A Parametric Method for Remapping and Calibrating Fisheye Images for Glare Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Generating and Calibrating HDR Images for Glare Analysis
2.2. Imaging Projection Distortion in HDR Images
3. Methodology
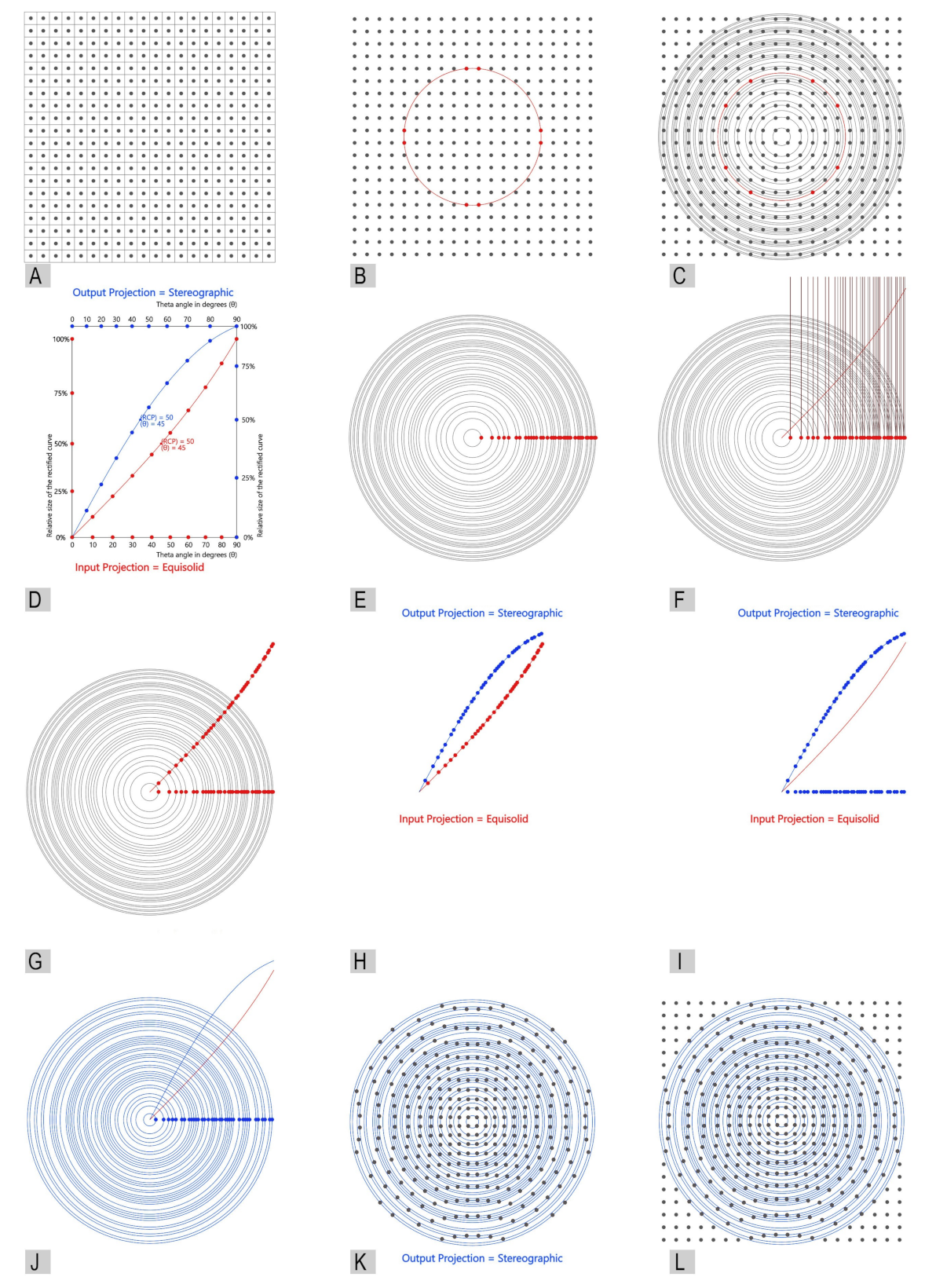
3.1. Phase 1: A New Method for Defining and Remapping Fisheye Projections
3.1.1. Defining Fisheye Projections (Rectified Curve)
3.1.2. New Method for Remapping Fisheye Projections
3.1.3. Developing Fisheye Remapping Tool
3.2. Phase 2: Application of the New Remapping Method for Physical Fisheye Lens
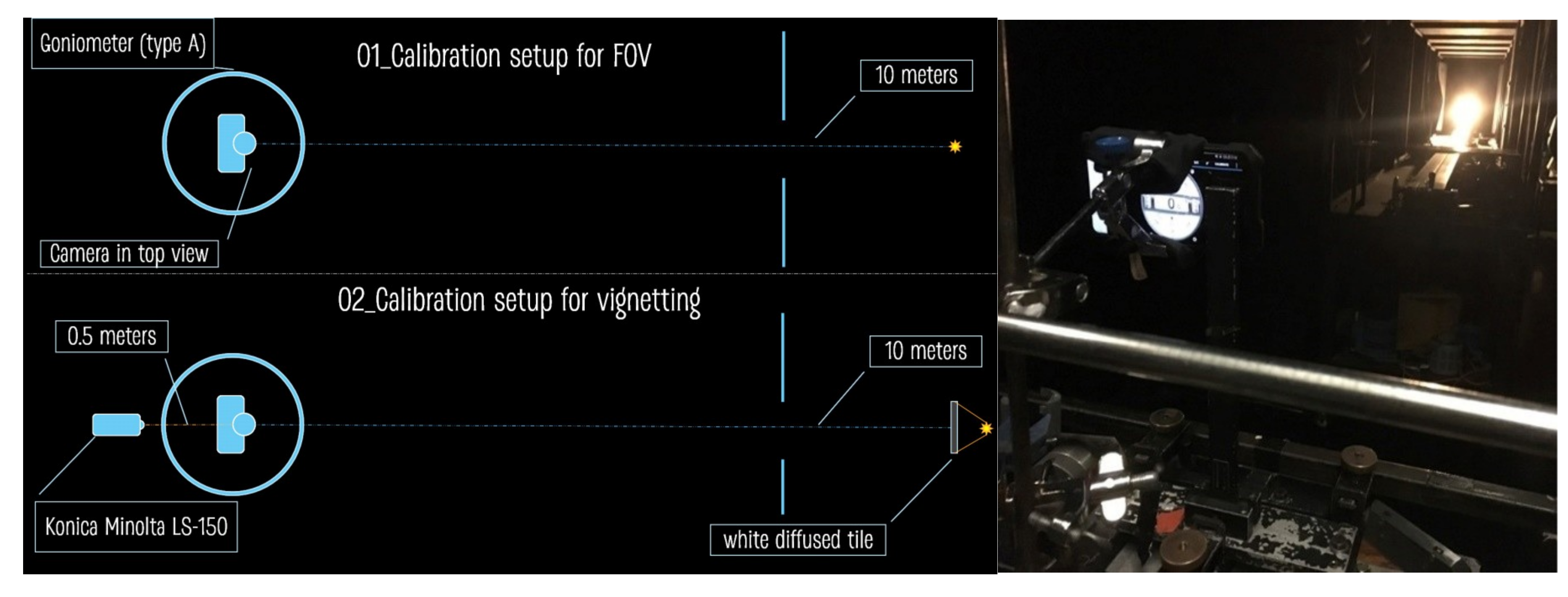
3.2.1. Laboratory Measurements
3.2.2. Image Processing Procedure
3.2.3. Glare Analysis
3.3. Phase 3: Validation
3.3.1. First Validation Test: Pixel Remapping
3.3.2. Second Validation Test: Color Distortion
4. Discussion and Limitations
- (1)
- The maximum luminance reading that can be captured with the device due to hardware limitation, and
- (2)
- The limitation of taking the same field of view in both devices; since we had 10 cm gap between them, each device had a slightly different FOV. In some cases, the main glare source was shaded in one of the two captured images, as shown in Figure 20, which caused random errors.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tzempelikos, A. Advances on daylighting and visual comfort research. Build. Environ. 2017, 100, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, A. High dynamic range imaging and its application in building research. Adv. Build. Energy Res. 2007, 1, 177–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, A.; Wilson, M. Determining lens vignetting with HDR techniques. In Proceedings of the XII National Conference on Lighting, Varna, Bulgaria, 10–12 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hirning, M.B.; Isoardi, G.L.; Cowling, I. Discomfort glare in open plan green buildings. Energy Build. 