Towards Performance-Based Design of Masonry Buildings: Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
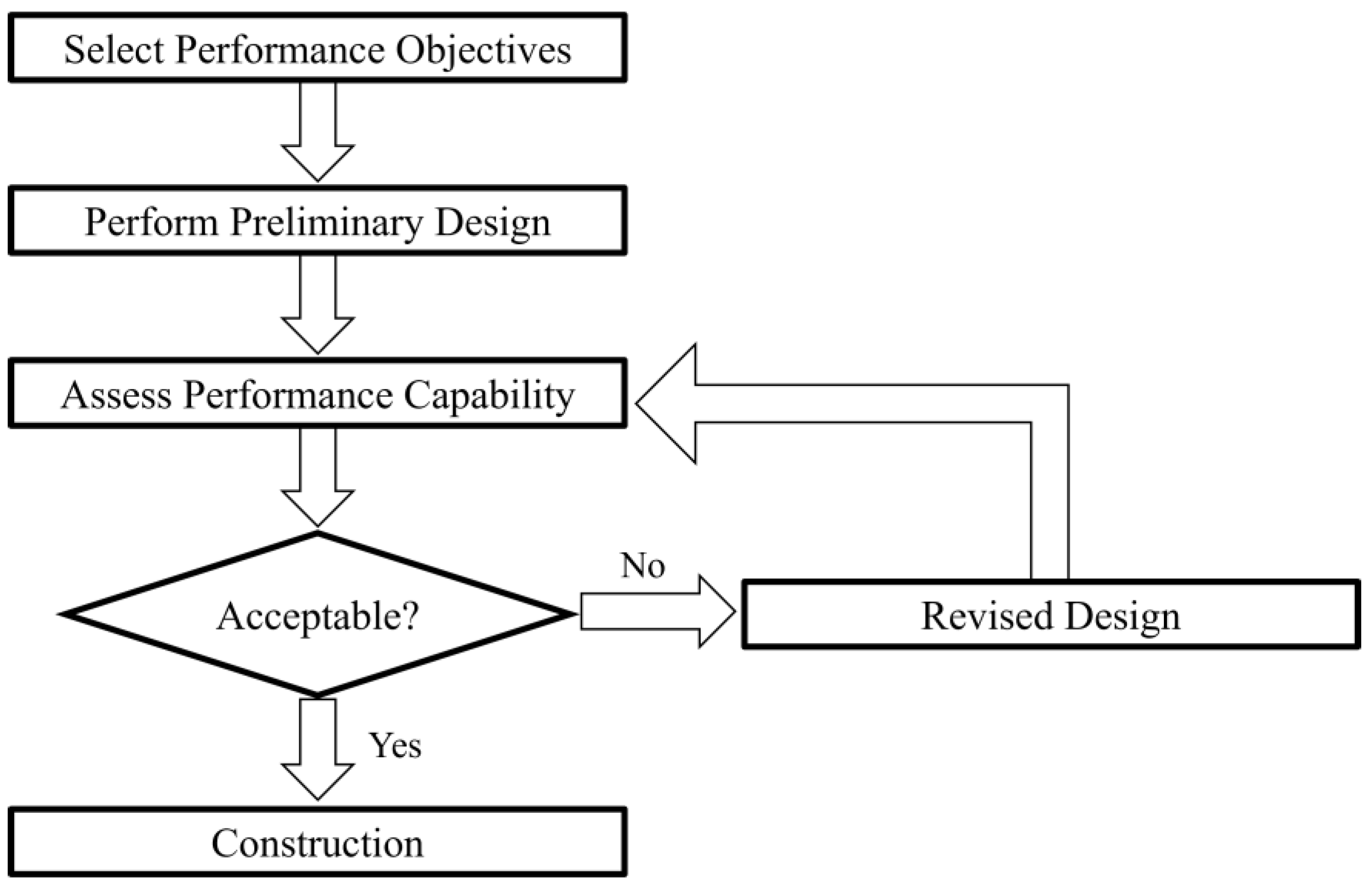
2. History and Development of Performance-Based Design
3. Experimental Studies of Masonry Walls/Buildings
3.1. Masonry Shear Wall Tests
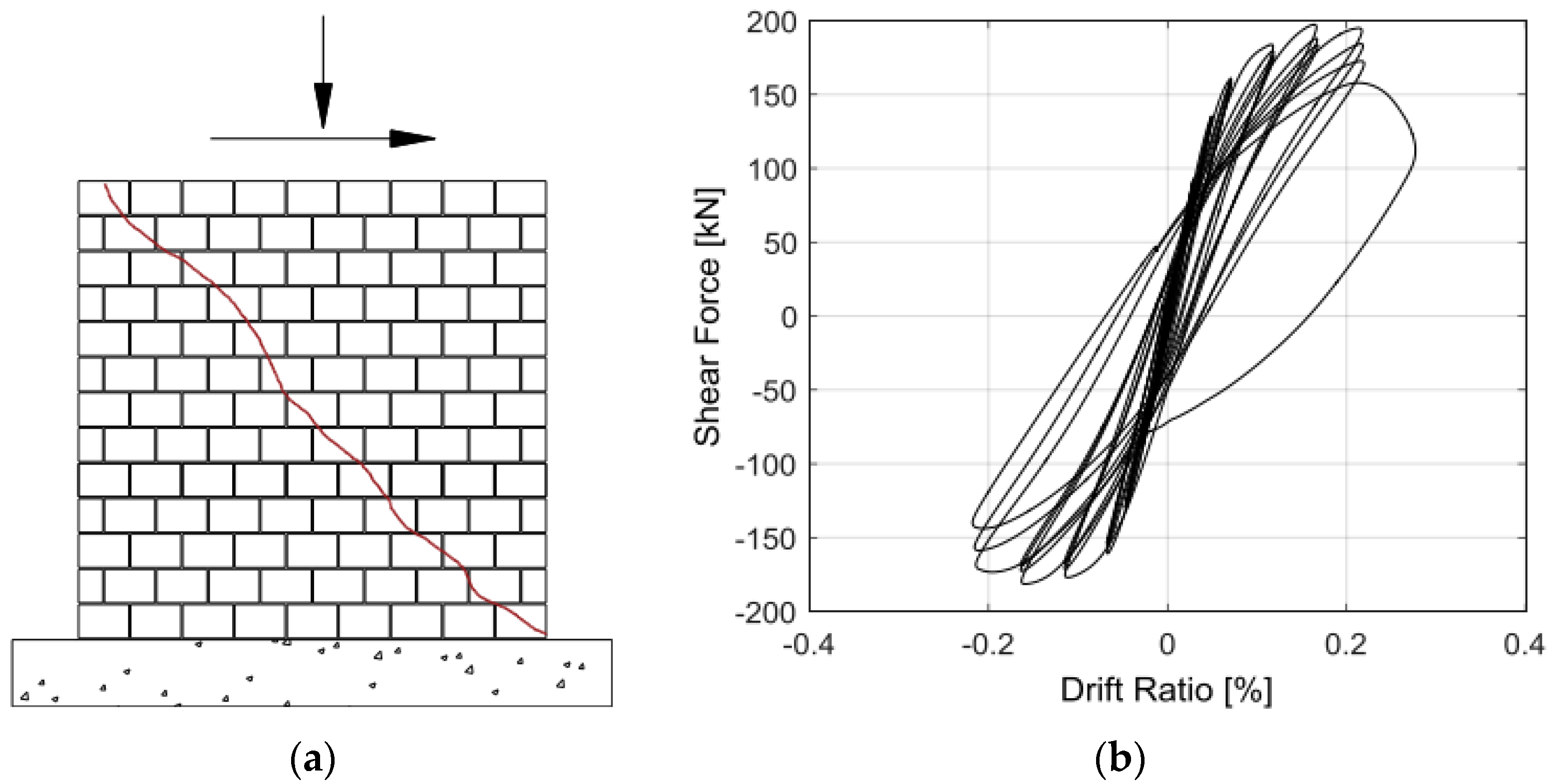
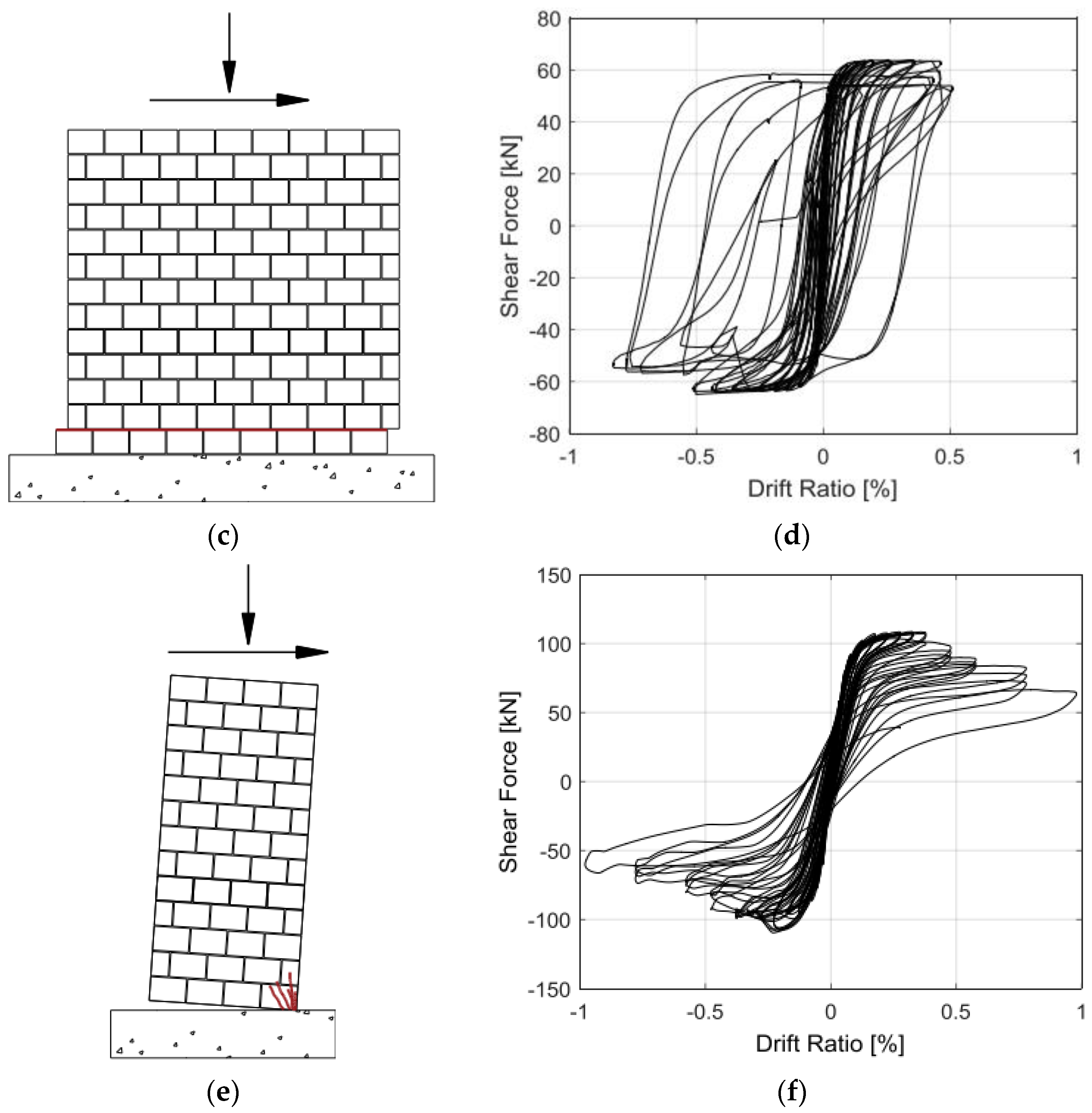
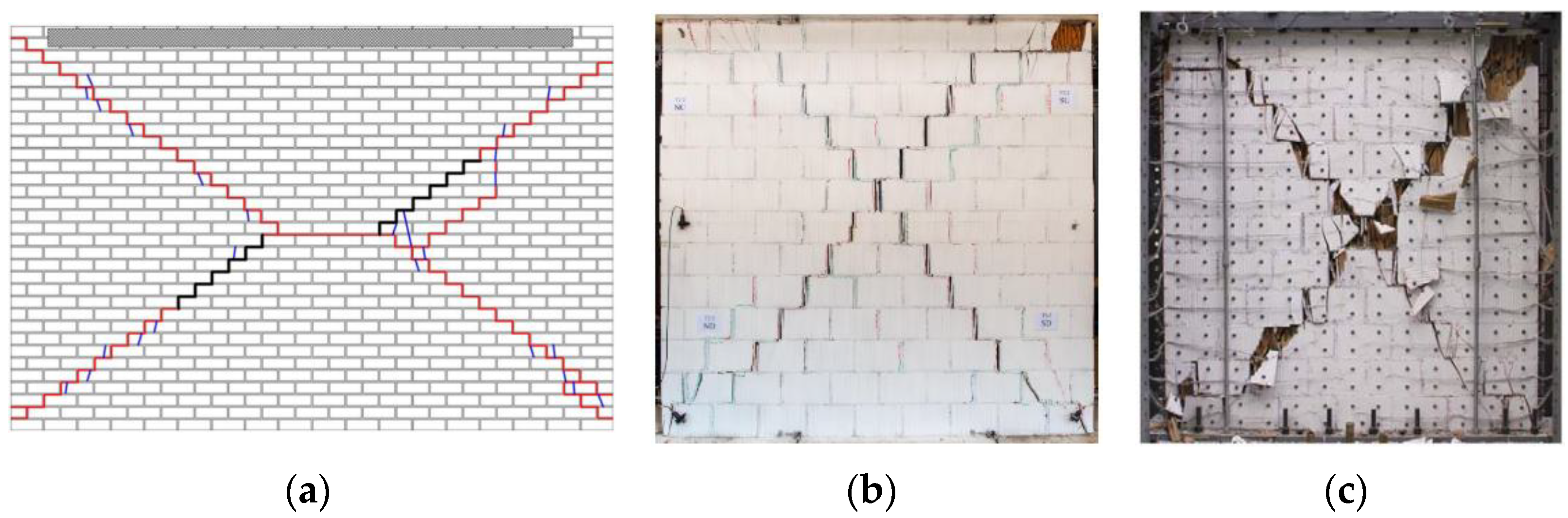
3.1.1. Unreinforced Masonry Shear Walls
3.1.2. Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls
| Grout Type | Loading Conditions | Boundary Conditions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| F, P | SC | FF | [20,21,22,23] |
| F | SC | C | [51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,64,65,66,73,75,76] |
| F | SC | FF | [63] |
| F, P | SC | C | [67] |
| F, P | SC | FF, C | [68,69,70,71,72] |
| F | SC | NA * | [74] |
| F | D | C | [77] |
| P | SC | C | [79] |
| P | SM, SC, D | C | [95] |
| P | SC | FF | [80] |
| F, P | SC | C | [81,82] |
| P | SC | NA * | [91] |
| P | SC | C, FF | [97] |
| P | SC | C | [83,84,85,86,88,89,90,92,93,94] |
| P | SM | C | [98] |
| P | D | C | [87] |
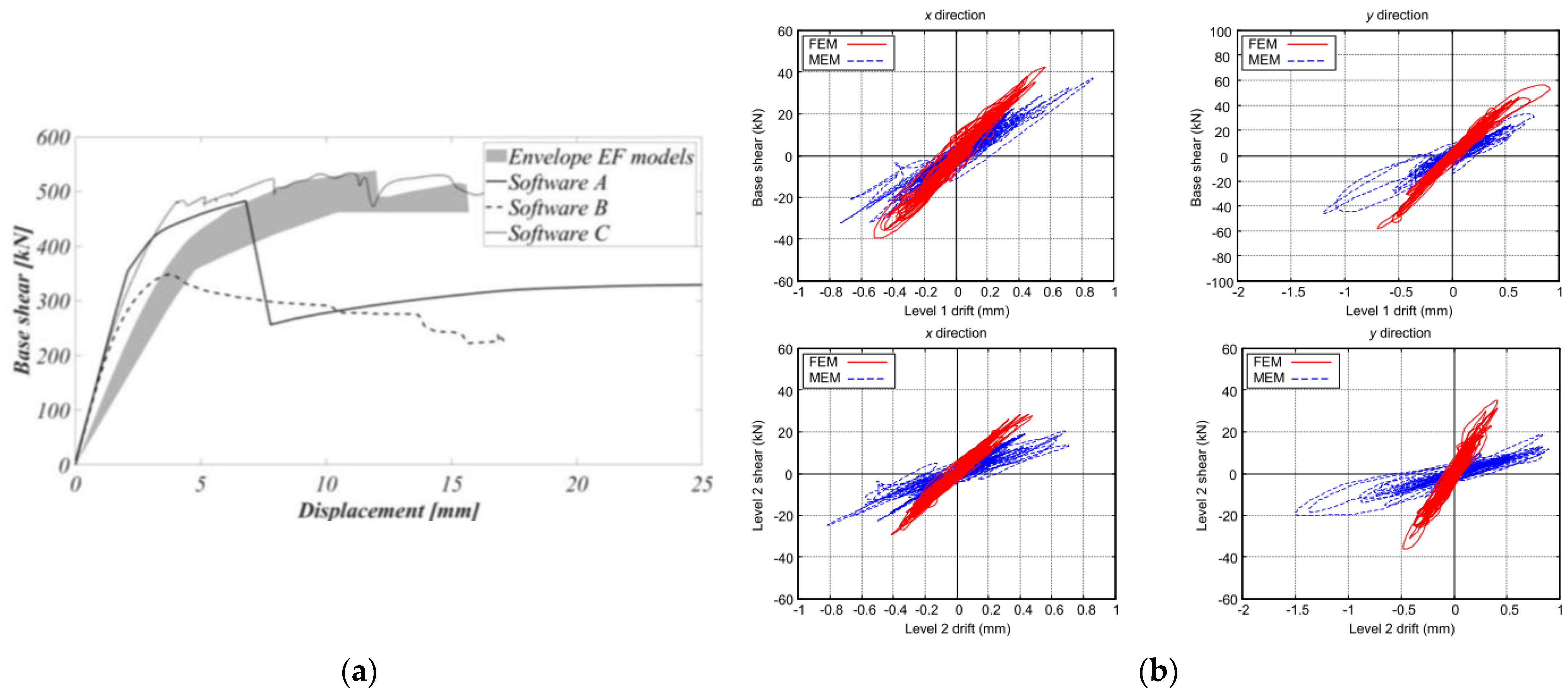
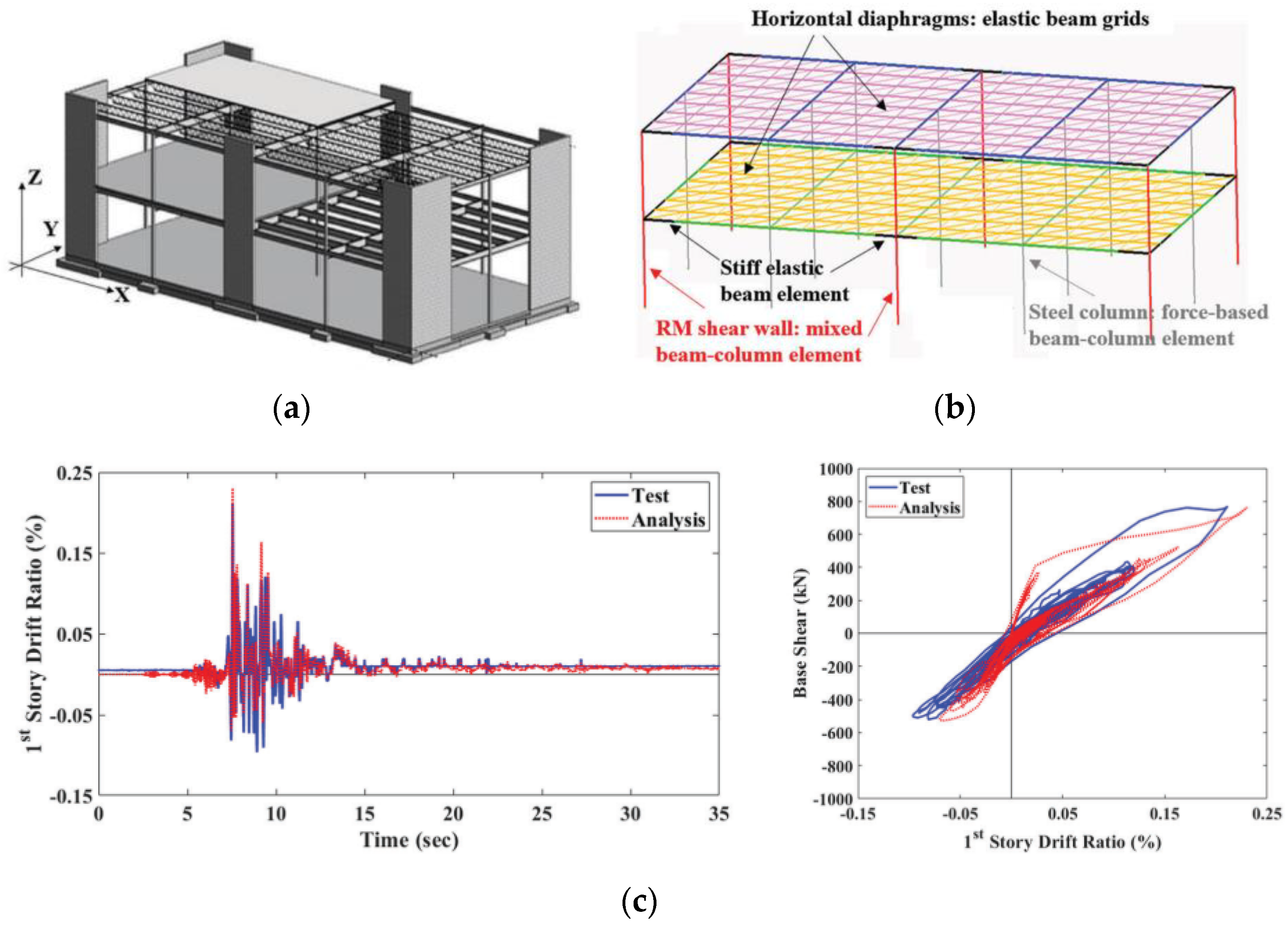
3.2. Building System Tests
3.3. Future Research Needs
4. Numerical Studies of Masonry Walls/Buildings
4.1. Micro Models
4.1.1. Unreinforced Masonry Shear Walls and Buildings
4.1.2. Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls and Buildings
4.2. Macro Models
4.2.1. Unreinforced Masonry Shear Walls and Buildings
4.2.2. Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls and Buildings
4.3. Future Research Needs
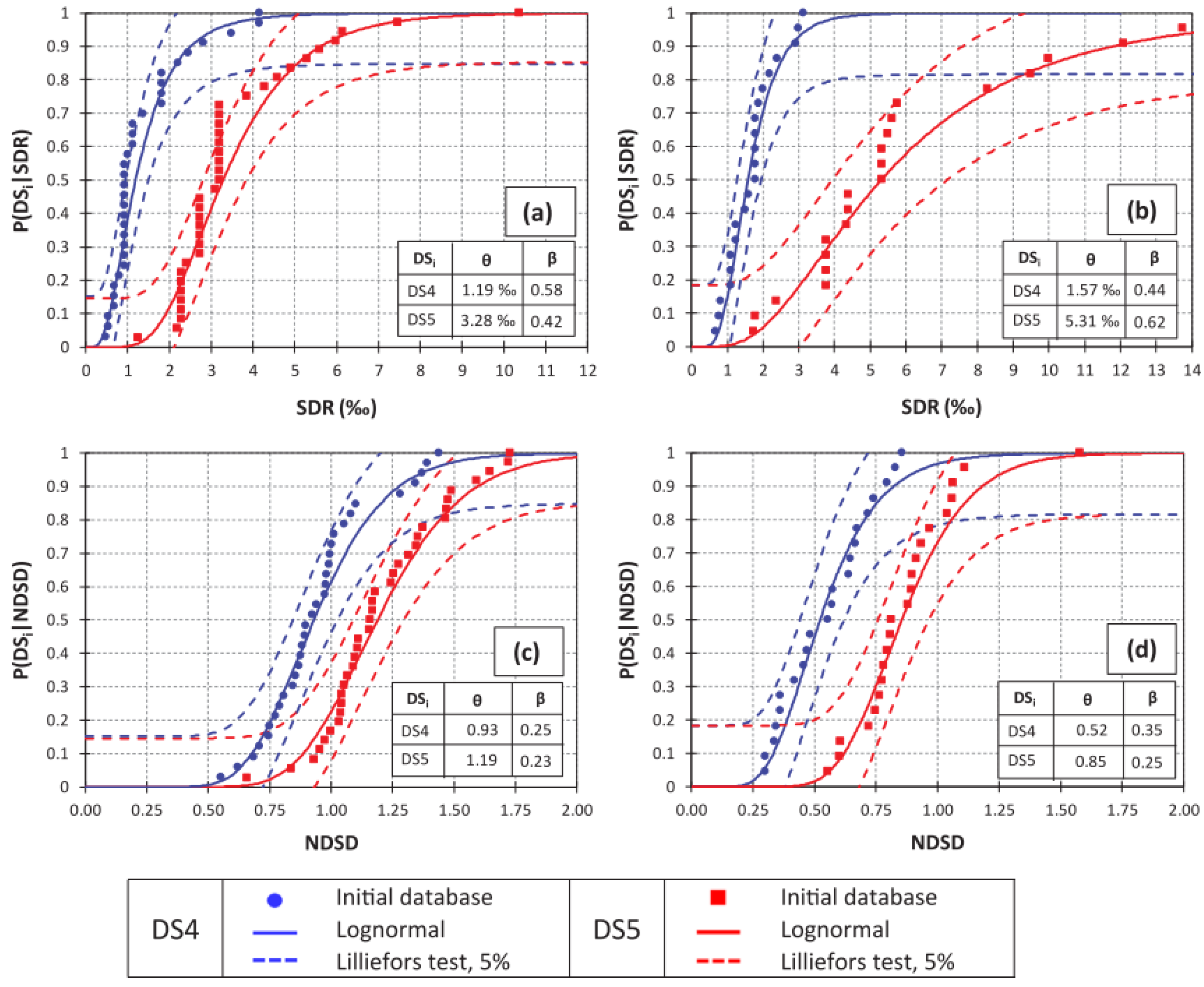
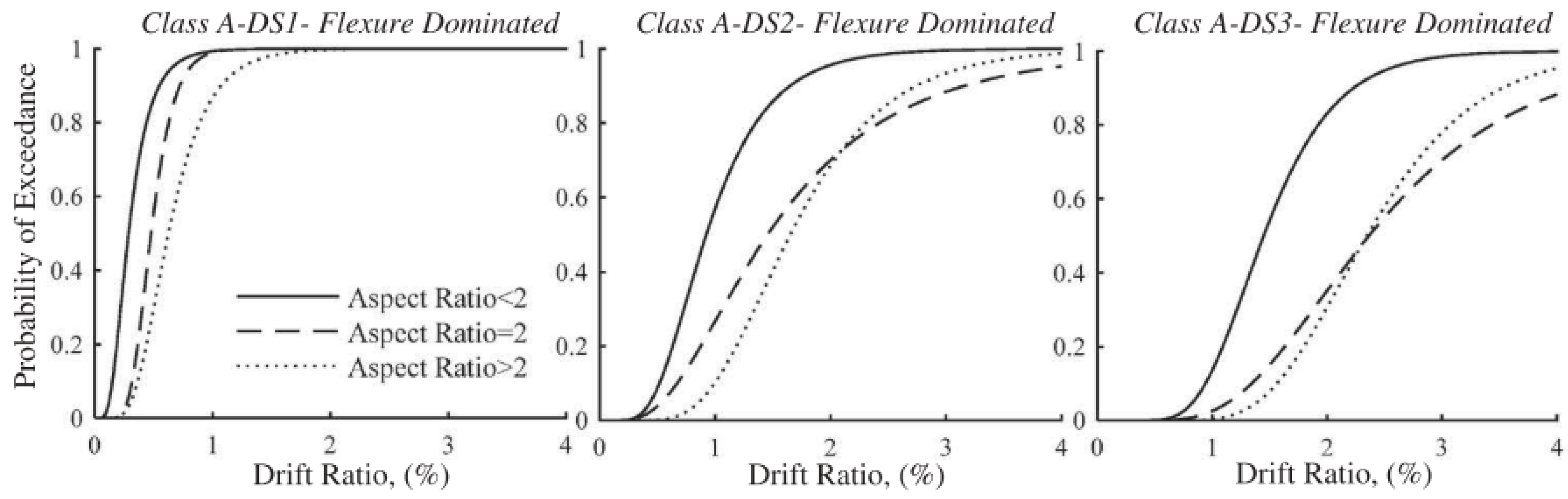
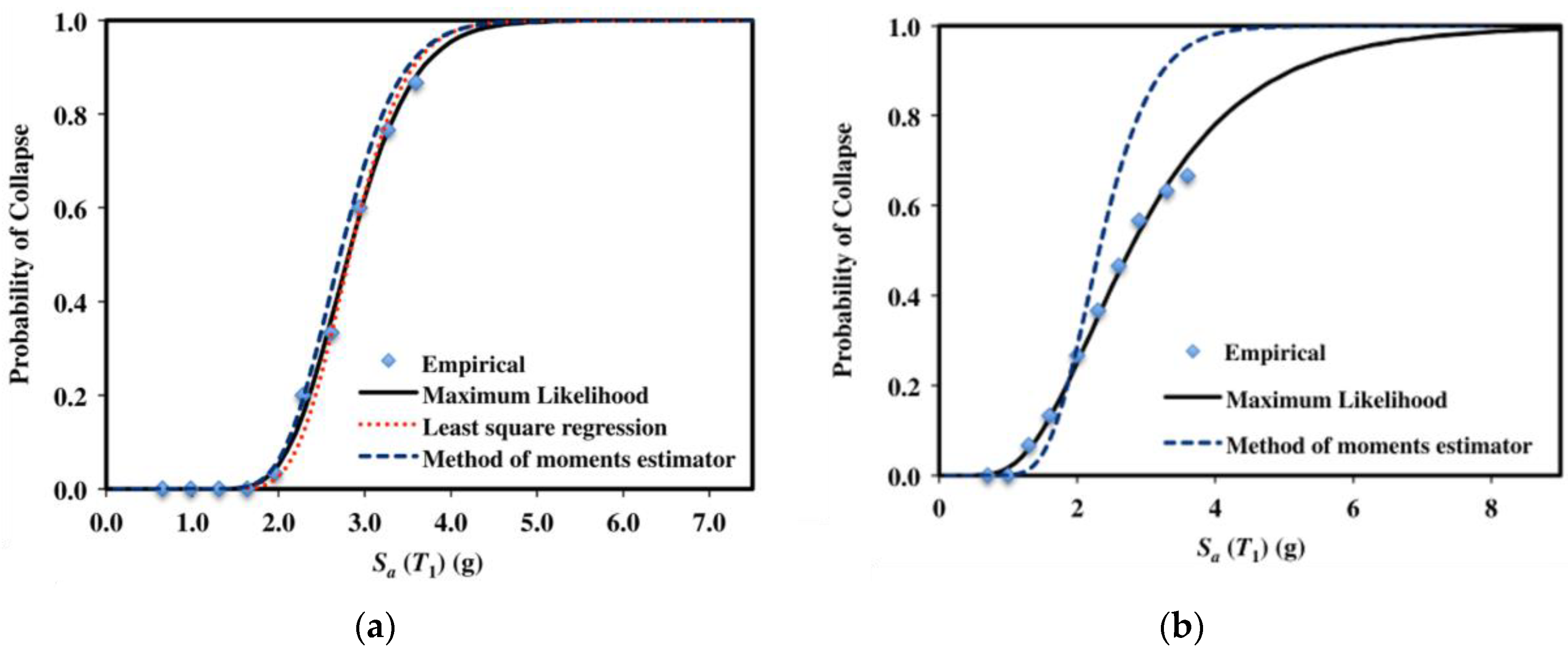
5. Fragility and Performance Assessment of Masonry Walls/Buildings
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ingham, J.M.; Biggs, D.T.; Moon, L.M. How Did Unreinforced Masonry Buildings Perform in the February 2011 Christchurch Earthquake? Struct. Eng. 2011, 89, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Dizhur, D.; Ingham, J.; Moon, L.; Griffith, M.; Schultz, A.; Senaldi, I.; Magenes, G.; Dickie, J.; Lissel, S.; Centeno, J.; et al. Performance of Masonry Buildings and Churches in the 22 February 2011 Christchurch Earthquake. Bull. N. Z. Soc. Earthq. Eng. 2011, 44, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacific Earthquake Engineering Center. Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Design of Tall Buildings; Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center, College of Engineering, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, A.; Zha, A.L.; Caamaño-Withall, Z.A.; Conte, J.P.; Restrepo, J.I. Simplified Risk-Targeted Performance-Based Seismic Design Method for Ordinary Standard Bridges. J. Bridg. Eng. 2022, 27, 04022089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Conte, J.P.; Gill, P.E. Probabilistic Performance-Based Optimum Seismic Design Framework: Illustration and Validation. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2019, 120, 517–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Conte, J.P. Probabilistic Performance-Based Optimum Design of Seismic Isolation for a California High-Speed Rail Prototype Bridge. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 47, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braverman, J.; Morante, R. Evaluation of ASCE 4-16 and AISC 43-18 (Draft) for Use in the Risk-Informed Performance-Based Seismic Design of Nuclear Power Plant Structures, Systems, and Components; Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL): Upton, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 18, ISBN 2207222020. [Google Scholar]
- CSA S304-14; Design of Masonry Structures. Canadian Standards Association: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 2014.
- Masonry Society. Building Code Requirements and Specification for Masonry Structures (TMS 402/602-16); The Masonry Society: Boulder, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council of Canada. National Building Code of Canada; NRCC: Ottawa, ON, USA, 2015.
- NIST. Research Required to Support Full Implementation of Performance-Based Seismic Design; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA; U.S. Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Hwang, S.H.; Kim, S.; Yang, K.H. In-Plane Lateral Load Transfer Capacity of Unreinforced Masonry Walls Considering Presence of Openings. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 47, 103868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applied Technology Council. NEHRP Guidelines for the Seismic Rehabilitation of Buildings; FEMA 273; Federal Emergency Management Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; p. 435.
