Abstract
Piroplasmosis and anaplasmosis are serious tick-borne diseases (TBDs) that are concerning for the public and animal health. This study aimed to detect the molecular prevalence and epidemiological risk factors of Piroplasma and Anaplasma species in animal hosts and their associated ticks in Egypt. A total of 234 blood samples and 95 adult ticks were collected from animal hosts (112 cattle, 38 sheep, 28 goats, 26 buffaloes, 22 donkeys, and 8 horses) from six provinces of Egypt (AL-Faiyum, AL-Giza, Beni-Suef, Al-Minufia, Al-Beheira, and Matruh). Blood and tick samples were investigated by polymerase chain reaction coupled with sequencing targeting 18S and 16S RNA genes for Piroplasma and anaplasmataceae, respectively. Statistical analysis was conducted on the potential epidemiological factors. Of the 234 animals examined, 54 (23.08%) were positive for pathogens DNA distributed among the six provinces, where 10 (4.27%) were positive for Piroplasma, 44 (18.80%) for anaplasmataceae, and 5 (2.14%) were co-infected. Co-infections were observed only in cattle as Theileria annulata and Anaplasma marginale plus Babesia bigemina, A. marginale plus B. bigemina, and T. annulata plus B. bigemina. Piroplasmosis was recorded in cattle, with significant differences between their prevalence in their tick infestation factors. Animal species, age, and tick infestation were the potential risk factors for anaplasmosis. All ticks were free from piroplasms, but they revealed high prevalence rates of 72.63% (69/95) with anaplasmataceae. We identified T. annulata, B. bigemina, and A. marginale in cattle; A. platys in buffaloes; A. marginale and A. ovis in sheep; for the first time, A. ovis in goats; and Ehrlichia sp. in Rhipicephalus annulatus ticks. Our findings confirm the significant prevalence of piroplasmosis and anaplasmosis among subclinical and carrier animals in Egypt, highlighting the importance of the government developing policies to improve animal and public health security.
1. Introduction
Tick-borne diseases (TBDs) cause serious health concerns worldwide. TBDs generate severe health problems in Egypt, particularly in exotic and cross-bred cattle, affecting animals’ well-being and the livelihoods of their owners [1].
Piroplasms are apicomplexan tick-borne parasites that are found worldwide. They cause piroplasmosis (theileriosis and babesiosis) in Vertebrata and are hence medically and economically significant [2]. In Egypt, the most frequent TBDs are bovine theileriosis caused by Theileria annulata and bovine babesiosis caused by Babesia bovis and/or Babesia bigemina [1,3,4]. Members of the genus Theileria cause bovine theileriosis by acting as compulsory intercellular parasites, attacking both red and white blood cells of the hosts with their sporozoites, and reversible transformation to an uncontrolled proliferative state by the schizont stage, resulting in anemia, fever, leucopenia, and lymphoproliferative disease. The causal agent T. annulata infects host monocytes/macrophages and B lymphocytes and causes tropical theileriosis (Mediterranean theileriosis) [5]. Tropical theileriosis is common in Southern Europe, Asia, North Africa, and the Middle East [6,7,8]. In addition, infection with Babesia causes significant economic costs in cattle, including death, production loss, lower feed intake and feed conversion efficiency, abortion, tick control losses, and disease prevention losses [9,10]. The most prevalent clinical manifestations linked with Babesia species infections in cattle include anemia, hemoglobinemia, pyrexia, and hemoglobinuria [10,11].
Anaplasmosis is a non-contagious infectious bacterial disease caused by the family Anaplasmataceae (Anaplasma spp. and Ehrlichia spp.). Anaplasma marginale is found worldwide and affects erythrocytes. Affected animals remain carriers for the rest of their lives. Anaplasmosis causes significant economic losses in developing countries owing to its endemic nature [4,12]. The main signs of bovine anaplasmosis are quite varied, ranging from subclinical chronic infections to severe instances accompanied by fever, hemolytic anemia, abortions, productivity losses, and mortality [12,13]. Bovine anaplasmosis, which affects various animals, is endemic in tropical and subtropical areas [4,8,14,15].
