Review of Emerging Technologies for Reducing Ergonomic Hazards in Construction Workplaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
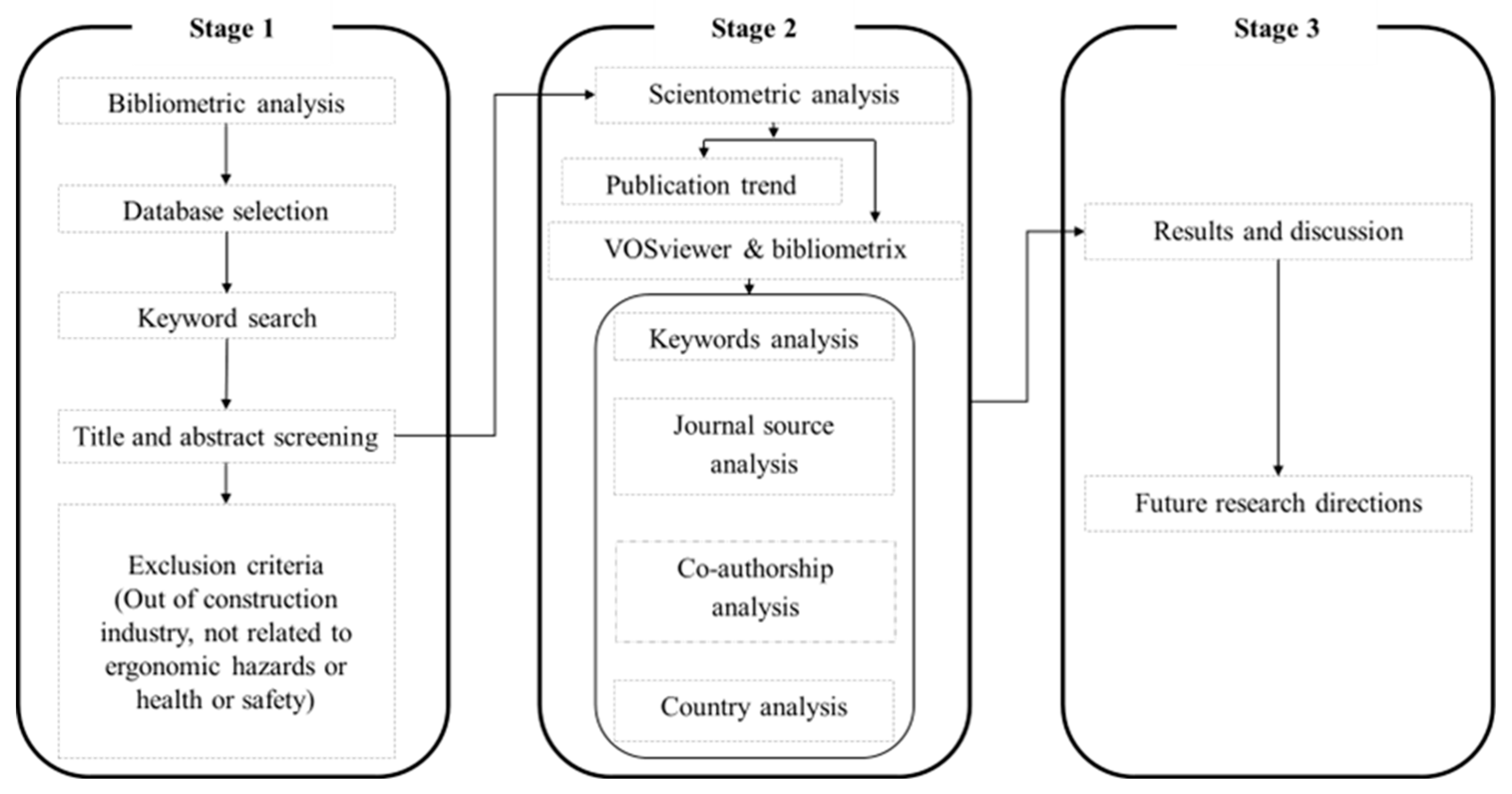
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bibliometric Analysis
Search Terminology and Data Processing
2.2. Scientometric Analysis
3. Results
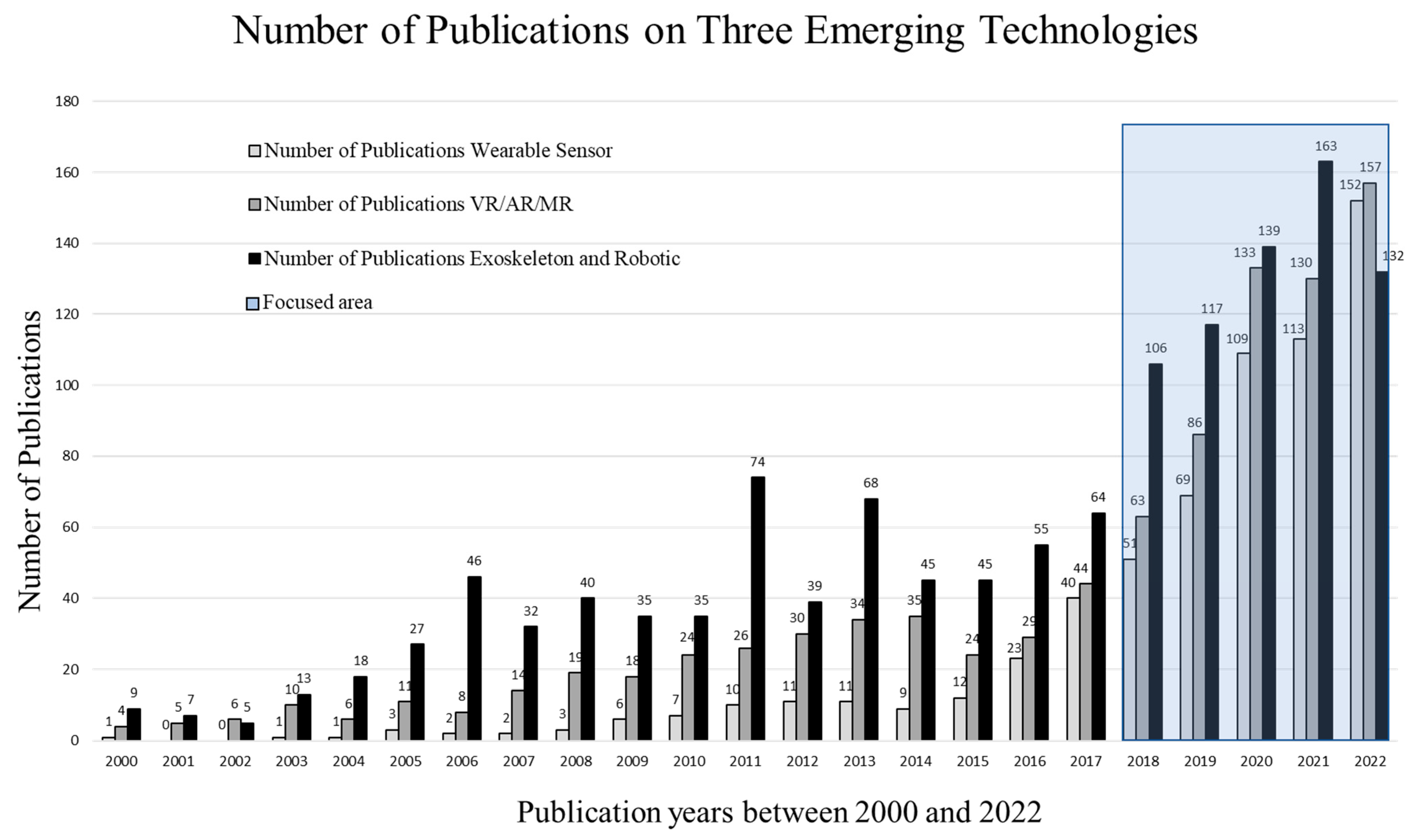
3.1. Annual Publication Trends
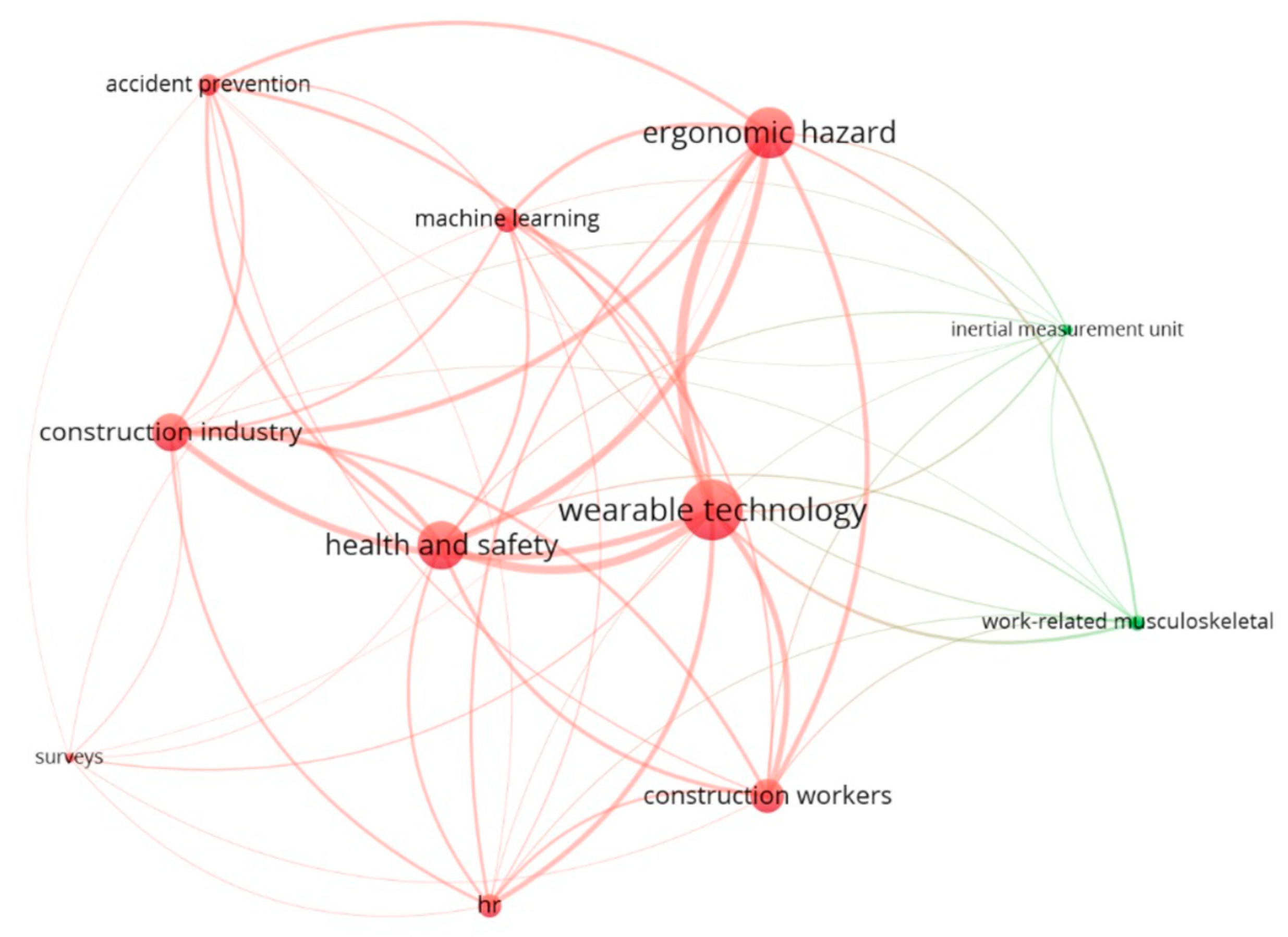
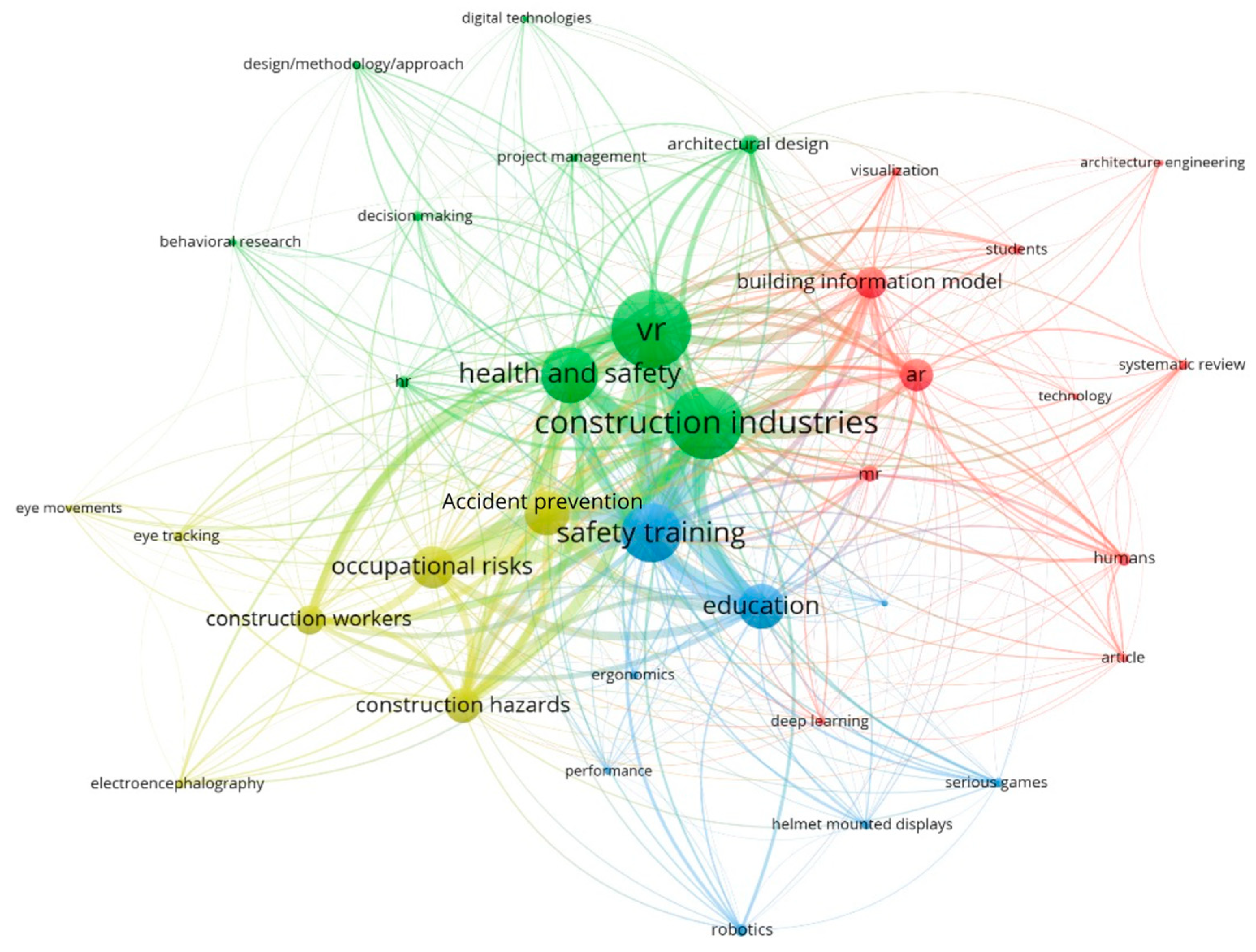
3.2. Keyword Analysis
3.3. Journal-Source Analysis
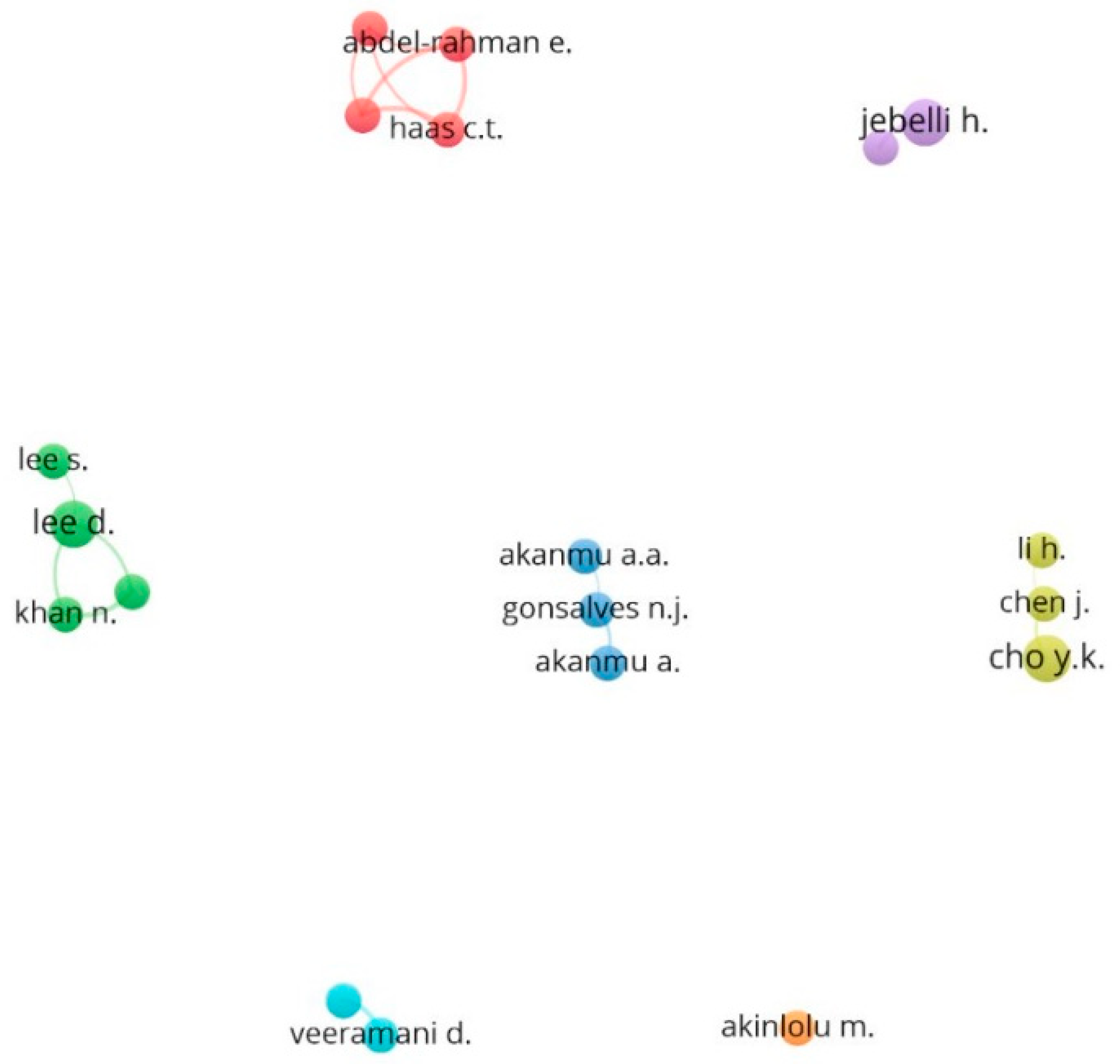
3.4. Coauthorship Analysis
3.5. Country Analysis
4. Discussion
Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alireza Ahankoob, A.A. Mitigating Ergonomic Injuries In Construction Industry. IOSR-JMCE 2013, 6, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, R.; Choi, J. Emerging Trends of Ergonomic Risk Assessment in Construction Safety Management: A Scientometric Visualization Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chander, D.S.; Cavatorta, M.P. An Observational Method for Postural Ergonomic Risk Assessment (PERA). Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2017, 57, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Lee, S. Automated Postural Ergonomic Risk Assessment Using Vision-Based Posture Classification. Autom. Constr. 2021, 128, 103725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.; Nicolakakis, N.; Raïq, H.; Messing, K.; Lippel, K.; Turcot, A. Underreporting Work Absences for Nontraumatic Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders to Workers’ Compensation: Results of a 2007–2008 Survey of the Québec Working Population. Am. J. Public Health 2014, 104, e94–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, X.S.; Choi, S.D.; Dement, J. Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders among Construction Workers in the United States from 1992 to 2014. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 74, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abinaya Ishwarya, G.K.; Rajkumar, D. Analysis of Ergonomic Risk Factors in Construction Industry. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 2415–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, M.N.H.; Jaafar, M.H.; Mohamed, A.S.A.; Azraai, N.Z.; Md Hossain, S. Implementation of Kinetic and Kinematic Variables in Ergonomic Risk Assessment Using Motion Capture Simulation: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menolotto, M.; Komaris, D.-S.; Tedesco, S.; O’Flynn, B.; Walsh, M. Motion Capture Technology in Industrial Applications: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diraneyya, M.M.; Ryu, J.; Abdel-Rahman, E.; Haas, C.T. Inertial Motion Capture-Based Whole-Body Inverse Dynamics. Sensors 2021, 21, 7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.R.; Lee, S.; Sun, C.; Jebelli, H.; Yang, K.; Choi, B. Wearable Sensing Technology Applications in Construction Safety and Health. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2019, 145, 03119007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sekula, P.; Ding, L. Machine Learning in Construction: From Shallow to Deep Learning. Dev. Built Environ. 