Static and Dynamic Analysis of Strain Gradient Planar Trusses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Axial Deformation of Gradient Prismatic Bars
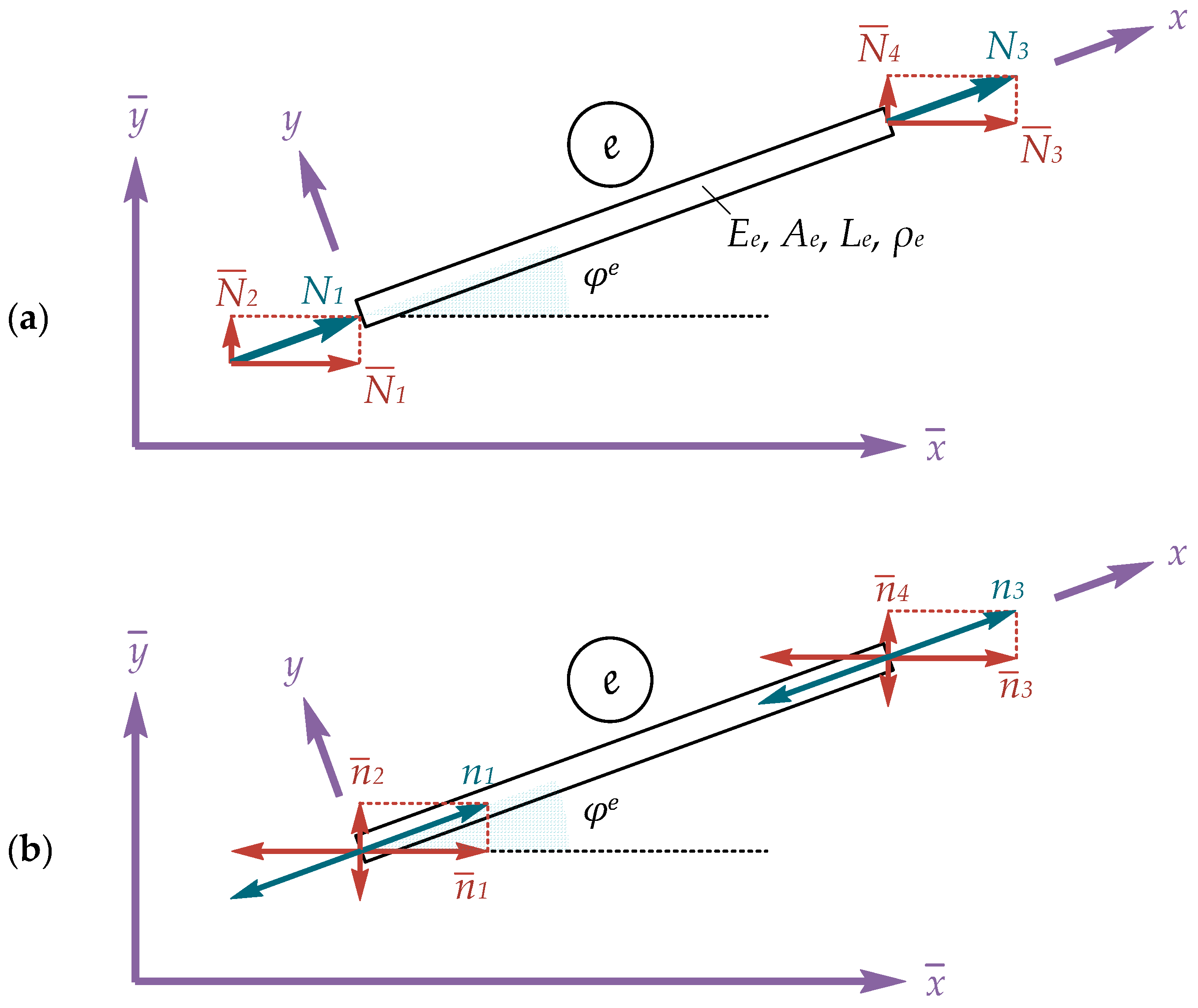
3. Gradient Truss Element
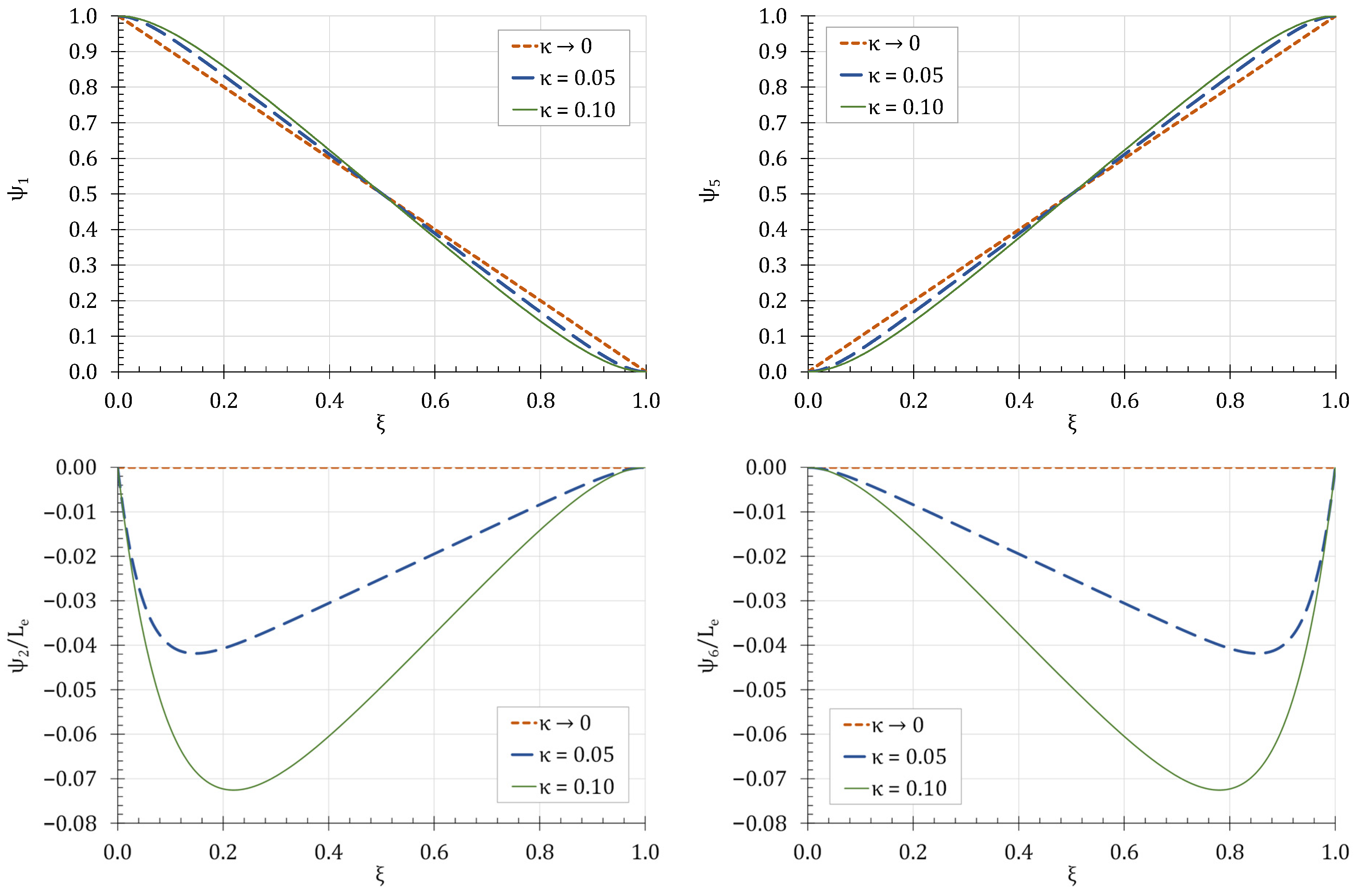
3.1. Exact Stiffness Matrix
3.2. Exact Consistent Mass Matrix
3.3. Consistent and Lumped Mass Matrices of the Classical Elasticity Theory
3.4. Transformation Matrix
4. Numerical Examples
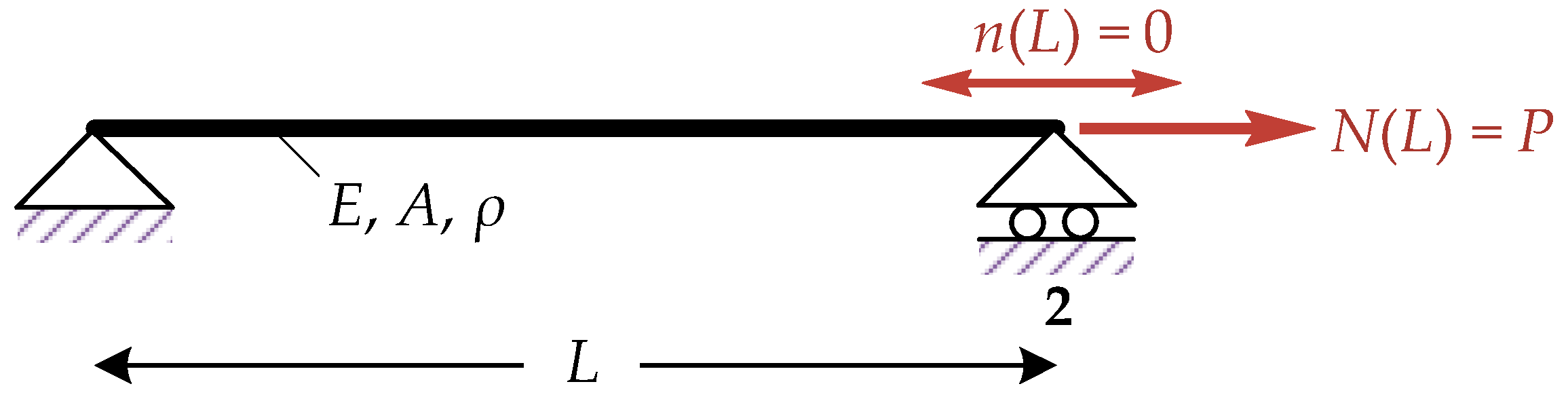
4.1. Axially Loaded Bar
4.2. Statically Determinate Gradient Truss
5. Conclusions
- The static analysis of the bar indicates that a single element is sufficient to accurately capture the response of the gradient bar using the proposed SGE theory. Furthermore, as the material’s characteristic length increases, the displacement decreases, reflecting a stiffening effect. This behavior also applies to the strain , although to a lesser extent.
- Dynamic analysis reveals that significantly influences the bar’s natural frequencies . Specifically, as increases, the stiffening effect becomes more pronounced, resulting in higher values of . This effect intensifies at higher frequencies.
- For the frame, both static and dynamic analyses confirm the same stiffening effect. However, its influence on strains remains negligible.
- The results from the dynamic analysis of the frame indicate that has a minimal effect on the mass matrix. The consistent mass matrices derived from both the SGE and CE theories yield closely related results. A similar trend is observed when comparing the CE lumped mass matrix with the FE formulation. Notably, consistent mass matrices consistently produce higher frequencies than lumped mass matrices.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben-Amoz, M. A Dynamic Theory for Composite Materials. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. ZAMP 1976, 27, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordolemis, A.; Aravas, N.; Giannakopoulos, A.E. Pretwisted Beams in Axial Tension and Torsion: Analogy with Dipolar Gradient Elasticity and Applications to Textile Materials. J. Eng. Mech. 2015, 141, 04015036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakes, R. Materials with Structural Hierarchy. Nature 1993, 361, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulos, A.E.; Knisovitis, C.; Zisis, T.; Tsiatas, G.C. Fiber Pull-out in a Flexoelectric Material. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 93, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulem, J.; Vardoulakis, I.G. Bifurcation Analysis in Geomechanics. In Bifurcation Analysis in Geomechanics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsepoura, K.G.; Papargyri-Beskou, S.; Polyzos, D.; Beskos, D.E. Static and Dynamic Analysis of a Gradient-Elastic Bar in Tension. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2002, 72, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papargyri-Beskou, S.; Tsepoura, K.G.; Polyzos, D.; Beskos, D.E. Bending and Stability Analysis of Gradient Elastic Beams. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2003, 40, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papargyri-Beskou, S.; Polyzos, D.; Beskos, D.E. Dynamic Analysis of Gradient Elastic Flexural Beams. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2003, 15, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulos, A.E.; Stamoulis, K. Structural Analysis of Gradient Elastic Components. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2007, 44, 3440–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, A.; Giannakopoulos, A.E. Structural Analysis Using a Dipolar Elastic Timoshenko Beam. Eur. J. Mech.-A/Solids 2013, 39, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamasphyros, G.I.; Markolefas, S.; Tsouvalas, D.A. Convergence and Performance of the H- and p-Extensions with Mixed Finite Element C0-Continuity Formulations, for Tension and Buckling of a Gradient Elastic Beam. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2007, 44, 5056–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filopoulos, S.P.; Papathanasiou, T.K.; Markolefas, S.I.; Tsamasphyros, G.J. Dynamic Finite Element Analysis of a Gradient Elastic Bar with Micro-Inertia. Comput. Mech. 2010, 45, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, H.G.; Vardoulakis, I.; Velgaki, E.G. Dispersive Rayleigh-Wave Propagation in Microstructured Solids Characterized by Dipolar Gradient Elasticity. J. Elast. 2004, 74, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegios, I.P.; Papargyri-Beskou, S.; Beskos, D.E. Finite Element Static and Stability Analysis of Gradient Elastic Beam Structures. Acta Mech. 2015, 226, 745–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegios, I.P.; Hatzigeorgiou, G.D. Finite Element Free and Forced Vibration Analysis of Gradient Elastic Beam Structures. Acta Mech. 2018, 229, 4817–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiminas, E.L.; Koumousis, V.K. A Beam Finite Element Based on Gradient Elasticity. In Proceedings of the 10th HSTAM International Congress on Mechanics, Chania, Greece, 25–27 May 2013; Beskos, D.E., Stavroulakis, G.E., Eds.; Technical University of Crete Press: Chania, Greece, 2013; p. 123. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakopoulos, A.E.; Amanatidou, E.; Aravas, N. A Reciprocity Theorem in Linear Gradient Elasticity and the Corresponding Saint-Venant Principle. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 3875–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiatas, G.C. A New Efficient Method to Evaluate Exact Stiffness and Mass Matrices of Non-Uniform Beams Resting on an Elastic Foundation. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2014, 84, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, D.; Tsepoura, K.G.; Tsinopoulos, S.V.; Beskos, D.E. A Boundary Element Method for Solving 2-D and 3-D Static Gradient Elastic Problems: Part I: Integral Formulation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2003, 192, 2845–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| ) | SGE-N = 1 | SGE-N = 4 | FEM-N = 1 | SGE-N = 1 | SGE-N = 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.001 | 0.0303092 | 0.0303092 | 0.030315 | 0.00606305 | 0.00606305 |
