Abstract
Reservoir to multiple species of zoonotic pathogens, free-roaming cats (FRCs) interact with domestic and wild animals, vectors, and humans. To assess the potential for feline vector-borne pathogens to be vertically transmitted, this study surveyed ear tip and reproductive tissues of FRCs from two locations in the South Atlantic United States for Anaplasma, Bartonella, Ehrlichia, hemotropic Mycoplasma, and Rickettsia species. We collected ovary (n = 72), uterus (n = 54), testicle (n = 74), and ear tip (n = 73) tissue from 73 cats, and fetal (n = 20) and placental (n = 19) tissue from 11 queens. Pathogen DNA was amplified utilizing qPCR, confirmed by sequencing. Cats were more frequently Bartonella henselae positive on reproductive tissues (19%, 14/73) than ear tip (5%, 4/73; p = 0.02). B. henselae was amplified from fetus (20%, 4/20) and placenta samples (11%, 2/19). Bartonella spp. infection was more common in cats from North Carolina (76%, 26/34) than Virginia (13%, 5/39; p < 0.0001). Fourteen percent (10/73) of both ear tip and reproductive tissues were positive for hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. Anaplasma, Ehrlichia, and Rickettsia spp. DNA was not amplified from any cat/tissue. These findings suggest that B. henselae preferentially infected cats’ reproductive tissue and reinforces the importance of investigating the potential for B. henselae vertical transmission or induction of reproductive failure.
1. Introduction
Free roaming cats (FRC) exist in a unique position, regularly interacting with a diverse assortment of species including wild predators and prey, domestic animals and pets, arthropod vectors, and humans that often care for them. Each of these interfaces represents a unique opportunity for inter-species pathogen transmission. The cat’s status as a known or suspected reservoir host for multiple vector-borne pathogens [1,2,3], including Bartonella [4,5,6], hemotropic Mycoplasma [7], and Rickettsia [2] species increases the importance of understanding these diseases in FRC populations.
Identified as emerging pathogens of both animals and humans, the genus Bartonella comprises 45 species or subspecies, 13 of which are known to cause human disease [8]. Of these species, Bartonella henselae, Bartonella clarridgeiae, and Bartonella koehlerae are known to employ the cat as a reservoir host [4,5,6]. Isolation of four other Bartonella spp. from cat blood and tissue has also been documented [9,10,11,12]. Clinical manifestations of Bartonella spp. infection in the cat host are uncommon; however, associations have been made with central nervous system disease, ocular disease, immune complex disease, and endomyocarditis on the basis of epidemiologic studies and case reports [13,14,15,16,17]. B. henselae, as well as potentially other Bartonella spp. associated with the cat, are primarily vectored by Ctenocephalides felis, the cat flea [18].
Multiple Mycoplasma spp. are found in cats and can be classified as either respiratory or hemotropic in nature. Given our vector-borne focus, we chose to evaluate only the hemotropic Mycoplasma spp., three of which are commonly found in cats: Mycoplasma haemofelis (Mhf), Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum (Mhm), and Candidatus Mycoplasma turicensis (Mtc) [19]. Disease manifestations caused by hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. in cats, including lethargy, inappetence, tachycardia, and tachypnea, are typically related to the induction of hemolytic anemia [19]. Though not widely regarded as zoonotic in humans, Mhf infection in an HIV-positive patient co-infected with B. henselae has been reported, suggesting that Mhf may have zoonotic potential [20]. Historically assumed to be a vector-borne, specifically a flea-borne disease, the mechanism of hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. transmission between cats is currently unknown; however, direct transmission due to fighting is now suspected due to the strong association between infection and male sex and lack of evidence of flea-borne transmission [7,21,22,23]. An experimental transmission study using C. felis to transmit hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. resulted in only one of six recipient cats becoming transiently infected with Mhf and none of three recipient cats becoming infected with Mhm [24].
Pertinent to the present study is the knowledge gap regarding the role of vertical transmission of many vector-borne pathogens in maintaining reservoirs of infection. Reports vary widely based on pathogen and host, with evidence lacking for vertical transmission in Ehrlichia ewingii and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in dogs [25,26] and Cytauxzoon felis [27] in cats and evidence in favor of vertical transmission of Anaplasma platys, Babesia gibsoni, Borrelia burgdorferi, Leishmania infantum, and Trypanosoma cruzi in dogs [28,29,30,31,32,33,34], Babesia microti in humans and voles [32,35,36], and Hepatozoon canis in red foxes and dogs [37,38]. The possibility of vertical transmission is of particular importance for Bartonella spp., which have been suggested as a cause of reproductive failure in multiple species. A study by Guptill et al. reported B. henselae as a cause of reproductive failure in the domestic cat [39]. Few other studies have investigated the relationship between Bartonella spp. and reproduction. Boulouis et al. reported Bartonella birtlesii infection in pregnant mice having an abortifacient effect as well as increasing the rate of fetal resorption and death and decreasing fetal weight gain [40]. A case report documenting B. henselae DNA amplification and sequencing from a mother’s blood and cervical tissue, as well as her neonatal daughter’s brain and liver samples acquired during autopsy suggested that B. henselae could play a role in reproductive failure and neonatal loss in humans [41]. Unraveling the relationship between Bartonella spp. and reproduction is critical to determine their potential to interfere with reproductive function in a variety of species as well as be transmitted vertically as a means of non-vector-borne infection and maintenance in the reservoir host.
The primary objective of this study was to determine the prevalence of feline vector-borne pathogens, including Bartonella, hemotropic Mycoplasma, and Rickettsia spp., as well as Anaplasma and Ehrlichia spp. in the reproductive and ear tip tissues of FRCs in two distinct geographic locations. Due to previous literature suggesting Bartonella spp. as a cause of reproductive failure, we expected Bartonella spp. to be more common in the reproductive tissues than the ear tip tissues, while the proportion of samples with DNA from other feline vector-borne diseases was not expected to vary between ear tip and reproductive tissues. We also expected pathogen prevalence in cats to be consistent between the two geographic locations. The secondary objective was to determine if Bartonella spp. DNA was present in fetal cat tissues.
2. Results
2.1. Feline VBDs Detected
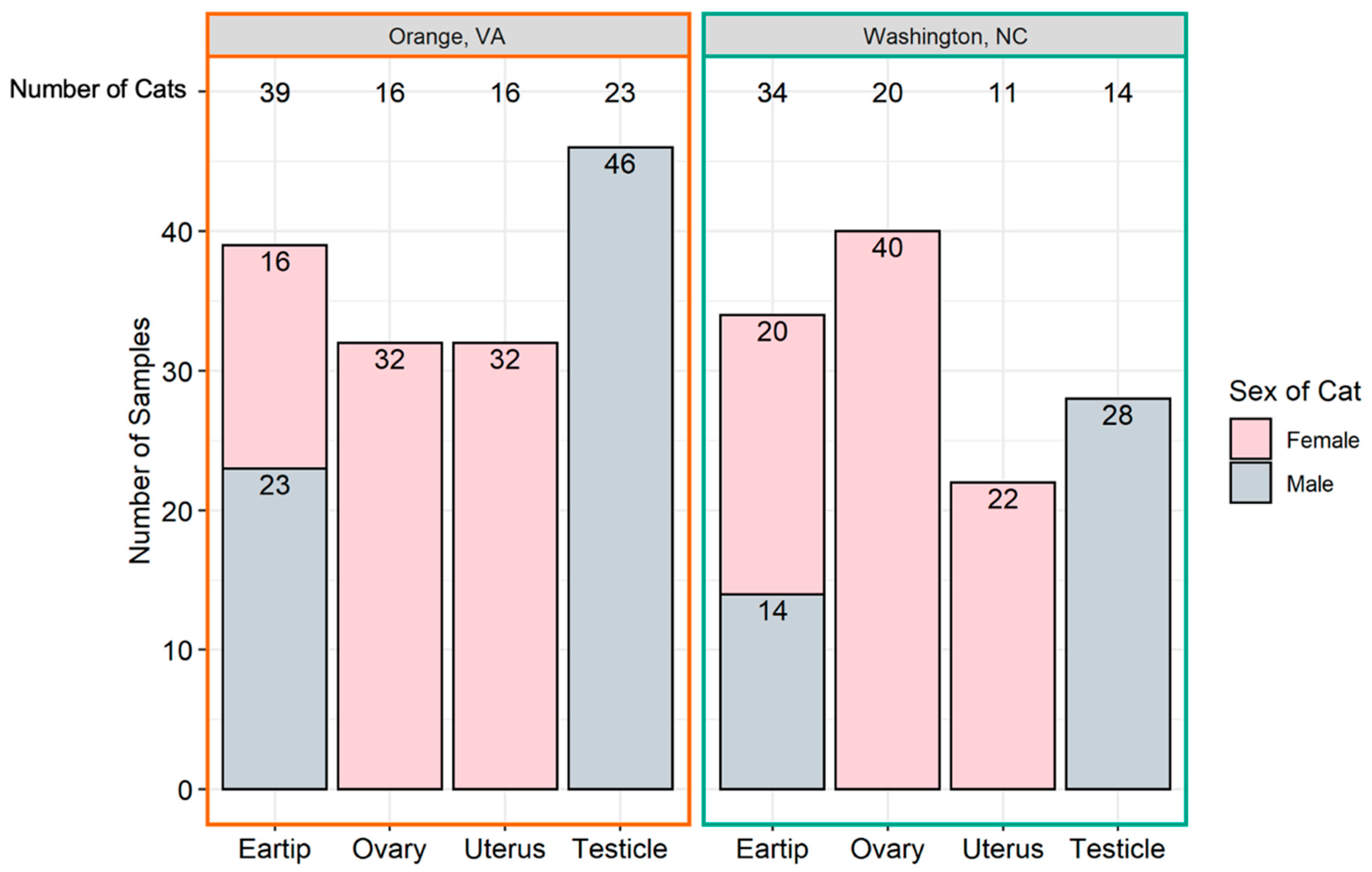
Ear tip and reproductive tissues were obtained from 73 cats, including 36 females (49%) and 37 males (51%). The number and type of samples obtained from each location is provided in Figure 1. Thirty-nine cats were from Orange, VA (54%) and 34 were from Washington, NC (46%). The proportion of female and male cats from Orange, VA and Washington, NC were not significantly different (p = 0.16). The mean weight of all cats was 3.13 kg; Orange, VA cats had a mean weight of 3.21 kg (standard deviation 1.13 kg), whereas Washington, NC cats had a mean weight of 3.04 kg (standard deviation 0.9 kg); there was no significant difference in weight by location (p = 0.44). Male cats (mean 3.46 kg, standard deviation 1.22 kg) were heavier than female cats (mean 2.73 kg, standard deviation 0.55 kg; p < 0.0001). Females had a mean number of 4.5 tissues tested (range 3–5), while all males had three tissues tested.