2014, 70, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirning, M.B.; Isoardi, G.L.; Coyne, S.; Garcia Hansen, V.R.; Cowling, I. Post occupancy evaluations relating to discomfort glare: A study of green buildings in Brisbane. Build. Environ. 2013, 59, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konis, K.; Lee, E.S.; Clear, R.D. Visual comfort analysis of innovative interior and exterior shading systems for commercial buildings using high. resolution luminance images. Leukos 2011, 7, 167–188. [Google Scholar]
- Borisuit, A.; Scartezzini, J.-L.; Thanachareonkit, A. Visual discomfort and glare rating assessment of integrated daylighting and electric lighting systems using HDR imaging techniques. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2010, 53, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnia, K.A.; Azizah, D.N.; Mangkuto, R.A.; Atmodipoero, R.T. Visual comfort assessment using high. dynamic range images under daylight condition in the Main Library Building of Institut Teknologi Bandung. Procedia Eng. 2017, 170, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienold, J.; Christoffersen, J. Evaluation methods and development of a new glare prediction model for daylight environments with the use of CCD cameras. Energy Build. 2006, 38, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzal, A.A.; Chutarat, A. A new daylight glare evaluation method. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2001, 44, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirning, M.B.; Isoardi, G.L.; Garcia-Hansen, V.R. Prediction of discomfort glare from windows under tropical skies. Build. Environ. 2017, 113, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsunaga, T.; Nayar, S.K. Radiometric self calibration. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Cat. No PR00149), Fort Collins, CO, USA, 23–25 June 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Cauwerts, C.; Bodart, M.; Deneyer, A. Comparison of the vignetting effects of two identical fisheye lenses. Leukos 2012, 8, 181–203. [Google Scholar]
