Simplified Estimation Method of Plastic Energy Dissipation for MDOF Systems Using Force Analogy Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
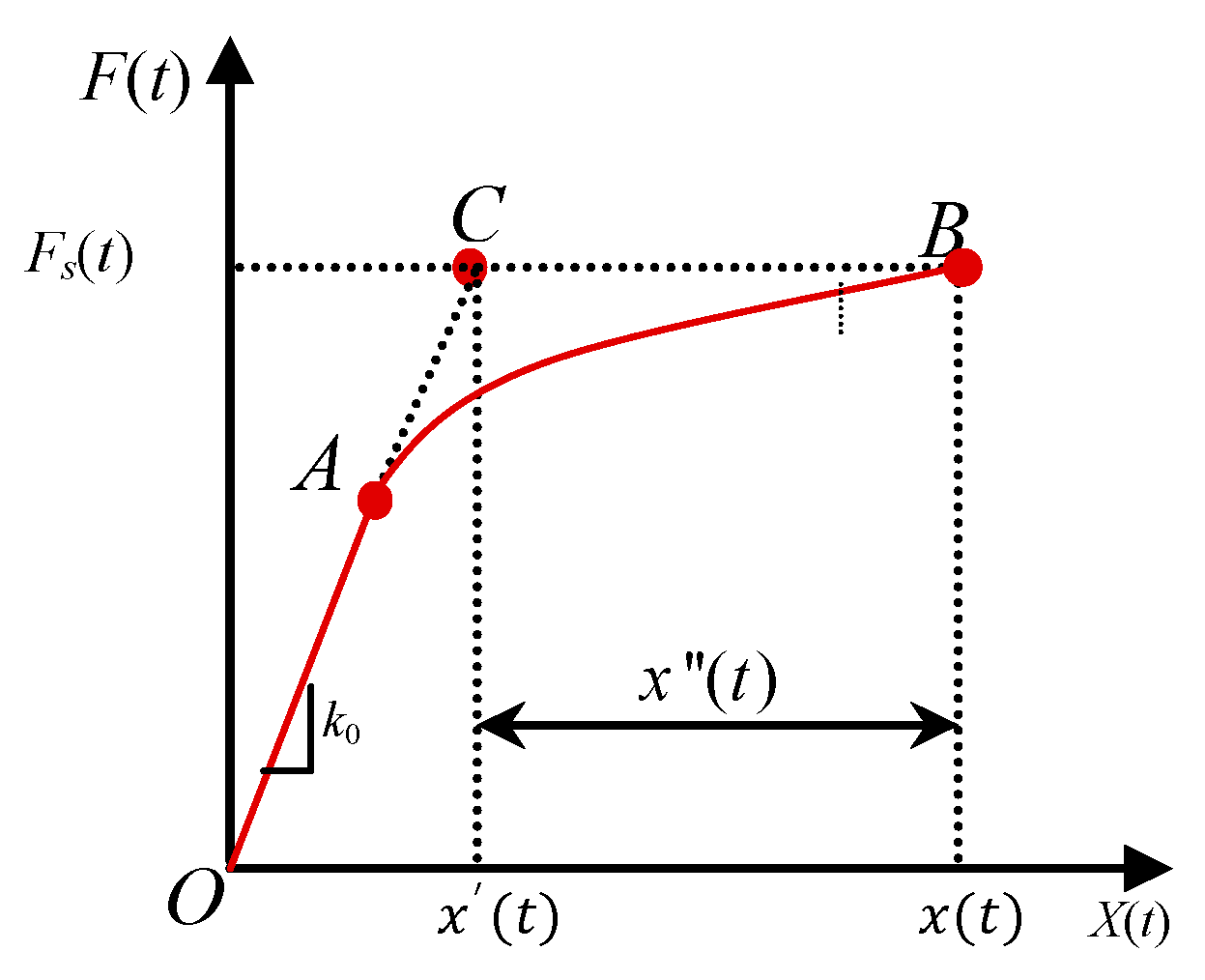
2. Formula of Plastic Energy Base on Force Analogy Method
3. Two Plastic Energy Estimation Methods Based on an Equivalent SDOF System
