Characterization of Anti-p54 Monoclonal Antibodies and Their Potential Use for African Swine Fever Virus Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
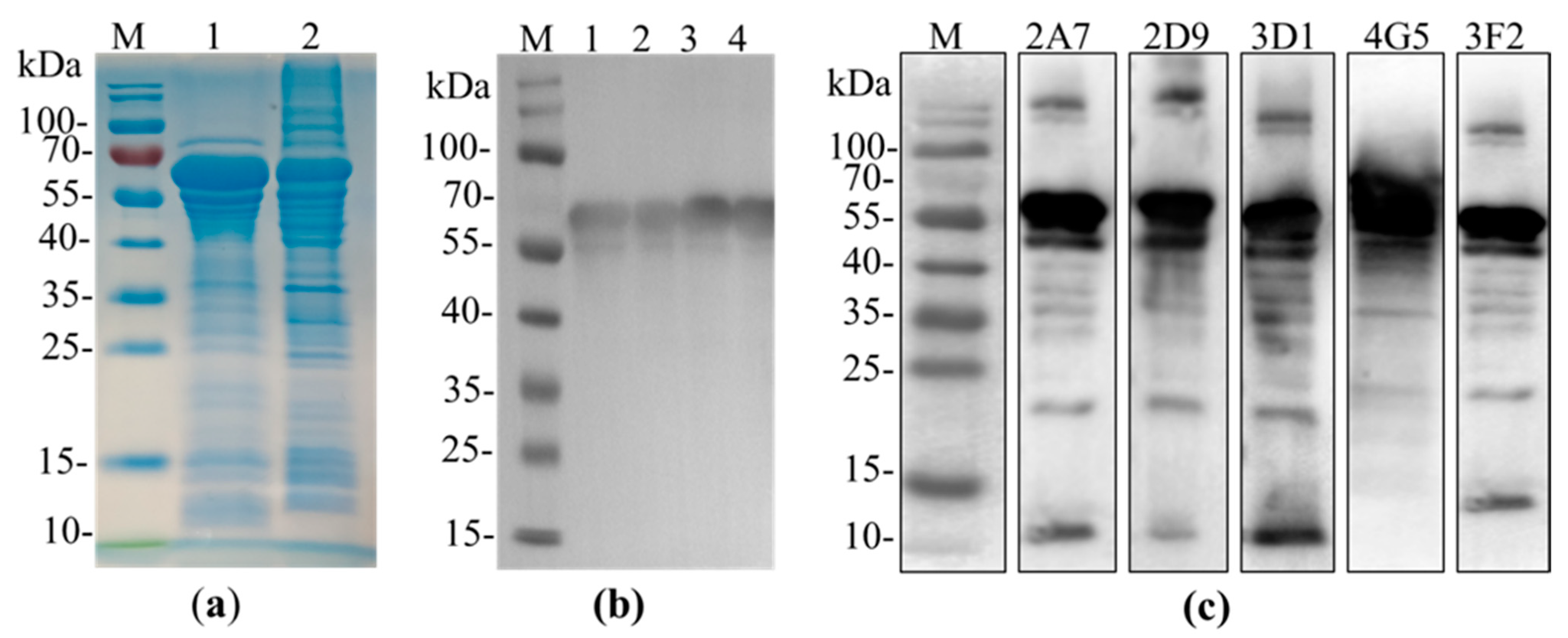
2.1. Expression of p54 Recombinant Protein
2.2. Anti-p54 Monoclonal Antibody Production
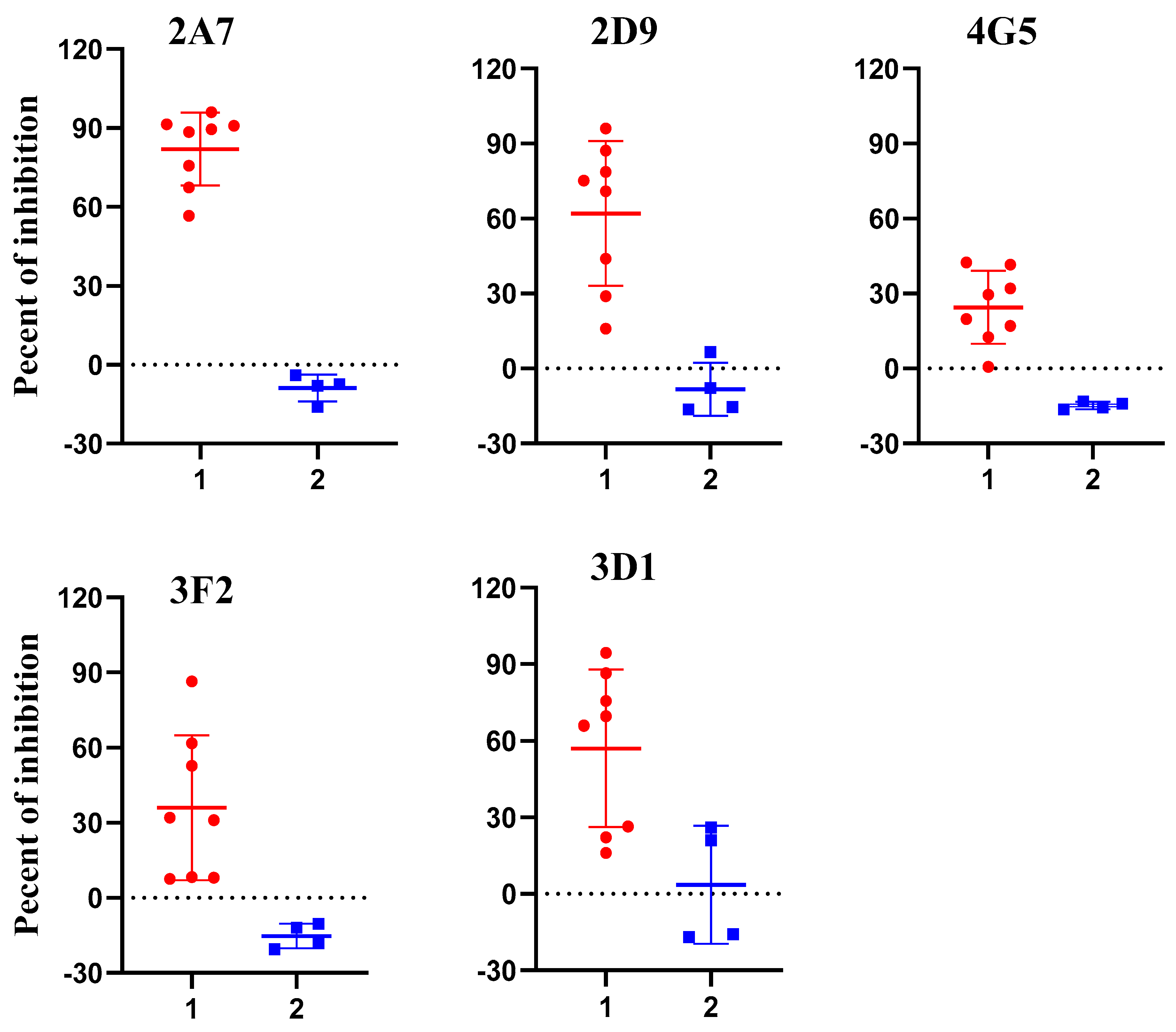
2.3. Assessing Potential Uses of p54 Monoclonal Antibodies for Competitive ELISA
2.4. Optimization of 2A7-Based Competitive ELISA
2.5. Standardization and Determining the Negative Cut-off Value for cELISA
2.6. Specificity and Repeatability Test
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Serum Samples
4.2. Constructing p54 Recombinant DNA
4.3. Expression and Purification of Recombinant ASFV-p54 Protein
4.4. P54 Monoclonal Antibody Production
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Indirect ELISA
4.7. Indirect Immunofluorescent Assay (IFA)
4.8. Establishment of Monoclonal Antibody Based-Competitive ELISA for African Swine Fever Antibody Detection
4.9. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, N.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Bu, Z.; et al. Architecture of African swine fever virus and implications for viral assembly. Science 2019, 366, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, M.L.; Andrés, G. African swine fever virus morphogenesis. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blome, S.; Gabriel, C.; Beer, M. Pathogenesis of African swine fever in domestic pigs and European wild boar. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salguero, F.J. Comparative Pathology and Pathogenesis of African Swine Fever Infection in Swine. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Núñez, A.; Neimanis, A.S.; Wikström-Lassa, E.; Montoya, M.; Crooke, H.; Gavier-Widén, D. African Swine Fever: Disease Dynamics in Wild Boar Experimentally Infected with ASFV Isolates Belonging to Genotype I and II. Viruses 2019, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Montoya, M.; Reis, A.L.; Dixon, L.K. African swine fever: A re-emerging viral disease threatening the global pig industry. Vet. J. 2018, 233, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, N.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Miao, F.; Chen, T.; Zhang, S.; Cao, P.; Li, X.; Tian, K.; et al. Emergence of African Swine Fever in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Netherton, C.L.; Goatley, L.C.; Reis, A.L.; Portugal, R.; Nash, R.H.; Morgan, S.B.; Gault, L.; Nieto, R.; Norlin, V.; Gallardo, C.; et al. Identification and Immunogenicity of African Swine Fever Virus Antigens. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- OIE. Global Situation of African Swine Fever. Report No. 47:2016–2020. Available online: https://rr-asia.oie.int/en/projects/asf/situational-updates-of-asf-in-asia-and-the-pacific/ (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Gallardo, C.; Blanco, E.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Carrascosa, A.L.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. Antigenic Properties and Diagnostic Potential of African Swine Fever Virus Protein pp62 Expressed in Insect Cells. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallardo, C.; Reis, A.L.; Kalema-Zikusoka, G.; Malta, J.; Soler, A.; Blanco, E.; Parkhouse, R.M.E.; Leitão, A.B. Recombinant Antigen Targets for Serodiagnosis of African Swine Fever. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perez-Filgueira, D.M.; Camacho, F.G.; Gallardo, C.; Resino-Talavan, P.; Blanco, E.; Gomez-Casado, E.; Alonso, C.; Escribano, J.M. Optimization and Validation of Recombinant Serological Tests for African Swine Fever Diagnosis Based on Detection of the p30 Protein Produced in Trichoplusia ni Larvae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3114–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cubillos, C.; Gómez-Sebastian, S.; Moreno, N.; Nuñez, M.C.; Mulumba-Mfumu, L.K.; Quembo, C.J.; Heath, L.; Etter, E.M.; Jori, F.; Escribano, J.M.; et al. African swine fever virus serodiagnosis: A general review with a focus on the analyses of African serum samples. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oviedo, J.; Rodriguez, F.; Gómez-Puertas, P.; Brun, A.; Gómez, N.; Alonso, C.; Escribano, J. High level expression of the major antigenic African swine fever virus proteins p54 and p30 in baculovirus and their potential use as diagnostic reagents. J. Virol. Methods 1997, 64, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barderas, M.G.; Rodríguez, F.; Gómez-Puertas, P.; Avilés, M.; Beitia, F.; Alonso, C.; Escribano, J.M. Antigenic and immunogenic properties of a chimera of two immunodominant African swine fever virus proteins. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.; Alcaraz, C.; Eiras, A.; Yáñez, R.J.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Alonso, C.; Escribano, J.M. Characterization and molecular basis of heterogeneity of the African swine fever virus envelope protein p54. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 7244–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alcaraz, C.; Brun, A.; Ruiz-Gonzalvo, F.; Escribano, J. Cell culture propagation modifies the African swine fever virus replication phenotype in macrophages and generates viral subpopulations differing in protein p54. Virus Res. 1992, 23, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Puertas, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Oviedo, J.M.; Brun, A.; Alonso, C.; Escribano, J.M. The