A Systematic Review of Epstein–Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1) Gene Variants in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
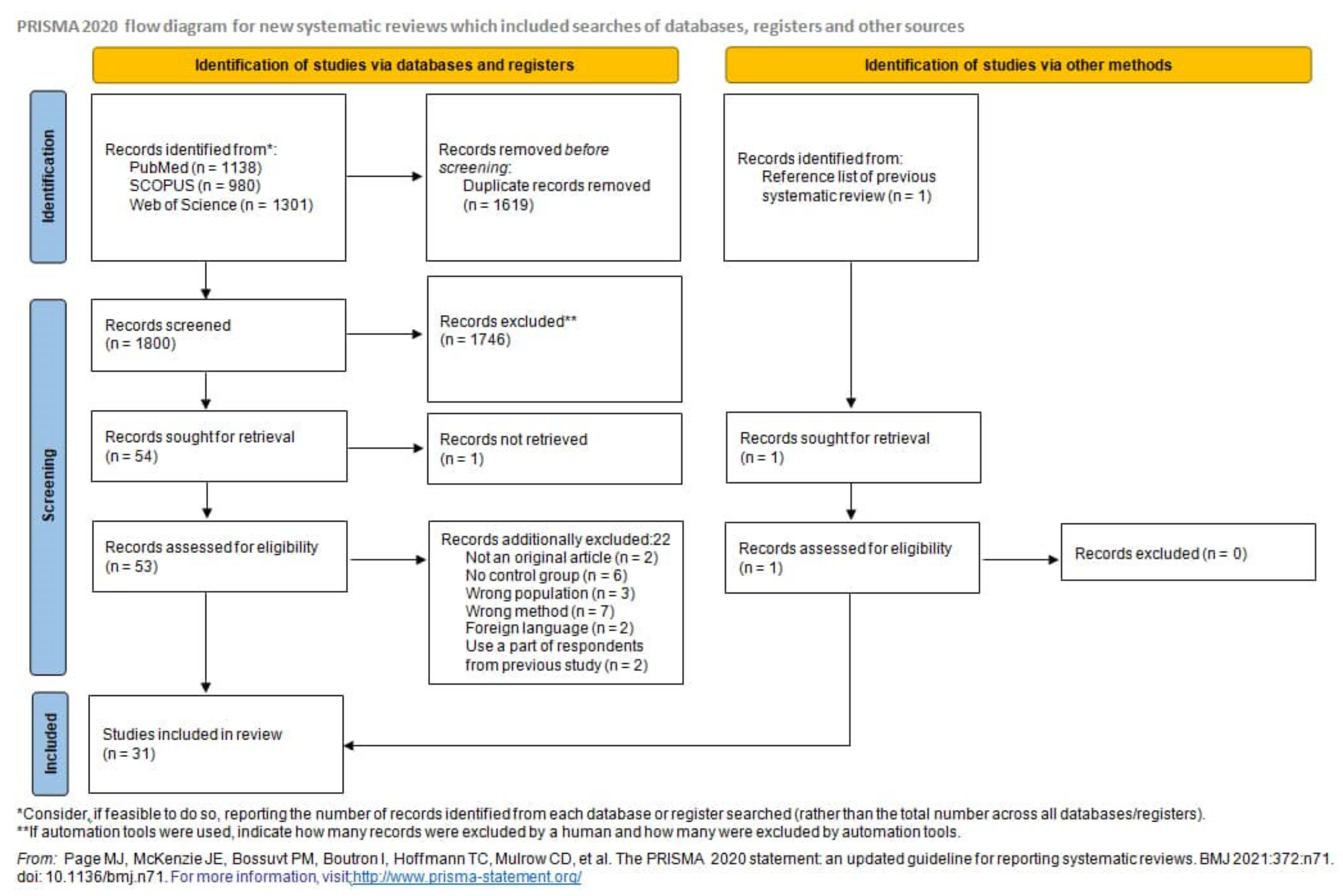
2.1. Systematic Review
2.2. Meta-Analysis of the Association between LMP1 Variants with NPC
2.2.1. Xhol Loss
2.2.2. The 30 bp Deletion
2.2.3. The 69 bp Deletion
2.2.4. B95-8 Variant
2.2.5. China1 Variant
2.2.6. Mediterranean (Med) Variant
2.2.7. North Carolina (NC) Variant
2.3. The Association between LMP1 Variants and NPC Susceptibility by Regions: Endemic and Non-Endemic
2.3.1. The 30 bp Deletion
2.3.2. Xhol Loss
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Selection
4.2. Database Search
4.3. Article Screening and Selection
4.4. Data Abstraction and Quality Assessment
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, W.H.; Qin, H. De Non-viral environmental risk factors for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 22, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Chang, E.T.; Adami, H.O. The enigmatic epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 1765–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Y.-X.; Jia, W.-H. Familial nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biol. 2002, 12, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, S.W.; Tsang, C.M.; Lo, K.W. Epstein-barr virus infection and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Schryver, A.; Friberg, S.; Klein, G.; Henle, W.; Henle, G.; De-Thi, G.; Clifford, P.; Ho, H.C. Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Antibody Patterns in Carcinoma of the Post-Nasal Space. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1969, 5, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henle, W.; Henle, G.; Burtin, P.; Cachin, Y.; De-Schryver, A.; De-the, G.; Diehl, V.; Adams, M.; Berry, T.; Hutkin, E.; et al. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr Virus In Naso-pharyngeal Carcinoma, Other Head and Neck Neoplasms, and Control Groups. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1970, 44, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Wakisaka, N.; Kondo, S.; Endo, K.; Sugimoto, H.; Hatano, M.; Ueno, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Yoshizaki, T. Progression of understanding for the role of Epstein-Barr virus and management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Liebowitz, D.; Kieff, E. An EBV Membrane Protein Expressed in Immortalized Lymphocytes Transforms Established Rodent Cells. Cell 1985, 43, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, R.K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. All Three Domains of the Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded Latent Membrane Protein LMP-1 Are Required for Transformation of Rat-1 Fibroblasts. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulwichit, W.; Edwards, R.H.; Davenport, E.M.; Baskar, J.F.; Godfrey, V.; Raab-Traub, N. Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces B cell lymphoma in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11963–11968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Costa, V.G.; Marques-Silva, A.C.; Moreli, M.L. The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1) 30-bp deletion and XhoI-polymorphism in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Oliveira, D.E.; Müller-Coan, B.G.; Pagano, J.S. Viral Carcinogenesis Beyond Malignant Transformation: EBV in the Progression of Human Cancers. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coffin, W.F., III; Erickson, K.D.; Hoedt-Miller, M.; Martin, J.M. The cytoplasmic amino-terminus of the Latent Membrane Protein-1 of Epstein-Barr Virus: Relationship between transmembrane orientation and effector functions of the carboxy-terminus and transmembrane domain. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5313–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gires, O.; Zimber-Strobl, U.; Gonnella, R.; Ueffing, M.; Marschall, G.; Zeidler, R.; Pich, D.; Hammerschmidt, W. Latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus mimics a constitutively active receptor molecule. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 6131–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.P.; Chang, Y.S. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1: Structure and functions. J. Biomed. Sci. 2003, 10, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.E.; Edwards, R.H.; Walling, D.M.; Raab-Traub, N. Sequence variation in the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 2729–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.H.; Seillier-Moiseiwitsch, F.; Raab-Traub, N. Signature Amino Acid Changes in Latent Membrane Protein 1 Distinguish Epstein-Barr Virus Strains. Virology 1999, 261, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smatti, M.K.; Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Ali, N.H.; Pintus, G.; Abou-Saleh, H.; Nasrallah, G.K. Epstein-barr virus epidemiology, serology, and genetic variability of LMP-1 oncogene among healthy population: An update. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knecht, H.; Bachmann, E.; Brousset, P.; Sandvej, K.; Nadal, D.; Bachmann, F.; Odermatt, B.; Delsol, G.; Pallesen, G. Deletions within the LMP1 oncogene of Epstein-Barr virus are clustered in Hodgkin’s disease and identical to those observed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Blood 1993, 82, 2937–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Hamid, M.; Chen, J.J.; Constantine, N.; Massoud, M.; Raab-Traub, N. EBV Strain Variation: Geographical Distribution and Relation to Disease State. Virology 1992, 190, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, K.-C.G.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Liu, M.-T.; Chung, T.-T.; Liu, S.-T. Prevalence of Taiwan Variant of Epstein-Barr Virus in Throat Washings from Patients with Head and Neck Tumors in Taiwan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.-S.; Su, I.-J.; Chung, P.-J.; Shu, C.-H.; Ng, C.-K.; Wu, S.-J.; Liu, S.-T. Detection of an Epstein-Barr-Virus Variant in T-Cell-Lymphoma Tissues Identical to the Distinct Strain Observed in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in the Taiwanese Population. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 62, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.L.; Lung, M.L.; Chan, K.H.; Griffin, B.E.; Ng, M.H. Tissue Distribution of Epstein-Barr Virus Genotypes. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7301–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, S.T.; Lo, K.W.; Leung, S.F.; Chan, W.Y.; Choi, P.H.; Johnson, P.J.; Lee, J.C.; Huang, D.P. Prevalence of LMP1 deletion variant of Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and gastric tumors in Hong Kong. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 66, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanim, F.; Yao, Q.Y.; Niedobitek, G.; Sihota, S.; Rickinson, A.B.; Young, L.S. Analysis of Epstein-Barr virus gene polymorphisms in normal donors and in virus-associated tumors from different geographic locations. Blood 1996, 88, 3491–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.J.; Lay, J.D.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, J.Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Su, I.J. Genomic analysis of Epstein-Barr virus in nasal and peripheral T-cell lymphoma: A comparison with nasopharyngeal carcinoma in an endemic area. J. Med. Virol. 1996, 50, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.Y.; Yuen, S.T.; Chung, L.P.; Chan, A.S.Y.; Wong, M.P. Prevalence of mutations and 30-bp deletion in the C-terminal region of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 oncogene in reactive lymphoid tissue and non-nasopharyngeal EBV-associated carcinomas in Hong Kong Chinese. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 72, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunewald, V.; Bonnet, M.; Boutin, S.; Yip, T.; Louzir, H.; Levrero, M.; Seigneurin, J.M.; Raphael, M.; Touitou, R.; Martel-Renoir, D.; et al. Amino-acid change in the Epstein-Barr-virus ZEBRA protein in undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinomas from Europe and North Africa. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 75, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, P.; Novikova, E.; Scherback, L.; Janik, C.; Pavlish, O.; Arkhipov, V.; Nicholls, J.; Müller-Lantzsch, N.; Gurtsevitch, V.; Grässer, F.A. The LMP1 gene isolated from Russian nasopharyngeal carcinoma has no 30-bp deletion. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 91, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-G.; Sandvej, K.; Li, P.-J.; Ji, X.-L.; Yan, Q.-H.; Zhang, X.-P.; Da, J.-P.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.J. Epstein-Barr virus gene polymorphisms in Chinese Hodgkin’s disease cases and healthy donors: Identification of three distinct virus variants. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-S.; Song, K.-H.; Mai, H.-Q.; Jia, W.-H.; Feng, B.-J.; Xia, J.-C.; Zhang, R.-H.; Huang, L.-X.; Yu, X.-J.; Feng, Q.