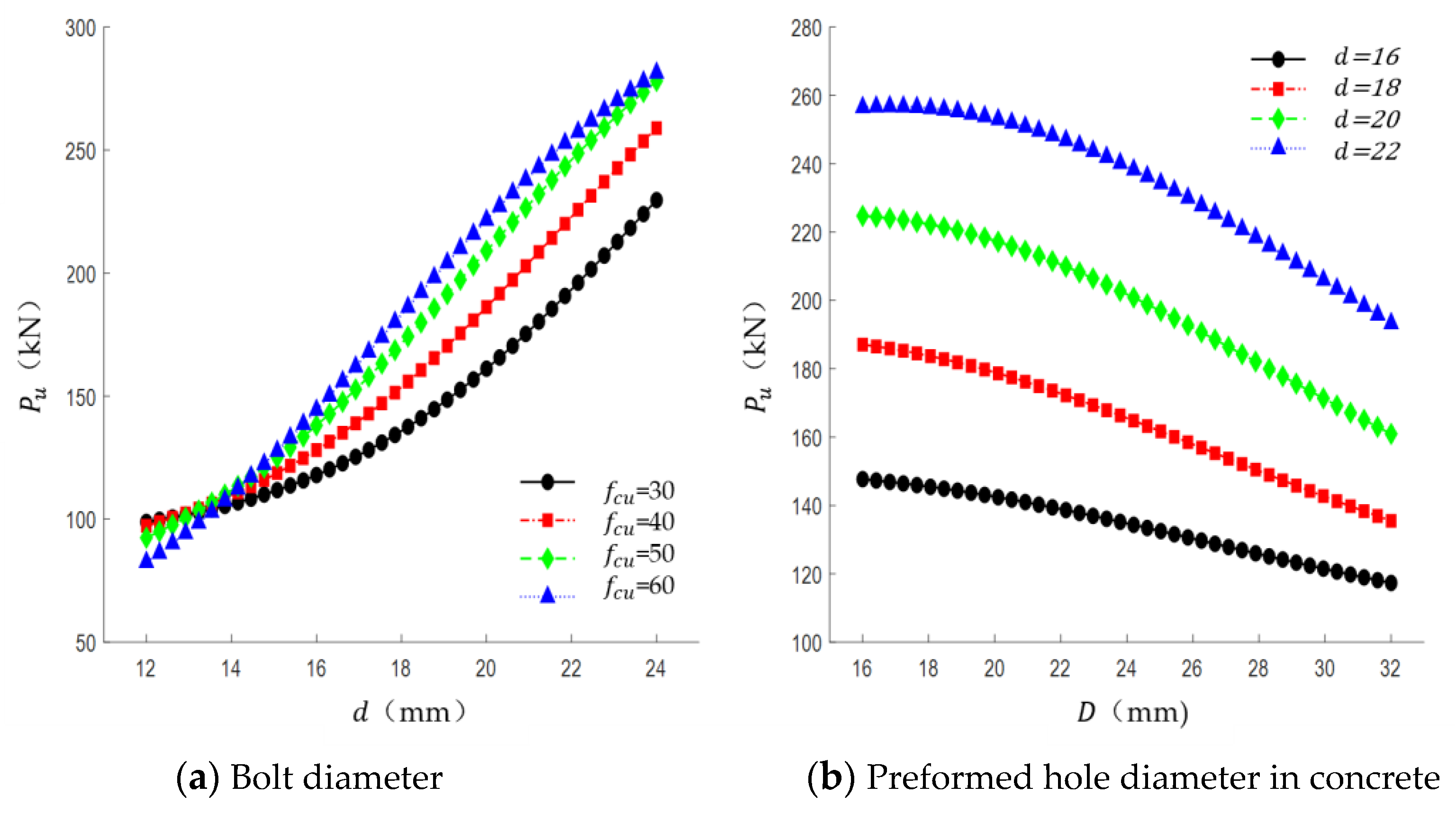
5.2. Research on Variables in Studies
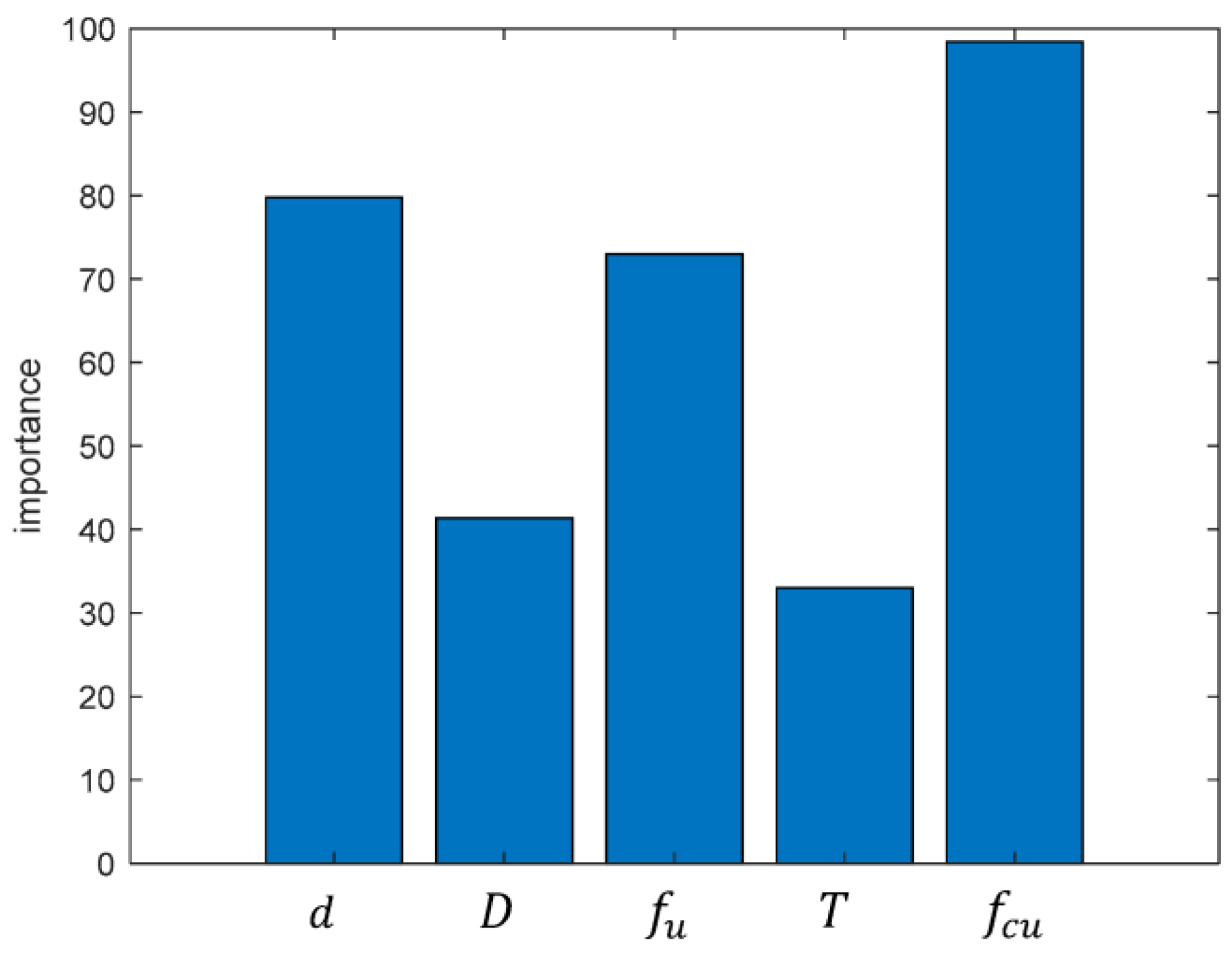
5.2.1. Analysis of the Importance of Research Variables
- : The predicted value for the -th sample after increasing the variable by 10%;
- : The predicted value for the -th sample after decreasing the variable by 10%.