Remarkably, the majority of animals that recovered from clinical sickness caused by Theileria and Babesia parasites became carriers [16,17]. Furthermore, subclinical infections appeared in some animals due to their resistance to clinical piroplasmosis. Therefore, carrier and subclinical case detection is a serious step for appraising the level of risk caused by piroplasms (Theileria and Babesia) [18]. Similarly, because anaplasmosis is endemic in Egypt, herd screening for Anaplasmataceae was suggested in the absence of signs or symptoms of infection [12]. Because of the low bacteremia, detecting infection in carriers by standard microscopy techniques is difficult. Hence, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique has been detecting infections with low parasitemia and/or bacteremia [19,20]. In addition, when antibodies are not yet detectable by serological methods, the PCR technique can detect pathogen DNA in the acute phase of infection [20,21]. Therefore, for the epidemiological investigation of Theileria, Babesia, Anaplasma, and Ehrlichia infection, DNA-detection techniques such as PCR assays followed by sequencing are preferred [18,22,23]. To conduct an epidemiological investigation in six Egyptian provinces, this study aimed to detect the molecular prevalence, distribution, and risk factors associated with piroplasm and Anaplasmataceae in animal hosts and their associated ticks, and analyze their phylogeny. As a result, depending on the outcomes of such surveys, hemopathogen control strategies could be optimized.
2. Results
2.1. Prevalence of Pathogens
Of the 234 animals examined, 54 apparent healthy animals (23.08%) were detected as positive for pathogens DNA, 10 (4.27%) were positive for Piroplasma, 44 (18.80%) were positive for Anaplasmataceae, and 5 (2.14%) were co-infected (Table 1). Generally, the overall prevalence of Anaplasmataceae was significantly higher than that of Piroplasma (χ2 = 21.407, p < 0.001). The prevalence of Anaplasmataceae in Al-Faiyum and Matruh was significantly higher (p ≤ 0.001) than that of Piroplasma Moreover, the prevalence of Anaplasmataceae was higher in Al-Beheira and Al-Giza than that of Piroplasma, but the differences between the two pathogens in these two provinces were not significant (p > 0.05). However, in Beni-Suef, the prevalence of Piroplasma was not significantly higher (p > 0.05) than in Anaplasmataceae (Table 1).

Table 1.
Prevalence of hemopathogens (Piroplasma and Anaplasmataceae) in domestic animals from six provinces in Egypt from December 2019 to March 2020.
2.2. Analysis of Epidemiological Factors
All domestic animals (buffaloes, sheep, goats, donkeys, and horses) were free from piroplasmosis, except cattle that exhibited an 8.93% (10/112) prevalence rate, whereas different animal hosts revealed variable prevalence rates with anaplasmosis. Horses were free from Anaplasmataceae DNA (Table 2). Anaplasmosis detection between animal hosts exhibited a significant difference (χ2 = 38.923, p < 0.001), where the highest prevalence was found in sheep and the lowest was in donkeys. In addition, the prevalence of Anaplasmataceae in cattle was significantly higher than that of Piroplasma (χ2 = 8.526, p = 0.004), whereas other animals were free from Piroplasma (Table 2). Regarding sex, all animals positive for Piroplasma were females, whereas males were free from piroplasmosis. However, the difference in the prevalence of Anaplasmataceae was insignificant between females and males. In females, the prevalence of Piroplasma was significantly lower than that of Anaplasmataceae (χ2 = 11.524, p = 0.001) (Table 2). For age, the prevalence rate of piroplasmosis was recorded in animals aged >1 and ≤1 year, without significant difference between them (χ2 = 0.400, p = 0.527) (Table 2). Nevertheless, the prevalence rate of anaplasmosis in animals aged >1 year was significantly higher than in those aged ≤1 year (χ2 = 16.67, p < 0.001) (Table 2). In general, Anaplasmataceae was higher than Piroplasma in both ages (<1 and >1 year), but the increase in Anaplasmataceae was significant in those aged >1 year (χ2 = 22.261, p < 0.001) (Table 2). Regarding tick infestation, significant differences were found between infested and non-infested animals by ticks in Piroplasma (χ2 = 11.842, p = 0.001) and Anaplasmataceae (χ2 = 12.789, p < 0.001). Both infested and non-infested animals in anaplasmosis revealed a higher significant rate than Piroplasma detection (Table 2).

Table 2.
Risk factors associated with the prevalence of Piroplasma and Anaplasmataceae.