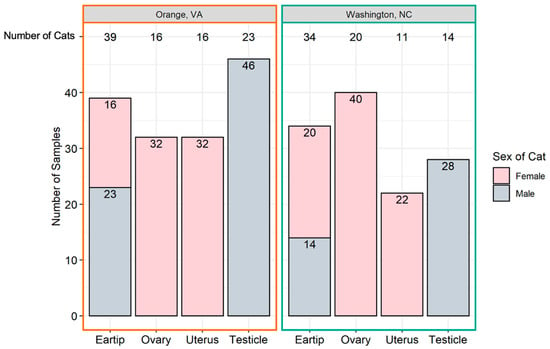
Figure 1.
Number of tissue samples collected. The total number of samples (y-axis) originating from each tissue (x-axis) is represented above by geographic location. The total number of cats from which each sample type was collected is at the top of the graph.
Thirty-eight of 73 cats (52%) were qPCR positive for one or more pathogen on one or more tissue sample. Forty-two percent (31/73) of cats were positive for one or more Bartonella spp. by qPCR, and 16% (12/73) of cats were positive for one or more hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. by qPCR. Anaplasma, Ehrlichia, and Rickettsia spp. DNA was not amplified from any of the tissues tested from any cat.
2.2. Bartonella spp.
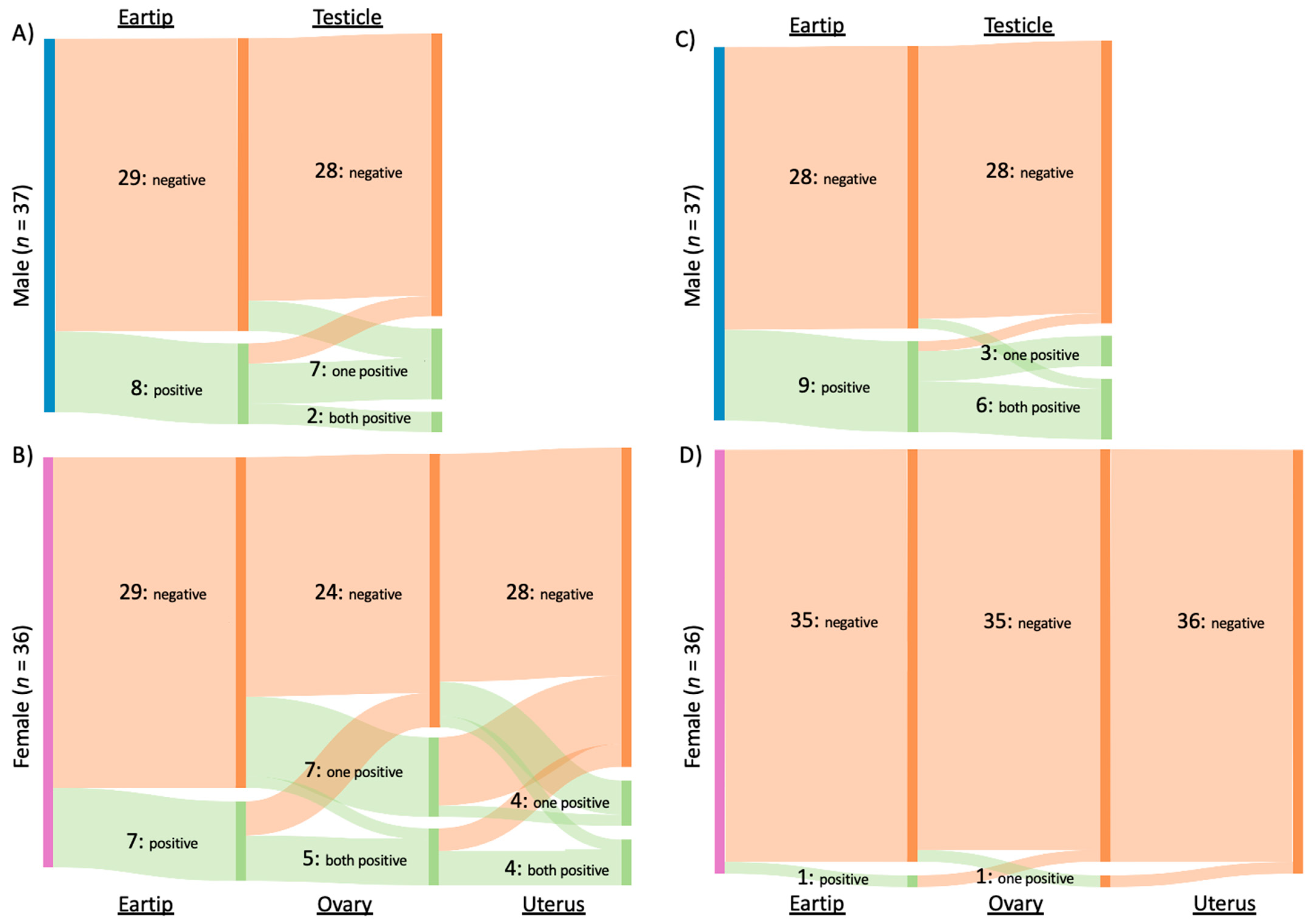
Of the 31 cats infected with Bartonella spp., B. henselae was amplified from 16 cats, B. clarridgeiae from 15 cats, and B. koehlerae from two cats. Both B. clarridgeiae and B. henselae DNA were amplified from 10% (3/31) of infected cats, all of which were males from Washington, NC. When considering all Bartonella spp. together, 34% (25/73) of cats were qPCR positive from reproductive tissue, compared to 21% (15/73) that were qPCR positive from ear tip tissue (p = 0.09). The type of tissues that tested positive for Bartonella spp. infection is summarized in Figure 2A and 2B for male and female cats, respectively.
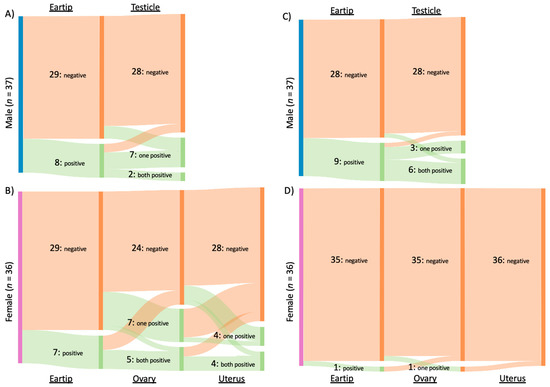
Figure 2.
Number and type of tissue from which Bartonella spp. and Hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. were amplified. Type of tissue samples from which Bartonella spp. (A,B) or hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. (C,D) DNA was amplified from male (A,C) and female (B,D) cats. Each column represents a tissue (indicated at top or bottom) with the number cats of negative, one of two tissues positive, or both tissues positive indicated by the labelled bar. x.
