Treponema pallidum among Female Sex Workers: A Cross-Sectional Study Conducted in Three Major Cities in Northern Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sample Characteristics
2.2. Exposure to T. pallidum and Active Syphilis
2.3. Factors of Exposure to T. pallidum
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
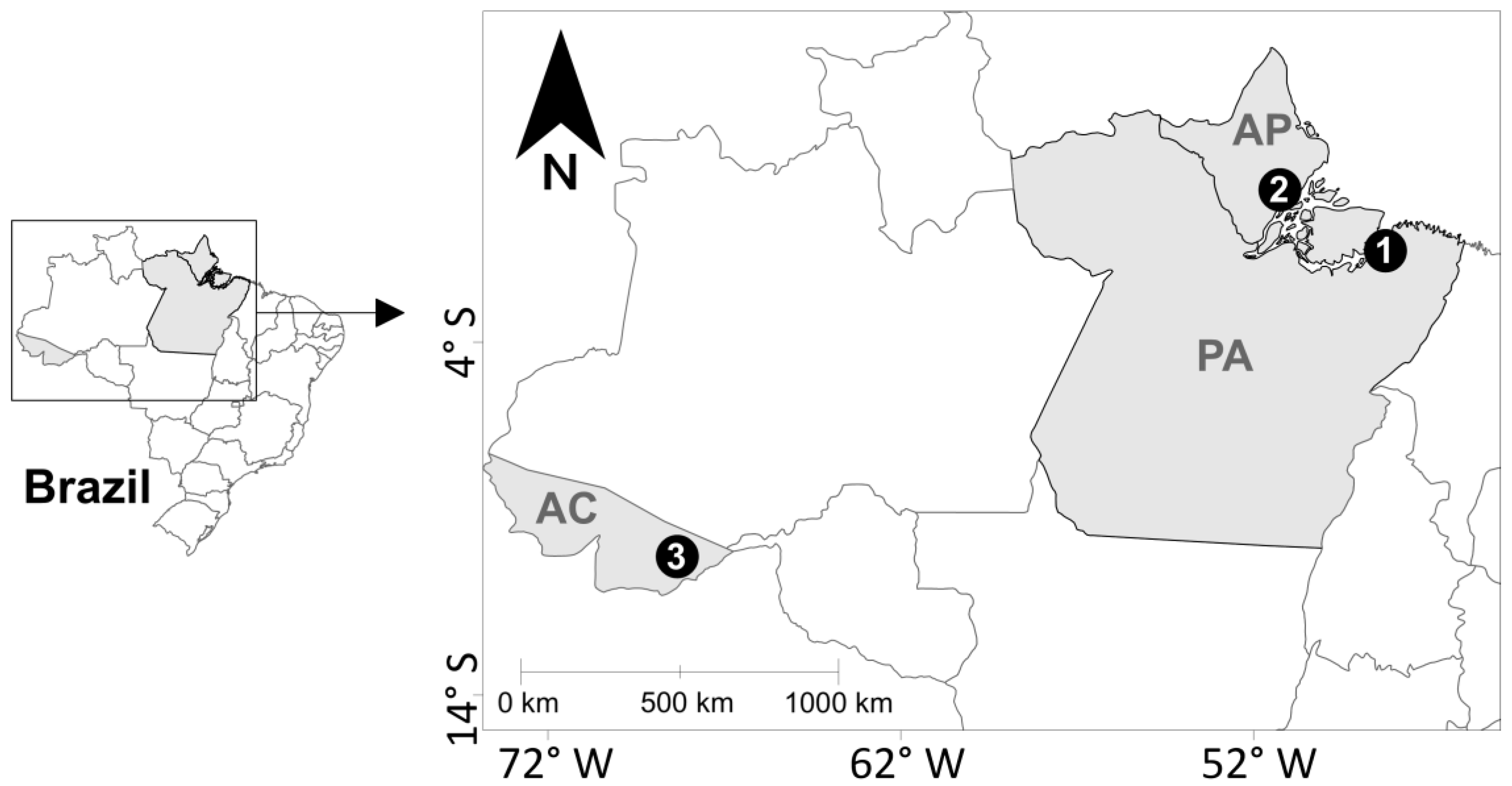
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Sampling
4.3. Study Design
4.4. Laboratory Tests
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peeling, R.W.; Mabey, D.; Kamb, M.L.; Chen, X.S.; Radolf, J.D.; Benzaken, A.S. Syphilis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, D.T.; Wasserheit, J.N. From epidemiological synergy to public health policy and practice: The contribution of other sexually transmitted diseases to sexual transmission of HIV infection. Sex. Transm. Infect. 1999, 75, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, S.D.; Ghanem, K.G.; Rompalo, A.M.; Erbelding, E.J. HIV seroconversion among public sexually transmitted disease clinic patients: Analysis of risks to facilitate early identification. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 2006, 42, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupin, N. Syphilis. Rev. Med. Interne. 2016, 37, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs). 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sexually-transmitted-infections-(stis) (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Ministry of Health Brazil. Boletim Epidemiológico de Sífilis. 2017. Available online: http://www.aids.gov.br/pt-br/pub/2017/boletim-epidemiologico-de-sifilis-2017 (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Ministry of Health Brazil. Boletim Epidemiológico de Sífilis 2019. Available online: https://www.saude.gov.br/images/pdf/2019/outubro/30/Boletim-S--filis-2019-internet.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Health Observatory (GHO) Data: Sex Workers and Syphilis. Available online: https://www.who.int/gho/sti/sex_workers/en/ (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Augusto, Â.; Young, P.W.; Horth, R.Z.; Inguane, C.; Sathane, I.; Ngale, K.; Benedetti, M.; Cummings, B.; Botão, C.F.; Baltazar, C.A.; et al. Hight burden of HIV infection and risk behaviors among female sex workers in three main urban areas of Mozambique. AIDS Behav. 2016, 20, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vickerman, P.; Ndowa, F.; O’Farrell, N.; Steen, R.; Alary, M.; Delany-Moretlwe, S. Using mathematical modelling to estimate the impact of periodic presumptive treatment on the transmission of sexually transmitted infections and HIV among female sex workers. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2010, 86, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Report on Global Sexually Transmitted Infection Surveillance. 