Descriptive Comparison of ELISAs for the Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies in Animals: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
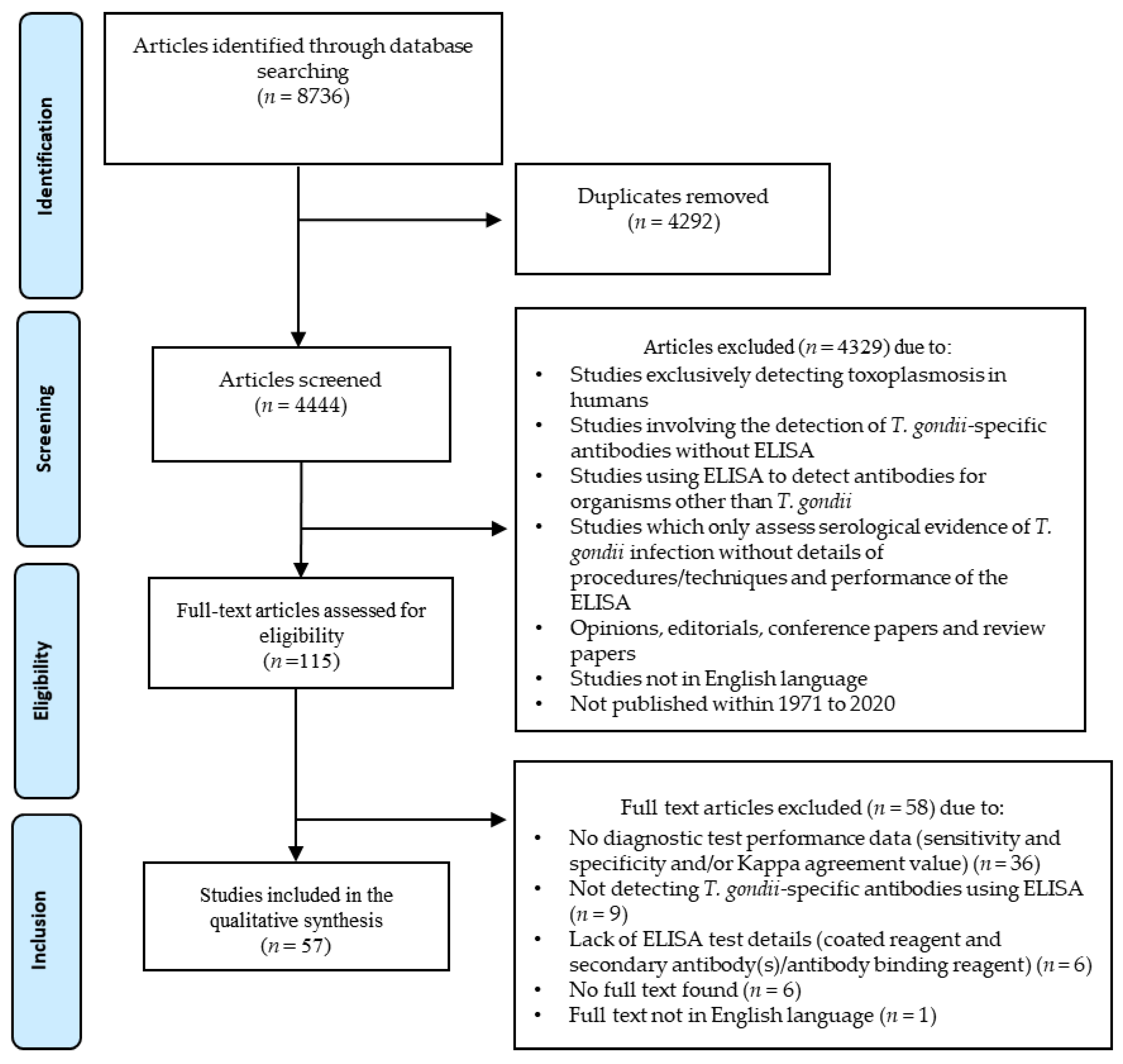
2.1. Literature Search and Eligible Articles
2.2. General Characteristics of Studies Included in the Review
2.3. Type of Antigen Used in ELISAs
2.4. Types of Antibodies Detected and Use of Secondary Antibodies/Antibody-Binding Reagents
2.5. Types of ELISAs Used
2.6. Diagnostic Performance
2.6.1. Milk and Meat Juice ELISAs
2.6.2. Use of Single Recombinant Antigens
2.6.3. Use of Combinations of Recombinant Antigens
2.6.4. Recombinant Chimeric Antigens
2.6.5. Comparison of Native and Recombinant/Chimeric Antigens
2.6.6. Diagnostic Performance of Non-Species-Specific Antibody Binding Reagents
2.6.7. Cross-Reactivity of ELISAs Used for Animals
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Review Protocol
4.2. Search Strategy
4.3. Quality Assessment and Selection
4.4. Data Extraction and Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.P.; Beattie, C.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Man; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; ISBN 0849346185. [Google Scholar]
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, E. Toxoplasmosis. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2007, 12, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis—A waterborne zoonosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajadhar, A.A.; Scandrett, W.B.; Forbes, L.B. Parásitos zoonóticos transmitidos por los alimentos y el agua en las granjas. Rev. Sci. Tech. l’OIE 2006, 25, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, S.; Basso, W.; Benavides Silván, J.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Maksimov, P.; Gethmann, J.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in farm animals: Risk factors and economic impact. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00037:00031–e00037:00032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferra, B.; Holec-Gasior, L.; Kur, J. Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in farm animals (horses, swine, and sheep) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using chimeric antigens. Parasitol. Int. 2015, 64, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, D.; Maley, S.W.; Wright, S.E.; Rodger, S.; Bartley, P.; Innes, E.A. Toxoplasma gondii and ovine toxoplasmosis: New aspects of an old story. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 149, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainar, R.C.; De La Cruz, C.; Asensio, A.; Domínguez, L.; Vázquez-Boland, J.A. Prevalence of agglutinating antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in small ruminants of the Madrid region, Spain, and identification of factors influencing seropositivity by multivariate analysis. Vet. Res. Commun. 1996, 20, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S.A.; Samelius, G.; Al-Adhami, B.; Huyvaert, K.P.; Bailey, L.L.; Alisauskas, R.T.; Gajadhar, A.A.; Jenkins, E.J. Estimating Toxoplasma gondii exposure in Arctic foxes (Vulpes lagopus) while navigating the imperfect world of wildlife serology. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.; Jones, J. Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans and animals in the United States. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1257–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. A review of toxoplasmosis in wild birds. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 106, 121–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowater, R.O.; Norton, J.; Johnson, S.; Hill, B.; O’Donoghue, P.; Prior, H. Toxoplasmosis in Indo-Pacific humpbacked dolphins (Sousa chinensis), from Queensland. Aust. Vet. J. 2003, 81, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sangster, C.; Gordon, A.; Hayes, D. Systemic toxoplasmosis in captive flying-foxes. Aust. Vet. J. 2012, 90, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, K.K.; Mørk, T.; Sigurðardóttir, Ó.G.; Åsbakk, K.; Åkerstedt, J.; Bergsjø, B.; Fuglei, E. Acute toxoplasmosis in three wild Arctic foxes (Alopex lagopus) from Svalbard; one with co-infections of Salmonella Enteritidis PT1 and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis serotype 2b. Res. Vet. Sci. 2005, 78, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frenkel, J.K.; Dubey, J.P.; Miller, N.L. Toxoplasma gondii in cats: Fecal stages identified as coccidian oocysts. Science 1970, 167, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lindsay, D.S.; Speer, C.A. Structures of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites, bradyzoites, and sporozoites and biology and development of tissue cysts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, J.P. Advances in the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, D.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii: Transmission, diagnosis and prevention. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2002, 8, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma: The next 100 years. Microb. Infect. 2008, 10, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, W.; Bretislav, K.; Fraser, I.L.; Gereon, S.; Lais, P.; Maria, C.V.; Pavlo, M.; Peter, D.; Sonja, H.; Xaver, S. Assessment of diagnostic accuracy of a commercial ELISA for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection in pigs compared with IFAT, TgSAG1-ELISA and Western blot, using a Bayesian latent class approach. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva, D.; Morris, J.C.; Johnson, J.D.; Holliman, R.E. Polymerase chain reaction for detection of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Med. Microbiol. 1990, 32, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.-D.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zhu, X.-Q. Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis and typing of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sudan, V.; Tewari, A.K.; Singh, H. Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in bovines from Kerala, India using a recombinant surface antigen 1 ELISA. Biologicals 2015, 43, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.L.; Gennari, S.M.; Machado, R.Z.; Navarro, I.T. Toxoplasma gondii: Detection by mouse bioassay, histopathology, and polymerase chain reaction in tissues from experimentally infected pigs. Exp. Parasitol. 2006, 113, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Long-term persistence of Toxoplasma gondii in tissues of pigs inoculated with T. gondii oocysts and effect of freezing on viability of tissue cysts in pork. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1988, 49, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Oocyst shedding by cats fed isolated bradyzoites and comparison of infectivity of bradyzoites of the veg strain Toxoplasma gondii to cats and mice. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaran, N.; O’Handley, R.M.; Grigg, M.E.; Fenwick, S.G.; Thompson, R.C.A. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in wild kangaroos using an ELISA. Parasitol. Int. 2009, 58, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lind, P.; Haugegaard, J.; Wingstrand, A.; Henriksen, S.A. The time course of the specific antibody response by various elisas in pigs experimentally infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekkesin, N.; Keskin, K.; Kılınc, C.; Orgen, N.; Molo, K. Detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii: Evaluation of two commercial immunoassay systems. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2011, 44, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cakir-Koc, R. Production of anti-SAG1 IgY antibody against Toxoplasma gondii parasites and evaluation of antibody activity by ELISA method. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2947–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villard, O.; Cimon, B.; L’Ollivier, C.; Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Godineau, N.; Houze, S.; Paris, L.; Pelloux, H.; Villena, I.; Candolfi, E. Serological diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 84, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Feng, W.; Jiping, L.; Quan, L.; Zedong, W. Evaluation of an indirect ELISA using recombinant granule antigen GRA1, GRA7 and soluble antigens for serodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in chickens. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 100, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, F.; Shang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Q. A comparative study of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence in mink using a modified agglutination test, a Western blot, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2015, 27, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Titilincu, A.; Mircean, V.; Iovu, A.; Cozma, V. Development of an indirect ELISA test using tachyzoite crude antigen for sero-diagnosis of sheep Toxoplasma gondii infection. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. Cluj Napoca 2009, 66, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Tumurjav, B.; Terkawi, M.A.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Jia, H.; Goo, Y.-K.; Yamagishi, J.; Nishikawa, Y.; Igarashi, I.; Sugimoto, C.; et al. Serodiagnosis of ovine toxoplasmosis in Mongolia by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with recombinant Toxoplasma gondii matrix antigen 1. Jap. J. Vet. Res. 2010, 58, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Felin, E.; Anu, N.r.; Maria, F.-A. Comparison of commercial ELISA tests for the detection of Toxoplasma antibodies in the meat juice of naturally infected pigs. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 238, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payne, R.A.; Joynson, D.H.M.; Wilsmore, A.J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the measurement of specific antibodies in experimentally induced ovine toxoplasmosis. Epidemiol. Infect. 1988, 100, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engvall, E.; Perlmann, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA III. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J. Immunol. 1972, 109, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Yolken, R.; Kim, H.; Clem, T.; Wyatt, R.; Kalica, A.; Chanock, R.; Kapikian, A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Lancet 1977, 310, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viera, A.; Garrett, J. Understanding interobserver agreement: The kappa statistic. Fam. Med. 2005, 37, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Šimundić, A.-M. Measures of diagnostic accuracy: Basic definitions. EJIFCC 2009, 19, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Adhami, B.H.; Alvin, A.G. A new multi-host species indirect ELISA using protein A/G conjugate for detection of anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgG antibodies with comparison to ELISA-IgG, agglutination assay and Western blot. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 200, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynoso-Palomar, A.; Moreno-Gálvez, D.; Villa-Mancera, A. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii parasite in captive Mexican jaguars determined by recombinant surface antigens (SAG1) and dense granular antigens (GRA1 and GRA7) in ELISA-based serodiagnosis. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, H.R.; Dubey, J.P.; Lambillotte, D.N. Comparison of a commercial ELISA with the modified agglutination test for detection of Toxoplasma infection in the domestic pig. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 128, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelbaset, A.E.; Doaa, S.; Hend, A.; Mahmoud Abd Ellah, R.; Makoto, I.; Mohamed Hassan, K.; Xuan, X. Evaluation of recombinant antigens in combination and single formula for diagnosis of feline toxoplasmosis. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 172, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casartelli-Alves, L.; Boechat, V.C.; Macedo-Couto, R.; Ferreira, L.C.; Nicolau, J.L.; Neves, L.B.; Millar, P.R.; Vicente, R.T.; Oliveira, R.V.C.; Muniz, A.G.; et al. Sensitivity and specificity of serological tests, histopathology and immunohistochemistry for detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection in domestic chickens. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 204, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holec-Gąsior, L.; Ferra, B.; Grąźlewska, W. Toxoplasma gondii tetravalent chimeric proteins as novel antigens for detection of specific immunoglobulin G in sera of small ruminants. Animals 2019, 9, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardini, L.; Maksimov, P.; Herrmann, D.C.; Bacigalupe, D.; Rambeaud, M.; Machuca, M.; Moré, G.; Basso, W.; Schares, G.; Venturini, M.C. Evaluation of an in-house TgSAG1 (P30) IgG ELISA for diagnosis of naturally acquired Toxoplasma gondii infection in pigs. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 189, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudan, V.; Tewari, A.K.; Singh, H. Detection of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in Indian cattle by recombinant SAG2 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Acta Parasitol. 2019, 64, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olamendi-Portugal, M.; Ortega-S, J.A.; Medina-Esparza, L.; García-Vázquez, Z.; Cantu, A.; Correa, D.; Caballero-Ortega, H.; Cruz-Vázquez, C.; Sánchez-Alemán, M.A. Serosurvey of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in white-tailed deer from Northern Mexico. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 189, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, J.J.; Kirchgessner, M.S.; Whipps, C.M.; Mohammed, H.O.; Bunting, E.M.; Wade, S.E. Prevalence of antibodies to Toxoplasma Gondii in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus Virginianus) in New York state, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glor, S.B.; Edelhofer, R.; Grimm, F.; Deplazes, P.; Basso, W. Evaluation of a commercial ELISA kit for detection of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in serum, plasma and meat juice from experimentally and naturally infected sheep. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoo, W.G.; Kim, S.-M.; Won, E.J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Dai, F.; Woo, H.C.; Nam, H.-W.; Kim, T.I.; Han, J.-H.; Kwak, D.; et al. Tissue fluid enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay for piglets experimentally infected with Toxoplasma gondii and survey on local and imported pork in Korean retail meat markets. Korean J. Parasitol. 2018, 56, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, M.M.; Saad, M.F.; Abdel-Salam, A.B. Milk as a substitute for serum in diagnosis of toxoplasmosis in goats. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Olivieri, E.; Stradiotto, K.; Villa, L.; Manfredi, M.T.; Zanzani, S.A. Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in bulk tank milk samples of caprine dairy herds. J. Parasitol. 2018, 104, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Tewari, A.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Maharana, B.; Sudan, V.; Raina, O.K.; Rao, J.R. Detection of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in domesticated ruminants by recombinant truncated SAG2 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2015, 47, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Fang, R.; Nie, H.; Feng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J. Use of protein AG in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in four species of animals. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armas Valdes, Y.; Obregon Alvarez, D.; Grandia Guzman, R.; Mitat Valdes, A.; Roque Lopez, E.; Perez Ruano, M.; Entrena Garcia, A.A. Validation of an inhibition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay system for the diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis). Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epizoot. 