Abstract
In this position paper, we present the results of an ongoing theoretical investigation into the phenomenon of interactive architecture. Interaction in architecture deals with the meaningful exchange of information and physical acts between building and person. This goes beyond responsive systems like automated doors, shading systems, and so on. Most examples of interactive architecture are technological explorations that probe possibilities and the potential for interaction. In this paper we claim that this is not enough. The notion of interactive architecture is explored through social aspects, user experience, situatedness, and agent-based theory. From this we argue that interactive buildings need comprehensive and consistent styles of interaction rather than a series of isolated and unrelated interaction events. Different people in various contexts require different sets of behavior from an interactive building. These sets are conceptualized as interaction narratives, following the work of Maria Lehman. We argue that such narratives can provide a better fit of the interactive building with the user, and lead to a more profound understanding of such systems.
1. Introduction
Buildings rarely are conceived from the very first step of their design as things that must change a lot. This is a rather strange contradiction with the long time-span that buildings fulfill their function. During this lifetime changes occur along various time scales—the inhabitants will change, usually in cycles of decades; the needs of the inhabitants change in cycles of years; their activities and ways of using the building change per season; they have their weekly and daily rhythms, and during the day many different things happen inside the building. This applies to all types of buildings, domestic, work, industry, entertainment, and so on. Usually buildings are conceived as more or less unchanging containers in which these dynamics take place, without the need of changing the building in a drastic way. Changing buildings is costly, takes much time, and labor; therefore, physically changing buildings is avoided rather than embraced. Conventional design methods are ill-equipped to take changes described above into account, nor are there methods able to deliver building designs that appropriately incorporate such changes. Some attempts have been undertaken to deal with change, mainly through conventional means—like division of the building into parts with various time-spans or assigning a mandate for change to different parties who have a stake in the building [1].
In this paper, we are concerned with advanced technologies that make buildings much more dynamic than the traditional notion of buildings outlined above. Our perspective comes from the architect. We aim to develop a framework in which interaction is an integrated part when conceiving building designs. Thus, we are less concerned with the technical realization of interactive systems than the question, what are interactive buildings, and how are they designed. The notion of interactive buildings, which attributes much more dynamics to the building itself, has its roots in the work of Cedric Price (1935–2003) and Gordon Pask (1928–1996). The Interaction Centre, Kentish Town, by architect Cedric Price, realized in 1971, was one of the first contemporary examples of kinetic and flexible architecture. It was a more modest version of his earlier vision of the Fun Palace (together with Joan Littlewood in 1961), an unrealized educational structure, which could be changed according to the desires of the visitors [2] (pp. 60). Already in 1969, Gordon Pask argued that architects design systems, rather than buildings, and should therefore consult cybernetics to design such buildings [3].
Advances in contemporary technology bring the notion of interactive architecture to a completely new level. It has become indeed possible to create building components that can move, change shape, or do other things that make buildings much more flexible and adaptable in easy ways. This means that the design of buildings shifts from the design of a more or less passive envelope and space program, to the question for the building, “what should I do next?” This question, and the answer to this question, is beyond contemporary architectural (design) theory. However, Pask’s suggestion 50 years ago can now be reframed in the contemporary theory of agent-based systems [4], a concept that originates from artificial intelligence. According to Russell and Norvig [5], agents are components that can sense the world they are in, and affect change in that world, based on their autonomous reasoning. They define the so-called “ideal rational agent” as one that: “For each possible percept sequence, do whatever action is expected to maximize performance measure, on the basis of evidence provided by the percept sequence and built-in knowledge of the agent” (Ibid., page 23). This definition, however abstract, included important clues for the design of interactive buildings:
- Percept sequence: the sequence of events that is registered by the agent, in our case, the building. The implication is twofold; first, interactive buildings need to sense a relevant range of things happening in and around the building, and second, these series of events form a sequence that through a consistent interpretation can lead to meaningful inferences to what is happening.
- Action: anything that the agent may change in the world. The implication is that interactive buildings are not passive receivers of events, but actors by themselves.