5.2.2. Analysis of the Sensitivity of Research Variables
5.3. Formulation Development
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marshall, W.T.; Nelson, H.M.; Banerjee, H.K. An experimental study of the use of high-strength friction-grip bolts as shear connectors in composite beams. J. Struct. Eng. 1971, 49, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, G.; Engelhardt, M.D.; Klingner, R.E. Behavior of post-installed shear connectors under static and fatigue loading. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2010, 66, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, S.W.; Uy, B.; Mirza, O.; Zhu, X. Flexural behaviour of composite steel-concrete beams utilizing blind bolt shear connectors. Eng. Struct. 2016, 114, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, A.; Pi, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, L. Experimental study on shear behavior of high strength bolt connection in prefabricated steel-concrete composite beam. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 159, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderpour, H.; Mirrashid, M.; Parsa, P. Failure mode prediction of reinforced concrete columns using machine learning methods. Eng. Struct. 2021, 248, 113263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Zou, X.; Sneed, L.H.; Bao, Y.; Wang, L. Prediction of FRP-concrete interfacial bond strength based on machine learning. Eng. Struct. 2023, 274, 115156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, Q.-V.; Truong, V.-H.; Thai, H.-T. Machine learning-based prediction of CFST columns using gradient tree boosting algorithm. Compos. Struct. 2020, 259, 113505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J. Prediction of the Debonding Failure of Beams Strengthened with FRP through Machine Learning Models. Buildings 2023, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, J.; Tan, X. BP-ANN based bond strength prediction for FRP reinforced concrete at high temperature. Eng. Struct. 2022, 257, 114026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, D.; Hu, T. Data-Driven Model for Predicting the Compressive Strengths of GFRP-Confined Reinforced Concrete Columns. Buildings 2023, 13, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Vu, T.; Vo, T.P.; Thai, H.-T. Efficient machine learning models for prediction of concrete strengths. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 266, 120950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidi, S.; Sharifi, Y. Load-carrying capacity of locally corroded steel plate girder ends using artificial neural network. Thin-Walled Struct. 2016, 100, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, F.; Shafighfard, T.; Khan, R.M.A.; Szczuko, P.; Mieloszyk, M. Prediction of Maximum Tensile Stress in Plain-Weave Composite Laminates with Interacting Holes via Stacked Machine Learning Algorithms: A Comparative Study. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 195, 110315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgarkhani, N.; Kazemi, F.; Jankowski, R. Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Residural Drift and Seismic Risk Assessment of Steel Moment-Resisting Frames Considering Soil-Structure Interaction. Comput. Struct. 2023, 289, 107181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, Y.; Moghbeli, A.; Hosseinpour, M.; Sharifi, H. Study of Neural Network Models for the Ultimate Capacities of Cellular Steel Beams. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2019, 44, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarothi, S.Z.; Ahmed, K.S.; Khan, N.I.; Ahmed, A.; Nehdi, M.L. Predicting bearing capacity of double shear bolted connections using machine learning. Eng. Struct. 2021, 251, 113497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, M.; Daei, M.; Zeynalian, M.; Ataei, A. Neural networks-based formulation for predicting ultimate strength of bolted shear connectors in composite cold-formed steel beams. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 118, 105614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Jiao, J. Static behavior of high strength friction-grip bolt shear connectors in composite beams. Steel Compos. Struct. 2022, 42, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.M.A.; Shafighfard, T.; Ali, H.Q.; Mieloszyk, M.; Yildiz, M. Strength Prediction and Experimental Damage Investigations of Plain Woven CFRPs with Interacting Holes Using Mul-ti-Instrument Measurements. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 3594–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Ying, X.; Zhou, L.; Yu, Z. Unified calculation method and its application in determining the uniaxial mechanical properties of concrete. Front. Arch. Civ. Eng. China 2011, 5, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, H.; Uy, B.; Bradford, M. The effects of partial shear connection in composite flush end plate joints Part II—Analytical study and design appraisal. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2005, 62, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bradford, M.A. Numerical simulation of steel pretensioned bolted end-plate connections of different types and details. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbat, B.G.; Russell, H.G. Friction Coefficient of Steel on Concrete or Grout. J. Struct. Eng. 1985, 111, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Chen, Q.-W.; Xing, Y.; Xu, Y.-N.; Zhu, Y. Experimental Study of Friction Resistance between Steel and Concrete in Prefabricated Composite Beam with High-Strength Frictional Bolt. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1292513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1994-1-1; Eurocode 4: Design of Composite Steel and Concrete Structures-Part 1-1: General Rules and Rules for Buildings. European Committee for Standardizaton: Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- GB 50010-2010; Code for Design of Concrete Structures. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Xin, Y. Analysis of compressive strength relationship between concrete cylinder specimen and cube specimen. China Water Power Electrif. 2015, 7, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Yan-Bin, L.; Cai-Jun, S.; Qi, G.; Chen, Q.-W. Experimental Study on Shear Performance of High-Strength Bolted Connections in Restorable Composite Beams. China J. Highw. Transp. 2023, 36, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataei, A.; Zeynalian, M. A study on structural performance of deconstructable bolted shear connectors in composite beams. Structures 2020, 29, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Lu, S.; Jing, X. Shear performance of high-strength bolt connector considering different pad and bolt hole. Structures 2020, 28, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSI/AISC 360-16; Specification for Structural Steel Buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction: Chicago, IL, USA, 2016.
