Abstract
Choosing a proper construction project is a vital subject for entrepreneurs to reduce their costs. In real cases, vagueness and uncertain data drive decisions based on uncertainty. The intuitionistic fuzzy sets (IFSs) theory could assist decision-makers (DMs) in inscribing inadequate knowledge. Nevertheless, this paper provides a new integrated decision analysis model with IFSs. The suggested procedure includes a new decision flow under uncertain situations to define the significance of criteria. In this regard, the weighting of subjective DMs is required for this manner; the only input data needed are an alternative evaluation matrix. Then, a case study on sustainable energy project selection is explained to show the purpose of the suggested model. In this regard, four main criteria, technological, economic, social, and environmental, and seven alternatives from different kinds of energies are introduced to select the appropriate energy project. In this model, the weights of criteria are defined based on a new combined method based on two CRITIC and ideal points approaches. The proposed soft computing model computed the ranking of main alternatives by integrating the ARAS and EDAS approaches; the final outcomes indicate that the second alternative has higher values than other alternatives concerning nuclear energy. Afterward, sensitivity and comparative analyses are generated to determine the efficiency and validity of the proposed model. The sensitivity analysis changes the criteria weights. The comparative analysis compares the IF-TOPSIS method and the proposed model and computes the different degrees to confirm the efficiency of the introduced soft computing model.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, one of the most important projects in various types of industries is construction projects. This kind of project has different significant practices, which affect management operations [1]. Prior papers have determined that the construction project and its operations have considerable effects on the environment [2,3]. Moreover, the construction sector is distinguished from other industrial sectors by the long-term nature of its output [4]. The sustainable execution of a construction project over its life cycle is an essential perspective in achieving sustainable development goals. The reports of the World Commission on Environment and Development describe sustainable development as meeting the basic needs of society and satisfying their hopes for better life without compromising the capabilities of future generations. The concept of sustainable development is based on the balance among social, economic, and environmental dimensions [4,5].
Sustainability has diverse varieties of criteria that are related to its different aspects. The selection of each criterion is critical in the management of construction projects. The selection of criteria is performed regularly by decision-makers (DMs) and/or through participatory procedures, as well as by integrating existing sets of criteria provided in the literature. However, the knowledge about the robustness of the selection phase, its utility, accuracy, validity, and feasibility are usually limited [6]. In this respect, the multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) approaches are utilized to select the appropriate criteria for the evaluation of construction projects. Furthermore, the main alternatives for the construction projects are chosen using MCDM methods.
In the procedure of decision making, the data about attributes are regularly uncertain or fuzzy due to the expanding complexity of the real application situation and the vagueness of the natural subjective reality of human thinking. This reality has encouraged many authors to utilize the fuzzy set theory to model the uncertainty and vagueness in decision flows. Moreover, the fuzzy set theory is applied to management decision-making problems [7,8]. However, to overcome the disadvantage of fuzzy sets (FSs), the intuitionistic fuzzy set (IFS) was proposed by joining a non-membership degree. The notion of IFSs is introduced as an extension of the FS. Apart from the degree of membership, which is presented in the FS, in IFSs, a degree of non-membership is added. These two degrees may not add up to one, and the complement of their sum to one is the so-called degree of uncertainty. The IFS represents an object simultaneously from both the advantage and disadvantage aspects. The last two decades have observed the strong expansion of the IFSs since they address the fuzziness of things more comprehensively [9]. The IFS helps to increase the closeness of the problem to real-world applications [10].
In the literature, the use of fuzzy logic in solving various problems in the construction sector, where incomplete and imprecise information exists, has been widely recognized [11]. Many fuzzy-based methods and techniques have been proposed to solve various decision-making problems. One of the main aims of reviewing the literature is to determine the strength points of the proposed integrated soft computing model and the lack of this method to select the appropriate alternatives in different uncertain conditions. For instance, Florez et al. [12] described the effect of sustainability on the selection of optimal materials in a construction project. They aimed at maximizing the number of LEED material-related credits. Ebrahimnejad et al. [13] proposed a two-phase group decision-making approach to evaluate and select a construction project under fuzzy conditions. Rezakhani [14] introduced the fuzzy MCDM technique to choose the appropriate risk factor in construction projects. Tsai et al. [15] generated the MCDM-based approach for the selection of construction methods in green building projects. Dėjus and Antuchevičienė [16] proposed an MCDM method based on WASPAS and entropy approaches to assess the safety and health solutions in the construction site. Tamošaitienė