Research on Recycling and Utilization of Shredded Waste Mask Fibers to Prepare Sustainable Engineered Cementitious Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
2.2. Mixture Proportions and Specimen Preparation
2.3. Experimental Methods and Analysis
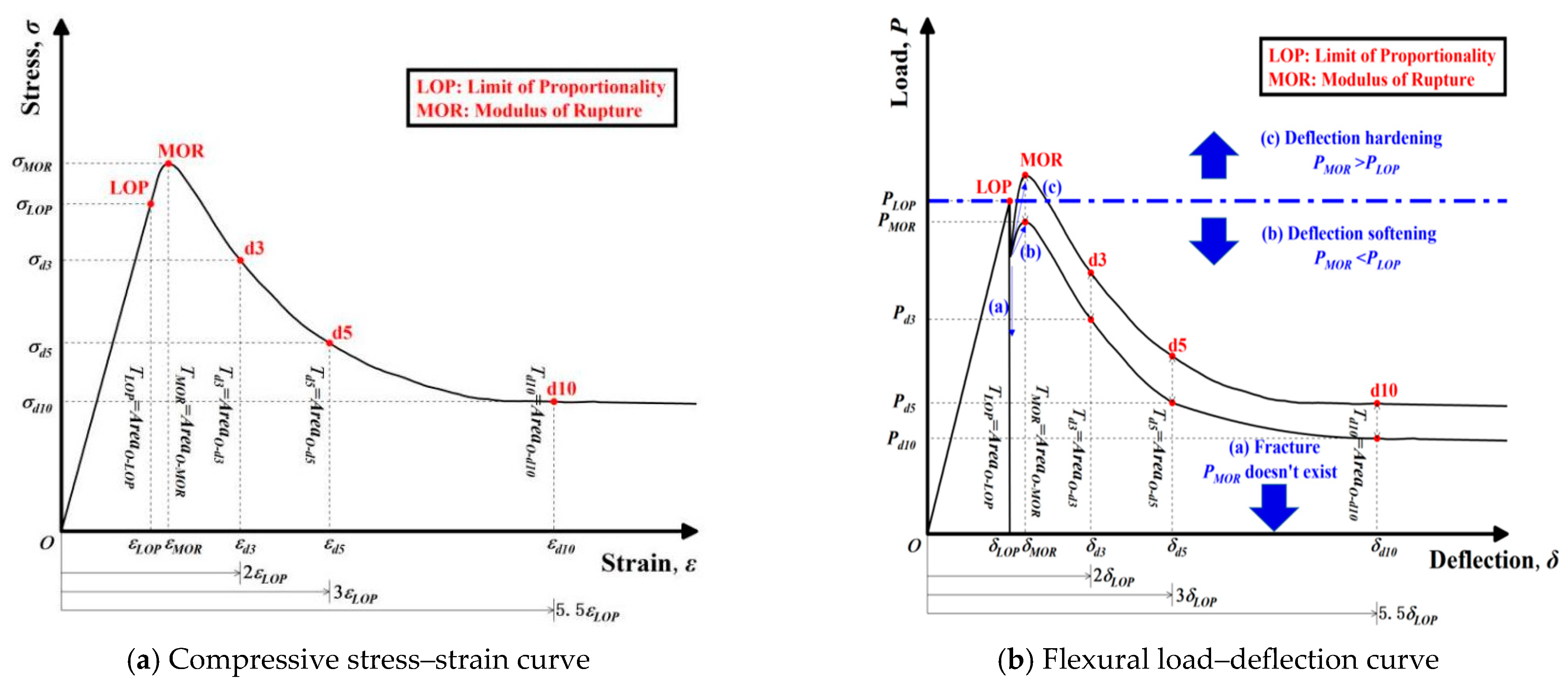
2.3.1. Flexural and Compressive Tests
2.3.2. Mechanical Property Analysis
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mechanical Properties Under Compression
3.1.1. Compressive Stress–Strain Curves
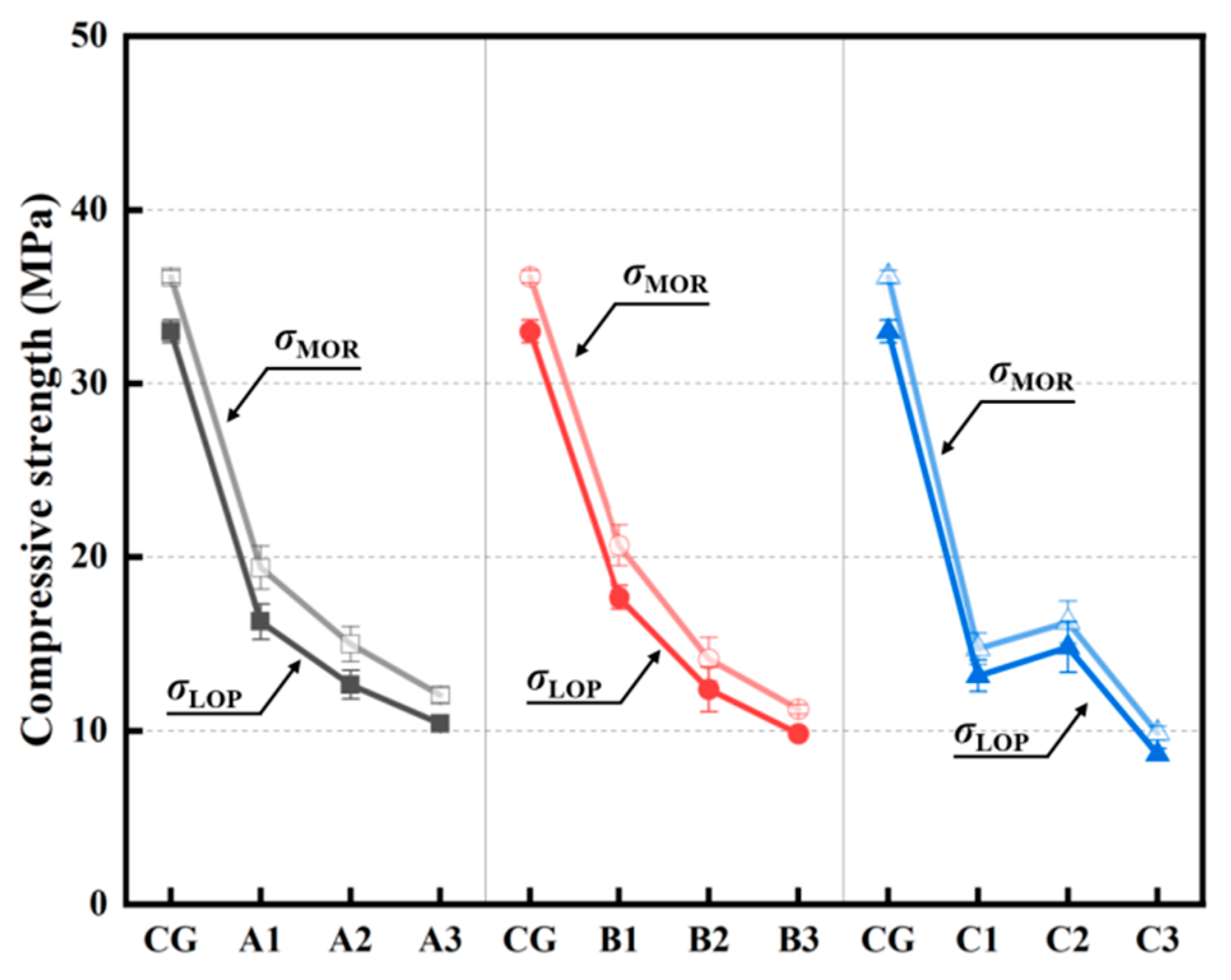
3.1.2. Compressive Strengths (Load-Bearing Capacity)
3.1.3. Compressive Strains (Deformability)
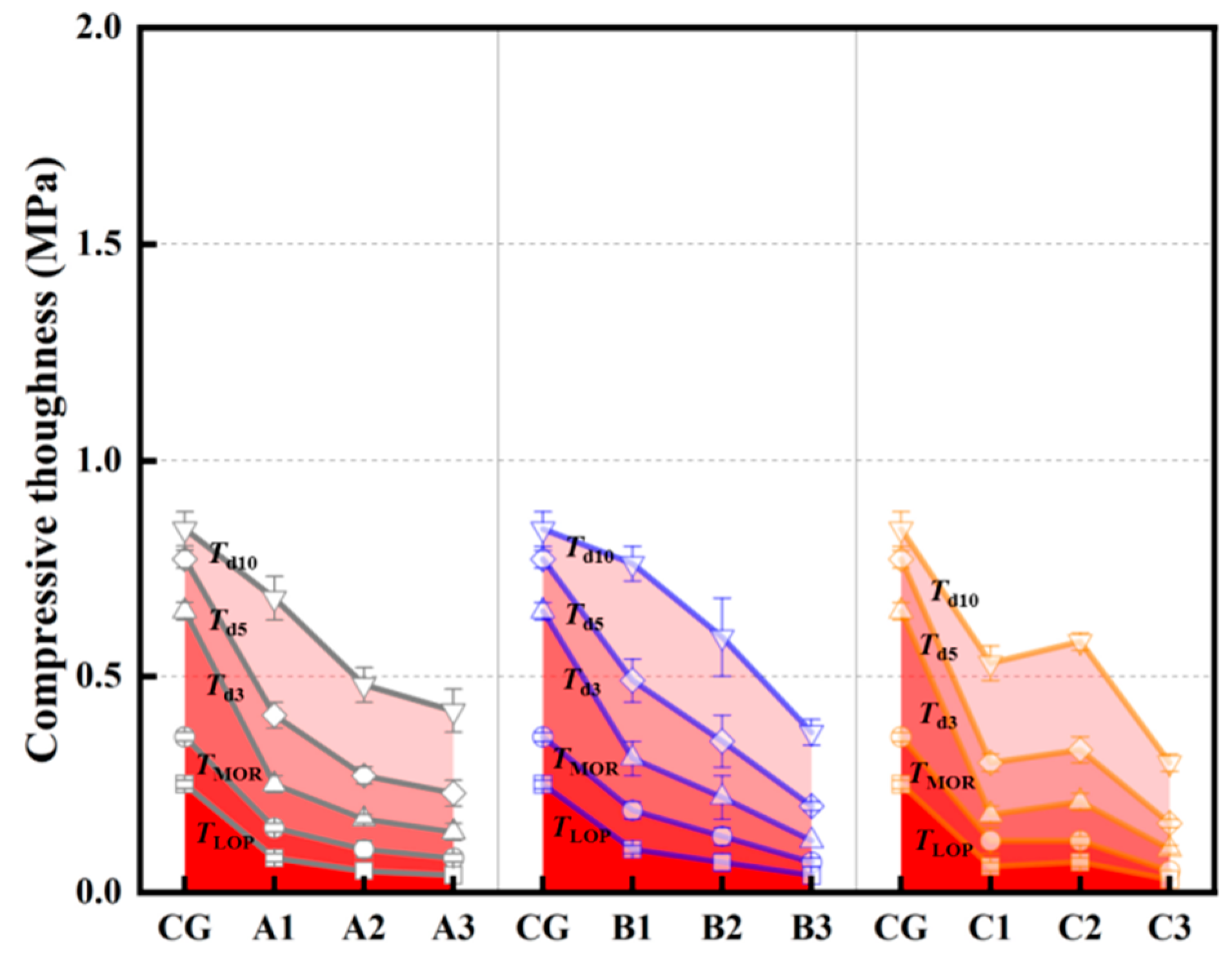
3.1.4. Compressive Toughness (Energy Absorption Capability)
3.2. Mechanical Properties in Flexure
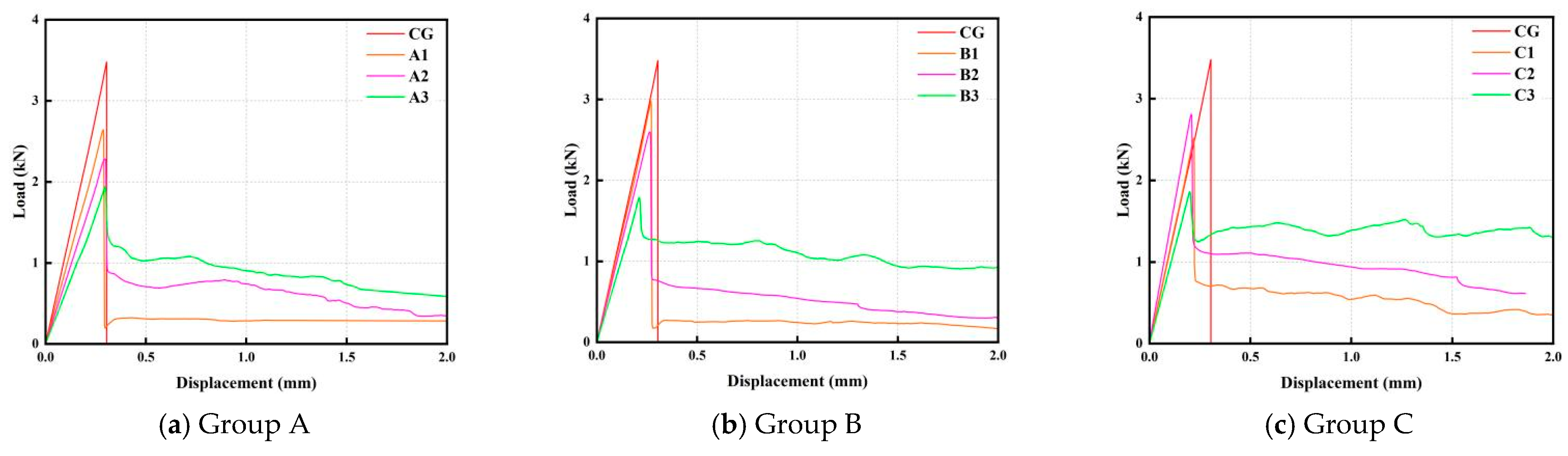
3.2.1. Flexural Load–Deflection Curves
3.2.2. Flexural Strength (Load-Bearing Capacity)
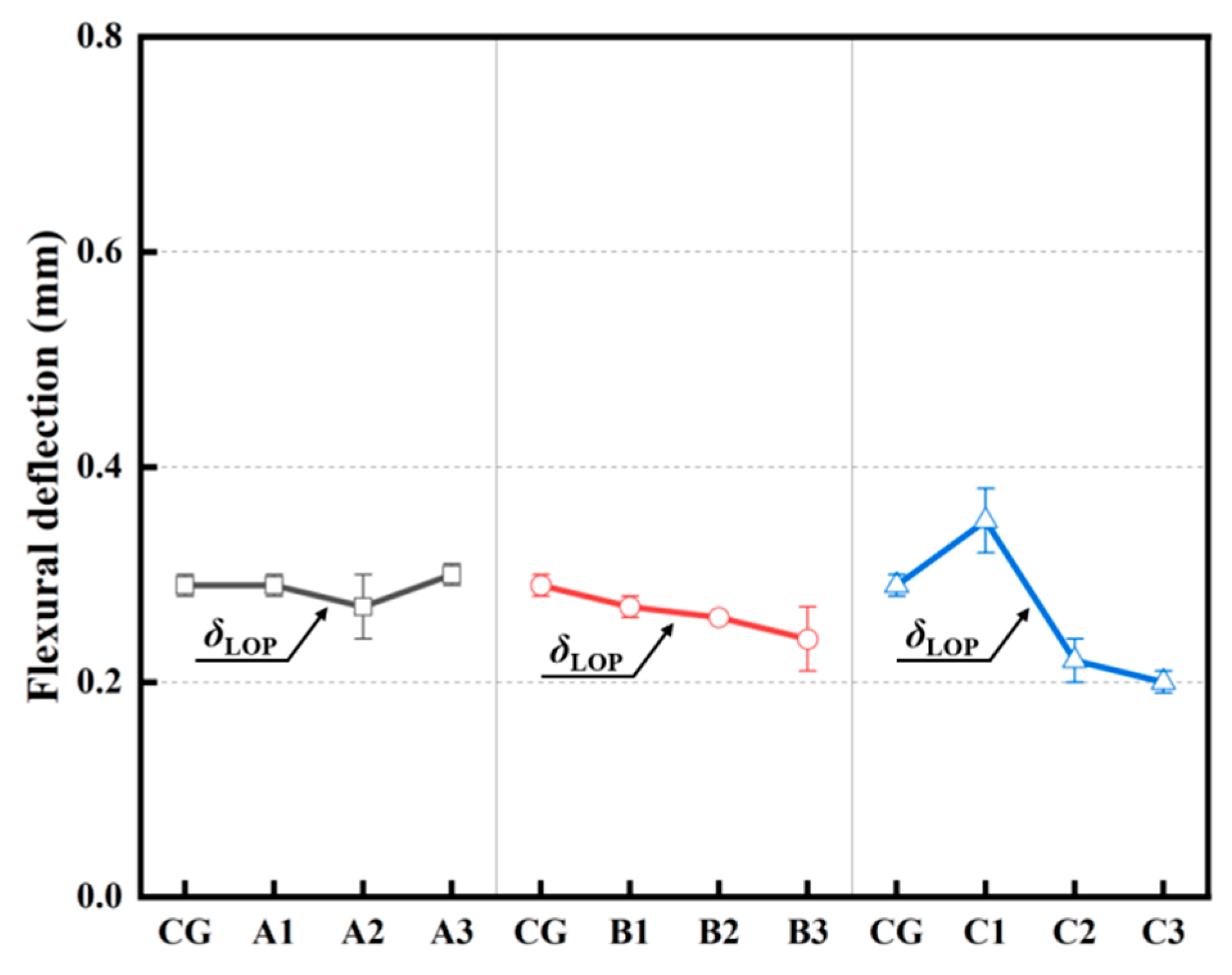
3.2.3. Flexural Deflections (Deformability)
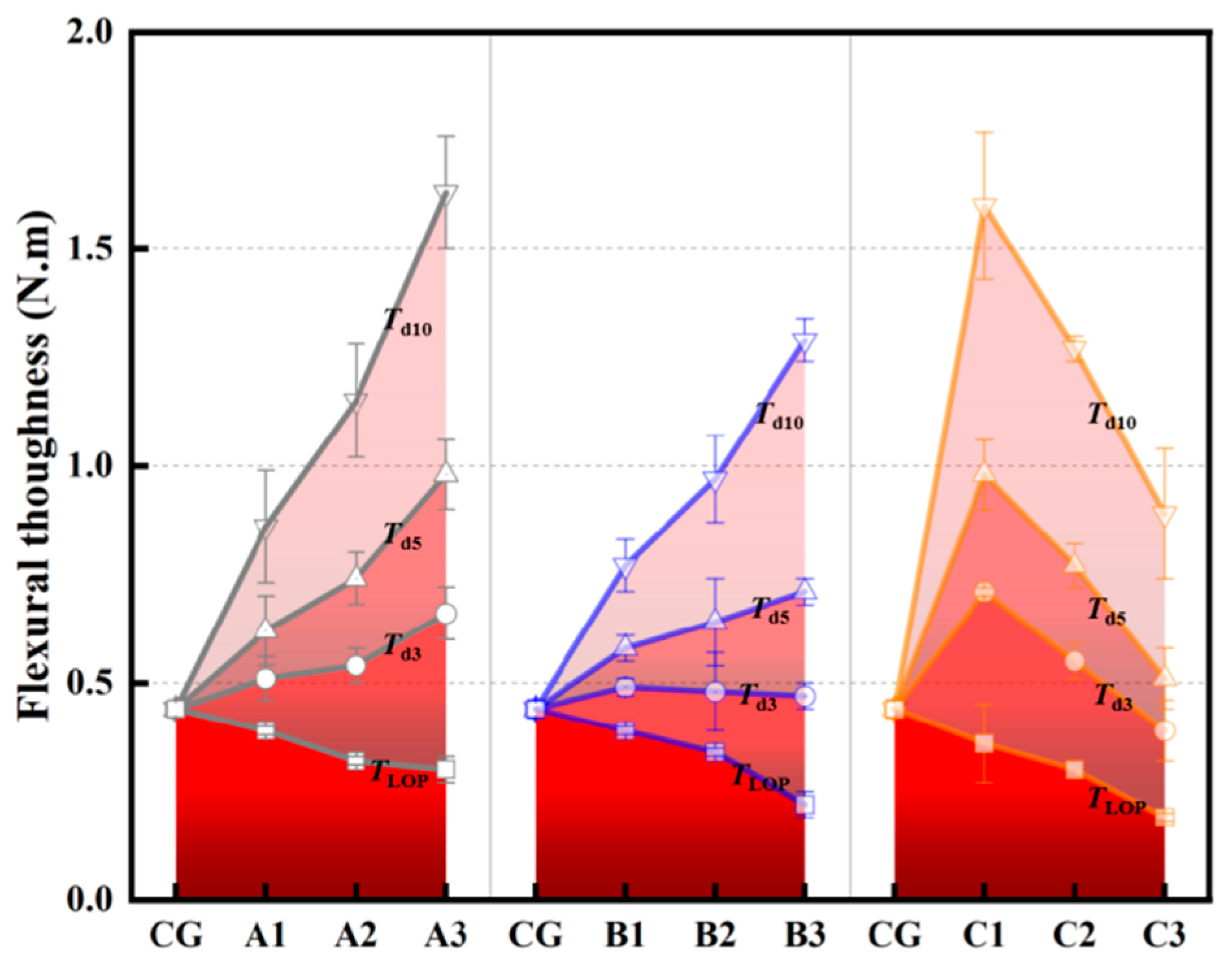
3.2.4. Flexural Toughness (Energy Absorption Capability)
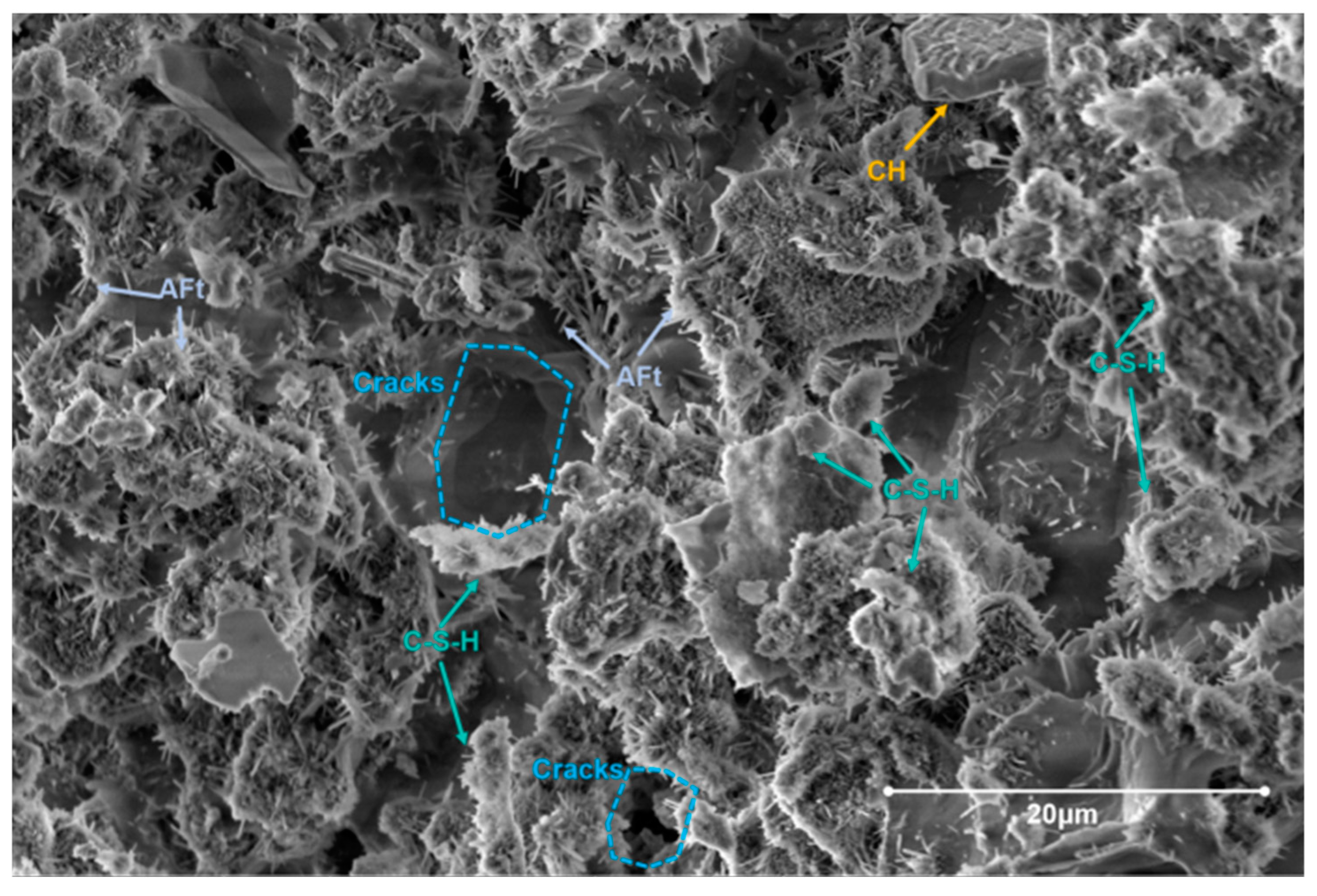
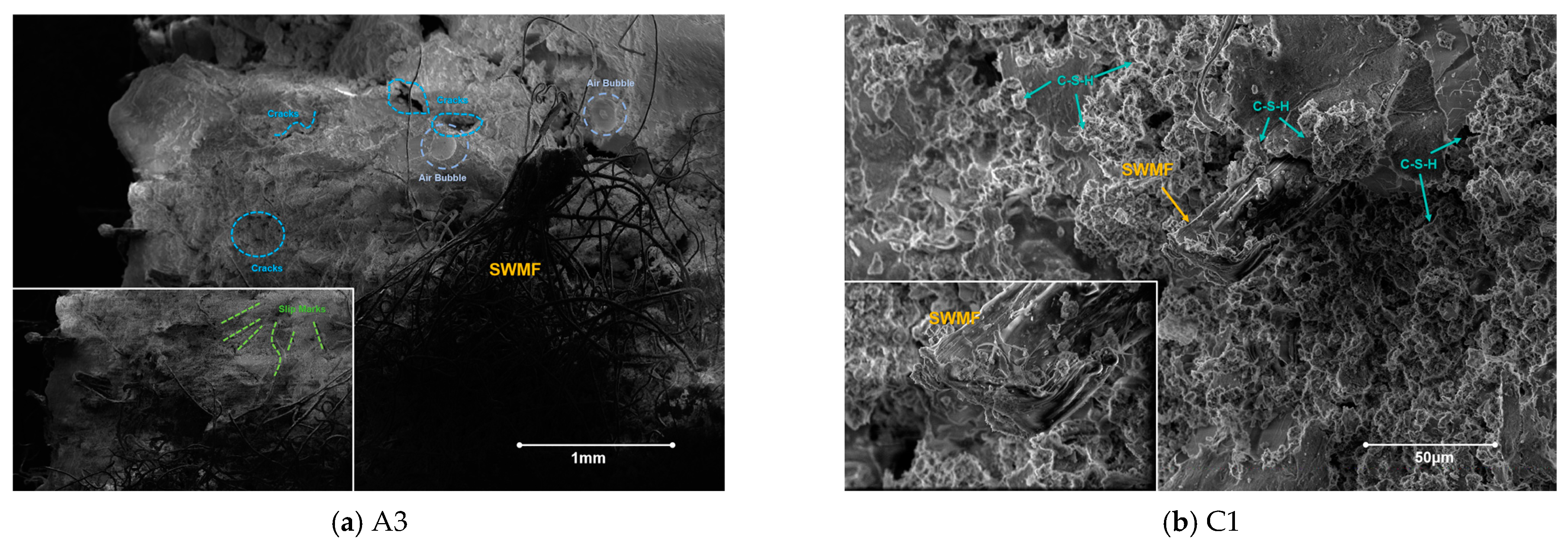
3.3. Microscopic Material and Morphology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, X.-P.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Xu, A.; Fu, X.-L.; Che, C.; Tian, Z.-J.; Bi, Y.