- Maximize performance: the vector of quantifiable variables that sets the value of how well the agent is doing. For a rational agent, the choice what to do next is determined by which way a better value of the performance can be obtained. The extension of this concept to interactive buildings challenges the question what performance is. Since buildings have an impact not only on technical and environmental aspects, but also social, aesthetic, and psychological, the equation becomes much more complex and should also include qualitative aspects.
- Built-in knowledge: the knowledge that is necessary to assess the meaning of the percept sequence with respect to the performance criteria. Not all percepts that an agent receives are important to the current performance, and thus should not have an impact on the decision of what to do next. For this assessment, knowledge is necessary. The implication for interactive buildings, to a certain extent, is a model of self and should be maintained.
For the outset of this discussion, we pose that agent-based theory is well-suited to describe interactive buildings. Thus, the architectural discourse should include research and understanding of computer science, interaction design, and cognitive science. In this paper, we provide a concise critical reading of such sources. We claim that interaction narratives form an approach to unify such concepts in an architectural and productive way.
2. Interaction in Architecture until Contemporary Disruption
Since the late 1980s technologies have developed that make it possible to dynamically change building (components). Examples of such technologies are media facades, kinetic structures, ambient environments, smart homes, and so on. Early experimentation made use of these technologies in short loops, meaning a sensor set; a controller deciding on some action based on the sensor information and an actuator or device that displays or acts in some way. Media facades are the oldest examples of such systems (e.g., Zeitgallery by Christian Möller in Frankfurt, 1992 [6] (pp. 95). In this paper, there is not enough space to elaborate on the historical development of such systems. We can note however, that today the technological loops become more extended and complex with technologies such as Internet of Things, wearables, and cloud computing [7]. These technologies tend to converge, greatly expanding the potential of interactive architecture [8]. It means that it has become easier for dynamic building components to be aware of the environment, to be much more linked to extensive sensor networks and the Internet, and to better anticipate (multiple) user needs. The complexity of communication chains between many such components has led some researchers to call these systems ecosystems [9]. As the name ecosystem suggests, we are dealing with highly interconnected systems that need to be approached in a more organic way.
3. The Case for Interaction
Many interactive systems have been developed already, mostly as installations, art pieces, or additions to spaces. Much of this work is informed by technological opportunity and experimentation. Yet, a comprehensive approach to understand from an interaction perspective is largely missing. The most notable exceptions from the architectural point of view are Michael Fox [10], who has created several interactive buildings in the past two decades, and Robert Kronenburg [2], who investigates the fundamental aspect of change in architecture.
There is rising awareness from the field of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) towards the field of architecture (most strongly defended by Malcolm McCullough’s book Digital Ground [11]), but the two fields are still much apart [12,13,14]. Given the recent nature of the phenomenon of interactive architecture, there is no conclusive evidence yet that unambiguously states the (dis)advantages of interactive architecture. Some experimental work does provide us with clues about this, however. Schnädelbach and his team built a bio-feedback based interactive prototype, called ExoBuilding [15], and conducted several experiments while measuring physiological responses from users. They noted a positive effect on the users in physiological sense, while on the other hand most users found the explicit bio-feedback disturbing and unpleasant. Coyle et al. noted several systems for mental health interventions that have positive effects on people, for example online treatments, mobile support, therapeutic computer games, virtual and augmented reality exposure therapies, relational agents, and robotic companions [16]. Wouters et al. (2016) analyzed in more detail the spatial and social aspects dealing with successful engagement of people with an interactive installation [17]. They identified encounters, triggers, and activation loops as important mechanisms in establishing and sustaining interaction.
4. Limitation of Contemporary Interactive Systems
There are many terms used in the literature to describe various kinds of interactive systems for buildings. In fact, there is a confusing amount of terms, many of which are not clearly defined, overlapping, or similar in meaning. From passive buildings to interactive buildings we can see a gradient development of dynamic, responsive, and interactive buildings. From each step, dynamic to responsive to interactive, the building has an increasing amount of user involvement in the changes that occur in the building (Figure 1).
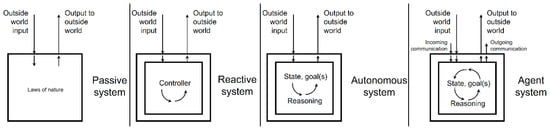
Figure 1.
