Serological Evidence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Semi-Domesticated Eurasian Tundra Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Norway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Anti-HEV Seroprevalence in Semi-domesticated Reindeer
2.2. Seroprevalence of Previously Examined Viruses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Sampling
4.2. Serology
4.3. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamar, N.; Izopet, J.; Pavio, N.; Aggarwal, R.; Labrique, A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Dalton, H.R. Hepatitis E virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Izopet, J.; Nicot, F.; Simmonds, P.; Jameel, S.; Meng, X.-J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; Van Der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; et al. Update: Proposed reference sequences for subtypes of hepatitis E virus (species Orthohepevirus A). J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, F.; Dimeglio, C.; Migueres, M.; Jeanne, N.; Latour, J.; Abravanel, F.; Ranger, N.; Harter, A.; Dubois, M.; Lameiras, S.; et al. Classification of the Zoonotic Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 Into Distinct Subgenotypes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 634430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatits, T.; Schulze zur Wiesch, J.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Lohse, A.W.; Pischke, S. The Clinical Perspective on Hepatitis E. Viruses 2019, 11, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tei, S.; Kitajima, N.; Takahashi, K.; Mishiro, S. Zoonotic transmission of hepatitis E virus from deer to human beings. Lancet 2003, 362, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Tan, B.H.; Teo, E.C.; Lim, S.G.; Dan, Y.Y.; Wee, A.; Aw, P.P.; Zhu, Y.; Hibberd, M.L.; Tan, C.K.; et al. Chronic Infection with Camelid Hepatitis E Virus in a Liver Transplant Recipient Who Regularly Consumes Camel Meat and Milk. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 355–357.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maunula, L.; Kaupke, A.; Vasickova, P.; Söderberg, K.; Kozyra, I.; Lazic, S.; van der Poel, W.H.; Bouwknegt, M.; Rutjes, S.; Willems, K.A.; et al. Tracing enteric viruses in the European berry fruit supply chain. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 167, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, Z.; Crossan, C.; Craft, J.; Scobie, L. First Report of the Presence of Hepatitis E Virus in Scottish-Harvested Shellfish Purchased at Retail Level. Food Env. Virol. 2018, 10, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terio, V.; Bottaro, M.; Pavoni, E.; Losio, M.N.; Serraino, A.; Giacometti, F.; Martella, V.; Mottola, A.; Di Pinto, A.; Tantillo, G. Occurrence of hepatitis A and E and norovirus GI and GII in ready-to-eat vegetables in Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 249, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, P.E.; Ijaz, S.; Brailsford, S.R.; Brett, R.; Dicks, S.; Haywood, B.; Kennedy, I.; Kitchen, A.; Patel, P.; Poh, J.; et al. Hepatitis E virus in blood components: A prevalence and transmission study in southeast England. Lancet 2014, 384, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivero-Juarez, A.; Aguado, R.; Lopez-Lopez, P.; Sanchez-Frias, M.; Frias, M.; Briceño, J.; de la Mata, M.; Torre-Cisneros, J.; Rivero, A. Prevalence of hepatitis E virus infection in liver donors in Spain. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1218–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bigna, J.J.; Modiyinji, A.F.; Nansseu, J.R.; Amougou, M.A.; Nola, M.; Kenmoe, S.; Temfack, E.; Njouom, R. Burden of hepatitis E virus infection in pregnancy and maternofoetal outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Wu, S.; Cai, J.; Zhang, A.J.; Leung, K.H.; Chung, T.W.; Chan, J.F.W.; Chan, W.M.; Teng, J.L.L.; et al. Rat Hepatitis E Virus as Cause of Persistent Hepatitis after Liver Transplant. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andonov, A.; Robbins, M.; Borlang, J.; Cao, J.; Hatchette, T.; Stueck, A.; Deschaumbault, Y.; Murnaghan, K.; Varga, J.; Johnston, B. Rat Hepatitis E Virus Linked to Severe Acute Hepatitis in an Immunocompetent Patient. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.; Yip, C.C.; Wu, S.; Chew, N.F.; Leung, K.H.; Chan, J.F.; Zhao, P.S.; Chan, W.M.; Poon, R.W.; Tsoi, H.W.; et al. Transmission of Rat Hepatitis E Virus Infection to Humans in Hong Kong: A Clinical and Epidemiological Analysis. Hepatology 2021, 73, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, J.; Wehmeyer, M.H.; Pischke, S. Acute Hepatitis E: Two Sides of the Same Coin. Viruses 2016, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lhomme, S.; Marion, O.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Kamar, N. Clinical Manifestations, Pathogenesis and Treatment of Hepatitis E Virus Infections. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamar, N.; Rostaing, L.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J. How Should Hepatitis E Virus Infection Be Defined in Organ-Transplant Recipients? Arab. Archaeol. Epigr. 2013, 13, 1935–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, H.R.; van Eijk, J.J.J.; Cintas, P.; Madden, R.G.; Jones, C.; Webb, G.W.; Norton, B.; Pique, J.; Lutgens, S.; Devooght-Johnson, N.; et al. Hepatitis E virus infection and acute non-traumatic neurological injury: A prospective multicentre study. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xiang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yao, Y.; Bortolanza, M.; Cao, H.; Li, L. Extrahepatic manifestations related to hepatitis E virus infection and their triggering mechanisms. J. Infect. 2021, 83, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinall, E.J.; Couturier, E.; Faber, M.; Said, B.; Ijaz, S.; Tavoschi, L.; Takkinen, J.; Adlhoch, C. On Behalf of the Country Experts. Hepatitis E virus infection in Europe: Surveillance and descriptive epidemiology of confirmed cases, 2005 to 2015. Euro Surveill. 2017, 22, 30561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bura, M.; Łagiedo-Żelazowska, M.; Michalak, M.; Sikora, J.; Mozer-Lisewska, I. Comparative Seroprevalence of Hepatitis A and E Viruses in Blood Donors from Wielkopolska Region, West-Central Poland. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lange, H.; Øverbø, J.; Borgen, K.; Dudman, S.; Hoddevik, G.; Urdahl, A.M.; Vold, L.; Sjurseth, S.K. Hepatitis E in Norway: Seroprevalence in humans and swine. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olsøy, I.B.; Henriksen, S.; Weissbach, F.H.; Larsen, M.; Borgen, K.; Abravanel, F.; Kamar, N.; Paulssen, E.J.; Hirsch, H.H.; Rinaldo, C.H. Seroprevalence of hepatitis E virus (HEV) in a general adult population in Northern Norway: The Tromsø study. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 208, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartl, J.; Otto, B.; Madden, R.G.; Webb, G.; Woolson, K.L.; Kriston, L.; Vettorazzi, E.; Lohse, A.W.; Dalton, H.R.; Pischke, S. Hepatitis E Seroprevalence in Europe: A Meta-Analysis. Viruses 2016, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, A.; Lin, J.; Magnius, L.; Karlsson, M.; Belák, S.; Widén, F.; Norder, H. Markers for Ongoing or Previous Hepatitis E Virus Infection Are as Common in Wild Ungulates as in Humans in Sweden. Viruses 2016, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sacristán, C.; Madslien, K.; Sacristán, I.; Klevar, S.; das Neves, C.G. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Moose (Alces alces), Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus), Red Deer (Cervus elaphus), Roe Deer (Capreolus capreolus), and Muskoxen (Ovibos moschatus) from Norway. Viruses 2021, 13, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukinova, O.S.; Kyuregyan, K.K.; Karlsen, A.A.; Potemkin, I.A.; Kichatova, V.S.; Semenov, S.I.; Stepanov, K.M.; Rumyantseva, T.D.; Mikhailov, M.I. Serological Evidence of Hepatitis E Virus Circulation Among Reindeer and Reindeer Herders. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021, 21, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hætta, L.B. Ressursregnskap for Reindriftsnæringen Reindriftsåret 1. april 2019–31. mars 2020; (Report nr 43/2020 10.12.2020); Retrived from Research on Landbruksdirektoratet.no Website. Available online: https://www.landbruksdirektoratet.no/nb/filarkiv/rapporter/Ressursregnskapet%20for%20reindriftsn%C3%A6ringen_2019-2020_ny%20versjon.pdf/_/attachment/inline/e0377ef7-bc0e-4538-b294-0b238f41a57e:7085e4f9664f4d9b6c4e028cb5c5659581c7c982/Ressursregnskapet%20for%20reindriftsn%C3%A6ringen_2019-2020_ny%20versjon.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2021).
