Detection of Toxocara cati Larvae from Ostrich and Wild Boar Meat Intended for Human Consumption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
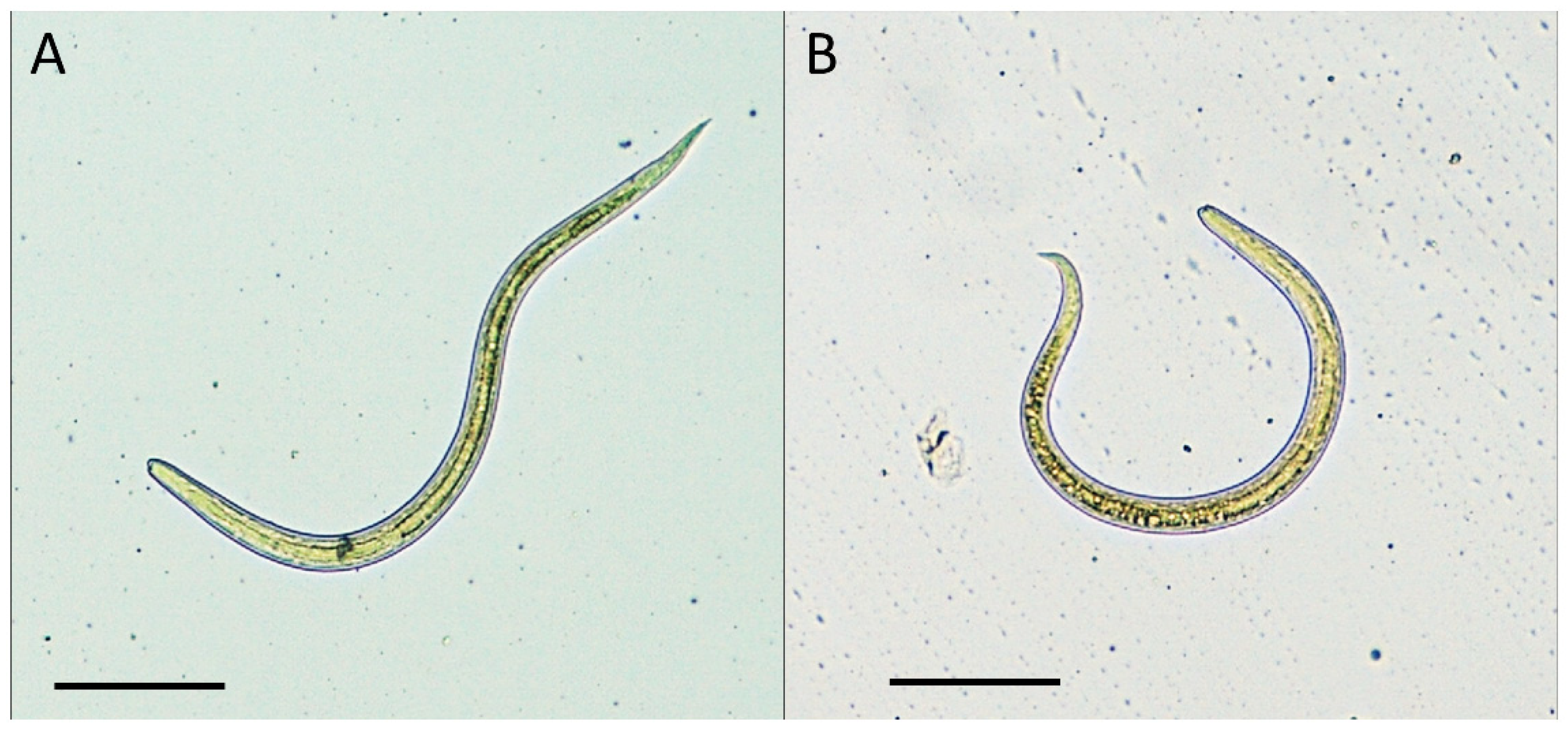
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Enzymatic Digestion
4.2. Molecular Tools
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parsons, J.C. Ascarid infections of cats and dogs. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1987, 17, 1307–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M. Toxocara cati: An underestimated zoonotic agent. Trends Parasitol. 2003, 19, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glickman, L.T.; Schantz, P.M. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of zoonotic toxocariasis. Epidemiol. Rev. 1981, 3, 230–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strube, C.; Heuer, L.; Janecek, E. Toxocara spp. infections in paratenic hosts. Vet Parasitol. 2013, 193, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bowman, D.D. The anatomy of the third-stage larva of Toxocara canis and Toxocara cati. 1st ed. Adv. Parasitol. 2020, 109, 39–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Bowman, D.D. Visceral larval migrans of Toxocara canis and Toxocara cati in non-canid and non-felid hosts. Adv. Parasitol. 2020, 109, 63–88. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, C.R. Food-Borne Nematode Infections. In Foodborne Parasites. Food Microbiology and Food Safety Series, 1st ed.; Ortega, Y.R., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 135–160. [Google Scholar]
- Magnaval, J.F.; Glickman, L.T.; Dorchies, P.; Morassin, B. Highlights of human toxocariasis. Korean J. Parasitol. 2001, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubinsky-Elefant, G.; Hirata, C.E.; Yamamoto, J.H.; Ferreira, M.U. Human toxocariasis: Diagnosis, worldwide seroprevalences and clinical expression of the systemic and ocular forms. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2010, 104, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finsterer, J.; Auer, H. Parasitoses of the human central nervous system. J. Helminthol. 2013, 87, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, A. Toxocariasis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 114, 217–228. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Holland, C.V.; Wang, T.; Hofmann, A.; Fan, C.K.; Maizels, R.M.; Hotez, P.J.; Gasser, R.B. Human toxocariasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, H.; Walochnik, J. Toxocariasis and the clinical spectrum. Adv. Parasitol. 2020, 109, 111–130. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, G.H.; Zheng, W.B.; Hong, S.J.; Sugiyama, H.; Zhu, X.Q.; Elsheikha, H.M. Toxocariasis: A silent threat with a progressive public health impact. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macpherson, C.N. The epidemiology and public health importance of toxocariasis: A zoonosis of global importance. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centre for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/npi/ (accessed on 24 August 2021).