2015. Available online: https://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/rtis/stis-surveillance-2015/en/ (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- Ferreira-Júnior, O.; Guimarães, M.; Damacena, G.N.; de Almeida, W.; de Souza-Júnior, P.; Szwarcwald, C.L.; Brazilian FSW Group. Prevalence estimates of HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C among female sex workers (FSW) in Brazil. Medicine 2016, 97, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuelter-Trevisol, F.; Custódio, G.; Silva, A.C.; Oliveira, M.B.; Wolfart, A.; Trevisol, D.J. HIV, hepatitis B and C, and syphilis prevalence and coinfection among sex workers in Southern Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2013, 46, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalcante, N.; Lima, H.; Tabosa, D.F.; Barbosa, E.; Costa, N.; Costa, L.; Frade, P.; Martins, L.C.; Silva-Oliveira, G.C.; Oliveira-Filho, A.B. Syphilis in female sex workers: An epidemiological study of the highway system of the state of Pará, northern Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, e20180064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.L.; Dos Santos Madeira, L.; Pereira, M.; da Silva, R.M.; de Luna Sales, J.B.; Azevedo, V.N.; Feitosa, R.; Monteiro, J.C.; de Oliveira Guimarães Ishak, M.; Ishak, R.; et al. Prevalence of syphilis in female sex workers in three countryside cities of the state of Pará, Brazilian Amazon. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, E.C.; Souza, S.B.; Costa, C.; Costa, L.M.; Pinheiro, L.; Machado, L.; Silva-Oliveira, G.C.; Martins, L.C.; Frade, P.; Oliveira-Filho, A.B. Treponema pallidum in female sex workers from the Brazilian Marajó Archipelago: Prevalence, risk factors, drug-resistant mutations and coinfections. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 115, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towns, J.M.; Leslie, D.E.; Denham, I.; Azzato, F.; Fairley, C.K.; Chen, M. Painful and multiple anogenital lesions are common in men with Treponema pallidum PCR-positive primary syphilis without herpes simplex virus coinfection: A cross-sectional clinic-based study. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2016, 92, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seña, A.C.; Zhang, X.H.; Li, T.; Zheng, H.P.; Yang, B.; Yang, L.G.; Salazar, J.C.; Cohen, M.S.; Moody, M.A.; Radolf, J.D.; et al. A systematic review of syphilis serological treatment outcomes in HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected persons: Rethinking the significance of serological non-responsiveness and the serofast state after therapy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cárcamo, C.P.; Campos, P.E.; García, P.J.; Hughes, J.P.; Garnett, G.P.; Holmes, K.K.; Peru PREVEN Study Team. Prevalences of sexually transmitted infections in young adults and female sex workers in Peru: A national population-based survey. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patterson, T.L.; Strathdee, S.A.; Semple, S.J.; Chavarin, C.V.; Abramovitz, D.; Gaines, T.L.; Mendoza, D.; Staines, H.; Aarons, G.A.; Magis Rodríguez, C. Prevalence of HIV/STIs and correlates with municipal characteristics among female sex workers in 13 Mexican cities. Salud Publica Mex. 2019, 61, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahuerta, M.; Sabidó, M.; Giardina, F.; Hernández, G.; Palacios, J.F.; Ortiz, R.; Fernández, V.H.; Casabona, J.; UALE Project. Comparison of users of an HIV/syphilis screening community-based mobile van and traditional voluntary counselling and testing sites in Guatemala. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2011, 87, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirzazadeh, A.; Shokoohi, M.; Karamouzian, M.; Ashki, H.; Khajehkazemi, R.; Salari, A.; Abedinzadeh, N.; Nadji, S.A.; Sharifi, H.; Kazerooni, P.A.; et al. Declining trends in HIV and other sexually transmitted infections among female sex workers in Iran could be attributable to reduced drug injection: A cross-sectional study. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2020, 96, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health Brazil. Manual Técnico Para Diagnóstico da Sífilis. Available online: http://www.aids.gov.br/pt-br/pub/2016/manual-tecnico-para-diagnostico-da-sifilis (accessed on 13 December 2020).
- Mejia, A.; Bautista, C.T.; Leal, L.; Ayala, C.; Prieto, F.; de la Hoz, F.; Alzate, M.L.; Acosta, J.; Sanchez, J.L. Syphilis infection among female sex workers in Colombia. J. Immigr. Minor. Health 2009, 11, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.H.; Jiang, T.; Shao, D.; Xue, W.; Ye, F.S.; Wang, M.; He, M.H. High prevalence of syphilis among street-based female sex workers in Nanchang, China. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 5, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhi, G.K.; Mahanta, J.; Hazarika, I.; Armstrong, G.; Adhikary, R.; Mainkar, M.; Paranjape, R.S. Syphilis infection among female sex workers in Nagaland, Northeast India: Analysing their vulnerability to the infection. Int. J. STD AIDS 2013, 24, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frade, P.; Raiol, N.C.; da Costa, L.M.; Pinheiro, L.; Silva-Oliveira, G.C.; Pinho, J.; Lemos, J.; Martins, L.C.; Oliveira-Filho, A.B. Factors associated with exposure to hepatitis B virus in female sex workers from the Marajó Archipelago, northern Brazil. Int. J. STD AIDS 2019, 30, 1127–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, F.R.; Mousquer, G.J.; Castro, L.S.; Puga, M.A.; Tanaka, T.S.; Rezende, G.R.; Pinto, C.S.; Bandeira, L.M.; Martins, R.M.; Francisco, R.B.; et al. HIV seroprevalence and high-risk sexual behavior among female sex workers in Central Brazil. AIDS Care 2014, 26, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.A.; Caetano, K.A.A.; França, D.D.S.; Pinheiro, R.S.; Moraes, L.C.; Teles, S.A. Vulnerabilidade aás Doenças Sexualmente Transmissiíveis em mulheres que comercializam sexo em rota de prostituicçáo e turismo sexual na Regiaáo Central do Brasil. Rev. Latino Am. Enfermagem. 2013, 21, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Costa, L.M.; Raiol, N.C.; Lisboa, B.; Frade, P.; Blandtt, L.; Silva-Oliveira, G.C.; Machado, L.; Martins, L.C.; Oliveira-Filho, A.B. Prevalence and risk fac- tors for HIV infection among female sex workers: Distinct offers of sexual services in a municipality of the Brazilian Amazon. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2019, 35, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Filho, A.B.; Aires, D.; Cavalcante, N.S.; Raiol, N.C.; Lisboa, B.; Frade, P.; da Costa, L.M.; Pinheiro, L.; Machado, L.; Martins, L.C.; et al. Hepatitis C virus among female sex workers: A cross-sectional study conducted along rivers and highways in the Amazon region. Pathogens 2019, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frade, P.C.; Raiol, N.C.; da Costa, L.M.; Pinheiro, L.M.; Silva-Oliveira, G.C.; Pinho, J.R.; Lemos, J.A.; Martins, L.C.; Oliveira-Filho, A.B. Prevalence and genotyping of hepatitis B virus: A cross-sectional study conducted with female sex workers in the Marajó Archipelago, Brazil. Int. J. STD AIDS 2019, 30, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Filho, A.B.; Silva, F.Q.; Santos, F.; Cardoso, Y.; Di Miceli, J.; Resque, R.L.; Silva-Oliveira, G.C.; Martins, L.C.; Pinheiro, L.; Machado, L.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors for HIV-1 infection in people who use illicit drugs in northern Brazil. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 114, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE) Brazil. Cidades e Estados, Brasil. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/cidades-e-estados (accessed on 10 January 2021).
| Characteristics | Belém (N = 360) | Macapá (N = 31) | Rio Branco (N = 24) | All (N = 415) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Age (years) | ||||
| Mean | 43.0 | 30.5 | 25.1 | 35.1 |
| Range | 15–71 | 15–46 | 14–36 | 14–71 |
| Marital status | ||||
| Single | 276 (76.7) | 17 (54.8) | 20 (83.4) | 313 (75.4) |
| Married | 58 (16.1) | 10 (32.2) | 2 (8.3) | 70 (16.9) |
| Divorced/widowed | 26 (7.2) | 4 (12.9) | 2 (8.3) | 32 (7.7) |
| School years | ||||
| ≤8 | 258 (71.7) | 22 (71.0) | 17 (70.8) | 297 (71.6) |
| >8 | 102 (28.3) | 9 (29.0) | 7 (29.2) | 118 (28.4) |
| Monthly income | ||||
| Up to one wage * | 256 (71.1) | 23 (74.2) | 15 (62.5) | 294 (70.8) |
| More than one wage | 102 (28.9) | 8 (25.8) | 9 (37.5) | 121 (29.2) |
| Use of illicit drugs | ||||
| Yes | 202 (56.1) | 16 (51.6) | 14 (58.3) | 232 (55.9) |
| No | 158 (43.9) | 15 (48.4) | 10 (41.7) | 183 (44.1) |
| Condom use ** | ||||
| Yes | 235 (65.3) | 18 (58.0) | 16 (66.7) | 269 (64.8) |
| No | 10 (2.8) | 3 (9.7) | 2 (8.3) | 15 (3.6) |
| Sometimes | 115 (31.9) | 10 (32.3) | 6 (25.0) | 131 (31.6) |
| Anal sex ** | ||||
| Yes (often/sometimes) | 106 (29.4) | 12 (38.7) | 8 (33.3) | 126 (30.4) |
| No | 254 (70.6) | 19 (61.3) | 16 (66.7) | 289 (69.6) |
| Clients per week ** | ||||
| Average | 10.3 | 7.8 | 11.5 | 9.5 |
| Range | 6–24 | 5–23 | 4–40 | 5–40 |
| Clients from other states of Brazil | ||||
| Yes | 220 (61.1) | 10 (32.3) | 19 (79.2) | 249 (60.0) |
| No | 84 (23.3) | 8 (25.8) | 3 (12.5) | 95 (22.9) |
| Do not know | 56 (15.6) | 13 (41.9) | 2 (8.3) | 71 (17.1) |
| Clients from other countries | ||||
| Yes | 121 (33.6) | 8 (25.8) | 17 (70.8) | 146 (35.2) |
| No | 153 (42.5) | 16 (51.6) | 5 (20.9) | 174 (41.9) |
| Do not know | 86 (23.9) | 7 (22.6) | 2 (8.3) | 95 (22.9) |
| STI history ≠ | ||||
| Yes | 80 (22.2) | 8 (25.8) | 8 (33.3) | 96 (23.1) |