| 0.1 | 0.0297089 | 0.0297089 | - | 0.00606305 | 0.00606305 |
| 0.2 | 0.0291026 | 0.0291026 | - | 0.00606305 | 0.00606305 |
| 0.3 | 0.0284963 | 0.0284963 | - | 0.00606304 | 0.00606304 |
| 0.4 | 0.0278900 | 0.0278900 | - | 0.00606300 | 0.00606300 |
| 0.5 | 0.0272837 | 0.0272837 | - | 0.00606249 | 0.00606249 |
| n | SGE-N = 1 | SGE-N = 3 | SGE-N = 5 | SGE-N = 7 | SGE-N = 10 | SGE-N = 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1835.46 | 1705.15 | 1697.66 | 1696.30 | 1695.84 | 1695.70 |
| 2 | 41,472.2 | 5408.71 | 5214.88 | 5177.50 | 5164.70 | 5160.91 |
| 3 | - | 9588.46 | 9097.55 | 8922.84 | 8860.53 | 8841.76 |
| 4 | - | 20,018.5 | 13,546.2 | 13,103.4 | 12,922.0 | 12,865.6 |
| n | g = 0.1 | g = 0.2 | g = 0.3 | g = 0.4 | g = 0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1659.31 | 1695.84 | 1735.34 | 1777.43 | 1821.74 |
| 2 | 5008.12 | 5164.70 | 5364.32 | 5594.30 | 5845.76 |
| 3 | 8447.83 | 8860.53 | 9444.89 | 10,142.0 | 10,921.5 |
| 4 | 12,039.9 | 12,922.0 | 14,220.9 | 15,780.6 | 17,529.6 |
| nth Mode | SGE-N = 15 | CE-N = 15 Consistent | CE-N = 15 Lumped | FEM-N = 4 Lumped | FEM-N = 12 Lumped |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1625.95 | 1625.97 | 1624.49 | 1614.57 | 1623.83 |
| 2 | 4895.38 | 4896.04 | 4855.94 | 4597.91 | 4843.71 |
| 3 | 8217.56 | 8220.64 | 8034.98 | 6881.25 | 7980.71 |
| 4 | 11,628.10 | 11,636.5 | 11,127.2 | 8116.99 | 10,981.16 |
| FEM | g = 0.001 | g = 0.1 | g = 0.2 | g = 0.3 | g = 0.4 | g = 0.5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.006821 | −0.006817 | −0.006403 | −0.005984 | −0.005566 | −0.005149 | −0.004735 | |
| - | −0.000364 | −0.000364 | −0.000364 | −0.000364 | −0.000362 | −0.000355 | |
| −0.028799 | −0.028788 | −0.027614 | −0.026429 | −0.025244 | −0.024059 | −0.022880 | |
| −0.034863 | −0.034848 | −0.033423 | −0.031983 | −0.030543 | −0.029104 | −0.027671 | |