2021, 6, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baduge, S.K.; Thilakarathna, S.; Perera, J.S.; Arashpour, M.; Sharafi, P.; Teodosio, B.; Shringi, A.; Mendis, P. Artificial Intelligence and Smart Vision for Building and Construction 4.0: Machine and Deep Learning Methods and Applications. Autom. Constr. 2022, 141, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasarainen, M.; Paavola, S.; Vetoshkina, L. A Systematic Literature Review on Extended Reality: Virtual, Augmented and Mixed Reality in Working Life. IJVR 2021, 21, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Kim, K.; Ma, S.; Ueda, J. A Robotic Wearable Exoskeleton for Construction Worker’s Safety and Health. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress 2018, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–4 April 2018; pp. 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Dutta, A.; Dai, F. Exoskeletons for manual material handling – A review and implication for construction applications. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Nussbaum, M.A. Performance Evaluation of a Wearable Inertial Motion Capture System for Capturing Physical Exposures during Manual Material Handling Tasks. Ergonomics 2013, 56, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanko, R.M. Validation of a markerless motion capture system for human movement analysis. In Proceedings of the International Society of Biomechanics XXth Congress & American Society of Biomechanics 29th Annual Meeting, Cleveland, OH, USA, 31 July–5 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, J.; Alwasel, A.; Haas, C.T.; Abdel-Rahman, E. Analysis of Relationships between Body Load and Training, Work Methods, and Work Rate: Overcoming the Novice Mason’s Risk Hump. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 04020097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; McFarland, T.; Haas, C.T.; Abdel-Rahman, E. Automatic Clustering of Proper Working Posture. In Proceedings of the EG-ICE 2020 Workshop on Intelligent Computing in Engineering, Virtual, 1–4 July 2020; pp. 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, R.H.; Rahman, M.; Rahman, M. Comparative Study on Antimicrobial Activity of Four Bangladeshi Medicinal Plants Used as Antimicrobial Finishes on Cotton Fabric. JTSFT 2021, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H. Sustainable Bricks from Thermoplastic Waste and Cost Comparison with Traditional Bricks. JOJMS 2022, 7, 555701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, S.; Khosravani, M.R. Progress and Challenges in Fabrication of Wearable Sensors for Health Monitoring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 312, 112105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilovas, E. Evaluation of Quality and Personalisation of VR/AR/MR Learning Systems. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2016, 35, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Cui, G.; Lu, S. Ambidextrous Learning of Engineering Project Team: Relying on Control or BIM AI VR AR MR? Int. J. Eng. Bus. Manag. 2020, 12, 184797902094874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, D.P.; Lewis, C.L. Robotic Lower Limb Exoskeletons Using Proportional Myoelectric Control. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 2119–2124. [Google Scholar]
