Rhipicephalus sanguineus Complex in the Americas: Systematic, Genetic Diversity, and Geographic Insights
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Molecular Identification
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
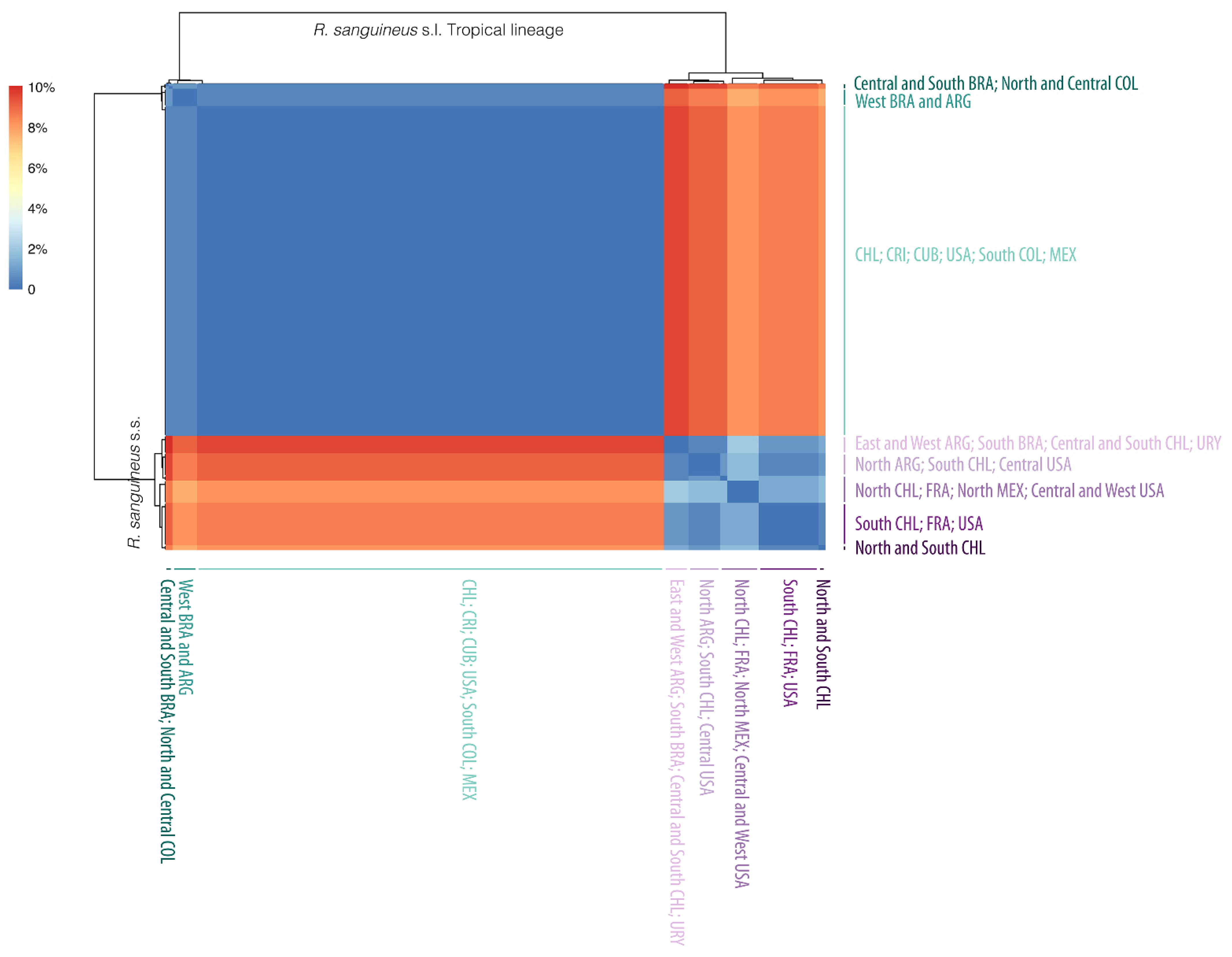
2.3. Genetic Analysis
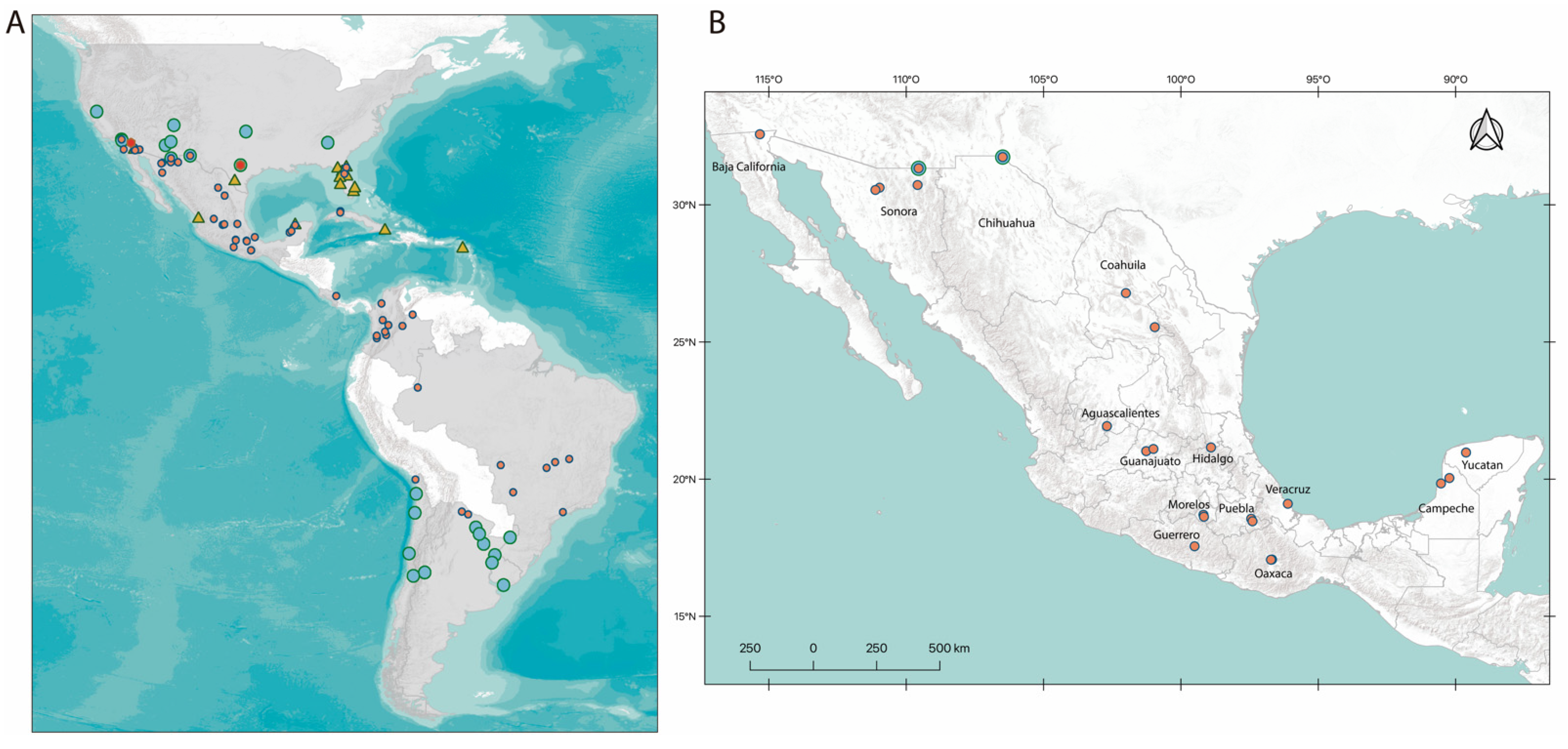
2.4. Geographic Distribution
3. Discussion
3.1. Genetic Diversity
3.2. Geographic Distribution
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Tick Collection and Identification
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Genetic Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Sánchez, M.E.; Franco, L.G.; Nava, S.; Rueda, L.M.; Robbins, R.G. Nombres de Especies de Garrapatas Duras (Acari: Ixodidae: Ixodidae). Available online: http://rafaela.inta.gob.ar/nombresgarrapatas/ (accessed on 22 March 2021).
