- Article
Listeria monocytogenes in Jiaxing: Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals New Threats to Public Health
- Lei Gao,
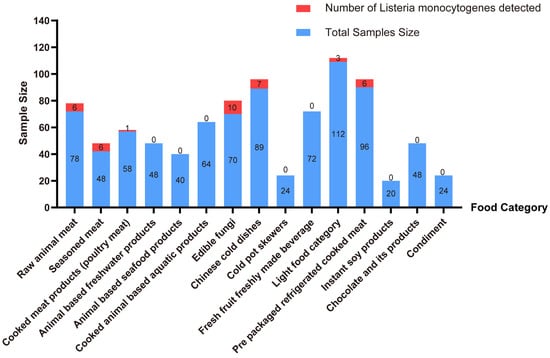
- Wenjie Gao and
- Guoying Zhu
- + 5 authors
(1) Background: Listeria monocytogenes (Lm) is recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) as one of the four principal foodborne pathogens. This study aimed to investigate the molecular characteristics of Lm isolates from Jiaxing, China, using whole-genome sequencing (WGS) to enhance our understanding of their molecular epidemiology. (2) Methods: A total of 39 foodborne Lm isolates and 7 clinical Lm isolates were analyzed via WGS to identify resistance genes, virulence factors, lineage, sequence type (ST), and clonal complex (CC). Antibiotic susceptibility was assessed using Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) testing, and serotypes were confirmed via multiplex PCR. (3) Results: We found that 39 food isolates were mainly lineage II (66.67%), with 13 STs; ST8 was the dominant ST, and 2 new types, ST3210 and ST3405, were found. Among the seven clinical isolates, lineage I was dominant (57.14%), and ST87 was the dominant ST. Serotype 1/2a was dominant, accounting for 54.35%, followed by 1/2b, which accounted for 36.96%. The overall antimicrobial resistance rate was 13.04%, with a multidrug resistance rate of 2.17%. All strains harbored LIPI-1 and LIPI-2, and five strains carried LIPI-3 genes: one strain belonged to ST619 of lineage I, two strains belonged to ST224 of lineage I, and two strains belonged to ST11 of lineage II. (4) Conclusions: This study clarified the genotype and serotype characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes in Jiaxing, as well as their molecular characteristics relating to drug resistance and virulence, thus providing a technical basis for improving exposure risk assessment of Listeria monocytogenes. Continuous monitoring, prevention, and control are recommended to further improve regional public health and safety.
19 January 2026