- Young, A.J.; Ferris, D.P. State of the Art and Future Directions for Lower Limb Robotic Exoskeletons. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awolusi, I.; Marks, E.; Hallowell, M. Wearable Technology for Personalized Construction Safety Monitoring and Trending: Review of Applicable Devices. Autom. Constr. 2018, 85, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpala, I.; Nnaji, C.; Karakhan, A.A. Utilizing Emerging Technologies for Construction Safety Risk Mitigation. Pract. Period. Struct. Des. Constr. 2020, 25, 04020002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musarat, M.A.; Alaloul, W.S.; Irfan, M.; Sreenivasan, P.; Rabbani, M.B.A. Health and Safety Improvement through Industrial Revolution 4.0: Malaysian Construction Industry Case. Sustainability 2022, 15, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyekum, K.; Pittri, H.; Botchway, E.A.; Amudjie, J.; Kumah, V.M.A.; Kotei-Martin, J.N.; Oduro, R.A. Exploring the Current Technologies Essential for Health and Safety in the Ghanaian Construction Industry. Merits 2022, 2, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, B.; Othman, I.; Pomares, J.C.; Chong, H.-Y. A Research Framework of Mitigating Construction Accidents in High-Rise Building Projects via Integrating Building Information Modeling with Emerging Digital Technologies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, J.; Soave, F.; Bryan-Kinns, N.; Tokarchuk, L.; Farkhatdinov, I. Extended Reality (XR) Remote Research: A Survey of Drawbacks and Opportunities. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 6 May 2021; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Ikuma, L.; Hondzinski, J.; De Queiroz, M. Application of Assistive Wearable Robotics to Alleviate Construction Workforce Shortage: Challenges and Opportunities. In Proceedings of the Computing in Civil Engineering 2017, Seattle, WA, USA, 22 June 2017; pp. 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Chen, C.; Yin, X. Recent Advancements of Robotics in Construction. Autom. Constr. 2022, 144, 104591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peternel, L.; Tsagarakis, N.; Caldwell, D.; Ajoudani, A. Robot Adaptation to Human Physical Fatigue in Human–Robot Co-Manipulation. Auton. Robot. 2018, 42, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuvayanond, W.; Prasittisopin, L. Design for Manufacture and Assembly of Digital Fabrication and Additive Manufacturing in Construction: A Review. Buildings 2023, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxas, C.L.C.; Bautista, C.R.; Dela Cruz, O.G.; Dela Cruz, R.L.C.; De Pedro, J.P.Q.; Dungca, J.R.; Lejano, B.A.; Ongpeng, J.M.C. Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DfMA) and Design for Deconstruction (DfD) in the Construction Industry: Challenges, Trends and Developments. Buildings 2023, 13, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadakorn, W.; Prasertsuk, S.; Prasittisopin, L. 3D Cement Printing: DFMA Guideline of Patterned Load-Bearing Walls for Small Residential Units. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Civil Engineering and Architecture, Hanoi, Vietnam, 16–18 December 2022; Kang, T., Ed.; Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2024; Volume 369, pp. 19–28, ISBN 978-981-9940-48-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, J.; Seo, J.; Jebelli, H.; Lee, S. Automated Action Recognition Using an Accelerometer-Embedded Wristband-Type Activity Tracker. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2019, 145, 04018114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Diraneyya, M.M.; Ryu, J.; Haas, C.T.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M. Jerk as an Indicator of Physical Exertion and Fatigue. Autom. Constr. 2019, 104, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; McFarland, T.; Haas, C.T.; Abdel-Rahman, E. Automatic Clustering of Proper Working Postures for Phases of Movement. Autom. Constr. 2022, 138, 104223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Banting, B.; Abdel-Rahman, E.; Haas, C.T. Ergonomic Characteristics of Expert Masons. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2023, 149, 04022150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diego-Mas, J.A.; Alcaide-Marzal, J.; Poveda-Bautista, R. Effects of Using Immersive Media on the Effectiveness of Training to Prevent Ergonomics Risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onososen, A.O.; Musonda, I. Research Focus for Construction Robotics and Human-Robot Teams towards Resilience in Construction: Scientometric Review. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2023, 21, 502–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.T.; Adamczyk, P.G.; Dai, F.; Veeramani, D.; Senior, M.W. Upper Extremity Exoskeletons in Construction, a Field-Based Study. In Proceedings of the ICRA 2022 Future of Construction Workshop, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xue, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X. Exploring the Emerging Evolution Trends of Urban Resilience Research by Scientometric Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. VOSviewer Manual; Universiteit Leiden: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-Tool for Comprehensive Science Mapping Analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rumman, A. Scopus Content Coverage Guide. 2019. Available online: https://www2.scopus.com/authid/detail.uri?authorId=57203454424 (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- McBurney, M.K.; Novak, P.L. What Is Bibliometrics and Why Should You Care? In Proceedings of the IEEE International Professional Communication Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 20 September 2002; IEEE: Portland, OR, USA, 2002; pp. 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.R.; Wuest, T. A Review of Sustainable Composites Supply Chains. In Advances in Production Management Systems. Smart Manufacturing and Logistics Systems: Turning Ideas into Action; Kim, D.Y., Von Cieminski, G., Romero, D., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 663, pp. 448–455. ISBN 978-3-031-16406-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, B.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; Sepasgozar, S.; Luo, H.; He, L. A Scientometric Analysis and Critical Review of Construction Related Ontology Research. Autom. Constr. 2019, 101, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, H.; Shafie, M.R.; Hajiabadi, M.; Raihan, A.S.; Ahmed, I. Chatbots and ChatGPT: A Bibliometric Analysis and Systematic Review of Publications in Web of Science and Scopus Databases. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.05436. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Nordin, N.A.; Aini, A.M. Urban Green Space and Subjective Well-Being of Older People: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.; Diraneyya, M.M.; Haas, C.T.; Abdel-Rahman, E. Analysis of the Limits of Automated Rule-Based Ergonomic Assessment in Bricklaying. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2021, 147, 04020163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Seo, J.; Ryu, J.; Lee, S. Challenges and Opportunities of Understanding Construction Workers’ Physical Demands through Field Energy Expenditure Measurements Using a Wearable Activity Tracker. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress 2016, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 24 May 2016; pp. 2730–2739. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.; Seo, J.; Jebelli, H.; Lee, S. Feasibility Analysis of Heart Rate Monitoring of Construction Workers Using a Photoplethysmography (PPG) Sensor Embedded in a Wristband-Type Activity Tracker. Autom. Constr. 2016, 71, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebelli, H.; Lee, S. Feasibility of Wearable Electromyography (EMG) to Assess Construction Workers’ Muscle Fatigue. In Advances in Informatics and Computing in Civil and Construction Engineering; Mutis, I., Hartmann, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 181–187. ISBN 978-3-030-00219-0. [Google Scholar]
- Motabar, H.; Nimbarte, A.D. The Effect of Task Rotation on Activation and Fatigue Response of Rotator Cuff Muscles during Overhead Work. Appl. Ergon. 2021, 97, 103461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Pan, L.; Fang, H.; Wu, X.; Yu, H.; Cai, S.; Yu, B.; Wan, Y. Academic Review and Perspectives on Robotic Exoskeletons. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 2294–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A. A Comparative Study to Explore the Advantages of Passive Exoskeletons by Monitoring the Muscle Activity of Workers 2021; University of Gävle: Gävle, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Renner, T. Exoskeleton with Lightweight Plastic Components Finds Applications in Medicine, Manufacturing, and Agriculture. Plast. Eng. 2018, 74, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Maeda, J. The SMART System: An Integrated Application of Automation and Information Technology in Production Process. Comput. Ind. 1998, 35, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; McFarland, T.; Banting, B.; Haas, C.T.; Abdel-Rahman, E. Health and Productivity Impact of Semi-Automated Work Systems in Construction. Autom. Constr. 2020, 120, 103396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, I.; Skitmore, M. Three-Dimensional Printing in the Construction Industry: A Review. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2015, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnagrat, A.J.A.; Ismail, R.; Idrus, S.Z.S. The Significant and Challenges of Extended Reality Technologies in Learning and Training during Covid-19 Pandemic. J. Hum. Centered Technol. 2022, 1, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, B.; See, Z.S.; Day, J. Crisis and Extended Realities: Remote Presence in the Time of COVID-19. Media Int. Aust. 2021, 178, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, T.; Wilczewski, H.; Paige, S.R.; Soni, H.; Welch, B.M.; Bunnell, B.E. Extended Reality for Enhanced Telehealth during and beyond COVID-19. JMIR Serious Games 2021, 9, e26520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.S.Y. Use of Extended Reality in Medicine during the COVID-19 Pandemic. In Extended Reality Usage During COVID 19 Pandemic; Pillai, A.S., Guazzaroni, G., Eds.; Intelligent Systems Reference Library; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 216, pp. 1–14. ISBN 978-3-030-91393-9. [Google Scholar]
