Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Buildings: A Scientometric Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
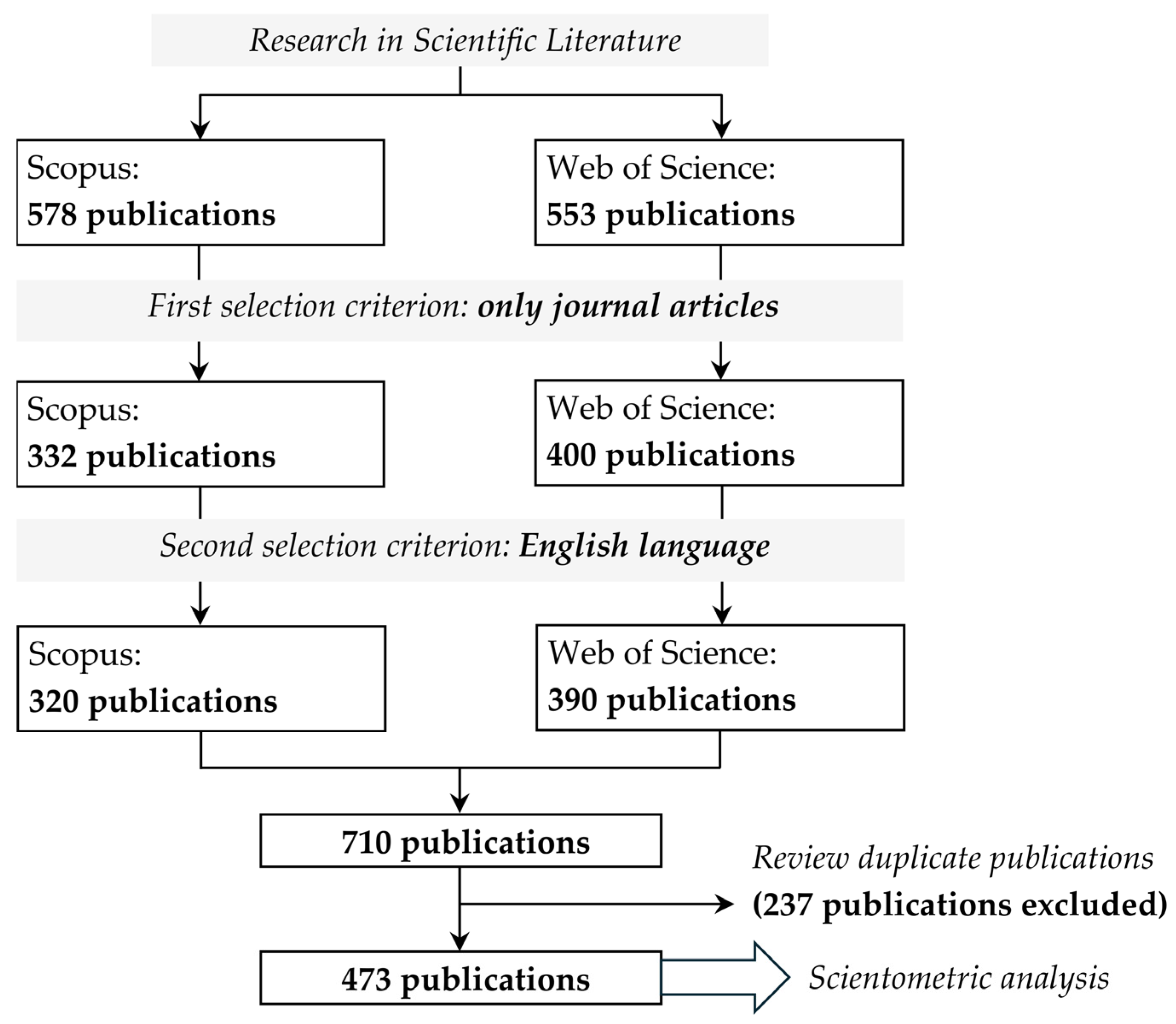
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scientometric Approach
2.2. Research Methodology
2.3. Scientometric Analysis Techniques
2.4. Network Structure and Measures
3. Results
3.1. Research Trends in LCSA of Buildings
Growth in Publications
3.2. Research Structure on LCSA of Buildings
3.2.1. Keywords Co-Occurrence Network
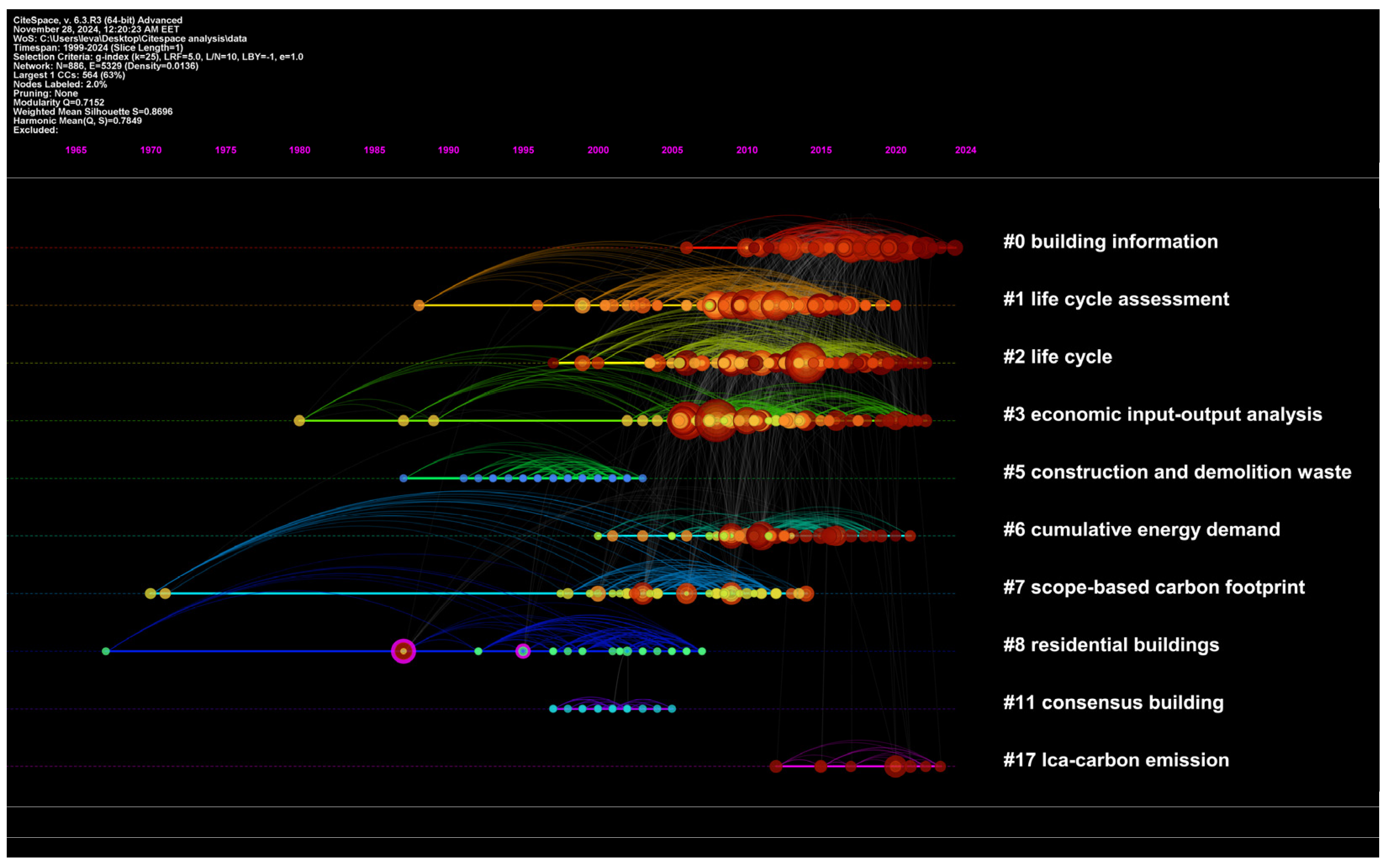
3.2.2. Document Co-Citation Network
3.3. Emerging Trends in Building LCSA Research
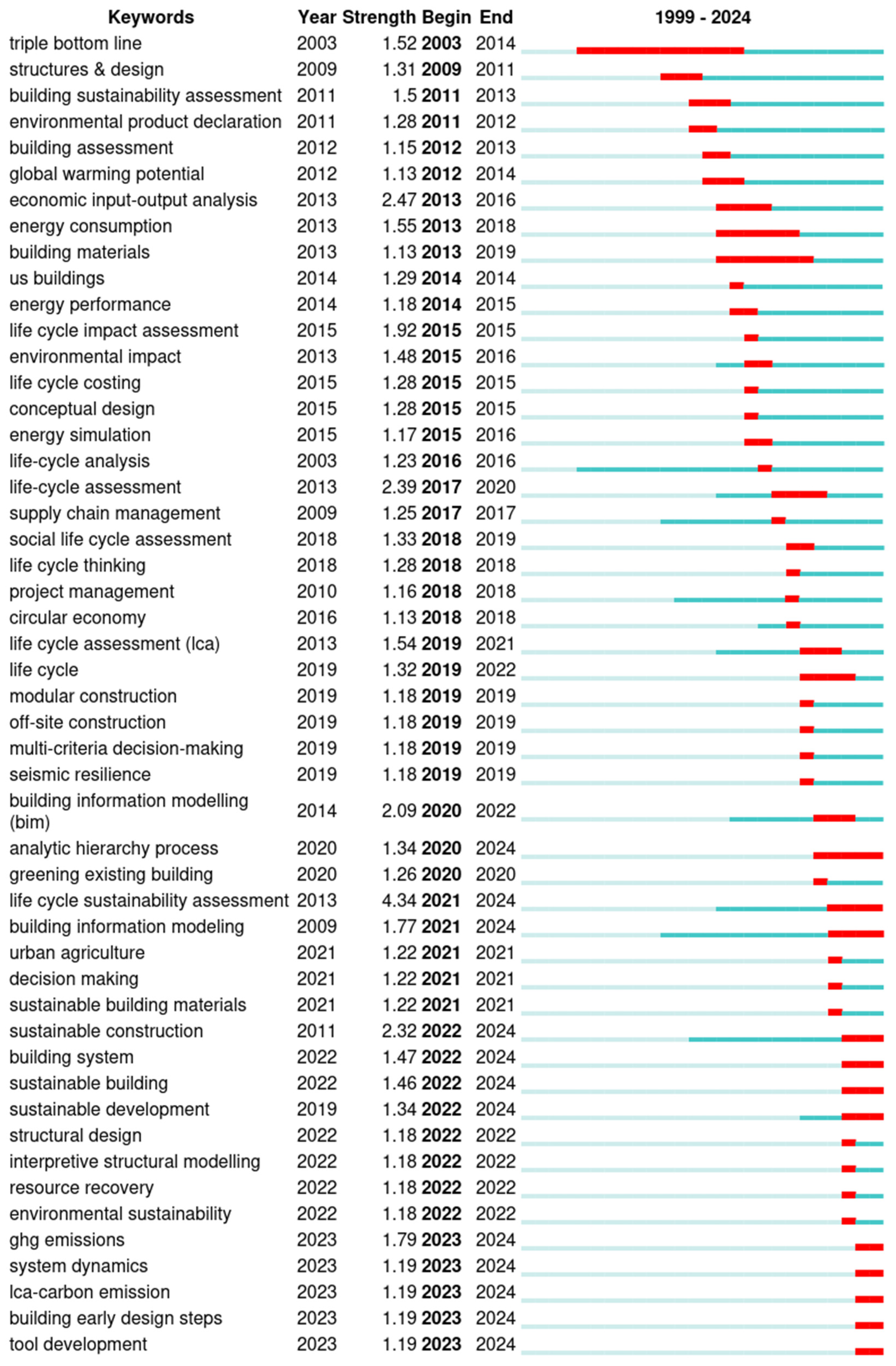
Keyword Citation Bursts
3.4. Leading Academic Outlets
Journal Direct Citation Network
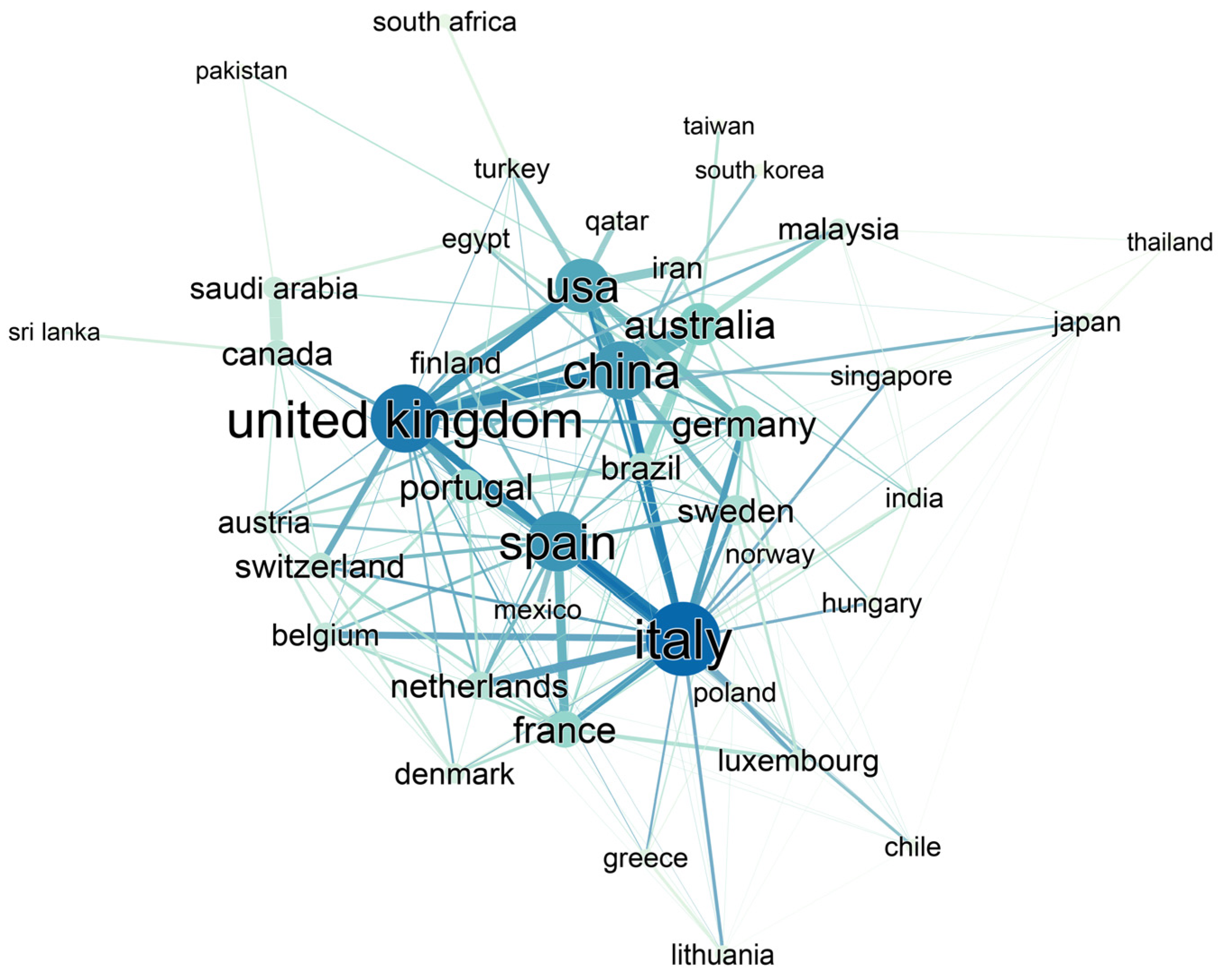
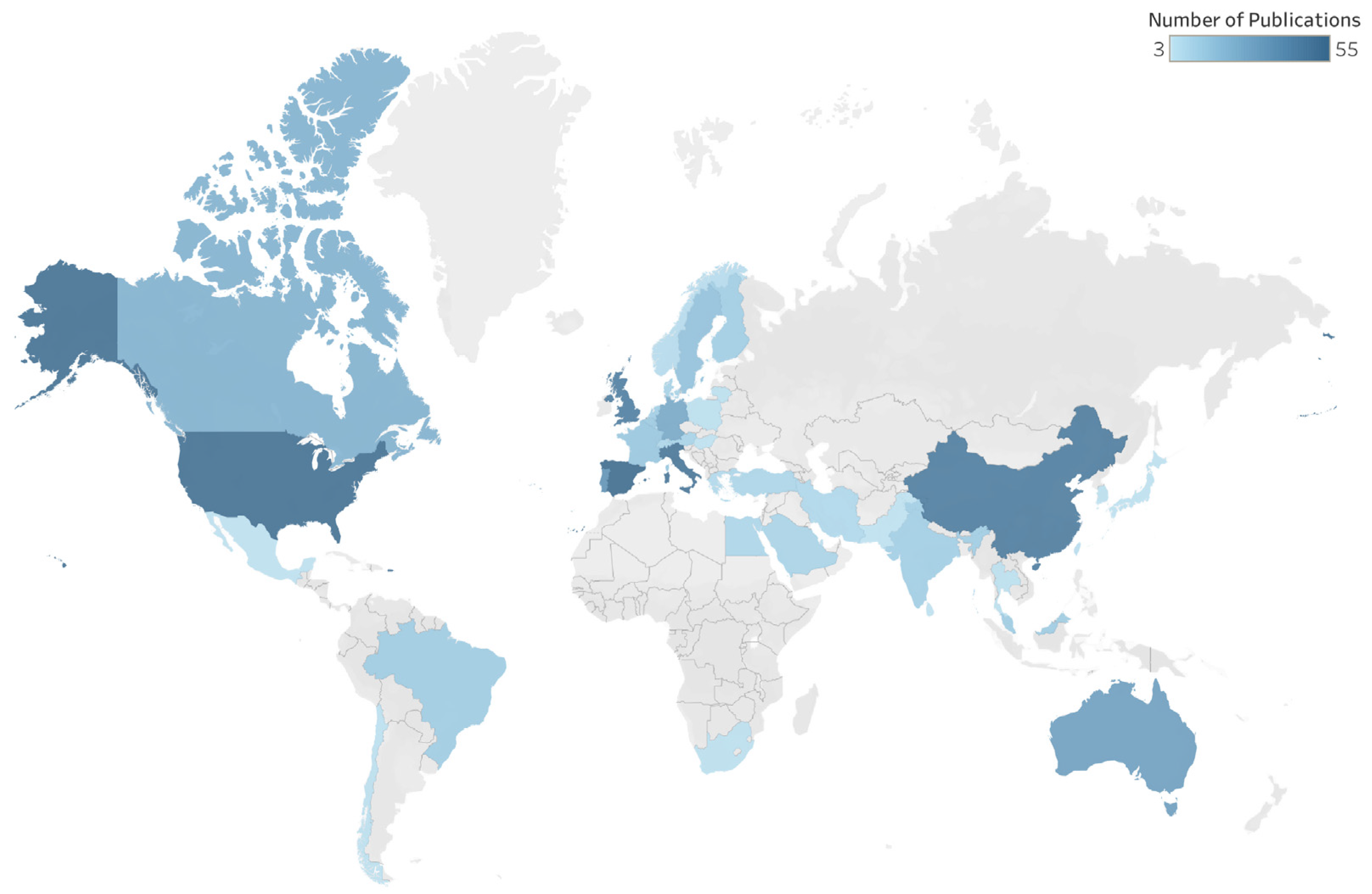
3.5. Global Collaboration in Building LCSA Research
Country Co-Authorship Networkk
4. Discussion
4.1. Central Themes and Methodologies
4.2. Publication Outlets and International Collaboration Networks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Environment Programme. Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction: Beyond Foundations: Mainstreaming Sustainable Solutions to Cut Emissions from the Buildings Sector; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Ng, S.T. A Modeling Framework to Evaluate Sustainability of Building Construction Based on LCSA. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Musa, N.; Onn, C.C.; Ramesh, S.; Liang, L.; Wang, W. Evolution of Sustainability in Global Green Building Rating Tools. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramian, M.; Yetilmezsoy, K. Life Cycle Assessment of the Building Industry: An Overview of Two Decades of Research (1995–2018). Energy Build. 2020, 219, 109917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, C.; Trentin, A.W.D.S.; Braun, A.B.; Thomé, A. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment: A Systematic Literature Review through the Application Perspective, Indicators, and Methodologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. The European Green Deal; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019.
- European Commission. A New Circular Economy Action Plan for a Cleaner and More Competitive Europe; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020.
- European Parliament and Council. Directive 2010/31/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 May 2010 on the Energy Performance of Buildings (Recast). Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L153, 13–35. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and Council. Directive 2012/27/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2012 on Energy Efficiency, Amending Directives 2009/125/EC and 2010/30/EU and Repealing Directives 2004/8/EC and 2006/32/EC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2012, L315, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and Council. Directive (EU) 2018/2002 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 December 2018 Amending Directive 2012/27/EU on Energy Efficiency. Off. J. Eur. Union 2018, L328, 210–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Feng, H. Is Energy-Efficient Building Sustainable? A Case Study on Individual Housing in Canada under BCESC Energy Updates. Build. Environ. 