- Haach, V.G.; Vasconcelos, G.; Lourenço, P.B. Proposal of a Design Model for Masonry Walls Subjected to In-Plane Loading. J. Struct. Eng. 2013, 139, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEN (European Committee for Standardization). Design of Masonry Structures—Part 1-1: General Rules for Reinforced and Unreinforced Masonry Structures; EN 1996-1-1; Eurocode 6; CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo, K. Statistical Prediction Methods for the In-Plane Shear Strength of Partially Grouted Masonry Walls. Master’s Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, D.P. Performance-Based Engineeringconcepts for Unreinforced Masonry Building Structures. Prog. Struct. Eng. Mater. 2001, 3, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerema, P.; Ashour, A.; Shedid, M.; El-Dakhakhni, W. System-Level Displacement- and Performance-Based Seismic Design Parameter Quantifications for an Asymmetrical Reinforced Concrete Masonry Building. J. Struct. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celano, T.; Argiento, L.U.; Ceroni, F.; Casapulla, C. Literature Review of the In-Plane Behavior of Masonry Walls: Theoretical vs. Experimental Results. Materials 2021, 14, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Kioumarsi, M.; Zucconi, M. State of the Art of Simplified Analytical Methods for Seismic Vulnerability Assessment of Unreinforced Masonry Buildings. Eng. Struct. 2021, 239, 112280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Altri, A.M.; Sarhosis, V.; Milani, G.; Rots, J.; Cattari, S.; Lagomarsino, S.; Sacco, E.; Tralli, A.; Castellazzi, G.; de Miranda, S. Modeling Strategies for the Computational Analysis of Unreinforced Masonry Structures: Review and Classification. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2020, 27, 1153–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattari, S.; Calderoni, B.; Caliò, I.; Camata, G.; de Miranda, S.; Magenes, G.; Milani, G.; Saetta, A. Nonlinear Modeling of the Seismic Response of Masonry Structures: Critical Review and Open Issues towards Engineering Practice. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 20, 1939–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dakhakhni, W.; Ashour, A. Seismic Response of Reinforced-Concrete Masonry Shear-Wall Components and Systems: State of the Art. J. Struct. Eng. 2017, 143, 03117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vision, S. Performance Based Seismic Engineering of Buildings; Structural Engineers Association of California: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- FEMA P-2082; NEHRP Recommended Seismic Provisions for New Buildings and Other Structures. Building Seismic Safety Council: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- Vaiana, N.; Rosati, L. Classification and Unified Phenomenological Modeling of Complex Uniaxial Rate-Independent Hysteretic Responses. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2023, 182, 109539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiana, N.; Capuano, R.; Rosati, L. Evaluation of Path-Dependent Work and Internal Energy Change for Hysteretic Mechanical Systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 186, 109862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampoli, M.; Petrini, F.; Augusti, G. Performance-Based Wind Engineering: Towards a General Procedure. Struct. Saf. 2011, 33, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, R.; Hall, J.; Davis, J. Performance-Based Management of Flood Defence Systems. In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers: Water Management; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 2004; Volume 157, pp. 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Burgess, I.; Wald, F.; Gillie, M. Performance-Based Fire Engineering of Structures; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780203868713. [Google Scholar]
- Quiel, S.E.; Marjanishvili, S.M.; Katz, B.P. Performance-Based Framework for Quantifying Structural Resilience to Blast-Induced Damage. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, C4015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Bi, K.; Chen, W.; Pham, T.M.; Li, J. Towards next Generation Design of Sustainable, Durable, Multi-Hazard Resistant, Resilient, and Smart Civil Engineering Structures. Eng. Struct. 2023, 277, 115477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, M.K. In-Plane Behaviour of Unreinforced Masonry (URM) Walls with Openings in Australian Heritage Construction. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Newcastle, Newcastle, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Salmanpour, A.H. Displacement Capacity of Structural Masonry. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, D.P.; Shah, N. Cyclic Load Testing of Unreinforced Masonry Walls; Advanced Construction Technology Center Report, No. 92-26-10; University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign: Champaign, IL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Raijmakers, T.M.J. Deformation Controlled Tests in Masonry Shear Walls: Report B-92-1156; TNO-Bouw: Delft, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Anthoine, A.; Magonette, G.; Magenes, G. Shear-Compression Testing and Analysis of Brick Masonry Walls. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Vienna, Austria, 28 August–2 September 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Churilov, S.; Dumova-Jovanoska, E. In-Plane Shear Behaviour of Unreinforced and Jacketed Brick Masonry Walls. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 50, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzaleh, A.S. Seismic In-Plane Behavior of Post-Tensioned Existing Clay Brick Masonry Walls. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, C.; Masia, M.J.; Page, A.W.; Griffith, M.C.; Derakhshan, H.; Mojsilović, N. Experimental Testing of Unreinforced Masonry Walls with Openings Subject to Cyclic In-Plane Shear. In Brick and Block Masonry-Trends, Innovations and Challenges, Proceedings of the 16th International Brick and Block Masonry Conference (IBMAC 2016), Padova, Italy, 26–30 June 2016; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; pp. 26–30.