- Osei-Kyei, R.; Narbaev, T.; Ampratwum, G. A Scientometric Analysis of Studies on Risk Management in Construction Projects. Buildings 2022, 12, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redzwan, N.; Ramli, R. A Bibliometric Analysis of Research on Stochastic Mortality Modelling and Forecasting. Risks 2022, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, S.; Liang, Y.; Ahmad, W.; Althoey, F.; Alyami, S.H.; Javed, M.F.; Deifalla, A.F. A Scientometric Review on Mapping Research Knowledge for 3D Printing Concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Ahmad, W.; Amin, M.N.; Nazar, S. A Scientometric-Analysis-Based Review of the Research Development on Geopolymers. Polymers 2022, 14, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Kong, L.; Luo, X.; Wong, A.Y.L. An Automatic and Non-Invasive Physical Fatigue Assessment Method for Construction Workers. Autom. Constr. 2019, 103, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, S.; Li, H.; Antwi-Afari, M.F.; Wong, A.Y.L. Associations between Physical or Psychosocial Risk Factors and Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders in Construction Workers Based on Literature in the Last 20 Years: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2021, 83, 103113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E.L.; Teizer, J. Real-Time LiDAR for Monitoring Construction Worker Presence Near Hazards and in Work Areas in a Virtual Reality Environment. In Proceedings of the EG-ICE 2021 Workshop on Intelligent Computing in Engineering, Berlin, Germany, 30 June–2 July 2021; pp. 592–602. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, E.L.; Solberg, A.; Golovina, O.; Teizer, J. Active Personalized Construction Safety Training Using Run-Time Data Collection in Physical and Virtual Reality Work Environments. Constr. Innov. 2022, 22, 531–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cho, Y.K. Rapid Scan-to-Building Information Modeling Using Robotics and Artificial Intelligence for Construction Applications. Res. Companion Build. Inf. Model. 2022, 212–229. [Google Scholar]
- Umeokafor, N.; Umar, T.; Evangelinos, K. Bibliometric and Scientometric Analysis-Based Review of Construction Safety and Health Research in Developing Countries from 1990 to 2021. Saf. Sci. 2022, 156, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Seo, J.; Liu, M.; Lee, S.; Haas, C.T. Action Recognition Using a Wristband-Type Activity Tracker: Case Study of Masonry Work. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress 2016, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 24 May 2016; pp. 790–799. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Diraneyya, M.M.; Ryu, J.; Haas, C.T.; Abdel-Rahman, E. Automated Monitoring of Physical Fatigue Using Jerk. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, Banff, AB, Canada, 21–24 May 2019; Volume 36, pp. 989–997. [Google Scholar]
