Genetic Characterisation of South African and Mozambican Bovine Rotaviruses Reveals a Typical Bovine-like Artiodactyl Constellation Derived through Multiple Reassortment Events
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genome Assembly and Genotyping
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
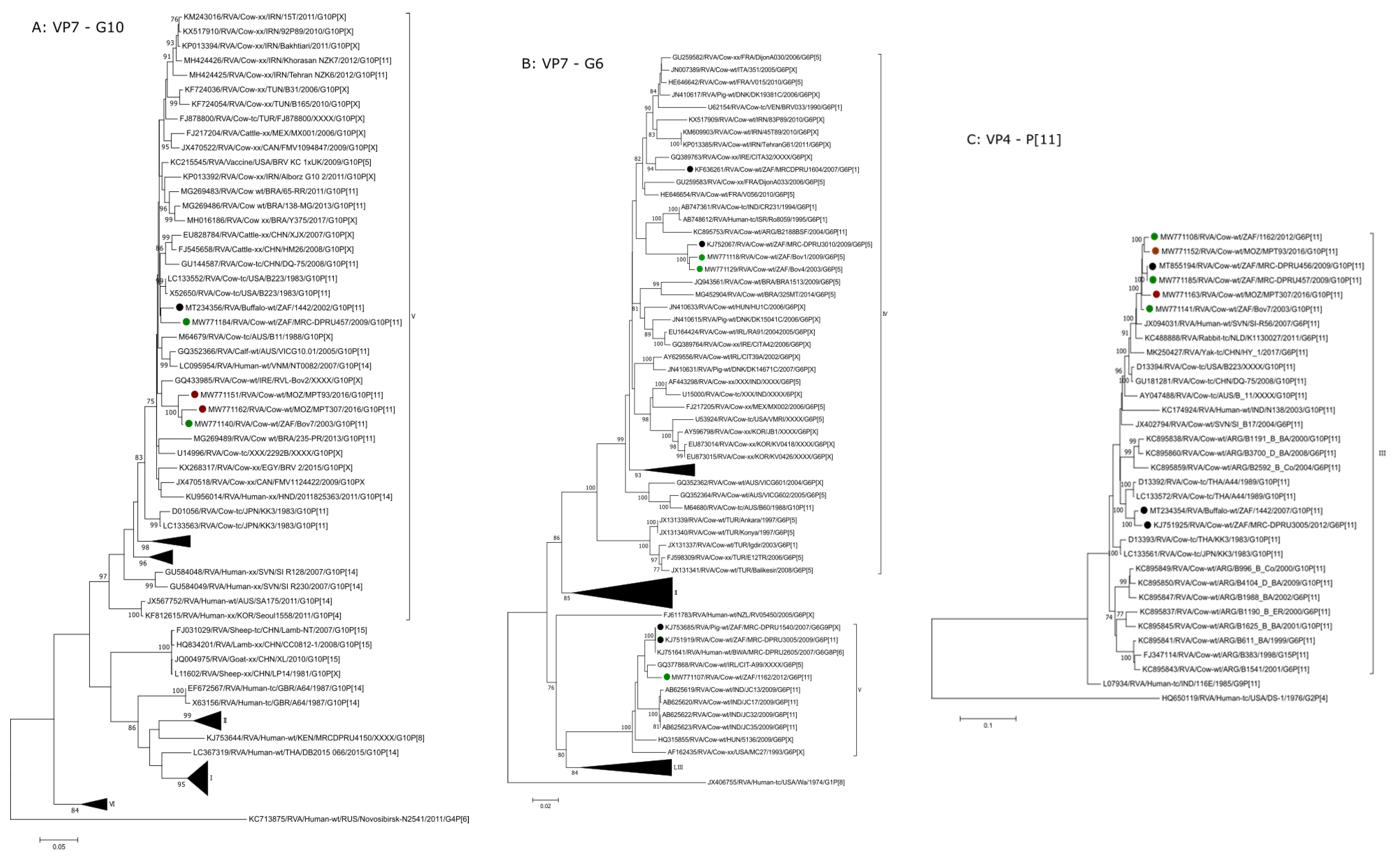
2.2.1. G6 and G10
2.2.2. P[11] and P[5]
2.2.3. I2
2.2.4. R2, M2, C2
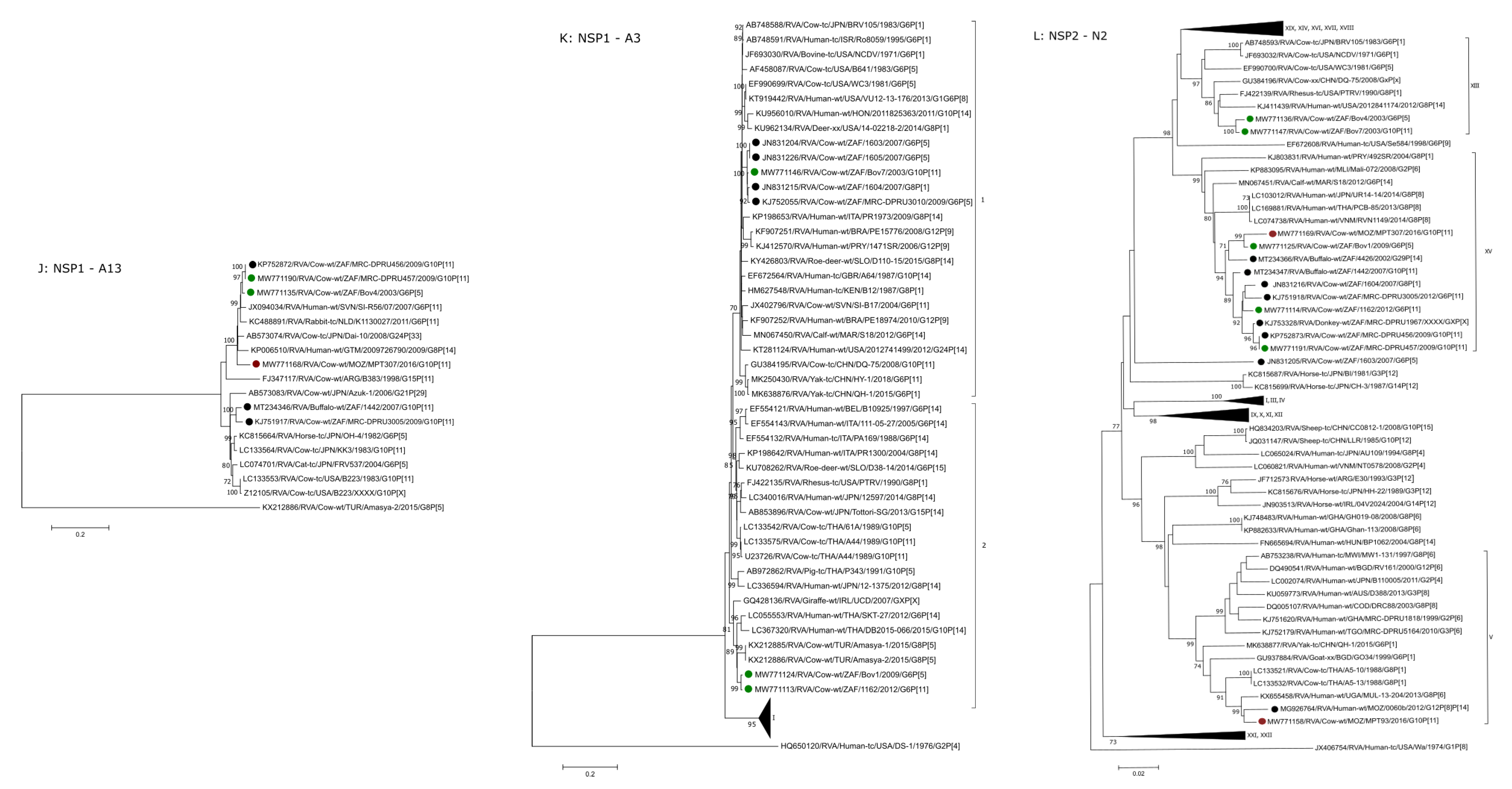
2.2.5. A13, A11 and A3
2.2.6. N2
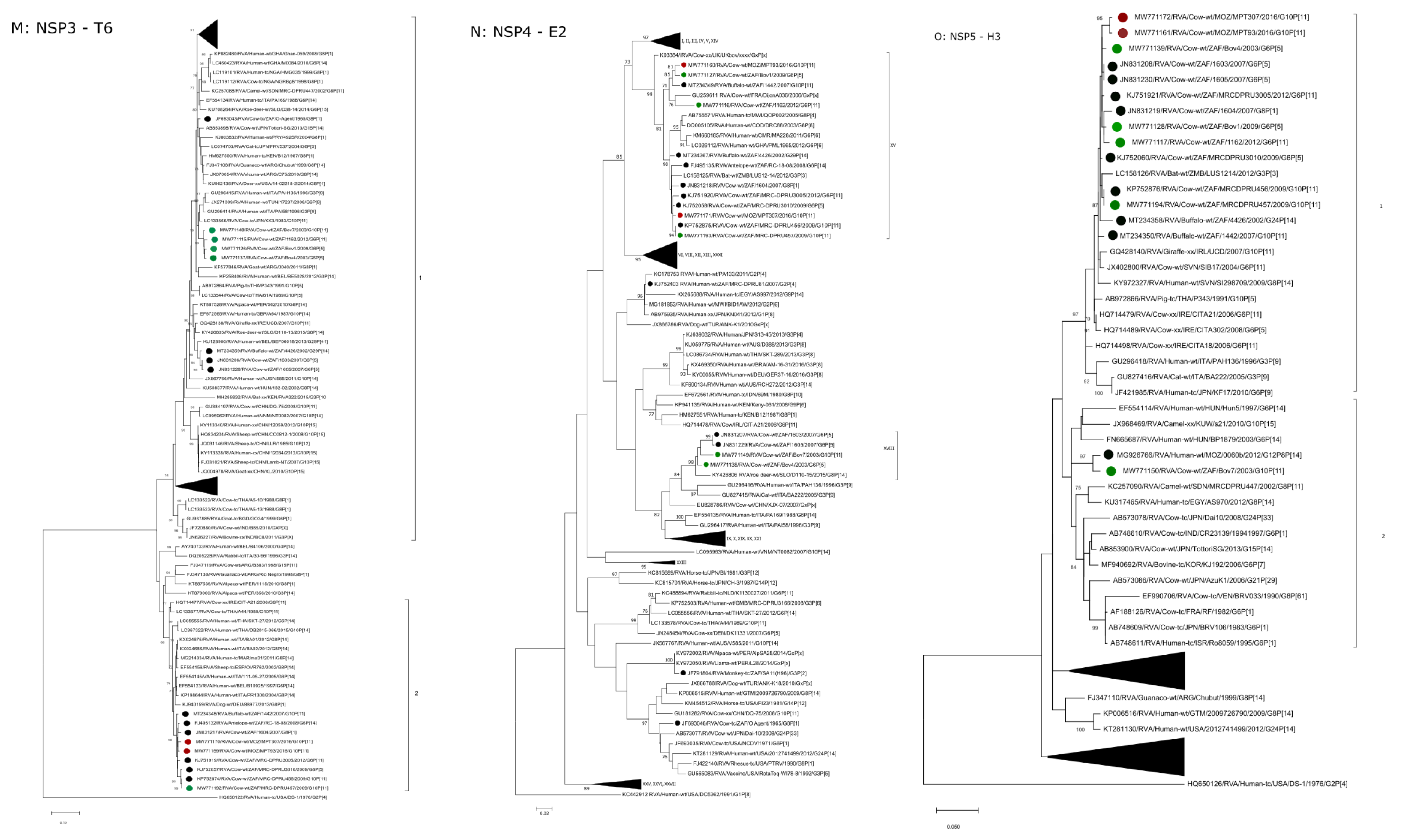
2.2.7. T6
2.2.8. E2
2.2.9. H3
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Statement
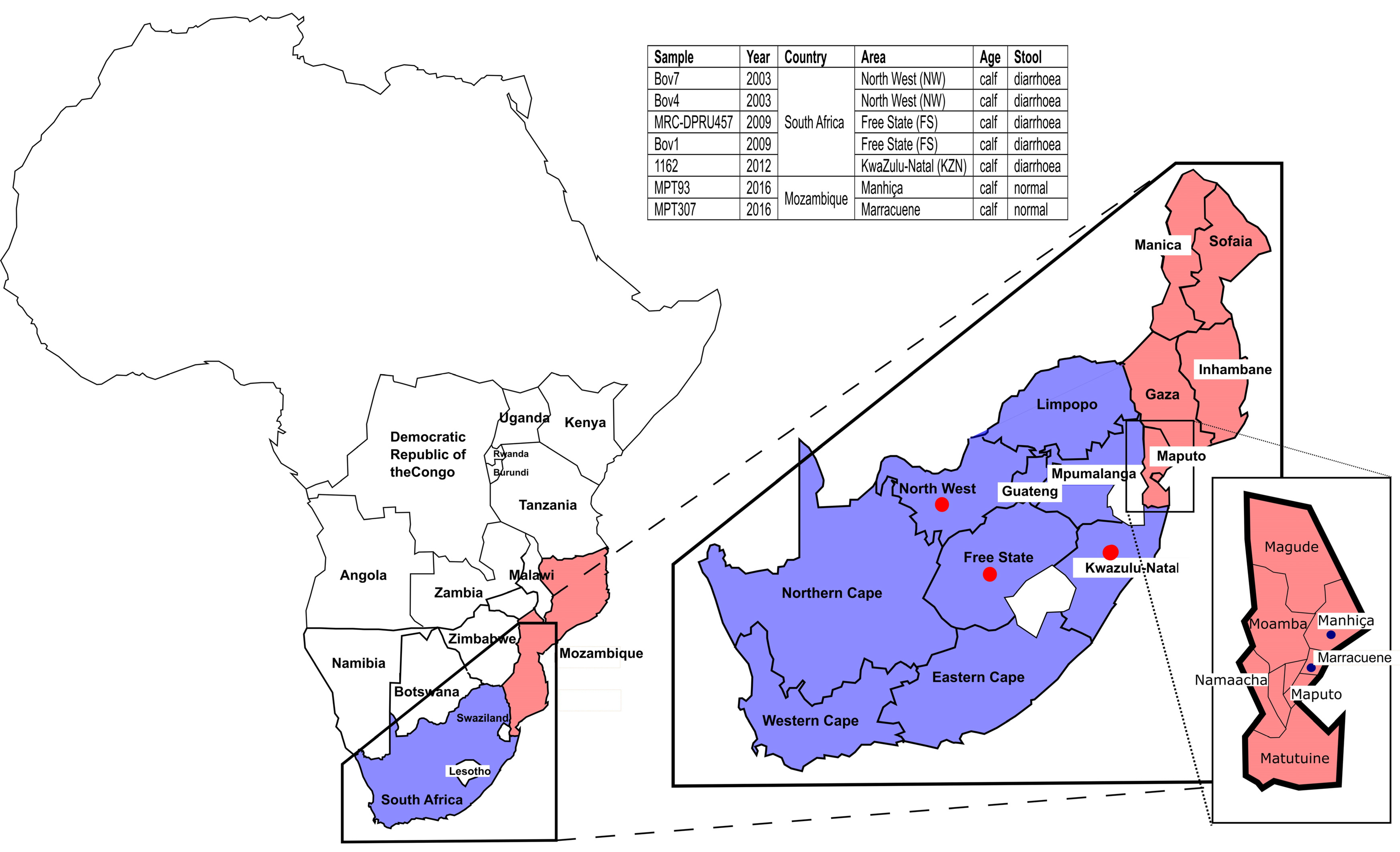
4.2. Samples
4.3. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis and Sequencing
4.4. Maximum Likelihood Phylogenetic Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martella, V.; Bányai, K.; Matthijnssens, J.; Buonavoglia, C.; Ciarlet, M. Zoonotic Aspects of Rotaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estes, M.; Greenberg, H. Rotaviruses. In Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; Rahman, M.; Attoui, H.; Bányai, K.; Estes, M.K.; Gentsch, J.R.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Kirkwood, C.D.; Martella, V.; et al. Recommendations for the Classification of Group A Rotaviruses Using All 11 Genomic RNA Segments. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; Heiman, E.; Arijs, I.; Delbeke, T.; McDonald, S.M.; Palombo, E.A.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Maes, P.; Patton, J.T.; et al. Full Genome-Based Classification of Rotaviruses Reveals a Common Origin between Human Wa-Like and Porcine Rotavirus Strains and Human DS-1-like and Bovine Rotavirus Strains. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3204–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Van Ranst, M. Genotype Constellation and Evolution of Group A Rotaviruses Infecting Humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, R.E. Some infectious causes of diarrhea in young farm animals. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1990, 3, 345–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, H.; Lá szló, B.; Jakab, F.; Ganesh, B.; De Grazia, S.; Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; Martella, V.; Bányai, K. Review of Group A Rotavirus Strains Reported in Swine and Cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strydom, A.; Donato, C.; Peenze, I.; Potgieter, A.C.; Seheri, M.; O’Neill, H.G. Genetic Characterisation of Novel G29P[14] and G10P[11] Rotavirus Strains from African Buffalo. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Potgieter, C.A.; Ciarlet, M.; Parreno, V.; Martella, V.; Banyai, K.; Garaicoechea, L.; Palombo, E.A.; Novo, L.; Zeller, M.; et al. Are Human P[14] Rotavirus Strains the Result of Interspecies Transmissions from Sheep or Other Ungulates That Belong to the Mammalian Order Artiodactyla? J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2917–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Mino, S.; Papp, H.; Potgieter, C.; Novo, L.; Heylen, E.; Zeller, M.; Garaicoechea, L.; Badaracco, A.; Lengyel, G.; et al. Complete Molecular Genome Analyses of Equine Rotavirus a Strains from Different Continents Reveal Several Novel Genotypes and a Largely Conserved Genotype Constellation. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jere, K.C.; Mlera, L.; O’Neill, H.G.; Peenze, I.; Van Dijk, A.A. Whole Genome Sequence Analyses of Three African Bovine Rotaviruses Reveal That They Emerged through Multiple Reassortment Events between Rotaviruses from Different Mammalian Species. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaga, M.M.; Jere, K.C.; Esona, M.D.; Seheri, M.L.; Stucker, K.M.; Halpin, R.A.; Akopov, A.; Stockwell, T.B.; Peenze, I.; Diop, A.; et al. Whole Genome Detection of Rotavirus Mixed Infections in Human, Porcine and Bovine Samples Co-Infected with Various Rotavirus Strains Collected from Sub-Saharan Africa. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 31, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strydom, A.; Motanyane, L.; Nyaga, M.M.; João, E.D.; Cuamba, A.; Mandomando, I.; Cassocera, M.; de Deus, N.; O’Neill, H. Whole-Genome Characterization of G12 Rotavirus Strains Detected in Mozambique Reveals a Co-Infection with a GXP[14] Strain of Possible Animal Origin. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troeger, C.; Khalil, I.A.; Rao, P.C.; Cao, S.; Blacker, B.F.; Ahmed, T.; Armah, G.; Bines, J.E.; Brewer, T.G.; Colombara, D.V.; et al. Rotavirus Vaccination and the Global Burden of Rotavirus Diarrhea among Children Younger Than 5 Years. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple Sequence Alignment with High Accuracy and High Throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dennis, F.E.; Fujii, Y.; Haga, K.; Damanka, S.; Lartey, B.; Agbemabiese, C.A.; Ohta, N.; Armah, G.E.; Katayama, K. Identification of Novel Ghanaian G8P[6] Human-Bovine Reassortant Rotavirus Strain by next Generation Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagomi, T.; Doan, Y.H.; Dove, W.; Ngwira, B.