2018, 37, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka, J.; Karamon, J.; Cencek, T.; Dutkiewicz, J. Preliminary assessment of usefulness of cELISA test for screening pig and cattle populations for presence of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2011, 18, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Opsteegh, M.; Teunis, P.; Mensink, M.; Züchner, L.; Titilincu, A.; Langelaar, M.; van der Giessen, J. Evaluation of ELISA test characteristics and estimation of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence in Dutch sheep using mixture models. Prev. Vet. Med. 2010, 96, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koethe, M.; Bittame, A.; Spekker, K.; Mercier, C.; Straubinger, R.K.; Fehlhaber, K.; Tenter, A.M.; Ludewig, M.; Pott, S.; Bangoura, B.; et al. Prevalence of specific IgG-antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in domestic turkeys determined by kinetic ELISA based on recombinant GRA7 and GRA8. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 180, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terkawi, M.A.; Kameyama, K.; Rasul, N.H.; Xuan, X.; Nishikawa, Y. Development of an immunochromatographic assay based on dense granule protein 7 for serological detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamidinejat, H.; Nabavi, L.; Mayahi, M.; Ghourbanpoor, M.; Pourmehdi Borojeni, M.; Norollahi Fard, S.; Shokrollahi, M. Comparison of three diagnostic methods for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii in free range chickens. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 31, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, N.; Wei, F.; Liu, Q. Evaluation of an indirect elisa using recombinant granule antigen GRA 7 for serodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in cats. J. Parasitol. 2015, 101, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, W.; Sollberger, E.; Schares, G.; Küker, S.; Ardüser, F.; Moore-Jones, G.; Zanolari, P. Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum infections in South American camelids in Switzerland and assessment of serological tests for diagnosis. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endrias Zewdu, G.; Mukarim, A.; Tsehaye, H.; Tessema, T.S. Comparison between enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and modified agglutination test (MAT) for detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection in sheep and goats slaughtered in an export abattoir at Debre-Zeit, Ethiopia. Glob. Vet. 2013, 11, 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, J.J.; Holly, A.W.; Hussni, O.M.; Stephanie, L.S.; Susan, E.W. Chimeric protein A/G conjugate for detection of anti–Toxoplasma gondii immunoglobulin G in multiple animal species. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, J.J.; White, H.A.; Schaaf, S.L.; Mohammed, H.O.; Wade, S.E. Modification of a commercial Toxoplasma gondii immunoglobulin G enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for use in multiple animal species. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2011, 23, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holec-Gąsior, L.; Ferra, B.; Hiszczyńska-Sawicka, E.; Kur, J. The optimal mixture of Toxoplasma gondii recombinant antigens (GRA1, P22, ROP1) for diagnosis of ovine toxoplasmosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 206, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ge, W.; Huang, S.-Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Liu, Q. Evaluation of recombinant granule antigens GRA1 and GRA7 for serodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tenter, A.M.; Vietmeyer, C.; Rommel, M. ELISAs based on recombinant antigens for sero-epidemiological studies on Toxoplasma gondii infections in cats. Parasitology 1994, 109, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velmurugan, G.V.; Tewari, A.K.; Rao, J.R.; Surajit, B.; Kumar, M.U.; Mishra, A.K. High-level expression of SAG1 and GRA7 gene of Toxoplasma gondii (Izatnagar isolate) and their application in serodiagnosis of goat toxoplasmosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 154, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.M.; Lourenço, E.V.; Silva, D.A.O.; Mineo, J.R. Optimisation of cut-off titres in Toxoplasma gondii specific ELISA and IFAT in dog sera using immunoreactivity to SAG-1 antigen as a molecular marker of infection. Vet. J. 2002, 163, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.H.; Cui, L.L.; Zhang, L.S. Comparison of a commercial ELISA with the modified agglutination test for detection of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in sera of naturally infected dogs and cats. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2012, 7, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseininejad, M.; Azizi, H.R.; Hosseini, F.; Schares, G. Development of an indirect ELISA test using a purified tachyzoite surface antigen SAG1 for sero-diagnosis of canine Toxoplasma gondii infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 164, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.L.; Navarro, I.T.; Vidotto, O.; Gennari, S.M.; Machado, R.Z.; Pereira, B.D.; Sinhorini, I.L. Toxoplasma gondii: Comparison of a rhoptry-ELISA with IFAT and MAT for antibody detection in sera of experimentally infected pigs. Exp. Parasitol. 2006, 113, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaanse, K.; Firestone, S.M.; Lynch, M.; Rendall, A.R.; Sutherland, D.R.; Hufschmid, J.; Traub, R. Comparison of the modified agglutination test and real-time PCR for detection of Toxoplasma gondii exposure in feral cats from Phillip Island, Australia, and risk factors associated with infection. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 12, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Chandrashekara, S. Sample size estimation and power analysis for clinical research studies. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2012, 5, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S. A short history, principles, and types of ELISA, and our laboratory experience with peptide/protein analyses using ELISA. Peptides 2015, 72, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halevy, B.; Sarov, I. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of specific IgA antibodies to mumps virus. J. Clin. Pathol. 1982, 35, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein-Schneegans, A.-S.; Gavériaux, C.; Fonteneau, P.; Loor, F. Indirect double sandwich ELISA for the specific and quantitative measurement of mouse IgM, IgA and IgG subclasses. J. Immunol. Methods 1989, 119, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plebani, A.; Avanzini, M.A.; Massa, M.; Ugazio, A.G. An avidin-biotin ELISA for the measurement of serum and secretory IgD. J. Immunol. Methods 1984, 71, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Hou, Y.; Hu, J.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Ji, K. Enhanced sensitivity of capture IgE-ELISA based on a recombinant Der f 1/2 fusion protein for the detection of IgE antibodies targeting house dust mite allergens. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3497–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sroka, J.; Cencek, T.; Ziomko, I.; Karamon, J.; Zwoliński, J. Preliminary assessment of ELISA, MAT, and LAT for detecting Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in pigs. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2008, 52, 545–549. [Google Scholar]
- Dhakal, R.; Gajurel, K.; Pomares, C.; Talucod, J.; Press, C.J.; Montoya, J.G. Significance of a positive Toxoplasma Immunoglobulin M test result in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3601–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharifi, K.; Hosseini Farash, B.R.; Tara, F.; Khaledi, A.; Sharifi, K.; Shamsian, S.A.A. Diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis by IgG and IgM antibodies and IgG avidity in pregnant women from Mashhad, Eastern Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2019, 14, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.; Qu, L.; Gong, R.; Si, J. Evaluation of a recombinant multiepitope peptide for serodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietkiewicz, H.; Hiszczyńska-Sawicka, E.; Kur, J.; Petersen, E.; Nielsen, H.V.; Paul, M.; Stankiewicz, M.; Myjak, P. Usefulness of Toxoplasma gondii recombinant antigens (GRA1, GRA7 and SAG1) in an immunoglobulin G avidity test for the serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 100, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, H. Research progress on surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chahed Bel-Ochi, N.; Bouratbine, A.; Mousli, M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant SAG1 antigen to detect Toxoplasma gondii-specific immunoglobulin G antibodies in human sera and saliva. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cong, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Gong, J.; Cong, H.; Xin, Q.; He, S. Analysis of structures and epitopes of surface antigen glycoproteins expressed in bradyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Galvan, G.; Araujo, F.G.; Suzuki, Y.; Remington, J.S.; Parmley, S. Serodiagnosis of recently acquired Toxoplasma gondii infection using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a combination of recombinant antigens. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2000, 7, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasper, L.H.; Bradley, M.S.; Pfefferkorn, E.R. Identification of stage-specific sporozoite antigens of Toxoplasma gondii by monoclonal antibodies. J. Immunol. 1984, 132, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hiszczyńska-Sawicka, E.; Kur, J.; Pietkiewicz, H.; Holec-Gasior, L.; Gąsior, A.; Myjak, P. Efficient production of the Toxoplasma gondii GRA6, p35 and SAG2 recombinant antigens and their applications in the serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis. Acta Parasitol. 2005, 50, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, J.; Lamb, E.; Wasmuth, J.; Grujic, O.; Grigg, M.E.; Boulanger, M.J. Structural and functional characterization of sporoSAG: A SAG2-related surface antigen from Toxoplasma gondii. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 12063–12070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahn, H.-J.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-E.; Nam, H.-W. Interactions between secreted GRA proteins and host cell proteins across the parasitophorous vacuolar membrane in the parasitism of Toxoplasma gondii. Korean J. Parasitol. 2006, 44, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, D.; Vercammen, M.; Saman, E. Evaluation of recombinant dense granule antigen 7 (GRA7) of Toxoplasma gondii for detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies and analysis of a major antigenic domain. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1999, 6, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pfrepper, K.-I.; Enders, G.; Gohl, M.; Krczal, D.; Hlobil, H.; Wassenberg, D.; Soutschek, E. Seroreactivity to and avidity for recombinant antigens in toxoplasmosis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dodangeh, S.; Fasihi-Ramandi, M.; Daryani, A.; Valadan, R.; Sarvi, S. In silico analysis and expression of a novel chimeric antigen as a vaccine candidate against Toxoplasma gondii. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajissa, K.; Zakaria, R.; Suppian, R.; Mohamed, Z. An evaluation of a recombinant multiepitope based antigen for detection of Toxoplasma gondii specific antibodies. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camussone, C.; Gonzalez, V.N.; Belluzo, M.A.S.; Pujato, N.; Ribone, M.A.E.; Lagier, C.M.; Marcipar, I.N.S. Comparison of recombinant Trypanosoma cruzi peptide mixtures versus multiepitope chimeric proteins as sensitizing antigens for immunodiagnosis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhao, J.-W.; Sun, Z.-Q.; Song, Y.-Z.; Sun, Q.-W.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Wang, H.-H.; Guo, X.-K.; Liu, Y.-F.; et al. Evaluation of a novel fusion protein antigen for rapid serodiagnosis of tuberculosis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2011, 25, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipti, C.A.; Jain, S.K.; Navin, K. A novel recombinant multiepitope protein as a hepatitis C diagnostic intermediate of high sensitivity and specificity. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 47, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rispens, T.; Vidarsson, G. Chapter 9—Human IgG subclasses. In Antibody Fc; Ackerman, M.E., Nimmerjahn, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 159–177. ISBN 978-0-12-394802-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, P.J.; Tagwira, M.; Matthewman, L.; Mason, P.R.; Wright, E.P. Reactions of sera from laboratory, domestic and wild animals in Africa with protein a and a recombinant chimeric protein AG. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1993, 16, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, P.K.; Hartley, C.A.; Browning, G.F.; Devlin, J.M. Marsupial and monotreme serum immunoglobulin binding by proteins A, G and L and anti-kangaroo antibody. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 427, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöbel, K.; Schönberg, A.; Staak, C. A new non-species dependent ELISA for detection of antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi s. l. in zoo animals. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 291, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, F.G.; Dubey, J.P.; Remington, J.S. Antigenic similarity between the coccidian parasites Toxoplasma gondii and Hammondia hammondi 1. J. Protozool. 1984, 31, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, J.K.; Dubey, J.P. Hammondia hammondi gen. nov., sp.nov., from domestic cats, a new coccidian related to Toxoplasma and Sarcocystis. Z. Parasitenkd. 1975, 46, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engvall, E.; Perlmann, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry 1971, 8, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Type | ELISA | Host Species | Positive % (n/N) | Se (%) | Sp (%) | Agreement (Kappa Value) | Reference Test Used | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | In-house | Goat | 20 (120/600) | 88.7 | 97.4 | ND | MAT (serum and milk) | [55] |
| ID Screen® Toxoplasmosis Indirect Multi-species (IDvet) | Goat | 59 (59/100) | 97.55 | 97.8 | 0.949 | Same commercial ELISA with serum | [56] | |
| Meat Juice/Tissue fluid | PrioCHECK Toxoplasma Ab porcine ELISA(Prionics) | Pig | 41.1 (37/90) | 96.4 | 83.9 | 0.74 | MAT | [37] |
| Pigtype®Toxoplasma Ab (Qiagen) | Pig | 27.8 (25/90) | 89.3 | 100 | 0.92 | MAT | [37] | |
| ID Screen® Toxoplasmosis Indirect Multi-species (IDvet) | Pig | 24.4 (22/90) | 78.6 | 100 | 0.83 | MAT | [37] | |
| Toxoplasma gondii Antibody Test Kit (SafePath Laboratories) | Pig | 1.1 (1/90) | 3.6 | 100 | 0.05 | MAT | [37] | |
| Toxoplasma gondii Antibody Test Kit (SafePath Laboratories) | Pig | 88.5 (62/70) | 88.6 | 98 | ND | Mouse bioassay | [45] | |
| In-house | Pig | 6.2 (60/969) | 96.7 | 100 | ND | Commercial ELISA Kit | [54] |
| Antigen Category | Antigen | Positive % (n/N) | Host Species | Se (%) | Sp (%) | Agreement (Kappa Value) | Reference Test Used for Comparison | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface antigens (SAG) | SAG1 | 75 (39/52) | Jaguar | 92.5 | 83.3 | 0.74 | Commercial ELISA (TLA) | [44] |
| SAG1 | 71.8 (181/252) | Cattle | 84.38 | 87.9 | 0.73 | IFAT | [24] | |
| SAG1 | 44.6 (25/56) | Goat | 83.3 | 84.4 | ND | MAT | [73] | |
| SAG2 | ND | Cat | 91.89 | 88.1 | 0.67 | LAT | [46] | |
| SAG2 | 41.26 (26/63) | Goat | 82.14 | 91.4 | 0.741 | IFAT | [57] | |
| SAG2 | 50 (30/60) | Sheep | 81.25 | 85.7 | 0.667 | IFAT | [57] | |
| SAG2 | 64.44 (29/45) | Cattle | 87.1 | 85.7 | 0.701 | IFAT | [57] | |
| SAG2 | 61.5 (115/258) | Cattle | 80 | 88.6 | 0.689 | IFAT | [50] | |
| Dense granule proteins (GRA) | GRA1 | 15.3 (20/131) | Mink | 78.9 | 95.5 | 0.73 | WB | [34] |
| GRA1 | 75 (39/52) | Jaguar | 92.5 | 83.3 | 0.74 | Commercial ELISA (TLA) | [44] | |
| GRA1 | 16.4 (18/110) | Chicken | 81.3 | 94.7 | 0.72 | WB | [33] | |
| GRA1 | 16.2 (42/259) | Dog | 81 | 95.4 | 0.66 | ELISA (TLA) | [71] | |
| GRA2 | ND | Cat | 27.3 | 96.52 | 0.3 | LAT | [46] | |
| GRA6 | ND | Cat | 82.43 | 88.7 | 0.62 | LAT | [46] | |
| GRA7 | ND | Cat | 35.1 | 89.9 | 0.27 | LAT | [46] | |
| GRA7 | 21.6 (40/185) | Cat | 89.7 | 92.5 | 0.92 | IFAT/MAT | [65] | |
| GRA7 | 13 (17/131) | Mink | 84.2 | 99.1 | 0.83 | WB | [34] | |