et al. [17] assessed the risk of a commercial center construction project with an MCDM method under fuzzy conditions. The study used a technique for order of preference by similarity to the ideal solution (TOPSIS)-F method to rank objects with an optimality degree. Taylan et al. [18] proposed a selection procedure to assess the construction project risk with the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and TOPSIS methods in fuzzy environments. Mousavi et al. [10] introduced a fuzzy grey approach to select the options in the inception planning of the manufacturing process. Gitinavard and Mousavi [19] assessed a construction project with a new MCDM approach based on IF conditions. Mousavi and Mousavi et al. [20] presented an IF VIKOR multi-attribute group decision-making approach for complex decision-making problems. The paper used two application examples to validate the provided approach. Prascevic and Prascevic [21] expanded a fuzzy AHP method to select and rank the alternatives for the construction project management. Pavlovskis et al. [22] evaluated the redevelopment building possibilities with an MCDM method and BIM approach. Chatterjee et al. [23] proposed an integrated MCDM method to assess the management risk of the construction project. Wang et al. [24] evaluated the risks of construction projects with an MCDM approach based on the VIKOR method under fuzzy conditions. Dahooie et al. [25] used the additive ratio assessment (ARAS) method with fuzzy interval values to assess the project. This paper applied a case study of oil and gas drilling. Atanassov et al. [26] proposed a generalized net model by considering the multi-criteria decision-making method using an intercriteria analysis. This paper introduced an index matrix of elements regarding the dependencies between the criteria under IF situations. Chalekaee et al. [27] proposed an integrated MCDM approach to evaluate the change response delay of the construction project under the grey numbers requirement. Davoudabadi et al. [28] introduced a compromise solution with a linear assignment method under uncertainty conditions to select the construction project. Afterwards, Gunduz and Khader [29] utilized an analytic network process (ANP) approach to evaluate safety performance management in construction projects. Mohandes et al. [30] developed a new risk assessment model to assess construction labors’ safety level. The research integrated the fuzzy best–worst method (FBWM) with the interval-valued fuzzy TOPSIS (IVFTOPSIS). Fallahpour et al. [31] proposed an integrated fuzzy programming with an MCDM method to select an appropriate decision in construction projects under sustainability requirements. This paper developed a combination of fuzzy preference programming (FPP) as a modification of the fuzzy AHP approach to evaluate the sustainability of construction projects. Zhang et al. [32] used a hybrid multi-expert multi-criteria decision-making model by integrating the best–worst method (BWM) and combined compromise solution (CoCoSo) method based on the rough boundary intervals for a supplier selection in housing development. Peng et al. [33] proposed an integrated multi-criteria decision-making framework for sustainable supplier selection under picture fuzzy environment.
Mousavi et al. [34] proposed a hesitant fuzzy ELECTRE I-based MCDM method to evaluate risk preferences in an imprecise setting in flexible manufacturing systems. Banihashemi et al. [35] introduced a fuzzy SWARA–TOPSIS approach for construction scheduling to assess trade-off among time-cost and quality. Tamošaitienė et al. [36] applied the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process (FAHP) technique to prioritize the criteria of appropriate repair and maintenance methods for commercial buildings. Naik et al. [37] introduced an MCDM method based on criteria importance through intercriteria correlation (CRITIC) and evaluation based on distance from the average solution (EDAS) approach to compute the weights and rankings of alternatives, respectively. Kao et al. [38] proposed a fuzzy MCDM model to select the supplier in supply chain management. Li et al. [39] provided LGBWM and IFNs to select personnel with a data-driven decision-making structure. Seker and Kahraman [40] introduced a Pythagorean cubic fuzzy approach based on the TOPSIS and TODIM methods to select suitable software. Zhang and Chen [41] generated the multi-criteria group decision-making approach by considering the cloud model and TOPSIS method to determine the alternative under an uncertain condition. Salimian et al. [42] proposed a new combined model based on extended VIKOR and MARCOS approaches to select a sustainable supplier in organ transplantation networks with respect to interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy (IVIF). Salimian et al. [43] introduced the integrated IVIF model based on the RPR, MABAC, and WASPAS approaches in an infrastructure project assessment problem. Ghorui et al. [44] introduced the MCDM methodology with IF uncertainty requirements to select the cloud service providers.
This paper proposes the integration of approaches to obtain the weights of criteria and the ranking of alternatives, where weights of criteria are computed by combining the CRITIC and ideal point methods, and the ranks of alternatives are calculated by integrating the EDAS and ARAS approaches under uncertainty. Moreover, this paper utilizes IFSs to increase the accuracy of the decision process from DMs to make a suitable decision in real-world applications. Afterward, a real case study is presented to validate the efficiency of the proposed integrated soft computing model. The main contributions of the paper are as follows:
- Introducing a new integrated weighting method based on the CRITIC and ideal point approaches under uncertainty.
- Extending an ideal point approach for weighting criteria in an IF environment.