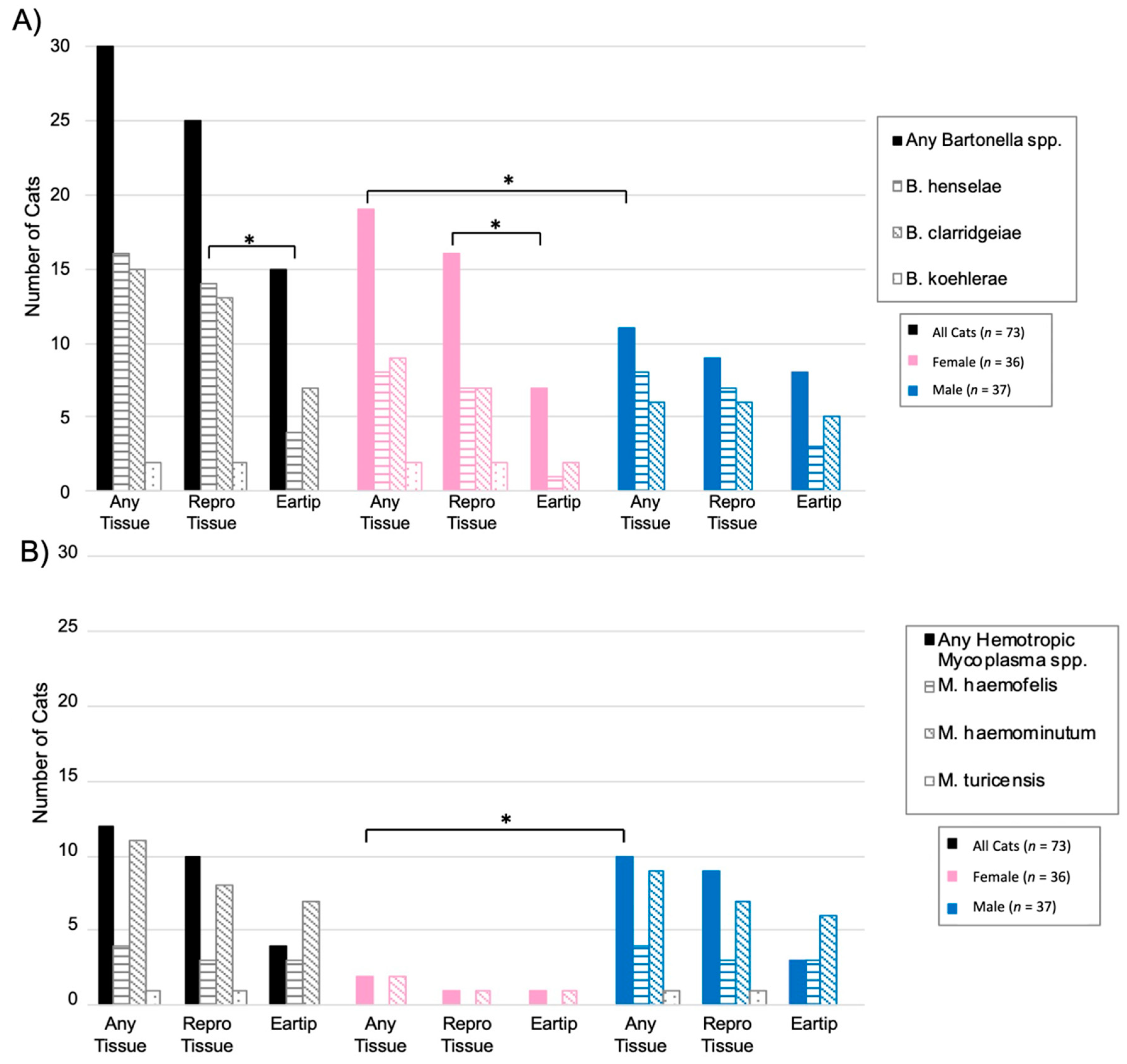
When considering each Bartonella species separately, significantly more cats were positive on reproductive tissue (14/73, 19%) than ear tip (4/73, 5%) for B. henselae (p = 0.02). Of the four cats with B. henselae-positive ear tip tissues, reproductive tissue(s) were also positive for two cats. In comparison, B. clarridgeiae was found in similar proportions from reproductive tissues (9/73, 12%) and ear tip tissue (11/73, 15%; p = 0.81). Bartonella koehlerae was only detected in two cats, both female from Washington, NC, with DNA being amplified from either ovary or uterine tissue, but not ear tip tissue. Figure 3A summarizes Bartonella spp. qPCR results from each tissue type. B. henselae and B. clarridgeiae DNA was amplified from all included tissue types, while B. koehlerae DNA was only amplified from the ovary or uterus.
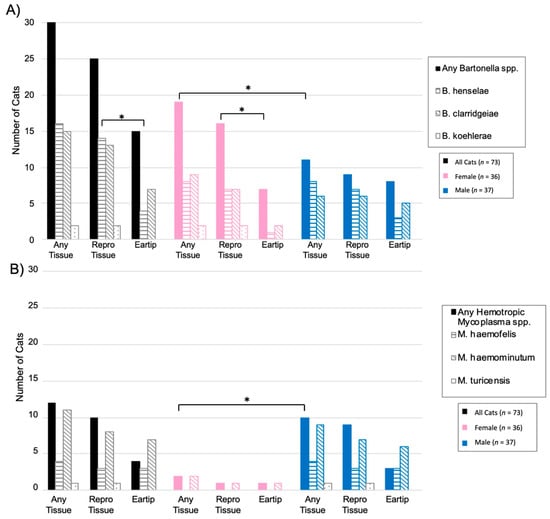
Figure 3.
Number of cats infected with Bartonella spp. and hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. by tissue type. (A) Total number of cats positive for any Bartonella spp., B. henselae, B. clarridgeiae, and B. koehlerae on either ear tip or reproductive tissues by sex. (B) Total number of cats positive for any hemotropic Mycoplasma spp., Mhf, Mhm, and Mtc on either ear tip or reproductive tissues by sex. * Statistical significance considered at p < 0.05 by Fisher’s exact test.
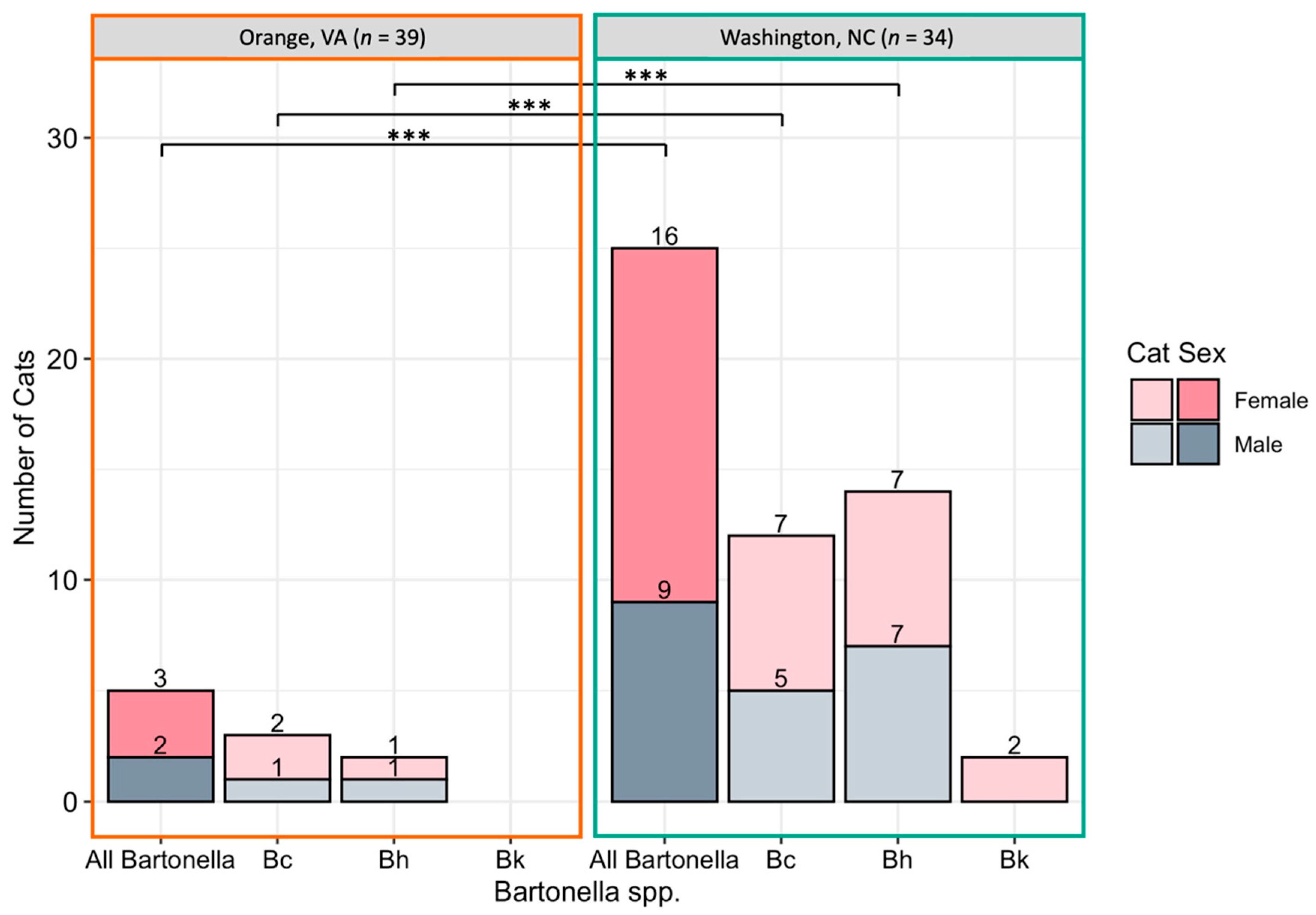
Bartonella spp. DNA was more often amplified from female cats than male cats with 56% (20/36) of female cats Bartonella spp. qPCR positive by one or more tissue, compared to 30% (11/37) of male cats (p = 0.03; Figure 3A Bartonella infection was significantly more common in cats sampled at the North Carolina location than the Virginia location, with 78% (29/37) of cats from North Carolina Bartonella spp. qPCR positive compared to only 13% (5/39) of cats from Virginia (p < 0.0001). Bartonella spp. detection at each location is displayed in Figure 4. There was a significant difference in the prevalence of both B. henselae (p < 0.001) and B. clarridgeiae (p < 0.001) between Washington, NC and Orange, VA with both species being more commonly detected in Washington, NC. Cat weight was not significantly associated with Bartonella spp.: the mean weight of Bartonella spp.-positive cats was 2.93 kg compared to a mean weight of 3.26 kg for negative cats (p = 0.16).
