Identity of Microfilariae Circulating in Dogs from Western and South-Western Romania in the Last Decade
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gabrielli, S.; Mangano, V.; Furzi, F.; Oliva, A.; Vita, S.; Poscia, R.; Fazii, P.; Di Paolo, J.; Marocco, R.; Mastroianni, C.; et al. Molecular Identification of New Cases of Human Dirofilariosis (Dirofilaria repens) in Italy. Pathogens 2021, 10, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otranto, D.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Brianti, E.; Traversa, D.; Petrić, D.; Genchi, C.; Capelli, G. Vector-borne helminths of dogs and humans in Europe. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Dirofilariosis in the Americas: A more virulent Dirofilaria immitis? Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, S.; Diakou, A.; Di Cesare, A.; Colombo, M.; Traversa, D. Canine and Feline Parasitology: Analogies, Differences, and Relevance for Human Health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e0026620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuca, L.; Vismarra, A.; Lebon, W.; Beugnet, F.; Morchon, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Cringoli, G.; Kramer, L.; Genchi, M. New insights into the biology, diagnosis and immune response to Dirofilaria repens in the canine host. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 277, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakou, A.; Kapantaidakis, E.; Tamvakis, A.; Giannakis, V.; Strus, N. Dirofilaria infections in dogs in different areas of Greece. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, G.; Genchi, C.; Baneth, G.; Bourdeau, P.; Brianti, E.; Cardoso, L.; Danesi, P.; Fuehrer, H.-P.; Giannelli, A.; Ionică, A.M.; et al. Recent advances on Dirofilaria repens in dogs and humans in Europe. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Overview on Dirofilaria immitis in the Americas, with notes on other filarial worms infecting dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 282, 109113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brianti, E.; Panarese, R.; Napoli, E.; De Benedetto, G.; Gaglio, G.; Bezerra-Santos, M.A.; Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Otranto, D. Dirofilaria immitis infection in the Pelagie archipelago: The southernmost hyperendemic focus in Europe. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Heartworm Society. Current Canine Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management of Heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) Infection in Dogs. 2020. Available online: https://d3ft8sckhnqim2.cloudfront.net/images/pdf/2020_AHS_Canine_Guidelines.pdf?1580934824 (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- ESCCAP. GL5: Control of Vector-Borne Diseases in Dogs and Cats, 3rd ed.; ESCCAP: Worcestershire, UK, 2019; Available online: https://www.esccap.org/page/GL5+Control+of+VectorBorne+Diseases+in+Dogs+and+Cats/29/ (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- Sonnberger, K.; Fuehrer, H.-P.; Sonnberger, B.; Leschnik, M. The Incidence of Dirofilaria immitis in Shelter Dogs and Mosquitoes in Austria. Pathogens 2021, 10, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H. The prevalence of Dirofilaria immitis and D. repens in the Old World. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 280, 108995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mircean, V.; Dumitrache, M.O.; Györke, A.; Pantchev, N.; Jodies, R.; Mihalca, A.; Cozma, V. Seroprevalence and Geographic Distribution of Dirofilaria immitis and Tick-Borne Infections (Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, and Ehrlichia canis) in Dogs from Romania. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciucă, L.; Musella, V.; Miron, L.D.; Maurelli, M.P.; Cringoli, G.; Bosco, A.; Rinaldi, L. Geographic distribution of canine heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) infection in stray dogs of eastern Romania. Geospat. Health 2016, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, D.; Silaghi, C.; Lescai, D.; Pfister, K. Epidemiological aspects on vector-borne infections in stray and pet dogs from Romania and Hungary with focus on Babesia spp. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 110, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionică, A.M.; Matei, I.A.; Mircean, V.; Dumitrache, M.O.; D’Amico, G.; Győrke, A.; Pantchev, N.; Annoscia, G.; Albrechtová, K.; Otranto, D.; et al. Current surveys on the prevalence and distribution of Dirofilaria spp. and Acanthocheilonema reconditum infections in dogs in Romania. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 114, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomazatos, A.; Cadar, D.; Török, E.; Maranda, I.; Horváth, C.; Keresztes, L.; Spinu, M.; Jansen, S.; Jöst, H.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; et al. Circulation of Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens in the Danube Delta Biosphere Reserve, Romania. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak, G.; Ionică, A.M.; Szasz, I.; Taulescu, M.; Mihalca, A.D. A case of inguinal hernia associated with atypical Dirofilaria repens infection in a dog. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuca, L.; Roman, C.; Prisco, F.; Miron, L.; Acatrinei, D.; Paciello, O.; Maurelli, M.P.; Vismarra, A.; Cringoli, G.; Rinaldi, L. First report of Dirofilaria repens infection in a microfilaraemic cat from Romania. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 22, 100497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pană, D.; Rădulescu, A.; Mitrea, I.L.; Ionita, M. First report on clinical feline heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) infection in Romania. Helminthologia 2020, 57, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionică, A.M.; Matei, I.A.; D’Amico, G.; Ababii, J.; Daskalaki, A.A.; Sándor, A.D.; Enache, D.V.; Gherman, C.M.; Mihalca, A.D. Filarioid infections in wild carnivores: A multispecies survey in Romania. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsarraf, M.; Levytska, V.; Mierzejewska, E.J.; Poliukhovych, V.; Rodo, A.; Alsarraf, M.; Kavalevich, D.; Dwużnik-Szarek, D.; Behnke, J.M.; Bajer, A. Emerging risk of Dirofilaria spp. infection in Northeastern Europe: High prevalence of Dirofilaria repens in sled dog kennels from the Baltic countries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panayotova-Pencheva, M.; Šnábel, V.; Dakova, V.; Čabanová, V.; Cavallero, S.; Trifonova, A.; Mirchev, R.; Hurníková, Z.; Vasilková, Z.; Miterpáková, M. Dirofilaria immitis in Bulgaria: The first genetic baseline data and an overview of the current status. Helminthologia 2020, 57, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, M.; Zuzana, H.; Daniela, V.; Lenka, B. Different epidemiological pattern of canine dirofilariosis in two neighboring countries in Central Europe—the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laidoudi, Y.; Otranto, D.; Stolowy, N.; Amrane, S.; Manoj, R.S.; Polette, L.; Watier-Grillot, S.; Mediannikov, O.; Davoust, B.; L’Ollivier, C. Human and Animal Dirofilariasis in Southeast of France. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakou, A.; Di Cesare, A.; Morelli, S.; Colombo, M.; Halos, L.; Simonato, G.; Tamvakis, A.; Beugnet, F.; Paoletti, B.; Traversa, D. Endoparasites and vector-borne pathogens in dogs from Greek islands: Pathogen distribution and zoonotic implications. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, R.; Mag, V.; Gyurkovszky, M.; Takács, N.; Vörös, K.; Solymosi, N. The current situation of canine dirofilariosis in Hungary. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 119, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Morelli, S.; Simonato, G.; Di Cesare, A.; Veronesi, F.; di Regalbono, A.F.; Grassi, L.; Russi, I.; Tiscar, P.; Morganti, G.; et al. Exposure to Major Vector-Borne Diseases in Dogs Subjected to Different Preventative Regimens in Endemic Areas of Italy. Pathogens 2021, 10, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruccelli, A.; Ferrara, G.; Iovane, G.; Schettini, R.; Ciarcia, R.; Caputo, V.; Pompameo, M.; Pagnini, U.; Montagnaro, S. Seroprevalence of Ehrlichia spp., Anaplasma spp., Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, and Dirofilaria immitis in Stray Dogs, from 2016 to 2019, in Southern Italy. Animals 2020, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, S.; Gori, F.; Colombo, M.; Traversa, D.; Sarrocco, G.; Simonato, G.; Nespeca, C.; Di Cesare, A.; di Regalbono, A.F.; Veronesi, F.; et al. Simultaneous Exposure to Angiostrongylus vasorum and Vector-Borne Pathogens in Dogs from Italy. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, S.; Stosic, M.Z.; Marcic, D.; Hernández, I.; Potkonjak, A.; Otasevic, S.; Ruzic, M.; Morchón, R. Seroepidemiological Study of Canine and Human Dirofilariasis in the Endemic Region of Northern Serbia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Morchón, R.; Costa-Rodríguez, N.; Matos, J.I.; Falcón-Cordón, Y.; Carretón, E. Current Distribution of Selected Vector-Borne Diseases in Dogs in Spain. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 564429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuehrer, H.-P.; Morelli, S.; Unterköfler, M.S.; Bajer, A.; Bakran-Lebl, K.; Dwużnik-Szarek, D.; Farkas, R.; Grandi, G.; Heddergott, M.; Jokelainen, P.; et al. Dirofilaria spp. and Angiostrongylus vasorum: Current Risk of Spreading in Central and Northern Europe. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satjawongvanit, H.; Phumee, A.; Tiawsirisup, S.; Sungpradit, S.; Brownell, N.; Siriyasatien, P.; Preativatanyou, K. Molecular Analysis of Canine Filaria and Its Wolbachia Endosymbionts in Domestic Dogs Collected from Two Animal University Hospitals in Bangkok Metropolitan Region, Thailand. Pathogens 2019, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loymek, S.; Phuakrod, A.; Zaelai, K.; Sripumkhai, W.; Vongjaroensanti, P.; Wongkamchai, S. Investigation on the Prevalence of Canine Microfilaremia in Thailand Using a Novel Microfluidic Device in Combination with Real-Time PCR. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidoudi, Y.; Marié, J.-L.; Tahir, D.; Watier-Grillot, S.; Mediannikov, O.; Davoust, B. Detection of Canine Vector-Borne Filariasis and Their Wolbachia Endosymbionts in French Guiana. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimal, S.; Adhikari, A.; Acharya, R.; Singh, D.K.; Joshi, N.P.; Shrestha, B.; Kaphle, K.; El-Dakhly, K.M.; Giannelli, A. Occurrence of Dirofilaria immitis in Stray Dogs from Nepal. Acta Parasitol. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, A.; Sharifi, I.; Aflatoonian, M.R.; Mostafavi, M.; Parizi, M.H.; Mashayekhi, J.; Mashayekhi, M.; Nikpour, S.; Bamorovat, M. Dirofilariosis caused by Dirofilaria immitis in the south of Kerman province, Iran. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 154, 104863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, S.; Braff, J.; Place, J.; Buch, J.; Dewage, B.G.; Knupp, A.; Beall, M. Canine infection with Dirofilaria immitis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Anaplasma spp., and Ehrlichia spp. in the United States, 2013–2019. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, D.; Anvari, D.; Narouei, E.; Narouei, E.; Daryani, A.; Daryani, A.; Sarvi, S.; Sarvi, S.; Moosazadeh, M.; Moosazadeh, M.; et al. The global status of Dirofilaria immitis in dogs: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on published articles. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 131, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panarese, R.; Iatta, R.; Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Szlosek, D.; Braff, J.; Liu, J.; Beugnet, F.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Beall, M.J.; Otranto, D. Comparison of Diagnostic Tools for the Detection of Dirofilaria immitis Infection in Dogs. Pathogens 2020, 9, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trancoso, T.A.L.; Lima, N.D.C.; Barbosa, A.S.; Leles, D.; Fonseca, A.B.M.; Labarthe, N.V.; Bastos, O.M.P.; Uchôa, C.M.A. Detection of Dirofilaria immitis using microscopic, serological and molecular techniques among dogs in Cabo Frio, RJ, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2020, 29, e017219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysmołek, M.E.; Klockiewicz, M.; Sobczak-Filipiak, M.; Długosz, E.; Wiśniewski, M. Case Studies of Severe Microfilaremia in Four Dogs Naturally Infected with Dirofilaria repens as the Primary Disease or a Disease Complicating Factor. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 577466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Venco, L.; Genchi, M. Guideline for the laboratory diagnosis of canine and feline Dirofilaria infections. In Mappe Parassitologighe 8, Dirofilaria Immitis and Dirofilaria Repens in Dog and Cat and Human Infection; Genchi, C., Rinaldi, L., Cringoli, G., Eds.; Rolando Editore: Salamanca, Spain, 2007; pp. 