- Proposing a new combined ranking method based on the ARAS and EDAS approaches under uncertainty.
- Expanding an MCDM problem for the weighting and ranking of IFS situations.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Preliminaries of IFSs are presented in Section 1. The details of the proposed approach are given in Section 2. The real case study is presented in Section 3. The sensitivity analysis and comparative analysis are presented in Section 4 and Section 5. Finally, conclusions and future research directions are given.
2. Preliminaries
This section presents the basic definitions related to the notion of IFSs. These formulations are determined as follows.
Definition 1.
Let R be a universe of discourse. The IFS P from R is a goal presented in Equation (1) [45]:
where is the value of the membership function, and the value of non-membership function is . Moreover, is the hesitance degree. Hence, each is presented as
Definition 2.
Let Y and T be two IFSs from a set of R. The significant operators are described in Equations (2)–(8) [46,47]:
Definition 3.
Score function is computed by Equation (9) [48]:
Definition 4.
Euclidean distance is computed by Equation (10) [49]:
Definition 5.
Positive and negative normalized matrixes IF are introduced in Equation (11) :
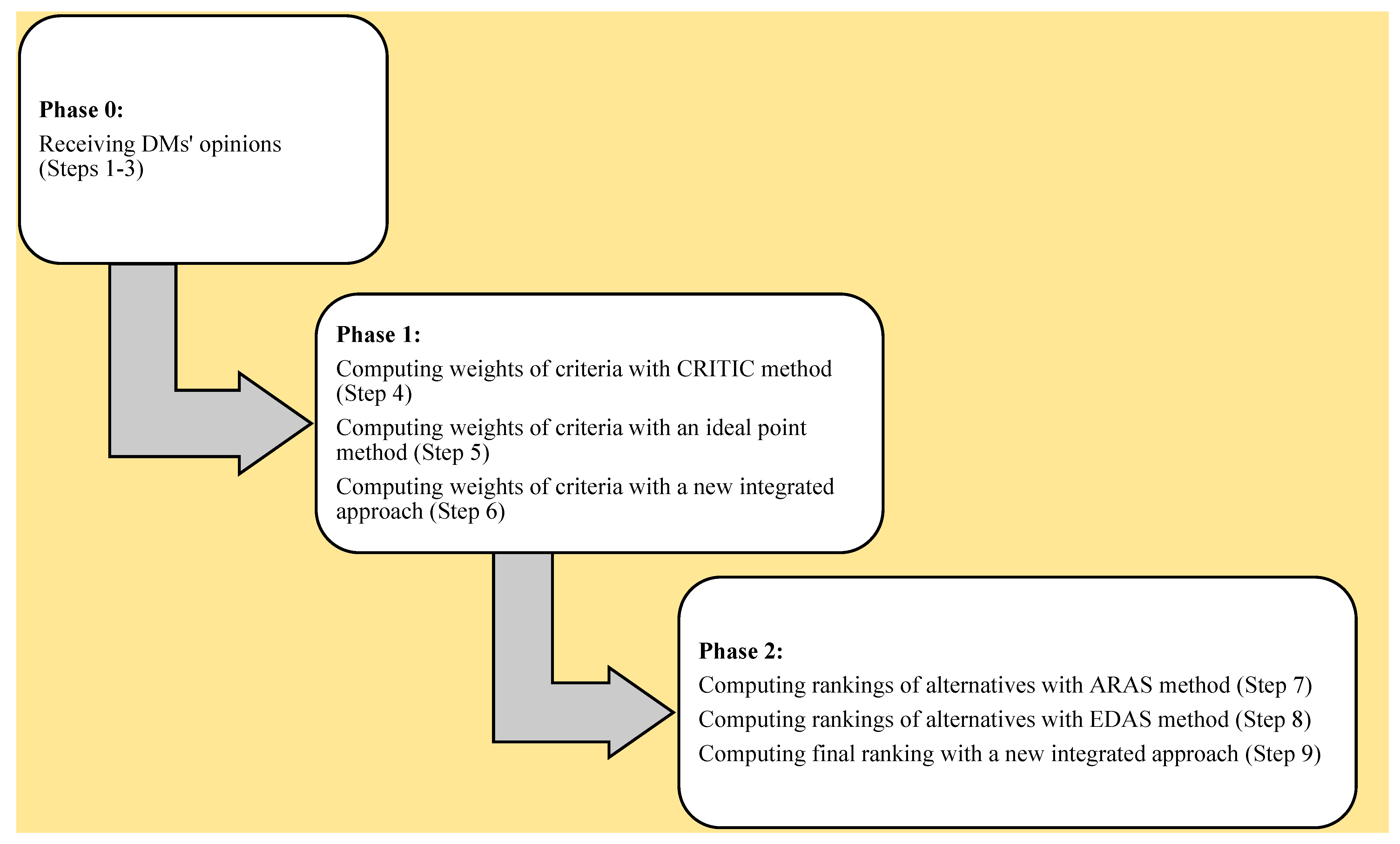
3. Proposed New Integrated Soft Computing Model
This section proposes an integrated soft computing approach to obtain the weights of the criteria (j = 1, 2, …, m) and ranks of alternatives (i = 1, 2, …, n) through DMs’ opinions (k = 1, 2, …, K). The provided model is based on recent literature [50,51,52,53]. This model contains three phases: data gathering in Phase 0, weighting of criteria in Phase 1, and ranking of alternatives in Phase 2. In this respect, the information is collected from each DM, and the procedure starts to compute the weights of the criteria by an integrated approach based on the CRITIC and ideal point methods. The proposed integrated weighting method has advantages of both the CRITIC and ideal point approaches. The CRITIC method composes total priority data included in the assessment criteria based on the analysis of the evaluation matrix. Therefore, the objective weight is performed by quantifying the inherent knowledge of each estimation criterion. The procedure of specifying objective weight does not contain the criteria’s standard deviation; it includes the correlation between criteria and other criteria [54]. Furthermore, the advantage of the ideal point procedure for the complex MCDM problem is that it can develop entire sets of weights for each criterion [55]. Hence, the proposed method has the main advantages of both weighting methods. Afterward, a new integrated method is used to obtain the rankings of alternatives by the ARAS and EDAS methods. The proposed combined ranking method employs advantages of both the ARAS and EDAS approaches. For this reason, the ARAS method is provided to improve the deviations of score values from the optimal degrees [56]. Other advantages of the ARAS method are that the calculations described in the modeling procedure of the decision-making problem are specific; moreover, the issues have a deep sense [57]. The main advantage of the EDAS method is that it has high efficiency and requires less calculation in comparison with other decision-making problems and a variety of approaches [58]. According to the previous explanations, the proposed ranking method is an efficient approach that has advantages of both the ARAS and EDAS methods concurrently. This approach includes an uncomplicated mathematical structure for the purpose of finding the best alternative. The model is presented in an IF environment. In other words, the main usage of this paper is regarded as the selection and evaluation problem that has sensitivity and needs to select the suitable situation in a high-risk environment. The real-world applications need to make an appropriate decision or select the better option. For this reason, the proposed soft computing model has the advantage of using the ARAS and EDAS methods under IF conditions. This method, by gathering expert opinions, helps to compute the ranking of the alternatives based on the best mentions. Moreover, this method adds the weights of the criteria and DMs that have an impact on the final outcomes. In this respect, the main advantages of using the IFS are described below:
- IFSs evaluate both benefits (memberships) and weaknesses (non-memberships) of a considered answer, and the ambiguous area is taken into account, as well [59].
- IFSs transform an unclear practice unit problem into a specific and well-described optimization problem.
- IFSs, unlike ordinary fuzzy sets, keep a metric degree of uncertainty [60].
- The IFS separates the positive and negative information for membership of an element in the set [61].
The steps of the proposed new integrated soft computing model are below:
Phase 0. Gathering the different DMs’ opinions.
Step 1. Computing the decision matrix from experts’ judgments by Equation (12).
This step creates a decision matrix with dimensions i and j based on the DMs’ opinions to compute the weights of the criteria with a proposed integration approach.
Step 2. Aggregating the decision matrix with subjective DMs’ weights.
In this step, the effect of the DMs’ opinions is applied by considering the weights of each expert on the decision-making matrix elements.
Step 3. Normalizing the decision matrix by Definition 5.
In this respect, the aggregated decision matrix with the different DMs’ opinions is normalized according to Definition 5 by considering the positive and negative natures of the criteria.
Phase 1. Computing the criteria weights.
Step 4. Calculating the weights of criteria by the CRITIC method with the following sub-steps:
Sub-step 4.1. Computing the score function by Definition 3.
This step computes the score function according to Definition 3 by considering the membership and non-membership values of the criteria.