- Bakkes, D.K.; Ropiquet, A.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Matloa, D.E.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Horak, I.G.; Mans, B.J.; Matthee, C.A. Adaptive radiation and speciation in Rhipicephalus ticks: A medley of novel hosts, nested predator-prey food webs, off-host periods and dispersal along temperature variation gradients. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 162, 107178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latreille, P.A. Genera Crustaceorum et Insectorum Secundum Ordinem Naturalem in Familia Disposita, Iconibus Exemplisque Plurimis Explicata; Paris et Argentorati: Paris, France, 1806; Volume 1, 302p. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes-Filho, J.; Marcili, A.; Nieri-Bastos, F.A.; Richtzenhain, L.J.; Labruna, M.B. Genetic analysis of ticks belonging to the Rhipicephalus sanguineus group in Latin America. Acta Trop. 2011, 117, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, S.; Mastropaolo, M.; Venzal, J.M.; Mangold, A.J.; Guglielmone, A.A. Mitochondrial DNA analysis of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato (Acari: Ixodidae) in the Southern Cone of South America. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 190, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, S.; Beati, L.; Venzal, J.M.; Labruna, M.B.; Szabó, M.; Petney, T.; Saracho-Bottero, M.N.; Tarragona, E.L.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Silva, M.; et al. Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille, 1806): Neotype designation, morphological re-description of all parasitic stages and molecular characterization. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, M.P.; Mangold, A.J.; João, C.F.; Bechara, G.H.; Guglielmone, A.A. Biological and DNA evidence of two dissimilar populations of the Rhipicephalus sanguineus tick group (Acari: Ixodidae) in South America. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 130, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Latrofa, M.S.; Annoscia, G.; Giannelli, A.; Parisi, A.; Otranto, D. Morphological and genetic diversity of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato from the New and Old Worlds. Parasit Vectors 2013, 6, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moraes-Filho, J.; Krawczak, F.S.; Costa, F.B.; Soares, J.F.; Labruna, M.B. Comparative Evaluation of the Vector Competence of Four South American Populations of the Rhipicephalus sanguineus Group for the Bacterium Ehrlichia canis, the Agent of Canine Monocytic Ehrlichiosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139386. [Google Scholar]
- Hekimoğlu, O.; Sağlam, İ.K.; Özer, N.; Estrada-Peña, A. New molecular data shed light on the global phylogeny and species limits of the Rhipicephalus sanguineus complex. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemtsova, G.E.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Reeves, W.K.; Hahn, M.; Snellgrove, A.; Levin, M.L. Phylogeography of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato and its relationships with climatic factors. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2016, 69, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrone, J.J. Biogeographical regionalisation of the Neotropical region. Zootaxa 2014, 3782, 1–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demma, L.J.; Traeger, M.S.; Nicholson, W.L.; Paddock, C.D.; Blau, D.M.; Eremeeva, M.E.; Dasch, G.A.; Levin, M.L.; Singleton, J., Jr.; Zaki, S.R.; et al. Rocky Mountain spotted fever from an unexpected tick vector in Arizona. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremeeva, M.E.; Zambrano, M.L.; Anaya, L.; Beati, L.; Karpathy, S.E.; Santos-Silva, M.M.; Salceda, B.; MacBeth, D.; Olguin, H.; Dasch, G.A.; et al. Rickettsia rickettsii in Rhipicephalus ticks, Mexicali, Mexico. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicuttin, G.L.; Tarragona, E.L.; De Salvo, M.N.; Mangold, A.J.; Nava, S. Infection with Ehrlichia canis and Anaplasma platys (Rickettsiales: Anaplasmataceae) in two lineages of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato (Acari: Ixodidae) from Argentina. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2015, 6, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Caballero, A.; Moreno, B.; González, C.; Martínez, G.; Adames, M.; Pachar, J.V.; Varela-Petrucelli, J.B.; Martínez-Mandiche, J.; Suárez, J.A.; Domínguez, L.; et al. Descriptions of two new cases of Rocky Mountain spotted fever in Panama, and coincident infection with Rickettsia rickettsii in Rhipicephalus sanguineus s.l. in an urban locality of Panama City, Panama. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eremeeva, M.E.; Bosserman, E.A.; Demma, L.J.; Zambrano, M.L.; Blau, D.M.; Dasch, G.A. Isolation and identification of Rickettsia massiliae from Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks collected in Arizona. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5569–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beeler, E.; Abramowicz, K.F.; Zambrano, M.L.; Sturgeon, M.M.; Khalaf, N.; Hu, R.; Dasch, G.A.; Eremeeva, M.E. A focus of dogs and Rickettsia massiliae-infected Rhipicephalus sanguineus in California. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cicuttin, G.L.; Brambati, D.F.; Rodríguez Eugui, J.I.; Lebrero, C.G.; De Salvo, M.N.; Beltrán, F.J.; Gury Dohmen, F.E.; Jado, I.; Anda, P. Molecular characterization of Rickettsia massiliae and Anaplasma platys infecting Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks and domestic dogs, Buenos Aires (Argentina). Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicuttin, G.L.; Vidal, P.; Nazarena De Salvo, M.; Beltrán, F.J.; Gury Dohmen, F.E. Molecular detection of Rickettsia massiliae and Anaplasma platys infecting Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks and dogs, Bahía Blanca (Argentina). Rev. Chilena Infectol. 2014, 31, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snellgrove, A.N.; Krapiunaya, I.; Ford, S.L.; Stanley, H.M.; Wickson, A.G.; Hartzer, K.L.; Levin, M.L. Vector competence of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu stricto for Anaplasma platys. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, N.; Weeks, E.; Beati, L.; Kaufman, P.E. Prevalence and distribution of pathogen infection and permethrin resistance in tropical and temperate populations of Rhipicephalus sanguineus s.l. collected worldwide. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2021, 35, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Calderón, L.; Ábrego-Sánchez, L.; Solórzano-Morales, A.; Alberti, A.; Tore, G.; Zobba, R.; Jiménez-Rocha, A.E.; Dolz, G. Molecular detection and identification of Rickettsiales pathogens in dog ticks from Costa Rica. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicuttin, G.; De Salvo, M.N.; Silva, D.A.; Brito, M.; Nava, S. Ehrlichia canis (Rickettsiales: Anaplasmataceae) en garrapatas Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato del linaje templado (Acari. Ixodidae), provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina. Fave Cienc. Vet. 2017, 16, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebastian, P.S.; Mera, Y.; Sierra, R.; Neira, G.; Hadid, J.; Flores, F.S.; Nava, S. Epidemiological link between canine monocytic ehrlichiosis caused by Ehrlichia canis and the presence of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu stricto in Argentina. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal, Z.; Stephenson, N.; Foley, J. Possible Northward Introgression of a Tropical Lineage of Rhipicephalus sanguineus Ticks at a Site of Emerging Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. J. Parasitol. 2018, 104, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Pérez, A.M.; Sánchez-Montes, S.; Foley, J.; Guzmán-Cornejo, C.; Colunga-Salas, P.; Pascoe, E.; Becker, I.; Delgado-de la Mora, J.; Licona-Enriquez, J.D.; Suzan, G. Molecular evidence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto and Rickettsia massiliae in ticks collected from a domestic-wild carnivore interface in Chihuahua, Mexico. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salceda-Sánchez, B.; Sánchez-Montes, S.; Soto-Gutiérrez, J.J.; Sandoval-Espinosa, M.R. A case of gynandromorphism in Rhipicephalus sanguineus s.l. from Mexico. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2020, 82, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazán, C.; González-Álvarez, V.H.; Fernández de Mera, I.G.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R.; de la Fuente, J. Molecular identification and characterization of Anaplasma platys and Ehrlichia canis in dogs in Mexico. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieracci, E.G.; Pérez-de la Rosa, J.D.; Luna-Rubio, D.; Solis-Perales, M.E.; Velasco-Contreras, M.; Drexler, N.A.; Nicholson, W.L.; Pérez-de la Rosa, J.J.; Chung, I.H.; Kato, C.; et al. Seroprevalence of spotted fever group rickettsiae in canines along the United States-Mexico border. Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pérez, A.M.; Chaves, A.; Sánchez-Montes, S.; Foley, P.; Uhart, M.; Barrón-Rodríguez, J.; Becker, I.; Suzán, G.; Foley, J. Diversity of rickettsiae in domestic, synanthropic, and sylvatic mammals and their ectoparasites in a spotted fever-epidemic region at the western US-Mexico border. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruickshank, R.H. Molecular markers for the phylogenetics of mites and ticks. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2002, 7, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeyaprakash, A.; Hoy, M.A. First divergence time estimate of spiders, scorpions, mites and ticks (subphylum: Chelicerata) inferred from mitochondrial phylogeny. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2009, 47, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.L.; Zhang, B. Prospects of using DNA barcoding for species identification and evaluation of the accuracy of sequence databases for ticks (Acari: Ixodida). Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Salas, D.; Solis-Cortés, M.; Zazueta-Islas, H.M.; Flores-Vásquez, F.; Cruz-Romero, A.; Aguilar-Domínguez, M.; Salguero-Romero, J.L.; de León, A.P.; Fernández-Figueroa, E.A.; Lammoglia-Villagómez, M.Á.; et al. Molecular detection of Theileria equi in horses from Veracruz, Mexico. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuny-Fernández, N.M.; Ferrer, M.M.; Ruenes-Morales, M.R. Centros de origen, domesticación y diversidad genética de la ciruela mexicana, Spondias purpurea (Anacardiaceae). Acta Bot. Mex. 2017, 121, 7–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colunga-Salas, P.; Hernández-Canchola, G.; Sánchez-Montes, S.; Lozano-Sardaneta, Y.N.; Becker, I. Genetic diversity of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto: Novel strains from Mexican wild rodents. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benham, S.A.; Gaff, H.D.; Bement, Z.J.; Blaise, C.; Cummins, H.K.; Ferrara, R.; Moreno, J.; Parker, E.; Phan, A.; Rose, T.; et al. Comparative population genetics of Amblyomma maculatum and Amblyomma americanum in the mid-Atlantic United States. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-de la Mora, J.; Sánchez-Montes, S.; Licona-Enríquez, J.D.; Delgado-de la Mora, D.; Paddock, C.D.; Beati, L.; Colunga-Salas, P.; Guzmán-Cornejo, C.; Zambrano, M.L.; Karpathy, S.E.; et al. Rickettsia parkeri and Candidatus Rickettsia andeanae in Tick of the Amblyomma maculatum Group, Mexico. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 836–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Montes, S.; López-Pérez, A.M.; Guzmán-Cornejo, C.; Colunga-Salas, P.; Becker, I.; Delgado-de la Mora, J.; Licona-Enríquez, J.D.; Delgado-de la Mora, D.; Karpathy, S.E.; Paddock, C.D.; et al. Rickettsia parkeri in Dermacentor parumapertus Ticks, Mexico. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keirans, J.E.; Litwak, T.R. Pictorial key to the adults of hard ticks, family Ixodidae (Ixodida: Ixodoidea), east of the Mississippi River. J. Med. Entomol. 