- Messali, F.; Esposito, R.; Ravenshorst, G.J.P.; Rots, J.G. Experimental Investigation of the In-Plane Cyclic Behaviour of Calcium Silicate Brick Masonry Walls. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 18, 3963–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, M.K.; Masia, M.J.; Griffith, M.C. In-Plane Response of Perforated Unreinforced Masonry Walls under Cyclic Loading: Experimental Study. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, T.; Milani, G.; Kaushik, H.B. Experimental and Numerical Analyses of Unreinforced Masonry Wall Components and Building. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Moya, L.; Fajardo, C.; Morita, K. Experimental Study on Dynamic Behavior of Unreinforced Masonry Walls. J. Disaster Res. 2013, 8, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Porto, F. In-Plane Cyclic Behaviour of Thin Layer Joint Masonry Walls. Ph.D. Thesis, Universita’ Degli Studi di Trento, Trento, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Magenes, G.; Morandi, P.; Penna, A. D 7.1c Test Results on the Behaviour of Masonry under Static Cyclic in Plane Lateral Loads; University of Pavia: Agropoli, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Petry, S.; Beyer, K. Cyclic Test Data of Six Unreinforced Masonry Walls with Different Boundary Conditions. Earthq. Spectra 2015, 31, 2459–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmanpour, A.H.; Mojsilović, N.; Schwartz, J. Displacement Capacity of Contemporary Unreinforced Masonry Walls: An Experimental Study. Eng. Struct. 2015, 89, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magenes, G.; Penna, A.; Galasco, A.; da Paré, M. In-Plane Cyclic Shear Tests of Undressed Double Leaf Stone Masonry Panels. In Proceedings of the 8th International Masorny Conference, Dresden, Germany, 4–7 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, M. What TCCMAR Taught Us. Mag. Mason. Constr. 1998, 11, 523–529. [Google Scholar]
- Shing, P.B.; Schuller, M.; Hoskere, V.S. In-Plane Resistance of Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 1990, 116, 619–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shing, B.P.B.; Member, A.; Noland, J.L.; Klamerus, E.; Spaeh, H. Inelastic Behaviors of Concrete Masonry Shear Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 1990, 115, 2204–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashi, K.; Hiroshi, I.; Yoshiharu, Y.; Ryogo, K. Seismic Capacity of Reinforced Masonry Walls Including Effects of Axial Stress. In Proceedings of the 4th Canadian Masonry Symposium, Fredericton, NB, USA, 2–4 June 1986; pp. 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminosono, T.; Teshigawara, M.; Haraishi, H.; Fujiissawa, M.; Nakaoka, A. Expermental Study on Seismic Performance of Reinforced Masonry Walls. In Proceedings of the Ninth World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Tokyo, Japan, 2–9 August 1988; pp. VI-109–VI-114. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, A. Effect of Shear Reinforcement in Concrete Masonry Walls. In Proceedings of the First Joint Technical Coordinating Committee on Masonry Research; U.S.-Japan Coordinated Earthquake Research Program: Gaitherburg, MD, USA, 1985; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Shing, P.B.; Schuller, M.; Houskere, V.S.; Carter, E. Flexural and Shear Response of Reinforced Masonry Walls. Struct. J. 1990, 87, 646–656. [Google Scholar]
- Shing, P.B.; Schuller, M.H.; Hoskere, V.S. Strength and Ductility of Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls. In Proceedings of the 5th North American Masonry Conference, Boulder, CO, USA, 3–6 June 1990; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shing, P.B.; Klamerus, E.; Spaeh, H.; Noland, J.L. Seismic Performance of Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls. In Proceedings of the 9th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Tokyo, Japan, 2–9 August 1988; Volume 6, pp. 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, A. Shear Strength of Reinforced Hollow Unit Masonry Walls. In Proceedings of the 4th North American Masonry Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 16–19 August 1987; pp. 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kaminosorno, T.; Teshigawara, M.; Hirashi, H. Seismic Capacity of Reinforced Masonry Walls and Beams. In Proceedings of the 18th Joint Meeting of the U.S. Japan Cooperative Programs in Natural Resource Panel on Wind and Seismic Effects, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 20–21 February 1987; pp. 307–319. [Google Scholar]
- Masonry Standards Joint Committee; American Concrete Institute; Structural Engineering Institute; Masonry Society (U.S.). Building Code Requirements and Specification for Masonry Structures; The Masonry Society: Longmont, CO, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781929081431. [Google Scholar]
- AIJ Standards for Structural Design of Masonry Structures (1989 Edition); Architectural Institute of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 1993.
- Kikuchi, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Yoshida, K.; Tanaka, A.; Urasaki, H.; Kijima, Y.; Mizumasa, N. Experimental Study on Seismic Capacity of Reinforced Fully Grouted Concrete Masonry Walls. In Proceedings of the 13th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1–6 August 2004; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Shedid, M.M.T. Ductility of Reinforced Concrete Masonry Shear Walls. Master’s Thesis, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shedid, M.T.; El-Dakhakhni, W.W.; Drysdale, R.G. Behavior of Fully Grouted Reinforced Concrete Masonry Shear Walls Failing in Flexure: Experimental Results. J. Struct. Eng. 2008, 134, 1754–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedid, M.T. Strategies to Enhance Seismic Performance of Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls. Ph.D. Thesis, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Voon, K.C.; Ingham, J.M. Experimental In-Plane Strength Investigation of Reinforced Concrete Masonry Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2006, 132, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutalan, F.A. Displacement-Based Seismic Design and Tools for Reinforced Masonry Shear-Wall Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman, J.D. Effects of Key Parameters on the Performance of Concrete Masonry Shear Walls under In-Plane Loading. Master’s Thesis, Washington State University, Pullman, WA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoi, C.M. Experimental Performance of Concrete Masonry Shear Walls under In-Plane Loading. Master’s Thesis, Washington State University, Pullman, WA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, J.F. Quasi-Static Testing of Cantilever Masonry Shear Wall Segments. Master’s Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cyrier, W.B. Performance of Concrete Masonry Shear Walls with Integral Confined Concrete Boundary Elements. Master’s Thesis, Washington State University, Pullman, WA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, F. Experimental Studies on Behavior of Fully Grouted Reinforced-Concrete Masonry Shear Walls. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2015, 14, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyam, M.A.; El-Dakhakhni, W.W.; Shedid, M.T.; Drysdale, R.G. Seismic Response Evaluation of Ductile Reinforced Concrete Block Structural Walls. I: Experimental Results and Force-Based Design Parameters. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2016, 30, 04015066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, H.M.S. In-Plane Shear Behaviour of Fully Grouted Reinforced Masonry Shear Wall. Ph.D. Thesis, Concordia University, Montréal, QC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Seif ElDin, H.M.; Galal, K. In-Plane Seismic Performance of Fully Grouted Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, S.; El-Dakhakhni, W.W.; Tait, M.J. Shake Table Seismic Performance Assessment of Lightly Reinforced Concrete Block Shear Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, S.; El-Dakhakhni, W.W.; Tait, M.J. Seismic Fragility Evaluation of Lightly Reinforced Concrete-Block Shear Walls for Probabilistic Risk Assessment. J. Struct. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, A.E. NIST Research Program on the Seismic Resistance of Partially-Grouted Masonry Shear Walls; NISTIR 5481; US National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1994; p. 110. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, A.E. Seismic Resistance of Partially-Grouted Masonry Shear Walls. In Proceedings of the Eleven World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Acapulco, Mexico, 23–28 June 1996; pp. 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki, M. Behaviour of Partially Grouted Masonry Shear Walls under Cyclic Reversed Loading. Ph.D. Thesis, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hamedzadeh, A. On the Shear Strength of Partially Grouted Concrete Masonry. Master’s Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bolhassani, M. Improvement of Seismic Performance of Ordinary Reinforced Partially Grouted Concrete Masonry Shear Walls. Ph.D. Thesis, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, P.; Sandoval, C.; Almazán, J.L. Experimental Study on In-Plane Cyclic Response of Partially Grouted Reinforced Concrete Masonry Shear Walls. Eng. Struct. 2016, 126, 598–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, S.; Vargas, L.; Sandoval, C.; Araya-Letelier, G. Behavior of Partially Grouted Concrete Masonry Walls under Quasi-Static Cyclic Lateral Loading. Materials 2020, 13, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizaee, S. Assessing Bond Beam Horizontal Reinforcement Efficacy with Different End Anchorage Conditions in Concrete Block Masonry Shear Walls. Master’s Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kasparik, T.; Tait, M.J.; El-Dakhakhni, W.W. Seismic Performance Assessment of Partially Grouted, Nominally Reinforced Concrete-Masonry Structural Walls Using Shake Table Testing. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2014, 28, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmapruk, J.; ElGawady, M.A.; Hassanli, R. Experimental and Analytical Study on the Shear-Strength of Partially Grouted Masonry Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Leiva, D.A.; Picado-Arguedas, A.; Sánchez-Vargas, N. In-Plane Cyclic Performance of Confined Partially Grouted Masonry Walls with Joint and Vertical Reinforcement. Eng. Struct. 2021, 245, 112881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, S.; Sandoval, C.; Araya-Letelier, G.; Inzunza, E.; Milani, G. Quasi-Static Testing of Concrete Masonry Shear Walls with Different Horizontal Reinforcement Schemes. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 38, 102201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmapruk, J.H. Shear Strength of Partially Grouted Squat Masonry Shear Walls. Master’s Thesis, Washington State University, Pullman, WA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nolph, S.M. In-Plane Shear Performance of Partially Grouted Masonry Shear Walls. Master’s Thesis, Washington State University, Pullman, WA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nolph, S.M.; ElGawady, M.A. Static Cyclic Response of Partially Grouted Masonry Shear Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2012, 138, 864–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, N. In-Plane Cyclic Testing of Reinforced Concrete Masonry Walls to Assess the Effect of Varying Reinforcement Anchorage and Boundary Conditions. Master’s Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaževič, M.; Lutman, M.; Petković, L. Seismic Behavior of Masonry Walls: Experimental Simulation. J. Struct. Eng. 1996, 122, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voon, K.C.; Ingham, J.M. Shear Strength of Concrete Masonry Walls; Report No. 611; Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Auckland: Auckland, New Zealand, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Minaie, E.; Mota, M.; Moon, F.L.; Hamid, A.A. In-Plane Behavior of Partially Grouted Reinforced Concrete Masonry Shear Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2010, 136, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oan, A. Diagonal Shear of Partially Grouted Concrete Masonry Panels. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Psilla, N.; Tassios, T.P. Design Models of Reinforced Masonry Walls under Monotonic and Cyclic Loading. Eng. Struct. 2009, 31, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, P.B.; Avila, L.; Vasconcelos, G.; Alves, J.P.P.; Mendes, N.; Costa, A.C. Experimental Investigation on the Seismic Performance of Masonry Buildings Using Shaking Table Testing. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 11, 1157–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldemir, A.; Binici, B.; Canbay, E.; Yakut, A. Lateral Load Testing of an Existing Two Story Masonry Building up to near Collapse. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 15, 3365–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Moon, F.L.; Leon, R.T.; Kahn, L.F. Lateral Load Tests on a Two-Story Unreinforced Masonry Building. J. Struct. Eng. 2006, 132, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, J.; Bruneau, M. Pseudo-Dynamic Testing of Unreinforced Masonry Building with Flexible Diaphragm. J. Struct. Eng. 2003, 6, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G.L.; Klingner, R.E.; Hayes, J.R.J.; Sweeney, S.C. Seismic Response of Low-Rise Masonry Buildings with Flexible Roof Diaphragms; Report No. SR-01-19; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Construction Engineering Research Laboratory: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Cohen, G.L.; Klingner, R.E.; Hayes, J.R.; Sweeney, S.C. Seismic Evaluation of Low-Rise Reinforced Masonry Buildings with Flexible Diaphragms: I. Seismic and Quasi-Static Testing. Earthq. Spectra 2004, 20, 779–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, N.; Lourenço, P.B.; Campos-Costa, A. Shaking Table Testing of an Existing Masonry Building: Assessment and Improvement of the Seismic Performance. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 43, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, L.; Vasconcelos, G.; Lourenço, P.B. Experimental Seismic Performance Assessment of Asymmetric Masonry Buildings. Eng. Struct. 2018, 155, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomazevic, M. Seismic Behavior of Plain- and Reinforced-Masonry Buildings. J. Struct. Eng. 1994, 120, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavros, M. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Seismic Performance of Reinforced Masonry Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mavros, M.; Ahmadi, F.; Shing, P.B.; Klingner, R.E.; McLean, D.; Stavridis, A. Shake-Table Tests of a Full-Scale Two-Story Shear-Dominated Reinforced Masonry Wall Structure. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavridis, A.; Ahmadi, F.; Mavros, M.; Shing, P.B.; Klingner, R.E.; McLean, D. Shake-Table Tests of a Full-Scale Three-Story Reinforced Masonry Shear Wall Structure. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutras, A.A.; Shing, P.B. Seismic Behavior of a Partially Grouted Reinforced Masonry Structure: Shake-Table Testing and Numerical Analyses. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 49, 1115–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Koutras, A.A.; Shing, P.B. Evaluation of Collapse Resistance of Reinforced Masonry Wall Systems by Shake-Table Tests. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 50, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, P.B.; Rots, J.; Blaauwendraad, J. Two Approaches for the Analysis of Masonry Structures. Heron 1995, 40, 313–340. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A.W. Finite Element Model for Masonry. J. Struct. Div. 1978, 104, 1267–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, B. Modeling of Masonry Structures Using a New 3D Cohesive Interface Material Model Considering Dilatancy Softening. Eng. Struct. 2023, 277, 115466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, H.R.; Shing, P.B. Interface Model Applied to Fracture of Masonry Structures. J. Struct. Eng. 1994, 120, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Wang, X.; Kong, J.; Li, S.; Xie, L. Numerical Simulation of Masonry-Infilled RC Frames Using XFEM. J. Struct. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutromanos, I.; Shing, P.B. Cohesive Crack Model to Simulate Cyclic Response of Concrete and Masonry Structures. ACI Struct. J. 2012, 109, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambanco, G.; Rizzo, S.; Spallino, R. Numerical Analysis of Masonry Structures via Interface Models. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2001, 190, 6493–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, K.F.; Cunningham, L.S.; Gillie, M. Simulating Masonry Wall Behaviour Using a Simplified Micro-Model Approach. Eng. Struct. 2017, 151, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Li, Y.; Cruz Noguez, C. Modeling and Parameter Importance Investigation for Simulating In-Plane and out-of-Plane Behaviors of Un-Reinforced Masonry Walls. Eng. Struct. 2021, 248, 113233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, P.B. Computational Strategies for Masonry Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lourenço, P.B.; Rots, J.G. Multisurface Interface Model for Analysis of Masonry Structures. J. Eng. Mech. 1997, 123, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citto, C. Two-Dimentional Interface Model Applied to Masonry Structures. Master’s Thesis, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- DaPorto, F.; Guidi, G.; Garbin, E.; Modena, C. In-Plane Behavior of Clay Masonry Walls: Experimental Testing and Finite-Element Modeling. J. Struct. Eng. 2010, 136, 1379–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Amirtham, R.; Pandey, M. Plasticity Based Approach for Failure Modelling of Unreinforced Masonry. Eng. Struct. 2014, 80, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zijl, G.P.A.G. Modeling Masonry Shear-Compression: Role of Dilatancy Highlighted. J. Eng. Mech. 2004, 130, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, S.; Dhanasekar, M. A Non-Linear Interface Element Model for Thin Layer High Adhesive Mortared Masonry. Comput. Struct. 2014, 144, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, A.J.; Dolatshahi, K.M. A Three-Dimensional Cyclic Meso-Scale Numerical Procedure for Simulation of Unreinforced Masonry Structures. Comput. Struct. 2013, 120, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Barbato, M. New Constitutive Model for Interface Elements in Finite-Element Modeling of Masonry. J. Eng. Mech. 2019, 145, 04019022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macorini, L.; Izzuddin, B.A. A Non-Linear Interface Element for 3D Mesoscale Analysis of Brick-masonry Structures. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2011, 85, 1584–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatshahi, K.M.; Aref, A.J. Two-Dimensional Computational Framework of Meso-Scale Rigid and Line Interface Elements for Masonry Structures. Eng. Struct. 2011, 33, 3657–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadlou, M.; Ahmadi, E.; Kashani, M.M. Micromechanical Modelling of Mortar Joints and Brick-Mortar Interfaces in Masonry Structures: A Review of Recent Developments. Structures 2020, 23, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.C.; Yalamanchili, K.K. Three-Dimensional Failure Analysis of Composite Masonry Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 1996, 122, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambacq, J.; Ulloa, J.; Lombaert, G.; François, S. A Variationally Coupled Phase Field and Interface Model for Fracture in Masonry. Comput. Struct. 2022, 264, 106744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouchal, F.; Lebon, F.; Titeux, I. Contribution to the Modelling of Interfaces in Masonry Construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2428–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Altri, A.M.; de Miranda, S.; Castellazzi, G.; Sarhosis, V. A 3D Detailed Micro-Model for the in-Plane and out-of-Plane Numerical Analysis of Masonry Panels. Comput. Struct. 2018, 206, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, F.; Leonetti, L.; Luciano, R.; Nevone Blasi, P. An Adaptive Multiscale Strategy for the Damage Analysis of Masonry Modeled as a Composite Material. Compos. Struct. 2016, 153, 972–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandoren, B.; DeProft, K.; Simone, A.; Sluys, L.J. Mesoscopic Modelling of Masonry Using Weak and Strong Discontinuities. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 255, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambanco, G.; LaMalfa Ribolla, E.; Spada, A. Meshless Meso-Modeling of Masonry in the Computational Homogenization Framework. Meccanica 2018, 53, 1673–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drougkas, A.; Roca, P.; Molins, C. Experimental Analysis and Detailed Micro-Modeling of Masonry Walls Subjected to in-Plane Shear. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 95, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfia, S.; Sacco, E. Multiscale Damage Contact-Friction Model for Periodic Masonry Walls. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2012, 205–208, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xiangli, C.; Bin, L. Modeling of Influence of Heterogeneity on Mechanical Performance of Unreinforced Masonry Shear Walls. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaimoon, K.; Attard, M.M. Modeling of Unreinforced Masonry Walls under Shear and Compression. Eng. Struct. 2007, 29, 2056–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berto, L.; Saetta, A.; Scotta, R.; Vitaliani, R. Shear Behaviour of Masonry Panel: Parametric FE Analyses. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2004, 41, 4383–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambarotta, L.; Lagomarsino, S. Damage Models for the Seismic Response of Brick Masonry Shear Walls. Part I: The Mortar Joint Model and Its Applications. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1997, 26, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Sheikh, A.; Visintin, P.; Griffith, M. An Interfacial Damage-Plastic Model for the Simulation of Masonry Structures under Monotonic and Cyclic Loadings. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 271, 108645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minga, E.; Macorini, L.; Izzuddin, B.A. A 3D Mesoscale Damage-Plasticity Approach for Masonry Structures under Cyclic Loading. Meccanica 2018, 53, 1591–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.V.; Lourenço, P.B. Implementation and Validation of a Constitutive Model for the Cyclic Behaviour of Interface Elements. Comput. Struct. 2004, 82, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Altri, A.M.; Messali, F.; Rots, J.; Castellazzi, G.; de Miranda, S. A Damaging Block-Based Model for the Analysis of the Cyclic Behaviour of Full-Scale Masonry Structures. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2019, 209, 423–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavartanoo, F.; Kang, T.H.-K. Dry-Stack Masonry Wall Modeling Using Finite-Element Method. J. Struct. Eng. 2022, 148, 04022176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Sheikh, A.; Griffith, M.; Visintin, P. A Damage-Plasticity Based Interface Model for Simulating in-Plane/out-of-Plane Response of Masonry Structural Panels. Comput. Struct. 2022, 260, 106721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Sousamli, M.; Messali, F.; Rots, J.G. A Sub-Stepping Iterative Constitutive Model for Cyclic Cracking-Crushing-Shearing in Masonry Interface Elements. Comput. Struct. 2021, 257, 106654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, C.; Macorini, L.; Izzuddin, B.A. Mesoscale Modeling of a Masonry Building Subjected to Earthquake Loading. J. Struct. Eng. 2021, 147, 04020294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shing, P.B.; Cao, L. Analysis of Partially Grouted Masonry Shear Walls; NIST GCR Report; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bolhassani, M.; Hamid, A.A.; Moon, F.L. Enhancement of Lateral In-Plane Capacity of Partially Grouted Concrete Masonry Shear Walls. Eng. Struct. 2016, 108, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Fenves, G.L. Plastic-Damage Model for Cyclic Loading of Concrete Structures. J. Eng. Mech. 1998, 124, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, S.; Sandoval, C.; Arnau, O. Shear Response of Partially-Grouted Reinforced Masonry Walls with a Central Opening: Testing and Detailed Micro-Modelling. Mater. Des. 2017, 118, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, S.; Arnau, O.; Sandoval, C. Detailed Micro-Modeling Approach and Solution Strategy for Laterally Loaded Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls. Eng. Struct. 2019, 201, 109786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, S.; Milani, G.; Sandoval, C. Simplified Micro-Modeling of Partially-Grouted Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls with Bed-Joint Reinforcement: Implementation and Validation. Eng. Struct. 2021, 234, 111987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fib. Fib Model Code for Concrete Structures 2010; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–402. [Google Scholar]