- GB 50017; Code for Design of Steel Structures. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.




| Specimen | Concrete Strength (MPa) | Bolt (mm) | (MPa) | Bolt Pretension (kN) | Preformed Hole Diameter | Failure Mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete Slab (mm) | Steel Flange (mm) | ||||||
| PT1 | 45.6 | 16 | 1083 | 80.7 | 20 | 18 | B.F. |
| PT2 | 60.2 | 16 | 1303 | 101.2 | 20 | 18 | B.F. |
| PT3 | 74.8 | 20 | 1024 | 126.4 | 24 | 22 | B.F. |
| PT4 | 61.6 | 16 | 1083 | 77.3 | 20 | 18 | B.F. |
| PT5 | 73.1 | 22 | 990 | 76.3 | 26 | 24 | B.F. |
| PT6 | 68.9 | 20 | 1024 | 77.9 | 24 | 22 | B.F. |
| Test | PT1 | PT2 | PT3 | PT4 | PT5 | PT6 | Average | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | 142.4 | 168.4 | 257.1 | 158.3 | 266.1 | 240.3 | |||
| FEA | 148.6 | 175.2 | 242.1 | 154.3 | 268.4 | 230.6 | |||
| T/FEA | 0.96 | 0.96 | 1.06 | 1.03 | 0.99 | 1.04 | |||
| FEFM | B.F. | B.F. | B.F. | B.F. | B.F. | B.F. | |||
| 1.01 | 0.04 |
| Reference | Specimen | /mm | /mm | /Mpa | /Mpa | /kN | /kN | Failure Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xing et al. [28] | PT1 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 75.4 | 21 | 150.5 | B.F. |
| PT2 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 75.4 | 21.3 | 141.9 | B.F. | |
| PT3 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 75.4 | 21.5 | 150.4 | B.F. | |
| PT4 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 77.1 | 41.3 | 133.5 | B.F. | |
| PT5 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 77.1 | 41.5 | 160.5 | B.F. | |
| PT6 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 77.1 | 41.9 | 158.9 | B.F. | |
| PT7 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 70.8 | 61.1 | 160.9 | B.F. | |
| PT8 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 70.8 | 60.9 | 159.3 | B.F. | |
| PT9 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 70.8 | 60.8 | 168.5 | B.F. | |
| PT10 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 73.1 | 83.7 | 156.5 | B.F. | |
| PT11 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 73.1 | 81.9 | 154.1 | B.F. | |
| PT12 | 16 | 20 | 1083 | 73.1 | 81.6 | 154.8 | B.F. | |
| PT13 | 16 | 20 | 1303 | 72.4 | 101.9 | 209.9 | B.F. | |
| PT14 | 16 | 20 | 1303 | 72.4 | 101.6 | 193.3 | B.F. | |
| PT15 | 16 | 20 | 1303 | 72.4 | 102.4 | 200.9 | B.F. | |
| PT16 | 16 | 24 | 1083 | 79.2 | 82.1 | 144.1 | B.F. | |
| PT17 | 16 | 24 | 1083 | 79.2 | 82 | 145.6 | B.F. | |
| PT18 | 16 | 24 | 1083 | 79.2 | 81.4 | 153.8 | B.F. | |
| PT19 | 20 | 24 | 1083 | 71.3 | 80.3 | 240.4 | B.F. | |
| PT20 | 20 | 24 | 1083 | 71.3 | 125.6 | 249.7 | B.F. | |
| PT21 | 20 | 24 | 1083 | 71.3 | 126.8 | 257.5 | B.F. | |
| PT22 | 22 | 26 | 1083 | 77.7 | 80.1 | 265 | B.F. | |
| PT23 | 22 | 26 | 1083 | 77.7 | 120.5 | 246.2 | B.F. | |
| PT24 | 22 | 26 | 1083 | 77.7 | 150.4 | 269.7 | B.F. | |
| Zhang et al. [4] | T1-1 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 50 | 80 | 207 | B.F. |
| T1-2 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 50 | 100 | 207.5 | B.F. | |
| T1-3 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 50 | 120 | 207.5 | B.F. | |
| T1-4 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 50 | 155 | 212.5 | B.F. | |
| T2-1 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 50 | 155 | 156.3 | B.F. | |
| T2-2 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 50 | 155 | 231.3 | C.F. | |
| T2-3 | 24 | 28 | 1150 | 50 | 155 | 266.8 | C.F. | |
| T3-1 | 20 | 22 | 1150 | 50 | 155 | 209.2 | C.F. | |
| T3-2 | 20 | 26 | 1150 | 50 | 155 | 172.5 | B.F. | |
| T4-1 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 40 | 155 | 169.8 | C.F. | |
| T4-2 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 45 | 155 | 172.8 | C.F. | |
| Kwon et al. [2] | HTFGB-05ST | 22 | 25 | 1020 | 30.2 (24.5) a | 175 | 246 | B.F. |
| HTFGB-06ST | 22 | 25 | 1020 | 30.2 (24.5) a | 175 | 225 | B.F. | |
| Ataei et al. [29] | PT1 | 12 | 16 | 955 | 30.9 (25) a | 0 | 82 | B.F. |
| PT2 | 12 | 20 | 955 | 30.9 (26) a | 0 | 79.8 | B.F. | |
| PT3 | 12 | 16 | 1319 | 30.9 (27) a | 0 | 83 | B.F. | |