2023, 239, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Pinheiro, M.D.; de Brito, J.; Mateus, R. A Critical Analysis of LEED, BREEAM and DGNB as Sustainability Assessment Methods for Retail Buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 66, 105825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faqih, F.; Zayed, T. A Comparative Review of Building Component Rating Systems. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 33, 101588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattinzioli, T.; Sol-Sánchez, M.; Moreno, B.; Alegre, J.; Martínez, G. Sustainable Building Rating Systems: A Critical Review for Achieving a Common Consensus. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 512–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, J.G.; Traverso, M. Application of Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment in the Construction Sector: A Systematic Literature Review. Processes 2021, 9, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaker Esteghamati, M.; Sharifnia, H.; Ton, D.; Asiatico, P.; Reichard, G.; Flint, M.M. Sustainable Early Design Exploration of Mid-Rise Office Buildings with Different Subsystems Using Comparative Life Cycle Assessment. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 48, 104004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamad, M.; Abu-Hamd, M. Life Cycle Assessment Framework for Embodied Environmental Impacts of Building Construction Systems. Sustainability 2021, 13, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, I.; Rezgui, Y.; Beach, T.; Petri, I. Social Life Cycle Assessment in the Construction Sector: Current Work and Directions for Future Research. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2024, 29, 1827–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H. The Sustainability Study and Exploration in the Building Commercial Complex System Based on Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)–Emergy–Carbon Emission Analysis. Processes 2023, 11, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Asutosh, A.; Wu, G.; Wei, G.; Shi, Y.; Yang, M. Sustainability Study of a Residential Building near Subway Based on LCA-Emergy Method. Buildings 2022, 12, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwodo, M.; Anumba, C.J. Exergy-Based Life Cycle Assessment of Buildings: Case Studies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ng, S.T.; Liu, P. Towards the Principles of Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment: An Integrative Review for the Construction and Building Industry. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 95, 104604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawumi, T.O.; Chan, D.W.M. A Scientometric Review of Global Research on Sustainability and Sustainable Development. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Sandanayake, M.; Hou, L.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, G. A Systematic Review of Green Construction Research Using Scientometrics Methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Chan, M.; Morda, R.; Lou, C.X.; Vrcelj, Z. A Scientometric Review of Sustainable Infrastructure Research: Visualization and Analysis. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2023, 23, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C.; Huo, X.; Owusu-Manu, D.-G. A Scientometric Analysis and Visualization of Global Green Building Research. Build. Environ. 2019, 149, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuni, I.Y.; Shen, G.Q.P.; Osei-Kyei, R. Scientometric Review of Global Research Trends on Green Buildings in Construction Journals from 1992 to 2018. Energy Build. 