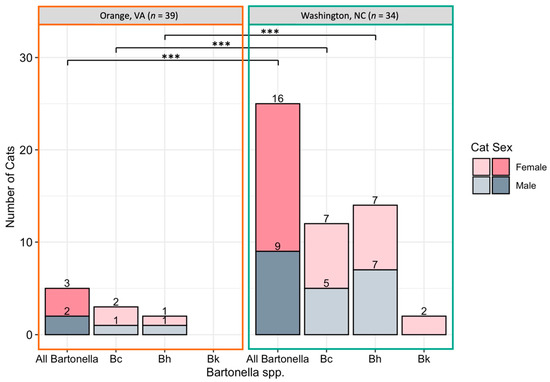
Figure 4.
Number of cats infected with Bartonella spp. by location. Cats were considered positive if one or more tissue samples were qPCR positive for all Bartonella spp., B. clarridgeiae (Bc), B. henselae (Bh), or B. koehlerae (Bk). *** Statistical significance considered at p < 0.0001 by Fisher’s exact test.
When utilizing a logistic regression model to analyze independent associations of location, weight, and sex with Bartonella spp. qPCR results, geographic location was the only variable independently associated with Bartonella spp.-positive PCR: cats in Washington, NC had 21.77 times higher odds of having one or more tissue Bartonella spp. qPCR positive (95% CI 6.65–86.45, p < 0.0001) compared to cats in VA. When utilizing the logistic regression model to analyze the associations of these same three variables (location, sex, and weight) with B. henselae or B. clarridgeiae amplification specifically, similar results were found with only location being significantly associated with detection of either species.
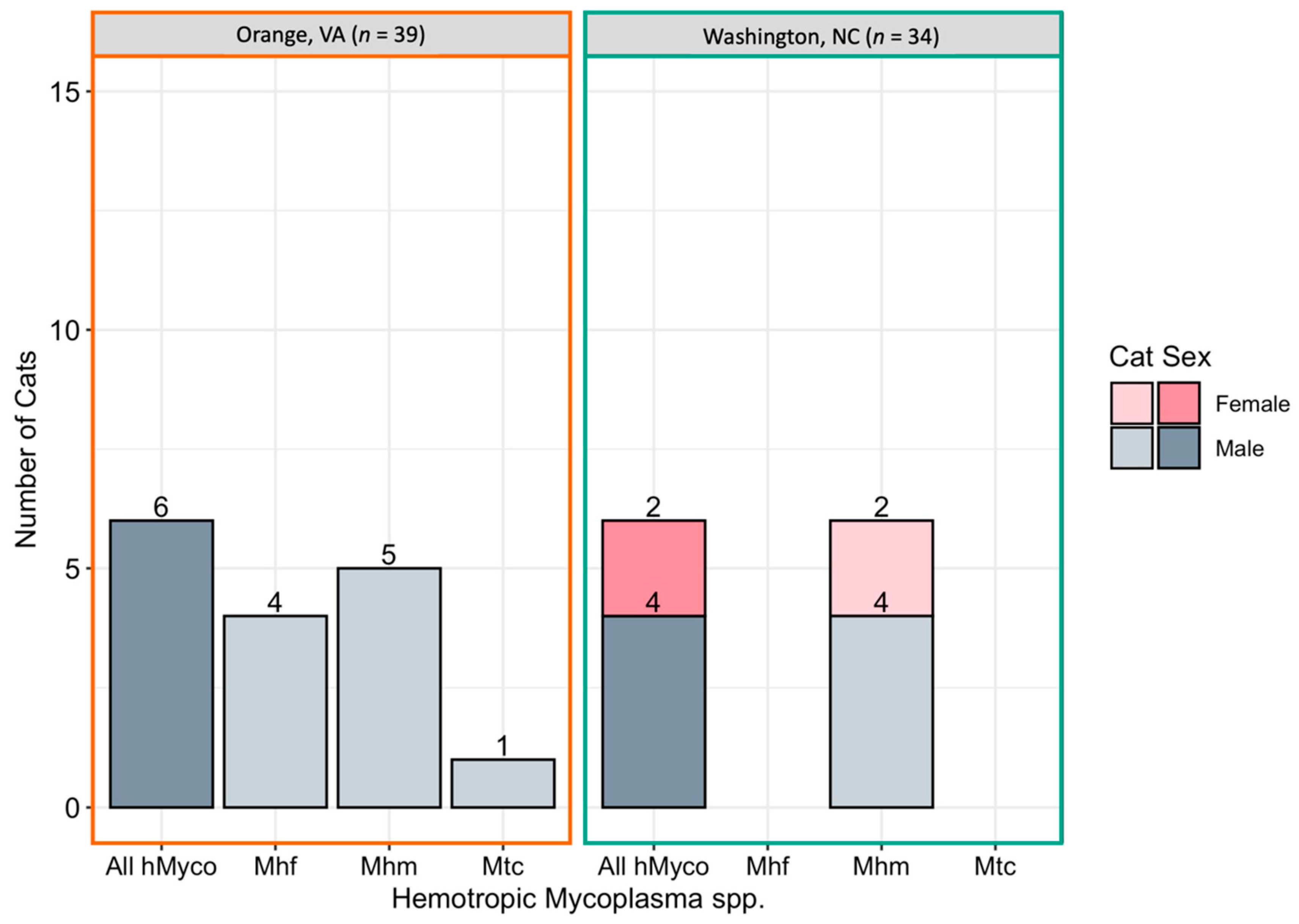
2.3. Hemotropic Mycoplasma spp.
Overall, hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. (hMyco) DNA was qPCR amplified from one or more tissues from 12 of 73 cats (16%). Mhm was amplified from 11 cats, Mhf was amplified from four cats, and Mtc from one cat (Figure 5). Based on qPCR, two cats were coinfected with Mhm and Mhf and one cat was coinfected with Mhm, Mhf, and Mtc; all cats coinfected with multiple hMyco species were males from Orange, VA. The proportions of ear tip tissue and reproductive tissue positive for hMyco DNA on qPCR were equal, at 14% (10/73) (p = 1; Figure 3B). The type of tissues that tested positive for hMyco infection is summarized in Figure 2C,D for male and female cats, respectively.
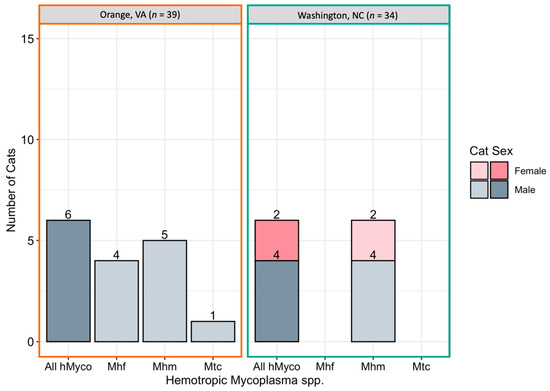
Figure 5.
Number of cats infected with hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. by location. Cats were considered positive if one or more tissue samples were qPCR positive for hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. (All hMyco), M. haemofelis (Mhf), M. haemominutum (Mhm), and Candidatus M. turicensis (Mtc).
