Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein: Expression, Purification, and Its Biochemical Characterization and Utility in Serological Assay Development to Assess Immunological Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
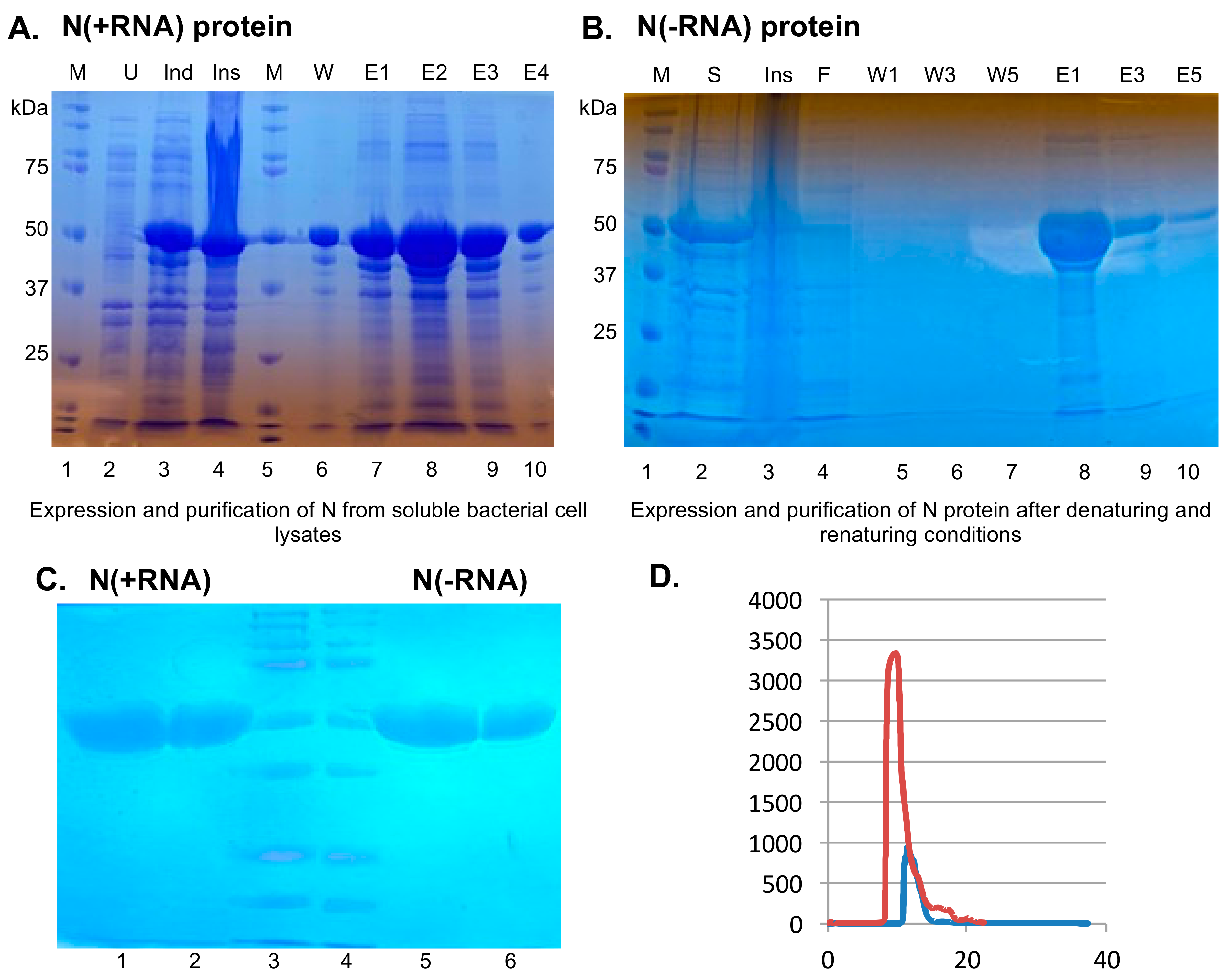
2.1. Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 N Protein from the Soluble Fraction of Bacterial Cell Lysates Contains Bacterial RNAs
2.2. Purification of Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Devoid of Bacterial RNAs
2.3. Both N(+RNA) and N(−RNA) Proteins Can Be Specifically Detected by an Anti-N Antibody
2.4. N(−RNA) Shows Higher Sensitivity Level Than N(+RNA) to Detect Anti-N Antibody by ELISA
2.5. The SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Preferentially Binds ssRNA In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmids
4.2. Expression and Purification of the Recombinant N Protein from the Soluble Fraction of Bacterial Cell Lysates
4.3. Purification of the Recombinant N Protein without Associated Bacterial RNAs
4.4. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
4.5. Evaluation of the Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Using Reagents of a Commercial Human IgG/IgM ELISA Kit
4.6. Comparison of N(+RNA) and N(−RNA) in the N-Based ELISA with Serially Diluted Anti-N Monoclonal Antibody (mAb)
4.7. Homemade N-Based Cat IgG ELISA
4.8. Cat Serum Samples
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Monoclonal Antibodies for Treatment of COVID-19. FDA 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-monoclonal-antibodies-treatment-covid-19 (accessed on 28 January 2021).