-S.; et al. The 30-bp deletion variant: A polymorphism of latent membrane protein 1 prevalent in endemic and non-endemic areas of nasopharyngeal carcinomas in China. Cancer Lett 2002, 176, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.X.; Zong, Y.S.; Wu, Q.L.; Han, A.J.; Liang, Y.J. Loss of an XhoI-site within N-terminal region of Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ai Zheng 2003, 22, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza, G.; Santón, A.; Vidal, A.M.; Bellas, C. Latent membrane protein-1 oncogene deletions in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Caucasian patients. Acta Otolaryngol. 2003, 123, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.L.; Peh, S.C.; Sam, C.K. Analyses of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 in Malaysian nasopharyngeal carcinoma: High prevalence of 30-bp deletion, Xho1 polymorphism and evidence of dual infections. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 69, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabay, P.; De Matteo, E.; Merediz, A.; Preciado, M.V. High frequency of Epstein Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 30 bp deletion in a series of pediatric malignancies in Argentina. Arch. Virol. 2004, 149, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C.; Cherng, J.M.; Lin, H.J.; Tsang, C.W.; Liu, Y.X.; Lee, S.P. Amino acid changes in functional domains of latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma of southern China and Taiwan: Prevalence of an HLA A2-restricted “epitope-loss variant”. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2023–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, J.; Hahn, P.; Kremmer, E.; Fröhlich, T.; Arnold, G.J.; Sham, J.; Kwong, D.; Grässer, F.A. Detection of wild type and deleted latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) of Epstein-Barr virus in clinical biopsy material. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 116, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zong, Y.S.; He, J.H.; Lin, S.X.; Zhong, B.L.; Liang, Y.J. Comparison of Epstein-Barr virus infection and 30 bp-deleted LMP1 gene among four histological types of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin. Med. J. 2004, 117, 608–611. [Google Scholar]
- Dardari, R.; Khyatti, M.; Cordeiro, P.; Odda, M.; ElGueddari, B.; Hassar, M.; Menezes, J. High frequency of latent membrane protein-1 30-bp deletion variant with specific single mutations in Epstein-Barr virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Moroccan patients. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadhri-Guiga, B.; Khabir, A.M.; Mokdad-Gargouri, R.; Ghorbel, A.M.; Drira, M.; Daoud, J.; Frikha, M.; Jlidi, R.; Gargouri, A. Various 30 and 69 bp deletion variants of the Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 may arise by homologous recombination in nasopharyngeal carcinoma of Tunisian patients. Virus Res. 2006, 115, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, H.; Yap, Y.; Yip, W.; Seow, H. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 (LMP-1) 30-bp deletion and Xho I-loss is associated with type III nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Malaysia. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiwawech, D.; Srivatanakul, P.; Karalak, A.; Ishida, T. Association between EBNA2 and LMP1 subtypes of Epstein-Barr virus and nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Thais. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 42, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.J.; Bei, J.X.; Mai, S.J.; Xu, J.F.; Chen, L.Z.; Zhang, R.H.; Yu, X.J.; Hong, M.H.; Zeng, Y.X.; Kang, T. The dominance of China 1 in the spectrum of Epstein-Barr virus strains from cantonese patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banko, A.; Lazarevic, I.; Cupic, M.; Stevanovic, G.; Boricic, I.; Jovanovic, T. Carboxy-terminal sequence variation of LMP1 gene in Epstein-Barr-virus-associated mononucleosis and tumors from Serbian patients. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtsevitch, V.E.; Iakovleva, L.S.; Shcherbak, L.N.; Goncharova, E.V.; Smirnova, K.V.; Diduk, S.V.; Kondratova, V.N.; Maksimovich, D.M.; Lichtenstein, A.V.; Seniuta, N.B. The LMP1 oncogene sequence variations in patients with oral tumours associated or not associated with the Epstein Barr. Mol. Biol. 2013, 47, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyuta, N.; Yakovleva, L.; Goncharova, E.; Scherback, L.; Diduk, S.; Smirnova, K.; Maksimovich, D.; Gurtsevitch, V. Epstein-barr virus latent membrane protein 1 polymorphism in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and other oral cavity tumors in Russia. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, M.; Marinho-Dias, J.; Ribeiro, J.; Esteves, M.; Maltez, E.; Baldaque, I.; Breda, E.; Monteiro, E.; Medeiros, R.; Sousa, H. Characterization of Epstein-Barr virus strains and LMP1-deletion variants in Portugal. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niya, M.H.K.; Tameshkel, F.S.; Keyvani, H.; Esghaei, M.; Panahi, M.; Zamani, F.; Tabibzadeh, A. Epstein–Barr virus molecular epidemiology and variants identification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 29, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, T.; Machado, R.; Russo, D.P.; Herman, S.W.; Teegala, S.; Costantino, P. Viral markers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis on the detection of p16INK4a, human papillomavirus (HPV), and Ebstein-Barr virus (EBV). Am. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Med. Surg. 2021, 42, 102762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katabi, N.; Lewis, J.S. Update from the 4th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Head and Neck Tumours: What Is New in the 2017 WHO Blue Book for Tumors and Tumor-Like Lesions of the Neck and Lymph Nodes. Head Neck Pathol. 2017, 11, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.; Suh, Y.-E.; Paleri, V.; Devlin, D.; Ayaz, B.; Pertl, L.; Thavaraj, S. Oncogenic human papillomavirus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An observational study of correlation with ethnicity, histological subtype and outcome in a UK population. Infect. Agent Cancer 2013, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, N.; Patel, S.; Osborn, V.; McBride, S.; Riaz, N.; Lee, A.; Katabi, N.; Sherman, E.; Lee, N.Y.; Tsai, C.J. Prognostic significance of human papillomavirus and Epstein-Bar virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck 2020, 42, 2364–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rickinson, A. The Global Landscape of EBV-Associated Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pathmanathan, R.; Prasad, U.; Sadler, R.; Flynn, K.; Raab-Traub, N. Clonal proliferations of cells infected with Epstein-Barr virus in preinvasive lesions related to nasopharyngeal carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Ordoñez, B. An Update on Epstein-Barr Virus and Nasopharyngeal Carcinogenesis. Head Neck Pathol. 2007, 1, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsang, C.M.; Yip, Y.L.; Lo, K.W.; Deng, W.; To, K.F.; Hau, P.M.; Lau, V.M.Y.; Takada, K.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Lung, M.L.; et al. Cyclin D1 overexpression supports stable EBV infection in nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2012, 109, E3473–E3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.-F.; Zabarovsky, E.R.; Chen, F.; Cao, S.L.; Ernberg, I.K.; Winberg, G. Isolation and sequencing of the Epstein-Barr virus BNLF-1 gene (LMP1) from a Chinese nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72, 2399–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banko, A.V.; Lazarevic, I.B.; Folic, M.M.; Djukic, V.B.; Cirkovic, A.M.; Karalic, D.Z.; Cupic, M.D.; Jovanovic, T.P. Characterization of the variability of Epstein-Barr virus genes in nasopharyngeal biopsies: Potential predictors for carcinoma progression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, C.W.; Eliopoulos, A.G.; Blake, S.M.; Barker, R.; Young, L.S. Identification of functional differences between prototype Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP1 and a nasopharyngeal carcinoma-derived LMP1 in human epithelial cells. Virology 2000, 272, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, R.H.; Sitki-Green, D.; Moore, D.T.; Raab-Traub, N. Potential Selection of LMP1 Variants in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanda, T.; Yajima, M.; Ikuta, K. Epstein-Barr virus strain variation and cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, H.; Chiang, A.K.S. From conventional to next generation sequencing of Epstein-Barr virus genomes. Viruses 2016, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology A Proposal for Reporting B ECAUSE OF PRESSURE FOR TIMELY. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; Robertson, J.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, ED000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- RevMan|Cochrane Training. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/online-learning/core-software-cochrane-reviews/revman (accessed on 29 June 2021).


