2019, 190, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, M.; Chàfer, M.; Cabeza, L.F.; Jiménez, L.; Boer, D. Circular Economy in the Building and Construction Sector: A Scientific Evolution Analysis. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirkhani, M.; Martek, I.; Luther, M.B. Mapping Research Trends in Residential Construction Retrofitting: A Scientometric Literature Review. Energies 2021, 14, 6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh, M.O.; Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C.; Jafari, A.; Brilakis, I.; Chen, W.; Nani, G.; Kwame Yevu, S. Scientometric Mapping of Global Research on Green Retrofitting of Existing Buildings (GREB): Pathway towards a Holistic GREB Framework. Energy Build. 2022, 277, 112532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdosi, H.; Abbasianjahromi, H.; Banihashemi, S.; Ravanshadnia, M. BIM Applications in Sustainable Construction: Scientometric and State-of-the-Art Review. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2023, 23, 1969–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Shen, M.; Peh, L.C. Transition from Building Information Modeling (BIM) to Integrated Digital Delivery (IDD) in Sustainable Building Management: A Knowledge Discovery Approach Based Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.; Santos, J.; Leite, F.; Escórcio, P. Using BIM to Improve Building Energy Efficiency—A Scientometric and Systematic Review. Energy Build. 2021, 250, 111292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, G.B. Interoperability in Building Information Modeling for AECO/FM Industry. Autom. Constr. 2020, 113, 103122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, Y.; Seyis, S. Mapping the Scientific Research of the Life Cycle Assessment in the Construction Industry: A Scientometric Analysis. Build. Environ. 2021, 204, 108086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Hossain, M.U.; Liu, M.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Chen, X.; Cao, G. BIM Integrated LCA for Promoting Circular Economy towards Sustainable Construction: An Analytical Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Elshaboury, N. Science Mapping Analysis of Embodied Energy in the Construction Industry. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 1362–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalimov, V.V.; Mulchenko, Z.M. Measurement of Science: Study of the Development of Science as an Information Process; Foreign Technology Division: Washington, DC, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, D.J. Science Studies: An Advanced Introduction; New York University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-0-8147-3564-0. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. Science Mapping: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2017, 2, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingers, J.; Leydesdorff, L. A Review of Theory and Practice in Scientometrics. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 246, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Goerlandt, F.; Reniers, G. An Overview of Scientometric Mapping for the Safety Science Community: Methods, Tools, and Framework. Saf. Sci. 2021, 134, 105093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C.; Adabre, M.A.; Edwards, D.J.; Hosseini, M.R.; Ameyaw, E.E. Artificial Intelligence in the AEC Industry: Scientometric Analysis and Visualization of Research Activities. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Lu, C.; Shen, R.; Lu, T.; Ma, B.; Hua, Y. Knowledge Mapping of Drug-Induced Liver Injury: A Scientometric Investigation (2010–2019). Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. A Tale of Two Databases: The Use of Web of Science and Scopus in Academic Papers. Scientometrics 2020, 123, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Visualizing Bibliometric Networks. In Measuring Scholarly Impact; Ding, Y., Rousseau, R., Wolfram, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 285–320. ISBN 978-3-319-10376-1. [Google Scholar]
- Nieminen, J. On the Centrality in a Graph. Scand. J. Psychol. 1974, 15, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.C. Centrality in Social Networks Conceptual Clarification. Soc. Netw. 1978, 1, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbeck, J. Network Structure and Measures. In Analyzing the Social Web; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 25–44. ISBN 978-0-12-405531-5. [Google Scholar]
- Opsahl, T.; Agneessens, F.; Skvoretz, J. Node Centrality in Weighted Networks: Generalizing Degree and Shortest Paths. Soc. Netw. 2010, 32, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ibekwe-SanJuan, F.; Hou, J. The Structure and Dynamics of Cocitation Clusters: A Multiple-perspective Cocitation Analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 2010, 61, 1386–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.D.F.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Travieso, G.; Villas Boas, P.R. Characterization of Complex Networks: A Survey of Measurements. Adv. Phys. 2007, 56, 167–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöpffer, W.; Renner, I. Life-Cycle Based Sustainability Assessment of Products. In Environmental Management Accounting for Cleaner Production; Schaltegger, S., Bennett, M., Burritt, R.L., Jasch, C., Eds.; Eco-Efficiency in Industry and Science; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 24, pp. 91–102. ISBN 978-1-4020-8912-1. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 14040:2006; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- ISO 14044:2006; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Hunkeler, D.; Lichtenvort, K.; Rebitzer, G. Environmental Life Cycle Costing, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-429-14044-0. [Google Scholar]
- Swarr, T.E.; Hunkeler, D.; Klöpffer, W.; Pesonen, H.-L.; Ciroth, A.; Brent, A.C.; Pagan, R. Environmental Life-Cycle Costing: A Code of Practice. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2011, 16, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Guidelines for Social Life Cycle Assessment of Products; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2009; ISBN 978-92-807-3021-0. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Towards a Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2011; ISBN 978-92-807-3175-0. [Google Scholar]