- Calderón, S.; Sandoval, C.; Milani, G.; Arnau, O. Detailed Micro-Modeling of Partially Grouted Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls: Extended Validation and Parametric Study. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2021, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutras, A. Assessment of the Seismic Behavior of Fully and Partially Grouted Reinforced Masonry Structural Systems through Finite Element Analysis and Shake-Table Testing. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, San Diego, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Koutras, A.A.; Shing, P.B. Finite-Element Modeling of the Seismic Response of Reinforced Masonry Wall Structures. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 50, 1125–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutras, A.A.; Shing, P.B. Numerical and Experimental Assessment of an Improved Design Detail for Partially Grouted Reinforced Masonry Wall Structures. J. Struct. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmeligy, O.; Aly, N.; Galal, K. Sensitivity Analysis of the Numerical Simulations of Partially Grouted Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls. Eng. Struct. 2021, 245, 112876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.S.; Vecchio, F.J.; Trommels, H. Vector2 & Formworks User’s Manual, 2nd ed.; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Berto, L.; Saetta, A.; Scotta, R.; Vitaliani, R. An Orthotropic Damage Model for Masonry Structures. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2002, 55, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelà, L.; Cervera, M.; Roca, P. An Orthotropic Damage Model for the Analysis of Masonry Structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 41, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambarotta, L.; Lagomarsino, S. Damage Models for the Seismic Response of Brick Masonry Shear Walls. Part II: The Continuum Model and Its Applications. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1997, 26, 441–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchini, A.; Lourenço, P.B. A Coupled Homogenisation-Damage Model for Masonry Cracking. Comput. Struct. 2004, 82, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelà, L.; Cervera, M.; Roca, P. Continuum Damage Model for Orthotropic Materials: Application to Masonry. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapitta, L.; Mouzakis, H.; Carydis, P. Explicit Finite-Element Analysis for the in-Plane Cyclic Behavior of Unreinforced Masonry Structures. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2011, 40, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderini, C.; Lagomarsino, S. Continuum Model for In-Plane Anisotropic Inelastic Behavior of Masonry. J. Struct. Eng. 2008, 134, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, P.B. Anisotropic Softening Model for Masonry Plates and Shells. J. Struct. Eng. 2000, 126, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, H.R.; Shing, P.B. An Appraisal of Smeared Crack Models for Masonry Shear Wall Analysis. Comput. Struct. 1991, 41, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, P.B.; De Borst, R.; Rots, J.G. A Plane Stress Softening Plasticity Model for Orthotropic Materials. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1997, 40, 4033–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, P.B.; Rots, J.G.; Blaauwendraad, J. Continuum Model for Masonry: Parameter Estimation and Validation. J. Struct. Eng. 1998, 124, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Buhan, P.; De Felice, G. A Homogenization Approach to the Ultimate Strength of Brick Masonry. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1997, 45, 1085–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, C.; Macorini, L.; Izzuddin, B.A. An Anisotropic Plastic-Damage Model for 3D Nonlinear Simulation of Masonry Structures. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2023, 124, 1253–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.; Oller, S.; Oñate, E.; Lubliner, J. A Homogeneous Constitutive Model for Masonry. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1999, 46, 1651–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacila, J.; Camata, G.; Salsavilca, J.; Tarque, N. Pushover Analysis of Confined Masonry Walls Using a 3D Macro-Modelling Approach. Eng. Struct. 2019, 201, 109731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Slip-Enhanced Plastic-Damage Constitutive Model for Masonry Structures. Eng. Struct. 2022, 254, 113792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, C.; Addessi, D.; Vestroni, F. Static and Dynamic Nonlinear Response of Masonry Walls. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 155, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biye, W.; Junwu, D.; Wen, B.; Yongqiang, Y. Triaxial Elastoplastic Damage Constitutive Model of Unreinforced Clay Brick Masonry Wall. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2022, 22, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Vulnerability Assessment and Collapse Simulation of Unreinforced Masonry Structures Subjected to Sequential Ground Motions. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 20, 8151–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, P.; Molins, C.; Marí, A.R. Strength Capacity of Masonry Wall Structures by the Equivalent Frame Method. J. Struct. Eng. 2005, 131, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruch, M.; Spacone, E.; Shing, P.B. Cyclic Analyses of Reinforced Concrete Masonry Panels Using a Force-Based Frame Element. J. Struct. Eng. 2019, 145, 04019063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeldin, M.; Wiebe, L.; El-Dakhakhni, W. Seismic Collapse Risk Assessment of Reinforced Masonry Walls with Boundary Elements Using the FEMA P695 Methodology. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addessi, D.; Mastrandrea, A.; Sacco, E. An Equilibrated Macro-Element for Nonlinear Analysis of Masonry Structures. Eng. Struct. 2014, 70, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gentilini, C.; Yu, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhao, S. A Unified Model for the Seismic Analysis of Brick Masonry Structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 184, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirsaheb, H.; Javad Moradi, M.; Milani, G. A Multi-Pier MP Procedure for the Non-Linear Analysis of in-Plane Loaded Masonry Walls. Eng. Struct. 2020, 212, 110534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Moon, F.L.; Yi, T. A Macroelement for the Nonlinear Analysis of In-Plane Unreinforced Masonry Piers. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 2242–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanin, F.; Penna, A.; Beyer, K. A Three-Dimensional Macroelement for Modelling the in-Plane and out-of-Plane Response of Masonry Walls. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 49, 1365–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Shing, P.B. A Beam-Column Element for Modeling Nonlinear Flexural and Shear Behaviors of Reinforced Masonry Walls. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 51, 1918–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracchi, S.; Mandirola, M.; Rota, M.; Penna, A. A New Macroelement-Based Strategy for Modelling Reinforced Masonry Piers. In Brick and Block Masonry—From Historical to Sustainable Masonry; CRC Press: London, UK, 2020; pp. 900–907. ISBN 9780367565862. [Google Scholar]