| PT4 | 12 | 20 | 1319 | 30.9 (28) a | 0 | 83.5 | B.F. | |
| PT5 | 16 | 20 | 955 | 30.9 (29) a | 0 | 118 | B.F. | |
| PT6 | 16 | 25 | 955 | 30.9 (30) a | 0 | 130.1 | B.F. | |
| PT7 | 16 | 20 | 1319 | 30.9 (31) a | 0 | 161.5 | B.F. | |
| PT8 | 16 | 25 | 1319 | 30.9 (32) a | 0 | 183.7 | B.F. | |
| PT9 | 20 | 25 | 955 | 30.9 (33) a | 0 | 180 | B.F. | |
| PT10 | 16 | 20 | 1319 | 49.4 (40) a | 0 | 165.2 | B.F. | |
| PT11 | 16 | 25 | 1319 | 49.4 (41) a | 0 | 189.2 | B.F. | |
| PT12 | 20 | 25 | 955 | 49.4 (42) a | 0 | 196.2 | B.F. | |
| Zhao et al. [30] | K24-S-1 | 20 | 24 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 177.3 | C.F. |
| K24-S-2 | 20 | 24 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 174.5 | C.F. | |
| K24-S-3 | 20 | 24 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 176.4 | C.F. | |
| K24-M-1 | 20 | 24 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 181.3 | C.F. | |
| K24-M-2 | 20 | 24 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 178.6 | C.F. | |
| K24-M-3 | 20 | 24 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 182 | C.F. | |
| K24-L-1 | 20 | 24 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 186.6 | C.F. | |
| K24-L-2 | 20 | 24 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 179.5 | C.F. | |
| K24-L-3 | 20 | 24 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 184 | C.F. | |
| K28-L-1 | 20 | 28 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 162.8 | C.F. | |
| K28-L-2 | 20 | 28 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 161.8 | C.F. | |
| K28-L-3 | 20 | 28 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 168.1 | C.F. | |
| K32-L-1 | 20 | 32 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 137.9 | C.F. | |
| K32-L-2 | 20 | 32 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 135.8 | C.F. | |
| K32-L-3 | 20 | 32 | 1158 | 46.7 | 155 | 138.6 | C.F. | |
| FEA | FEA-1 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 16 | 30 | 101.7 | B.F. |
| FEA-2 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 16 | 40 | 107.3 | B.F. | |
| FEA-3 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 16 | 50 | 109.1 | B.F. | |
| FEA-4 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 16 | 60 | 110.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-5 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 40 | 30 | 107.8 | B.F. | |
| FEA-6 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 40 | 40 | 109.2 | B.F. | |
| FEA-7 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 40 | 50 | 111.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-8 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 40 | 60 | 112.6 | B.F. | |
| FEA-9 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 80 | 30 | 114.6 | B.F. | |
| FEA-10 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 80 | 40 | 116.4 | B.F. | |
| FEA-11 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 80 | 50 | 117.3 | B.F. | |
| FEA-12 | 16 | 20 | 830 | 80 | 60 | 118.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-13 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 16 | 30 | 116.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-14 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 16 | 40 | 118.1 | B.F. | |
| FEA-15 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 16 | 50 | 119.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-16 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 16 | 60 | 121 | B.F. | |
| FEA-17 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 40 | 30 | 117.8 | B.F. | |
| FEA-18 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 40 | 40 | 119.6 | B.F. | |
| FEA-19 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 40 | 50 | 121.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-20 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 40 | 60 | 122.9 | B.F. | |
| FEA-21 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 80 | 30 | 123.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-22 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 80 | 40 | 126.3 | B.F. | |