2.3. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analyses of Pathogen in Animal Hosts
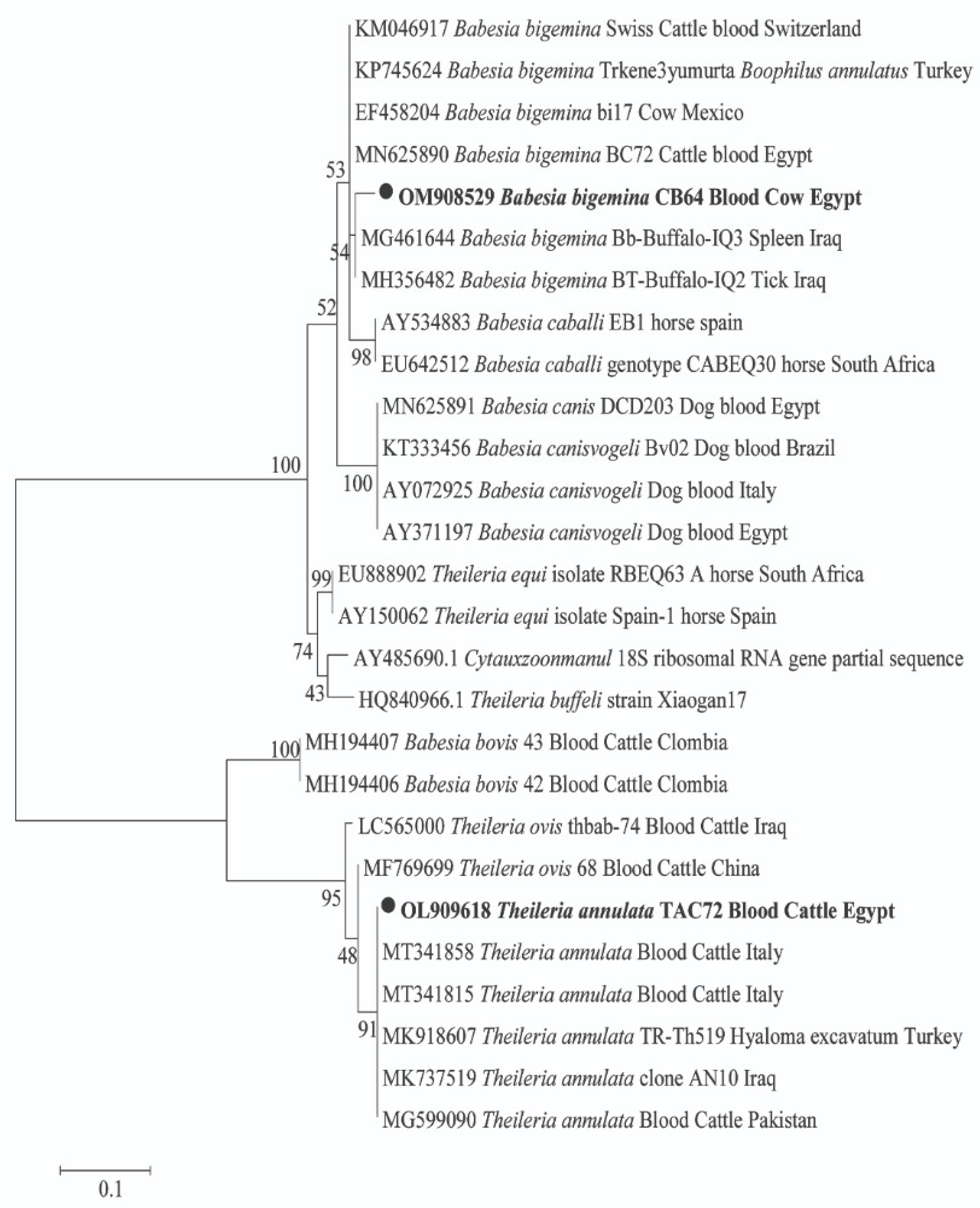
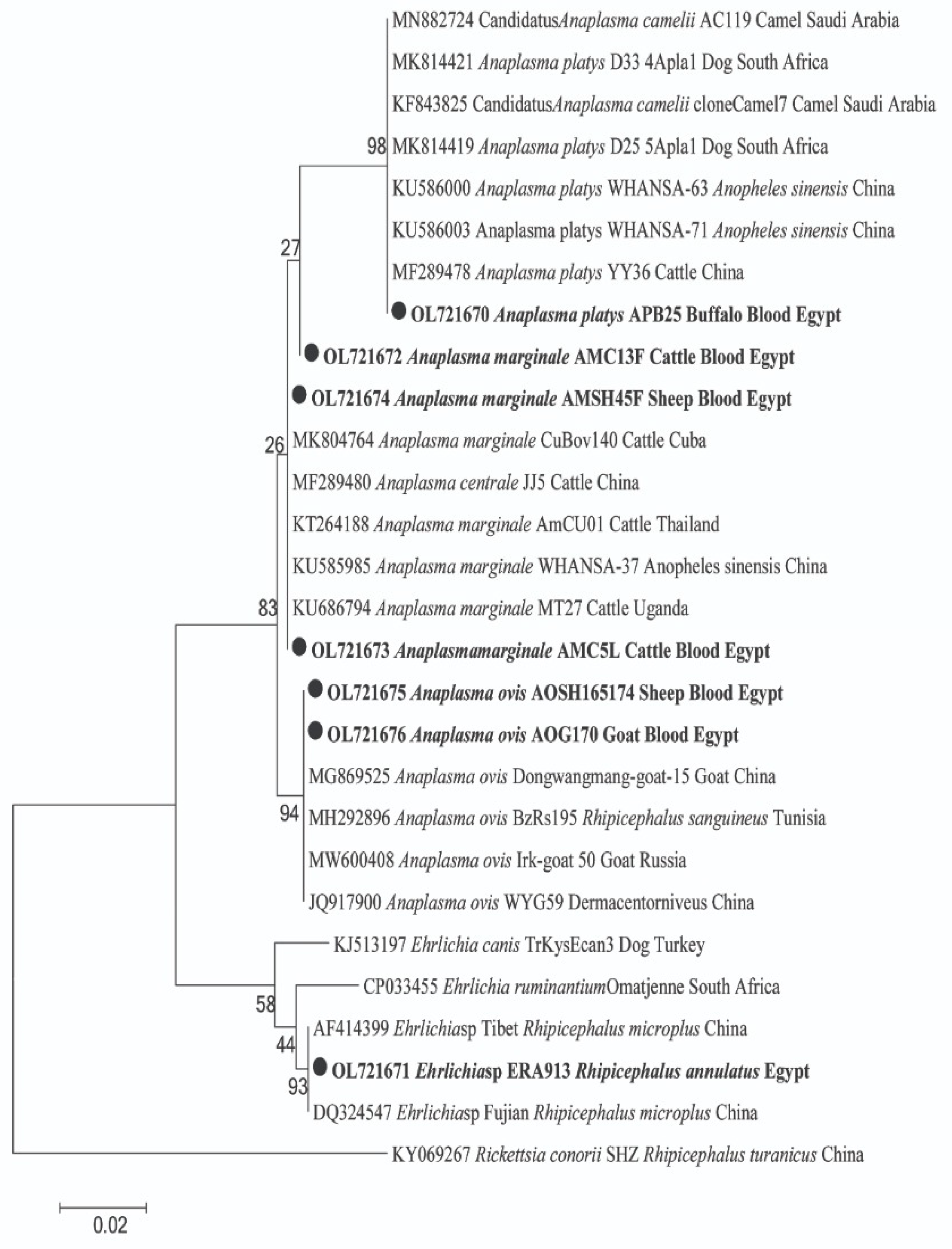
For pathogens in animal hosts, DNA sequencing confirmed the amplification of 18S and 16S rRNA genes for Piroplasma and Anaplasmataceae, respectively. For Piroplasma, 10 cattle were detected with two species of Theileria and Babesia; T. annulata was found in 5 cows and B. bigemina in 9 cows, with 4 cows co-infected with both species (GenBank: OL909618 and OM908529; respectively) (Figure 1). By BLAST analysis, we identified a potential new genotype of T. annulata with 99% (361/364) similarity to the T. annulata detected in cattle from Italy (GenBank: MT341858). Moreover, a potential new B. bigemina genotype that was detected with 97% (334/345) similarity to the B. bigemina was detected in a tick from a buffalo in Iraq (GenBank: MH356482). The phylogenetic position of both Piroplasma was illustrated in Figure 1. Furthermore, BLAST analysis of the obtained sequences of Anaplasmataceae revealed that cattle and sheep were positive for two different genotypes of A. marginale. One genotype was derived from cattle and sheep (GenBank: OL721673 and OL721674) with 100% (431/431) similarity to A. marginale detected in cattle blood from Cuba (GenBank: MK804764). Another potential novel genotype of A. marginale was derived from one cattle (GenBank: OL721672) with 99% (430/431) similarity to the same reference. Moreover, sheep and goats were positive for A. ovis (GenBank: OL721675 and OL721676) with 100% (431/431) similarity to A. ovis detected in goat blood from China (GenBank: MG869525). Meanwhile, buffaloes were positive for A. platys (GenBank: OL721670) with 100% similarity to A. platys detected in cattle blood from China (GenBank: MF289478). The phylogenetic positions of these Anaplasma spp. are illustrated in Figure 2.