- Darbandy, M.; Rostamnezhad, M.; Hussain, S.; Khosravi, A.; Nahavandi, S.; Sani, Z. A New Approach to Detect the Physical Fatigue Utilizing Heart Rate Signals. Res. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 9, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanavelu, K.; Lamshe, R.; Poonguzhali, S.; Adalarasu, K.; Jagannath, M. Assessment of Human Fatigue during Physical Performance Using Physiological Signals: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2017, 10, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Sun, Y. A Muscle Fatigue Classification Model Based on LSTM and Improved Wavelet Packet Threshold. Sensors 2021, 21, 6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.; Lo, C.-Y. Smart Manufacturing Powered by Recent Technological Advancements: A Review. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 64, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amin, M.; Qin, R.; Tao, W.; Leu, M.C. Sensor Data Based Models for Workforce Management in Smart Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 2018 Institute of Industrial and Systems Engineers Annual Conference (IISE 2018), Orlando, FL, USA, 19–22 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, F.; Kelley, K. Connecting Hands and Heads: Retooling Engineering Technology for the “Smart” Manufacturing Workplace. Econ. Dev. Q. 2020, 34, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, R.; Chowdhury, N.I.; Rahman, H.; Syed, A.B.; Ryu, J. Analysis of the User Perception of Chatbots in Education Using A Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling Approach. 2017. arXiv 2017, arXiv:2311.03636. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Jang, H.S.; Choi, S. Strategies for Contractors to Sustain Growth in the Global Construction Market. Habitat Int. 2010, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Category | Source | Numbers (N) | Citations (C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wearable sensors | Automation in Construction | 9 | 244 |
| Journal of Construction Engineering and Management | 7 | 233 | |
| Construction Research Congress | 5 | 13 | |
| Advanced Engineering Informatics | 4 | 73 | |
| Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management | 4 | 11 | |
| Sensors | 3 | 79 | |
| Journal of Building Engineering | 2 | 29 | |
| Safety Science | 2 | 79 | |
| XR | Automation in Construction | 12 | 790 |
| Construction Research Congress | 9 | 29 | |
| Advanced Engineering Informatics | 7 | 114 | |
| Construction Innovation | 7 | 62 | |
| Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management | 6 | 103 | |
| Journal of Construction Engineering and Management | 5 | 39 | |
| Proceedings of the International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction | 5 | 7 | |
| ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition, Conference Proceedings | 4 | 1 | |
| International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 4 | 426 | |
| Safety Science | 4 | 67 | |
| Smart and Sustainable Built Environment | 4 | 25 | |
| Exoskeletons and robotics | Proceedings of the International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction | 35 | 106 |
| Automation in Construction | 5 | 202 | |
| Computing in Civil Engineering | 4 | 5 | |
| Construction Research Congress | 3 | 5 |
| Category | Author | Documents (N) | Citations (C) | Total Link Strength (T) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wearable sensors | Li, H. | 10 | 276 | 34 |