| FEA-23 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 80 | 50 | 126.8 | B.F. | |
| FEA-24 | 16 | 20 | 900 | 80 | 60 | 127.3 | B.F. | |
| FEA-25 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 20 | 40 | 133.3 | B.F. | |
| FEA-26 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 20 | 50 | 133.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-27 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 20 | 60 | 135.3 | B.F. | |
| FEA-28 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 50 | 40 | 135.7 | B.F. | |
| FEA-29 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 50 | 50 | 136.7 | B.F. | |
| FEA-30 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 50 | 60 | 138.4 | B.F. | |
| FEA-31 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 100 | 40 | 144 | B.F. | |
| FEA-32 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 100 | 50 | 144.8 | B.F. | |
| FEA-33 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 100 | 60 | 144.8 | B.F. | |
| FEA-34 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 20 | 40 | 157 | B.F. | |
| FEA-35 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 20 | 50 | 158.3 | B.F. | |
| FEA-36 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 20 | 60 | 158.6 | B.F. | |
| FEA-37 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 50 | 40 | 159.2 | B.F. | |
| FEA-38 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 50 | 50 | 160.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-39 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 50 | 60 | 161.4 | B.F. | |
| FEA-40 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 100 | 40 | 164.4 | B.F. | |
| FEA-41 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 100 | 50 | 167.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-42 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 100 | 60 | 167.6 | B.F. | |
| FEA-43 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 25 | 40 | 169.9 | B.F. | |
| FEA-44 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 25 | 50 | 175.1 | B.F. | |
| FEA-45 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 25 | 60 | 177.6 | B.F. | |
| FEA-46 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 62.5 | 40 | 172.1 | B.F. | |
| FEA-47 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 62.5 | 50 | 178.4 | B.F. | |
| FEA-48 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 62.5 | 60 | 180.2 | B.F. | |
| FEA-49 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 125 | 40 | 177.4 | B.F. | |
| FEA-50 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 125 | 50 | 184.6 | B.F. | |
| FEA-51 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 125 | 60 | 186.1 | B.F. | |
| FEA-52 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 25 | 40 | 180.8 | B.F. | |
| FEA-53 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 25 | 50 | 190.9 | B.F. | |
| FEA-54 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 25 | 60 | 194.6 | B.F. | |
| FEA-55 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 62.5 | 40 | 181.8 | B.F. | |
| FEA-56 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 62.5 | 50 | 193.1 | B.F. | |
| FEA-57 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 62.5 | 60 | 196.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-58 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 125 | 40 | 189.1 | B.F. | |
| FEA-59 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 125 | 50 | 197.4 | B.F. | |
| FEA-60 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 125 | 60 | 202.1 | B.F. | |
| FEA-61 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 31 | 50 | 211.7 | B.F. | |
| FEA-62 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 31 | 60 | 219.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-63 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 77.5 | 50 | 212.6 | B.F. | |
| FEA-64 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 77.5 | 60 | 221.3 | B.F. | |
| FEA-65 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 155 | 50 | 218.7 | B.F. | |
| FEA-66 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 155 | 60 | 226.1 | B.F. | |