-Z. Recycle of discarded masks in civil engineering: Current status and future opportunities with silane coupling agent modified discarded masks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 405, 133266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World-Health-Organization. Advice on the Use of Masks in the Context of COVID-19: Interim Guidance; World-Health-Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ueki, H.; Furusawa, Y.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Imai, M.; Kabata, H.; Nishimura, H.; Kawaoka, Y. Effectiveness of face masks in preventing airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2. mSphere 2020, 5, e00637-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royo-Bordonada, M.A.; García-López, F.J.; Cortés, F.; Zaragoza, G.A. Face masks in the general healthy population. Scientific and ethical issues. Gac. Sanit. 2021, 35, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rab, S.; Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Vaishya, R. Face masks are new normal after COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 1617–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arizton. Face Mask Market—Global Outlook & Forecast 2021–2026. 2022. Available online: https://www.reportlinker.com/p05934703/Face–Mask–Market–Global–Outlook–and–Forecast.html?utm source=GNW (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Prata, J.C.; Silva, A.L.P.; Walker, T.R.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. COVID-19 Pandemic repercussions on the use and management of plastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7760–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeev, P.; Ramesh, A.; Navaratnam, S.; Sanjayan, J. Using fibre recovered from face mask waste to improve printability in 3D concrete printing. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 139, 105047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, D. Mechanical behavior of self-compacting recycled concrete reinforced with recycled disposable medical mask fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 429, 136314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadare, O.O.; Okoffo, E.D. COVID-19 face masks: A potential source of microplastic fibers in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammendolia, J.; Saturno, J.; Brooks, A.L.; Jacobs, S.; Jambeck, J.R. An emerging source of plastic pollution: Environmental presence of plastic personal protective equipment (PPE) debris related to COVID-19 in a metropolitan city. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmartin-Lynch, S.; Saberian, M.; Li, J.; Roychand, R.; Zhang, G. Preliminary evaluation of the feasibility of using polypropylene fibres from COVID-19 single-use face masks to improve the mechanical properties of concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zand, A.D.; Heir, A.V. Emerging challenges in urban waste management in Tehran, Iran during the COVID-19 pandemic. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 162, 105051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zentar, R.; Wang, D.; Dong, L.; Sun, D. Recycling single use surgical face mask waste for reinforcing cement-treated/untreated dredged marine sediments: Strength, deformation and micro-mechanisms analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, H.; Chowdhury, T.; Sait, S.M. Estimating marine plastic pollution from COVID-19 face masks in coastal regions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuah, E.E.Y.; Agyemang, E.P.; Dankwa, P.; Fei-Baffoe, B.; Kazapoe, R.W.; Douti, N.B. Are used face masks handled as infectious waste? Novel pollution driven by the COVID-19 pandemic. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2022, 13, 200062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, M.M.; Inoue, T.; Septiariva, I.Y.; Suryawan, I.W.K.; Kato, S.; Harryes, R.K.; Yokota, K.; Notodarmojo, S.; Suhardono, S.; Ramadan, B.S. Identification of face mask waste generation and processing in tourist areas with thermo-chemical process. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2023, 48, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Luo, X.; Hai, Y.; Yu, C. Experimental investigation of face mask fiber-reinforced fully recycled coarse aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 447, 138141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ting, Z.; You, Z.; Kim, H.; Shah, K.J. Uncontrolled disposal of used masks resulting in release of microplastics and co-pollutants into environment. Water 2022, 14, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoniem, A.G.; Nour, L.A.; Zeleňáková, M.; Dolníková, E.; Katunský, D.; El-Feky, M.H. Axial compressive and cyclic lateral behavior of a structural masonry prism constructed from crushed COVID-19 face masks concrete bricks. Eng. Rep. 2024, 6, e12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xin, C.; Sun, Y.; Di, J.; Meng, F.; Zhou, X. Experimental study on the mechanical properties of disposable mask waste–reinforced gangue concrete. Materials 2024, 17, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, D.; Xu, X.; Yuan, Y. Pyrolysis characteristics, kinetics, thermodynamics and volatile products of waste medical surgical mask rope by thermogravimetry and online thermogravimetry-Fourier transform infrared-mass spectrometry analysis. Fuel 2021, 295, 120632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koniorczyk, M.; Bednarska, D.; Masek, A.; Cichosz, S. Performance of concrete containing recycled masks used for personal protection during coronavirus pandemic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberian, M.; Li, J.; Kilmartin-Lynch, S.; Boroujeni, M. Repurposing of COVID-19 single-use face masks for pavements base/subbase. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajam, L.; Trabelsi, A.; Kammoun, Z. Valorisation of face mask waste in mortar. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2022, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tan, C.; Xu, W.; Zhang, T.; Xiong, B.; Wang, S.; Du, D. Mechanical properties and constitutive relation of recycled aggregate concrete reinforced with face mask fibre and basalt fibre under uniaxial cyclic compression. Structures 2024, 69, 107364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Akbar, A.; Mohamed, A.M.; Fathi, D.; Saeed, F. Recycling of waste facial masks as a construction material, A step towards sustainability. Materials 2022, 15, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Opulencia, M.J.C.; Chandra, T.; Chandra, S.; Muda, I.; Dias, R.; Chetthamrongchai, P.; Jalil, A.T. An environmentally friendly solution for waste facial masks recycled in construction materials. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrshoudi, F.; Mohammadhosseini, H.; Tahir, M.M.; Alyousef, R.; Alghamdi, H.; Alharbi, Y.R.; Alsaif, A. Sustainable use of waste polypropylene fibers and palm oil fuel ash in the production of novel prepacked aggregate fiber-reinforced concrete. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 175-2007; General Purpose Portland Cement. Chinese National Standard: Beijing, China, 1999.