- Riseth, J.Å.; Tømmervik, H.; Forbes, B.C. Sustainable and Resilient Reindeer Herding. In Reindeer and Caribou—Health and Disease; Tryland, M., Kutz, S., Eds.; CRC Press—Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 23–43. [Google Scholar]
- Tryland, M.; Romano, J.S.; Nymo, I.H.; Breines, E.M.; Murguzur, F.J.A.; Kjenstad, O.C.; Li, H.; Cunha, C.W. A Screening for Virus Infections in Eight Herds of Semi-domesticated Eurasian Tundra Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Norway, 2013–2018. Front. Veter Sci. 2021, 8, 707787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, M.; Cortés, R.; Pina, S.; Peralta, B.; Allepuz, A.; Cortey, M.; Casal, J.; Martín, M. Longitudinal study of hepatitis E virus infection in Spanish farrow-to-finish swine herds. Vet Microbiol. 2011, 148, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-N.; Lin, Q.-X.; Li, S.-M.; Xie, K.-P.; Hou, J.; Chen, R. Hepatitis E virus re-infection accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma development and relapse in a patient with liver cirrhosis: A case report and review of literature. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, M.S.; Walimbe, A.M.; Arankalle, V.A. Retrospective serological analysis of hepatitis E patients: A long-term follow-up study. J. Viral Hepatol. 1999, 6, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krain, L.J.; Nelson, K.E.; Labrique, A.B. Host Immune Status and Response to Hepatitis E Virus Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 139–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jolles, A.E.; Beechler, B.R.; Dolan, B.P. Beyond mice and men: Environmental change, immunity and infections in wild ungulates. Parasite Immunol. 2015, 37, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Fons, F.; Vidal, D.; Vicente, J.; Acevedo, P.; Fernández-de-Mera, I.G.; Montoro, V.; Gortázar, C. Epidemiological risk factors of Aujeszk™ s disease in wild boars (Sus scrofa) and domestic pigs in Spain. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2008, 54, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meester, M.; Tobias, T.J.; Bouwknegt, M.; Kusters, N.E.; Stegeman, J.A.; van der Poel, W.H.M. Infection dynamics and persistence of hepatitis E virus on pig farms—A review. Porc. Health Manag. 2021, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbur, P.G.; Kasorndorkbua, C.; Gilbert, C.; Guenette, D.; Potters, M.B.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U.; Toth, T.E.; Meng, X.J. Comparative Pathogenesis of Infection of Pigs with Hepatitis E Viruses Recovered from a Pig and a Human. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anheyer-Behmenburg, H.E.; Szabo, K.; Schotte, U.; Binder, A.; Klein, G.; Johne, R. Hepatitis E Virus in Wild Boars and Spillover Infection in Red and Roe Deer, Germany, 2013–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boadella, M. Hepatitis E in wild ungulates: A review. Small Rumin. Res. 2015, 128, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøntvedt, C.A.; Madslien, K.; Nordstoga, A.; Hamnes, I.S.; Bergsjø, B.; Urdahl, A.M.; Slettemeås, J.S.; Norström, M.; Danielsen, A.V.; Welde, H.; et al. Surveillance of Wild Boar Health in Norway—Results from 2018 and 2019; Contract No.: Report 14–2020; Norwegian Veterinary Institute: Oslo, Norway, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Niendorf, S.; Harms, D.; Hellendahl, K.; Heuser, E.; Böttcher, S.; Jacobsen, S.; Bock, C.-T.; Ulrich, R. Presence and Diversity of Different Enteric Viruses in Wild Norway Rats (Rattus norvegicus). Viruses 2021, 13, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Hilgensloh, L.; Voigt, U.; Marklewitz, M.; Siebert, U.; Drosten, C.; Drexler, J.F. Hepatitis E Virus Infection in European Brown Hares, Germany, 2007–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1233–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnaud, E.; Rogée, S.; Garry, P.; Rose, N.; Pavio, N. Thermal Inactivation of Infectious Hepatitis E Virus in Experimentally Contaminated Food. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5153–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mrzljak, A.; Balen, I.; Barbic, L.; Ilic, M.; Vilibic-Cavlek, T. Hepatitis E virus in professionally exposed: A reason for concern? World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutjes, S.A.; Lodder-Verschoor, F.; Lodder, W.J.; van der Giessen, J.; Reesink, H.; Bouwknegt, M.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Seroprevalence and molecular detection of hepatitis E virus in wild boar and red deer in The Netherlands. J. Virol Methods. 2010, 168, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiry, D.; Mauroy, A.; Saegerman, C.; Licoppe, A.; Fett, T.; Thomas, I.; Brochier, B.; Thiry, E.; Linden, A. Belgian Wildlife as Potential Zoonotic Reservoir of Hepatitis E Virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RCoreTeam. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria, 2018. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 25 September 2021).