- Economidou, M.; Todeschi, V.; Bertoldi, P.; D’Agostino, D.; Zangheri, P.; Castellazzi, L. Review of 50 Years of EU Energy Efficiency Policies for Buildings. Energy Build. 2020, 225, 110322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrini, A.; Lentini, G.; Cuman, S.; Bodrato, A.; Marenco, L. From Nearly Zero Energy Buildings (NZEB) to Positive Energy Buildings (PEB): The next Challenge—The Most Recent European Trends with Some Notes on the Energy Analysis of a Forerunner PEB Example. Dev. Built Environ. 2020, 3, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börner, K.; Chen, C.; Boyack, K.W. Visualizing Knowledge Domains. Annu. Rev. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 179–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherven, K. Mastering Gephi Network Visualization, 1st ed.; Packt Publishing: Birmingham, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-1-78398-735-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ingrao, C.; Messineo, A.; Beltramo, R.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Ioppolo, G. How Can Life Cycle Thinking Support Sustainability of Buildings? Investigating Life Cycle Assessment Applications for Energy Efficiency and Environmental Performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwodo, M.N.; Anumba, C.J. A Review of Life Cycle Assessment of Buildings Using a Systematic Approach. Build. Environ. 2019, 162, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Hou, Y.; Ding, L.; Li, P. Visualized Literature Review on Sustainable Building Renovation. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilches, A.; Garcia-Martinez, A.; Sanchez-Montañes, B. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of Building Refurbishment: A Literature Review. Energy Build. 2017, 135, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schamne, A.N.; Nagalli, A.; Soeiro, A.A.V.; Poças Martins, J.P.D.S. BIM in Construction Waste Management: A Conceptual Model Based on the Industry Foundation Classes Standard. Autom. Constr. 2024, 159, 105283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschetti, R.; Brattebø, H. Combining Life Cycle Environmental and Economic Assessments in Building Energy Renovation Projects. Energies 2017, 10, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Ferreira, M.; Barbosa, R. Relevance of Embodied Energy and Carbon Emissions on Assessing Cost Effectiveness in Building Renovation—Contribution from the Analysis of Case Studies in Six European Countries. Buildings 2018, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, R.; Silva, S.M.; De Almeida, M.G. Environmental and Cost Life Cycle Analysis of the Impact of Using Solar Systems in Energy Renovation of Southern European Single-Family Buildings. Renew. Energy 2019, 137, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wu, L.; Zhao, W.; Ma, W.; Hao, J. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment: An Index System for Building Energy Retrofit Projects. Buildings 2024, 14, 2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.R.; Martek, I.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Aibinu, A.A.; Arashpour, M.; Chileshe, N. Critical Evaluation of Off-Site Construction Research: A Scientometric Analysis. Autom. Constr. 2018, 87, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Searching for Intellectual Turning Points: Progressive Knowledge Domain Visualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5303–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soust-Verdaguer, B.; Llatas, C.; García-Martínez, A. Critical Review of Bim-Based LCA Method to Buildings. Energy Build. 2017, 136, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potrč Obrecht, T.; Röck, M.; Hoxha, E.; Passer, A. BIM and LCA Integration: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, K.; AzariJafari, H. Challenges and Opportunities for Integrating BIM and LCA: Methodological Choices and Framework Development. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 67, 102728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.P.; Almeida, M.; Braganca, L.; Mateus, R. BIM-Based Energy Analysis and Sustainability Assessment-Application to Portuguese Buildings. Buildings 2021, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Costa, A.A.; Silvestre, J.D.; Pyl, L. Integration of LCA and LCC Analysis within a BIM-Based Environment. Autom. Constr. 2019, 103, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.P.; Villaschi, F.S.; Braganca, L. Assessing Life Cycle Environmental and Economic Impacts of Building Construction Solutions with BIM. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boje, C.; Menacho, Á.J.H.; Marvuglia, A.; Benetto, E.; Kubicki, S.; Schaubroeck, T.; Navarrete Gutiérrez, T. A Framework Using BIM and Digital Twins in Facilitating LCSA for Buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkington, J. Cannibals with Forks: The Triple Bottom Line of 21st Century Business; Capstone Publishing: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Onat, N.C.; Kucukvar, M.; Tatari, O.; Egilmez, G. Integration of System Dynamics Approach toward Deepening and Broadening the Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment Framework: A Case for Electric Vehicles. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 1009–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichter, M.; Piccardo, C. Assessing Life Cycle Sustainability of Building Renovation and Reconstruction: A Comprehensive Review of Case Studies and Methods. Build. Environ. 2024, 262, 111817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini Toosi, H.; Lavagna, M.; Leonforte, F.; Del Pero, C.; Aste, N. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment in Building Energy Retrofitting; A Review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 60, 102248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A.; Thomas, A. System Dynamics Modelling Coupled with Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) for Sustainability-Related Policy Analysis and Decision-Making in the Built Environment. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2023, 12, 534–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A.; Thomas, A. A Framework for Dynamic Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment and Policy Analysis of Built Environment through a System Dynamics Approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

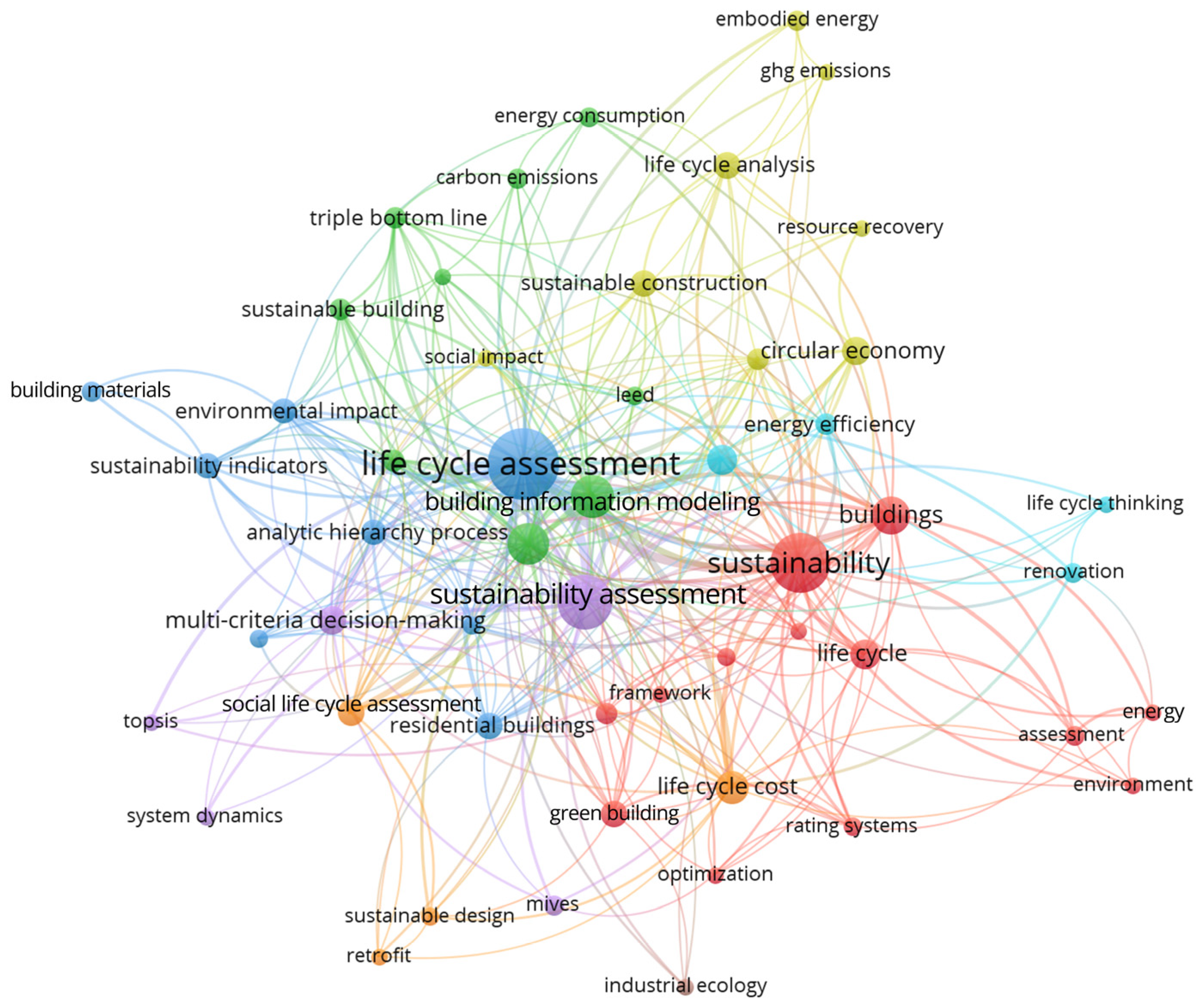


| Rank | Node | Degree | Weighted Degree | Betweenness Centrality | Closeness Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | life cycle assessment | 44 | 223 | 275.98 | 0.88 |
| 2 | sustainability | 35 | 135 | 151.19 | 0.76 |
| 3 | sustainability assessment | 32 | 101 | 114.08 | 0.73 |
| 4 | life cycle sustainability assessment | 29 | 79 | 72.39 | 0.70 |
| 5 | buildings | 25 | 67 | 63.47 | 0.66 |
| 6 | building information modeling | 23 | 79 | 38.08 | 0.65 |
| 7 | life cycle cost | 21 | 52 | 39.94 | 0.63 |
| 8 | multi-criteria decision-making | 21 | 37 | 31.59 | 0.63 |
| 9 | analytic hierarchy process | 19 | 34 | 13.74 | 0.61 |
| 10 | environmental impact | 17 | 33 | 17.27 | 0.60 |
| 11 | residential buildings | 17 | 30 | 16.68 | 0.60 |
| 12 | life cycle costing | 16 | 45 | 11.55 | 0.59 |
| 13 | social life cycle assessment | 16 | 37 | 12.19 | 0.59 |