- JGJ 63-2006; Standard of Water for Concrete. Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Jin, H.; Liu, W.; Tang, L. Investigation of using limestone calcined clay cement (LC3) in engineered cementitious composites: The effect of propylene fibers and the curing system. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 2117–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17671-1999; Method of Testing Cements-Determination of Strength (ISO Method). Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1999. (In Chinese)
- ASTM C 1018-97; Structural Test Method for Flexural Toughness and First Crack Strength of Fiber Reinforced Concrete (Using Beam with Third Point Loading). American Society of Testing and Materials (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1998.
- Kim, D.J.; Naaman, A.E.; El-Tawil, S. Comparative flexural behavior of four fiber reinforced cementitious composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Swalqah, R.A.; Al-Kheetan, M.J.; Jweihan, Y.S.; Al-Hamaiedeh, H. Synergistic effect of treated polypropylene-based disposable face masks on durability and mechanical properties of concrete. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 13221–13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, A.; Farooq, F.; Shafique, M.; Aslam, F.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H. Sugarcane bagasse ash-based engineered geopolymer mortar incorporating propylene fibers. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 33, 101492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, T.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, S.; Tan, J.; Liu, Z.; Su, J. The influence of fiber type and length on the cracking resistance, durability and pore structure of face slab concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 282, 122706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Cao, M.; Khan, M.; Yin, H.; Guan, J. Review on different testing methods and factors affecting fracture properties of fiber reinforced cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, A.; Kodur, V.K.R.; Liew, K.M. Microstructural changes and mechanical performance of cement composites reinforced with recycled carbon fibers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 121, 104069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, R.; Baskir, G.; Camp, J.; Camp, J.; Capka, R.; Curtis, S.; Davids, G.; Frevert, L.; Hatch, H.; Herrmann, A.; et al. Report Card for America’s Infrastructure; The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, V.C.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Ogawa, A.; Saito, T. Interface tailoring for strain-hardening polyvinyl alcohol-engineered cementitious composite (PVA-ECC). ACI Mater. J. 2002, 99, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, J.-P.; Bai, Y.-L. Linkage of multi-scale performances of nano-CaCO3 modified ultra-high performance engineered cementitious composites (UHP-ECC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
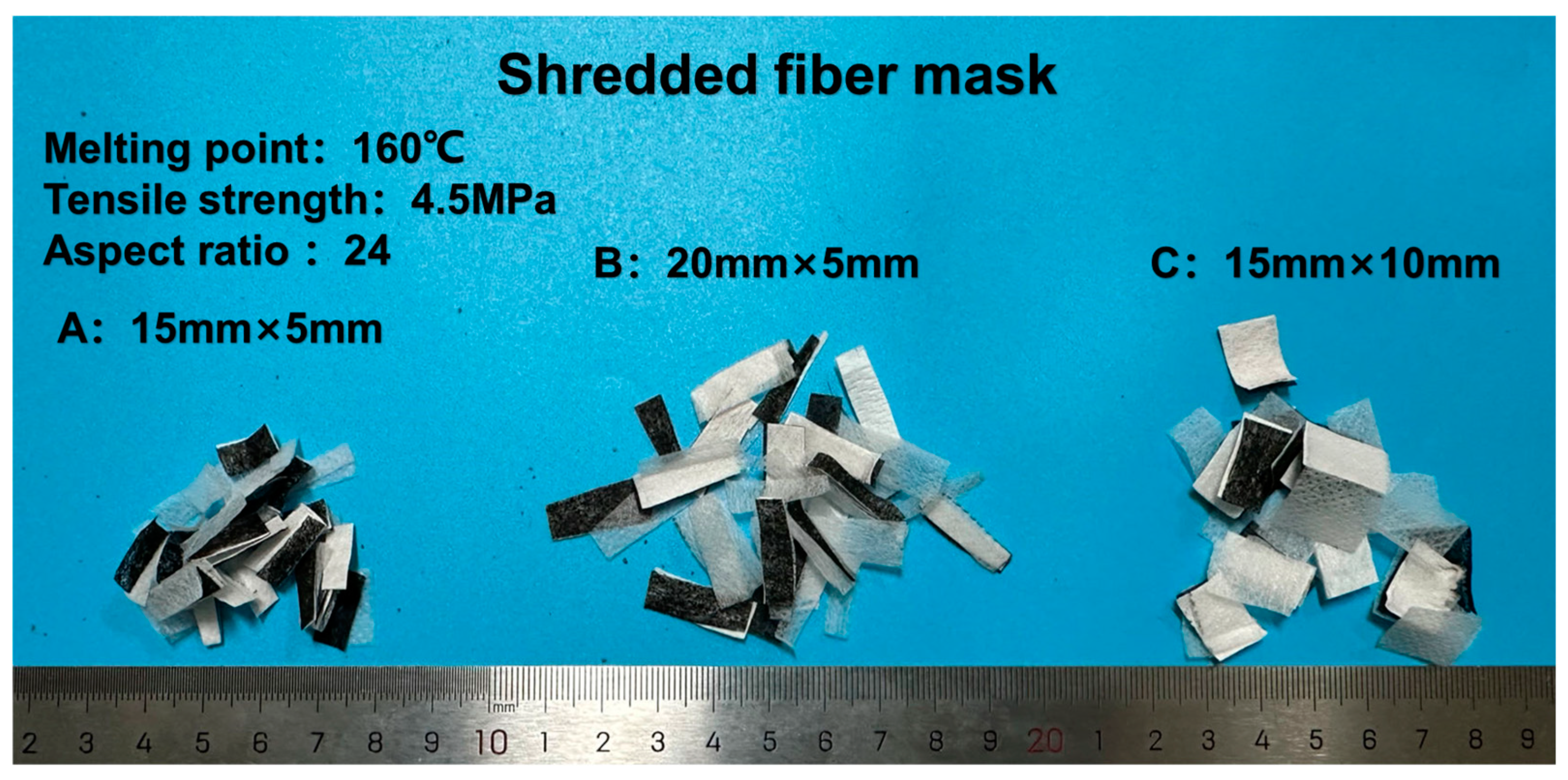




| % | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | K2O | Fe2O3 | MgO | SO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | 20.31 | 5.62 | 61.78 | 1.55 | 3.54 | 2.11 | 2.47 |
| Mixture No. | w/b | Cement | SWMF (Vol%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 0.4 | 1 | 0 | |
| A | A-1 | 0.4 | 1 | 1 |
| A-2 | 0.4 | 1 | 2 | |
| A-3 | 0.4 | 1 | 3 | |