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: AnRPackage for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
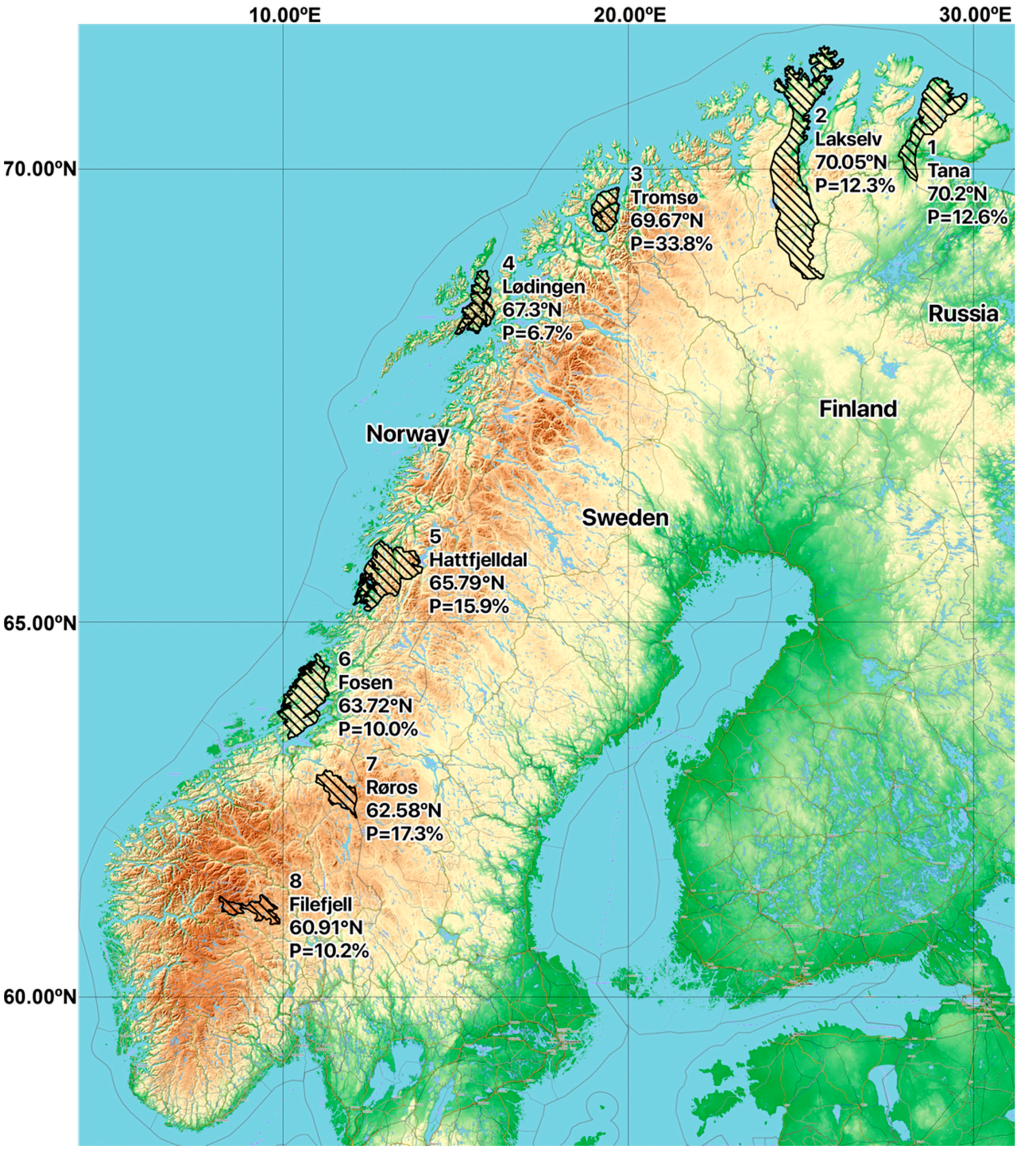

| Location of Herd | Adults | Calves | Seropositive Animals (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Females | Males | Females | Males | ||
| 1. Tana | 10/65 | 0/1 | 1/19 | 1/10 | 12/95; 12.6% |
| 2. Lakselv | 5/33 | 1/5 | 1/11 | 0/8 | 7/57; 12.3% |
| 3. Tromsø | 5/12 | 0/0 | 5/23 | 13/33 | 23/68; 33.8% |
| 4. Lødingen | 1/15 | 0/2 | 0/2 | 1/11 | 2/30; 6.7% |
| 5. Hattfjelldal | 6/26 | 2/3 | 2/19 | 3/34 | 13/82; 15.9% |
| 6. Fosen | 4/24 | 0/6 | 1/4 | 0/16 | 5/50; 10.0% |
| 7. Røros | 7/31 | 1/5 | 3/21 | 2/18 | 13/75; 17.3% |
| 8. Filefjell | 1/14 | 3/14 | 1/16 | 1/15 | 6/59; 10.2% |
| Total | 39/220; 17.7% | 7/36; 19.4% | 14/117; 12.0% | 21/143; 14.7% | 81/516; 15.7% |
| 46/256; 18.0% | 35/260; 13.5% | ||||
| Year of Sampling | Number of Animals Included | Seropositive Animals (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 177 | 30 (16.9%) |
| 2014 | 124 | 16 (12.9%) |
| 2015 | 115 | 19 (16.5%) |
| 2016 | 60 | 9 (15.0%) |
| 2017 | 40 | 7 (17.5%) |
| Total | 516 | 81 (15.7%) |
| Herd | In HEV Seronegative Animals | In HEV Seropositive Animals | Fold in HEV Seropositive/ Seronegative Animals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pestivirus seropositive n = 89 (5 herds) | Tana n = 95 | 12/83 (14.5%) | 2/12 (16.7%) | 1.2 |
| Tromsø n = 68 | 2/45 (4.4%) | 4/23 (17.4%) | 4.0 | |
| Lødingen n = 30 | 3/28 (10.7%) | 0/2 | - | |
| Hattfjelldal n = 82 | 26/69 (37.7%) | 11/13 (84.6%) | 2.2 | |
| Røros n = 75 | 24/62 (38.7%) | 5/13 (38.5%) | 1.0 | |
| TOTAL n = 350 | 67/287 (23.3%) | 22/63 (35.0%) | 1.5 | |
| Alpha-herpesvirus seropositive n = 221 (All 8 herds) | Tana n = 95 | 49/83 (59%) | 10/12 (83.3%) | 1.4 |
| Lakselv n = 57 | 26/50 (52%) | 4/7 (57.1%) | 1.1 | |
| Tromsø n = 68 | 7/45 (15.6%) | 7/23 (30.4%) | 1.9 | |
| Lødingen n = 30 | 11/28 (39.3%) | 0/2 | - | |
| Hattfjelldal n = 82 | 22/69 (31.9%) | 7/13 (53.8%) | 1.7 | |
| Fosen n = 50 | 21/45 (46.7%) | 2/5 (40%) | 0.9 | |
| Røros n = 75 | 21/62 (33.9%) | 8/13 (61.5%) | 1.8 | |
| Filefjell n = 59 | 21/53 (35.6%) | 5/6 (83.3%) | 2.3 | |
| TOTAL n = 516 | 178/435 (40.9%) | 43/81 (53.0%) | 1.3 | |
| Gamma-herpesvirus seropositive n = 54 (All 8 herds) | Tana n = 95 | 3/83 (3.6%) | 1/12 (8.3%) | 2.3 |