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Nakagomi, O.; Cunliffe, N.A. G8 Rotaviruses with Conserved Genotype Constellations Detected in Malawi over 10 Years (1997-2007) Display Frequent Gene Reassortment among Strains Co-Circulating in Humans. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1273–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Rahman, M.; van Ranst, M. Two out of the 11 Genes of an Unusual Human G6P[6] Rotavirus Isolate Are of Bovine Origin. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2630–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bwogi, J.; Jere, K.C.; Karamagi, C.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Namuwulya, P.; Baliraine, F.N.; Desselberger, U.; Iturriza-Gomara, M. Whole Genome Analysis of Selected Human and Animal Rotaviruses Identified in Uganda from 2012 to 2014 Reveals Complex Genome Reassortment Events between Human, Bovine, Caprine and Porcine Strains. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komoto, S.; Tacharoenmuang, R.; Guntapong, R.; Ide, T.; Tsuji, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Tharmaphornpilas, P.; Sangkitporn, S.; Taniguchi, K. Reassortment of Human and Animal Rotavirus Gene Segments in Emerging DS-1-like G1P[8] Rotavirus Strains. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komoto, S.; Pongsuwanna, Y.; Tacharoenmuang, R.; Guntapong, R.; Ide, T.; Higo-Moriguchi, K.; Tsuji, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Taniguchi, K. Whole Genomic Analysis of Bovine Group A Rotavirus Strains A5-10 and A5-13 Provides Evidence for Close Evolutionary Relationship with Human Rotaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 195, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Alam, M.M.; Ahmed, M.U.; Talukdar, R.I.; Paul, S.K.; Kobayashi, N. Complete Genome Constellation of a Caprine Group A Rotavirus Strain Reveals Common Evolution with Ruminant and Human Rotavirus Strains. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strydom, A.; João, E.D.; Motanyane, L.; Nyaga, M.M.; Christiaan Potgieter, A.; Cuamba, A.; Mandomando, I.; Cassocera, M.; de Deus, N.; O’Neill, H.G. Whole Genome Analyses of DS-1-like Rotavirus A Strains Detected in Children with Acute Diarrhoea in Southern Mozambique Suggest Several Reassortment Events. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 69, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickett, B.E.; Sadat, E.L.; Zhang, Y.; Noronha, J.M.; Squires, R.B.; Hunt, V.; Liu, M.; Kumar, S.; Zaremba, S.; Gu, Z.; et al. ViPR: An Open Bioinformatics Database and Analysis Resource for Virology Research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. JModelTest 2: More Models, New Heuristics and High-Performance Computing Europe PMC Funders Group. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agbemabiese, C.A.; Nakagomi, T.; Damanka, S.A.; Dennis, F.E.; Lartey, B.L.; Armah, G.E. Sub-genotype phylogeny of the non-G, non-P genes of genotype 2 Rotavirus A strains. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaracco, A.; Garaicoechea, L.; Matthijnssens, J.; Louge Uriarte, E.; Odeón, A.; Bilbao, G. Phylogenetic analyses of typical bovine rotavirus genotypes G6, G10, P[5] and P[11] circulating in Argentinean beef and dairy herds. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 18, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Strain | VP7 | VP4 | VP6 | VP1 | VP2 | VP3 | NSP1 | NSP2 | NSP3 | NSP4 | NSP5/6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RVA/Cow-wt/MOZ/MPT93/2016/G10P[11] | G10 | P[11] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M2 | A11 | N2 | T6 | E2 | H3 |