Sub-step 4.2. Computing the standard deviation of criteria by Equation (14):
This step obtains the standard deviation of the criteria using the aggregation operator to aggregate the alternatives.
Sub-step 4.3. Calculating the correlation degree between pairs of criteria with Equation (16):
where is a symmetric matrix with dimensions .
Sub-step 4.4. Obtaining the quantities of information about criteria by Equation (17):
This step computes the quantities of criteria information by utilizing the correlation degree between criteria, which is calculated from a symmetric matrix.
Sub-step 4.5. Computing the weights of criteria by Equation (18):
The criteria weights are computed from information quantity degrees and take values between 0 and 1.
Step 5. Computing the weights of criteria by an extended ideal point approach.
Sub-step 5.1. Constructing the weighted decision matrix by Equation (19):
In this step, the impact of criteria weights is determined in the decision matrix. The primary values of criteria weights that are used in this step are taken from the CRITIC results.
Sub-step 5.2. Computing the ideal point , where . Moreover, the ideal value of each criterion is computed by .
Sub-step 5.3. Obtaining the difference between alternative i and the ideal point by Equation (20):
In this step, the difference degree is computed from the Euclidean distance formulation that is presented in Definition 4.
Sub-step 5.4. Constructing an optimization model using the linear equal weight summation method by Equation (21):
s.t.
This step presents a linear mathematical formulation to optimize the summation value weight of the equal linear method.
Sub-step 5.5. Computing the Lagrange form of the model by Equation (23):
In this formulation, is a Lagrange multiplier. The Hessian matrix of L with regard to is n × n oblique matrix with oblique details as . Because the constraint (22) is a non-empty convex set and the objective function (21) is convex, the optimal solutions would be the global optimal solutions, which are achieved by modifying L with respect to and together:
Sub-step 5.6. Computing the weights of criteria with differentiations of L form and by Equation (25):
Step 6. Obtaining normalized final weights of criteria by Equation (26):
where .
This step obtains the final criteria weights by considering the integration approach that uses one aggregation value . Therefore, the final criteria weights take values between 0 and 1.
Phase 2. Computing the ranking of the alternatives.
Step 7. Computing the ranking of the alternatives by using the ARAS method.
Sub-step 7.1. Obtaining a normalized weighted decision matrix from Equation (28):
This step uses the final criteria weights that are obtained from the proposed integrated weighting approach and shows the effect of the criteria weight on the decision matrix and final ranking results directly.
Sub-step 7.2. Calculating the overall performance rating () and utility degree () from the score function that is computed from the matrix by Definition 3:
where is an optimal value that is introduced in Equations (31) and (32) for benefit and cost nature criteria, respectively:
Step 8. Calculating the rankings of alternatives by the EDAS method.
Sub-step 8.1. Computing the average value in regards to the criteria by Equation (33):
This step computes the average value by considering the normalized weighted matrix.
Sub-step 8.2. Calculating the positive and negative ideal distances from the average value by Equations (34) and (35), respectively:
Sub-step. 8.3. Computing the weighted summation of the positive and negative distances by Equations (36) and (37):
Sub-step. 8.4. Normalizing the positive and negatives distances by Equations (38) and (39):
Sub-step 8.5. Obtaining the score function for and by Definition 4.
This step considers the score function regarding the membership and non-membership values of each alternative.
Sub-step 8.6. Computing the assessment score of each alternative from Equation (40):
Step 9. Calculating the final rankings of alternatives from Equation (41):
where .
This step computes the final rankings of alternatives by considering the integrated value . The final rank is computed with descending degrees of alternatives’ scores. The framework of the introduced model is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Structure of the introduced model.
4. Case Study
This section introduces a real case study to validate the efficiency of the suggested soft computing approach. This section utilizes the proposed model to select an appropriate sustainable energy project. This case was generated in an energy project environment that was provided by Kaya and Kahraman [62].
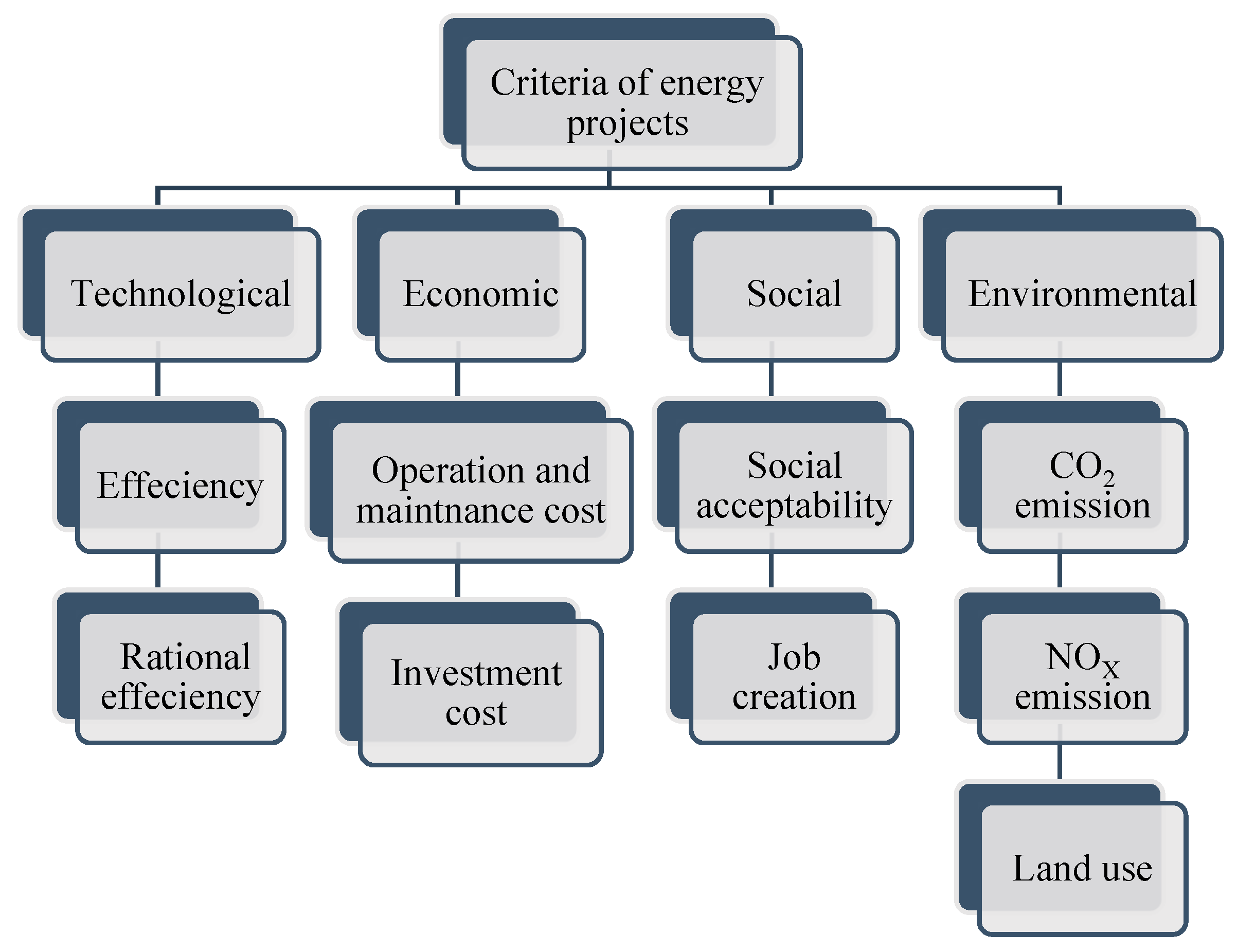
In this respect, seven alternatives are proposed with various kinds of energy projects. These alternatives consist of conventional (), nuclear (), solar (), wind (), hydraulic (), biomass (), and combined heat and power () energy installations. Moreover, nine criteria are introduced in four categories: technological, economic, social, and environmental. The interrelations among these criteria are shown in Figure 2 (Kaya and Kahraman, 2011). In this regard, three DMs are invited to judge the values of decision matrix. In addition, the subjective weights of the DMs are introduced from the study of Davoudabadi et al. [28]. Moreover, Table 1 determines the linguistic values of the IFS (Hashemi et al., 2013). Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 present the experts’ opinions to construct the decision matrixes with the linguistic variables. Moreover, the third, fourth, seventh, and eighth criteria have cost nature, and the others have benefit nature. For example, Table 2 shows , which, compared to second alternative, has a very low degree that is kept from the first DM, and this point is shown with IF value [0.10, 0.75].
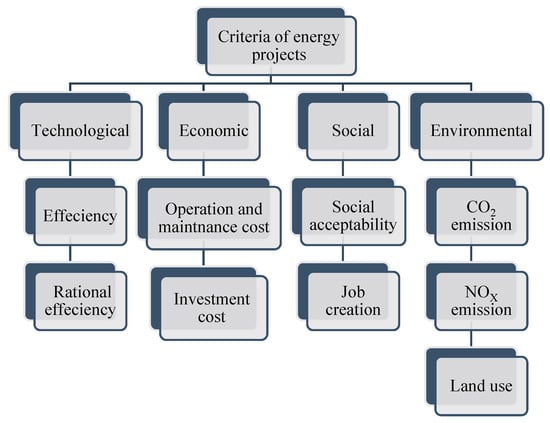
Figure 2.
Criteria for assessment of energy projects.