| Author, Year | Country | NPC Cases | Controls | LMP1 Gene Variants in NPC Group | LMP1 Gene Variants in Control Group | Method | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Design | n | EBV+ | Sample Characteristics | n | EBV+ | Sample Characteristics | 30 bp Del | Xhol-Loss | Ncol Loss | 69 bp Del | 27 bp Del | B95-8 | China1 | Med | China2 | China3 | Alaskan | NC | Other | ||||
| Abdel- Hamid, 1992 [21] | Multicenter (Southern China, Malaysia, continental United States, Alaska, Egypt, and equatorial Africa) | NR | 56 | 56 | Biopsy | 22 | 22 | Total | 33 | 3 | Hybridization | ||||||||||||
| 2 | 2 | PGC | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | 13 | BL | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 6 | Non-HL | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | HL | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Jeng, 1994 [22] | Taiwan | NR | 32 | 25 | Biopsy | 197 | 103 | Total | 22 | 63 | Sequencing | ||||||||||||
| 53 | 25 | Healthy laboratory worker volunteers | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | 12 | Patients with tonsillitis and pharyngitis | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 118 | 66 | Other head and neck carcinoma | 46 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Miller, 1994 [17] | Multicenter (China, Malaysa, USA, Alaska, Mediteran) | NR | 17 | 17 | Biopsy | 8 | 8 | Total | 7 | 6 | 2 Xhol loss 2 30 bp del | PCR and sequencing | |||||||||||
| 2 | 2 | Posttransplant lymphoma | 1 Xhol loss 0 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | BL | 0 Xhol loss 0 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 4 | OHL | 0 Xhol loss 1 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | PGC | 1 Xhol loss 1 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Chang, 1995 [23] | Taiwan | NR | 48 | 48 | Biopsy | 128 | 78 | Total | 48 | 48 | 0 | 68 Xhol loss 10 Ncol loss 68 30 bp del | PCR, restriction-enzyme digestion, sequencing | ||||||||||
| 40 | 25 | Normal nasopharynx tissues | 23 Xhol loss. 2 Ncol loss 23 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 78 | 44 | TWs | 37 Xhol loss. 7 Ncol loss 37 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | 7 | TCL | 6 Xhol loss 1 Ncol loss 6 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 1 | HL | 1 Xhol loss 0 Ncol loss 1 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | BCL | 1 Xhol loss 0 Ncol loss 1 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Chen, 1996 [24] | Not reported | NR | 40 | 40 | Biopsy | 56 | 56 | Total | 28 | 53 30 bp del | PCR and sequencing | ||||||||||||
| 10 | 10 | Non-NPC biopsy samples | 7 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | 24 | TWs | 16 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | 22 | PB lymphocytes | 20 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cheung, 1996 [25] | China | NR | 77 | 77 | Biopsy and xenografts | 24 | 24 | Total | 72 | 77 | 21 30 bp del 24 Xhol loss | ||||||||||||
| 11 | 11 | Biopsy samples of gastric carcinomas and gastric lymphomas | 10 30 bp del 11 Xhol loss | PCR-RFLP | |||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | 13 | TWs of healthy individuals defined as disease-free close relatives of existing NPC patients | 11 30 bp del 13 Xhol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Khanim, 1996 [26] | Multicenter (UK, Taiwan, China, Europe, Africa, New Guinea) | NR | 30 | 30 | Biopsy | 37 | 35 | Total | 24 | 19 | 8 30 bp del 0 Xhol loss | PCR, RFLP, sequencing | |||||||||||
| 4 | 4 | Gastric adenocarcinoma biopsies | 2 30 bp del 0 Xhol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 | 23 | HL | 2 30 bp del 0 Xhol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 8 | IM | 4 30 bp del 0 Xhol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wu, 1996 [27] | China | NR | 30 | 30 | Biopsy | 22 | 22 | Total | 28 | 20 Xhol loss | PCR and sequencing | ||||||||||||
| 19 | 19 | nasal and extranasal TCL | 17 Xhol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 3 | IM | 3 Xhol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Leung, 1997 [28] | China | NR | 1 | 1 | EBV+ metastatic NPC in the lung biopsy | 92 | 92 | Total | 1 | 61 | PCR and sequencing | ||||||||||||