| GRA7 | 76.9 (40/52) | Jaguar | 97.5 | 91.6 | 0.89 | Commercial ELISA (TLA) | [44] | |
| GRA7 | 15.5 (17/110) | Chicken | 100 | 98.9 | 0.96 | WB | [33] | |
| GRA7 | 55.9 (33/59) | Pig | 90.63 | 85.2 | 0.76 | LAT | [63] | |
| GRA7 | 42.8 (24/56) | Goat | 80 | 84.4 | ND | MAT | [73] | |
| GRA7 | 16.2 (42/259) | Dog | 91 | 97.7 | 0.8 | ELISA (TLA) | [71] | |
| GRA14 | 47.4 (28/59) | Pig | 81.25 | 92.6 | 0.73 | LAT | [63] | |
| GRA15 | ND | Cat | 17.57 | 86.4 | 0.04 | LAT | [46] | |
| Microneme proteins (MIC) | MIC3 | 41.1 (81/197) | Pig | ND | ND | 0.86 | MAT | [58] |
| MIC3 | 45.8 (11/24) | Dog | ND | ND | 0.85 | MAT | [58] | |
| MIC10 | ND | Cat | 16.21 | 85.8 | 0.02 | LAT | [46] | |
| Other peptide fragments | H4 | 25.81 (79/306) | Cat | 93 | 100 | ND | DAT, IFAT, DT | [72] |
| H11 | 12.41 (38/306) | Cat | 64 | 100 | ND | DAT, IFAT, DT | [72] |
| Combination of Antigens | Antigens | Positive % (n/N) | Host Species | Se (%) | Sp (%) | Agreement (Kappa Value) | Reference Test Used for Comparison | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | H4 + H11 | 31.37 (96/306) | Cat | 95 | 100 | ND | DAT, DT, IFAT | [72] |
| M2 | SAG1 + GRA1 | 75 (39/52) | Jaguar | 95 | 91.6 | 0.84 | Commercial ELISA (TLA) | [44] |
| M3 | SAG1 + GRA7 | 76.9 (40/52) | Jaguar | 97.5 | 91.6 | 0.89 | Commercial ELISA (TLA) | [44] |
| 46.4 (26/56) | Goat | 86.6 | 84.4 | ND | MAT | [73] | ||
| M4 | SAG2 + GRA1 | 81.5 (88/108) | Sheep | 100 | 95 | ND | ND | [70] |
| M5 | SAG2 + GRA6 | ND | Cat | 94.59 | 89.6 | 0.72 | LAT | [46] |
| M6 | SAG2 + GRA7 | ND | Cat | 90.54 | 85.5 | 0.62 | LAT | [46] |
| M7 | SAG2 + ROP1 | 81.5 (88/108) | Sheep | 100 | 95 | ND | ND | [70] |
| M8 | GRA1 + ROP1 | 81.5 (88/108) | Sheep | 100 | 100 | ND | ND | [70] |
| M9 | GRA1 + GRA7 | 76.9 (40/52) | Jaguar | 97.5 | 91.6 | 0.89 | Commercial ELISA (TLA) | [44] |
| M10 | GRA2 + GRA7 | ND | Cat | 44.59 | 89.3 | 0.35 | LAT | [46] |
| M11 | GRA6 + GRA7 | ND | Cat | 74.32 | 89 | 0.58 | LAT | [46] |
| M12 | GRA7 + GRA8 | 20.2 (387/1913) | Turkey | 92.6–100 | 78.1–100 | ND | ND | [62] |
| M13 | SAG1 + MIC1 + MAG1 | 37.21 (32/86) | Horse | 88.9 | 100 | ND | DAT, IFAT | [7] |
| 57.07 (109/191) | Sheep | 77.9 | 92.2 | ND | DAT, IFAT | [7] | ||
| 42.86 (72/168) | Pig | 88.9 | 100 | ND | DAT, IFAT | [7] | ||
| M14 | SAG2 + GRA1 + ROP1 | 32.56 (28/86) | Horse | 77.8 | 100 | ND | DAT, IFAT | [7] |
| 73.30 (140/191) | Sheep | 100 | 100 | ND | DAT, IFAT | [7] | ||
| 39.29 (66/168) | Pig | 81.5 | 100 | ND | DAT, IFAT | [7] | ||
| 81.5 (88/108) | Sheep | 100 | 100 | ND | ND | [70] | ||
| M15 | GRA1 + GRA2 + GRA6 | 36.05 (24/86) | Horse | 66.7 | 100 | ND | DAT, IFAT | [7] |
| 70.16 (129/191) | Sheep | 92.1 | 100 | ND | DAT, IFAT | [7] | ||
| 46.43 (44/168) | Pig | 54.3 | 100 | ND | DAT, IFAT | [7] | ||
| M16 | GRA2 + GRA6+ GRA7 + GRA15 | ND | Cat | 70.27 | 86.1 | 0.5 | LAT | [46] |
| M17 | SAG2 + GRA2 + GRA6 + GRA7 + GRA15 | ND | Cat | 89.19 | 95.4 | 0.81 | LAT | [46] |
| Combination of Chimeric Recombinant Antigens | Species | Positive % (n/N) | Se (%) | Sp (%) | Reference Test | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM1 | GRA1-GRA2-GRA6 | Horse | 36.1 (31/86) | 86.1 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | [7] |
| Sheep | 70.2 (134/191) | 95.7 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |||
| Pig | 46.4 (78/168) | 96.3 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |||
| CM2 | MIC1-MAG1-SAG1s | Horse | 31.4 (27/86) | 75 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |
| Sheep | 71.7 (137/191) | 97.9 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |||
| Pig | 22.0 (37/168) | 45.7 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |||
| CM3 | SAG1L-MIC1-MAG1 | Horse | 32.6 (28/86) | 77.8 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |
| Sheep | 73.3 (140/191) | 100 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |||
| Pig | 43.5 (73/168) | 90.1 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |||
| CM4 | SAG2-GRA1-ROP1S | Horse | 21 (18/86) | 50 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |
| Sheep | 73.3 (140/191) | 100 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |||
| Pig | 13.7 (23/168) | 28.4 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |||
| CM5 | SAG2-GRA1-ROP1L | Horse | 41.9 (36/86) | 100 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |
| Sheep | 73.3 (140/191) | 100 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |||
| Pig | 45.2 (76/168) | 93.8 | 100 | DAT, IFAT | |||
| CM6 | AMA1N-SAG2-GRA1-ROP1 | Sheep | Not clearly mentioned | 97.9 | 97.62 | LAT, IFAT | [48] |
| Goat | Not clearly mentioned | 88.9 | 100 | LAT, IFAT | |||
| CM7 | AMA1C-SAG2-GRA1-ROP1 | Sheep | Not clearly mentioned | 95.8 | 95.24 | LAT, IFAT | |
| Goat | Not clearly mentioned | 95.6 | 97.56 | LAT, IFAT | |||
| CM8 | AMA1-SAG2-GRA1-ROP1 | Sheep | Not clearly mentioned | 97.9 | 100 | LAT, IFAT | |
| Goat | Not clearly mentioned | 95.6 | 100 | LAT, IFAT | |||
| CM9 | SAG2-GRA1-ROP1-GRA2 | Sheep | Not clearly mentioned | 97.9 | 97.62 | LAT, IFAT | |
| Goat | Not clearly mentioned | 57.8 | 95.12 | LAT, IFAT |
| Species | Antigen (s) | Se (%) | Sp (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat | M17 (SAG2 + GRA2 + GRA6 + GRA7 + GRA15) | 89.19 | 95.36 | [46] |
| TLA | 97.29 | 93.62 | ||
| Cat | GRA7 | 89.7 | 92.5 | [65] |
| TLA | 84.6 | 99.3 | ||
| Cat | M1 (H4 + H11) | 95 | 100 | [72] |
| TSA | 98 | 99 | ||
| Pig | CM5 (SAG2-GRA1-ROP1L) | 93.8 | 100 | [7] |
| TLA | 100 | 100 | ||