| Lakselv n = 57 | 7/50 (14.0%) | 1/7 (14.3%) | 1.0 | |
| Tromsø n = 68 | 3/45 (6.7%) | 1/23 (4.3%) | 0.6 | |
| Lødingen n = 30 | 1/28 (3.6%) | 0/2 | - | |
| Hattfjelldal n = 82 | 10/69 (14.5%) | 3/13 (23,1%) | 1.6 | |
| Fosen n = 50 | 7/45 (15.6%) | 0/5 | - | |
| Røros n = 75 | 6/62 (9.7%) | 4/13 (30.8%) | 3.1 | |
| Filefjell n = 59 | 7/59 (11.9%) | 0/6 | - | |
| TOTAL n = 516 | 44/435 (10.1%) | 10/81 (12.3%) | 1.2 |
| Location | Year of Sampling | Adults | Calves | Animals per Year | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Females | Males | Total | Females | Males | Total | |||
| 1. Tana | 2013 | 19 | 1 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| 2014 | 16 | 0 | 16 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 17 | |
| 2015 | 11 | 0 | 11 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 18 | |
| 2016 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 20 | |
| 2017 | 9 | 0 | 9 | 10 | 1 | 11 | 20 | |
| Total | 65 | 1 | 66 (69%) | 19 | 10 | 29 (21%) | 95 | |
| 2. Lakselv | 2013 | 9 | 3 | 12 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 18 |
| 2014 | 14 | 0 | 14 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 19 | |
| 2015 | 10 | 2 | 12 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 20 | |
| Total | 33 | 5 | 38 (67%) | 11 | 8 | 19 (23%) | 57 | |
| 3. Tromsø | 2013 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 18 | 25 | 25 |
| 2014 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 8 | 18 | 23 | |
| 2015 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 13 | 20 | |
| Total | 12 | 0 | 12 (18%) | 23 | 33 | 56 (82%) | 68 | |
| 4. Lødingen | 2013 | 7 | 2 | 9 | 11 | 2 | 13 | 22 |
| 2014 | 8 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | |
| Total | 15 | 2 | 17 (57%) | 11 | 2 | 13 (43%) | 30 | |
| 5. Hattfjelldal | 2013 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 7 | 12 | 19 | 25 |
| 2015 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 14 | 14 | 17 | |
| 2016 | 8 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 20 | |
| 2017 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 10 | 20 | |
| Total | 26 | 3 | 29 (35%) | 19 | 34 | 53 (65%) | 82 | |
| 6. Fosen | 2013 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 10 | 11 | 20 |
| 2014 | 12 | 2 | 14 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 20 | |
| 2015 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 10 | |