Table 1.
Linguistic terms for expert judgments.

Table 2.
Linguistic variables decision matrix from the first DM.

Table 3.
Linguistic variables decision matrix from the second DM.

Table 4.
Linguistic variables decision matrix from the third DM.
The normalized decision matrix is shown in Table 5. The score matrix in the CRITIC method is given in Table 6. Furthermore, the symmetric score matrix with dimensions is determined in Table 7. These are calculated from Definition 4. The quantities of and are demonstrated in Table 8. Moreover, in ideal point method, the amounts of and are determined in Table 9. After that, the values of are reported in Table 10. Furthermore, the value of Z = 0.36051.

Table 5.
Normalized decision matrix.

Table 6.
Score matrix.

Table 7.
Score of symmetric matrixes.

Table 8.
Amounts of and .

Table 9.
Amounts of ideal point method parameters.

Table 10.
Distance values.
Moreover, the weights of the criteria are computed by using the CRITIC method and ideal point approach. Afterwards, the final weights are obtained from Equation (27), and the results are introduced in Table 11. Table 11 presents weights of criteria determined by the CRITIC method, the ideal method, and the final aggregation weights with a new combination procedure.

Table 11.
Weights of criteria.
Afterwards, the score matrix () is determined in Table 12. Moreover, the values of and are shown in Table 13. The ranking values of the alternatives by ARAS, EDAS, and integrated methods are presented in Table 14. The ARAS, EDAS, and final ranking values are computed by using Equations (30), (40), and (41). The results reveal that the second alternative has a higher priority than other projects.

Table 12.
Score matrix .

Table 13.
and values.

Table 14.
Ranking of alternatives.
Based on the information, the DMs agreed with each other for evaluating projects and confirming each other.
5. Discussion of Results
In this section, the two types of analyses are presented to evaluate the efficiency and performance of the proposed soft computing model. In this respect, the sensitivity analysis is introduced to compare the effect of the criteria weights on the final ranking results. Moreover, the ranking outcomes are assessed with different values of . Afterward, comparative analysis is introduced to evaluate the performance and reliability of the proposed approach with the IF-TOPSIS method whose results confirm the proposed soft computing model. Furthermore, a different degree is presented to assess the proposed method with the IF-TOPSIS approach.
5.1. Sensitivity Analysis
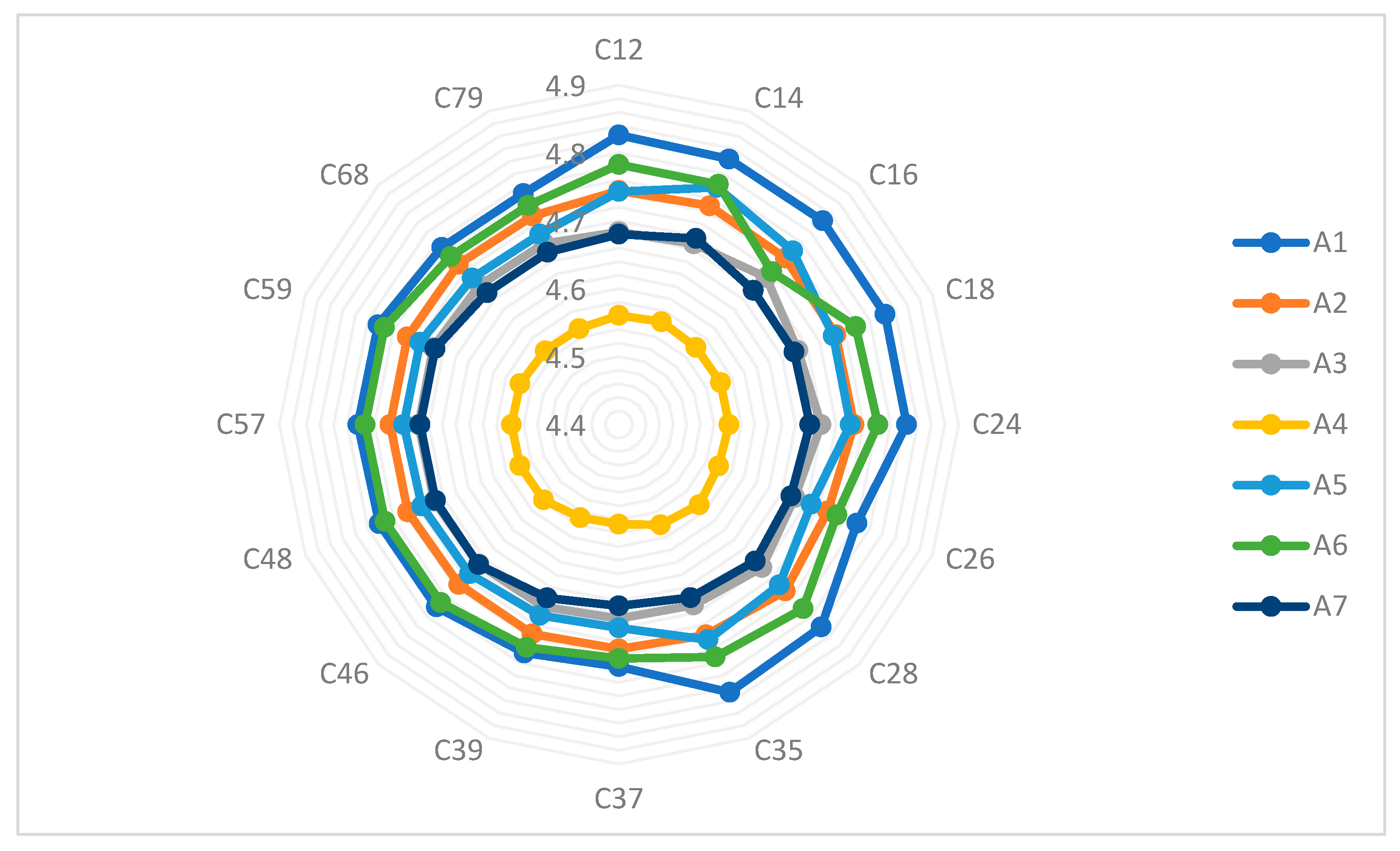
The sensitivity analysis of the obtained consequences from utilizing the introduced approach was carried out to assess the robustness of the ranking method. Hence, the reliability of the ranking method was analyzed by computing the rankings of alternatives with different values of criteria’s weights. Figure 3 determines the reliability of the ranking method by changing the weights of the criteria.
Figure 3.
Impact of weights of criteria on final ranks.
In this respect, shows the weight of criteria that changes from the t to p value. Hence, this figure demonstrates that the final ranking degrees do not change with the various weights of criteria, and these are independent of the weights of criteria in all stages. Figure 3 determines that the first alternative has higher priority compared to other alternatives.
The impact of the value on results is determined in Table 15. This value obtains the amounts from 0.1 to 0.9, and the final outcomes show that the second alternative has higher value than the others, and the final ranking results are independent of .