- Marucci, G.; Interisano, M.; La Rosa, G.; Pozio, E. Molecular identification of nematode larvae different from those of the Trichinella genus detected by muscle digestion. Vet Parasitol. 2013, 194, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2015/1375 of 10 August 2015 laying down specific rules on official controls for Trichinella in meat. Off. J. Eur. Union 2015, 58, 7–34. [Google Scholar]
- Euzéby, J. Recherche des larves de Trichines dans des biopsies de muscles sous-cutanes chez le porc. In Diagnostic Expérimental des Helminthoses Animales; Tome, I., Ed.; Informations Techniques Vétérinaires, Bulletin de l’Académie Vétérinaire de France Année: Paris, France, 1982; pp. 139–140. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, G.; Schantz, P. Toxocara visceral larva migrans after ingestion of raw lamb liver. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 15, 743–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, Y.; Hong, S.T.; Yun, J.Y.; Park, H.K.; Oh, J.H.; Kim, Y.E.; Jeon, B.S. Meningitis by Toxocara canis after ingestion of raw ostrich liver. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2012, 27, 1105–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.K.; Woo, S.J.; Hwang, J.M. Toxocara optic neuropathy after ingestion of raw meat products. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2014, 91, e267–e273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, C.N.L. Human behaviour and the epidemiology of parasitic zoonoses. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taira, K.; Saitoh, Y.; Okada, N.; Sugiyama, H.; Kapel, C.M.O. Tolerance to low temperatures of Toxocara cati larvae in chicken muscle tissue. Vet Parasitol. 2012, 189, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for food of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2004, 102–109. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2004/853/oj (accessed on 6 October 2021).
- UNI EN ISO 18743:2015 Microbiology of the Food Chain. Detection of Trichinella Larvae in Meat by Artificial Digestion Method. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/63251.html (accessed on 4 August 2021).
- Kang, S.; Sultana, T.; Loktev, V.B.; Wongratanacheewin, S.; Sohn, W.M.; Eom, K.S.; Park, J.K. Molecular identification and phylogenetic analysis of nuclear rDNA sequences among three opistorchid liver fluke species (Opistorchidae: Trematoda). Parasitol. Int. 2008, 119, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danesi, P.; Falcaro, C.; Dukik, K.; Jiang, Y.; Rizzoli, A.P.; Allavena, R.; Simpson, V.; Ravagnan, S.; Zanardello, C.; Capelli, G.; et al. Molecular Diagnosis of Emmonsia-Like Fungi Occurring in Wild Animals. Mycopathologia 2019, 185, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michelutti, A.; Sgubin, S.; Falcaro, C.; Cagnin, V.; Zoroaster, A.; Danesi, P. Detection of Toxocara cati Larvae from Ostrich and Wild Boar Meat Intended for Human Consumption. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101290
Michelutti A, Sgubin S, Falcaro C, Cagnin V, Zoroaster A, Danesi P. Detection of Toxocara cati Larvae from Ostrich and Wild Boar Meat Intended for Human Consumption. Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101290
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichelutti, Alice, Sofia Sgubin, Christian Falcaro, Valentina Cagnin, Alessia Zoroaster, and Patrizia Danesi. 2021. "Detection of Toxocara cati Larvae from Ostrich and Wild Boar Meat Intended for Human Consumption" Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101290
APA StyleMichelutti, A., Sgubin, S., Falcaro, C., Cagnin, V., Zoroaster, A., & Danesi, P. (2021). Detection of Toxocara cati Larvae from Ostrich and Wild Boar Meat Intended for Human Consumption. Pathogens, 10(10), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101290