| 14 | life cycle | 16 | 28 | 21.63 | 0.59 |
| 15 | green building | 16 | 22 | 13.96 | 0.59 |
| 16 | construction | 14 | 27 | 8.50 | 0.58 |
| 17 | energy efficiency | 14 | 17 | 8.40 | 0.58 |
| 18 | triple bottom line | 13 | 24 | 7.16 | 0.57 |
| 19 | multiple-criteria decision analysis | 13 | 20 | 9.38 | 0.57 |
| 20 | life cycle analysis | 13 | 18 | 15.34 | 0.56 |
| 21 | benchmarking | 13 | 17 | 5.54 | 0.57 |
| 22 | circular economy | 12 | 23 | 9.21 | 0.57 |
| 23 | sustainable building | 12 | 19 | 5.55 | 0.56 |
| 24 | sustainable construction | 12 | 19 | 5.24 | 0.57 |
| 25 | sustainability indicators | 11 | 20 | 6.93 | 0.55 |
| 26 | rating systems | 11 | 16 | 5.72 | 0.56 |
| 27 | sustainable development | 11 | 11 | 7.69 | 0.55 |
| 28 | social impact | 10 | 14 | 1.79 | 0.55 |
| 29 | indicators | 10 | 12 | 5.26 | 0.55 |
| 30 | modular construction | 10 | 12 | 1.70 | 0.55 |
| 31 | framework | 9 | 9 | 3.01 | 0.54 |
| 32 | economic input-output analysis | 8 | 13 | 1.97 | 0.54 |
| 33 | optimization | 8 | 10 | 3.22 | 0.53 |
| 34 | assessment | 7 | 16 | 2.10 | 0.50 |
| 35 | renovation | 7 | 14 | 2.62 | 0.53 |
| 36 | energy consumption | 7 | 11 | 1.55 | 0.54 |
| 37 | sustainable design | 7 | 11 | 0.84 | 0.52 |
| 38 | building sustainability assessment | 7 | 10 | 2.25 | 0.53 |
| 39 | leed | 7 | 9 | 2.34 | 0.53 |
| 40 | environment | 7 | 9 | 2.24 | 0.53 |
| 41 | carbon emissions | 7 | 8 | 1.57 | 0.53 |
| 42 | energy | 6 | 11 | 1.26 | 0.50 |
| 43 | retrofit | 6 | 7 | 0.86 | 0.53 |
| 44 | topsis | 5 | 10 | 0.08 | 0.52 |
| 45 | mives | 5 | 9 | 0.84 | 0.51 |
| 46 | embodied energy | 5 | 8 | 0.87 | 0.51 |
| 47 | industrial ecology | 5 | 7 | 0.10 | 0.53 |
| 48 | ghg emissions | 5 | 6 | 1.07 | 0.52 |
| 49 | life cycle thinking | 5 | 6 | 0.62 | 0.53 |
| 50 | resource recovery | 4 | 6 | 0.32 | 0.47 |
| 51 | system dynamics | 4 | 6 | 0.00 | 0.51 |
| 52 | building materials | 3 | 7 | 0.13 | 0.48 |
| ID | Size | Silhouette Value | LSI Label | Other Significant Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 106 | 0.84 | building information | building information modeling; industry foundation classes; building design process; data structure |
| 1 | 92 | 0.822 | life cycle assessment | environmental impact; life cycle sustainability assessment; sustainability assessment; life cycle thinking; modular building; multicriteria decision |
| 2 | 90 | 0.767 | life cycle | life cycle assessment; life cycle thinking; environmental performance; eco-efficiency analysis; life cycle cost; sustainability indicators; environmental impact; planetary boundaries |
| 3 | 85 | 0.844 | economic input-output analysis | hybrid lca; life cycle assessment; life cycle sustainability assessment; multi-criteria decision analysis; prospective lca; system dynamics |
| 5 | 43 | 1 | construction and demolition waste | life-cycle analysis; triple bottom line; sustainable jobs; unemployment |
| 6 | 41 | 0.908 | cumulative energy demand | life cycle assessment; global warming; buildings sustainability; dynamic energy simulation; optimization analysis; renewable energy |
| 7 | 37 | 0.961 | scope-based carbon footprint | life cycle assessment; carbon flow; environmental product declaration; stakeholder involvement; sustainability science |
| 8 | 34 | 0.979 | residential buildings | sustainable facades; multicriteria decision-making; sustainable assessment; sustainable development; residential high-rise buildings; sustainability indicators; analytic hierarchy process; urban density |