Table 15.
Impact of on final ranking results.
5.2. Comparative Analysis
This section provides a comparative analysis to measure the performance of the proposed model versus other approaches. For this reason, the proposed soft computing model’s rankings are compared with those of the IF-TOPSIS approach according to Park et al. [63]. Their results are depicted in Table 16 which shows that the proposed model has a higher performance than that of the related literature. The outcome determines the second alternative has a higher degree than other alternatives, and this point is confirmed by the other approach. Therefore, the integrated proposed model is validated to rank the alternatives of the MCDM problems.

Table 16.
Performance of the proposed method.
Table 16 shows that the final ranking results are similar from three types of approaches, and the proposed model has some different advantages from other methods. The proposed approach has the benefits of using the IF-ARAS method along with the IF-EDAS approach. Moreover, the proposed hybrid method is able to handle the uncertain conditions by considering the membership and non-membership degrees with IFSs. Ultimately, the proposed model is a more efficient tool than the previous approach to rank the main alternatives to the MCDM problem.
Another way to determine the performance of the proposed soft computing method is related to computing the different degrees (DDs) between the proposed method and the IF-TOPSIS approach. According to this issue, DDs are obtained by Equation (42). In this respect, x and y are two alternative values, and x > y [64].
Hence, this procedure determines that the method with a high degree of DDs is better than the other. Table 17 shows that the proposed IF ranking method has higher DD values than other analysis methods and demonstrates the efficiency and reliability of the introduced approach. It is worth mentioning that the high level of DDs in the model provides more special distinction of the ultimate alternative’s significance. According to this section, the proposed method has high values in more positions that determine the efficiency of the introduced approach.