Increasing degrees of interaction in buildings.
In Figure 1 the box indicates the system; ingoing arrows are percepts and communications from the outside world; outgoing arrows are actions and communications to the outside world. Difference between systems can be described by their internal state and input, output types. Passive systems arguably are not interactive at all; they are included to define the extreme end of the spectrum between non-interactive buildings and interactive buildings. Passive systems are mechanistically defined agents which respond to inputs from the outside world in predetermined ways. Reactive systems employ a simple controller system similar to “if X then Y” production systems. Autonomous systems record their own state and have a set of goals that they want to achieve. They use reasoning algorithms to select actions that minimize the distance between goal and current state. Agent systems can receive and send communications to other agents. Their reasoning algorithms are more complex and may also include utility-based prediction models that allow the agent to compare various future action sequences before actually deciding on the action it will perform in the outside world.
In research literature, we can find many different terms for responsive building, with each having a specific and different meanings. These terms are: Building Automation Systems, Smart Homes, sentient buildings, adaptive buildings, dynamic buildings, kinetic architecture, intelligent buildings, and portable buildings. In our research, we are particularly concerned with interactive buildings. The term interaction is often used to indicate anything that responds in some way to a kind of input. This very broad interpretation renders the term interaction quite meaningless and might as well indicate simple reactive systems such as automatic sliding doors. For this reason, we want to limit the use of the term interactive buildings only to such buildings that support a meaningful exchange of information between the user and the building, and the exchange influences changes in both the user and the building. Such levels of interaction today are not yet realized as buildings to the best of our knowledge, but mostly as installations or art pieces. Yet, we believe that the step towards such kinds of buildings is not far away in the future. Thus, we would do well to prepare a critical theoretical foundation for the design of such systems, which informs architects for the design of such buildings.
4.1. Social Aspects of Interactive Systems
A lot of research has been done on smart homes and intelligent environments with the major focus of this work on energetically optimal and sustainable well-performing buildings [18]. Surely sustainability is very important but there are strong clues that there are many more factors at play that would promote other behavior orientation than only energy performance. Walldén and Mäkinen [19] note that acceptance of smart environments depends not only on usefulness, but also on ease of use and trust, social influence, as well as on societal level cultural, economic, and legal factors. When we engage in an interactive exchange between user and system, the interaction takes on a deeper meaning than just pressing buttons. People will attribute personality traits to the system, so the system will be increasingly perceived as a social thing. In this sense, Tay et al. [20] observed that concerning social robot acceptance, attributed characters such as occupational role, gender, and personality of the robot play an important role. Partala and Saari [21] conclude that successful technology adoption depend on emotional design as much as functionality and usefulness. How this emotional design should be achieved remains an open question. From the work of the researchers above, we may infer that interactive systems need a variety of roles to best support the user.
Interaction has social implications as well. Mostly interactive installations are conceived between a system and one user. However, evidence from research shows that with the increasing number of people, the nature of the interaction changes as well. For example, the honeypot effect, [17] is the phenomenon where people who are engaged with a system stimulate by-passers to observe and ultimately engage with the system. Claes and Vande Moere [22] demonstrated identical displays compared in a public setting and isolated setting and how using a narrative and no narrative lead to a difference in comprehension and ease of use. Valkanova et al. demonstrated the impact of citizen-driven data visualization on perception, behavior change, social awareness, and public participation [23].
4.2. User Experience and Situatedness in Interactive Systems
In the field of interaction design, the concept of user experience is used to express a more user-grounded orientation of how systems and people may relate [24]. Although the concept of user experience is widely used in the field of Human-Computer Interaction, there is generally no accepted definition of user experience yet. There are marked differences in its conception and application based on geographical location and background [25]. What seems to play an important role in the success of an interactive system is the sense of locus of control [26]—meaning the degree to which an individual reflects about his/her capabilities to exert control in an environment. As a more concrete example, Meerbeek and his team [27] found many inadequacies in automated exterior blinds systems. They defined four different user profiles that perform better for the user (minimal, regular, active, and system control with manual override). The recognition of multiple user profiles is important, and leads to the (yet unanswered) question how to dynamically choose the proper user profile. Concerning the integration of interaction in the architectural design process, Houben et al. [28] claim that successful integration of interactive systems in architectural design projects can only be achieved when architects perceive said systems as a material that they can approach in much the same way they aim to express an architectural message.