- Inanici, M. Evaluation of high dynamic range photography as a luminance data acquisition system. Lighting Res. Technol. 2006, 38, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, D.B. Vignette and Exposure Calibration and Compensation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 2276–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Hansen, V.R.; Cowley, M.; Smith, S.S.; Isoardi, G. Testing the accuracy of luminance maps acquired by smart phone cameras. In Proceedings of the CIE Centenary Conference “Towards a New Century of Light”; Commission Internationale l’Eclairage: Paris, France, 2013; pp. 951–955. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, C. Comparison and calibration of mobile phone fisheye lens and regular fisheye lens via equidistant model. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 9379203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debevec, P.E.; Malik, J. Recovering high dynamic range radiance maps from photographs. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 Classes; ACM: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2008; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, M.A.; Borman, S.; Stevenson, R.L. Dynamic range improvement through multiple exposures. In Proceedings of the 1999 International Conference on Image Processing (Cat. 99CH36348), Kobe, Japan, 24–28 October 1999; pp. 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Kannala, J.; Brandt, S.S. A generic camera model and calibration method for conventional, wide-angle, and fish-eye lenses. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dersch, H. Panorama Tools—Open Source Software for Immersive Imaging. 2007. Available online: https://webuser.hs-furtwangen.de/~dersch/IVRPA.pdf (accessed on 30 Septemper 2019).