- Kesavan, P.; Menon, A. A Macro-Element with Bidirectional Interaction for Seismic Analysis of Unreinforced Masonry Walls. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 52, 1740–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliò, I.; Marletta, M.; Pantò, B. A New Discrete Element Model for the Evaluation of the Seismic Behaviour of Unreinforced Masonry Buildings. Eng. Struct. 2012, 40, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foraboschi, P.; Vanin, A. Non-Linear Static Analysis of Masonry Buildings Based on a Strut-and-Tie Modeling. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 55, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanin, F.; Penna, A.; Beyer, K. Equivalent-Frame Modeling of Two Shaking Table Tests of Masonry Buildings Accounting for Their Out-of-Plane Response. Front. Built Environ. 2020, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, A.; Lagomarsino, S.; Galasco, A. A Nonlinear Macroelement Model for the Seismic Analysis of Masonry Buildings. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 43, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldin, G.; Amadio, C.; Macorini, L. A Macro-Model with Nonlinear Springs for Seismic Analysis of URM Buildings. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 45, 2261–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirlioglu, K.; Gonen, S.; Soyoz, S.; Limongelli, M.P. In-Plane Seismic Response Analyses of a Historical Brick Masonry Building Using Equivalent Frame and 3D FEM Modeling Approaches. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2020, 14, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracchi, S.; Penna, A. A Novel Macroelement Model for the Nonlinear Analysis of Masonry Buildings. Part 2: Shear Behavior. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 50, 2212–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracchi, S.; Galasco, A.; Penna, A. A Novel Macroelement Model for the Nonlinear Analysis of Masonry Buildings. Part 1: Axial and Flexural Behavior. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 50, 2233–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Kioumarsi, M. A Novel Macroelement for Seismic Analysis of Unreinforced Masonry Buildings Based on MVLEM in OpenSees. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 49, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisse, F.; Marques, R.; Cattari, S.; Lourenço, P.B. Finite Element and Equivalent Frame Modeling Approaches for URM Buildings: Implications of Different Assumptions in the Seismic Assessment. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 61, 105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruch, M.; Spacone, E.; Camata, G. Nonlinear Analysis of Masonry Structures Using Fiber-Section Line Elements. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 48, 1345–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Shing, P.B. Practical Nonlinear Analysis Methods for Flexure-Dominated Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2022, 148, 04022109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloustros, S.; Pelà, L.; Cervera, M.; Roca, P. An Enhanced Finite Element Macro-Model for the Realistic Simulation of Localized Cracks in Masonry Structures: A Large-Scale Application. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2018, 12, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addessi, D.; Liberatore, D.; Masiani, R. Force-Based Beam Finite Element (FE) for the Pushover Analysis of Masonry Buildings. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2015, 9, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberatore, D.; Addessi, D. Strength Domains and Return Algorithm for the Lumped Plasticity Equivalent Frame Model of Masonry Structures. Eng. Struct. 2015, 91, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penelis, G.G. An Efficient Approach for Pushover Analysis of Unreinforced Masonry (URM) Structures. J. Earthq. Eng. 2006, 10, 359–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababaie Mobarake, A.; Khanmohammadi, M.; Mirghaderi, S.R. A New Discrete Macro-Element in an Analytical Platform for Seismic Assessment of Unreinforced Masonry Buildings. Eng. Struct. 2017, 152, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzini, C.F.; Ottonelli, D.; Degli Abbati, S.; Marano, C.; Cordasco, E.A. Modelling the Seismic Response of a 2-Storey URM Benchmark Case Study: Comparison among Different Equivalent Frame Models; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 20, ISBN 1051802101173. [Google Scholar]
- Ottonelli, D.; Manzini, C.F.; Marano, C.; Cordasco, E.A.; Cattari, S. A Comparative Study on a Complex URM Building: Part I—Sensitivity of the Seismic Response to Different Modelling Options in the Equivalent Frame Models. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 20, 2115–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena-Garcia-Cruz, M.V.; Cattari, S.; Bento, R.; Morales-Esteban, A. Comparative Study of Alternative Equivalent Frame Approaches for the Seismic Assessment of Masonry Buildings in OpenSees. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 66, 105877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagomarsino, S.; Cattari, S.; Angiolilli, M.; Bracchi, S.; Rota, M.; Penna, A. Modelling and Seismic Response Analysis of Existing URM Structures. Part 2: Archetypes of Italian Historical Buildings. J. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 27, 1849–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Pacheco, J.; González-Drigo, R.; Pujades Beneit, L.G.; Barbat, A.H.; Calderón-Brito, J. Traditional High-Rise Unreinforced Masonry Buildings: Modeling and Influence of Floor System Stiffening on Their Overall Seismic Response. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2021, 15, 1547–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmouden, Y.; Lestuzzi, P. An Equivalent Frame Model for Seismic Analysis of Masonry and Reinforced Concrete Buildings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagomarsino, S.; Penna, A.; Galasco, A.; Cattari, S. TREMURI Program: An Equivalent Frame Model for the Nonlinear Seismic Analysis of Masonry Buildings. Eng. Struct. 2013, 56, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.; Lourenço, P.B. Unreinforced and Confined Masonry Buildings in Seismic Regions: Validation of Macro-Element Models and Cost Analysis. Eng. Struct. 2014, 64, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannizzaro, F.; Castellazzi, G.; Grillanda, N.; Pantò, B.; Petracca, M. Modelling the Nonlinear Static Response of a 2-Storey URM Benchmark Case Study: Comparison among Different Modelling Strategies Using Two- and Three-Dimensional Elements. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 20, 2085–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betti, M.; Galano, L.; Vignoli, A. Time-History Seismic Analysis of Masonry Buildings: A Comparison between Two Non-Linear Modelling Approaches. Buildings 2015, 5, 597–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aşıkoğlu, A.; Vasconcelos, G.; Lourenço, P.B.; Pantò, B. Pushover Analysis of Unreinforced Irregular Masonry Buildings: Lessons from Different Modeling Approaches. Eng. Struct. 2020, 218, 110830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekar, M.; Haider, W. Explicit Finite Element Analysis of Lightly Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls. Comput. Struct. 2008, 86, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, A.; Shedid, M.; Okail, H.; Abdelrahman, A. Numerical Modeling of Reinforced Masonry Walls under Lateral Loading at the Component Level Response as Opposed to System Level Response. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2019, 10, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor-E-Khuda, S.; Thambiratnam, D.P. In-Plane and out-of-Plane Structural Performance of Fully Grouted Reinforced Masonry Walls with Varying Reinforcement Ratio—A Numerical Study. Eng. Struct. 2021, 248, 113288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Weigel, T.A. Damage States for Reinforced CMU Masonry Shear Walls. In Advances in Engineering Structures, Mechanics & Construction; Solid Mechanics and Its Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 140, pp. 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FEMA. Earthquake Loss Estimation Methodology HAZUS (1999); Federal Emergency Management Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Murcia-Delso, J.; Shing, P.B. Fragility Analysis of Reinforced Masonry Shear Walls. Earthq. Spectra 2012, 28, 1523–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, K.; Kennedy, R.; Bachman, R. Creating Fragility Functions for Performance-Based Earthquake Engineering. Earthq. Spectra 2007, 23, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, J.; Negrete, M. Drift-Based Fragility Assessment of Confined Masonry Walls in Seismic Zones. Eng. Struct. 2009, 31, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Letelier, G.; Calderón, S.; Sandoval, C.; Sanhueza, M.; Murcia-Delso, J. Fragility Functions for Partially-Grouted Masonry Shear Walls with Bed-Joint Reinforcement. Eng. Struct. 