Interactions in systems with multiple components quickly lead to complex relationships and decision situations that are difficult to predict. Beer demonstrated for a simple case (walking behavior of a legged agent under dynamic conditions) that the behavior of the agent is the result of the coupling of two dynamic systems—namely the agent and the environment—and cannot be assigned to just one of the systems [29]. This coupling is also known by the term situatedness, meaning that we cannot understand an agent’s behavior unless we consider the way it is linked to its environment. Clancey additionally stated that much of what we do is a re-coordination of previous combinations of perceiving (or sensing), conceiving (or deciding), and moving (or acting) rather than the manipulation of an explicit knowledge model [30] (pp. 1–2).
For the design of interactive architecture this means that responsive buildings are by definition situated—which means that we cannot suffice with simple input–response schemes to guide the behavior of interactive buildings. With multiple components, also the concept of agency needs to be extended to the interaction of multiple agents together. Classical agent frameworks use utility as a measure to decide what to do. However, with multiple agents, and situatedness in the equation, utility values are not sufficient anymore. In multi-agent systems it is acknowledged that agents need to communicate and may not share the same utility- or agenda. Thus, agents need also to build assumptions about the other agents and assign levels of trust to agents in the system [31]. The most important implication, which cannot be stressed enough, is that we have to move beyond a utilitarian interpretation of performance maximization.
4.3. The Challenge for Architecture of Interactive Buildings
Based on the previous discussion we may conclude that there is no simple single solution that will work for complex systems like interactive buildings. Systems may have different goals: apart from performance, interactions may also be geared towards sustaining, servicing, symbolizing, and entertaining. Systems can engage in different styles with the user, such as in an instructive way, as a conversation, series of manipulations, or in an explorative way [32]. Mark Meagher stressed the “poetic potential” of responsive architecture, and notes that “…architects must develop a deep understanding of multiple types of change in buildings [33].” Cameline Bolbroe argued for a shift in attention away from the object to an “act of inhabitation,” dealing with temporality, memory, learning, and emergence [34]. It seems evident that we need various interaction styles that an interactive building may adopt. This introduces the question how the building system would figure out which interaction style is the most appropriate, and how in an interactive manner the user different interaction styles may be adopted.
5. The Interaction Narrative
Settling on the proper interaction style with a user seems to be intimately bound with the user’s experience, desires, and expectations. One approach that offers an integrated view of this is discussed by Maria Lehman [35]. Lehman’s work is based in the domain of sensory design in healthcare environments. She notes that people’s experiences are multi-sensory and that for a successful design it is necessary to connect well to the narrative of people in the building. In a healthcare situation, the narrative includes things as contemplation, visitors, sleep, recovery milestones, exercise, activities of daily living, medication, distraction, education, transition home, and pain management. A narrative, in other words, is a coherent story of the inhabitant, which needs to be supported by the activities or interactions of the building. In the more specific case of cancer treatment, Gillian Hayes and her team [36] have noted that “…New technologies must accompany people on this journey while accommodating huge shifts in uses needs, motivations, energy levels and goals.” We can generalize this to areas outside of healthcare. In 1999 Per Galle argued that a proper description of design should not be object-based but action-based—a notion which has strong links with the concept of narrative [37].
In our view the concept of narrative as described by Lehman is very relevant to interactive architecture. It has strong appeal because it enforces a consistent unfolding of events between the user and the building—thus it supports single interaction styles by making them clearer or readable for the user. Additionally, it enforces consistent reasons for role-switching between the user, the building, and the user-building relationship—thus it supports the decision process how to switch from one interaction style to another. The concept of narrative is very close to the notion of scenario, that is often used by architects to speculate about possible uses of their yet unrealized designs [38,39,40,41].