- Bettonvil, F. Fisheye lenses. WGN J. Int. Meteor Organ. 2005, 33, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, W.T.; Jones, T.R.; Pasztor, E.C. Example-based super-resolution. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2002, 22, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, K.S.; Nguyen, T.Q. An Adaptable-k Nearest Neighbors Algorithm for MMSE Image Interpolation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten, D. Grasshopper-Algorithmic Modeling for Rhino Software Version 0.9077. 2014. Available online: http://www.grasshopper3d.com (accessed on 5 September 2014).
- Sherif, A.; Sabry, H.; Wagdy, A.; Mashaly, I.; Arafa, R. Shaping the slats of hospital patient room window blinds for daylighting and external view under desert clear skies. Solar Energy 2016, 133, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagdy, A.; Fathy, F.; Altomonte, S. Evaluating the daylighting performance of dynamic façades by using new annual climate-based metrics. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Passive and Low Energy Architecture; PLEA 2016: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 941–947. [Google Scholar]
- Wagdy, A.; Garcia-Hansen, V.; Isoardi, G.; Allan, A.C. Multi-region contrast method–A new framework for post-processing HDRI luminance information for visual discomfort analysis. In Proceedings of the PLEA 2017: Design to Thrive, Edinburgh, Scotland, 3–5 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wagdy, A.; Sherif, A.; Sabry, H.; Arafa, R.; Mashaly, I. Daylighting simulation for the configuration of external sun-breakers on south oriented windows of hospital patient rooms under a clear desert sky. Solar Energy 2017, 149, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, K.; Wagdy, A.; Isoardi, G.; Allan, A.C.; Garcia-Hansen, V. A methodology to simulate annual blind use in large open plan offices. In Proceedings of the Building Simulation 2019: 16th Conference of IBPSA, Rome, Italy, 2–4 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wagdy, A. New Parametric workflow based on validated day-lighting simulation. Build. Simul. Cairo 2013, 2013, 412–420. [Google Scholar]
- Inanici, M. Evalution of High Dynamic Range Image-Based Sky Models in Lighting Simulation. Leukos 2010, 7, 69–84. [Google Scholar]
- Jakubiec, J.A.; Van Den Wymelenberg, K.; Inanici, M.; Mahic, A. Improving the accuracy of measurements in daylit interior scenes using high dynamic range photography. In Proceedings of the Passive and Low Energy Architecture (PLEA) 2016 Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 11–13 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jakubiec, J.A.; Van Den Wymelenberg, K.; Inanici, M.; Mahic, A. Accurate measurement of daylit interior scenes using high dynamic range photography. In Proceedings of the CIE 2016 Lighting Quality and Energy Efficiency Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 3–5 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pierson, C.; Wienold, J.; Bodart, M. Daylight Discomfort Glare Evaluation with Evalglare: Influence of Parameters and Methods on the Accuracy of Discomfort Glare Prediction. Buildings 2018, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, G.J. The RADIANCE lighting simulation and rendering system. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 459–472. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



















| Camera Settings | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure Time (Shutter Speed) Phone | ||||||||||||||||