1989, 26, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirección General de Salud Animal: DGSA-SAGAR. Manual de Identificación de Las Especies de Garrapatas de Importancia en México del Centro Nacional de Servicios de Constatación de la Comisión Nacional de Sanidad Agropecuaria; Secretaría de Agricultura, Ganadería, Desarrollo Rural, Pesca y Alimentación SAGARPA: Mexico City, Mexico, 1992; p. 152. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, P.R.; Bechara, G.H.; Denardi, S.E.; Saito, K.C.; Nunes, E.T.; Szabó, M.P.; Mathias, M.I. Comparison of the external morphology of Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille, 1806) (Acari: Ixodidae) ticks from Brazil and Argentina. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 129, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, D.E.; Klompen, J.S.; Keirans, J.E.; Black, W.C. Population genetics of Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) based on mitochondrial 16S and 12S genes. J. Med. Entomol. 1996, 33, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Langguth, J.; Pfeffer, M.; Kattner, S.; Küpper, T.; Friese, D.; Dobler, G.; Guglielmone, A.A.; Nava, S. Genetic analysis of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato ticks parasites of dogs in Africa north of the Sahara based on mitochondrial DNA sequences. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 239, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornok, S.; Sándor, A.D.; Tomanović, S.; Beck, R.; D’Amico, G.; Kontschán, J.; Takács, N.; Görföl, T.; Bendjeddou, M.L.; Földvári, G.; et al. East and west separation of Rhipicephalus sanguineus mitochondrial lineages in the Mediterranean Basin. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Šlapeta, J.; Chandra, S.; Halliday, B. The “tropical lineage” of the brown dog tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato identified as Rhipicephalus linnaei (Audouin, 1826). Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colunga-Salas, P.; Hernández-Canchola, G. Bats and humans during the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak: The case of bat-coronaviruses from Mexico. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New Methods for Selecting Partitioned Models of Evolution for Molecular and Morphological Phylogenetic Analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombart, T. adegenet: A R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| GenBank Accession Number | Species | Sex | Source | Collection Date | State | Municipality | Locality | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MZ618782 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 11 September 2019 | Aguascalientes | Calvillo | El Mirador | −102.694 | 21.933 |
| MZ618783 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 11 September 2019 | Aguascalientes | Calvillo | El Mirador | −102.694 | 21.933 |
| MZ618784 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 11 September 2019 | Aguascalientes | Calvillo | El Mirador | −102.694 | 21.933 |
| MZ618785 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 19 September 2019 | Baja California | Mexicali | Ejido Sinaloa | −115.327 | 32.572 |
| MZ618786 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 19 September 2019 | Baja California | Mexicali | Ejido Sinaloa | −115.327 | 32.572 |
| MZ618787 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 19 September 2019 | Baja California | Mexicali | Alianza para la Producción (La Choyera) | −115.327 | 32.572 |
| MZ618788 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 9 September 2019 | Baja California | Mexicali | Ejido Cuernavaca | −115.327 | 32.572 |
| MZ618789 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 9 September 2019 | Baja California | Mexicali | Ejido Cuernavaca | −115.327 | 32.572 |
| MZ618790 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Environment | 24 June 2019 | Campeche | Tenabo | Tenabo | −90.225 | 20.040 |
| MZ618791 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Environment | 24 June 2019 | Campeche | Tenabo | Tenabo | −90.225 | 20.040 |