| Total | 24 | 6 | 30 (60%) | 4 | 16 | 20 (40%) | 50 | |
| 7. Røros | 2013 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 17 | 22 |
| 2014 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 19 | |
| 2015 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 14 | |
| 2016 | 9 | 1 | 10 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 20 | |
| Total | 31 | 5 | 36 (48%) | 21 | 18 | 39 (52%) | 75 | |
| 8. Filefjell | 2013 | 5 | 7 | 12 | 7 | 6 | 13 | 25 |
| 2014 | 7 | 3 | 10 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 18 | |
| 2015 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 16 | |
| Total | 14 | 14 | 28 (47%) | 16 | 15 | 31 (53%) | 59 | |
| Total | 220 | 36 | 256 | 124 | 136 | 260 | 516 | |
| Live | Slaughtered | |
|---|---|---|
| Calves (n = 260) | 219 (84.2%) | 41 (15.8%) |
| Adults (n = 256) | 225 (87.9%) | 31 (12.1%) |
| Total (n = 516) | 444 (86.0%) | 72 (14.0%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rinaldo, C.H.; Nymo, I.H.; Sánchez Romano, J.; Breines, E.M.; Murguzur, F.J.A.; Tryland, M. Serological Evidence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Semi-Domesticated Eurasian Tundra Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Norway. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121542
Rinaldo CH, Nymo IH, Sánchez Romano J, Breines EM, Murguzur FJA, Tryland M. Serological Evidence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Semi-Domesticated Eurasian Tundra Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Norway. Pathogens. 2021; 10(12):1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121542
Chicago/Turabian StyleRinaldo, Christine Hanssen, Ingebjørg Helena Nymo, Javier Sánchez Romano, Eva Marie Breines, Francisco Javier Ancin Murguzur, and Morten Tryland. 2021. "Serological Evidence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Semi-Domesticated Eurasian Tundra Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Norway" Pathogens 10, no. 12: 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121542
APA StyleRinaldo, C. H., Nymo, I. H., Sánchez Romano, J., Breines, E. M., Murguzur, F. J. A., & Tryland, M. (2021). Serological Evidence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Semi-Domesticated Eurasian Tundra Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Norway. Pathogens, 10(12), 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121542