Mhf DNA was amplified from ear tip and testicle tissues. Mhm DNA was amplified from ear tip, ovary, and testicle tissue. Mtc DNA was amplified only from testicle tissue.
hMyco DNA was more likely to be amplified from male cats (10/37, 27%) than female cats (2/36, 6%; p = 0.02; Figure 3B). The proportion of cats with hMyco-positive qPCR was similar at both geographic locations, with 15% (6/39) of cats from Orange, VA hMyco PCR positive and 18% (6/34) of cats from Washington, NC (p = 1) hMyco PCR positive. The number of cats positive for hMyco by location and sex is summarized in Figure 5. Cat weight was significantly associated with hMyco infection: the mean weight of hMyco-positive cats was 4.31 kg compared to a mean weight of 2.90 kg for negative cats (p < 0.01). When only considering male cats, hMyco-qPCR-positive males (mean 4.71 kg) were heavier than the hMyco-negative males (mean 3.10 kg; p < 0.001). The two female cats were 2.65 kg and 2.05 kg, below the mean female cat weight of 2.72 kg (range 1.52–4.28 kg).
When utilizing the logistic regression model to analyze independent associations of location, weight, and sex with hMyco qPCR results, weight was the only variable independently associated with hMyco-positive PCR: for every 1 kg increase in weight, cats had 3.38 higher odds of being hMyco positive (95% CI 1.61–8.73, p = 0.00393). When utilizing the logistic regression model to analyze the associations of these same three variables (location, sex, and weight) with Mhm or Mhf amplification specifically, similar results were found with only weight being independently associated with the detection of either hMyco species.
2.4. Bartonella and Hemotropic Mycoplasma Comparison
When comparing hMyco to Bartonella spp., a significantly higher proportion of cats had Bartonella spp.-positive reproductive tissues than hMyco-positive reproductive tissues (35% vs. 13%, respectively; p < 0.01). In contrast, there was no statistically significant difference in the proportion of cats with ear tip tissue positive for Bartonella spp. versus hMyco (21% vs. 14%, respectively; p = 0.38).
2.5. Inter-Genus Coinfection
Coinfection of Bartonella spp. and hMyco was only documented in five cats. Mhm was the only hMyco found as a coinfection with a Bartonella spp. One male cat was coinfected with B. henselae (testicle) and Mhm (ear tip and testicle) and two male cats were coinfected with B. clarridgeiae (ear tip; ear tip and testicle) and Mhm (ear tip and testicle; ear tip). Both female cats who were infected with hMyco were also infected with a Bartonella spp.: one was coinfected with B. koehlerae (ovary) and Mhm (ovary), and the other was coinfected with B. henselae (ovary and uterus) and Mhm (ear tip).
2.6. Fetal and Placental Samples
Samples from fetuses and placentae were collected from 10 and nine queens, respectively. qPCR results from these tissues are provided in Table 1. Of the 20 fetal samples tested, 20% (4/20) were B. henselae qPCR positive. Of the 19 placental samples tested, 11% (2/19) were B. henselae qPCR positive. Bartonella henselae was the only Bartonella spp. amplified from fetal or placental samples.

Table 1.
Bartonella spp. qPCR results from cats with fetal or placenta tissue collected. Total number of positive samples divided by the total number of samples collected is reported in the second column. N/A, tissue not sampled for the cat(s). Neg, tissue was tested and was negative.
3. Discussion
In this study, we tested one ear tip and multiple reproductive tissues of free-roaming cats for DNA of multiple common feline vector-borne diseases. A significantly higher proportion of cats infected with B. henselae had B. henselae DNA amplified from reproductive tissue (19%) compared to ear tip tissue (5%, p = 0.02), whereas the same proportion of hMyco infected cats had hMyco DNA PCR amplified from ear tip (14%) and reproductive tissue (14%). In addition, only B. henselae DNA, not B. clarridgeiae, B. koehlerae, or hMyco DNA, was qPCR amplified from fetal or placenta tissues of pregnant queens. Anaplasma, Ehrlichia, and Rickettsia spp. DNA were not PCR amplified from any of the tissues tested from any cat.
It is important to consider whether the higher proportion of B. henselae PCR-positive reproductive tissues compared to ear tip may be influenced by the greater number of reproductive tissue samples tested, with an average of 2.75 reproductive tissue samples compared to a single ear tip sample per cat. However, despite the higher number of reproductive tissues tested, neither hMyco nor B. clarridgeiae displayed a greater rate of detection in reproductive tissues, indicating that the increased detection of B. henselae in reproductive tissues could be due to a greater pathogen burden in the blood or tissue tropism, and not simply greater sensitivity with testing of multiple samples.
Despite limited literature investigating the tissue tropism of Bartonella spp., the ear tip appears to be a prime site for Bartonella spp. detection, and the skin has been identified as an important niche for B. henselae [42]. The ear tip has specifically been reported as a site of Bartonella spp. cutaneous disease manifestation, as shown by a recent case report of B. henselae associated with ear tip vasculitis in a dog [43]. Therefore, even equivalent detection in the reproductive tissue could be significant, as it represents a bacterial burden equivalent to one of the pathogen’s reported primary niches [44]. The higher proportion of B. henselae in reproductive tissues compared to ear tip tissue highlights the importance of focusing future studies on the reproductive system as a site of Bartonella spp. pathology. Despite the rising popularity of pet cats and cat breeding, infertility in domestic cats remains understudied compared to dogs and other domestic animals [45,46]. Given the cat’s role as the reservoir for multiple Bartonella spp. and previous studies suggesting Bartonella spp. as a cause of reproductive failure in cats [39], further investigation of the link between Bartonella spp., the feline reproductive tract, and infertility is warranted.
The detection of Bartonella spp. in the reproductive tract, fetus, and placenta of cats also has implications for the maintenance of Bartonella spp. in their cat reservoir host. Two studies have indicated a lack of transplacental transmission of B. henselae naïve queens inoculated with cultured B. henselae strains [39,47]. By inoculation of B. henselae just prior to or during pregnancy, these studies fail to mimic pregnancy in a reservoir host which is chronically infected or has experienced multiple reinfection events via chronic parasitism by C. felis. Abbott et al. documented seroconversion of kittens born to a bacteremic queen, presumably associated with transplacental transfer of immunoglobulins [47]. Kittens with maternal immunity were subsequently infected by inoculation with the same culture-grown strain that infected the queen, developing low bacteremia, or with a different B. henselae strain, developing high bacteremia [48]. Importantly, studies investigating reproductive outcomes following Bartonella spp. inoculation in cats have utilized culture grown Bartonella spp., which previous literature has indicated may result in reduced virulence [47,49,50,51]. Therefore, future work must carefully consider the inoculum source and timepoint(s) to ensure study outcomes that most closely mimic natural infection.
Considering the human health implications of these findings, inoculation of rodents prior to pregnancy, whose discoid hemochorial placenta is more similar to that of humans than cats, with B. birtlesii indicated transplacental transmission was possible [40]. The sole case report supporting in utero or perinatal transmission of B. henselae in humans involved twins, one of whom died of a congenital heart defect (hypoplastic left heart syndrome) at 9 days of age [41]. Therefore, the present findings and previous work suggest future research should address if those Bartonella spp. associated with cats are able to be passed vertically from persistently bacteremic queens, as well as investigate the possible implications for Bartonella spp. as a pathogen of importance to human reproduction.
Hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. detection rates were identical by tissue type (ear tip and reproductive tissue for both male and female cats) for Mhm and Mhf, with Mtc being detected only in a testicle sample of a single cat, suggesting that these species do not display a predilection for either reproductive or ear tip tissue with equivalent detection by qPCR in both tissue types. This is expected as hMyco are erythrocytic organisms and both the skin and reproductive tissues are highly vascularized. Previous work has compared Mhf copy number in blood to those in specific tissue, determining that splenic and lung tissue harbored more Mhf; however, this work did not include reproductive or skin tissues [52]. Regarding host sex difference, the significantly greater detection of hMyco in cats of the male sex was expected, as it is an established pattern documented in several previous studies [19,53,54]. Failure of the logistic regression model to identify this pattern is likely due to the confounding relationship between cat sex and weight, as male cats (mean 3.53 kg) were significantly heavier than female cats (mean 2.72 kg).
The detection of multiple hMyco in a single cat has also been previously reported, including triple co-infection with Mhm, Mhf, and Mtc as reported by Skyes et al. [19]. From a One Health perspective, sick humans are rarely tested for the presence of hMyco infections; however, there are several recent reports describing DNA of feline, canine, ovine, and swine-adapted hMyco in human patients [20,55,56,57]. Although a majority of hMyco infections are thought to cause minimal pathology in most infected species, it is of interest that most reported human cases have involved co-infection with B. henselae [20,55,58] while inter-genus coinfection was common in our cats. hMyco coinfection with Bartonella spp. in two female cats reinforces the importance and need for further investigation into the effects of coinfection on transmission and disease manifestation.