| MZ618792 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Environment | 24 June 2019 | Campeche | Campeche | Campeche | −90.532 | 19.842 |
| MZ618793 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Environment | 20 June 2019 | Coahuila | Cuatrociénegas de Carranza | Antiguos Mineros del Norte (Santa Tecla) | −102.001 | 26.783 |
| MZ618794 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Environment | 20 June 2019 | Coahuila | Cuatrociénegas de Carranza | Antiguos Mineros del Norte (Santa Tecla) | −102.001 | 26.783 |
| MZ618795 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 20 June 2019 | Coahuila | Cuatrociénegas de Carranza | Antiguos Mineros del Norte (Santa Tecla) | −102.001 | 26.783 |
| MZ618796 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Dog | 8 July 2019 | Coahuila | Cuatrociénegas de Carranza | Cuatrociénegas de Carranza | −102.067 | 26.986 |
| MZ618797 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Environment | 25 June 2019 | Coahuila | Ramos Arispe | Cerro Cruz | −100.951 | 25.541 |
| MZ618798 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 27 June 2019 | Chihuahua | Juárez | Juárez | −106.487 | 31.739 |
| MZ618799 | R. sanguineus s.s. | ♀ | Dog | 4 July 2019 | Chihuahua | Juárez | Juárez | −106.487 | 31.739 |
| MZ618800 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 8 July 2019 | Chihuahua | Juárez | Juárez | −106.487 | 31.739 |
| MZ618801 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Environment | 30 May 2019 | Chihuahua | Juárez | Juárez | −106.487 | 31.739 |
| MZ618802 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Environment | 6 June 2019 | Chihuahua | Juárez | Juárez | −106.487 | 31.739 |
| MZ618803 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Dog | 30 July 2019 | Guanajuato | Guanajuato | Guanajuato | −101.263 | 21.019 |
| MZ618804 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Dog | 30 July 2019 | Guanajuato | Guanajuato | Guanajuato | −101.263 | 21.019 |
| MZ618805 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 30 July 2019 | Guanajuato | Guanajuato | Guanajuato | −101.263 | 21.019 |
| MZ618806 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Dog | 15 August 2019 | Guanajuato | Guanajuato | Guanajuato | −101.263 | 21.019 |
| MZ618807 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Environment | 23 August 2019 | Guanajuato | Dolores Hidalgo | Dolores Hidalgo | −101 | 21.100 |
| MZ618808 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 1 January 2019 | Guerrero | Chilpancingo de los Bravo | Chilpancingo de los Bravo | −99.501 | 17.552 |
| MZ618809 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 1 January 2019 | Guerrero | Chilpancingo de los Bravo | Chilpancingo de los Bravo | −99.501 | 17.552 |
| MZ618810 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 25 October 2019 | Hidalgo | Chapulhuacan | Chapulhuacan | −98.904 | 21.155 |
| MZ618811 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 25 October 2019 | Hidalgo | Chapulhuacan | Chapulhuacan | −98.904 | 21.155 |
| MZ618812 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 12 July 2019 | Morelos | Tlaquiltenango | Tlaquiltenango | −99.160 | 18.629 |
| MZ618813 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 15 July 2019 | Morelos | Tlaltizapán | Santa Rosa Treinta | −99.179 | 18.698 |
| MZ618814 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 12 July 2019 | Morelos | Tlaquiltenango | Tlaquiltenango | −99.160 | 18.629 |
| MZ618815 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 15 July 2019 | Morelos | Tlaltizapán | Santa Rosa Treinta | −99.179 | 18.698 |
| MZ618816 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Dog | 13 July 2019 | Oaxaca | Sta. Lucía del Camino | Santa Lucía del Camino | −96.683 | 17.067 |
| MZ618817 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Dog | 13 June 2019 | Oaxaca | Sta. Lucía del Camino | Santa Lucía del Camino | −96.683 | 17.067 |