| No | 280 (77.8) | 23 (74.2) | 16 (66.7) | 319 (76.9) |
| Exposure to T. pallidum | ||||
| Recent infection | 60 (16.7) | 4 (12.9) | 1 (4.2) | 65 (15.7) |
| Past infection | 71 (19.7) | 9 (29.0) | 5 (20.8) | 85 (20.5) |
| Rapid Plasma Reagin * | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay ** | Number/Total (%; 95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Nonreactive | Negative | 256/415 (61.6; 58.0–65.3) |
| Reactive | Negative | 9/415 (2.2; 0.0–4.8) |
| Reactive | Positive | 65/415 (15.7; 12.3–19.4) |
| Nonreactive | Positive | 85/415 (20.5; 17.4–24.4) |
| Nonreactive/reactive | Positive | 150/415 (36.1; 33.2–39.8) |
| Factors | Total Number of FSWs | Number of FSWs Exposed | Bivariate OR (95% CI) | Multivariate aOR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up to 8 years of study | 297 | 123 | 2.4 (1.3–3.7) | 2.9 (1.6–4.8) |
| Up to one minimum wage per month | 294 | 129 | 3.6 (2.2–6.3) | 4.1 (1.7–7.8) |
| Use of illicit drugs | 232 | 108 | 2.9 (1.8–4.6) | 3.7 (2.0–5.5) |
| Unprotected sex (inconsistent condom use) * | 146 | 88 | 5.1 (3.1–7.9) | 6.4 (3.2–9.0) |
| Anal sex (often + sometimes) * | 126 | 77 | 4.3 (2.4–6.8) | 4.6 (2.8–7.7) |
| More than 10 sexual partners per week * | 287 | 121 | 2.5 (1.5–4.1) | 3.3 (2.1–5.2) |
| STI history | 96 | 67 | 6.6 (3.9–10.7) | 7.1 (4.1–11.8) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Machado, L.F.A.; Monteiro, J.C.; Siravenha, L.Q.; Mota, M.P.; Souza, M.d.C.; Santos, A.S.d.; Moreira, M.R.C.; Laurentino, R.V.; Oliveira-Filho, A.B.; Queiroz, M.A.F.; et al. Treponema pallidum among Female Sex Workers: A Cross-Sectional Study Conducted in Three Major Cities in Northern Brazil. Pathogens 2021, 10, 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10080923
Machado LFA, Monteiro JC, Siravenha LQ, Mota MP, Souza MdC, Santos ASd, Moreira MRC, Laurentino RV, Oliveira-Filho AB, Queiroz MAF, et al. Treponema pallidum among Female Sex Workers: A Cross-Sectional Study Conducted in Three Major Cities in Northern Brazil. Pathogens. 2021; 10(8):923. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10080923
Chicago/Turabian StyleMachado, Luiz Fernando Almeida, Jacqueline Cortinhas Monteiro, Leonardo Quintão Siravenha, Marcelo Pereira Mota, Marlinda de Carvalho Souza, Adalto Sampaio dos Santos, Márcio Ronaldo Chagas Moreira, Rogério Valois Laurentino, Aldemir Branco Oliveira-Filho, Maria Alice Freitas Queiroz, and et al. 2021. "Treponema pallidum among Female Sex Workers: A Cross-Sectional Study Conducted in Three Major Cities in Northern Brazil" Pathogens 10, no. 8: 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10080923
APA StyleMachado, L. F. A., Monteiro, J. C., Siravenha, L. Q., Mota, M. P., Souza, M. d. C., Santos, A. S. d., Moreira, M. R. C., Laurentino, R. V., Oliveira-Filho, A. B., Queiroz, M. A. F., Lima, S. S., Ishak, R., & Ishak, M. d. O. G. (2021). Treponema pallidum among Female Sex Workers: A Cross-Sectional Study Conducted in Three Major Cities in Northern Brazil. Pathogens, 10(8), 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10080923