| RVA/Cow-wt/ZAF/MRC-DPRU457/2009/G10P[11] | G10 | P[11] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M2 | A13 | N2 | T6 | E2 | H3 |
| RVA/Cow-wt/MOZ/MPT307/2016/G10P[11] | G10 | P[11] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M2 | A13 | N2 | T6 | E2 | H3 |
| RVA/Cow-wt/ZAF/Bov7/2003/G10P[11] | G10 | P[11] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M2 | A3 | N2 | T6 | E2 | H3 |
| RVA/Cow-wt/ZAF/1162/2012/G6P[11] | G6 | P[11] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M2 | A3 | N2 | T6 | E2 | H3 |
| RVA/Cow-wt/ZAF/Bov4/2003/G6P[5] | G6 | P[5] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M2 | A13 | N2 | T6 | E2 | H3 |
| RVA/Cow-wt/ZAF/Bov1/2009/G6P[5] | G6 | P[5] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M2 | A3 | N2 | T6 | E2 | H3 |
| RVA/Cow-wt/MOZ/MPT93/2016/G10P[11] | G10 V | P[11] III | VI | V | Distinct | VI | A11 | V | T6 (1) | XV | H3 (1) |
| RVA/Cow-wt/ZAF/MRC-DPRU457/2009/G10P[11] | G10 V | P[11] III | Distinct? | XII | XIV | X | A13 | XV | T6 (1) | XV | H3 (1) |
| RVA/Cow-wt/MOZ/MPT307/2016/G10P[11] | G10 V | P[11] III | X | XII | XIV | X | A13 | XV | T6 (1) | XV | H3 (1) |
| RVA/Cow-wt/ZAF/Bov7/2003/G10P[11] | G10 V | P[11] III | Distinct? | XII | XIV | X | A3 (1) | XIII | T6 (2) | XVIII | H3 (2) |
| RVA/Cow-wt/ZAF/1162/2012/G6P[11] | G6 V | P[11] III | X | XII | XIV | X | A3 (2) | XV | T6 (2) | XV | H3 (1) |
| RVA/Cow-wt/ZAF/Bov4/2003/G6P[5] | G6 IV | P[5] | Distinct? | XII | XIV | X | A13 | XIII | T6 (2) | XVIII | H3 (1) |
