Application of TaqMan Real-Time PCR for Detecting ‘Candidatus Arsenophonus Phytopathogenicus’ Infection in Sugar Beet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Primers and Probes for qPCR
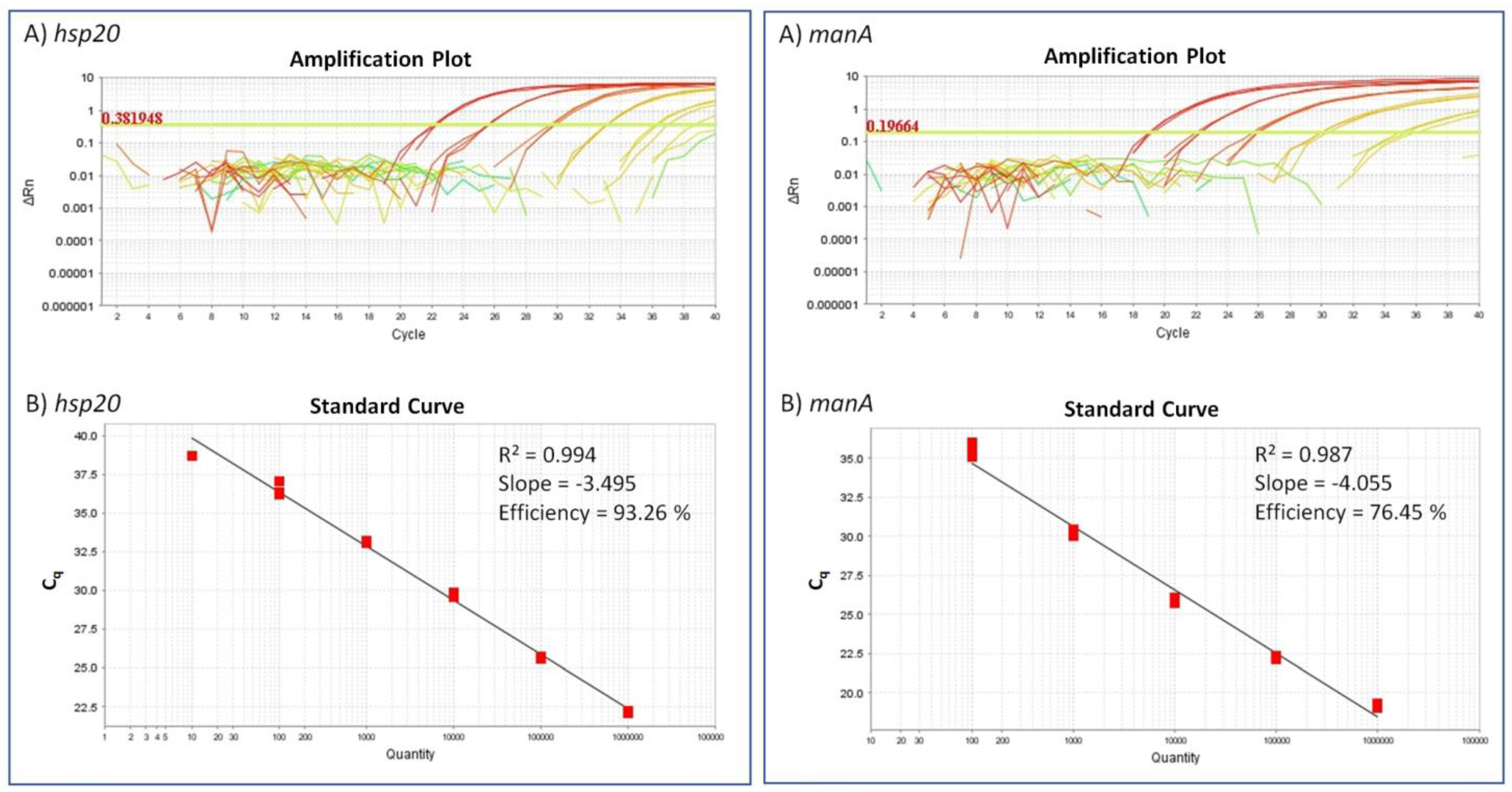
2.2. Detection Limit for the ‘Ca. A. Phytopathogenicus’-Specific TaqMan Assay
2.3. TaqMan qPCR versus End-Point PCR
2.4. Sampling Sites and Verification of the Amplification Products
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. DNA Templates
4.3. Gene Target Selection and Primer Design for the TaqMan qPCR Assay
4.4. TaqMan Assay Conditions
4.5. Quantification and Evaluation of TaqMan qPCRs, Using gBlocks
4.6. End-Point PCR and Gel Electrophoresis
4.7. Verification of Amplification Products
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pfitzer, R.; Schrameyer, K.; Voegele, R.T.; Maier, J.; Lang, C.; Varrelmann, M. Ursachen und Auswirkungen des Auftretens von “Syndrome des basses richesses” in deutschen Zuckerrübenanbaugebieten. Sugar Ind. 2020, 145, 234–244. [Google Scholar]
- Bressan, A.; Sémétey, O.; Nusillard, B.; Clair, D.; Boudon-Padieu, E. Insect vectors (Hemiptera: Cixiidae) and pathogens associated with the disease syndrome “basses richesses” of sugar beet in France. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gatineau, F.; Jacob, N.; Vautrin, S.; Larrue, J.; Lherminier, J.; Richard-Molard, M.; Boudon-Padieu, E. Association with the syndrome “basses richesses” of sugar beet of a phytoplasma and a bacterium-like organism transmitted by a Pentastiridius sp. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sémétey, O.; Gatineau, F.; Bressan, A.; Boudon-Padieu, E. Characterization of a γ-3 proteobacteria responsible for the syndrome “basses richesses” of sugar beet transmitted by Pentastiridius sp. (Hemiptera, Cixiidae). Phytopathology 2007, 97, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bressan, A.; Terlizzi, F.; Credi, R. Independent Origins of Vectored Plant Pathogenic Bacteria from Arthropod-Associated Arsenophonus Endosymbionts. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatineau, F.; Larrue, J.; Clair, D.; Lorton, F.; Richard-Molard, M.; Boudon-Padieu, E. A new natural planthopper vector of stolbur phytoplasma in the genus Pentastiridius (Hemiptera: Cixiidae). Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2001, 107, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sémétey, O.; Bressan, A.; Richard-Molard, M.; Boudon-Padieu, E. Monitoring of proteobacteria and phytoplasma in sugar beets naturally or experimentally affected by the disease syndrome “Basses richesses”. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 117, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, A.; Sémétey, O.; Nusillard, B.; Boudon-Padieu, E. The syndrome “basses richesses” of sugar beet in France is associated with different pathogen types and insect vectors. Bull. Insectology 2007, 60, 395–396. [Google Scholar]