| Horse | CM5 (SAG2-GRA1-ROP1L) | 100 | 100 | [7] |
| TLA | 100 | 100 | ||
| Mink | GRA7 | 84.2 | 99.1 | [34] |
| TSA | 68.4 | 96.4 | ||
| Sheep | CM5 (SAG2-GRA1-ROP1L) | 100 | 100 | [7] |
| TLA | 100 | 100 | ||
| Sheep | M14 (GRA1 + SAG2 + ROP1) | 100 | 100 | [70] |
| TLA | 100 | 100 | ||
| Sheep | CM8 (AMA1-SAG2-GRA1-ROP1) | 97.92 | 100 | [48] |
| TLA | 97.92 | 100 | ||
| Goat | CM8 (AMA1-SAG2-GRA1-ROP1) | 95.56 | 100 | [48] |
| TLA | 97.78 | 100 | ||
| Chicken | GRA7 | 100 | 98.9 | [33] |
| TSA | 93.8 | 97.9 | ||
| Dog | GRA7 | 91 | 97.7 | [71] |
| TLA | 88.1 | 96.8 |
| Conjugate | Species | Positive % (n/N) | Se (%) | Sp (%) | Agreement (Kappa Value) | Reference Test | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein A/G | Pig | 28.5 (4/14)–76.9 (10/12) | 88.6 | 93.9 | 0.8 | Commercial ELISA | [43] |
| 88.6 | 93.9 | 0.8 | MAT | [43] | |||
| 84.8 | 96.8 | 0.8 | WB | [43] | |||
| Cat | 100 (11/11) | ND | ND | 1 | MAT | [43] | |
| Mice | 0 (0/3)–100% (3/3) | ND | ND | 1 | MAT | [43] | |
| Seal | 0 (0/4)–(14/14) | ND | ND | 0.8 | MAT | [43] | |
| Mink | 13 (17/131)–15.3(20/131) | 68.4–84.2 | 95.5–99.1 | 0.7–0.8 | WB | [34] | |
| White-tailed deer | 42.2 (113/268) | 92 | 89 | ND | ND | [52] | |
| Alpaca Sheep Goat Horse Dog | 57.1 (8/14) Alpaca 58.8 (10/17) Sheep 64.7 (11/17) Goat 13.3 (2/15) Horse 48.2 (27/56) Dog | 92 (Overall value) | 89 (Overall value) | 0.81 (Overall value) | IHA | [68] | |
| Pig | Not clear | ND | ND | 0.9 | MAT | [58] | |
| Not clear | ND | ND | 0.8 | Commercial ELISA | [58] | ||
| Dog | 45.8 (11/24) | ND | ND | 0.9 | MAT | [58] | |
| Cat | 38.5 (5/13) | ND | ND | 0.9 | MAT | [58] | |
| Protein A | Goat | 22 (132/600) | 89.5 | 97.9 | ND | MAT | [55] |
| Dog | ND | 93 | 82 | 0.8 | IHA | [69] | |
| Cat | ND | 100 | 100 | 1 | IHA | [69] | |
| Dog | 84 (178/212) | 75-80 | 80-85 | ND | WB | [74] | |
| Dog | 34.7 (42/121) | ND | ND | 0.6 | MAT | [75] | |
| Cat | 35.5 (16/45) | ND | ND | 0.5 | MAT | [75] | |
| Protein G | Goat | ND | 97 | 100 | 0.9 | IHA | [69] |
| Horse | ND | 72 | 100 | 0.7 | IHA | [69] | |
| Alpaca | ND | 76 | 95 | 0.7 | IHA | [69] | |
| Sheep | ND | 91 | 100 | 0.9 | IHA | [69] |
| Possible Cross-Reactive Species | Host Species | Antigen(s) Used | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neospora caninum | Pig, Cat, Mice, Seal | Soluble tachyzoite | No cross-reactions were reported | [43] |
| Chicken | Sonicated tachyzoite antigens | No cross-reactions were reported Dual infection with T. gondii and N. caninum was reported | [64] | |
| Sheep | M14 (GRA1 + SAG2 + ROP1) | No cross-reactions were reported | [70] | |
| Goat, Sheep | CM6 (AMA1N-SAG2-GRA1-ROP1) CM7 (AMA1C-SAG2-GRA1-ROP1) CM8 (AMA1-SAG2-GRA1-ROP1) CM9 (SAG2-GRA1-ROP1-GRA2) | No cross-reactions were reported | [48] | |
| Dog | Native purified SAG1 (From tachyzoites) | No cross-reactions were reported | [76] | |
| Turkey | M12 (GRA7 & GRA8) | No cross-reactions were reported with N. caninum positive turkeys Cross-reactions were observed in turkeys which were experimentally infected with Hammondia hammondi and turkey- specific Eimeria spp. | [62] | |
| White-tailed deer | Crude extract antigen | No cross-reactions were reported Dual infection with T. gondii and N. caninum was reported | [51] | |
| Sarcocystis spp. | Cattle | Sonicated T. gondii antigens | Authors mentioned that some seropositive results for T. gondii in cattle could be due to cross-reactions with anti Neospora or anti Sarcocystis antibodies | [60] |
| Pig | Crude rhoptries | No cross-reactions were reported | [77] | |
| Besnoitia spp | Pig, Cat Mice, Seal | Soluble tachyzoite | No cross-reactions were reported | [43] |
| lsospora suis | Pig | Tachyzoite lysate | No cross-reactions were reported | [29] |
| Trichinella spp. | Pig, Cat Mice, Seal | Soluble tachyzoite | No cross-reactions were reported | [43] |
| Pig | Tachyzoite lysate | No cross-reactions were reported | [29] | |
| Ascaris suum | Pig | Tachyzoite lysate | No cross-reactions were reported | [29] |
| Bacteria species Salmonella Yersinia Actinobacillus | Pig | Tachyzoite lysate | No cross-reactions were reported | [29] |
| No specific species | Pigs | Purified native SAG1 | Authors mentioned the possibility of having low cross-reactions with purified native SAG 1 | [49] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liyanage, K.L.D.T.D.; Wiethoelter, A.; Hufschmid, J.; Jabbar, A. Descriptive Comparison of ELISAs for the Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies in Animals: A Systematic Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050605
Liyanage KLDTD, Wiethoelter A, Hufschmid J, Jabbar A. Descriptive Comparison of ELISAs for the Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies in Animals: A Systematic Review. Pathogens. 2021; 10(5):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050605
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiyanage, K. L. D. Tharaka D., Anke Wiethoelter, Jasmin Hufschmid, and Abdul Jabbar. 2021. "Descriptive Comparison of ELISAs for the Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies in Animals: A Systematic Review" Pathogens 10, no. 5: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050605
APA StyleLiyanage, K. L. D. T. D., Wiethoelter, A., Hufschmid, J., & Jabbar, A. (2021). Descriptive Comparison of ELISAs for the Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies in Animals: A Systematic Review. Pathogens, 10(5), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050605