African Swine Fever Virus Proteins p54 and p30 Are Involved in Two Distinct Steps of Virus Attachment and Both Contribute to the Antibody-Mediated Protective Immune Response. Virology 1998, 243, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, F.; Ley, V.; Gómez-Puertas, P.; García, R.; Rodriguez, J.; Escribano, J. The structural protein p54 is essential for African swine fever virus viability. Virus Res. 1996, 40, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.M.; García-Escudero, R.; Salas, M.L.; Andrés, G. African Swine Fever Virus Structural Protein p54 Is Essential for the Recruitment of Envelope Precursors to Assembly Sites. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4299–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alonso, C.; Miskin, J.; Hernáez, B.; Fernandez-Zapatero, P.; Soto, L.; Canto, C.; Rodríguez-Crespo, I.; Dixon, L.; Escribano, J.M. African Swine Fever Virus Protein p54 Interacts with the Microtubular Motor Complex through Direct Binding to Light-Chain Dynein. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 9819–9827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Mayoral, M.F.; Rodríguez-Crespo, I.; Bruix, M. Structural models of DYNLL1 with interacting partners: African swine fever virus protein p54 and postsynaptic scaffolding protein gephyrin. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollnberger, S.; Gutierrez-Castañeda, B.; Foster-Cuevas, M.; Corteyn, A.; Parkhouse, R.M.E. Identification of the principal serological immunodeterminants of African swine fever virus by screening a virus cDNA library with antibody. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, A.L.; Parkhouse, R.M.E.; Penedos, A.R.; Martins, C.; Leitão, A.B. Systematic analysis of longitudinal serological responses of pigs infected experimentally with African swine fever virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 2426–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhandwala, S.; Waghela, S.D.; Bray, J.; Martin, C.L.; Sangewar, N.; Charendoff, C.; Shetti, R.; Ashley, C.; Chen, C.-H.; Berghman, L.R.; et al. Induction of Robust Immune Responses in Swine by Using a Cocktail of Adenovirus-Vectored African Swine Fever Virus Antigens. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alcaraz, C.; Rodriguez, F.; Oviedo, J.; Eiras, A.; De Diego, M.; Alonso, C.; Escribano, J. Highly specific confirmatory Western blot test for African swine fever virus antibody detection using the recombinant virus protein p54. J. Virol. Methods 1995, 52, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, R. Validation of serological assays for diagnosis of infectious diseases. Rev. Sci. Tech. 1998, 17, 469–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejo, A.; Matamoros, T.; Guerra, M.; Andrés, G. A Proteomic Atlas of the African Swine Fever Virus Particle. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teklue, T.; Sun, Y.; Abid, M.; Luo, Y.; Qiu, H. Current status and evolving approaches to African swine fever vaccine development. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIE. African Swine Fever. In OIE Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; World Organization for Animal Health (OIE): Paris, France, 2012; pp. 1067–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M.; Mur, L.; Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Carrasco, L. An Update on the Epidemiology and Pathology of African Swine Fever. J. Comp. Pathol. 2015, 152, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, H.C.; Glas, P.S.; Schumann, K.R. Diagnostic specificity of the African swine fever virus antibody detection enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in feral and domestic pigs in the United States. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1665–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhao, D.; He, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Shan, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. A seven-gene-deleted African swine fever virus is safe and effective as a live attenuated vaccine in pigs. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Replication and virulence in pigs of the first African swine fever virus isolated in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, X.; He, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bu, Z. Genome sequences derived from pig and dried blood pig feed samples provide important insights into the transmission of Africa swine fever virus in China in 2018. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.T.; Niemela, S.L.; Miller, R.H. One-step preparation of competent Escherichia coli: Transformation and storage of bacterial cells in the same solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 2172–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groth, S.D.S.; Scheidegger, D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: Strategy and tactics. J. Immunol. Methods 1980, 35, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnasko, R. Methods in Molecular Biology. In ELISA; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1318, pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Mi, S.; Gong, W.; Shi, J.; Madera, R.; Ganges, L.; Borca, M.V.; Ren, J.; Cunningham, C.; Cino-Ozuna, A.G.; et al. A neutralizing monoclonal antibody-based competitive ELISA for classical swine fever C-strain post-vaccination monitoring. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Monoclonal Antibodies | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2A7 | 2D9 | 4G5 | 3F2 | 3D3 | |