| 11 | 23 | 1 | consensus building | decision support systems; social construction of technology (scot); environmental indicators; green building |
| 17 | 8 | 0.991 | lca-carbon emission | emergy method; building system; digital twin; building glass industry |
| 20 | 5 | 0.999 | climate impacts | energy-efficiency; life cycle impact assessment; environmental-economic sustainability assessment; windows |
| Rank | Journal | Number of Publications | Citations | Norm. Citations | Weighted Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sustainability | 45 | 1075 | 34.6554 | 117 |
| 2 | Building and Environment | 26 | 1358 | 33.6679 | 105 |
| 3 | Journal of Cleaner Production | 47 | 2464 | 69.457 | 96 |
| 4 | Journal of Building Engineering | 23 | 477 | 32.0788 | 87 |
| 5 | International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment | 24 | 1343 | 33.9517 | 80 |
| 6 | Buildings | 16 | 289 | 11.6312 | 50 |
| 7 | Energy and Buildings | 16 | 818 | 22.6977 | 46 |
| 8 | Sustainable Cities and Society | 9 | 286 | 11.4815 | 38 |
| 9 | Automation in Construction | 5 | 203 | 11.0385 | 19 |
| 10 | Engineering Construction and Architectural Management | 3 | 50 | 2.8435 | 18 |
| 11 | Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy | 6 | 96 | 2.654 | 12 |
| 12 | Energies | 5 | 80 | 2.0999 | 12 |
| 13 | Environmental Impact Assessment Review | 5 | 328 | 5.5342 | 12 |
| 14 | Environmental Science and Pollution Research | 6 | 36 | 4.2847 | 10 |
| 15 | Journal of Construction Engineering and Management | 6 | 121 | 4.2745 | 9 |
| 16 | Sustainable Production and Consumption | 7 | 64 | 10.1242 | 9 |
| 17 | Construction and Building Materials | 4 | 213 | 4.2149 | 8 |
| 18 | Resources Conservation and Recycling | 3 | 133 | 2.8756 | 7 |
| 19 | Smart and Sustainable Built Environment | 4 | 60 | 3.585 | 7 |
| 20 | Solar Energy | 3 | 78 | 3.1856 | 6 |
| Rank | Country | Number of Publications | Weighted Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Italy | 51 | 32 |
| 2 | United Kingdom | 44 | 29 |
| 3 | Spain | 55 | 25 |
| 4 | China | 48 | 24 |
| 5 | USA | 53 | 22 |
| 6 | Australia | 32 | 16 |
| 7 | France | 15 | 13 |
| 8 | Germany | 28 | 13 |
| 9 | Portugal | 37 | 12 |
| 10 | Sweden | 17 | 10 |
| 11 | Brazil | 13 | 9 |
| 12 | Netherlands | 12 | 9 |
| 13 | Canada | 24 | 8 |
| 14 | Switzerland | 9 | 8 |
| 15 | Belgium | 14 | 7 |
| 16 | Finland | 12 | 7 |
| 17 | Austria | 10 | 6 |
| 18 | Iran | 8 | 6 |
| 19 | Saudi Arabia | 10 | 6 |
| 20 | Denmark | 11 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poderytė, I.; Banaitienė, N.; Banaitis, A. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Buildings: A Scientometric Analysis. Buildings 2025, 15, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030381
Poderytė I, Banaitienė N, Banaitis A. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Buildings: A Scientometric Analysis. Buildings. 2025; 15(3):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030381
Chicago/Turabian StylePoderytė, Ieva, Nerija Banaitienė, and Audrius Banaitis. 2025. "Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Buildings: A Scientometric Analysis" Buildings 15, no. 3: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030381
APA StylePoderytė, I., Banaitienė, N., & Banaitis, A. (2025). Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Buildings: A Scientometric Analysis. Buildings, 15(3), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030381