| 1/24,000 | 1/16,000 | 1/8000 | 1/4000 | 1/2000 | 1/1000 | 1/500 | 1/250 | 1/125 | 1/60 | 1/30 | 1/15 | 1/8 | 1/4 | 1/2 | 1 | |
| Exposure Time (Shutter Speed) DSLR | ||||||||||||||||
| 1/8000 | 1/2000 | 1/500 | 1/125 | 1/30 | 1/8 | 1/2 | 2 | 8 | ||||||||
| ISO Phone | 64 | |||||||||||||||
| ISO DSLR | 400 | |||||||||||||||
| White balance: | daylight | |||||||||||||||
| Image quality: | *.jpg (max) | |||||||||||||||
| Color space: | sRGB | |||||||||||||||
| Focus: | infinity (auto is off) | |||||||||||||||
| Picture style: | standard | |||||||||||||||
| Theta Angle (θ) | Luminance of Diffusing Filter | Loss Percentage | Calibration Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 155 | 18.95% | 1.23 |
| 10 | 165 | 13.73% | 1.16 |
| 20 | 155.16 | 18.87% | 1.23 |
| 30 | 171.14 | 10.52% | 1.12 |
| 40 | 173.2 | 9.44% | 1.10 |
| 50 | 153.96 | 19.50% | 1.24 |
| 60 | 142.99 | 25.23% | 1.34 |
| 70 | 127.31 | 33.43% | 1.50 |
| 80 | 110.85 | 42.04% | 1.73 |
| 90 | 51.2 | 73.23% | 3.74 |
| Index | Max | Min | Average | Index | Max | Min | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGP | 20% | −54% | 9% | Lveil | 61% | −484% | 61% |
| Av_lum | 7% | −69% | 13% | Lveil_cie | 89% | −483% | 58% |
| E_v | 8% | −30% | 7% | DGR | 39% | −124% | 17% |
| DGI | 13% | −4609% | 167% | UGP | 19% | −284% | 19% |
| UGR | 19% | −282% | 19% | UGR_exp | 413% | −1547% | 70% |
| VCP | 56% | −128% | 14% | DGI_mod | 15% | −234% | 16% |
| CGI | 20% | −122% | 11% | Av_lum_pos | 3% | −34% | 7% |
| Lum_sources | 10% | −94% | 14% | Av_lum_pos2 | 2% | −26% | 5% |
| Omega_sources | 25% | −217% | 32% | Med_lum | −12% | −54% | 6% |
| Lum_backg | 18% | −31% | 8% | Med_lum_pos | 1% | −50% | 7% |
| E_v_dir | 26% | −444% | 60% | Med_lum_pos2: | −6% | −47% | 6% |
| luminance, Illuminance and Glare Metrics | Correlation | Sig. (2-Tailed) |
|---|---|---|
| DGP | 0.887 | p < 0.001 |
| Av_lum | 0.927 | p < 0.001 |
| E_v | 0.981 | p < 0.001 |
| Lum_backg | 0.861 | p < 0.001 |
| E_v_dir | 0.979 | p < 0.001 |
| DGI | 0.914 | p < 0.001 |
| UGR | 0.886 | p < 0.001 |
| VCP | 0.821 | p < 0.001 |
| CGI | 0.878 | p < 0.001 |
| Lum_sources | 0.564 | p < 0.001 |
| Omega_sources | 0.951 | p < 0.001 |
| Lveil | 0.973 | p < 0.001 |
| Lveil_cie | 0.929 | p < 0.001 |
| DGR | 0.768 | p < 0.001 |
| UGP | 0.886 | p < 0.001 |
| UGR_exp | 0.975 | p < 0.001 |
| DGI_mod | 0.911 | p < 0.001 |
| Av_lum_pos | 0.992 | p < 0.001 |
| Av_lum_pos2 | 0.993 | p < 0.001 |
| Med_lum | 0.972 | p < 0.001 |
| Med_lum_pos | 0.949 | p < 0.001 |
| Med_lum_pos2 | 0.957 | p < 0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wagdy, A.; Garcia-Hansen, V.; Isoardi, G.; Pham, K. A Parametric Method for Remapping and Calibrating Fisheye Images for Glare Analysis. Buildings 2019, 9, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings9100219
Wagdy A, Garcia-Hansen V, Isoardi G, Pham K. A Parametric Method for Remapping and Calibrating Fisheye Images for Glare Analysis. Buildings. 2019; 9(10):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings9100219
Chicago/Turabian StyleWagdy, Ayman, Veronica Garcia-Hansen, Gillian Isoardi, and Kieu Pham. 2019. "A Parametric Method for Remapping and Calibrating Fisheye Images for Glare Analysis" Buildings 9, no. 10: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings9100219
APA StyleWagdy, A., Garcia-Hansen, V., Isoardi, G., & Pham, K. (2019). A Parametric Method for Remapping and Calibrating Fisheye Images for Glare Analysis. Buildings, 9(10), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings9100219