| FEA-67 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 30 | 50 | 214.1 | B.F. | |
| FEA-68 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 30 | 60 | 222.3 | B.F. | |
| FEA-69 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 75 | 50 | 214.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-70 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 75 | 60 | 222.9 | B.F. | |
| FEA-71 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 150 | 50 | 219.9 | B.F. | |
| FEA-72 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 150 | 60 | 227.0 | B.F. | |
| FEA-73 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 30 | 60 | 239.1 | B.F. | |
| FEA-74 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 75 | 60 | 239.7 | B.F. | |
| FEA-75 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 150 | 60 | 243.5 | B.F. | |
| FEA-76 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 20 | 30 | 126.7 | C.F. | |
| FEA-77 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 50 | 30 | 131.2 | C.F. | |
| FEA-78 | 16 | 20 | 1000 | 100 | 30 | 135.9 | C.F. | |
| FEA-79 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 20 | 30 | 135.4 | C.F. | |
| FEA-80 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 50 | 30 | 141.4 | C.F. | |
| FEA-81 | 16 | 20 | 1150 | 100 | 30 | 145.1 | C.F. | |
| FEA-82 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 25 | 30 | 151.2 | C.F. | |
| FEA-83 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 62.5 | 30 | 153.8 | C.F. | |
| FEA-84 | 20 | 24 | 830 | 125 | 30 | 161.6 | C.F. | |
| FEA-85 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 25 | 30 | 156.2 | C.F. | |
| FEA-86 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 62.5 | 30 | 158.9 | C.F. | |
| FEA-87 | 20 | 24 | 900 | 125 | 30 | 166.2 | C.F. | |
| FEA-88 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 31 | 30 | 162.4 | C.F. | |
| FEA-89 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 31 | 40 | 194.0 | C.F. | |
| FEA-90 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 77.5 | 30 | 166.3 | C.F. | |
| FEA-91 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 77.5 | 40 | 193.1 | C.F. | |
| FEA-92 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 155 | 30 | 185.0 | C.F. | |
| FEA-93 | 20 | 24 | 1000 | 155 | 40 | 204.8 | C.F. | |
| FEA-94 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 31 | 30 | 169.4 | C.F. | |
| FEA-95 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 31 | 40 | 204.4 | C.F. | |
| FEA-96 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 31 | 50 | 227.1 | C.F. | |
| FEA-97 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 31 | 60 | 244.7 | C.F. | |
| FEA-98 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 77.5 | 30 | 170.8 | C.F. | |
| FEA-99 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 77.5 | 40 | 204.4 | C.F. | |
| FEA-100 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 77.5 | 50 | 227.9 | C.F. | |
| FEA-101 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 77.5 | 60 | 247.9 | C.F. | |
| FEA-102 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 155 | 30 | 187.7 | C.F. | |
| FEA-103 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 155 | 40 | 213.6 | C.F. | |
| FEA-104 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 155 | 50 | 232.0 | C.F. | |
| FEA-105 | 20 | 24 | 1150 | 155 | 60 | 252.4 | C.F. | |
| FEA-106 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 30 | 30 | 167.2 | C.F. | |
| FEA-107 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 30 | 40 | 197.4 | C.F. | |
| FEA-108 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 75 | 30 | 166.0 | C.F. | |
| FEA-109 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 75 | 40 | 198.3 | C.F. | |
| FEA-110 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 150 | 30 | 186.0 | C.F. | |
| FEA-111 | 22 | 26 | 830 | 150 | 40 | 202.9 | C.F. | |
| FEA-112 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 30 | 30 | 170.8 | C.F. | |
| FEA-113 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 30 | 40 | 203.6 | C.F. | |