Table 17.
Different degrees of the proposed approach and IF-TOPSIS method.
Table 17 is presented to confirm the results of the proposed method and the IF-TOPSIS approach in the final ranking outcomes. This table shows that the second alternative has a higher degree than others. After that, the first alternative has a high value in regard to solar and nuclear energies, respectively.
The proposed introduced approach has several limitations. The proposed model requires experts for its execution and for obtaining deductions from the procedure. Moreover, the introduced model is procedural and orderly; accordingly, every step should be performed with supervision, which consumes significant calculating costs. Moreover, if criteria and/or alternatives become multiple, the model can need assembled computations, and the procedure may be long.
6. Conclusions and Future Suggestions
The multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) methods are one of the essential tools that can be used by contractors in the selection of the most suitable construction projects. Hence, this paper introduced a new integrated intuitionistic fuzzy (IF) MCDM approach to assess the alternatives of different construction projects. Assurance of sustainability in construction projects usually requires increasing capital expenditures for organizations that are committed to supporting low carbon and more sustainable environment besides economic and social requirements. In this regard, the IF condition helps DMs to cope with vagueness and uncertain situations. For this purpose, this study utilized a linguistic term instead of a crisp value. Moreover, a novel model has proposed an integrated method to compute the weights of the criteria. This model combined the CRITIC method and ideal point approach. The calculations revealed that the seventh criterion (CO2 emission) had a higher weight value compared to other criteria. Furthermore, to evaluate the rankings of the alternatives, this study used a new combined method that included the ARAS and EDAS methods under uncertainty. Afterwards, this study applied a case study from the current literature to validate the proposed approach. This case determined that the second alternative had a higher priority than the others regarding the nuclear energy type. Finally, this paper introduced a sensitivity analysis to analyze the efficiency of the proposed model. This method performs well in computing the rankings of the alternatives and has high reliability when the weights of criteria are changed. Moreover, a sensitivity analysis of the aggregator value was conducted to determine the dependency of the proposed approach on this value. By changing the values of the criteria weights, the results showed that the first alternative had a higher priority than the others in various situations. Finally, the comparative analysis was conducted to determine the performance of the proposed approach by comparing the proposed method with the IF-TOPSIS approach from the literature. The final outcomes of the IF-TOPSIS method confirmed the performance of and validity of the proposed soft computing model by determining that the second alternative had higher priority than the others with two various ranking approaches. Furthermore, the different degree values were computed to demonstrate the efficiency and reliability of the introduced method. In this process, each method has high degree of different degree that is better than the other; in more situations, the IF proposed model has high different degree values than the IF-TOPSIS approach. This point determined the efficiency and performance of the introduced soft computing model by comparing it with the common approach.
The main advantage of the proposed soft computing model is its ability to select of the appropriate alternative with various natures in different industries by combining the two different and extreme methods, the ARAS and EDAS approaches, under the condition of uncertainty that was handled by the IF set (IFS). This model used the advantages of the ARAS and EDAS methods separately and employed the IFS to cope with an uncertain condition, which is an important case in real-world applications. Moreover, IFS is one of the most powerful uncertainty methods regarding the membership and non-membership degrees and helps to consider real-world situations. This advantage is one of the most critical benefits of the proposed model among the literature approaches.
In future research, the proposed method could be extended in an analysis with interdependent criteria. Furthermore, the DMs’ weights could be calculated by use of an objective method. Ultimately, the proposed method could use the interval value IF to cope with uncertain conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, data curation, validation, writing—original draft preparation, S.S.; supervision, methodology, S.M.M.; writing—review and editing, S.M.M. and J.A.; formal analysis, project administration, L.T. and J.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Akram, R.; Thaheem, M.J.; Nasir, A.R.; Ali, T.H.; Khan, S. Exploring the role of building information modeling in construction safety through science mapping. Saf. Sci. 2019, 120, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Langston, C. Multiple Criteria Sustainability Modelling: Case Study on School Buildings. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2004, 4, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.; Stephenson, P.; Bhutto, K. An Integrated Management System for Construction Quality, Safety and Environment: A Framework for IMS. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2005, 5, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tupenaite, L.; Zilenaite, V.; Kanapeckiene, L.; Gecys, T.; Geipele, I. Sustainability Assessment of Modern High-Rise Timber Buildings. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundtland, G.H. Our Common Future—Call for Action. Environ. Conserv. 1987, 14, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zeijl-Rozema, A.; Martens, P. An adaptive indicator framework for monitoring regional sustainable development: A case study of the INSURE project in Limburg, The Netherlands. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2010, 6, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A.; Klir, G.J.; Yuan, B. Fuzzy sets, fuzzy logic, and fuzzy systems. Selected papers by Lotfi A Zadeh. In Advances in Fuzzy Systems—Applications and Theory; World Scientific: Tokyo, Japan, 1996; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Qin, Y. Multi-attribute group decision making models under interval type-2 fuzzy environment. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2012, 30, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K.T. Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 1–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Mirdamadi, S.; Siadat, A.; Dantan, J.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. An intuitionistic fuzzy grey model for selection problems with an application to the inspection planning in manufacturing firms. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2015, 39, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plebankiewicz, E.; Zima, K.; Wieczorek, D. Modelling of time, cost and risk of construction with using fuzzy logic. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2021, 27, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez, L.; Castro, D.; Irizarry, J. Impact of sustainability perceptions on optimal material selection in con-struction projects. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies, Ancona, Italy, 28–30 June 2010; pp. 719–727. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimnejad, S.; Mousavi, S.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Hashemi, H.; Vahdani, B. A novel two-phase group decision making approach for construction project selection in a fuzzy environment. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 4197–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezakhani, P. Fuzzy MCDM Model for Risk Factor Selection in Construction Projects. Eng. J. 2012, 16, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-H.; Lin, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-F.; Chang, Y.-C.; Hsu, J.-L. Construction method selection for green building projects to improve environmental sustainability by using an MCDM approach. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2013, 56, 1487–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dėjus, T.; Antuchevičienė, J. Assessment of health and safety solutions at a construction site. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2013, 19, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamošaitienė, J.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z. Multi-criteria Risk Assessment of a Construction Project. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2013, 17, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylan, O.; Bafail, A.O.; Abdulaal, R.M.; Kabli, M.R. Construction projects selection and risk assessment by fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS methodologies. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 17, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Gitinavard, H.; Vahdani, B. Evaluating Construction Projects by a New Group Decision-Making Model Based on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Logic Concepts. Int. J. Eng. 2015, 28, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Vahdani, B. Cross-docking Location Selection in Distribution Systems: A New Intuitionistic Fuzzy Hierarchical Decision Model. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2016, 9, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prascevic, N.; Prascevic, Z. Application of fuzzy ahp for ranking and selection of alternatives in construction project management. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2017, 23, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovskis, M.; Antucheviciene, J.; Migilinskas, D. Assessment of Buildings Redevelopment Possibilities using MCDM and BIM Techniques. Procedia Eng. 2017, 172, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, K.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Tamošaitienė, J.; Adhikary, K.; Kar, S. A Hybrid MCDM Technique for Risk Management in Construction Projects. Symmetry 2018, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Li, L. Picture fuzzy normalized projection-based VIKOR method for the risk evaluation of construction project. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 64, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahooie, J.H.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Abolhasani, M.; Vanaki, A.; Turskis, Z. A Novel Approach for Evaluation of Projects Using an Interval–Valued Fuzzy Additive Ratio Assessment (ARAS) Method: A Case Study of Oil and Gas Well Drilling Projects. Symmetry 2018, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K.; Sotirova, E.; Andonov, V. Generalized Net Model of Multicriteria Decision Making Procedure Using Intercriteria Analysis. In Advances in Fuzzy Logic and Technology 2017: Proceedings of: EUSFLAT-2017–The 10th Conference of the European Society for Fuzzy Logic and Technology, September 11–15, 2017, Warsaw, Poland IWIFSGN’2017–The Sixteenth International Workshop on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets and Generalized Nets, September 13–15, 2017, Warsaw, Poland; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalekaee, A.; Turskis, Z.; Khanzadi, M.; Ghodrati Amiri, G.; Keršulienė, V. A New Hybrid MCDM Model with Grey Numbers for the Construction Delay Change Response Problem. Sustainability 2019, 11, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudabadi, R.; Mousavi, S.M.; Šaparauskas, J.; Gitinavard, H. Solving construction project selection problem by a new uncertain weighting and ranking based on compromise solution with linear assignment approach. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2019, 25, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, M.; Khader, B.K. Construction Project Safety Performance Management Using Analytic Network Process (ANP) as a Multicriteria Decision-Making (MCDM) Tool. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020, 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohandes, S.R.; Sadeghi, H.; Mahdiyar, A.; Durdyev, S.; Banaitis, A.; Yahya, K.; Ismail, S. Assessing construction labours’ safety level: A fuzzy mcdm approach. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2020, 26, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahpour, A.; Wong, K.Y.; Rajoo, S.; Olugu, E.U.; Nilashi, M.; Turskis, Z. A fuzzy decision support system for sustainable construction project selection: An integrated fpp-fis model. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2020, 26, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liao, H.; Al-Barakati, A.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Antuchevičienė, J. Supplier selection for housing development by an integrated method with interval rough boundaries. Int. J. Strat. Prop. Manag. 2020, 24, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.-J.; Tian, C.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.-Q. An integrated multi-criteria decision-making framework for sustainable supplier selection under picture fuzzy environment. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2020, 26, 573–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Gitinavard, H.; Vahdani, B. ELECTRE I-based group decision methodology with risk preferences in an imprecise setting for flexible manufacturing systems. J. Optim. Ind. Eng. 2021, 14, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banihashemi, S.A.; Khalilzadeh, M.; Antucheviciene, J.; Šaparauskas, J. Trading off Time–Cost–Quality in Construction Project Scheduling Problems with Fuzzy SWARA–TOPSIS Approach. Buildings 2021, 11, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamošaitienė, J.; Sarvari, H.; Cristofaro, M.; Chan, D.W.M. Identifying and prioritizing the selection criteria of appropriate repair and maintenance methods for commercial buildings. Int. J. Strat. Prop. Manag. 2021, 25, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, G.; Kishore, R.; Dehmourdi, S.A.M. Modeling a Multi-Criteria Decision Support System for Prequalification Assessment of Construction Contractors using CRITIC and EDAS Models. Oper. Res. Eng. Sci. Theory Appl. 2021, 4, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, J.C.; Wang, C.N.; Nguyen, V.T.; Husain, S.T. A Fuzzy MCDM Model of Supplier Selection in Supply Chain Management. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2022, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, R.; Wang, T. A data-driven decision-making framework for personnel selection based on LGBWM and IFNs. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 126, 109227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, S.; Kahraman, C. A Pythagorean cubic fuzzy methodology based on TOPSIS and TODIM methods and its application to software selection problem. Soft Comput. 2021, 26, 2437–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, W. Multi-criteria group decision-making with cloud model and TOPSIS for alternative selection under uncertainty. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 12509–12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimian, S.; Mousavi, S.M.; Antucheviciene, J. An Interval-Valued Intuitionistic Fuzzy Model Based on Extended VIKOR and MARCOS for Sustainable Supplier Selection in Organ Transplantation Networks for Healthcare Devices. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimian, S.; Mousavi, S.M.; Antuchevičienė, J. Evaluation of infrastructure projects by a decision model based on rpr, mabac, and waspas methods with interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int. J. Strat. Prop. Manag. 2022, 26, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorui, N.; Mondal, S.P.; Chatterjee, B.; Ghosh, A.; Pal, A.; De, D.; Giri, B.C. Selection of cloud service providers using MCDM methodology under intuitionistic fuzzy uncertainty. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 2403–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K. Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1986, 20, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K.T. New operations defined over the intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1994, 61, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yager, R.R. Some geometric aggregation operators based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2006, 35, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Yan, M.; Liu, X. Intuitionistic fuzzy soft decision-making method based on expectation score functions. J. Jilin Univ. 2018, 56, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Szmidt, E.; Kacprzyk, J. Distances between intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2000, 114, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z. A new additive ratio assessment (aras) method in multicriteria decision-making/naujas adityvinis kriterijų santykių įvertinimo metodas (aras) daugiakriteriniams uždaviniams spręsti. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2010, 16, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, C.; Ghorabaee, M.K.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Onar, S.C.; Yazdani, M.; Oztaysi, B. Intuitionistic fuzzy edas method: An application to solid waste disposal site selection. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2017, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, M.; Luo, H.; Huang, G.Q. Industrial robot selection using stochastic multicriteria acceptability analysis for group decision making. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2019, 122, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Garg, H. Intuitionistic fuzzy soft decision making method based on CoCoSo and CRITIC for CCN cache placement strategy selection. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 55, 1567–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Z. Pythagorean fuzzy MCDM method based on CoCoSo and CRITIC with score function for 5G industry evaluation. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 53, 3813–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaalem, M.; Comber, A.; Fisher, P. A Comparison of Fuzzy AHP and Ideal Point Methods for Evaluating Land Suitability. Trans. GIS 2011, 15, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Satapathy, S. MCDM Approach for Mitigation of Flooding Risks in Odisha (India) Based on Information Retrieval. Int. J. Cogn. Inform. Nat. Intell. 2020, 14, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Rabbani, A.; Yazdani-Chamzini, A.; Turskis, Z. An integrated model for extending brand based on fuzzy aras and anp methods. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2014, 15, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lei, F.; Wei, G.; Wang, R.; Wu, J.; Wei, C. EDAS Method for Multiple Attribute Group Decision Making with Probabilistic Uncertain Linguistic Information and Its Application to Green Supplier Selection. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2019, 12, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmidt, E.; Baldwin, J. Intuitionistic Fuzzy Set Functions, Mass Assignment Theory, Possibility Theory and Histograms. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–21 July 2006; pp. 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatibi, V.; Montazer, G.A. Intuitionistic fuzzy set vs. fuzzy set application in medical pattern recognition. Artif. Intell. Med. 2009, 47, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Yadav, S.P.; Kumar, S. Fuzzy system reliability evaluation using time-dependent intuitionistic fuzzy set. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2013, 44, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, T.; Kahraman, C. Multicriteria decision making in energy planning using a modified fuzzy TOPSIS methodology. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 6577–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Park, I.Y.; Kwun, Y.C.; Tan, X. Extension of the TOPSIS method for decision making problems under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 2544–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfeshan, Y.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Mousavi, S.; Vahedi-Nouri, B. A new weighted distance-based approximation methodology for flow shop scheduling group decisions under the interval-valued fuzzy processing time. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 91, 106248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).