| 55 | 52 | Resected tonsils from patients with chronic tonsillitis | 26 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 6 | LELC-LG | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 10 | LELCSG | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 5 | SNCAs | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | 16 | GACAs | 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Grunewald, 1998 [29] | Multicenter Europe (Italy and France), North Africa, Asia, Oceania | NR | 64 | 64 | Biopsy | 94 | 94 | Total | 46 | 9 | 3 | 44 30 bp del 4 69 bp del 34 Ncol loss | Sequencing | ||||||||||
| 12 | 12 | Post-transplant BCL | 4 30 bp del 0 69 bp del 5 Ncol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | 15 | Lymphomas of HIV patients (BL, BCL, primary brain lymphoma) | 3 30 bp del 0 69 bp del 9 Ncol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 10 | Lymphocytes from patients with IM | 3 30 bp del 1 69 bp del 5 Ncol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 6 | OHL | 1 30 bp del 2 69 bp del 1 Ncol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 51 | 51 | PB-cell pellets from HBD | 33 30 bp del 1 69 bp del 14 Ncol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Edwards, 1999 [18] | Multicenter (China, Malaysia, Taiwan, Mediterranean, USA, Alaska) | NR | 64 N terminus + 27 C terminus + 17 Full lenth LMP1 | 108 | Biopsy | 10 N terminus + 50 C terminus + 7 full lenth LMP1 | 67 | IM, PGC, BL, OHL, Post/transplant lymphoma | 15 | 47 | 0 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5 Xhol loss 19 30 bp del 2 China1 0 China2 0 China3 0 Med+ 2 Med- 1 Alaskan 2 NC | Sequencing | ||||
| Hahn, 2001 [30] | Russia | NR | 7 | 7 | Biopsy | 11 | 11 | NPC-like tumor of the parotid gland, healthy carriers’ PB lymphocytes | 0 | 3 | Sequencing | ||||||||||||
| Zhou, 2001 [31] | China | NR | 6 | 6 | Biopsy | 94 | 30 sequenced | Total | 2 | 5 | 10 30 bp del 11 Xhol loss | Sekvencing | |||||||||||
| 71 | 71 64 LMP1 positive (14 N terminus + 12 C terminus for sequencing) | HD biopsy | 8 30 bp del 10 Xhol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 | 21 (2 N terminus + 2 C terminus for sequencing) | TWs from healthy Chinese | 1 30 bp del 1 Xhol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 2 (only 2 C terminus sequencing) | Chinese nasal TNKLs | 1 30 bp del 0 Xhol loss | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang, 2002 [32] | China | NR | 154 | 97 | Total | 209 | 90 | Total | 74 | 58 | Sequencing | ||||||||||||
| 47 | 43 LMP1+ | Biopsy | 106 | 53 LMP1+ | TWs from breast, lung–non head and neck carcinoma stomach, colon, and ovary carcinoma patients | 36 | 36 | ||||||||||||||||
| 107 | 54 LMP1+ | TW | 103 | 37 LMP1+ | TWs from healthy donors | 38 | 22 | ||||||||||||||||
| Lin, 2003 [33] | China | NR | 63 | 63 | Biopsy | 10 | 10 | PBMCs from healthy donors | 54 | 0 | PCR with XhoI digestion and sequencing | ||||||||||||
| Plaza, 2003 [34] | Spain | NR | 27 | 27 | Biopsy | 27 | 27 | EBV-related IM | 18 | 8 | PCR | ||||||||||||
| Tan, 2003 [35] | Malaysia | NR | 150 | 74 LMP+ 48 Xhol | Total | 26 | 19 LMP+ 5 Xhol | Total | 1 30 bp del 0 Xhol loss | PCR and restriction enzyme digestion | |||||||||||||
| 120 | 49 LMP+ 21 Xhol | TW | 14 | 7 LMP+ 5 Xhol | TWs from healthy individuals | 11 | 17 | 0 30 bp del 0 Xhol loss | |||||||||||||||
| 30 | 25 LMP+ 27 Xhol | Biopsy | 12 | 12 LMP+ | Biopsy from controls with clinical symptoms indicative of nasopharyngeal carcinoma but whose postnasal space biopsies were confirmed as histologically normal | 25 | 25 | 1 30 bp del 0 Xhol loss | |||||||||||||||
| Chabay, 2004 [36] | Argentina | NR | 4 | 4 | Biopsy | 27 | 27 | Total | 16 | PCR and sequencing | |||||||||||||