3.1. Estimation Method Considering Only the First Mode Shape
3.2. Estimation Method Based on the Mode Decomposition Method
4. Numerical Analysis
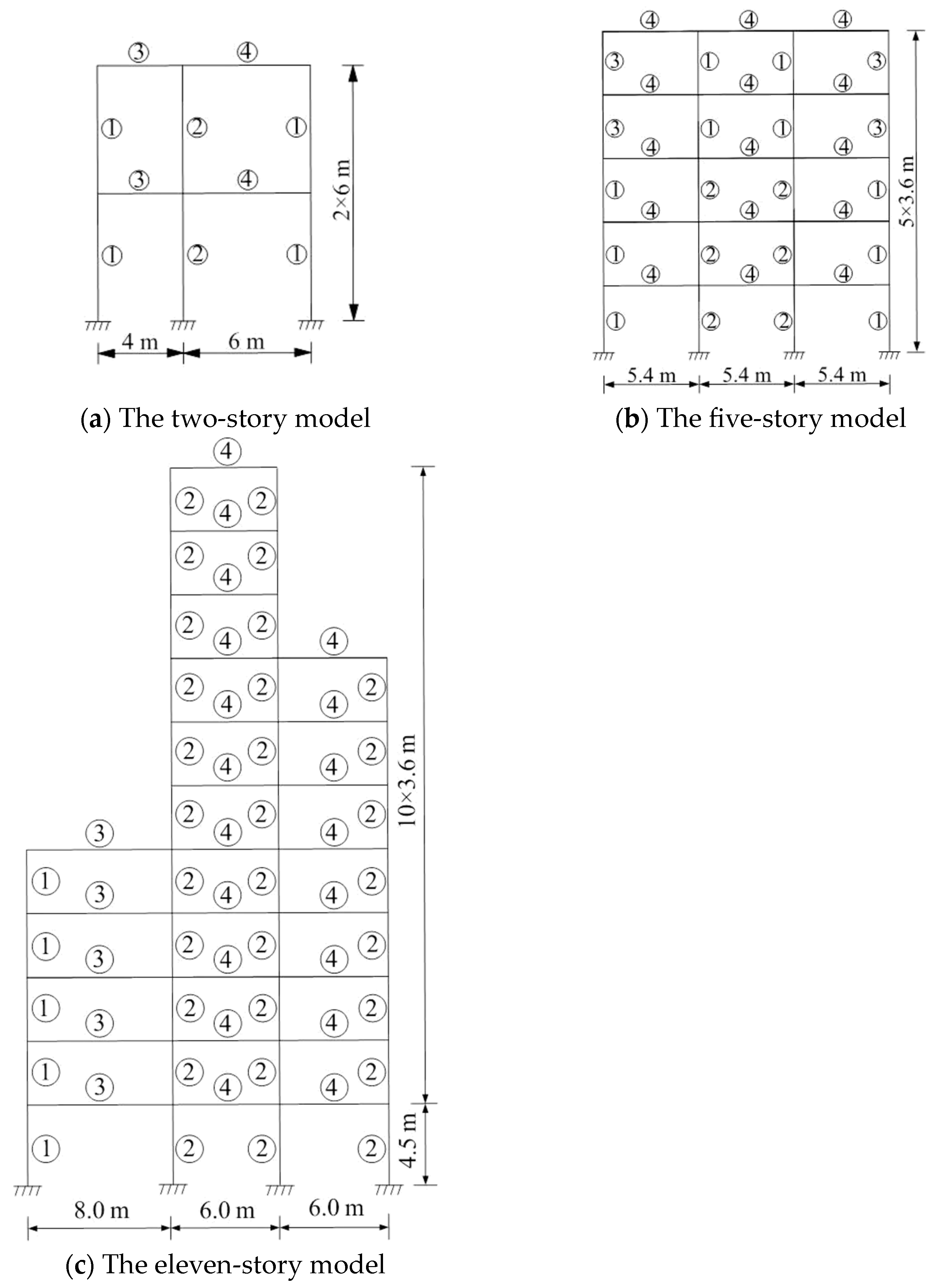
4.1. Structure Models
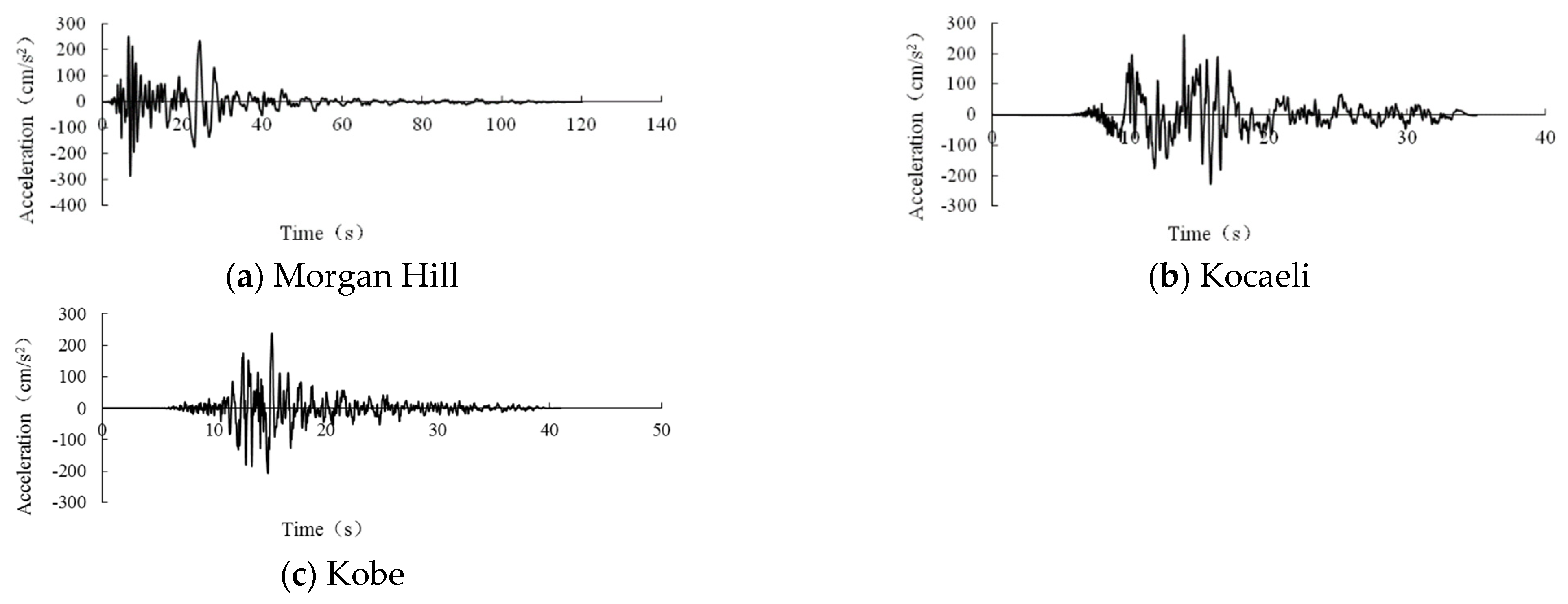
4.2. Earthquake Records
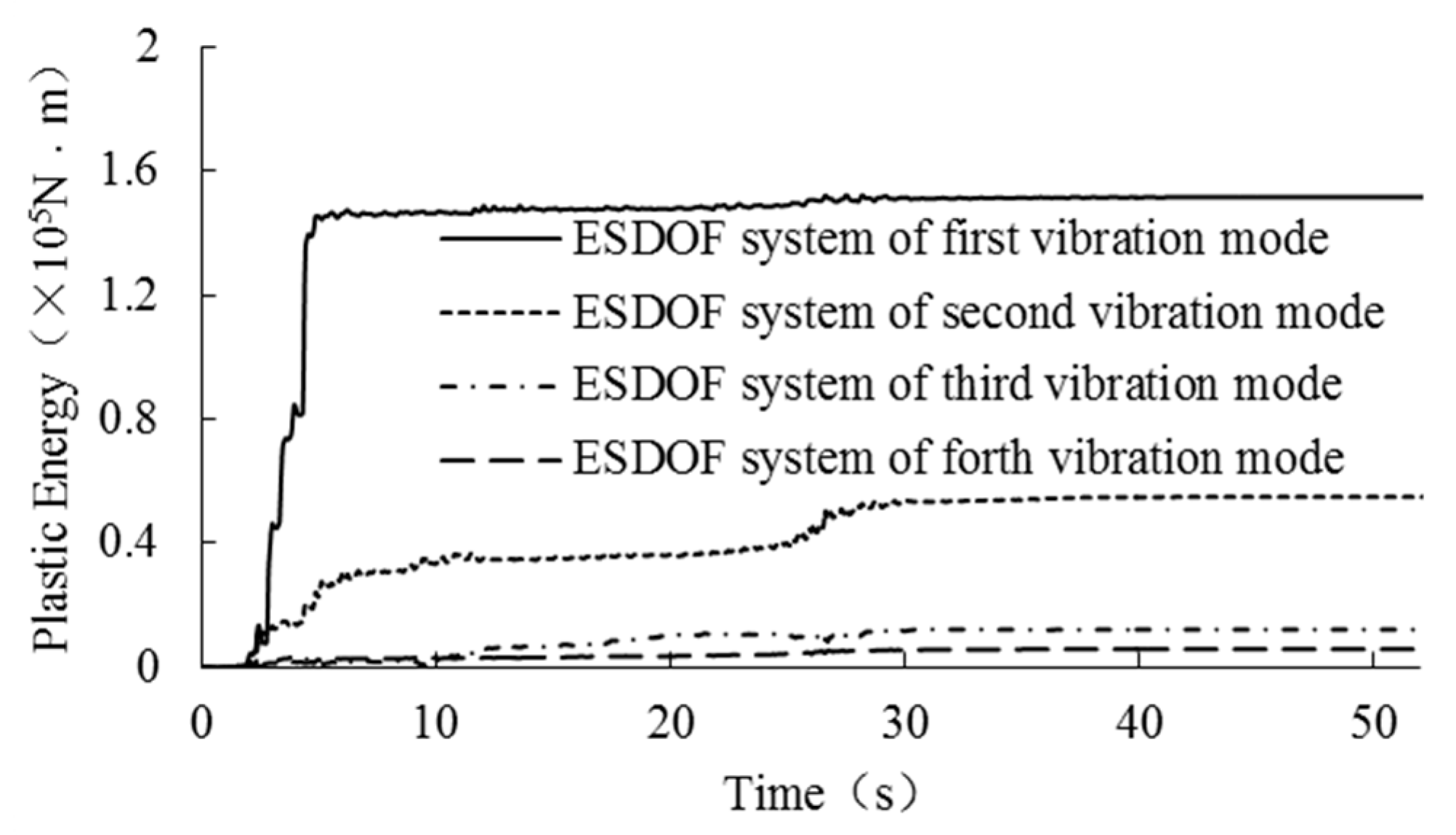
4.3. PE Calculation and Analysis Results
4.4. Comparison of the Two Estimation Methods
5. Conclusions
- Method 1 can be used only for structures where the seismic response is dominated by the ith mode shape. The PE of the MDOF system can be estimated by multiplying the PE for the corresponding order mode of the ESDOF system by the participation coefficient of that order mode shape. The generalized displacement of this method can use the displacement of the top floor of the structure, making it a simple and efficient method.
- Method 2 can be used for estimating the PE of multi-story or high-rise structures by using the sum of the PE for the first two or three modes of the ESDOF system. The errors between the two systems are small.