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, M.; Ciuca, L.; Vismarra, A.; Ciccone, E.; Cringoli, G.; Kramer, L.; Rinaldi, L. Evaluation of alternative reagents on the performance of the modified Knott’s test. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 298, 109555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnyder, M.; Deplazes, P. Cross-reactions of sera from dogs infected with Angiostrongylus vasorum in commercially available Dirofilaria immitis test kits. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, M.; Erdoğan, M. BMTW-Serological screening of canine heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) infections in Turkey. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2012, 125, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Lee, S.; Hayasaki, M.; Shiramizu, K.; Kim, D.; Cho, K. Seroprevalence of canine dirofilariosis in South Korea. Veter- Parasitol. 2003, 114, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lim, S.; Irwin, P.J.; Lee, S.; Oh, M.; Ahn, K.; Myung, B.; Shin, S. Comparison of selected canine vector-borne diseases between urban animal shelter and rural hunting dogs in Korea. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, L.; Silvestre-Ferreira, A.; Fontes-Sousa, A.; Balreira, A.; Morchón, R.; Carretón, E.; Vilhena, H.; Simón, F.; Montoya-Alonso, J. Seroprevalence of heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) in feline and canine hosts from central and northern Portugal. J. Helminthol. 2014, 89, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabuusu, R.M.; Stroup, D.F.; Pinckney, R.; Chriestmon, J.; Alexander, R.; Richards, C.; MacPherson, C. An analysis of time trends for canine heartworm disease in Grenada and its associated risk factors based on veterinary clinical pathology laboratory data base records between 2003 and 2015. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 179, 104989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, A.A.F.; Martinez, A.R.; Pinilla, J.C. Prevalence of Dirofilaria immitis in shelter dogs in Bucaramanga metropolitan area, Colombia. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 22, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traversa, D.; Di Cesare, A.; Conboy, G. Canine and feline cardiopulmonary parasitic nematodes in Europe: Emerging and underestimated. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laidoudi, Y.; Bedjaoui, S.; Medkour, H.; Latrofa, M.; Mekroud, A.; Bitam, I.; Davoust, B.; Otranto, D.; Mediannikov, O. Molecular Approach for the Diagnosis of Blood and Skin Canine Filarioids. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, M.; Guzel, M.; Koltas, I.; Demirkazik, M.; Aktas, H. Prevalence of Dirofilaria immitis in dogs from Hatay province, Turkey. J. Helminthol. 2009, 83, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, A.L.; Vieira, M.J.; Oliveira, J.; Simões, A.R.; Diez-Baños, P.; Gestal, J. Prevalence of canine heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) disease in dogs of central Portugal. Parasite 2014, 21, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gioia, G.; Lecová, L.; Genchi, M.; Ferri, E.; Genchi, C.; Mortarino, M. Highly sensitive multiplex PCR for simultaneous detection and discrimination of Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens in canine peripheral blood. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 172, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
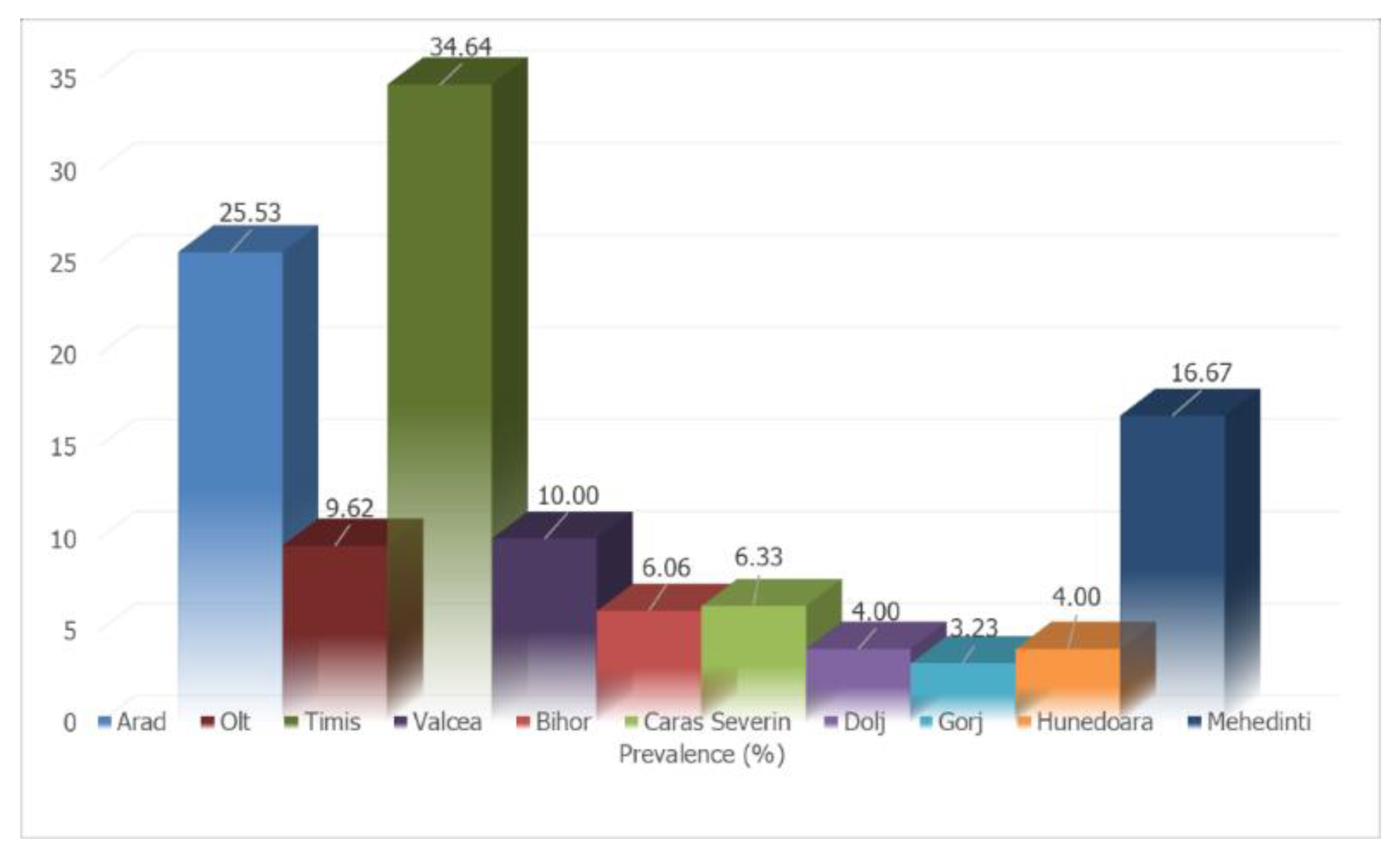
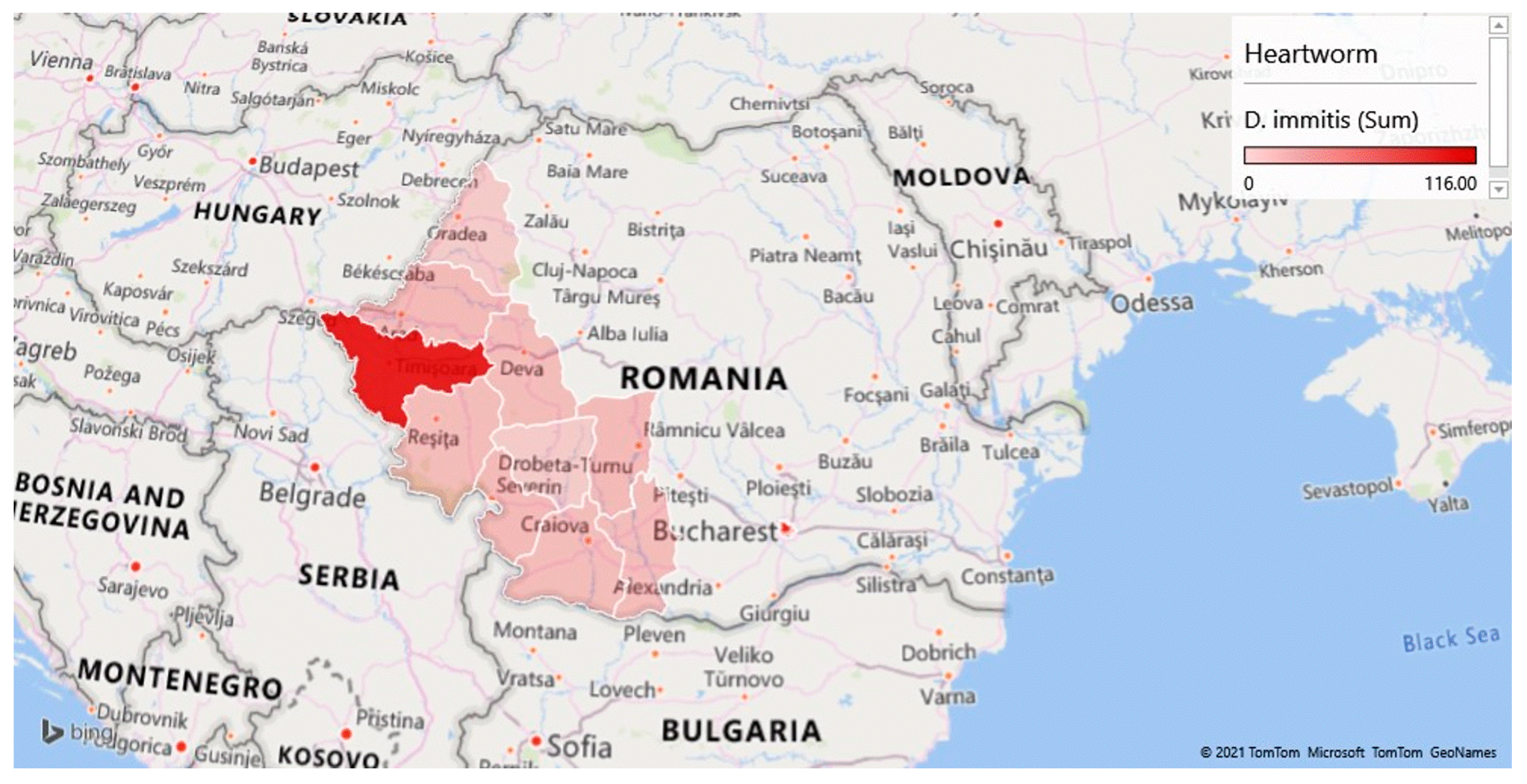

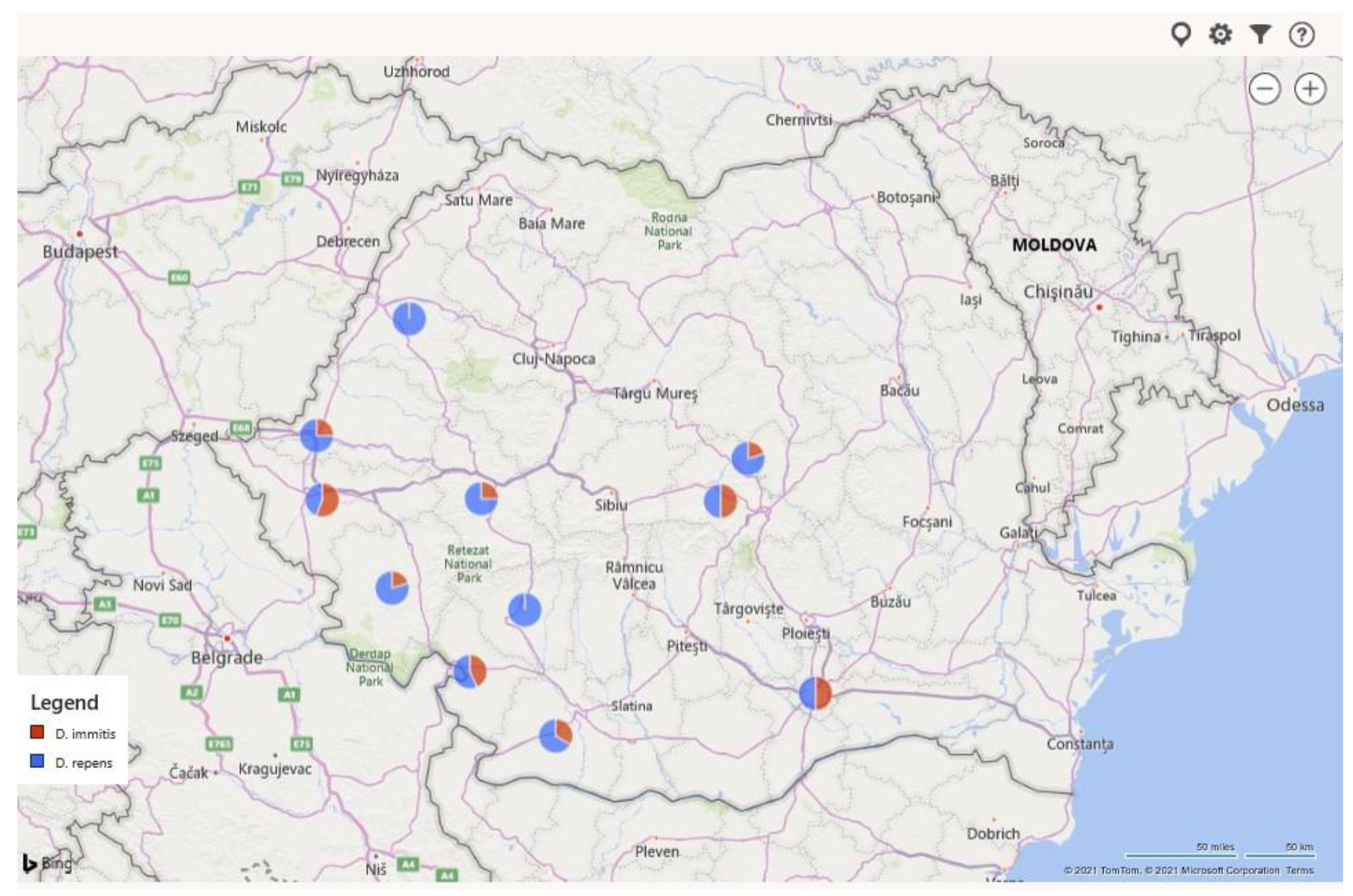
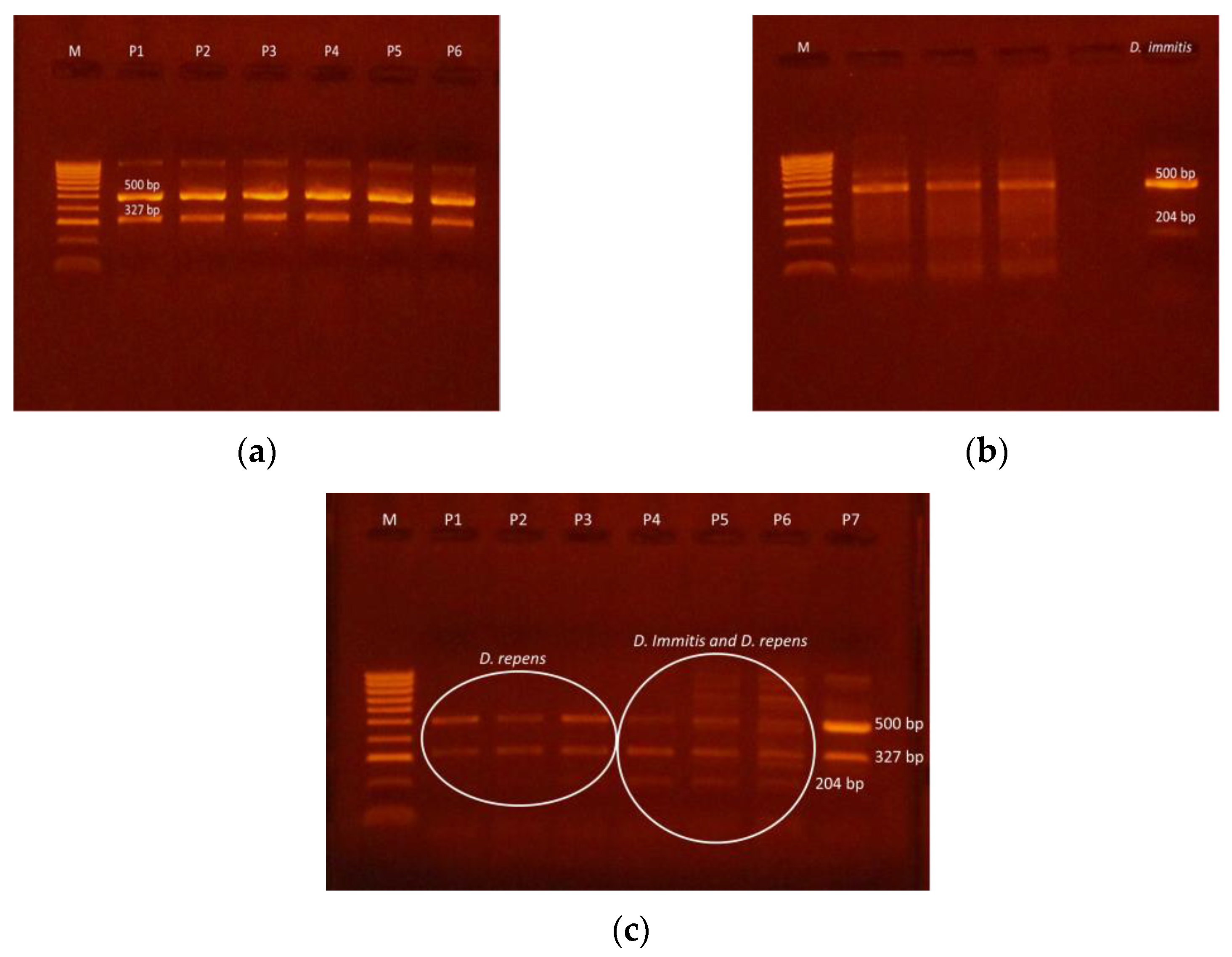

| CRT. NO. | COUNTIES | NO. SAMPLES | NO. POSITIVE | PREVALENCE (%) | D. immitis (NO.) | D. repens (NO.) | A. reconditum (NO.) | D. immitis + D. repens (NO.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arad | 47 | 12 | 25.53 | 3 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | Bihor | 33 | 2 | 6.06 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | Caras Severin | 79 | 5 | 6.33 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | Dolj | 75 | 3 | 4.00 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | Gorj | 62 | 2 | 3.23 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | Hunedoara | 100 | 4 | 4.00 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | Mehedinti | 42 | 7 | 16.67 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | Olt | 52 | 5 | 9.62 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | Timis | 537 | 186 | 34.64 | 93 | 69 | 1 | 23 |
| 10 | Valcea | 60 | 6 | 10.00 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 11 | Bucuresti | 1 | 1 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| TOTAL | 1088 | 233 | 21.42 | 106 | 102 | 1 | 24 | |
| Epidemiological Data | Positive | Negative | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | % | NO. | |
| Age | |||
| ≤1 years (n = 123) | 13 | 10.57 | 110 |
| 1 to ≤3 years (n = 238) | 54 | 22.69 | 184 |
| 3 to ≤6 years (n = 214) | 71 | 33.18 | 143 |
| >6 years (n= 202) | 65 | 32.18 | 137 |