| 11 | 11 | Non-neoplastic controls | 3 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | 16 | Non-NPC EBV-related malignancies (HL and non-HL) | 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Lin, 2004 [37] | Multicenter (China and Taiwan) | NR | 22 | 22 | Biopsy | 23 | 18 | NPI specimens from patients with no evidence of NPC, but with clinical symptoms that were compatible with NPC, were obtained from the same anatomical site. These biopsy samples were subsequently diagnosed as chronic inflammation or inflammation and necrosis | 15 | 21 | 12 30 bp del 12 Xhol loss | Sequencing | |||||||||||
| Nicholls, 2004 [38] | China | NR | 18 | 18 | Biopsy | 10 | 10 | Total | 18 | 8 30 bp del | |||||||||||||
| 5 | 5 | Peripheral TCL | 1 | 4 30 bp del 1 China1 1 Med- | Sequencing, monoclonal antibodies, peptide binding | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 2 | EBV+ HL | 1 30 bp del, 1 Med- | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 3 | Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease | 3 bp del, 3 China1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang, 2004 [39] | China | NR | 117 | 99 | Biopsy | 53 | 46 | Healthy donors PBMCs | 87 | 4 | Sequencing | ||||||||||||
| Dardari, 2006 [40] | Morocco | NR | 81 | 81 | Total | 30 | 14 PCR+ | Healthy donors PBMCs | 58 | 2 | 6 30 bp del 3 69 bp del | PCR and sequencing | |||||||||||
| 61 | 61 | Biopsy | 51 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | 20 | PBMCs | 7 | / | |||||||||||||||||||
| Hadhri-Guiga, 2006 [41] | Tunis | NR | 74 | 74 | Total | 20 | 17 | Control patients with clinical symptoms indicative of NPC but whose postnasal biopsies were confirmed as histologically normal | 43 | 2 | 9 30 bp del 0 69 bp del | Xhol digestion and sequencing | |||||||||||
| 42 | 42 | Biopsy | 28 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | 32 | PB lymphocytes | 15 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| See, 2008 [42] | Malaysia | NR | 77 | 77 | Total | 10 | 8 | Non-malignant nasopharyngeal tissue samples | 26 | 45 | 0 30 bp del 0 Xhol loss | Xhol digestion and sequencing | |||||||||||
| 42 | 42 | Biopsy | 19 | 34 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 35 | 35 | Plasma | 7 | 11 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Tiwawech, 2008 [43] | Thailand | Case– control | 75 | 75 | PB leukocytes | 44 | 44 | Total | 44 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 16 | PCR and sequencing | ||||
| 20 | 20 | Randomly recruited age-matched (mean age ± 5 years) healthy subjects | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | 24 | Non-NPC patients with cancer and other disease | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Li, 2009 [44] | China | NR | 150 | 150 | Total | 269 | 253 | Total | 74 | 1 | 131 | 3 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 87 30 bp del 91 China1 5 China2 30 B95-8 1 Med 12 other strains | PCR and sequencing | ||||
| 50 | 50 | Biopsy | 15 | 9 | Biopsy from patients with nasopharyngeal chronic inflammation | 39 | 0 | 94 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 30 bp del 14 China1 1 China2 | ||||||||
| 50 | 50 | TW | 9 | 9 | TW from patients with nasopharyngeal chronic inflammation | 30 | 1 | 37 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 30 bp del 8 China1 | ||||||||
| 50 | 50 | Serum | 9 | 9 | Blood from patients with nasopharyngeal chronic inflammation | 0 | 0 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||
| 55 | 55 | TW from patients with other cancers | 0 30 bp del 30 China1 20 B95-8 2 China2 1 Med 6 other strains | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 63 | 63 | Biopsy samples from patients with other cancers | 40 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 59 | 52 | TW from healthy Cantonese donors | 33 30 bp del 39 China1 10 B95-8 2 China2 6 other strains | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 59 | 56 | PB from healthy Cantonese donors | 0 30 bp del | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Banko, 2012 [45] | Serbia | NR | 16 | 16 | Biopsy | 37 | 37 | Total | 1 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 12 30 bp del 1 69 bp del 1 27 bp del 12 B95-8 12 China1 7 Med | Sequencing | |||