- The values of PE for both the MDOF and ESDOF systems increase with the enlargement in ground motion peak acceleration. However, the ratio between the sum of PE for the first several modes of the ESDOF system and the PE of the structure does not show linearity with the ground motion peak acceleration. However, the errors are all acceptable in actual projects.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Housner, G.W. Limit design of structures to resist earthquake. In Proceedings of the 1st World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Berkeley, CA, USA; 1956; pp. 5-1–5-11. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1573387450439651200 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Mckevitt, W.E. Hysteretic energy spectra in seismic design, Proceeding of 7th world conference on earthquake engineering. Struct. Asp. 2000, 7, 487–494. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, C.C.; Uang, C.M. Establishing absorbed energy spectra an attenuation approach. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2000, 29, 1441–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shen, P.; Hu, X. Study on input energy and momentary input energy spectra of earthquake strong motion. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vibration 2006, 26, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Ye, L. Cumulative hysteretic energy spectra of SDOF systems. Earthq. Resist. Eng. Retrofit. 2007, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fajfar, P.; Vidic, T.; Fischinger, M. Seismic demand in medium- and long-period structures. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1989, 18, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajfar, P.; Vidic, T. Consistent Inelastic Design Spectra Hysteretic and Input Energy. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1994, 23, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, Q.; He, W. Study and application of elasto-plastic energy spectrum model for long-period structure. J. Build. Struct. 2014, 35, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hiroshi, A. Earthquake-Resistant Limit-State Design for Building; University of Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, J.; Ye, L.; Qian, J. Inelastic seismic response of lumped mass MDOF systems based on energy concept. Eng. Mech. 2003, 20, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Chen, K. Energy dissipation history-based seismic damage evaluation of reinforced concrete frames. China Civ. Eng. J. 2013, 46 (Suppl. S2), 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Nurtug, A.; Sucuoglu, H. Prediction of seismic energy dissipation in SDOF systems. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1995, 24, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, H. Estimation of hysteretic energy of structures based on equivalent SDOF systems. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. 2007, 47, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.; Lin, W.; Guo, X. Research on input energy of structure based on equivalent SDOF systems. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2011, 31, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, B.; Zhao, D. Theoretical study and sensitivity analysis on the cumulative-plastic deformation energy in MDOFS. J. Vib. Shock. 2014, 33, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Merter, O.; Ucar, T. Energy-based design base shear for RC frames considering global failure mechanism and reduced hysteretic behavior. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2017, 63, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, A.S.; Yang, T.Y.; Fabricio, B.C.; Pan, S. Seismic design and performance evaluation of controlled rocking dual-fused bridge system. Eng. Struct. 2020, 212, 110467. [Google Scholar]