| FEA-114 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 30 | 50 | 226.0 | C.F. | |
| FEA-115 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 75 | 30 | 168.9 | C.F. | |
| FEA-116 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 75 | 40 | 204.5 | C.F. | |
| FEA-117 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 75 | 50 | 225.0 | C.F. | |
| FEA-118 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 150 | 30 | 188.9 | C.F. | |
| FEA-119 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 150 | 40 | 209.2 | C.F. | |
| FEA-120 | 22 | 26 | 900 | 150 | 50 | 230.8 | C.F. | |
| FEA-121 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 38 | 30 | 174.2 | C.F. | |
| FEA-122 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 38 | 40 | 210.3 | C.F. | |
| FEA-123 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 38 | 50 | 235.1 | C.F. | |
| FEA-124 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 38 | 60 | 255.2 | C.F. | |
| FEA-125 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 95 | 30 | 175.8 | C.F. | |
| FEA-126 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 95 | 40 | 212.2 | C.F. | |
| FEA-127 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 95 | 50 | 236.4 | C.F. | |
| FEA-128 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 95 | 60 | 254.4 | C.F. | |
| FEA-129 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 190 | 30 | 213.6 | C.F. | |
| FEA-130 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 190 | 40 | 239.4 | C.F. | |
| FEA-131 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 190 | 50 | 254.5 | C.F. | |
| FEA-132 | 22 | 26 | 1000 | 190 | 60 | 265.1 | C.F. | |
| FEA-133 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 38 | 30 | 176.6 | C.F. | |
| FEA-134 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 38 | 40 | 215.7 | C.F. | |
| FEA-135 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 38 | 50 | 243.0 | C.F. | |
| FEA-136 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 38 | 60 | 263.8 | C.F. | |
| FEA-137 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 95 | 30 | 177.6 | C.F. | |
| FEA-138 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 95 | 40 | 216.8 | C.F. | |
| FEA-139 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 95 | 50 | 245.0 | C.F. | |
| FEA-140 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 95 | 60 | 263.8 | C.F. | |
| FEA-141 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 190 | 30 | 217.2 | C.F. | |
| FEA-142 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 190 | 40 | 243.5 | C.F. | |
| FEA-143 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 190 | 50 | 262.1 | C.F. | |
| FEA-144 | 22 | 26 | 1150 | 190 | 60 | 275.5 | C.F. |
| P | P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hidden | Output | ||||
| H(1:1) | H(1:2) | H(1:3) | |||
| Bias | 2.864 | −1.5351 | 6.0514 | ||
| −0.1355 | 0.0233 | −0.1857 | |||
| 0.0537 | 0.085 | −0.1541 | |||
| Input | −0.0003 | 0.0016 | −0.0048 | ||
| 0.0027 | 0.0066 | 0.057 | |||
| −0.0261 | −0.0433 | −0.0664 | |||
| Bias | 182.0298 | ||||
| H(1:1) | −134.64 | ||||
| Hidden | H(1:2) | 78.9768 | |||
| H(1:3) | 33.4263 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Yin, X.; Sha, L.; Yang, D.; Hu, T. Data-Driven Prediction Model for High-Strength Bolts in Composite Beams. Buildings 2023, 13, 2769. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13112769
Li H, Yin X, Sha L, Yang D, Hu T. Data-Driven Prediction Model for High-Strength Bolts in Composite Beams. Buildings. 2023; 13(11):2769. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13112769
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Haolin, Xinsheng Yin, Lirong Sha, Dongdong Yang, and Tianyu Hu. 2023. "Data-Driven Prediction Model for High-Strength Bolts in Composite Beams" Buildings 13, no. 11: 2769. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13112769
APA StyleLi, H., Yin, X., Sha, L., Yang, D., & Hu, T. (2023). Data-Driven Prediction Model for High-Strength Bolts in Composite Beams. Buildings, 13(11), 2769. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13112769