| 30 | 30 | Plasma samples from patients with mononucleosis syndrome | 10 30 bp del 0 69 bp del 1 27 bp del 10 B95-8 10 China1 6 NC 4 Med | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 6 | Plasma samples after renal transplantation | 2 30 bp del 1 69 bp del 0 27 bp del 2 B95-8 2 China1 2 Med | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | HL biopsy | 0 30 bp del 0 69 bp del 0 27 bp del 1 Med | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Gurtsevitch, 2013 [46] | Russia | NR | 57 | 57 | Total | 69 | 55 | Total | 5 | 12 | 16 | 2 | 29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 4 | 19 30 bp del 1 69 bp del 21 B95-8 16 China1 5 Med+ 6 Med- 6 NC 0 other | Sequencing | |||
| 21 | 21 | Biopsy | 20 | 14 | OTOC (patients with cancer of the oral mucosa, tongue, sublingual tonsil, and some other malignant affections of the oral cavity) biopsy | 3 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | OTOC biopsy 7 30 bp del 1 69 bp del 2 B95-8 5 China1 3 Med+ 2 Med- 2 NC 0 other | |||||||
| 16 | 16 | PB | 20 | 13 | OTOC blood | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | OTOC blood 8 30 bp del 0 69 bp del 2 B95-8 7 China1 1 Med+ 1 Med- 1 NC 0 other | |||||||
| 20 | 19 | Blood donors | Blood donors 15 B95-8 1 China1 0 Med+ 1 Med- 2 NC 0 other | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | 20 | Lavage | 9 | 9 | OTOC oropharyngeal lavage | 1 | 5 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | OTOC lavage. 4 30 bp del 0 69 bp del 2 B95-8 3 China1 1 Med+ 2 Med- 1 NC 0 other | |||||||
| Senyuta, 2014 [47] | Russia | NR | 56 | 56 | Total | 54 | 54 | Total | 6 | 12 | 15 | 2 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 22 30 bp del 1 69 bp del 20 B95-8 17 China1 7 Med+ 6 Med- 7 NC 0 other | Sequencing | |||
| 22 | 22 | Biopsy | 14 | 14 | Biopsy from patients with other (non-nasopharyngeal carcinoma) tumors of the oral cavity—cancers of the mucous membrane of the tongue (3), floor of the mouth (2), cheek (1), retro molar area (3), lower jaw (4), and palate (5) | 4 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | Other ca biopsy 7 30 bp del 1 69 bp del 2 B95-8 5 China1 3 Med+ 2 Med- 2 NC 0 other | |||||||
| 15 | 15 | PB | 12 | 12 | Non-nasopharyngeal carcinoma blood samples | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | Blood other ca 9 30 bp del 0 69 bp del 1 B95-8 8 China1 1 Med+ 1 Med- 1 NC 0 other | |||||||
| 19 | 19 | Blood donors | Blood donors 1 30 bp del 0 69 bp del 15 B95-8 1 China1 0 Med+ 1 Med- 2 NC 0 other | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | 19 | TW | 9 | 9 | TW from other ca | 1 | 5 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | TW other ca 4 30 bp del 0 69 bp del 2 B95-8 3 China1 1 Med+ 2 Med- 1 NC 0 other | |||||||
| Neves, 2015 [48] | Portugal | Case– control | 41 | 41 | PB | 43 | 43 | PB from healthy controls | 0 | 11 | PCR | ||||||||||||
| Karbalaie, 2019 [49] | Iran | Cross- sectional | 7 | 7 | Biopsy | 3 | 3 | Nasal, vocal cord and tongue ca | 3 | 1 | PCR | ||||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banko, A.; Miljanovic, D.; Lazarevic, I.; Cirkovic, A. A Systematic Review of Epstein–Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1) Gene Variants in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081057
Banko A, Miljanovic D, Lazarevic I, Cirkovic A. A Systematic Review of Epstein–Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1) Gene Variants in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Pathogens. 2021; 10(8):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081057
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanko, Ana, Danijela Miljanovic, Ivana Lazarevic, and Andja Cirkovic. 2021. "A Systematic Review of Epstein–Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1) Gene Variants in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma" Pathogens 10, no. 8: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081057
APA StyleBanko, A., Miljanovic, D., Lazarevic, I., & Cirkovic, A. (2021). A Systematic Review of Epstein–Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1) Gene Variants in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Pathogens, 10(8), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081057