- Shargh, G.B.; Barati, R. Estimation of inelastic seismic input energy. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 142, 106505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaq, M.S.; Zhou, Y.; Song, G.; Xiao, Y. Plastic energy evaluation of bilinear SDOF systems with fluid viscous dampers. In The Structural Design of Tall and Special Buildings; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahin, S.A.; Bertero, V.V. An evaluation of inelastic seismic design spectra. J. Struct. Div. 1981, 107, 1777–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T. Theory of Inelastic Structures; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.K.F.; Yang, R. Inelastic dynamic response of structures using force analogy method. J. Eng. Mech. 1999, 125, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.K.F.; Yang, R. Earthquake Response and Energy Evaluation of Inelastic Structures. J. Eng. Mech. 2002, 128, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fahnestock, L.A.; Li, H.-N. Simulation of Steel Brace Hysteretic Response Using the Force Analogy Method. J. Struct. Eng. 2013, 129, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Li, H. Study on optimal placement and reasonable number of viscoelastic dampers by improved weight coefficient method. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 358709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, J.; Li, G. Study on failure mode of nonlinear vibration device based on FAM-MMBC for MDOF system. J. Build. Struct. 2017, 38, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Yu, D. Efficient inelasticity-separated finite element method for material nonlinearity analysis. J. Eng. Mech. 2018, 144, 0401800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Wang, M.; Jia, S.; Li, G. Static pushover analysis of frame structures based on force analogy method. J. Southwest Jiao Tong Univ. 2020, 55, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Wu, Z. The method of mode decomposition for the multi-story structure’s energy. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 1998, 30, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.; Ye, X. Research on modal decomposition method for structure’s energy response equation. J. Hefei Univ. Technol. 2010, 33, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, A.K.; Goel, R.K. A modal pushover analysis procedure for estimating seismic demands for buildings. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2002, 31, 561–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model Number | Serial Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Moment of inertia (N·m2) | 3.20 × 108 | 4.54 × 108 | 4.87 × 107 | 1.17 × 108 |
| Yielding moment (kN·m) | 2210 | 2998 | 601 | 1445 | |
| 2 | Moment of inertia (N·m2) | 3.20 × 108 | 4.54 × 108 | 2.0 × 108 | 6.99 × 108 |
| Yielding moment (kN·m) | 2210 | 2998 | 1445 | 601 | |
| 3 | Moment of inertia (N·m2) | 2.40 × 108 | 4.98 × 108 | 4.98 × 108 | 2.40 × 108 |
| Yielding moment (kN·m) | 1250 | 2160 | 1730 | 1000 |
| Model Number | Modal Order | Periods (s) | Frequency (s−1) | Mode of Vibration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1.20 | 5.2366 | 0.4396, 1 |
| 2 | 0.36 | 17.653 | 1, −0.6594 | |
| 2 | 1 | 1.97 | 3.1882 | 0.128, 0.377, 0.635, 0.856, 1 |
| 2 | 0.57 | 10.968 | −0.458, −0.978, −0.871, −0.023, 1 | |
| 3 | 0.28 | 22.432 | −0.889, −0.900, 0.571, 1, −0.766 | |
| 4 | 0.17 | 37.391 | 1, −0.117, −0.857, 0.982, −0.380 | |
| 5 | 0.112 | 54.041 | −0.960, 1, −0.756, 0.394, −0.110 | |
| 3 | 1 | 1.02 | 6.139 | - |
| 2 | 0.43 | 14.675 | - | |
| 3 | 0.25 | 25.040 | - | |
| 4 | 0.17 | 36.030 | - | |
| 5 | 0.11 | 53.712 | - | |
| 6 | 0.09 | 68.600 | - |
| Earthquake Records | Max. of PE and Error | Peak Values of Acceleration (cm/s2) | Average | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | Values | ||
| Morgan Hill | PE1 (kN·m) | 1497.3 | 2981.9 | 5241.7 | 8884.6 | |
| PES (kN·m) | 1557.0 | 3126.6 | 5478.6 | 9257.4 | ||
| PE1/PES (%) | 96.17 | 95.37 | 95.68 | 95.97 | 95.80 | |
| Error (%) | 3.83 | 4.63 | 4.32 | 4.03 | 4.20 | |
| Kocaeli | PE1 (kN·m) | 502.8 | 850.0 | 1239.3 | 1683.1 | |
| PES (kN·m) | 533.2 | 907.0 | 1323.2 | 1789.4 | ||