- Ćurčić, Ž.; Kosovac, A.; Stepanović, J.; Rekanović, E.; Kube, M.; Duduk, B. Multilocus Genotyping of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ Associated with Rubbery Taproot Disease of Sugar Beet in the Pannonian Plain. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zreik, L.; Bové, J.M.; Garnier, M. Phylogenetic characterization of the bacterium-like organism associated with marginal chlorosis of strawberry and proposition of a Candidatus taxon for the organism, ‘Candidatus Phlomobacter fragariae’. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sémétey, O.; Bressan, A.; Gatineau, F.; Boudon-Padieu, E. Development of a specific assay using RISA for detection of the bacterial agent of “basses richesses” syndrome of sugar beet and confirmation of a Pentastiridius sp. (Fulgoromopha, Cixiidae) as the economic vector. Plant Pathol. 2007, 56, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salar, P.; Sémétey, O.; Danet, J.-L.; Boudon-Padieu, E.; Foissac, X. ‘Candidatus Phlomobacter fragariae’ and the proteobacterium associated with the low sugar content syndrome of sugar beet are related to bacteria of the arsenophonus clade detected in hemipteran insects. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 126, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, R.; Menzel, W.; Lachmann, C.; Varrelmann, M. New insights into virus yellows distribution in Europe and effects of beet yellows virus, beet mild yellowing virus, and beet chlorosis virus on sugar beet yield following field inoculation. Plant Pathol. 2021, 70, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, N.M.; Nicolaisen, M.; Hansen, M.; Schulz, A. Distribution of phytoplasmas in infected plants as revealed by real-time PCR and bioimaging. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, B.; Kätzel, R.; Kube, M. Widespread occurrence of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma ulmi’ in elm species in Germany. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forootan, A.; Sjöback, R.; Björkman, J.; Sjögreen, B.; Linz, L.; Kubista, M. Methods to determine limit of detection and limit of quantification in quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2017, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, J.; Potoczniak, M.J.; Tobe, S.S. Using synthetic oligonucleotides as standards in probe-based qPCR. Biotechniques 2018, 64, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonants, P.; Griekspoor, Y.; Houwers, I.; Krijger, M.; van der Zouwen, P.; van der Lee, T.A.J.; van der Wolf, J. Development and evaluation of a triplex taqman assay and next-generation sequence analysis for improved detection of Xylella in plant material. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. Isolation of Plant DNA from Fresh Tissue. Focus 1990, 12, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Amplicon Size | Oligonucleotide | Length | Sequence (5′–3′) | Labelling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca. P. phytopathogenicus | 90 | SBR_hsp20_F | 21 | CACTTTTGCCGCTGATAGTCA | |
| SBR_hsp20_R | 20 | TGGAACTCACAGTAGCGGTT | |||
| SBR_hsp20_P | 23 | AACTCCTGTTGTTTATAACCAGG | 6-FAM/BHQ-1 | ||
| Ca. P. phytopathogenicus | 116 | SBR_manA_F | 20 | CAACCAGGTGAAGCGATGTT | |
| SBR_manA_R | 20 | TTGTTAGTTAATCCCGCGCG | |||