Narrative is usually associated with words and storytelling as can be readily seen in books and movies where the narrative is the prime structure. As such there is a very large amount of research on narrative in the written, spoken, and visual form. Our focus is on the role of narrative in technical systems, so we ignore narrative as a storytelling device by itself. Interactive narratives are stories, usually in computer games or installation art, where the user experiences a narrative through a storyline. Quite a lot of research and development has been invested in these kind of applications [42], although there is not much investigation into the user experience of such narratives [43]. Narratives have been advocated in computer system development as early as 1993 by Hasse Clausen [44]. Narratives are integrated today in the narrative of use cases [45], which has been the systematic approach to describe scenarios in software development since 1999 [46]. Moving closer to architectural design, Li-Shin Chang noted that a narrative does not need to be in the form of words but can contain objects as well, for example in landscape narratives [47]. Davidoff et al. observed in the context of control in smart homes for families, that just handing over control of the devices is not sufficient, but that the system should support families to control the things they value the most: “their time, their activities, and their relationship [48].”
Based on the discussion above, we propose that an interaction narrative is an organization of moments of interaction between the user and the system following a story that is consistent with an interaction style. Additionally, the interactive system has an interaction narrative for the way it switches between interaction styles—following a story that is consistent with user expectations.
With interactive architecture, we are fundamentally changing our understanding of buildings compared to almost all architectural thought of the past centuries, except for the earlier noted Cedric Price and Gordon Pask. Interaction narratives have the potential to unify technologies, aesthetical, and social aspects in a meaningful way. By respecting a narrative in the design process, it may be avoided that unbalanced attention goes to singular aspects of interaction, such as showcasing technology, or installations that do not deepen people’s understanding of the built environment. It must be noted that the implications of this change are unclear. It will require an orchestrated effort from architects, researchers, legislators, clients, and people to advance our understanding.
Are interaction narratives the only solution for the development of responsive buildings? One is right to point out that narratives are possibly but one of the many options for such future development. Contemporary architectural theory, however, does not deal with the question, “how should my building behave?” Rather it focuses on performance connected to geometry and material, for example [49,50,51], or at best, agency as a technological and cultural phenomenon [52,53]. At the moment, narratives form the most developed theories that may account for a comprehensive way to design responsive architecture.
6. Conclusions
At the beginning of this article it was observed that buildings have a long time-span of use, and in this time-span must fulfill a dynamic range of functions. Passive technologies alone are capable of covering some of this range, but not everything. For reasons of functionality, comfort, safety, and pleasure, increasing amounts of flexible additions are made to the building outfit, i.e., dynamic shading systems, intelligent HVAC installations, automatic doors, and so on. Today, technological advances make it possible to link up building components to each other locally and globally, for example through IoT technology. This leads to a revised notion of buildings, in which they become increasingly actively engaged with the needs of the users. At some point such systems become so advanced that we start to call them in an uncritical manner responsive or interactive.
It is this uncritical manner of use of the term responsive or interactive that we investigated in this article. We hope to have demonstrated that the notion of responsive architecture is more complex than just endlessly adding sensors, actuators, and components. Adding such things is an act that deeply changes the building, not only at the technical level, but also at the cultural and social level. There are three main points derived from the work:
- Agency: First of all, we must distance ourselves from the idea that a building is a passive thing to which we can add technology, and that by doing so, the building still is that unaffected passive thing. We must learn to see a building as an agent, one that interacts with other agents—be it other buildings, people, or software systems. Agent theory and multi-agent theory gives us the technical and formal tools by which we can create functional models of responsive buildings. Currently, agent theory is well-developed in the field of Artificial Intelligence for well over two decades, but the field of architecture has hardly touched upon this concept. This sets a theoretical agenda to incorporate the notion of agency in architecture.
- Situatedness: Second, we must understand that with a richer arsenal of possible responses by the building, also the context and the history of responses start to play a decisive role. In other words, responsive systems are situated. As stated by John Gero, situatedness means that “where you are when you do what you do matters.” [54] It is impossible, and even unnecessary, to try and capture all possible information flows for a responsive building. With the concept of situatedness, we can make an informed choice about what aspects of the context and history are taken into consideration by the responsive building. Making these choices explicit and integrating them into the reasoning process of the responsive building is an important step in the design of the building. This sets a theoretical agenda to formulate the proper selection of quantitative parameters from which a model of the context and history of the context can be built.