| −0.001516 | −0.001516 | −0.001516 | −0.001516 | −0.001516 | −0.001514 |
| n | g = 0.001 | g = 0.1 | g = 0.2 | g = 0.3 | g = 0.4 | g = 0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 577.970 | 588.199 | 600.109 | 613.669 | 628.893 | 645.734 |
| 2 | 1582.82 | 1622.14 | 1668.00 | 1720.09 | 1778.24 | 1841.69 |
| 3 | 2084.55 | 2112.87 | 2154.76 | 2208.43 | 2272.09 | 2343.45 |
| 4 | 2518.65 | 2527.20 | 2547.72 | 2576.97 | 2611.94 | 2649.96 |
| n | SGE Consistent | CE Consistent | CE Lumped | FEM Lumped |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 577.970 | 577.997 | 518.748 | 518.669 |
| 2 | 1582.82 | 1582.69 | 1347.55 | 1347.44 |
| 3 | 2084.55 | 2084.70 | 1596.44 | 1596.27 |
| 4 | 2518.65 | 2518.73 | 1821.88 | 1821.93 |
| n | SGE Consistent | CE Consistent | CE Lumped |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 645.734 | 650.292 | 583.992 |
| 2 | 1841.69 | 1718.49 | 1455.22 |
| 3 | 2343.45 | 2273.35 | 1748.52 |
| 4 | 2649.96 | 2564.37 | 1855.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsiatas, G.C.; Charalampakis, A.E.; Giannakopoulos, A.E.; Tsopelas, P. Static and Dynamic Analysis of Strain Gradient Planar Trusses. Buildings 2024, 14, 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14124031
Tsiatas GC, Charalampakis AE, Giannakopoulos AE, Tsopelas P. Static and Dynamic Analysis of Strain Gradient Planar Trusses. Buildings. 2024; 14(12):4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14124031
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsiatas, George C., Aristotelis E. Charalampakis, Antonios E. Giannakopoulos, and Panos Tsopelas. 2024. "Static and Dynamic Analysis of Strain Gradient Planar Trusses" Buildings 14, no. 12: 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14124031
APA StyleTsiatas, G. C., Charalampakis, A. E., Giannakopoulos, A. E., & Tsopelas, P. (2024). Static and Dynamic Analysis of Strain Gradient Planar Trusses. Buildings, 14(12), 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14124031