| PE1/PES (%) | 94.31 | 93.72 | 93.66 | 94.06 | 93.94 | |
| Error (%) | 5.69 | 6.28 | 6.34 | 5.94 | 6.06 | |
| Kobe | PE1 (kN·m) | 403.6 | 634.5 | 905.0 | 1208.8 | |
| PES (kN·m) | 405.6 | 639.4 | 908.0 | 1215.9 | ||
| PE1/PES (%) | 99.517 | 99.235 | 99.678 | 99.416 | 99.46 | |
| Error (%) | 0.483 | 0.765 | 0.322 | 0.584 | 0.54 | |
| Earthquake Records | Max. of PE and Error | Peak Values of Acceleration (cm/s2) | Average | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | Values | ||
| Morgan Hill | PE1 (kN·m) | 11,766 | 16,954 | 22,415 | 28,101 | |
| PES (kN·m) | 11,225 | 16,030 | 21,076 | 26,310 | ||
| PE1/PES (%) | 104.82 | 105.76 | 106.35 | 106.81 | 105.94 | |
| Error (%) | 4.82 | 5.76 | 6.35 | 6.81 | 5.94 | |
| Kocaeli | PE1 (kN·m) | 3197.8 | 5766.6 | 8599.6 | 11,463 | |
| PES (kN·m) | 3303.2 | 5813.9 | 8511.0 | 11,250 | ||
| PE1/PES (%) | 96.81 | 99.19 | 101.04 | 101.89 | 99.73 | |
| Error (%) | 3.20 | 0.82 | 1.04 | 1.89 | 1.58 | |
| Kobe | PE1 (kN·m) | 651.9 | 1047.2 | 1481.8 | 1978.8 | |
| PES (kN·m) | 685.2 | 1114.0 | 1586.6 | 2123.1 | ||
| PE1/PES (%) | 95.14 | 94.00 | 93.39 | 93.20 | 93.93 | |
| Error (%) | 4.86 | 6.00 | 6.61 | 6.80 | 6.07 | |
| Max. of PE and the Ratio | Peak Values of Acceleration (cm/s2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | |
| PE21 (kN·m) | 151.8 | 285.5 | 455.1 | 669.0 |
| PE22 (kN·m) | 55.0 | 85.9 | 129.1 | 184.7 |
| PE23 (kN·m) | 12.2 | 16.8 | 22.8 | 30.2 |
| PE (kN·m) | 226.2 | 402.2 | 630.9 | 919.0 |
| (PE21 + PE22 + PE23)/PE (%) | 96.84 | 96.53 | 96.20 | 96.21 |
| Earthquake Records | Max. of PE and Ratio | Peak Values of Acceleration (cm/s2) | Computing Time (s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | |||
| Chalfant Valley | PE (kN·m) | 151.37 | 286.39 | 441.77 | 601.37 | |
| PE1 (kN·m) | 148.81 | 285.02 | 447.17 | 611.38 | 9.813 | |
| PE21 (kN·m) | 150.03 | 285.06 | 443.89 | 607.36 | 16.261 | |
| Error of PE1 and PE (%) | 1.69 | 0.48 | 1.22 | 1.67 | ||
| Error of PE21 and PE (%) | 0.89 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 1.01 | ||
| Imperial Valley | PE (kN·m) | 1595.3 | 2532.4 | 3636.9 | 4818.9 | |
| PE1 (kN·m) | 1552.3 | 2450.4 | 3519.4 | 4677.3 | 1.820 | |
| PE21 (kN·m) | 1583.3 | 2506.7 | 3609.9 | 4817.5 | 4.164 | |
| Error of PE1 and PE (%) | 2.69 | 3.23 | 3.23 | 2.94 | ||
| Error of PE21 and PE (%) | 0.75 | 1.01 | 0.74 | 0.03 | ||
| San Fernando | PE (kN·m) | 224.60 | 608.90 | 1152.1 | 1810.2 | |
| PE1 (kN·m) | 219.67 | 600.16 | 1164.2 | 1853.7 | 2.602 | |
| PE21 (kN·m) | 214.13 | 594.47 | 1119.9 | 1750.3 | 5.369 | |
| Error of PE1 and PE (%) | 2.19 | 1.43 | 1.05 | 2.40 | ||
| Error of PE21 and PE (%) | 4.66 | 2.37 | 2.79 | 3.31 | ||
| Kocaeli | PE (kN·m) | 485.41 | 907.72 | 1453.6 | 2135.8 | |
| PE1 (kN·m) | 468.86 | 882.66 | 1419.1 | 2100.0 | 121.719 | |
| PE21 (kN·m) | 469.43 | 867.37 | 1367.3 | 1984.7 | 234.790 | |
| Error of PE1 and PE (%) | 3.41 | 2.76 | 2.37 | 1.67 | ||
| Error of PE21 and PE (%) | 3.29 | 4.45 | 5.94 | 7.07 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, Y.; Qu, J.; Shu, Y.; Tan, Y. Simplified Estimation Method of Plastic Energy Dissipation for MDOF Systems Using Force Analogy Method. Buildings 2023, 13, 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13051330
Mu Y, Qu J, Shu Y, Tan Y. Simplified Estimation Method of Plastic Energy Dissipation for MDOF Systems Using Force Analogy Method. Buildings. 2023; 13(5):1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13051330
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Yingna, Jiting Qu, Yu Shu, and Yanbin Tan. 2023. "Simplified Estimation Method of Plastic Energy Dissipation for MDOF Systems Using Force Analogy Method" Buildings 13, no. 5: 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13051330
APA StyleMu, Y., Qu, J., Shu, Y., & Tan, Y. (2023). Simplified Estimation Method of Plastic Energy Dissipation for MDOF Systems Using Force Analogy Method. Buildings, 13(5), 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13051330