| SBR_manA_P | 20 | TCTCTATGCCAGAACTCCGC | 6-FAM/BHQ-1 | ||
| B. vulgaris | 96 | BV_nad5_F | 20 | TGAATGACGAGTCGGACCAA | |
| BV_nad5_R | 20 | TCGGAGAGCACTGAATTCGA | |||
| BV_nad5_P | 20 | TACCCTTGCGTGCAATGATG | HEX/BHQ-1 |
| Copy Number | Cq Values of the hsp20-Target a | Cq Values of the manA-Target a |
|---|---|---|
| 1 × 106 | 22.2 (±0.07) | 19.2 (±0.12) |
| 1 × 105 | 25.7 (±0.05) | 22.2 (±0.10) |
| 1 × 104 | 29.7 (±0.12) | 25.9 (±0.15) |
| 1 × 103 | 33.1 (±0.04) | 30.1 (±0.19) |
| 1 × 102 | 36.5 (±0.37) | 35.5 (±0.41) |
| 1 × 101 | not detected (38.7 b) | not detected |
| 1 × 100 | not detected | not detected |
| Sampling Site | Variety | No of Samples | manA-qPCR * | hsp20-qPCR * | Coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gundelsheim (BW) | Eucalyptus | 7 | 29 (28–32) | 29 (26–31) | 49.264944, 9.160611 |
| Bondorf (BW) | Alcedo | 3 | not detected | not detected | 48.528556, 8.821111 |
| Wendershausen (HE) | LUNELLA KWS | 16 | not detected | not detected | 51.323417, 9.882556 |
| Massenbach (BW) | BTS 440 | 7 | 32 (29–38) | 30 (28–33) | 49.177556, 9.063472 |
| Gemmingen (BW) | Racoon | 5 | 31 (27–34) | 30 (26–32) | 49.159167, 9.003556 |
| Fürfeld (BW) | Raison | 7 | 28 (27–30) | 28 (27–29) | 49.212389, 9.052028 |
| Bickenbach (HE) | BTS 8750 N | 5 | 30 (29–32) | 30 (28–30) | 49.760708, 8.602995 |
| Ochsenfurt, Gollhofen (BY) | LUNELLA KWS | 6 | 28 (27–29) | 28 (27–29) | 49.577722, 10.184778 |
| Heddesheim (BW) | BTS7300 | 6 | 27 (26–29) | 28 (25–29) | 49.509024, 8.583888 |
| Ochsenfurt, Rodheim (BY) | BTS 440 | 6 | 30 (28–33) | 30 (28–33) | 49.587222, 10.150194 |
| Deutschhof (Südpfalz) (RP) | N/A | 6 | 28 (25–30) | 28 (26–29) | 49.086707, 8.020107 |
| Welsau (SN) | ADVENA KWS | 4 | 30 (28–32) | 29 (28–32) | 51.577121, 12.950829 |
| Target | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| hsp20 | 5′-GTTTCACTTTTGCCGCTGATAGTCAGCTTATTATTCAATACTGATATATCTAACTCCTGTTGTTTATAACCAGGAACCGCTACTGTGAGTTCCAGATTTTCTTTATCTTTTTGGTATAAATTGTA-3′ |
| manA | 5′-GAATTACAACCAGGTGAAGCGATGTTTCTCTATGCCAGAACTCCGCATGCTTATATTGAAGGTGTTGGTTTAGAAGTAATGGCCAATTCTGACAATGTACTGCGCGCGGGATTAACTAACAAACA-3′. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zübert, C.; Kube, M. Application of TaqMan Real-Time PCR for Detecting ‘Candidatus Arsenophonus Phytopathogenicus’ Infection in Sugar Beet. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111466
Zübert C, Kube M. Application of TaqMan Real-Time PCR for Detecting ‘Candidatus Arsenophonus Phytopathogenicus’ Infection in Sugar Beet. Pathogens. 2021; 10(11):1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111466
Chicago/Turabian StyleZübert, Christina, and Michael Kube. 2021. "Application of TaqMan Real-Time PCR for Detecting ‘Candidatus Arsenophonus Phytopathogenicus’ Infection in Sugar Beet" Pathogens 10, no. 11: 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111466
APA StyleZübert, C., & Kube, M. (2021). Application of TaqMan Real-Time PCR for Detecting ‘Candidatus Arsenophonus Phytopathogenicus’ Infection in Sugar Beet. Pathogens, 10(11), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111466