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. COVID-19 Vaccines. FDA 2021. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19/covid-19-vaccines (accessed on 27 February 2021).
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M.; O’Meara, M.J.; Rezelj, V.V.; Guo, J.Z.; Swaney, D.L.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, P.S. Coronavirus genomic RNA packaging. Virology 2019, 537, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Chen, C.-M.M.; Chiang, M.; Hsu, Y.; Huang, T. Transient oligomerization of the SARS-CoV N protein—Implication for virus ribonucleoprotein packaging. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, Y.L.; Teoh, K.T.; Lo, J.; Chan, C.M.; Kien, F.; Escriou, N.; Tsao, S.W.; Nicholls, J.M.; Altmeyer, R.; Peiris, J.S.M.; et al. The M, E, and N structural proteins of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus are required for efficient assembly, trafficking, and release of virus-like particles. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11318–11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.-H.; Chen, P.-J.; Yeh, S.-H. Nucleocapsid phosphorylation and RNA helicase DDX1 recruitment enables coronavirus transition from discontinuous to continuous transcription. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutta, N.K.; Mazumdar, K.; Gordy, J.T. The Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2: A Target for Vaccine Development. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00647-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, V.A.J.; Hernández-Carralero, E.; Paz-Cabrera, M.C.; Cabrera, E.; Hernández-Reyes, Y.; Hernández-Fernaud, J.R.; Gillespie, D.A.; Salido, E.; Hernández-Porto, M.; Freire, R. The Nucleocapsid protein triggers the main humoral immune response in COVID-19 patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 543, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algaissi, A.; Alfaleh, M.A.; Hala, S.; Abujamel, T.S.; Alamri, S.S.; Almahboub, S.A.; Alluhaybi, K.A.; Hobani, H.I.; Alsulaiman, R.M.; AlHarbi, R.H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 S1 and N-based serological assays reveal rapid seroconversion and induction of specific antibody response in COVID-19 patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.L.; Goldgof, G.M.; Shy, B.R.; Levine, A.G.; Balcerek, J.; Bapat, S.P.; Prostko, J.; Rodgers, M.; Coller, K.; Pearce, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence and neutralizing activity in donor and patient blood. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-K.; Hsu, Y.-L.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chao, F.-A.; Wu, M.-C.; Huang, Y.-S.; Hu, C.-K.; Huang, T.-H. Multiple nucleic acid binding sites and intrinsic disorder of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nucleocapsid protein: Implications for ribonucleocapsid protein packaging. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.; Sue, S.-C.; Yu, T.; Hsieh, C.-M.; Tsai, C.-K.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Lee, S.; Hsiao, H.; Wu, W.-J.; Chang, W.-L.; et al. Modular organization of SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006, 13, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Du, N.; Lei, Y.; Dorje, S.; Qi, J.; Luo, T.; Gao, G.F.; Song, H. Structures of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid and their perspectives for drug design. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinesh, D.C.; Chalupska, D.; Silhan, J.; Koutna, E.; Nencka, R.; Veverka, V.; Boura, E. Structural basis of RNA recognition by the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinzula, L.; Basquin, J.; Bohn, S.; Beck, F.; Klumpe, S.; Pfeifer, G.; Nagy, I.; Bracher, A.; Hartl, F.U.; Baumeister, W. High-resolution structure and biophysical characterization of the nucleocapsid phosphoprotein dimerization domain from the Covid-19 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 538, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yu, L.; Petros, A.M.; Gunasekera, A.; Liu, Z.; Xu, N.; Hajduk, P.; Mack, J.; Fesik, S.W.; Olejniczak, E.T. Structure of the N-terminal RNA-binding domain of the SARS CoV nucleocapsid protein. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 6059–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, I.-M.; Oldham, M.L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J. Crystal structure of the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus nucleocapsid protein dimerization domain reveals evolutionary linkage between corona- and arteriviridae. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17134–17139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cubuk, J.; Alston, J.J.; Incicco, J.J.; Singh, S.; Stuchell-Brereton, M.D.; Ward, M.D.; Zimmerman, M.I.; Vithani, N.; Griffith, D.; Wagoner, J.A.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is dynamic, disordered, and phase separates with RNA. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timani, K.-A.; Ye, L.; Ye, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Gong, Z. Cloning, sequencing, expression, and purification of SARS-associated coronavirus nucleocapsid protein for serodiagnosis of SARS. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 30, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Cao, H.; Xie, T.; Long, R.; Li, H.; Yang, T.; Yan, M.; Xie, Z. N-terminally truncated nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 as a better serological marker than whole nucleocapsid protein in evaluating the immunogenicity of inactivated SARS-CoV-2. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Liu, G.; Ma, H.; Zhao, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Mohammed, A.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; et al. Biochemical characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Ye, F.; Sun, T.; Yue, L.; Peng, S.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Du, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. In vitro biochemical and thermodynamic characterization of nucleocapsid protein of SARS. Biophys. Chem. 2004, 112, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, H.; Yuan, G.; Fu, Y.; Luo, Y. Low stability of nucleocapsid protein in SARS virus. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 11103–11108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dileepan, M.; Di, D.; Huang, Q.; Ahmed, S.; Heinrich, D.; Ly, H.; Liang, Y. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) exposure in pet cats and dogs in Minnesota, USA. Virulence 2021, 12, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.L.; Tan, S.S.; Saw, S.; Pajarillaga, A.; Zaine, S.; Khoo, C.; Wang, W.; Tambyah, P.; Jureen, R.; Sethi, S.K. Clinical evaluation of serological IgG antibody response on the Abbott Architect for established SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1256.e9–1256.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, C. A facile inhibitor screening of SARS coronavirus N protein using nanoparticle-based RNA oligonucleotide. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2173–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.-M.; Lin, S.-C.; Hsu, J.-N.; Chang, C.-K.; Chien, C.-M.; Wang, Y.-S.; Wu, H.-Y.; Jeng, U.-S.; Kehn-Hall, K.; Hou, M.-H. Structure-Based Stabilization of Non-native Protein-Protein Interactions of Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Proteins in Antiviral Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 3131–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Hou, M.-H.; Chang, C.-F.; Hsiao, C.-D.; Huang, T. The SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein--forms and functions. Antivir. Res. 2014, 103, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.-K.; Wu, M.P.-J.; Chen, S.-T.; Hou, M.-H.; Hong, M.-H.; Pan, F.-M.; Yu, H.-M.; Chen, J.-H.; Yao, C.-W.; Wang, A.H.-J. Biochemical and immunological studies of nucleocapsid proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome and 229E human coronaviruses. Proteomics 2005, 5, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Qavi, A.J.; Hachim, A.; Kavian, N.; Cole, A.R.; Moyle, A.B.; Wagner, N.D.; Sweeney-Gibbons, J.; Rohrs, H.W.; Gross, M.L.; et al. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 N protein reveals multiple functional consequences of the C-terminal domain. bioRxiv 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7709165/ (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Tarczewska, A.; Kolonko-Adamska, M.; Zarębski, M.; Dobrucki, J.; Ożyhar, A.; Greb-Markiewicz, B. The method utilized to purify the SARS-CoV-2 N protein can affect its molecular properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; He, S.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Q.; Chen, S.; Kang, S. Structural Insight Into the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein C-Terminal Domain Reveals a Novel Recognition Mechanism for Viral Transcriptional Regulatory Sequences. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 624765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di, D.; Dileepan, M.; Ahmed, S.; Liang, Y.; Ly, H. Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein: Expression, Purification, and Its Biochemical Characterization and Utility in Serological Assay Development to Assess Immunological Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081039
Di D, Dileepan M, Ahmed S, Liang Y, Ly H. Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein: Expression, Purification, and Its Biochemical Characterization and Utility in Serological Assay Development to Assess Immunological Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pathogens. 2021; 10(8):1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081039
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi, Da, Mythili Dileepan, Shamim Ahmed, Yuying Liang, and Hinh Ly. 2021. "Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein: Expression, Purification, and Its Biochemical Characterization and Utility in Serological Assay Development to Assess Immunological Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection" Pathogens 10, no. 8: 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081039
APA StyleDi, D., Dileepan, M., Ahmed, S., Liang, Y., & Ly, H. (2021). Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein: Expression, Purification, and Its Biochemical Characterization and Utility in Serological Assay Development to Assess Immunological Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pathogens, 10(8), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081039