| B | B-1 | 0.4 | 1 | 1 |
| B-2 | 0.4 | 1 | 2 | |
| B-3 | 0.4 | 1 | 3 | |
| C | C-1 | 0.4 | 1 | 1 |
| C-2 | 0.4 | 1 | 2 | |
| C-3 | 0.4 | 1 | 3 |
| Unit | CG | A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | C1 | C2 | C3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOP | PLOP | kN | 52.66 | 26.05 | 20.24 | 16.68 | 28.30 | 19.82 | 15.75 | 21.43 | 23.72 | 13.83 |
| σLOP | MPa | 32.91 | 16.28 | 12.65 | 10.42 | 17.69 | 12.39 | 9.84 | 13.16 | 14.82 | 8.64 | |
| εLOP | % | 1.52 | 0.96 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 1.10 | 1.02 | 0.77 | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.74 | |
| TLOP | MPa | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.03 | |
| MOR | PMOR | kN | 57.85 | 31.05 | 24.01 | 19.29 | 33.10 | 22.60 | 18.01 | 23.56 | 26.01 | 15.77 |
| σMOR | MPa | 36.15 | 19.4 | 15.00 | 12.06 | 20.69 | 14.13 | 11.25 | 14.73 | 16.26 | 9.86 | |
| εMOR | % | 1.83 | 1.35 | 1.24 | 1.18 | 1.56 | 1.47 | 1.09 | 1.27 | 1.21 | 0.99 | |
| TMOR | MPa | 0.36 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.05 | |
| d3 | Td3 | MPa | 0.66 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.10 |
| d5 | Td5 | MPa | 0.77 | 0.41 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 0.49 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.16 |
| d10 | Td10 | MPa | 0.84 | 0.68 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.76 | 0.59 | 0.37 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.30 |
| Parameters | Unit | CG | A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | C1 | C2 | C3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOP | PLOP | kN | 3.3 | 2.8 | 2.43 | 1.99 | 2.86 | 2.53 | 1.86 | 2.38 | 2.77 | 1.76 |
| fLOP | MPa | 7.51 | 6.35 | 5.44 | 4.51 | 6.95 | 5.92 | 4.2 | 5.83 | 6.49 | 4.41 | |
| δLOP | mm | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.35 | 0.22 | 0.2 | |
| TLOP | N·m | 0.44 | 0.39 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.36 | 0.3 | 0.19 | |
| d3 | Td3 | N·m | 0.44 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.66 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.71 | 0.55 | 0.39 |
| d5 | Td5 | N·m | 0.44 | 0.62 | 0.74 | 0.98 | 0.58 | 0.64 | 0.71 | 0.98 | 0.77 | 0.51 |
| d10 | Td10 | N·m | 0.44 | 0.86 | 1.15 | 1.63 | 0.77 | 0.97 | 1.29 | 1.60 | 1.27 | 0.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Wan, M.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J. Research on Recycling and Utilization of Shredded Waste Mask Fibers to Prepare Sustainable Engineered Cementitious Composites. Buildings 2025, 15, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030402
Li Y, Yan X, Wan M, Zhou J, Liu J. Research on Recycling and Utilization of Shredded Waste Mask Fibers to Prepare Sustainable Engineered Cementitious Composites. Buildings. 2025; 15(3):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030402
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yue, Xinyu Yan, Man Wan, Junyi Zhou, and Jun Liu. 2025. "Research on Recycling and Utilization of Shredded Waste Mask Fibers to Prepare Sustainable Engineered Cementitious Composites" Buildings 15, no. 3: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030402
APA StyleLi, Y., Yan, X., Wan, M., Zhou, J., & Liu, J. (2025). Research on Recycling and Utilization of Shredded Waste Mask Fibers to Prepare Sustainable Engineered Cementitious Composites. Buildings, 15(3), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030402