| Umer W. | 7 | 154 | 26 | |
| Antwi-Afari M.F. | 6 | 76 | 22 | |
| Anwer S. | 5 | 49 | 18 | |
| Nnaji C. | 5 | 53 | 6 | |
| Wong A.Y.L. | 5 | 137 | 19 | |
| Awolusi I. | 4 | 50 | 5 | |
| Choi B. | 4 | 230 | 10 | |
| Jebelli H. | 4 | 230 | 10 | |
| Lee S. | 4 | 174 | 9 | |
| Obonyo E. | 4 | 49 | 4 | |
| Zhao J. | 4 | 49 | 4 | |
| XR | Teizer J. | 9 | 62 | 16 |
| Gheisari M. | 6 | 170 | 4 | |
| Ahn C.R. | 5 | 136 | 4 | |
| Esmaeili B. | 5 | 105 | 3 | |
| Li X. | 5 | 516 | 4 | |
| Mora-Serrano J. | 5 | 22 | 3 | |
| Hasanzadeh S. | 4 | 8 | 1 | |
| Jacobsen E.L. | 4 | 15 | 5 | |
| Jeelani I. | 4 | 50 | 6 | |
| Kim N. | 4 | 33 | 4 | |
| Li J. | 4 | 16 | 2 | |
| Wang X. | 4 | 846 | 4 | |
| Exoskeletons and robotics | Cho Y.K. | 4 | 78 | 2 |
| Jebelli H. | 4 | 7 | 3 | |
| Lee D. | 4 | 20 | 5 | |
| Abdel-Rahman E. | 3 | 35 | 8 | |
| Akanmu A. | 3 | 3 | 2 | |
| Akanmu A.A. | 3 | 42 | 1 | |
| Akinlolu M. | 3 | 44 | 0 | |
| Chen J. | 3 | 46 | 3 | |
| Gonsalves N.J. | 3 | 12 | 3 | |
| Haas C.T. | 3 | 35 | 8 | |
| Khan N. | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Lee S. | 3 | 141 | 1 |
| Category | Country | Numbers (N) | Citations (C) | Total Link Strength (T) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wearable sensors | United States | 29 | 444 | 6 |
| Hong Kong | 11 | 294 | 14 | |
| China | 10 | 167 | 6 | |
| South Korea | 6 | 216 | 7 | |
| United Kingdom | 5 | 68 | 9 | |
| Saudi Arabia | 4 | 54 | 8 | |
| Canada | 3 | 20 | 3 | |
| Australia | 2 | 10 | 1 | |
| XR | United States | 46 | 571 | 4 |
| China | 17 | 487 | 15 | |
| Australia | 15 | 926 | 13 | |
| United Kingdom | 13 | 106 | 11 | |
| Hong Kong | 9 | 901 | 14 | |
| South Korea | 9 | 880 | 7 | |
| Denmark | 8 | 56 | 5 | |
| Chile | 7 | 30 | 7 | |
| Germany | 7 | 51 | 4 | |
| Spain | 6 | 34 | 6 | |
| Canada | 5 | 42 | 0 | |
| Italy | 5 | 122 | 0 | |
| New Zealand | 5 | 576 | 7 | |
| South Africa | 5 | 48 | 3 | |
| Exoskeletons and robotics | United States | 47 | 601 | 6 |
| China | 15 | 160 | 9 | |
| Hong Kong | 10 | 119 | 8 | |
| Italy | 8 | 69 | 1 | |
| South Korea | 8 | 27 | 2 | |
| Canada | 7 | 41 | 0 | |
| India | 7 | 36 | 1 | |
| United Kingdom | 7 | 243 | 8 | |
| Germany | 6 | 48 | 0 | |
| South Africa | 6 | 94 | 1 | |
| Japan | 5 | 8 | 0 | |
| Australia | 4 | 22 | 2 | |
| Switzerland | 4 | 89 | 4 | |
| United Arab Emirates | 4 | 60 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, M.H.; Ghasemi, A.; Dai, F.; Ryu, J. Review of Emerging Technologies for Reducing Ergonomic Hazards in Construction Workplaces. Buildings 2023, 13, 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13122967
Rahman MH, Ghasemi A, Dai F, Ryu J. Review of Emerging Technologies for Reducing Ergonomic Hazards in Construction Workplaces. Buildings. 2023; 13(12):2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13122967
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Md Hadisur, Alireza Ghasemi, Fei Dai, and JuHyeong Ryu. 2023. "Review of Emerging Technologies for Reducing Ergonomic Hazards in Construction Workplaces" Buildings 13, no. 12: 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13122967
APA StyleRahman, M. H., Ghasemi, A., Dai, F., & Ryu, J. (2023). Review of Emerging Technologies for Reducing Ergonomic Hazards in Construction Workplaces. Buildings, 13(12), 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13122967