When interpreting the significant difference in the prevalence of Bartonella spp. between the two geographic locations from which cats were tested in this study, two factors must be considered: cat sex and true geographic differences in pathogen total and species-specific prevalence. While the proportion of male and female cats from Orange, VA and Washington, NC was not significantly different (p = 0.16), there was a slightly higher proportion of female cats sampled in NC compared to VA (58% vs. 41%). When stratified by location, female cats (85%) and male cats (36%) from Washington, NC had the highest proportion of Bartonella spp. infection, followed by female (19%) and male (6%) cats from Orange, VA. Female cats from the same location as male cats consistently displayed higher infection prevalence, indicating a confounding relationship between sex, location, and Bartonella spp. infection in this study. Previous literature has not suggested a difference in Bartonella spp. infection prevalence between male and female cats [59,60], indicating that our sampling methodology may have resulted in increased detection of infection in females. This could reflect sampling bias, since more tissues per cat were tested for females than males (mean 4.5 tissues samples for females vs. two tissue samples for males) or due to a true difference in the pathogen’s presence in tissue, which would not be reflected in previous literature, which commonly utilizes blood samples for diagnostic assays.
The exclusive detection of Mhf and Mtc in Orange, VA, despite the similar rate of Mhm detection between locations, indicates that this observation may be attributed to true difference in prevalence between locations. The unexpected differences in the prevalence of both Bartonella spp. and hMyco between these relatively close (322 km) locations indicates that these species may display precise geographic variations in prevalence. This would be an important consideration when locations are grouped together in regional or national prevalence surveys.
The limitations of the current study included the sampling of only two locations, sampling at different times of the year, lack of accurate cat age data, and sampling by two different veterinary teams. All of these factors may have introduced variation in pathogen prevalence between locations. By only sampling two locations, we are unable to draw conclusions about the broader geographical patterns of Bartonella and hMyco species among cats in other regions. Sampling Washington, NC in March and Orange, VA throughout the year may have confounded our results if these species display varying prevalence throughout the year. The sampling of an unequal number of reproductive tissues (average 2.75 per cat) versus ear tip tissues (one per cat) may have resulted in an increased detection in reproductive tissues. While our microbiological results are specific based upon sequencing of amplicon DNA, a lack of sensitivity with qPCR likely resulted in some infected cats being considered uninfected [61].
4. Methods
4.1. Study Design and Sample Sources
The present study was performed as a prospective cross-sectional observational study of FRC ear tip and reproductive tissues collected from cats located in Washington, North Carolina in Beaufort County and Orange County, Virginia. Trap-neuter-release (TNR) programs were already in place to control the FRC populations locally and improve FRC welfare [62]. Volunteer veterinary personnel collected tissues removed for spay/neuter while cats were anesthetized. Samples from Washington, NC were collected in collaboration with Paws and Love, Inc. in March 2019. Samples from Orange, VA were collected in collaboration with the Orange County Humane Society TNR program and Paradocs Animal Hospital in May 2019 and November 2020 through January 2021. Ear tip biopsy was performed for the purpose of identifying FRCs that had previously undergone spay or neuter [62]. This study was approved by the North Carolina State University IACUC (Protocol #19–003).
4.2. Data and Specimen Collection
Cats were selected for study participation upon presentation to TNR program regardless of sex or ectoparasite infestation. All cats anesthetized for spay/neuter during the study time periods were enrolled. For the primary objective, cats were excluded if ear tip tissue was not collected, or if less than two testicle (male) or two ovary (female) samples were collected. Therefore, all cats had at least one ear tip and two reproductive tract tissue samples available for testing. For the secondary objective, only pregnant queens with at least 1 sample from the queen reproductive tract and 1 fetus sample were included. Demographic data including sex and weight were recorded by veterinary personnel at each location.
Following routine spay or neuter surgical procedures and ear tip removal by the attending veterinarian, the reproductive tracts (left and right ovary and uterine horn for females, left and right testicle for males) and ear tips were collected and labeled. All reproductive tissues from an individual cat were stored in the same container for transport, and each ear tip was stored individually. Shortly after collection, tissues were frozen and transported to the Intracellular Pathogens Research Laboratory (IPRL) in a Styrofoam box with ice packs. Samples remained frozen (−20 °C) until dissected for DNA extraction. Dissection was performed utilizing a disposable scalpel and tweezers, which were sanitized with 100% ethanol between samples in order to reduce the possibility of DNA carryover between tissues [63]. The tissues dissected from each organ included: one 1 × 1 cm section from the center of each ovary, one 1 × 1 cm section from each uterine horn, one 1 × 1 cm section from the center of each testicle, and a 1 × 1 cm section of the ear tip. Due to loss of samples during collection, uterus tissue was not available for 9 cats from NC; all other cats had all tissues sampled. Figure 1 provides a summary of the tissues collected from each location.
For investigation of Bartonella spp. in fetal and placental tissue, cats from whom fetal and/or placental tissues were collected were reported regardless of ear tip sample availability. For those early in gestation, the entire fetus was utilized for DNA extraction, while an approximately 1 × 1 cm sample from across the mid-abdomen was selected for later gestation fetuses. Fetal and placenta tissues underwent the same processing and qPCR procedures detailed below.
DNA extraction from tissues was performed utilizing the Qiagen DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) following manufacturer’s tissue extraction protocol. DNA concentration (ng/μL) and purity (A260/A280) were determined spectrophotometrically (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
4.3. Pathogen Detection
A housekeeping qPCR amplifying the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene was performed to ensure the presence of amplifiable DNA and to assess for potential PCR inhibition [64]. All samples had amplifiable DNA by the housekeeping qPCR.
Pathogen detection was performed with PCR reactions amplifying the Bartonella spp. ssrA gene [65] and 16S–23S intergenic spacer (ITS) region [61,66,67], hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. 16S rRNA region (this study), Rickettsia spp. 16S-23S ITS region [65], and Anaplasma and Ehrlichia spp.16S rRNA gene [68]. qPCR conditions for the detection of hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. are detailed below, while other assays were performed as detailed in cited literature. Primer sequences are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Primers targeting housekeeping genes and pathogens. GADPH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, ITS; intergenic spacer, FAM: 6-fluorescein amidite, IABkFQ: Iowa Black ® FQ.
Hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. amplification reaction was performed in a 25 µL reaction consisting of 12.5 µL of SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad), 5 µL of DNA, 0.1 µL of each primer at 50 µM, and 7.3 µL of molecular grade water. The reaction began with 3 min of denaturation at 98 ℃, then 35 cycles of 98 ℃ for 15 s, 62 ℃ for 15 s, and 72 ℃ for 15 s, and finally, a melt curve analysis from 65 ℃ to 90 ℃ at 0.5 ℃ increments. Validation confirmed detection of Mhf, Mhm, Mtc, Mycoplasma haematoparvum, Mycoplasma haemocanis, as well as additional hemotropic Mycoplasma spp. found in rhinoceros, antelope, llama, and bovine. The primers did not detect bacteria belonging to Anaplasma, Bartonella, Ehrlichia, or Rickettsia spp.
Three controls were included in each reaction, a non-template control consisting of molecular grade water, a negative control from a cat known to be negative for all PCR targets, and a positive plasmid control or bacterial culture control. Reactions were performed in a CFX96 Touch Real-Time Detection System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Sequencing of all positive samples was performed at GENEWIZ Inc. (Raleigh, NC, USA), analysis and editing of chromatograms performed utilizing SnapGene (Insightful Science, San Diego, CA, USA), and NCBI nucleotide BLAST (National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda, Maryland, USA) was utilized to compare sequences to known species.
A cat was considered PCR positive for a given pathogen if ≥1 of the cat’s samples generated an amplicon that could be confirmed to have >99% similarity by DNA sequencing. For Bartonella spp., a cat was considered positive if either the ssrA or ITS gene target was successfully amplified.
4.4. Statistical Methods
Descriptive statistics (mean and standard deviation for continuous data and proportions) were calculated. The proportion of PCR positive cats for each pathogen was compared by geographic location, tissue type, sex, and cat weight to determine associations. Fisher’s exact test was employed when examining categorical variables and two sample t-test employed for normally distributed continuous variables. Two multivariable logistic regression models examining the likelihood of a cat having one or more tissue samples positive for (1) Bartonella spp. or (2) hemotropic Mycoplasma spp., as the dependent variables were used to calculate adjusted ORs for explanatory variables (geographic location, sex, and weight). Values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. All analysis was performed in R, version 4.0.4 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) in Windows utilizing the packages cowplot [69], ggthemes [70], here [71], irr [72], janitor [73], stringr [74], and tidyverse [75,76].