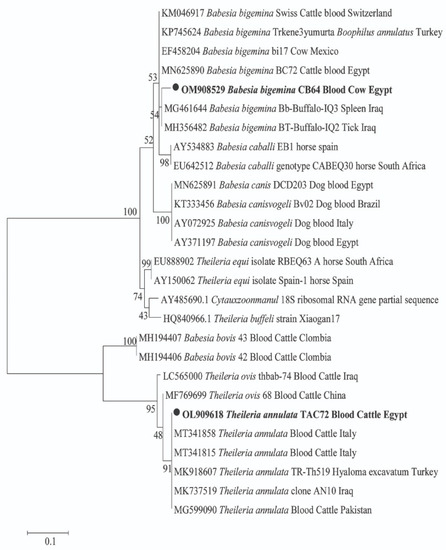
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of Theileria sp. and Babesia sp. 18S rRNA gene. The maximum likelihood method was constructed using MEGA X. Newly obtained sequences in this study are highlighted (bold).
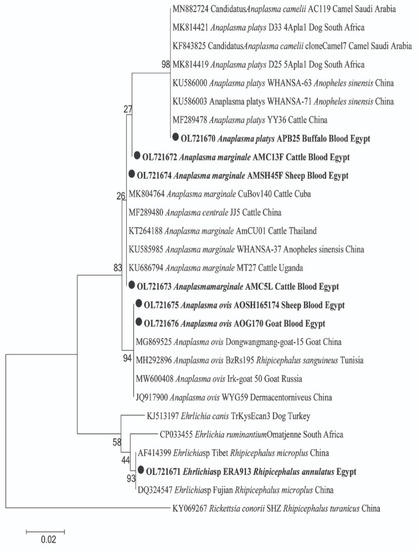
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree of Anaplasma sp. and Ehrlichia sp. 16S rRNA gene. The maximum likelihood method was constructed using MEGA X. Newly obtained sequences in this study are highlighted (bold). Rickettsia conorii was used as an out-group.
Finally, co-infection was detected in seven cattle that were positive for more than one tick-borne pathogen (7/112; 6.25%). Triple co-infections were observed in two cattle as T. annulata and A. marginale plus B. bigemina (2/112; 1.78%). In addition, five other co-infections were observed as A. marginale plus B. bigemina (3/112; 2.68%) and T. annulata plus B. bigemina (2/112; 1.78%).
2.4. Ticks and Associated Pathogens
Ticks were found only on cows and buffaloes. The cattle tick Rhipicephalus annulatus was observed on cows at all localities except Al-Minufia and beside one buffalo at Al-Faiyum (Table 3). All ticks were free from Piroplasma DNA, but they revealed high prevalence rates with Anaplasmataceae 72.63% (69/95) in R. annulatus. PCR and sequencing successfully detected DNA of Anaplasmatacae in tick samples, and the obtained good-quality sequences were identified as Ehrlichia sp. BLAST analysis revealed a potential novel Ehrlichia sp. (GenBank: OL721671) with 100% (469/469) similarity to Ehrlichia sp. detected in R. microplus from China (GenBank: AF414399). The phylogenetic position of this potentially novel Ehrlichia sp. was in a separate clade and clustered with other Ehrlichia spp. in a well-supported branch (bootstrap value 93). The phylogenetic position of this Ehrlichia sp. is presented in Figure 2.