- Narratives: Third, the situatedness thesis implies that the unfolding of a series of interaction events between agents is a meaningful act that develops in a logical way under a series of assumptions by the agents. Such a logical development of interaction events is a narrative, as recognized in the work by Maria Lehman. We pose that interaction narratives currently are the best viewpoint from which to develop responsive and interactive architecture. With the interaction narrative we inevitably move away from objective and quantifiable parameters that are part of agency and situatedness. From an engineering/technical point of view, this may raise the concern that narratives require too much subjective aspects to be actually useful in the design of responsive buildings. The concept of narrative, however, does not hide the subjective aspect of design, but indeed makes it an explicit part of the design discourse and thus something that can be compared and judged, albeit in a subjective manner. This sets a theoretical agenda of how proper interaction narratives should be constructed, how they can be formulated using agency and situatedness, and how they can be evaluated.
To conclude, creating an interactive building should be more than the unrelated collection of many responsive components in a building. The notion of interaction narrative allows the design team of interactive systems to bring all possible moments of interaction into a coherent whole. Since a narrative contains a sequence of events, it also forces designers to consider user interactions as they should happen after each other, and how they could guide the user from event to event. Whereas the traditional way of architects to conceive the possible use of buildings is through a spatial sequence, responsive building design requires the integration of events and spaces into narratives for people. The people aspect has to be stressed because the design of narratives cannot be done in a meaningful manner without more explicit consideration of all the possible users in a building. The challenge therefore is to come up with a design framework for responsive buildings that is much richer and more complex than contemporary approaches. It is our opinion that much of the success of future responsive buildings will lie in an approach that combines events, spaces, and people.
As we are at the beginning of interactive buildings, a lot of work and experiments are still ahead of us. This position paper makes the case for interaction narratives as a promising future direction. Our claim here is theoretical, and that is obviously its main weakness. The real impact of interactive architecture cannot only be studied in a theoretical approach. Future work must deal with physical prototypes that confront reality and people, and which is assessed in the wild. Whether user narratives truly fulfill this potential, can only be found by prototyping, user testing, and implementing designs in real buildings.
Prototyping and building responsive buildings play a crucial role if we want to reach a more mature understanding of what responsive and interactive buildings may be. Theoretical observations alone are not enough as they are most likely to overlook aspects that could not be foreseen only theoretically. Additionally, since we are building types of systems that have not existed before, our understanding can only grow in a continuous cycle of reflection and action. However, without theoretical reflection, we risk that our explorations are technology-driven only, without asking ourselves what we really want. We hope that the current discussion in this position paper contributes to that question.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the grant CELSA, grant number CELSA/18/020.
Acknowledgments
Part of the research reported in this paper is supported by the grant CELSA/18/020, which is a collaboration between CTU Prague, Prague, Czech Republic and KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium. The support of this grant is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Leupen, B.; Heijne, R.; van Zwol, J. Time-Based Architecture; 010 Publishers: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kronenburg, R. Flexible: Architecture that Responds to Change; Laurence King Publishing: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pask, G. Architectural relevance of cybernetics. Archit. Des. 1969, 39, 494–496. [Google Scholar]
- Achten, H. One and Many: An Agent Perspective on Interactive Architecture. In ACADIA 2014 Design Agency, Proceedings Proceedings of the 34th Annual Conference of the Association for Computer Aided Design in Architecture, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 23–25 October 2014; Gerber, D., Huang, A., Sanchez, J., Eds.; Riverside Architectural Press: Toronto, Canada, 2014; pp. 479–486. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mignonneau, L.; Sommerer, C. Media Facades as Architectural Interfaces. In The Art and Science of Interface and Interaction Design; Sommerer, C., Jain, L.C., Mignonneau, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Achten, H. Closing the Loop for Interactive Architecture-Internet of Things, Cloud Computing, and Wearables. In Real Time, Proceedings of the 33rd eCAADe Conference, Vienna, Austria, 16–18 September 2015; Martens, B., Wurzer, G., Grasl, T., Lorenz, W.E., Schaffranek, R., Eds.; Vienna University of Technology: Vienna, Austria, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 623–632. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, K.; McLeish, T. Designing Real Time Sense and Response Environments through UX Research. In Real Time, Proceedings of the 33rd eCAADe Conference Vienna, Austria, 16–18 September 2015; Martens, B., Wurzer, G., Grasl, T., Lorenz, W.E., Schaffranek, R., Eds.; Vienna University of Technology: Vienna, Austria, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 651–658. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, J.L.; Coutaz, J. An ecological view of Smart Home technologies. In Ambient Intelligence. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 9425; De Ruyter, B., Kameas, A., Chatzimisios, P., Mavrommati, I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, M.; Kemp, M. Interactive Architecture; Princeton Architectural Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- McCullough, M. Digital Ground: Architecture, Pervasive Computing, and Environmental Knowledge; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, N.; Green, K.; Marshall, P.; Dalton, R.; Hoelscher, C.; Mathew, A.; Kortuem, G.; Varoudis, T. Ar-CHI-Tecture: Architecture and Interaction. In CHI EA ‘12 CHI ’12 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 2743–2746. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, N.; Green, K.; Dalton, R.; Wiberg, M.; Hoelscher, C.; Mathew, A.; Schnädelbach, H.; Varoudis, T. Interaction and Architectural Space. In CHI EA ‘14 CHI ’14 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, F.; Haque, U. Urban Computing in the Wild: A survey on large scale participation and citizen engagement with ubiquitous computing, cyber physical systems, and Internet of Things. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2015, 81, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnädelbach, H.; Irune, A.; Kirk, D.; Glover, K.; Brundell, P. ExoBuilding: Physiologically driven adaptive architecture. ACM Trans. Comput. Hum. Interact. 2012, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, D.; Thieme, A.; Linehan, C.; Balaam, M.; Wallace, J.; Lindley, S. Preface Emotional Wellbeing. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2014, 72, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, N.; Downs, J.; Harrop, M.; Cox, T.; Oliveira, E.; Webber, S.; Vetere, F.; Vande Moere, A. Uncovering the Honeypot Effect: How Audiences Engage with Public Interactive Systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM Conference on Designing Interactive Systems (DIS ’16); ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, J.C. Past, Present and Future of Ambient Intelligence and Smart Environments. In Agents and Artificial Intelligence. Communications in Computer and Information Science 67; Filipe, J., Fred, A., Sharp, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Walldén, S.; Mäkinen, E. On accepting smart environments at user and societal levels. Univers. Inf. Soc. 2014, 13, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, B.; Jung, Y.; Park, T. When stereotypes meet robots: The double-edge sword of robot gender and personality in human-robot interaction. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 38, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partala, T.; Saari, T. Understanding the most influential user experiences in successful and unsuccessful technology adoptions. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 53, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, S.; Vande Moere, A. The impact of a narrative design strategy for information visualization on a public display. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Designing Interactive Systems (DIS 2017), Edinburgh, UK, 10–14 June 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 833–838. [Google Scholar]
- Valkanova, N.; Jorda, S.; Moere, A.V. Public visualization displays of citizen data: Design, impact and implications. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2015, 81, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, H.; Rogers, Y.; Preece, J. Interaction Design: Beyond Human-Computer Interaction, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, NH, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lallemand, C.; Gronier, G.; Koenig, V. User experience: A concept without consensus? Exploring practitioners’ perspectives through an international survey. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 43, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Shin, H.; Aum, H.; Kim, M.; Kim, J. Application of experiential locus of control to understand users’ judgments towards useful experience. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 54, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerbeek, B.; Kulve, M.T.; Gritti, T.; Aerts, M.; Van Loenen, E.; Aarts, E. Building automation and perceived control: A field study on motorized exterior blinds in Dutch offices. Build. Environ. 2014, 79, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, M.; Denef, B.; Mattelaer, M.; Claes, S.; Vande Moere, A. The Meaningful Integration of Interactive Media in Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM Conference Companion Publication Conference on Designing Interactive Systems (DIS ’17 Companion Volume), Edinburgh, UK, 10–14 June 2017; ACM: New York, USA, 2017; pp. 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Beer, R.D. A Dynamical Systems Perspective on Agent-Environment Interaction. In Artificial Intelligence: Critical Concepts Volume III; Chrisley, R., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2000; pp. 210–255. [Google Scholar]