5. Conclusions
This study provides evidence that B. henselae is more common in the reproductive tissue than the ear tip tissue of cats. This finding combined with B. henselae amplification from the fetal and placental samples of pregnant queens highlights the need for further investigation into the role of vertical transmission in the maintenance of B. henselae in this reservoir host, as well as any possible effects of Bartonella spp. infection on the reproduction of both cats and other mammalian species. Significant differences in Bartonella spp., Mhf, and Mtc detection between two sites in the South Atlantic United States indicates there may be precise geographic patterns of pathogen prevalence, which remain to be elucidated. Future research should focus on detailed pathologic and bacterial imaging analysis of infected reproductive and fetal tissues, attempted isolation of viable bacteria from fetal tissue, and in vivo studies of queens known to be infected with Bartonella, hemotropic Mycoplasma, or members of both genera.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.M., K.F. and E.L.; methodology, R.M.; software, C.M. and E.L.; validation, R.M.; formal analysis, C.M. and E.L.; investigation, C.M.; resources, E.B.B.; data curation, C.M. and E.L.; writing-original draft preparation, C.M., E.B.B. and E.L.; writing-review and editing, C.M., K.F., R.M., E.B.B. and E.L.; visualization, C.M. and E.L.; supervision, K.F., R.M., E.B.B. and E.L.; project administration, E.B.B.; funding acquisition, C.M., R.M., E.B.B. and E.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Spring 2020 Office of Undergraduate Research Awards. A portion of this project was completed while C.M. was supported by the North Carolina State University’s Comparative Medicine Institute Summer Interdisciplinary Research Initiative. Portions of this project were also completed while EL’s research was supported by the Comparative Medicine and Translational Research Program of the National Institutes of Health under award number T32OD011130, and by the University of Wisconsin School of Veterinary Medicine Companion Animal Fund Grant Award. Funding sources had no role in study conceptualization, data collection and analysis, or manuscript preparation and submission.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the North Carolina State University IACUC (Protocol #19-003).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available via Dryad (https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.x69p8czk4).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all of the incredible veterinarians, veterinary technicians, veterinary students, and volunteers who gave their time and expertise at trap–neuter–release clinics both for their efforts in controlling free-roaming cat populations and their enthusiastic cooperation in collecting tissue samples. Additionally, we would like to thank Barbara Qurollo and the whole Vector Borne Disease Diagnostics team for their work in qPCR design and validation.
Conflicts of Interest
In conjunction with Sushama Sontakke and North Carolina State University, Edward B. Breitschwerdt, DVM holds U.S. Patent No. 7,115,385: “Media and Methods for Cultivation of Microorganisms”, issued 3 October 2006. He is a co-founder, shareholder, and Chief Scientific Officer for Galaxy Diagnostics, a company that provides advanced diagnostic testing for the detection of Bartonella species infections. Ricardo Maggi is the Chief Technical Officer and also a shareholder and co-founder of Galaxy Diagnostics. All other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Qurollo, B. Feline Vector-Borne Diseases in North America. Vet. Clin. N. Am.—Small Anim. Pract. 2019, 49, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappin, M.R.; Tasker, S.; Roura, X. Role of vector-borne pathogens in the development of fever in cats: Flea-associated diseases. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2020, 22, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, S.; Diakou, A.; Di Cesare, A.; Colombo, M.; Traversa, D. Canine and Feline Parasitology: Analogies, Differences, and Relevance for Human Health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00266-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordick, D.L.; Hilyard, E.J.; Hadfield, T.L.; Wilson, K.H.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Brenner, D.J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella clarridgeiae, a Newly Recognized Zoonotic Pathogen Causing Inoculation Papules, Fever, and Lymphadenopathy (Cat Scratch Disease). J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avidor, B.; Graidy, M.; Efrat, G.; Leibowitz, C.; Shapira, G.; Schattner, A.; Zimhony, O.; Giladi, M. Bartonella koehlerae, a New Cat-Associated Agent of Culture-Negative Human Endocarditis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3462–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, J.E.; Glaser, C.A.; Jordan, W. Rochalimaea henselae Infection A New Zoonosis with the Domestic Cat as Reservoir. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1994, 271, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, J.E. Feline Hemotropic Mycoplasmas. Vet. Clin. N. Am.—Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 40, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, C.A.; Saha, S.; Mead, P.S. Cat-Scratch Disease in the United States, 2005-2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, T.A.; Balakrishnan, N.; Barbosa, I.C.; Mccoy, T. Bartonella spp. as a Possible Cause or Cofactor of Feline Endomyocarditis Left Ventricular Endocardial Fibrosis Complex. J. Comp. Pathol. 2018, 162, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomel, B.B.; Boulouis, H.; Breitschwerdt, E. Cat scratch disease and other Bartonella infections. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 224, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Stuckey, M.J.; Breitschwerdt, E.; Maggi, R.; Henn, J.B.; Koehler, J.E.; Chang, C.-C. Experimental infection of cats with Afipia felis and various Bartonella species or subspecies. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G.; Sigmon, B.; Nicholson, W.L. Isolation of Bartonella quintana from a woman and a cat following putative bite transmission. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leibovitz, K.; Pearce, L.; Brewer, M.; Lappin, M.R. Bartonella species antibodies and DNA in cerebral spinal fluid of cats with central nervous system disease. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2008, 10, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stützer, B.; Hartmann, K. Chronic Bartonellosis in Cats: What are the potential implications? J. Feline Med. Surg. 2012, 14, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Williams, C.; Wey, A.C.; Henn, J.B.; Maggi, R.; Carrasco, S.; Mazet, J.; Boulouis, H.J.; Maillard, R.; et al. Bartonella endocarditis: A pathology shared by animal reservoirs and patients. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1166, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittemore, J.C.; Hawley, J.R.; Radecki, S.V.; Steinberg, J.D.; Lappin, M.R. Bartonella Species Antibodies and Hyperglobulinemia in Privately Owned Cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketring, K.L.; Zuckerman, E.E.; Jr, W.D.H. Bartonella: A New Etiological Agent of Feline Ocular Disease. Pearls Vet. Pract. 2004, 40, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Floyd-Hawkins, K.; Chi, B.; Yamamoto, K.; Roberts-Wilson, J.; Gurfield, A.N.; Abbott, R.C.; Pedersen, N.C.; Koehler, J.E. Experimental transmission of Bartonella henselae by the cat flea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1952–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, J.E.; Terry, J.C.; Lindsay, L.L.; Owens, S.D. Prevalences of various hemoplasma species among cats in the United States with possible hemoplasmosis. J. Am. Vet. Med Assoc. 2008, 232, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, A.P.; Dos Santos, R.P.; Biondo, A.W.; Dora, J.M.; Goldani, L.Z.; De Oliveira, S.T.; Guimarães, A.M.D.S.; Timenetsky, J.; De Morais, H.A.; González, F.H.; et al. Hemoplasma infection in HIV-positive patient, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1922–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, J.E.; Wisnewki, N.; Lappin, M.R. Attempted transmission of Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum and Mycoplasma haemofelis by feeding cats infected Ctenocephalides felis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Englert, T.; Stuetzer, B.; Hawley, J.R.; Lappin, M.R. Risk factors of different hemoplasma species infections in cats. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willi, B.; Boretti, F.S.; Meli, M.L.; Bernasconi, M.V.; Casati, S.; Hegglin, D.; Puorger, M.; Neimark, H.; Cattori, V.; Wengi, N.; et al. Real-time PCR investigation of potential vectors, reservoirs, and shedding patterns of feline hemotropic mycoplasmas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3798–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, J.E.; Brewer, M.M.; Hawley, J.R.; Wisnewski, N.; Lappin, M.R. Evaluation of experimental transmission of Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum and Mycoplasma haemofelis by Ctenocephalides felis to cats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2005, 66, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashnits, E.; Grant, S.; Thomas, B.; Qurollo, B.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Evidence for vertical transmission of Mycoplasma haemocanis, but not Ehrlichia ewingii, in a dog. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plier, M.L.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Hegarty, B.C.; Kidd, L.B. Lack of Evidence for Perinatal Transmission of Canine Granulocytic Anaplasmosis From a Bitch to Her Offspring. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2009, 45, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.M.; Cohn, L.A.; Birkenheuer, A.J. Lack of evidence for perinatal transmission of Cytauxzoon felis in domestic cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 188, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.T.; Alves, M.L.; Spada, J.C.; Leonel, J.A.; Benassi, J.C.; Starke-Buzetti, W.A.; Ferreira, H.L.; Keid, L.B.; Soares, R.M.; Oliveira, T.M. Leishmania infantum in the reproductive organs of dogs. Cienc. Rural St. Maria 2021, 51, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Boggiatto, P.M.; Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Metz, K.; Gallup, J.M.; Hostetter, J.; Mullin, K.; Petersen, C.A. Transplacental transmission of Leishmania infantum as a means for continued disease incidence in North America. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Morales, O.; Ballinas-Verdugo, M.A.; Alejandre-Aguilar, R.; Reyes, P.A.; Arce-Fonseca, M. Trypanosoma cruzi connatal transmission in dogs with chagas disease: Experimental case report. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, J.M.; Burgess, E.C.; Wachal, M.D.; Steinber, H. Intrauterine transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1993, 54, 882–890. [Google Scholar]