| MZ618818 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Dog | 13 June 2019 | Oaxaca | Sta. Lucía del Camino | Santa Lucía del Camino | −96.683 | 17.067 |
| MZ618819 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 18 July 2019 | Oaxaca | Oaxaca de Juárez | Oaxaca de Juárez | −96.722 | 17.062 |
| MZ618820 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 1 August 2021 | Oaxaca | Oaxaca de Juárez | Oaxaca de Juárez | −96.722 | 17.062 |
| MZ618821 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 6 July 2021 | Puebla | Tehuacán | Tehuacán | −97.394 | 18.463 |
| MZ618822 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 6 July 2021 | Puebla | Tehuacán | Tehuacán | −97.394 | 18.463 |
| MZ618823 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 19 September 2019 | Puebla | Tehuacán | Tehuacán | −97.394 | 18.463 |
| MZ618824 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 19 September 2019 | Puebla | Tehuacán | Tehuacán | −97.394 | 18.463 |
| MZ618825 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Dog | 24 September 2019 | Puebla | Santiago Miahuatlán | Santiago Miahuatlán | −97.442 | 18.554 |
| MZ618826 | R. sanguineus s.s. | ♀ | Dog | 4 June 2019 | Sonora | Agua Prieta | Agua Prieta | −109.549 | 31.331 |
| MZ618827 | Tropical Linage | ♂ | Dog | 4 June 2019 | Sonora | Agua Prieta | Agua Prieta | −109.549 | 31.331 |
| MZ618828 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 24 June 2019 | Sonora | Sta. Ana | Santa Ana | −111.121 | 30.541 |
| MZ618829 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 7 May 2019 | Sonora | Fronteras | Esqueda | −109.590 | 32.721 |
| MZ618830 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 22 May 2019 | Sonora | Magdalena | Magdalena de Kino | −110.969 | 30.625 |
| MZ618831 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 4 August 2019 | Veracruz | Boca del Río | Boca del Río | −96.107 | 19.101 |
| MZ618832 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 8 February 2019 | Yucatán | Mérida | Mérida | −89.62 | 20.970 |
| MZ618833 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 3 March 2019 | Yucatán | Mérida | Mérida | −89.62 | 20.970 |
| MZ618782 | Tropical Linage | ♀ | Dog | 12 March 2019 | Yucatán | Mérida | Mérida | −89.62 | 20.970 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Montes, S.; Salceda-Sánchez, B.; Bermúdez, S.E.; Aguilar-Tipacamú, G.; Ballados-González, G.G.; Huerta, H.; Aguilar-Domínguez, M.; Mora, J.D.-d.l.; Licona-Enríquez, J.D.; Mora, D.D.-d.l.; et al. Rhipicephalus sanguineus Complex in the Americas: Systematic, Genetic Diversity, and Geographic Insights. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10091118
Sánchez-Montes S, Salceda-Sánchez B, Bermúdez SE, Aguilar-Tipacamú G, Ballados-González GG, Huerta H, Aguilar-Domínguez M, Mora JD-dl, Licona-Enríquez JD, Mora DD-dl, et al. Rhipicephalus sanguineus Complex in the Americas: Systematic, Genetic Diversity, and Geographic Insights. Pathogens. 2021; 10(9):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10091118
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Montes, Sokani, Beatriz Salceda-Sánchez, Sergio E. Bermúdez, Gabriela Aguilar-Tipacamú, Gerardo G. Ballados-González, Herón Huerta, Mariel Aguilar-Domínguez, Jesús Delgado-de la Mora, Jesús D. Licona-Enríquez, David Delgado-de la Mora, and et al. 2021. "Rhipicephalus sanguineus Complex in the Americas: Systematic, Genetic Diversity, and Geographic Insights" Pathogens 10, no. 9: 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10091118
APA StyleSánchez-Montes, S., Salceda-Sánchez, B., Bermúdez, S. E., Aguilar-Tipacamú, G., Ballados-González, G. G., Huerta, H., Aguilar-Domínguez, M., Mora, J. D.-d. l., Licona-Enríquez, J. D., Mora, D. D.-d. l., López-Pérez, A. M., Torres-Castro, M. A., Alcántara-Rodríguez, V., Becker, I., & Colunga-Salas, P. (2021). Rhipicephalus sanguineus Complex in the Americas: Systematic, Genetic Diversity, and Geographic Insights. Pathogens, 10(9), 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10091118