- Clancey, W.J. Situated Cognition: On Human Knowledge and Computer Representations; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, G. (Ed.) Multiagent Systems; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Achten, H. Buildings with an Attitude: Personality Traits for the Design of Interactive Architecture. In Faculty of Architecture, Computation and Performance, Proceedings of the 31st eCAADe Conference (Volume 1), Delft, The Netherlands, 18–20 September 2013; Stouffs, R., Sariyildiz, S., Eds.; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 477–485. [Google Scholar]
- Meagher, M. Designing for change: The poetic potential of responsive architecture. Front. Archit. Res. 2015, 4, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolbroe, C. Mapping the intangible: On adaptivity and relational prototyping in architectural design. In Architecture and Interaction. Human Computer Interaction in Space and Place; Dalton, N.S., Schnädelbach, H., Wiberg, M., Varoudis, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 205–229. [Google Scholar]
- Lehman, M.L. Environmental Sensory Design. In Intelligent Buildings: Design, Management, and Operation, 2nd ed.; Clements-Croome, D., Ed.; ICE Publishing: London, UK, 2013; pp. 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, G.R.; Abowd, G.D.; Davis, J.S.; Blount, M.L.; Ebling, M.; Mynatt, E.D. Opportunities for Pervasive Computing in Chronic Cancer Care. In Pervasive Computing. Pervasive 2008. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Indulska, J., Patterson, D.J., Rodden, T., Ott, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 5013, pp. 262–279. [Google Scholar]
- Galle, P. Design as intentional action: A conceptual analysis. Des. Stud. 1999, 20, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carp, J. Design participation: New roles, new tools. Des. Stud. 1986, 7, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasdogan, G. The role of user models in product design for assessment of user needs. Des. Stud. 1996, 17, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluoglu, B. Design knowledge communicated in studio critiques. Des. Stud. 2000, 21, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crilly, N.; Cardoso, C. Where next for research on fixation, inspiration and creativity in design? Des. Stud. 2017, 50, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Arie, U. The Narrative-Communication Structure in Interactive Narrative Works. In Interactive Storytelling. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 5915; Iurgel, I.A., Zagalo, N., Petta, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 152–162. [Google Scholar]
- Milam, D.; El-Nasr, M.S.; Wakkary, R. Looking at the interactive narrative experience through the eyes of the participants. In Interactive Storytelling, First Joint International Conference on Interactive Digital Storytelling; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 96–107. [Google Scholar]
- Clausen, H. Narratives as tools for the system designer. Des. Stud. 1993, 14, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, S.; Díez, D.; Díaz, P.; Aedo, I. Standardizing the narrative of use cases: A controlled vocabulary of web user tasks. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2013, 55, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booch, G.; Rumbaugh, J.; Jacobson, I. The Unified Modeling Language User Guide; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.-S.; Bisgrove, R.J.; Liao, M.-Y. Improving educational functions in botanic gardens by employing landscape narratives. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2008, 86, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidoff, S.; Lee, M.K.; Yiu, C.; Zimmerman, J.; Dey, A. UbiComp 2006: Ubiquitous Computing, Lecture Notes in Computer Science 4206; Dourish, P., Friday, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kolarevic, B.; Malkawi, A.M. Performative Architecture: Beyond Instrumentality; Spon Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lynn, G. Composites, Surfaces, and Software: High Performance Architecture; Yale School of Architecture: New Haven, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Berkel, B.; van Bos, C. Knowledge Matters; Frame Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gerber, D.J.; Ibañez, M. (Eds.) Paradigms in Computing: Making, Machines, and Models for Design Agency in Architecture; eVolo Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Velikov, K.; Thün, G. Towards an Architecture of Cyber-Physical Systems. In Paradigms in Computing: Making, Machines, and Models for Design Agency in Architecture; Gerber, D.J., Ibañez, M., Eds.; eVolo Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 331–347. [Google Scholar]
- Gero, J.S.; Kannengiesser, U. The Situated Function-Behaviour-Structure Framework. In Artificial Intelligence in Design’02; Gero, J.S., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).