- Matei, I.A.; Stuen, S.; Modrý, D.; Degan, A.; D’Amico, G.; Mihalca, A.D. Neonatal Anaplasma platys infection in puppies: Further evidence for possible vertical transmission. Vet. J. 2017, 219, 40–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latrofa, M.S.; Torres, F.D.; De Caprariis, D.; Cantacessi, C.; Capelli, G.; Lia, R.P.; Breitschwerdt, E.; Otranto, D. Vertical transmission of Anaplasma platys and Leishmania infantum in dogs during the first half of gestation. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fukumoto, S.; Suzuki, H.; Igarashi, I.; Xuan, X. Fatal experimental transplacental Babesia gibsoni infections in dogs. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tołkacz, K.; Bednarska, M.; Alsarraf, M.; Dwużnik, D.; Grzybek, M.; Welc-Falęciak, R.; Behnke, J.M.; Bajer, A. Prevalence, genetic identity and vertical transmission of Babesia microti in three naturally infected species of vole, Microtus spp. (Cricetidae). Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.; Purtill, K.; Wong, S.J.; Munoz, J.; Teal, A.; Madison-Antenucci, S.; Horowitz, H.W.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E.; Moore, J.M.; Abramowsky, C.; et al. Vertical transmission of Babesia microti, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodžić, A.; Mrowietz, N.; Cézanne, R.; Bruckschwaiger, P.; Punz, S.; Habler, V.E.; Tomsik, V.; Lazar, J.; Duscher, G.G.; Glawischnig, W.; et al. Occurrence and diversity of arthropod-transmitted pathogens in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in western Austria, and possible vertical (transplacental) transmission of Hepatozoon canis. Parasitology 2018, 145, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, T.; Inoue, M.; Tateyama, S.; Taura, Y.; Nakama, S. Vertical Transmission of Hepatozoon canis in Dogs. J. Veter-Med. Sci. 1993, 55, 867–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guptill, L.; Slater, L.N.; Wu, C.; Lin, T.; Glickman, L.T. Evidence of reproductive failure and lack of perinatal transmission of Bartonella henselae in experimentally infected cats. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 65, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulouis, H.J.; Barrat, F.; Bermond, D.; Bernex, F.; Thibault, D.; Heller, R.; Fontaine, J.-J.; Piémont, Y.; Chomel, B.B. Kinetics of Bartonella birtlesii infection in experimentally infected mice and pathogenic effect on reproductive functions. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 5313–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G.; Farmer, P.; Mascarelli, P.E. Molecular Evidence of Perinatal Transmission of Bartonella vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii and Bartonella henselae to a Child. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2289–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonellosis, One Health and all creatures great and small. Vet. Dermatol. 2017, 28, 96.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern, B.L.; Neupane, P.; Ericson, M.E.; Dencklau, J.C.; Linder, K.E.; Bradley, J.M.; McKeon, G.P.; Long, C.T.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella henselae in a dog with ear tip vasculitis. Vet. Dermatol. 2018, 29, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, A.; Dehio, C. Intruders below the Radar: Molecular Pathogenesis of Bartonella spp. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 42–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.M.; Taylor, D.J. Bacterial Reproductive Pathogens of Cats and Dogs. Vet. Clin. N. Am.—Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 42, 561–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontbonne, A.; Prochowska, S.; Niewiadomska, Z. Infertility in purebred cats—A review of the potential causes. Theriogenology 2020, 158, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.C.; Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Floyd-Hawkins, K.A.; Kikuchi, Y.; Koehler, J.E.; Pedersen, N.C. Experimental and Natural Infection with Bartonella henselae in Domestic Cats. Comp. Immun. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1997, 20, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischman, D.A.; Chomel, B.B.; Burgos, K.; Kasten, R.W.; Stuckey, M.J.; Durden, M.R.; Mirrashed, H.; Diniz, P.P.V. Impact of queen infection on kitten susceptibility to different strains of Bartonella henselae. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 180, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Kordick, D.L. Bartonella Infection in Animals: Carriership, Reservoir Potential, Pathogenicity, and Zoonotic Potential for Human Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordick, D.L.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Relapsing bacteremia after blood transmission of Bartonella henselae to cats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1997, 58, 492–497. [Google Scholar]
- Kordick, D.L.; Brown, T.T.; Shin, K.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Clinical and pathologic evaluation of chronic Bartonella henselae or Bartonella clarridgeiae infection in cats. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1536–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasker, S.; Peters, I.R.; Day, M.J.; Willi, B.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.J.; Helps, C. Distribution of Mycoplasma haemofelis in blood and tissues following experimental infection. Microb. Pathog. 2009, 47, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roura, X.; Peters, I.R.; Altet, L.; Tabar, M.-D.; Barker, E.; Planellas, M.; Helps, C.; Francino, O.; Shaw, S.E.; Tasker, S. Prevalence of hemotropic mycoplasmas in healthy and unhealthy cats and dogs in Spain. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, N.; Balzer, H.J.; Thüre, S.; Moritz, A. Prevalence of feline haemotropic mycoplasmas in convenience samples of cats in Germany. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2008, 10, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, J.E.; Lindsay, L.A.L.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Human coinfection with Bartonella henselae and two hemotropic mycoplasma variants resembling Mycoplasma ovis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3782–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, R.G.; Compton, S.M.; Trull, C.L.; Mascarelli, P.E.; Robert Mozayeni, B.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Infection with hemotropic Mycoplasma species in patients with or without extensive arthropod or animal contact. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3237–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.L.; Liang, A.B.; Yao, C.B.; Yang, Z.B.; Zhu, J.G.; Cui, L.I.; Yu, F.; Zhu, N.Y.; Yang, X.W.; Hua, X.G. Prevalence of Mycoplasma suis (Epierythrozoon suis) infection in swine and swine-farm workers in Shanghai, China. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2009, 70, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, R.G.; Mascarelli, P.E.; Havenga, L.N.; Naidoo, V.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Co-infection with Anaplasma platys, Bartonella henselae and Candidatus Mycoplasma haematoparvum in a veterinarian. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisanyong, W.; Takhampunya, R.; Boonmars, T.; Kerdsin, A.; Suksawat, F. Prevalence of Bartonella henselae, Bartonella clarridgeiae, and Bartonella vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii in pet cats from four provincial communities in Thailand. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2016, 46, 663–670. [Google Scholar]
- Guptill, L.; Wu, C.-C.; HogenEsch, H.; Slater, L.N.; Glickman, N.; Dunham, A.; Syme, H. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Genetic Diversity of Bartonella henselae Infections in Pet Cats in Four Regions of the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, R.G.; Richardson, T.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Miller, J.C. Development and validation of a droplet digital PCR assay for the detection and quantification of Bartonella species within human clinical samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 176, 106022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreisler, R.E.; Cornell, H.N.; Levy, J.K. Decrease in population and increase in welfare of community cats in a twenty-three year trap-neuter-return program in Key Largo, FL: The ORCAT program. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanat, M.; Maggi, R.G.; Linder, K.E.; Horton, S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Cross-contamination in the molecular detection of Bartonella from paraffin-embedded tissues. Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkenheuer, A.J.; Levy, M.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Development and Evaluation of a Seminested PCR for Detection and Differentiation of Babesia gibsoni (Asian Genotype) and B. canis DNA in Canine Blood Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 41, 4172–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyrrell, J.D.; Qurollo, B.A.; Tornquist, S.J.; Schlaich, K.G.; Kelsey, J.; Chandrashekar, R.; Breitschwerdt, E. Molecular identification of vector-borne organisms in Ehrlichia seropositive Nicaraguan horses and first report of Rickettsia felis infection in the horse. Acta Trop. 2019, 200, 105170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Bradley, J.M.; Maggi, R.G.; Lashnits, E.; Reicherter, P. Bartonella associated cutaneous lesions (BACL) in people with neuropsychiatric symptoms. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashnits, E.; Maggi, R.G.; Jarskog, F.; Bradley, J.; Breitschwerdt, E.; Froklich, F. Schizophrenia and Bartonella spp. Infection: A Pilot Case–Control Study. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, J.D.; Qurollo, B.A.; Mowat, F.M.; Kennedy-Stoskopf, S. Molecular Prevalence of Selected Vector-Borne Organisms in Captive Red Wolves (Canis rufus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2020, 51, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, C.O. cowplot: Streamlined Plot Theme and Plot Annotations for ggplot2. Published Online 2020. Available online: https://wilkelab.org/cowplot/ (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Arnold, J.B. ggthemes: Extra Themes, Scales and Geoms for ggplot2. Published Online 2021. Available online: https://github.com/jrnold/ggthemes (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Müller, K. Here: A Simpler Way to Find Your Files. Published Online 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=here (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Gamer, M.; Lemon, J.; IFPS. irr: Various Coefficients of Interrater Reliability and Agreement. Published Online 2019. Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Firke, S. janitor: Simple Tools for Examining and Cleaning Dirty Data. Published Online 2021. Available online: https://github.com/sfirke/janitor (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Wickham, H. stringr: Simple, Consistent Wrappers for Common String Operations. Published Online 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=stringr (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. tidyverse: Easily Install and Load the Tidyverse. Published Online 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=tidyverse (accessed on 1 March 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).