Shuni Virus Replicates at the Maternal-Fetal Interface of the Ovine and Human Placenta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses and Cells
2.2. Ethics Statement
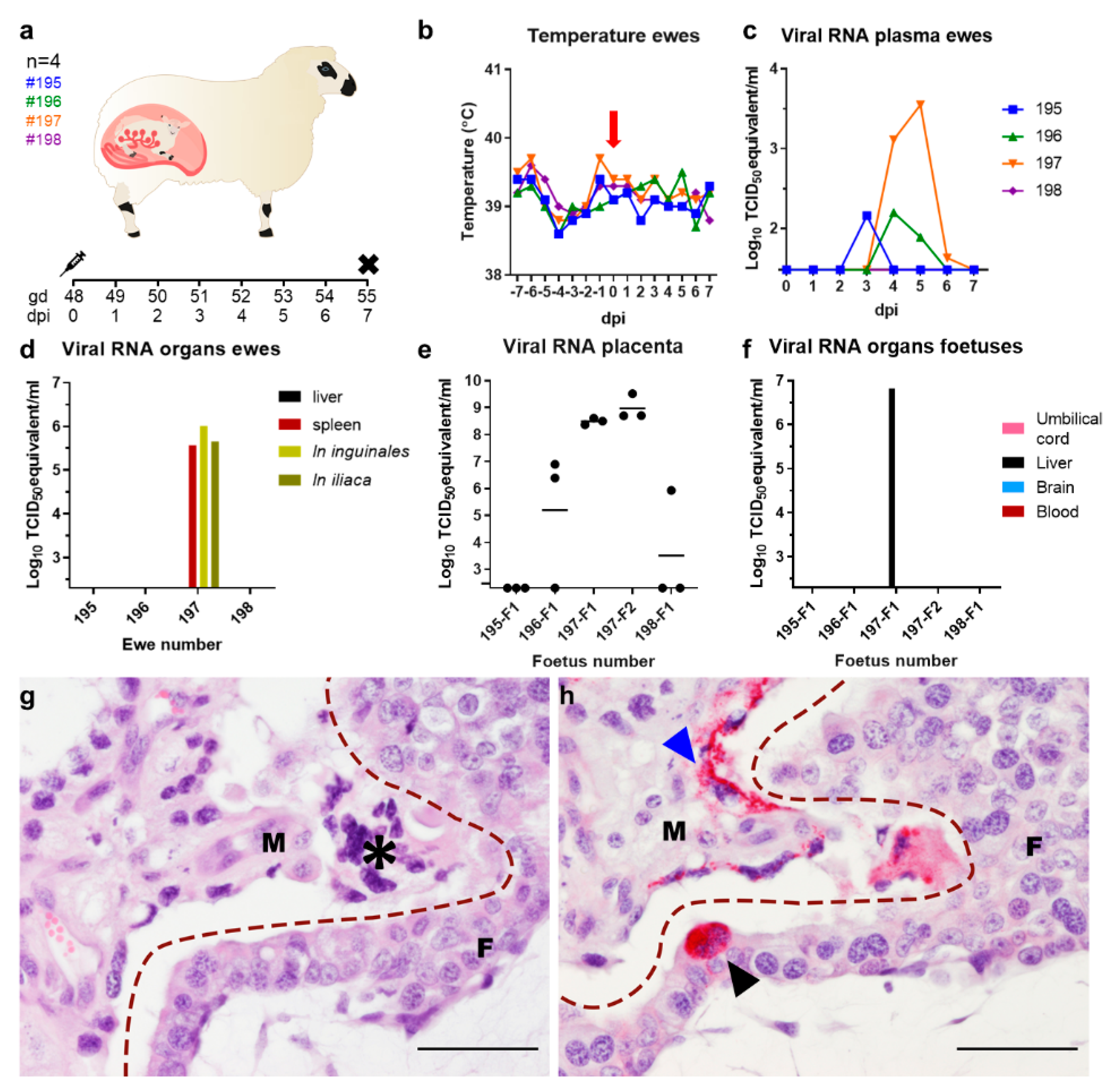
2.3. Pregnant Ewe Trial
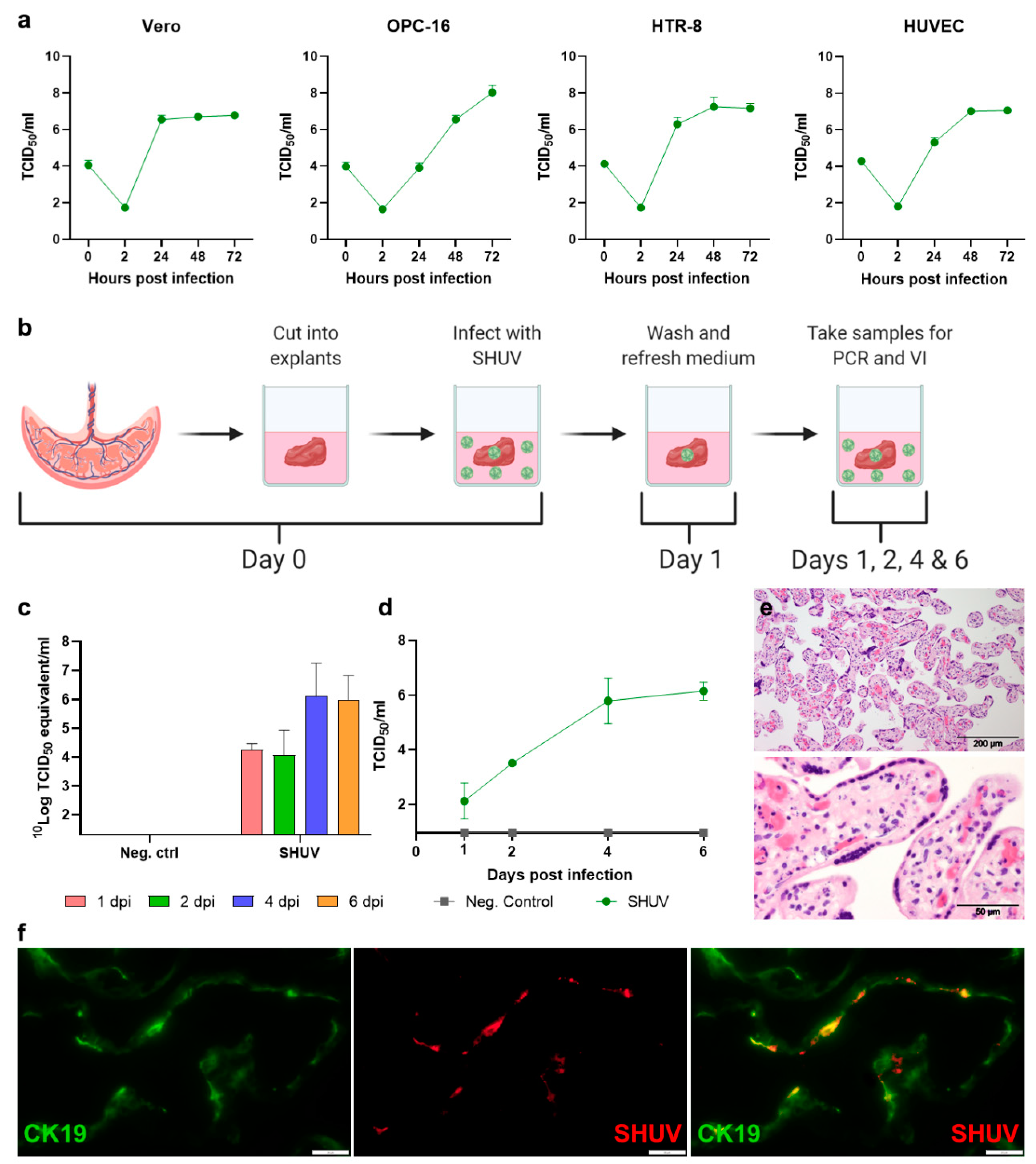
2.4. Experimental Infection of Human Term Placentas
2.5. Detection of Viral RNA
2.6. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Vertical Transmission of SHUV in Pregnant Ewes
3.2. SHUV Targets Human Trophoblasts
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Causey, O.R. Shuni (SHU) strain AN 10107. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1970, 19, 1139–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Causey, O.R.; Kemp, G.E.; Causey, C.E.; Lee, V.H. Isolations of Simbu-group viruses in Ibadan, Nigeria 1964-69, including the new types Sango, Shamonda, Sabo and Shuni. Ann. Trop Med. Parasitol. 1972, 66, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golender, N.; Wernike, K.; Bumbarov, V.; Aebischer, A.; Panshin, A.; Jenckel, M.; Khinich, Y.; Beer, M. Characterization of Shuni viruses detected in Israel. Virus Genes 2016, 52, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.H. Isolation of viruses from field populations of culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Nigeria. J. Med. Entomol. 1979, 16, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclntosh, B.M.; Jupp, P.G.; de Sousa, J. Further isolations of arboviruses from mosquitoes collected in Tongaland, South Africa, 1960–1968. J. Med. Entomol. 1972, 9, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohlmann, T.W.R.; Oymans, J.; Wichgers Schreur, P.J.; Koenraadt, C.J.M.; Kortekaas, J.; Vogels, C.B.F. Vector competence of biting midges and mosquitoes for Shuni virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, J.; Motlou, P.; van Eeden, C.; Pretorius, M.; Stivaktas, V.I.; Williams, J.; Snyman, L.P.; Buss, P.E.; Beechler, B.; Jolles, A.; et al. Shuni Virus in Wildlife and Nonequine Domestic Animals, South Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1521–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, M.; Human, S.; Van Eeden, C.; van Niekerk, S.; Williams, J.H.; Steyl, J. The role of zoonotic vector-borne viruses as neurological pathogens in horses and wildlife in South Africa. In Proceedings of the 9th Annual Congress of the Southern African Society for Veterinary Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, Pretoria, South Africa, 18–20 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eeden, C.; Williams, J.H.; Gerdes, T.G.; van Wilpe, E.; Viljoen, A.; Swanepoel, R.; Venter, M. Shuni virus as cause of neurologic disease in horses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.; Assis, I.; Beer, M.; Khinich, Y.; Koren, O.; Edery, N.; Eldar, A.; Wernike, K. Shuni virus in Israel: Neurological disease and fatalities in cattle. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Brenner, J.; Valdman, M.; Khinich, Y.; Bumbarov, V.; Panshin, A.; Edery, N.; Pismanik, S.; Behar, A. Malformations Caused by Shuni Virus in Ruminants, Israel, 2014–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2267–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eeden, C.; Swanepoel, R.; Venter, M. Antibodies against West Nile and Shuni viruses in veterinarians, South Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1409–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkland, P.D. Akabane virus infection. Rev. Sci Technol. 2015, 34, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsonson, I.M.; Della-Porta, A.J.; Snowdon, W.A. Congenital Abnormalities in Newborn Lambs After Infection of Pregnant Sheep with Akabane Virus. Infect. Immun. 1977, 15, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanase, T.; Murota, K.; Hayama, Y. Endemic and Emerging Arboviruses in Domestic Ruminants in East Asia. Front. Vet. Sci 2020, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumori, Y.; Aizawa, M.; Sakai, Y.; Inoue, D.; Kodani, M.; Tsuha, O.; Beppu, A.; Hirashima, Y.; Kono, R.; Ohtani, A.; et al. Congenital abnormalities in calves associated with Peaton virus infection in Japan. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, T.; Yoshida, K.; Ohashi, S.; Yanase, T.; Sueyoshi, M.; Kamimura, S.; Misumi, K.; Hamana, K.; Sakamoto, H.; Yamakawa, M. Arthrogryposis, hydranencephaly and cerebellar hypoplasia syndrome in neonatal calves resulting from intrauterine infection with Aino virus. Vet. Res. 2004, 35, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Ali, A.A.; Atta, M.S.; Cepica, A. Common, emerging, vector-borne and infrequent abortogenic virus infections of cattle. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2012, 59, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, S.; Greig, J.; Mascarenhas, M.; Young, I.; Waddell, L.A. La Crosse virus: A scoping review of the global evidence. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 147, E66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutuze, M.F.; Nzayirambaho, M.; Mores, C.N.; Christofferson, R.C. A Review of Bunyamwera, Batai, and Ngari Viruses: Understudied Orthobunyaviruses With Potential One Health Implications. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkas, H.; Bozidis, P.; Franks, A.; Papadopoulou, C. Oropouche Fever: A Review. Viruses 2018, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oymans, J.; Wichgers Schreur, P.J.; van Oort, S.; Vloet, R.; Venter, M.; Pijlman, G.P.; van Oers, M.M.; Kortekaas, J. Reverse Genetics System for Shuni Virus, an Emerging Orthobunyavirus with Zoonotic Potential. Viruses 2020, 12, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spearman, C. The Method of “Right and Wrong Cases” (Constant Stimuli) without Gauss’s Formulae. Br. J. Psychol. 1908, 2, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärber, G. Beitrag zur kollektiven Behandlung pharmakologischer Reihenversuche. Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 1931, 162, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oymans, J.; Wichgers Schreur, P.J.; van Keulen, L.; Kant, J.; Kortekaas, J. Rift Valley fever virus targets the maternal-foetal interface in ovine and human placentas. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oymans, J.; van Keulen, L.; Wichgers Schreur, P.J.; Kortekaas, J. Early Pathogenesis of Wesselsbron Disease in Pregnant Ewes. Pathogens 2020, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsonson, I.M.; McPhee, D.A.; Della-Porta, A.J.; McClure, S.; McCullagh, P. Transmission of Akabane virus from the ewe to the early fetus (32 to 53 days). J. Comp. Pathol. 1988, 99, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oymans, J.; van Keulen, L.; Vermeulen, G.M.; Wichgers Schreur, P.J.; Kortekaas, J. Shuni Virus Replicates at the Maternal-Fetal Interface of the Ovine and Human Placenta. Pathogens 2021, 10, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010017
Oymans J, van Keulen L, Vermeulen GM, Wichgers Schreur PJ, Kortekaas J. Shuni Virus Replicates at the Maternal-Fetal Interface of the Ovine and Human Placenta. Pathogens. 2021; 10(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleOymans, Judith, Lucien van Keulen, Guus M. Vermeulen, Paul J. Wichgers Schreur, and Jeroen Kortekaas. 2021. "Shuni Virus Replicates at the Maternal-Fetal Interface of the Ovine and Human Placenta" Pathogens 10, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010017
APA StyleOymans, J., van Keulen, L., Vermeulen, G. M., Wichgers Schreur, P. J., & Kortekaas, J. (2021). Shuni Virus Replicates at the Maternal-Fetal Interface of the Ovine and Human Placenta. Pathogens, 10(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010017