| Ig subclass | IgG1 | IgG1 | IgG1 | IgG1 | IgG1 |
| Light chain type | κ | κ | κ | κ | κ |
| Ingezim PPA COMPAC Result | Serum Samples Tested with P54-cELISA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total | |
| Positive | 173 | 14 | 187 |
| Negative | 2 | 176 | 178 |
| Total | 175 | 190 | 365 |
| Samples | Intra-Assay | Inter-Assay | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean OD Value | SD | CV% | Mean OD Value | SD | CV% | |
| Positive 1 | 0.090 | 0.003 | 2.78 | 0.0903 | 0.0103 | 11.36 |
| Positive 2 | 0.082 | 0.008 | 9.52 | 0.069 | 0.006 | 8.07 |
| Positive 3 | 0.072 | 0.008 | 11.27 | 0.057 | 0.005 | 8.77 |
| Positive 4 | 0.099 | 0.004 | 4.09 | 0.101 | 0.013 | 12.98 |
| Positive 5 | 0.150 | 0.004 | 2.40 | 0.137 | 0.023 | 16.80 |
| Negative 1 | 0.915 | 0.033 | 3.60 | 0.95 | 0.09 | 9.67 |
| Negative 2 | 0.945 | 0.007 | 0.78 | 0.89 | 0.05 | 5.79 |
| Negative 3 | 0.964 | 0.067 | 6.92 | 0.96 | 0.14 | 14.04 |
| Negative 4 | 0.927 | 0.016 | 1.67 | 1.04 | 0.06 | 5.91 |
| Negative 5 | 0.924 | 0.053 | 5.72 | 0.82 | 0.07 | 8.79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tesfagaber, W.; Wang, L.; Tsegay, G.; Hagoss, Y.T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huangfu, H.; Xi, F.; Li, F.; Sun, E.; et al. Characterization of Anti-p54 Monoclonal Antibodies and Their Potential Use for African Swine Fever Virus Diagnosis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020178
Tesfagaber W, Wang L, Tsegay G, Hagoss YT, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Huangfu H, Xi F, Li F, Sun E, et al. Characterization of Anti-p54 Monoclonal Antibodies and Their Potential Use for African Swine Fever Virus Diagnosis. Pathogens. 2021; 10(2):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020178
Chicago/Turabian StyleTesfagaber, Weldu, Lulu Wang, Ghebremedhin Tsegay, Yibrah Tekle Hagoss, Zhenjiang Zhang, Jiwen Zhang, Haoyue Huangfu, Fei Xi, Fang Li, Encheng Sun, and et al. 2021. "Characterization of Anti-p54 Monoclonal Antibodies and Their Potential Use for African Swine Fever Virus Diagnosis" Pathogens 10, no. 2: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020178
APA StyleTesfagaber, W., Wang, L., Tsegay, G., Hagoss, Y. T., Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., Huangfu, H., Xi, F., Li, F., Sun, E., Bu, Z., & Zhao, D. (2021). Characterization of Anti-p54 Monoclonal Antibodies and Their Potential Use for African Swine Fever Virus Diagnosis. Pathogens, 10(2), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020178