Table 3.
Detection of Anaplasma DNA in Rhipicephalus annulatus ticks collected from cows and buffaloes from five provinces in Egypt.
3. Discussion
Piroplasmosis and anaplasmosis are major tick-borne diseases that infect ruminants and other mammalian species in tropical and subtropical areas [24,25]. Fever, oculo-nasal discharge, increased heart and respiratory rate, aberrant mucous membrane, and low PCV (Packed cell volume) values are all signs of acute piroplasmosis or anaplasmosis in animals, making them medically and economically important [2,24]. These signs are common, although they are not pathognomonic; animals with persistent infections can be asymptomatic carriers. Carrier animals with no clinical symptoms are thought to be a major reservoir of infection for ticks, which can spread the disease to other animals [12,18,26]. The goal of this study was to investigate Piroplasma and Anaplasmataceae DNA in various animal hosts (cattle, sheep, goats, buffaloes, donkeys, and horses) and their associated ticks across six provinces in Egypt. A molecular investigation was performed in blood and tick samples. Epidemiological data of each animal were gathered, and data were statistically analyzed using the χ2 test in SPSS.
In this study, the overall prevalence of pathogens was 23.08%, where it was 4.27% for piroplasmosis in five provinces (Al-Minufia was free from piroplasm at the time of investigation) and 18.8% for anaplasmosis in all six provinces. Since 1966, many studies have stated the endemicity of piroplasmosis and anaplasmosis in several provinces in Egypt [27,28,29]. In accordance with our results, piroplasms (T. annulata and B. bigemina) in cattle were recorded in Al-Faiyum, Al-Beheira, Al-Giza, and Beni-Suef [4,22,27,30]. To our knowledge, piroplasmosis was detected for the first time among two cows in Matruh. This finding might be attributed to the trading of live animals or transferred from neighboring provinces such as Alexandria and Al-Beheira. Moreover, Al-Minufia was free from piroplasms. This finding was possibly due to the low number of investigated animals that might not be exposed to ticks. By contrast, other studies have reported piroplasms in cattle from Al-Minufia [22,27,31]. In addition, piroplasmosis was detected in other provinces such as Gharbia [32], Port Said [33], Dakahlia [24], El-Wady El-Geded [3,4], Assiut and Kharga [34], and Qena [4]. Globally, theileriosis and babesiosis were detected in animals from different countries such as Pakistan [8], Brazil [9], Malaysia [10], and Mozambique [11]. For anaplasmosis, we detected Anaplasma spp. in all studied provinces, which was parallel with those previously reported in the same provinces in Egypt [1,4,28,35]. Furthermore, anaplasmosis was reported previously in other provinces rather than the investigated ones [28] such as Dakahlia and Demiatta [24,36,37], Sohag and Qena [38], El-Wady El-Geded, El Minia, and Assiut [1,4,34]. Therefore, piroplasmosis and anaplasmosis circulate between animal hosts and provinces in Egypt. Additionally, anaplasmosis spreads globally between different animal hosts [13,14].