2019, 191, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, I.; Mohammadalizadeh, T.; Ahmadi, F.; Soroushian, S. Fragility Functions for Displacement-Based Seismic Design of Reinforced Masonry Wall Structures. J. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 26, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Dolatshahi, K.M.; Asjodi, A.H. Multivariable Fragility Curves for Unreinforced Masonry Walls. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 21, 3357–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asjodi, A.H.; Dolatshahi, K.M. Extended Fragility Surfaces for Unreinforced Masonry Walls Using Vision-Derived Damage Parameters. Eng. Struct. 2023, 278, 115467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoj, J.; Dolšek, M. Fragility Functions for Unreinforced Masonry Walls Made from Hollow Clay Units. Eng. Struct. 2017, 145, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, L.; Ashour, A.; Galal, K. Development of Fragility Curves for Reinforced-Masonry Structural Walls with Boundary Elements. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2018, 32, 04018034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, Z.; Elwood, K.J.; Alcocer, S.M. Backbone Model for Confined Masonry Walls for Performance-Based Seismic Design. J. Struct. Eng. 2009, 135, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, V.R.; Jangid, R.S. Seismic Response of Structures with Variable Friction Pendulum System. J. Earthq. Eng. 2009, 13, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsagar, V.A.; Jangid, R.S. Base Isolation for Seismic Retrofitting of Structures. Pract. Period. Struct. Des. Constr. 2008, 13, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghabeigi, P.; Farahmand-Tabar, S. Seismic Vulnerability Assessment and Retrofitting of Historic Masonry Building of Malek Timche in Tabriz Grand Bazaar. Eng. Struct. 2021, 240, 112418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.; Karbassi, A.; Lestuzzi, P. Evaluation of the Seismic Retrofitting of an Unreinforced Masonry Building Using Numerical Modeling and Ambient Vibration Measurements. Eng. Struct. 2018, 158, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbassi, A.; Nollet, M.J. Performance-Based Seismic Vulnerability Evaluation of Masonry Buildings Using Applied Element Method in a Nonlinear Dynamic-Based Analytical Procedure. Earthq. Spectra 2013, 29, 399–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankie, T.M.; Gencturk, B.; Elnashai, A.S. Simulation-Based Fragility Relationships for Unreinforced Masonry Buildings. J. Struct. Eng. 2013, 139, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyam, M.A.; Konstantinidis, D.; El-Dakhakhni, W. Collapse Fragility Evaluation of Ductile Reinforced Concrete Block Wall Systems for Seismic Risk Assessment. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2016, 30, 04016047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, H.; Walsh, K.Q.; Ingham, J.M.; Griffith, M.C.; Thambiratnam, D.P. Seismic Fragility Assessment of Nonstructural Components in Unreinforced Clay Brick Masonry Buildings. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 49, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, N.; DeLuca, F.; Sextos, A. Analytical Fragility Curves for Masonry School Building Portfolios in Nepal. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 19, 1121–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Q.; Li, G.; Song, B.; Lu, G.H.; Li, H.N. Failure Risk Assessment Method of Masonry Structures under Earthquakes and Flood Scouring. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 29, 3055–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losanno, D.; Ravichandran, N.; Parisi, F. Seismic Fragility Models for Base-Isolated Unreinforced Masonry Buildings with Fibre-Reinforced Elastomeric Isolators. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 52, 308–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
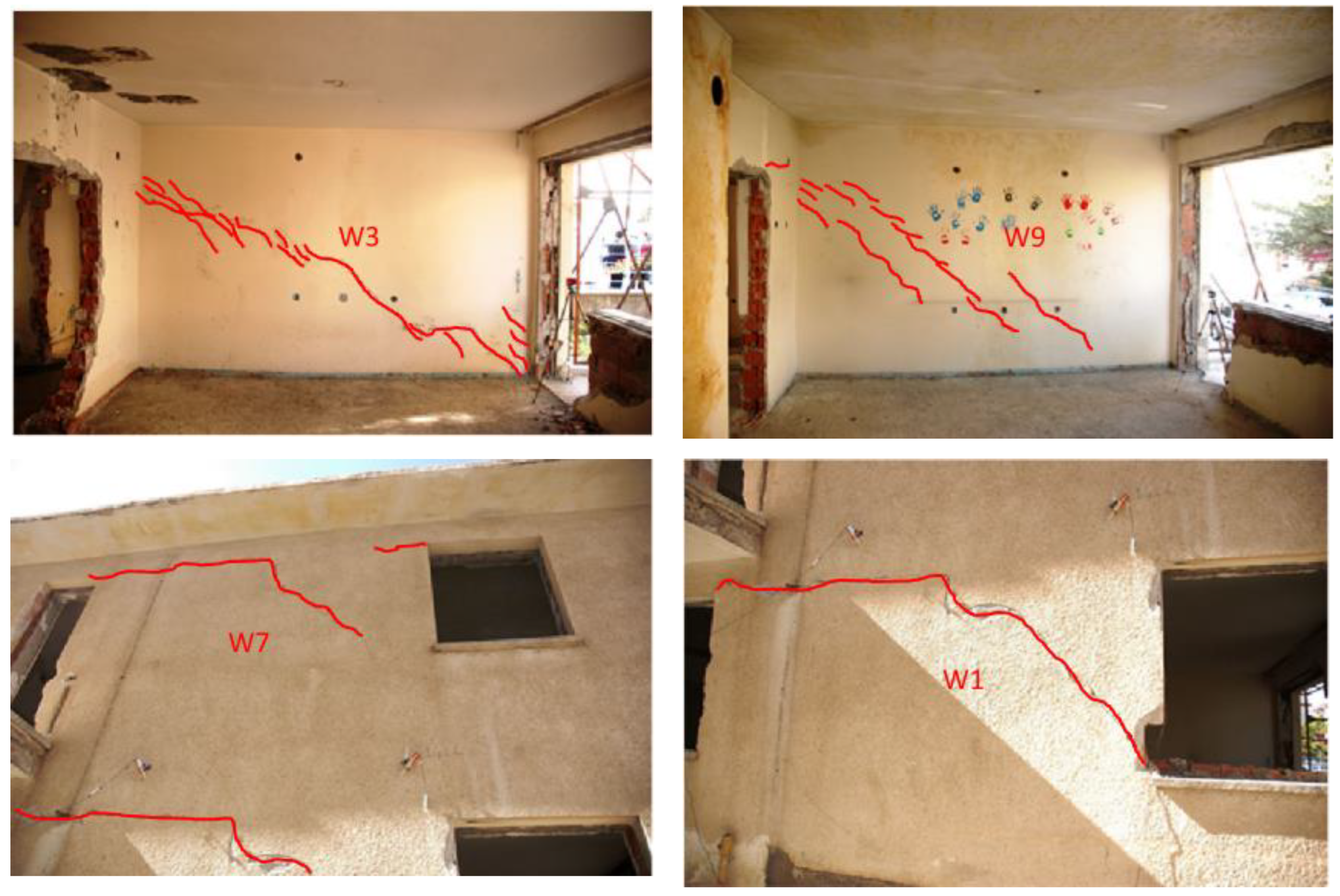
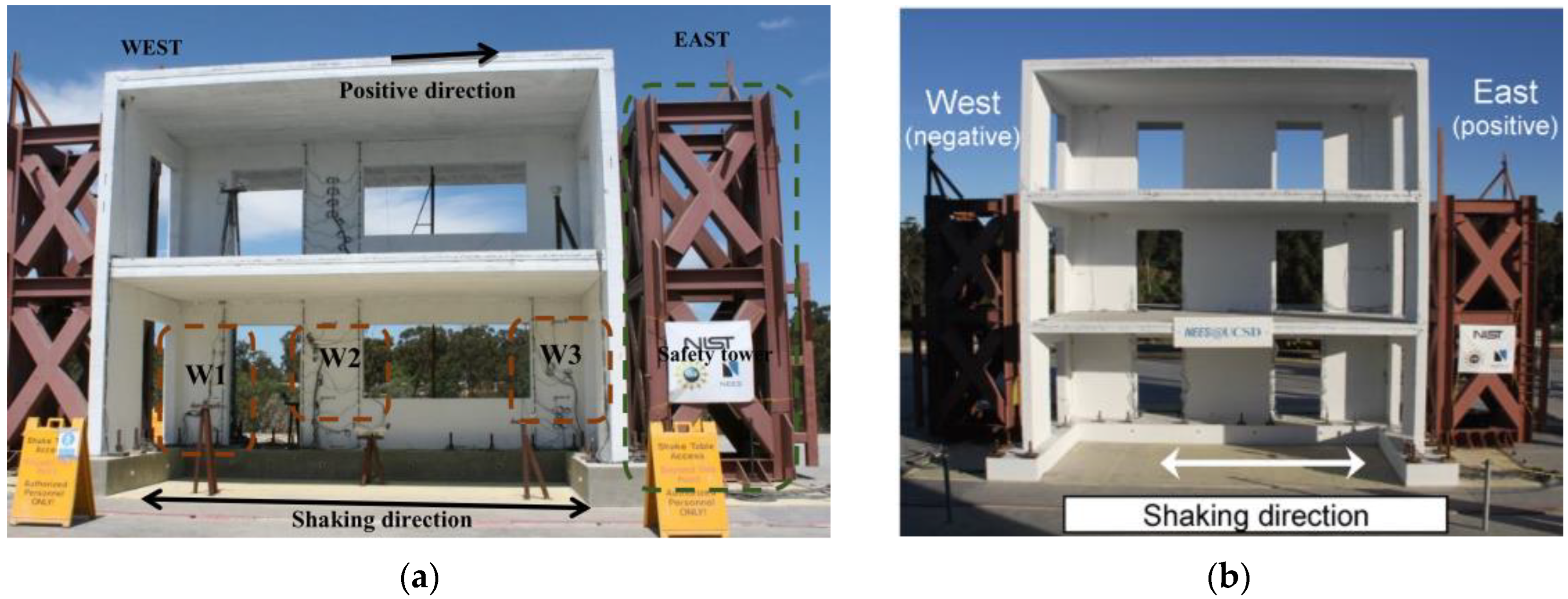
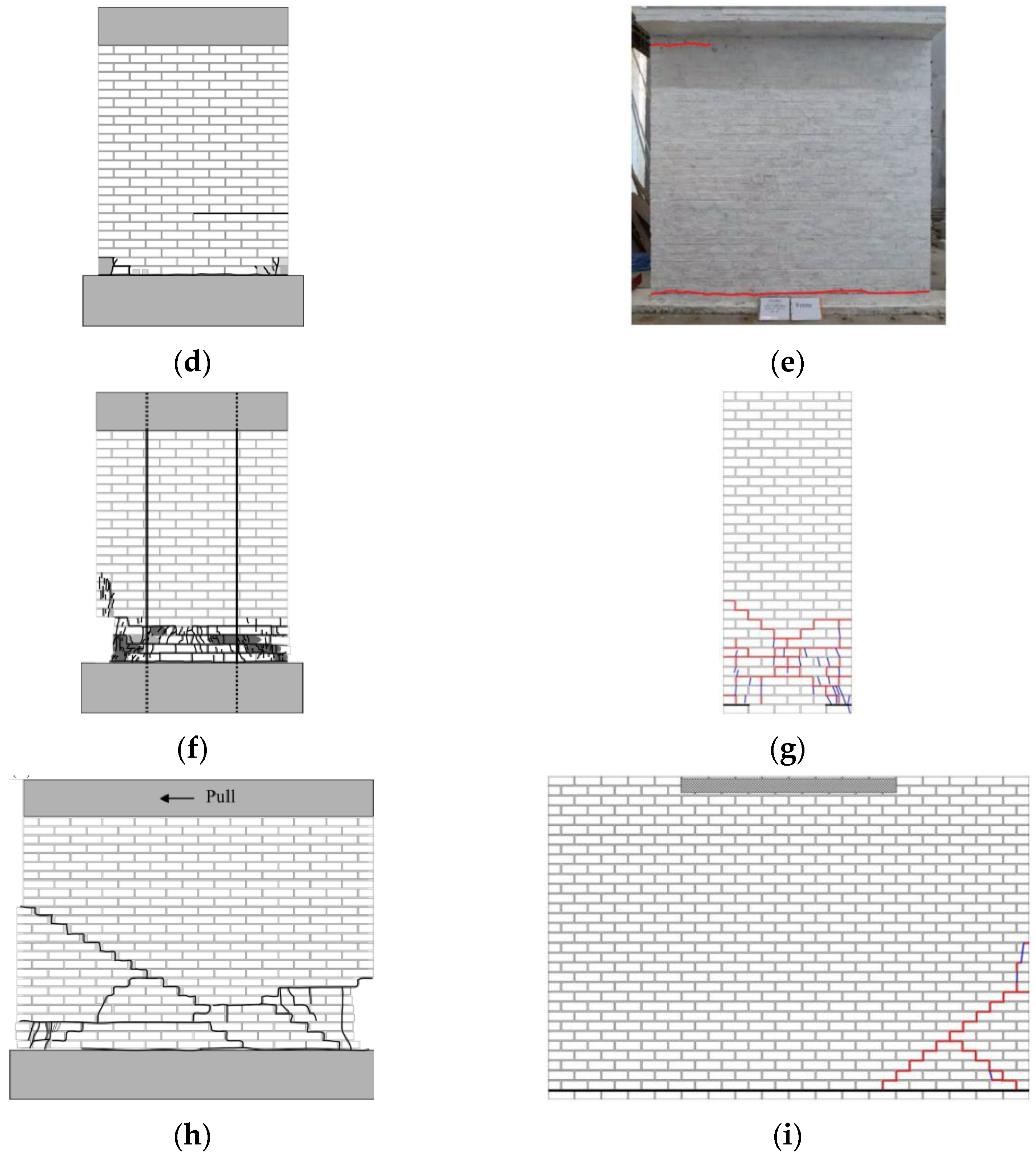
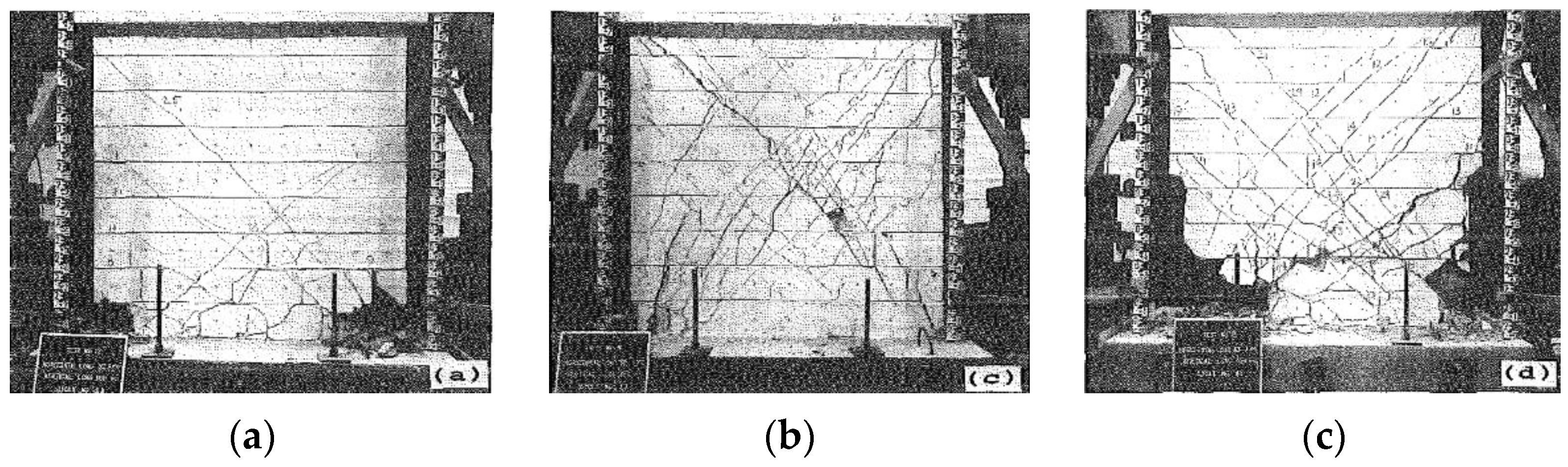
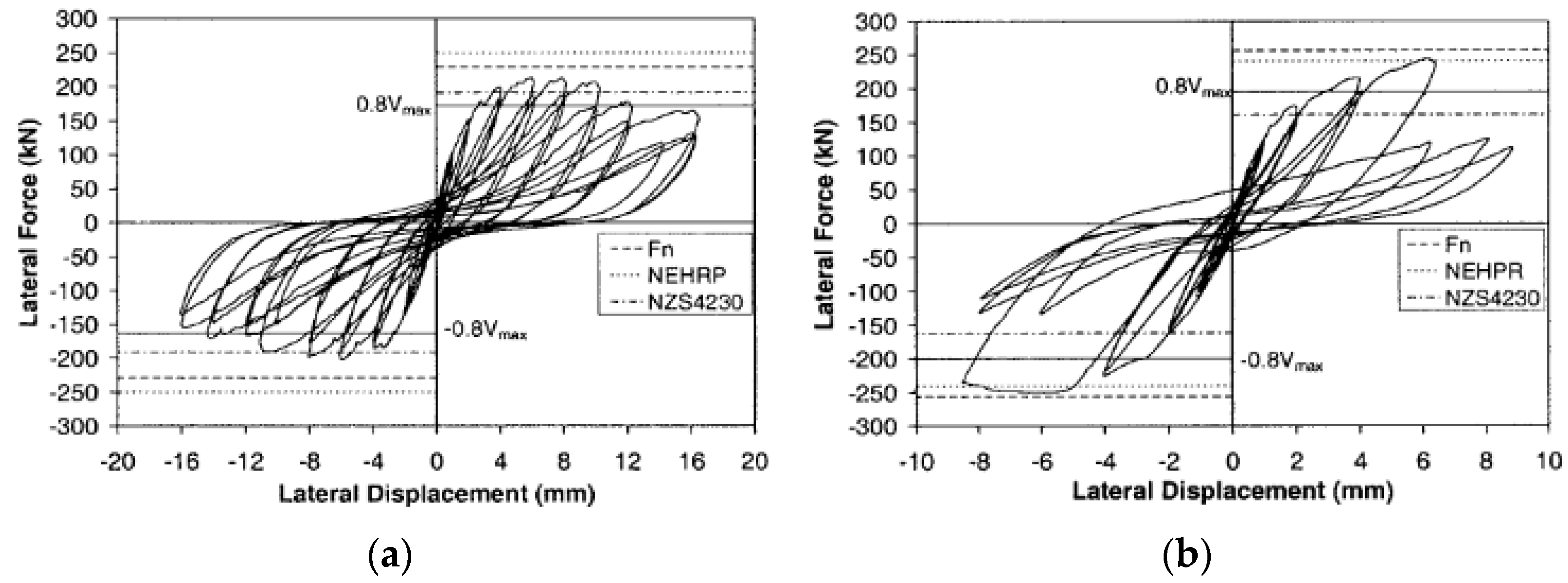

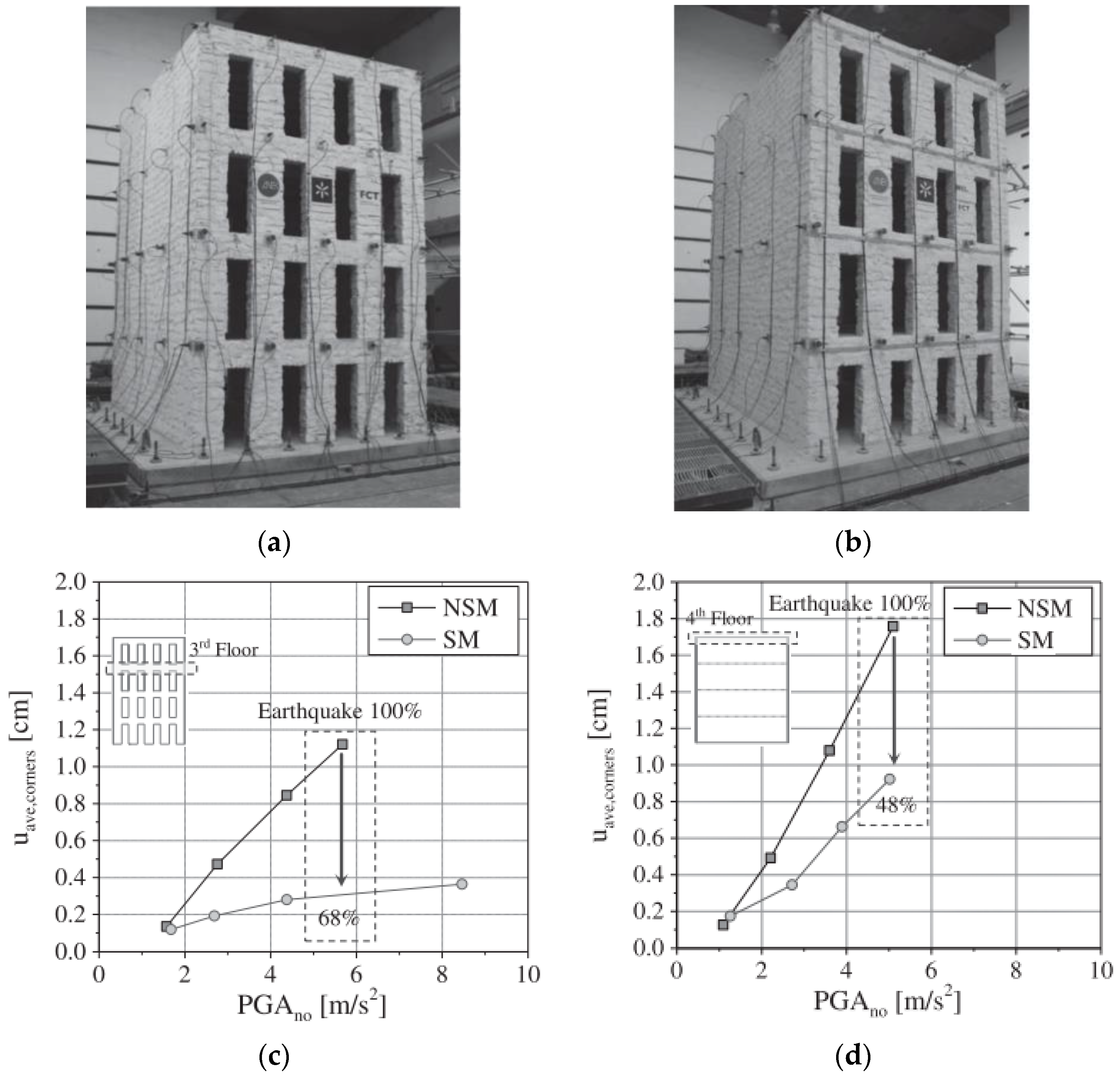
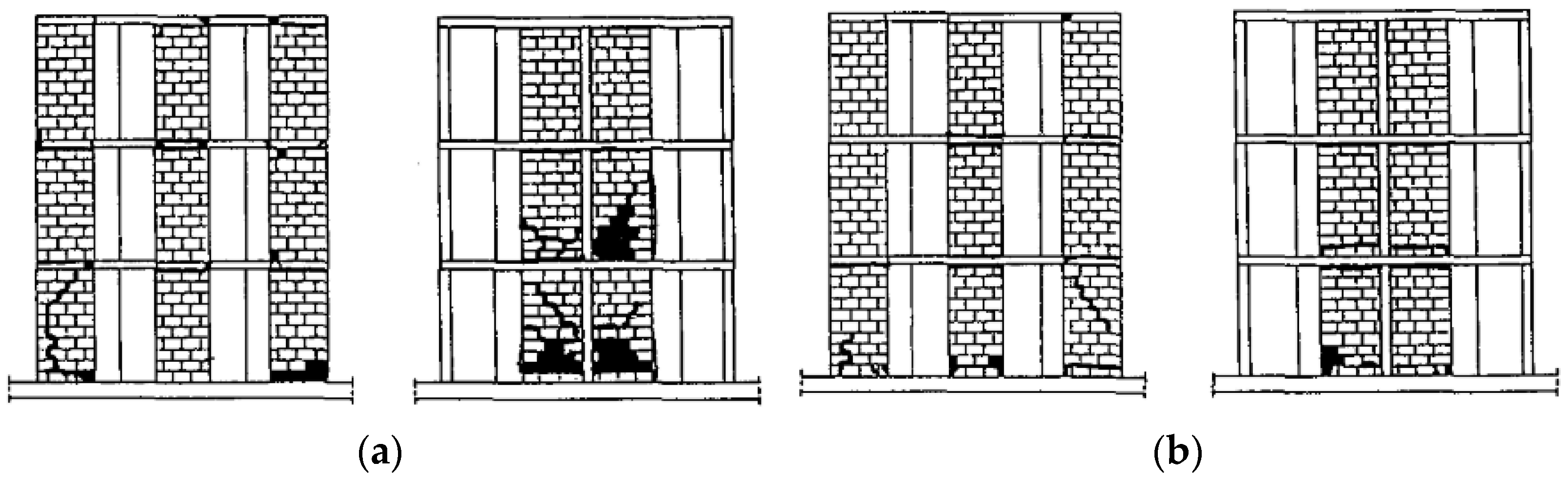

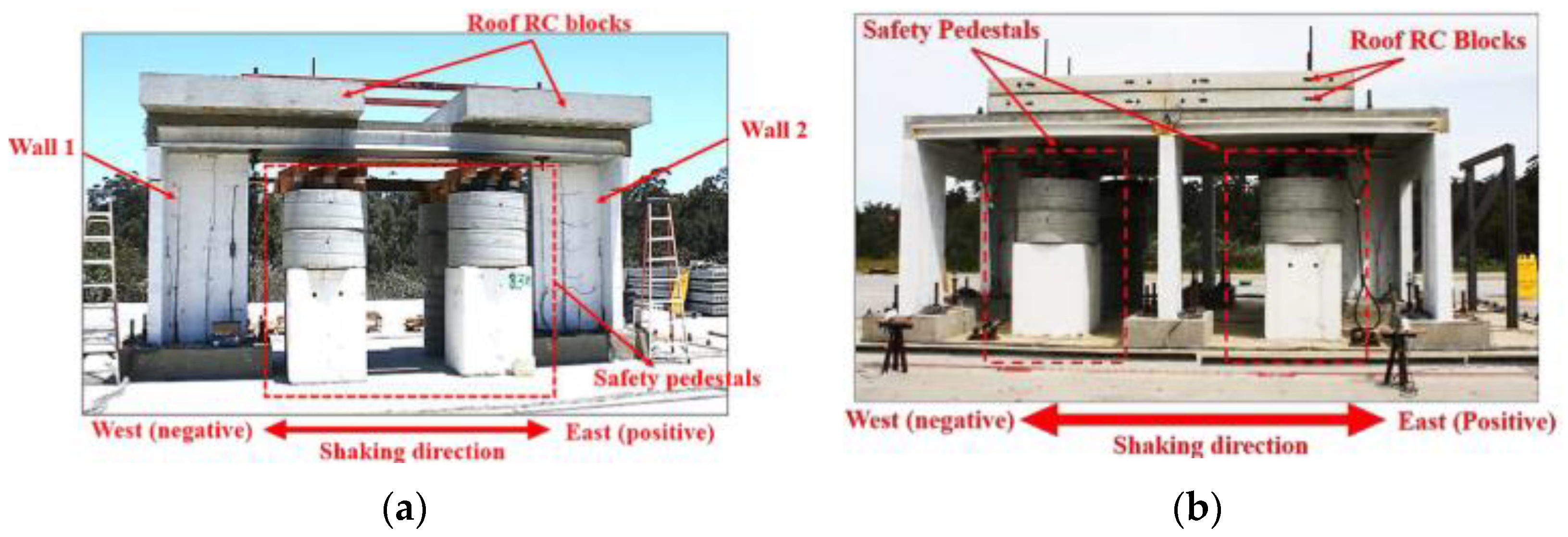
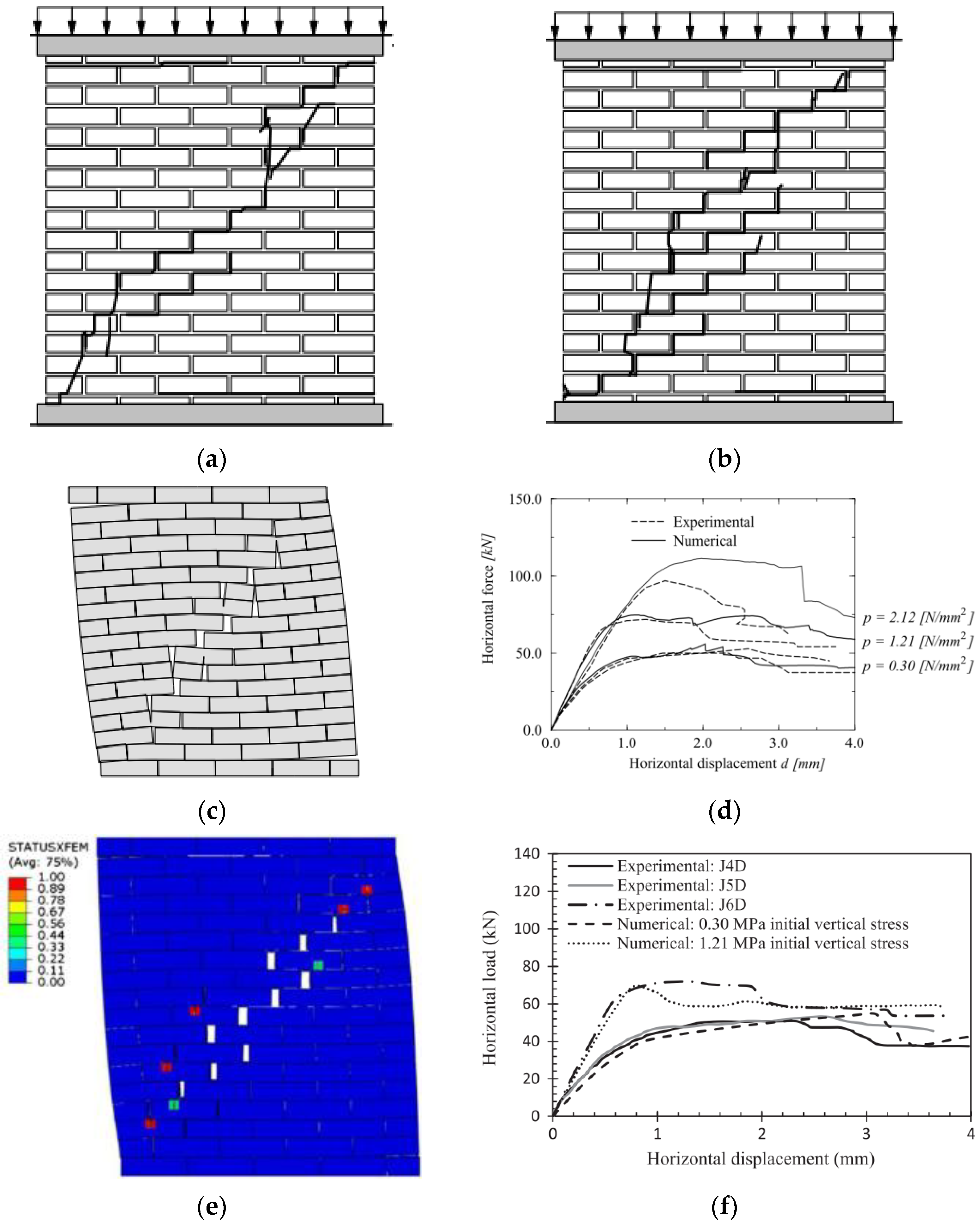
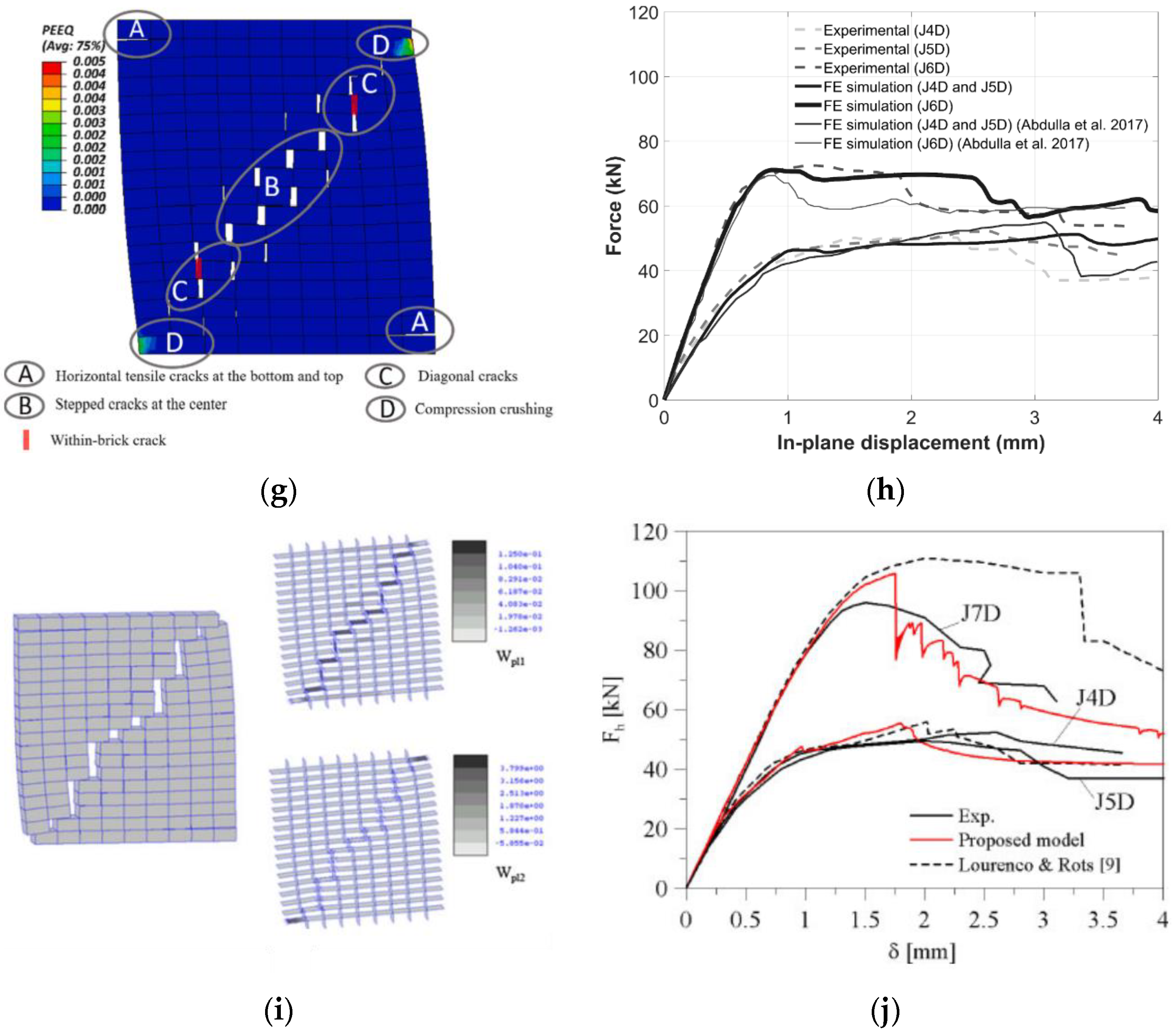
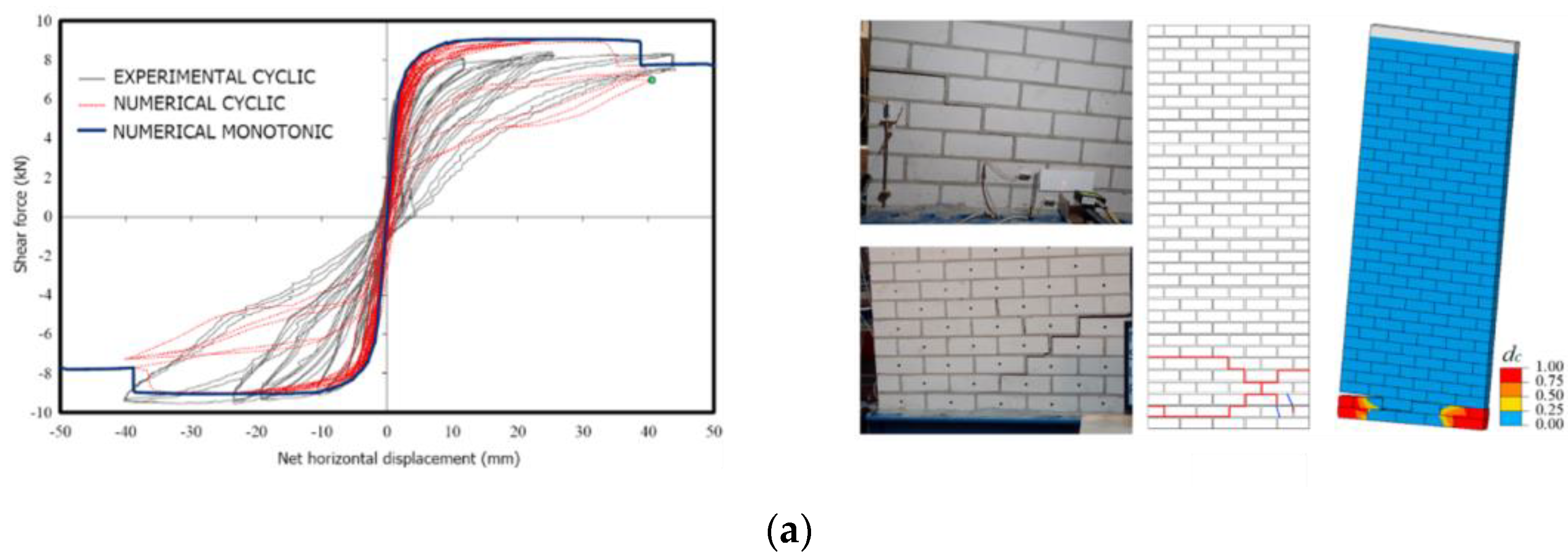
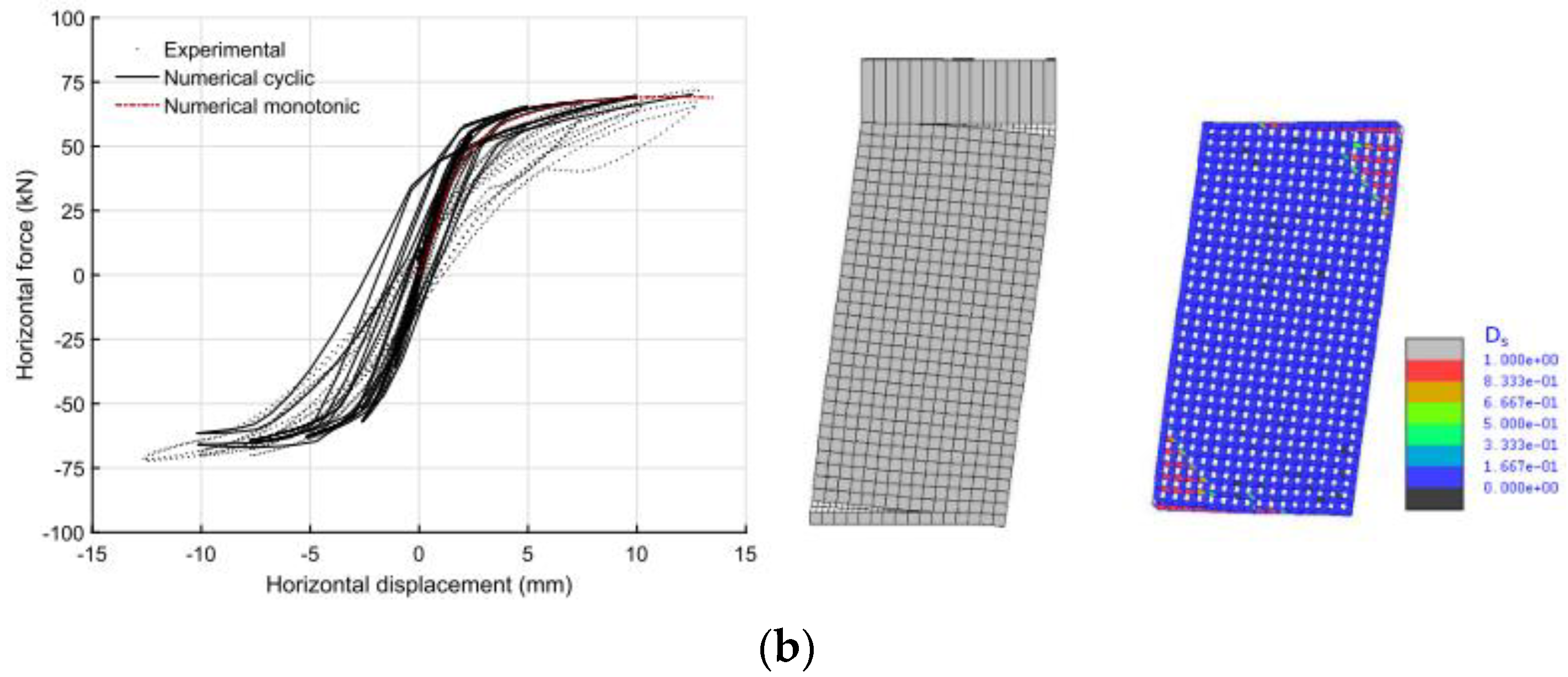
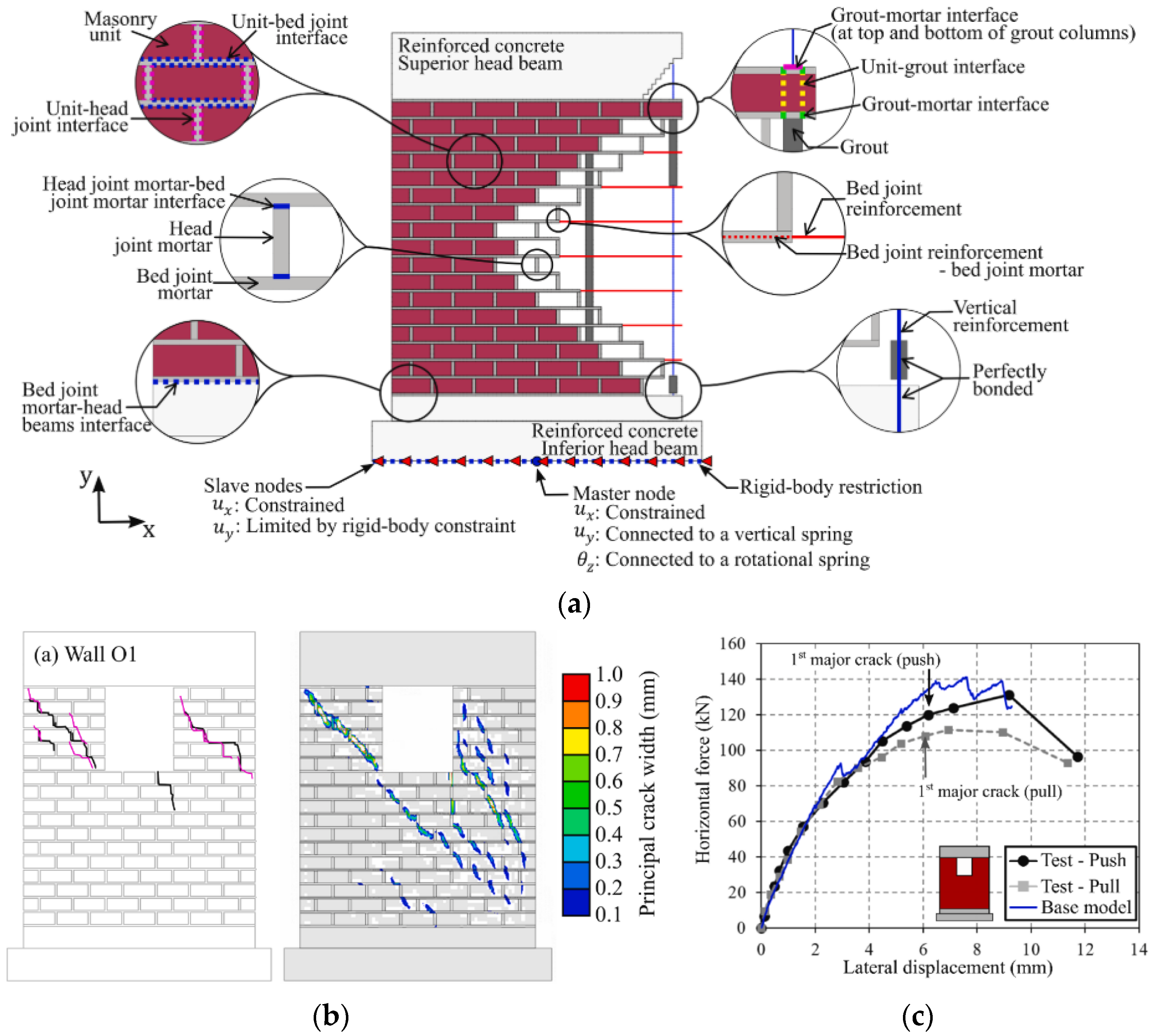
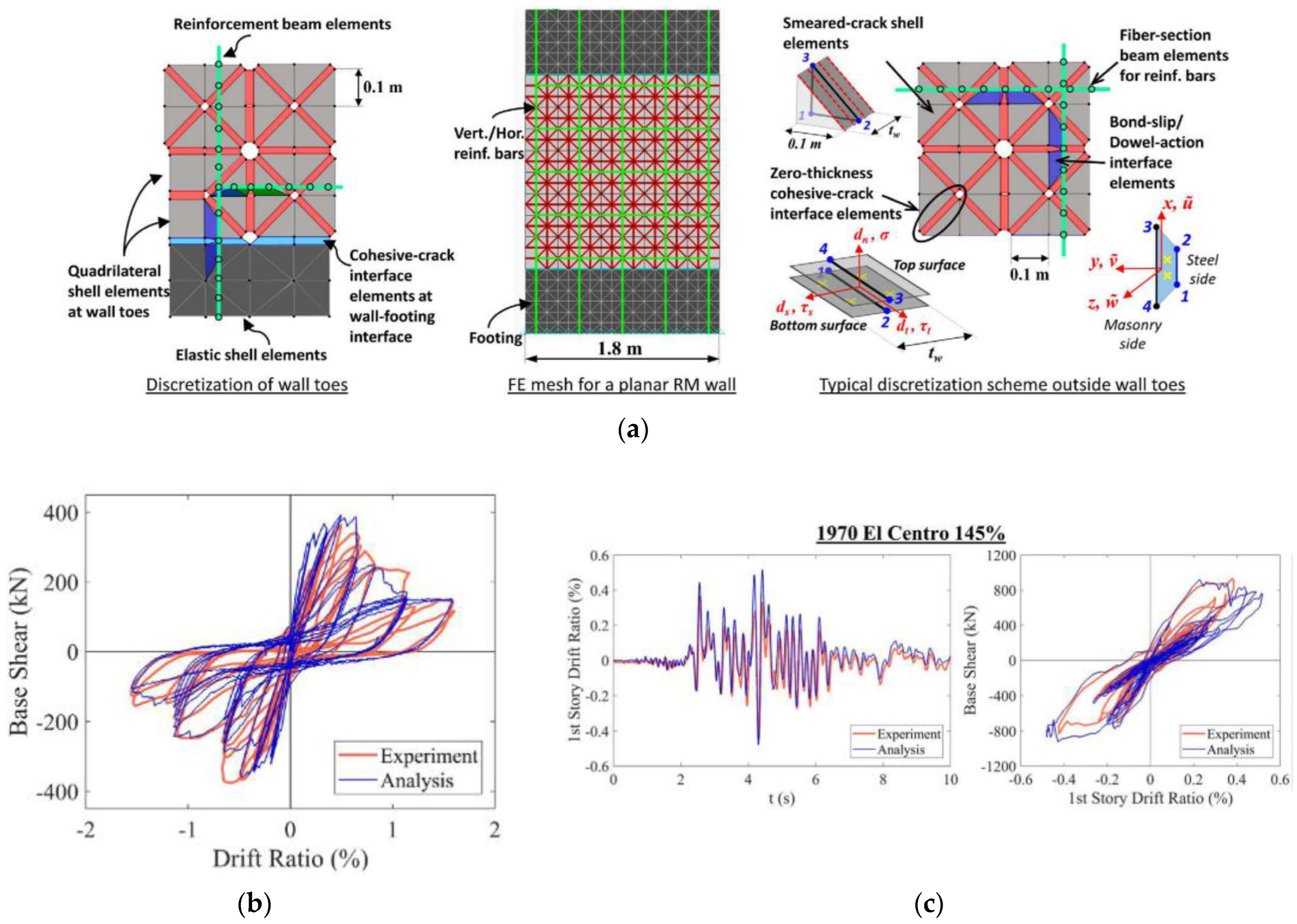
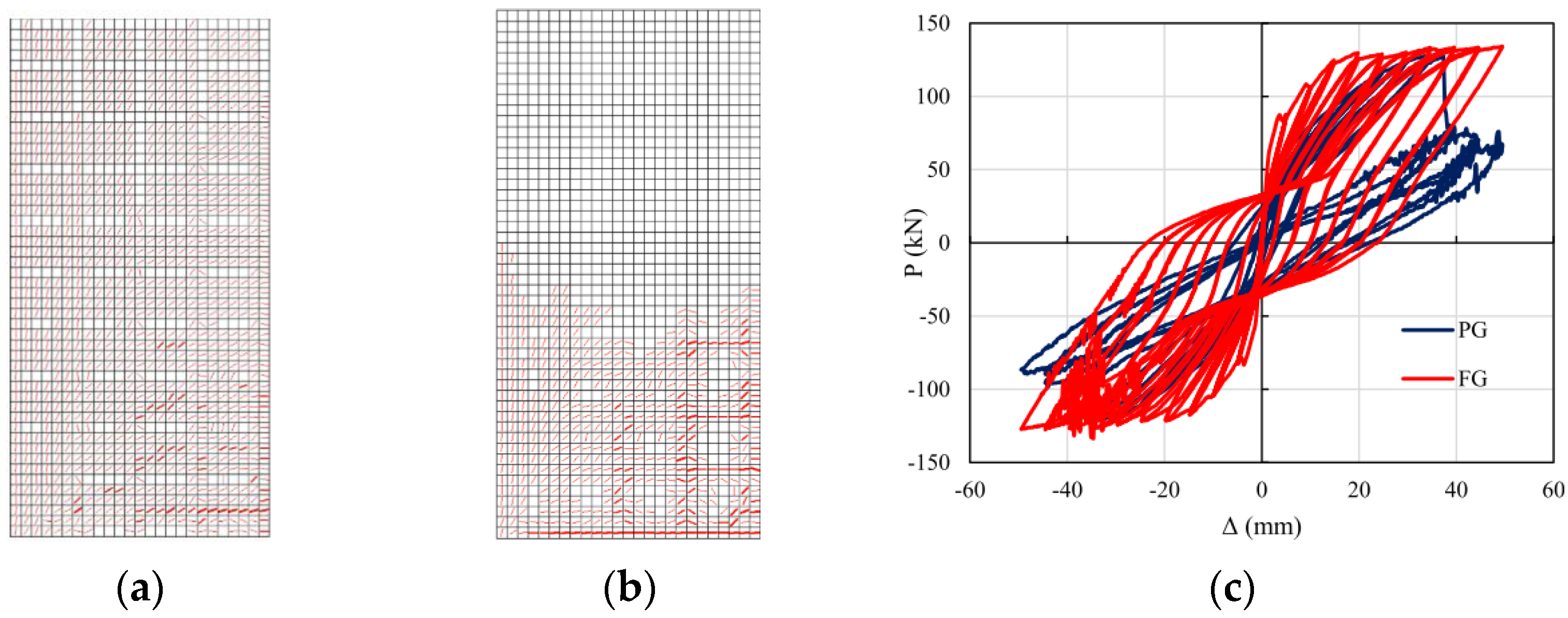
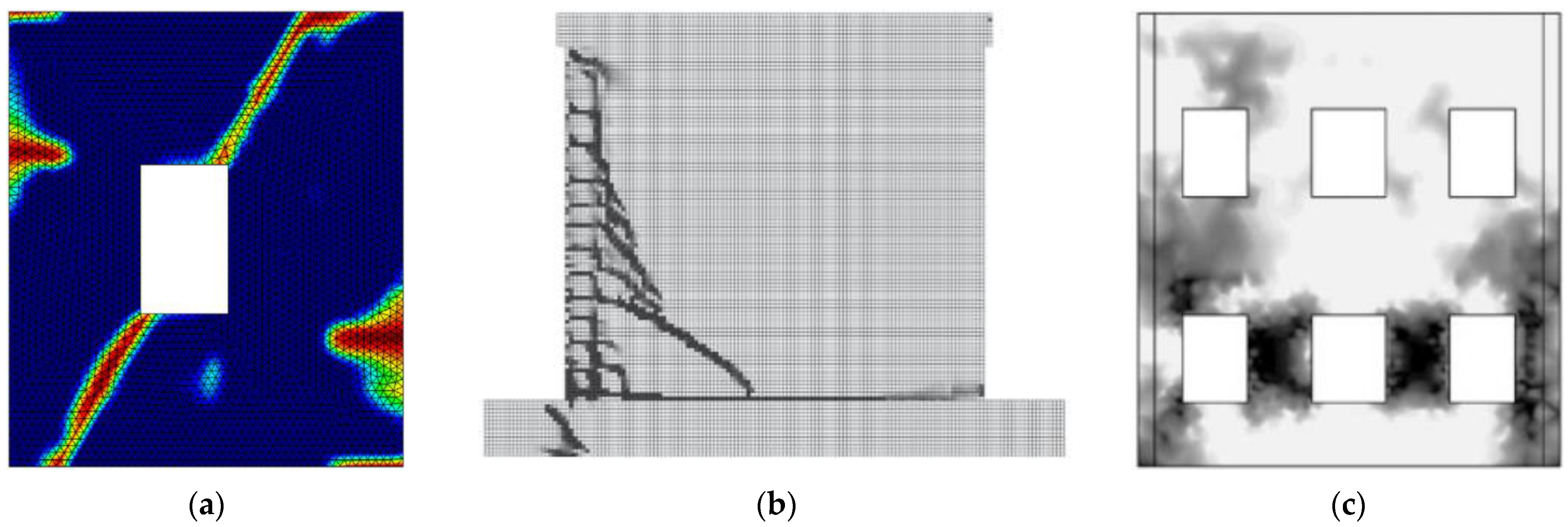
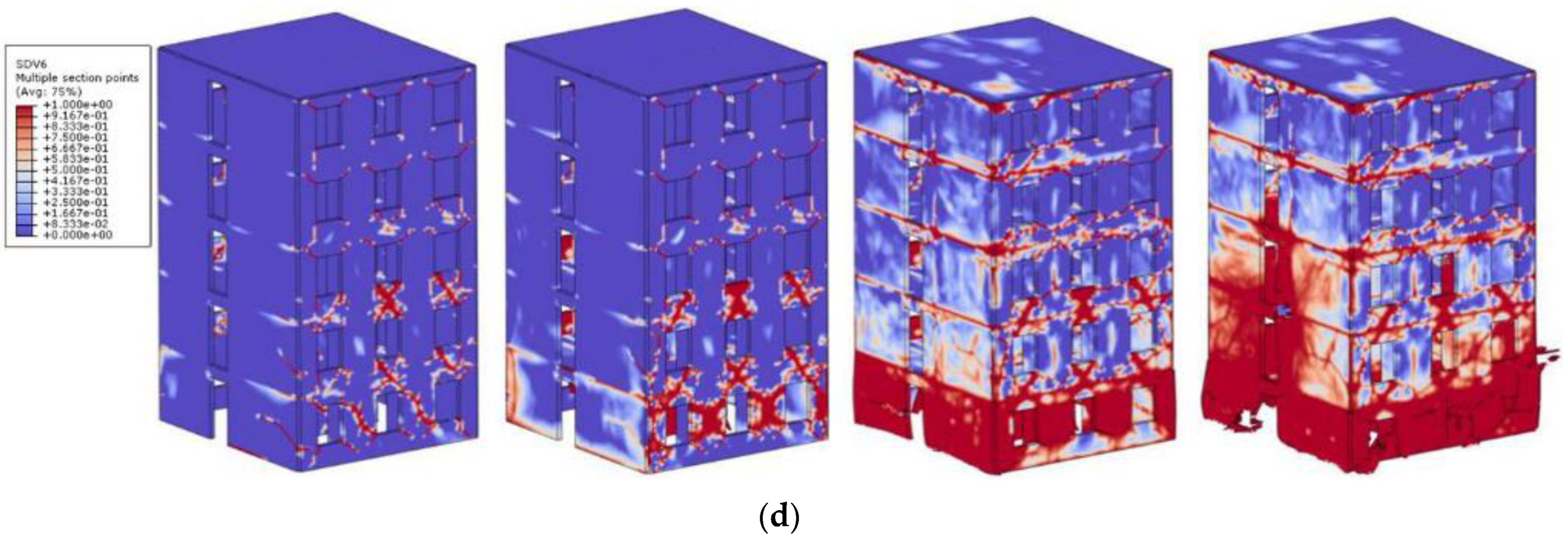
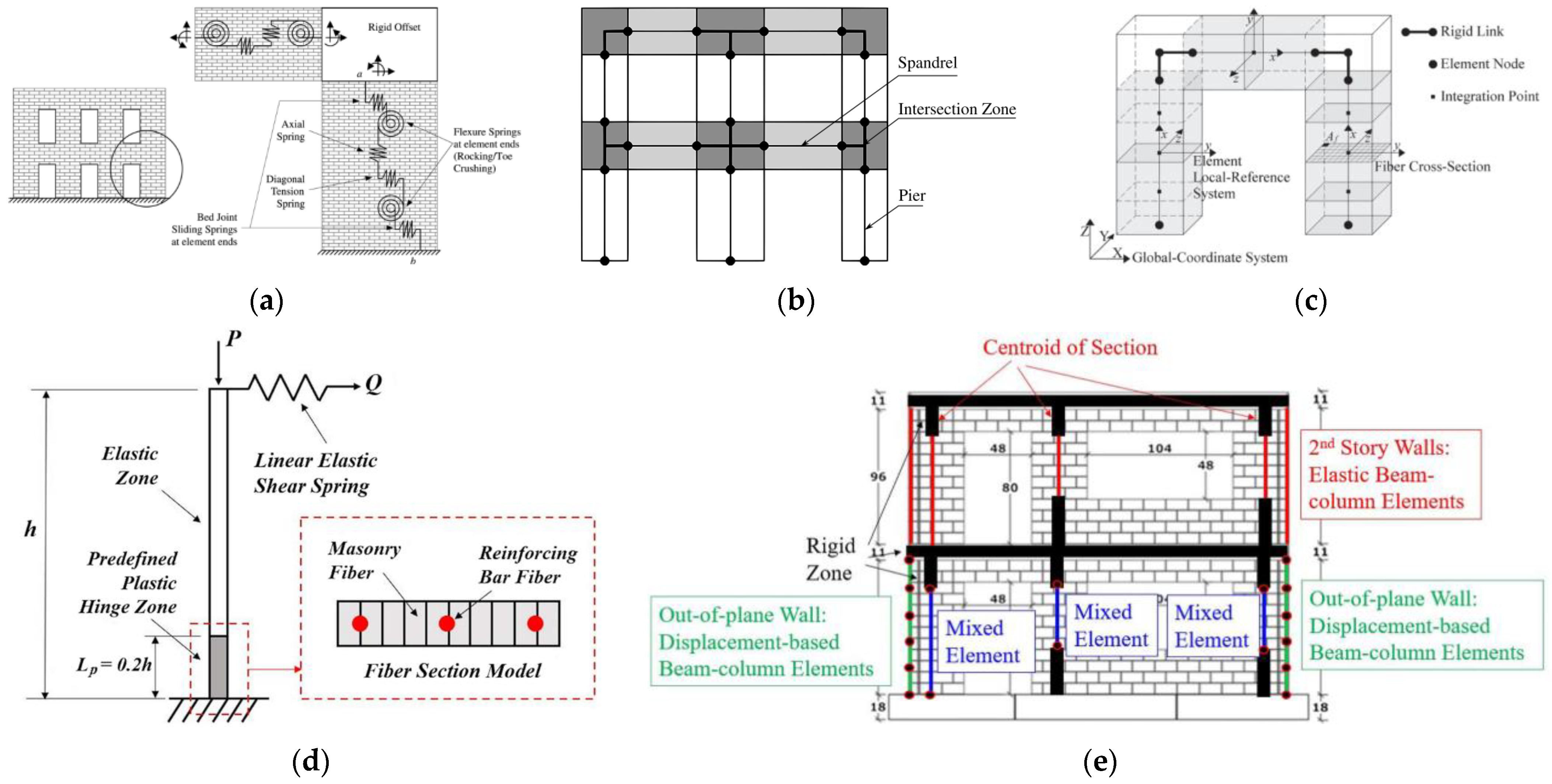
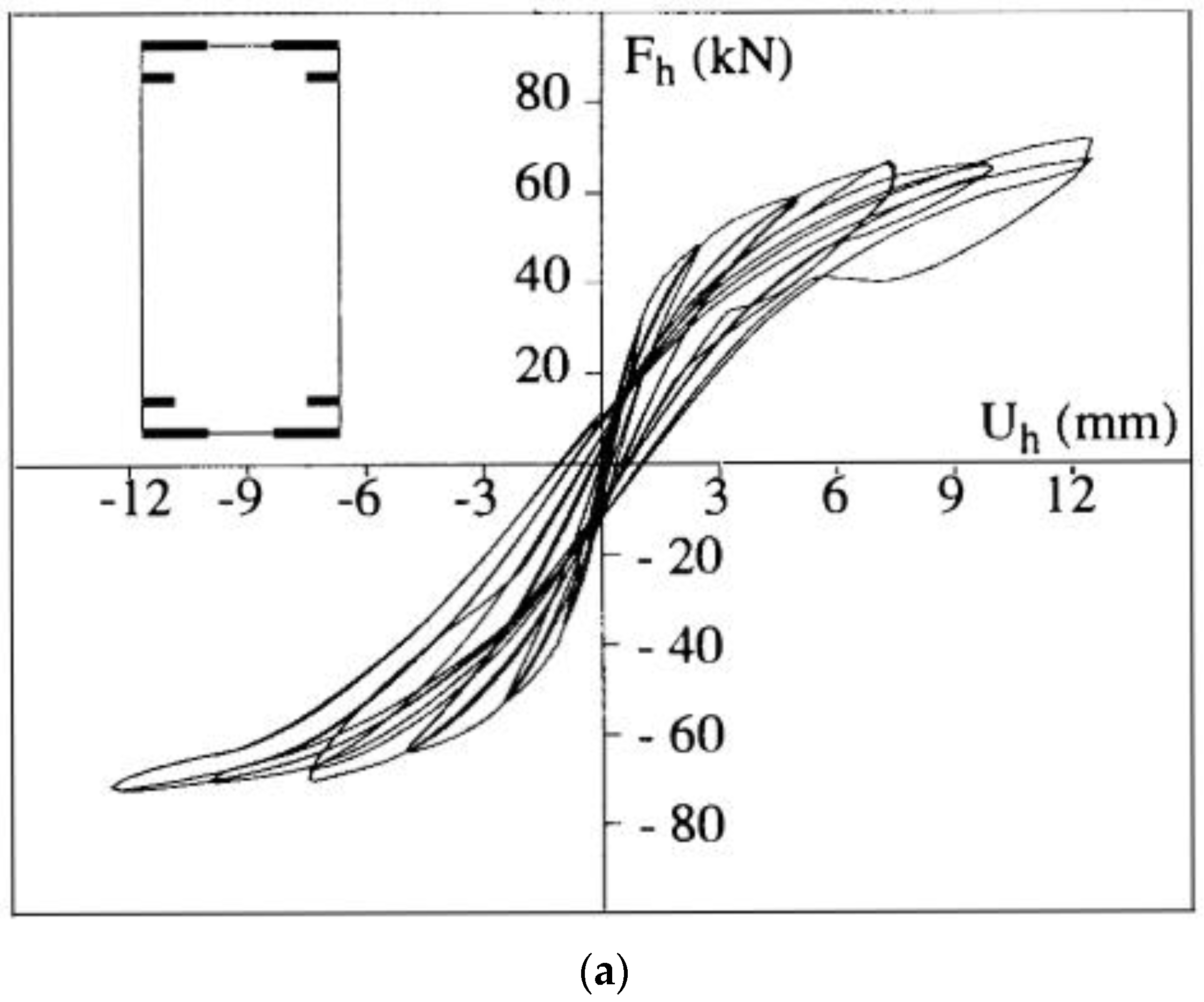
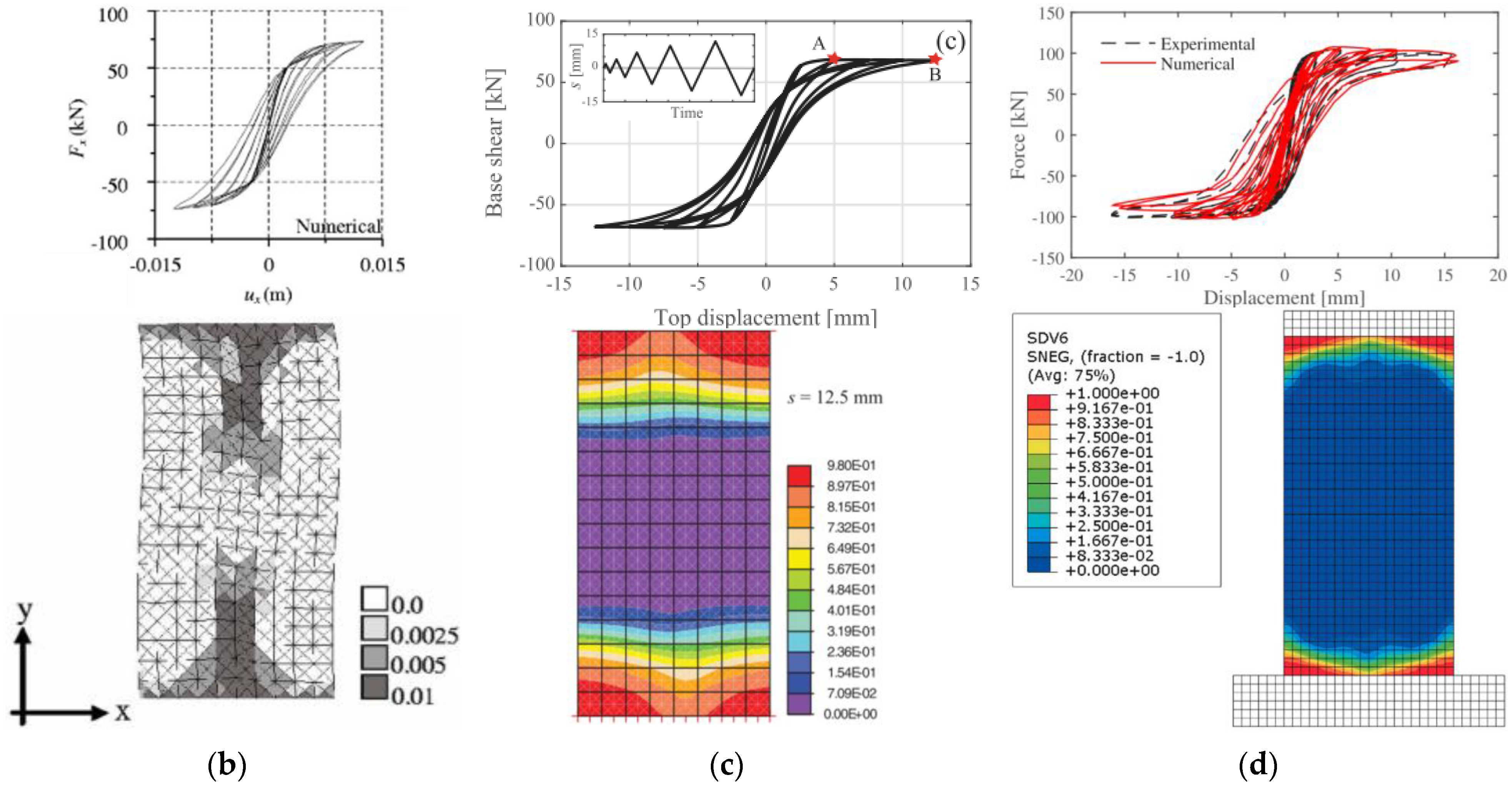
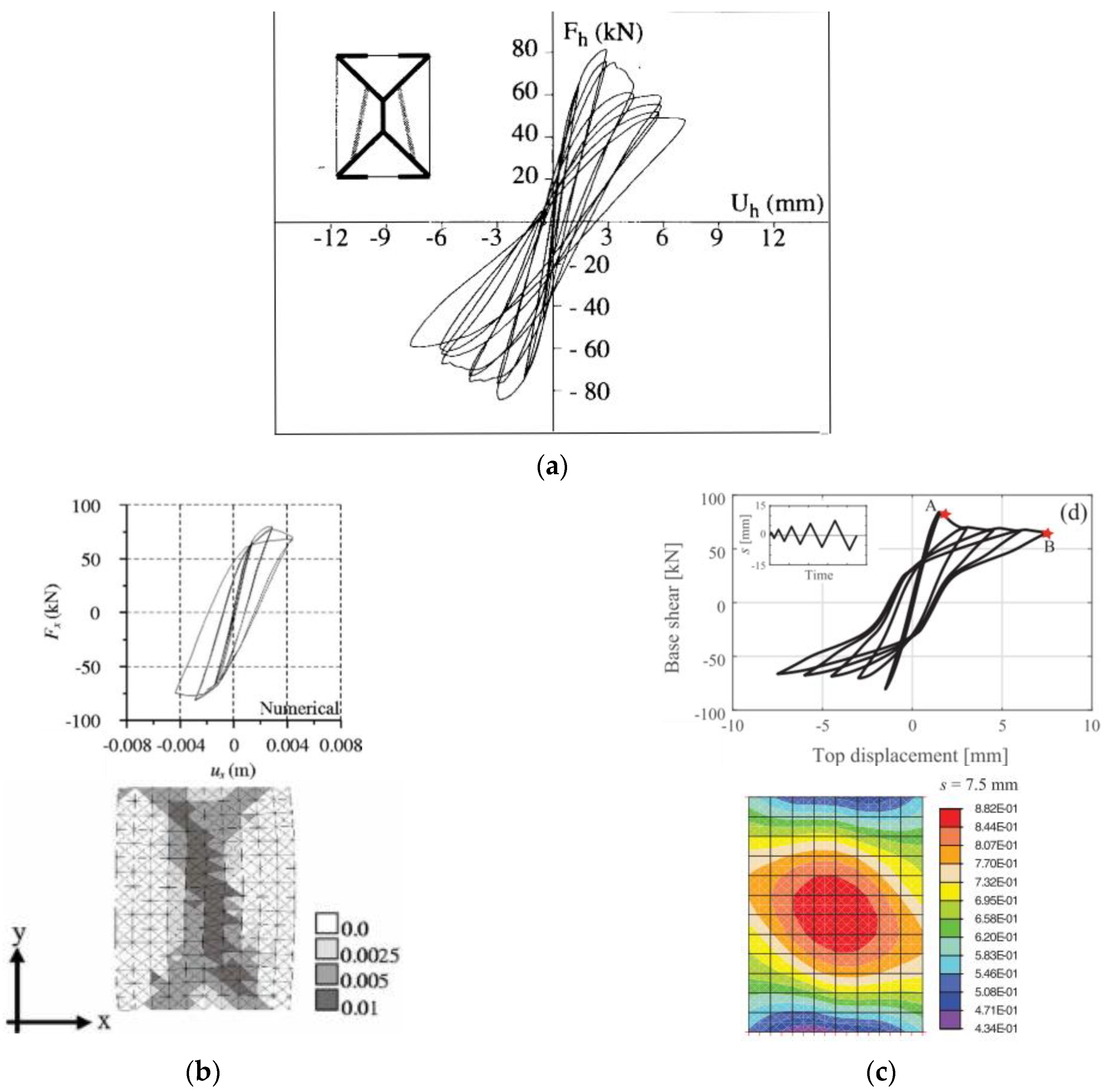
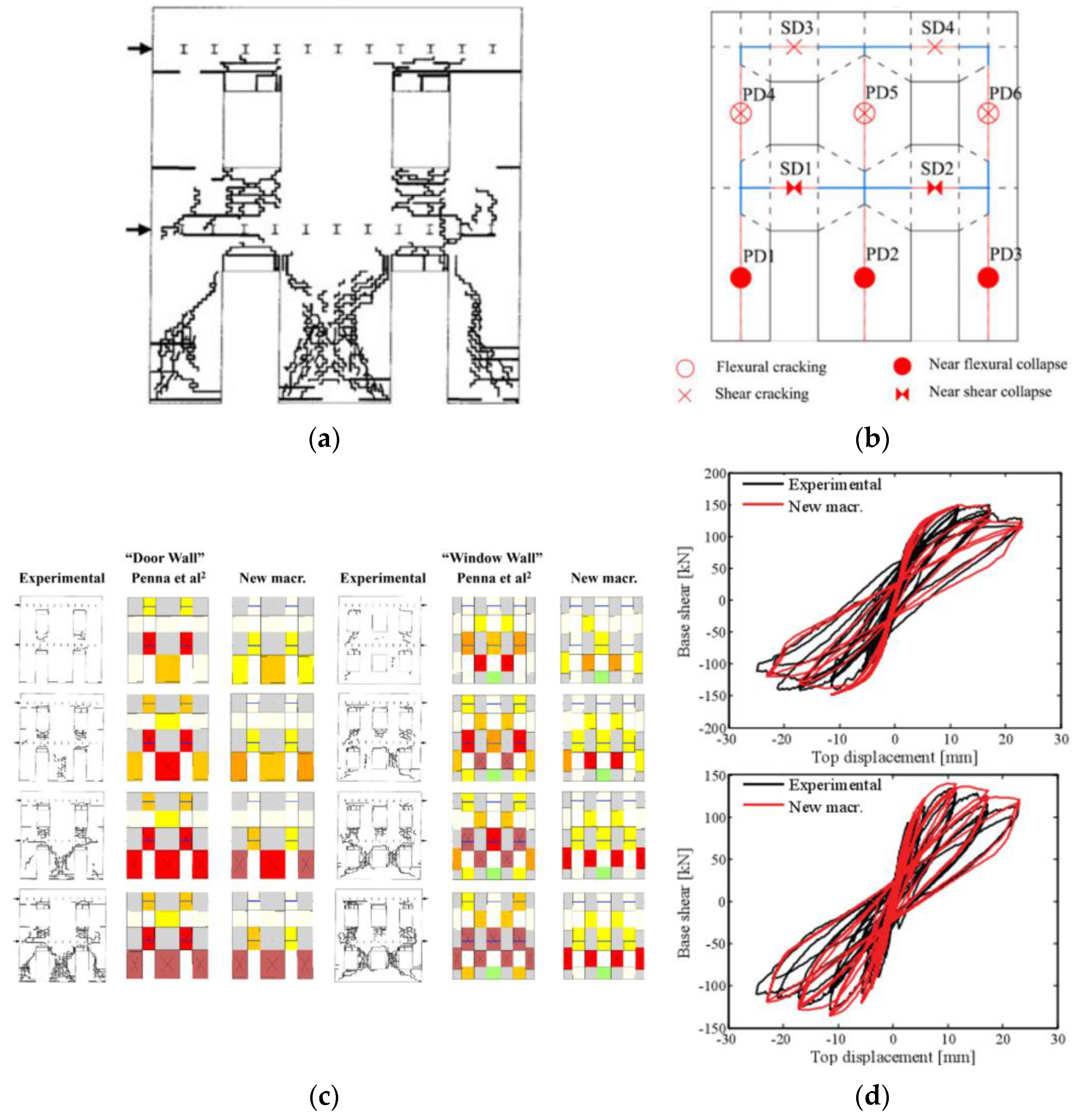
| Masonry Typology * | Investigating Factor | Loading Protocol | Boundary Conditions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU, SW | AR, AL | SC | C | [35] |
| SU, SW/PW | AL | SM | FF | [36] |
| SU, SW | AR | SC | FF | [37] |
| SU, SW | AR, AL | SC | FF | [38] |
| SU, SW | AR | SC | C | [39] |
| SU, PW | AR, AL | SC | C | [40] |
| SU, SW | AR, AL | SC | FF, C | [41] |
| SU, PW | AR, AL | SC | C | [42] |
| SU, PW | None | SC | C | [43] |
| SU, SW | AL | SM, SC | C | [45] |
| HU, SW | AL | SC | FF, C | [46] |
| HU, SW | AL | SC | Intermediate * | [47] |
| HU, SW | AR, AL | SC | FF, C | [34,48] |
| NA * | AR, AL | SC | FF | [49] |
| SU, SW | None | D | C | [44] |
| Damage States | Qualitative Definition (RM1L/RM2L *) | Quantitative Definition (Drift Ratio) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Code * | Moderate-Code * | Low-Code * | Pre-Code * | ||
| Slight | Diagonal hairline cracks on wall surfaces; large cracks around door and window openings in walls with large proportion of openings; minor separation of walls from the floor and roof diaphragms. | 0.0004 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 | 0.0003 |
| Moderate | Most wall surfaces exhibit diagonal cracks; some of the shear walls have exceeded their yield capacities indicated by larger diagonal cracks. Some walls may have visibly pulled away from the roof. | 0.0008 | 0.0007 | 0.0006 | 0.0005 |
| Extensive | Most shear walls with large openings have exceeded their yield capacities, and some of the walls have exceeded their ultimate capacities, indicated by large, through-the-wall diagonal cracks and visibly buckled wall reinforcement. Partial collapse of the roof may result from failure of wall to diaphragm connections. | 0.024 | 0.019 | 0.016 | 0.013 |
| Complete | Structure has collapsed or is in imminent danger of collapse due to failure of the wall anchorages or the wall panels. Approximately 13% (low-rise) of the total area of the building is expected to be collapsed. | 0.070 | 0.053 | 0.044 | 0.035 |
| Damage States | Description of Damage | Identification Criteria to Calibrate Fragility Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Slight flexural damage (DS1) |
| When a flexure-critical wall was loaded to 80% of its peak in-plane lateral resistance. |
| Moderate flexural damage (DS2) |
| When a flexure-critical wall was loaded to its peak in-plane lateral resistance. |
| Severe flexure damage (DS3) |
| When a flexure-critical wall was loaded beyond its peak resistance and exhibited a load drop of 20% with respect to the peak. |
| Moderate diagonal shear damage (DS4) |
| When major diagonal cracks crossing almost the entire length of a wall first occurred, based on experimental observations. |
| Severe diagonal shear damage (DS5) |
| When a shear-critical wall reached its peak shear resistance. |
| Severe sliding shear damage (DS6) |
| Derived analytically. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, B.; Li, Y. Towards Performance-Based Design of Masonry Buildings: Literature Review. Buildings 2023, 13, 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13061534
Zeng B, Li Y. Towards Performance-Based Design of Masonry Buildings: Literature Review. Buildings. 2023; 13(6):1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13061534
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Bowen, and Yong Li. 2023. "Towards Performance-Based Design of Masonry Buildings: Literature Review" Buildings 13, no. 6: 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13061534
APA StyleZeng, B., & Li, Y. (2023). Towards Performance-Based Design of Masonry Buildings: Literature Review. Buildings, 13(6), 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13061534