| NA * (n = 311) | 30 | 9.65 | 281 |
| Gender | |||
| Female (n = 371) | 82 | 22.10 | 289 |
| Male (n = 436) | 151 | 34.63 | 285 |
| NA (n= 281) | 0 | 0.00 | 281 |
| Breed | |||
| Purebreed (n = 276) | 88 | 31.88 | 188 |
| Crossbreed (n = 531) | 145 | 27.31 | 386 |
| NA (n = 281) | 0 | 0.00 | 281 |
| Habitat | |||
| Urban (n = 727) | 126 | 17.33 | 601 |
| Rural (n = 361) | 107 | 29.64 | 254 |
| Owner/shelter | |||
| owner (n = 1028) | 173 | 16.83 | 855 |
| shelter (n = 60) | 60 | 100.00 | 0 |
| Total | 233 | 21.42 | 855 |
| 1088 | |||
| Epidemiological Risk Factors | Compared Groups | p-Value | p-Value Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ≤1 year vs. 1 to ≤3 years | 0.0044 | very statistically significant |
| ≤1 year vs. 3 to ≤6 years | 0.0001 | highly statistically significant | |
| ≤1 year vs. >6 years | 0.0001 | highly statistically significant | |
| 1 to ≤3 years vs. 3 to ≤6 years | 0.0153 | statistically significant | |
| 1 to ≤3 years vs. >6 years | 0.0311 | statistically significant | |
| Gender | female vs. male | 0.0001 | highly statistically significant |
| Breed | purebred vs. crossbreed | 0.1903 | not statistically significant |
| Habitat | urban vs. rural | 0.0001 | highly statistically significant |
| Owner/shelter | owner vs. shelter | 0.0001 | highly statistically significant |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giubega, S.; Imre, M.; Ilie, M.S.; Imre, K.; Luca, I.; Florea, T.; Dărăbuș, G.; Morariu, S. Identity of Microfilariae Circulating in Dogs from Western and South-Western Romania in the Last Decade. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111400
Giubega S, Imre M, Ilie MS, Imre K, Luca I, Florea T, Dărăbuș G, Morariu S. Identity of Microfilariae Circulating in Dogs from Western and South-Western Romania in the Last Decade. Pathogens. 2021; 10(11):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111400
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiubega, Simona, Mirela Imre, Marius Stelian Ilie, Kálmán Imre, Iasmina Luca, Tiana Florea, Gheorghe Dărăbuș, and Sorin Morariu. 2021. "Identity of Microfilariae Circulating in Dogs from Western and South-Western Romania in the Last Decade" Pathogens 10, no. 11: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111400
APA StyleGiubega, S., Imre, M., Ilie, M. S., Imre, K., Luca, I., Florea, T., Dărăbuș, G., & Morariu, S. (2021). Identity of Microfilariae Circulating in Dogs from Western and South-Western Romania in the Last Decade. Pathogens, 10(11), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111400