| RVA/Cow-wt/ZAF/Bov1/2009/G6P[5] | G6 IV | P[5] | Distinct? | XII | XIV | X | A3 (2) | XV | T6 (2) | XV | H3 (1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strydom, A.; Donato, C.M.; Nyaga, M.M.; Boene, S.S.; Peenze, I.; Mogotsi, M.T.; João, E.D.; Munlela, B.; Potgieter, A.C.; Seheri, M.L.; et al. Genetic Characterisation of South African and Mozambican Bovine Rotaviruses Reveals a Typical Bovine-like Artiodactyl Constellation Derived through Multiple Reassortment Events. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101308
Strydom A, Donato CM, Nyaga MM, Boene SS, Peenze I, Mogotsi MT, João ED, Munlela B, Potgieter AC, Seheri ML, et al. Genetic Characterisation of South African and Mozambican Bovine Rotaviruses Reveals a Typical Bovine-like Artiodactyl Constellation Derived through Multiple Reassortment Events. Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101308
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrydom, Amy, Celeste M. Donato, Martin M. Nyaga, Simone S. Boene, Ina Peenze, Milton T. Mogotsi, Eva D. João, Benilde Munlela, A. Christiaan Potgieter, Mapaseka L. Seheri, and et al. 2021. "Genetic Characterisation of South African and Mozambican Bovine Rotaviruses Reveals a Typical Bovine-like Artiodactyl Constellation Derived through Multiple Reassortment Events" Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101308
APA StyleStrydom, A., Donato, C. M., Nyaga, M. M., Boene, S. S., Peenze, I., Mogotsi, M. T., João, E. D., Munlela, B., Potgieter, A. C., Seheri, M. L., de Deus, N., & O’Neill, H. G. (2021). Genetic Characterisation of South African and Mozambican Bovine Rotaviruses Reveals a Typical Bovine-like Artiodactyl Constellation Derived through Multiple Reassortment Events. Pathogens, 10(10), 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101308