On the basis of epidemiological factors, the prevalence rate of piroplasmosis in cattle was 8.93%, while other animal hosts were free from piroplasm. This result agreed with those of Elsify and his colleagues [22] and Abdullah and her colleagues [4], who recorded a high prevalence rate of piroplasmosis in cattle, whereas other animal hosts recorded a low prevalence rate or were free from piroplasms. For anaplasmosis, the overall prevalence rate of anaplasmosis was 18.8% in all animal species, except horses. In Egypt, several studies have recorded the endemicity of anaplasmosis in cattle [1,4,24,28,38,39], buffaloes [4,12], sheep [4,35], and donkeys [40]. However, anaplasmosis (A. ovis) was firstly detected in goats in Egypt. A recent study reported Anaplasma antibodies in goats [41]. Furthermore, the prevalence of anaplasmosis in cattle was significantly higher than that of piroplasmosis, which is in accordance with the findings of El-Ashker and his colleagues [24] and Abdullah and her colleagues [4]. Therefore, the finding of high prevalence rates of Piroplasma and Anaplasmatacea among apparent healthy animals with the increase in international animal trades implies the risk of emergence and re-emergence of new genotypes of pathogens from neighboring endemic countries [7,14]. Regarding sex, no significant difference was found in the prevalence rate of anaplasmosis between males and females, whereas piroplasmosis was only recorded in females, which was in agreement with the finding of Boussaadoun and his colleagues [42] in Northwest Tunisia. This finding might be attributed to the infection being linked to stress factors, such as pregnancy, parturition, and milk production [38]. Furthermore, the age of animal hosts is regarded as a significant risk factor; according to our observations, animals aged <1 year revealed insignificant higher prevalence rates of piroplasmosis than older ones. These results were in agreement with Al-Hosary and her colleagues [3], who reported a high prevalence of piroplasmosis in younger cattle. Conversely, some reports recorded a high prevalence of such diseases in older animals [27,30]. This finding may be related to the accumulation of infections, which increases protective immunity linked with immune system maturation [3]. However, a highly significant prevalence rate of anaplasmosis was recorded in older animals than in younger ones, which is in agreement with the findings of Parvizi and his colleagues [28]. Finally, a tick infestation is a fundamental risk factor for piroplasmosis and anaplasmosis. Related to our results, a highly significant prevalence rate of tick-infested animals was found in piroplasmosis and anaplasmosis than in non-infested animals. This investigation confirms the role of ticks as vectors in the spread of these diseases between animal hosts [34,40].
Regarding the phylogenetic analysis of pathogens, we identified two species of piroplasms, namely T. annulata and B. bigemina, in cattle based on the 18S rRNA gene. BLAST analysis revealed that two potential novel genotypes, T. annulata and B. bigemina, were identified (GenBank: OL909618 and OM908529, respectively). T. annulata and B. bigemina were reported in numerous studies in Egypt [3,4,24,38]. In addition, bovine theileriosis and babesiosis have been detected in countries such as Pakistan [8], Malaysia [10], the Philippines [43], and Burkina Faso [44].
With regard to Anaplasmataceae, BLAST analysis determined the two genotypes of A. marginale in cattle and sheep (GenBank: OL721672 and OL721674, respectively). In Egypt, A. marginale was reported as an endemic pathogen in cattle [1,4,24,28,39]. In accordance with our results, A. marginale was detected in sheep later by Abdullah and her colleagues [4]. Moreover, A. ovis was identified in sheep and goats (GenBank: OL721675 and OL721676). Studies have reported A. ovis in sheep in Egypt [4,35,45]. In Africa, other studies have identified A. ovis in sheep from Tunisia [46], Senegal [47], and Algeria [23]. To our knowledge, A. ovis has never been detected in goats in Egypt. Recently, some studies have reported goats infected with A. ovis in Iraq [48], Thailand [49], and Bangladesh [50]. Likewise, we found that buffaloes were positive for A. platys (GenBank: OL721670). According to our findings, A. platys was later detected in buffaloes in Egypt by Abdullah and her colleagues [4]. In parallel, a study detected A. platys in buffaloes in Thailand [51]. Finally, we recorded the co-infection rate in cattle (6.25%), including triple co-infections with T. annulata, A. marginale plus B. bigemina, and double co-infection with A. marginale plus B. bigemina, and T. annulata plus B. bigemina. Co-infections have been commonly reported in cattle [1,4,35,52,53].
Regarding pathogens’ DNA detection in ticks, we found cattle ticks (R. annulatus) positive for a potential novel Ehrlichia sp. (GenBank: OL721671), which clustered in a separate clade with other Ehrlichia spp. Therefore, further genetic studies are needed using species-specific primers for verifying the novelty of the family Anaplasmataceae and detecting co-infection with Anaplasma and Ehrlichia in ticks as the main vector of anaplasmosis. Recently, Abdullah and her colleagues [40] reported a new Ehrlichia sp. in R. annulatus collected from donkeys in Beni-Suef, Egypt, inferring that this new potential pathogen spreads among provinces, and R. annulatus is the main vector of this species in Egypt. This new species was detected in other countries such as China in R. microplus [54], Turkey in Hyalomma excavatum [55], and Pakistan in H. anatolicum [56]. Nevertheless, R. annulatus was free from piroplasms. Abdullah and her colleagues [40] confirmed our findings, stating that R. annulatus was Piroplasma negative.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Blood Sampling
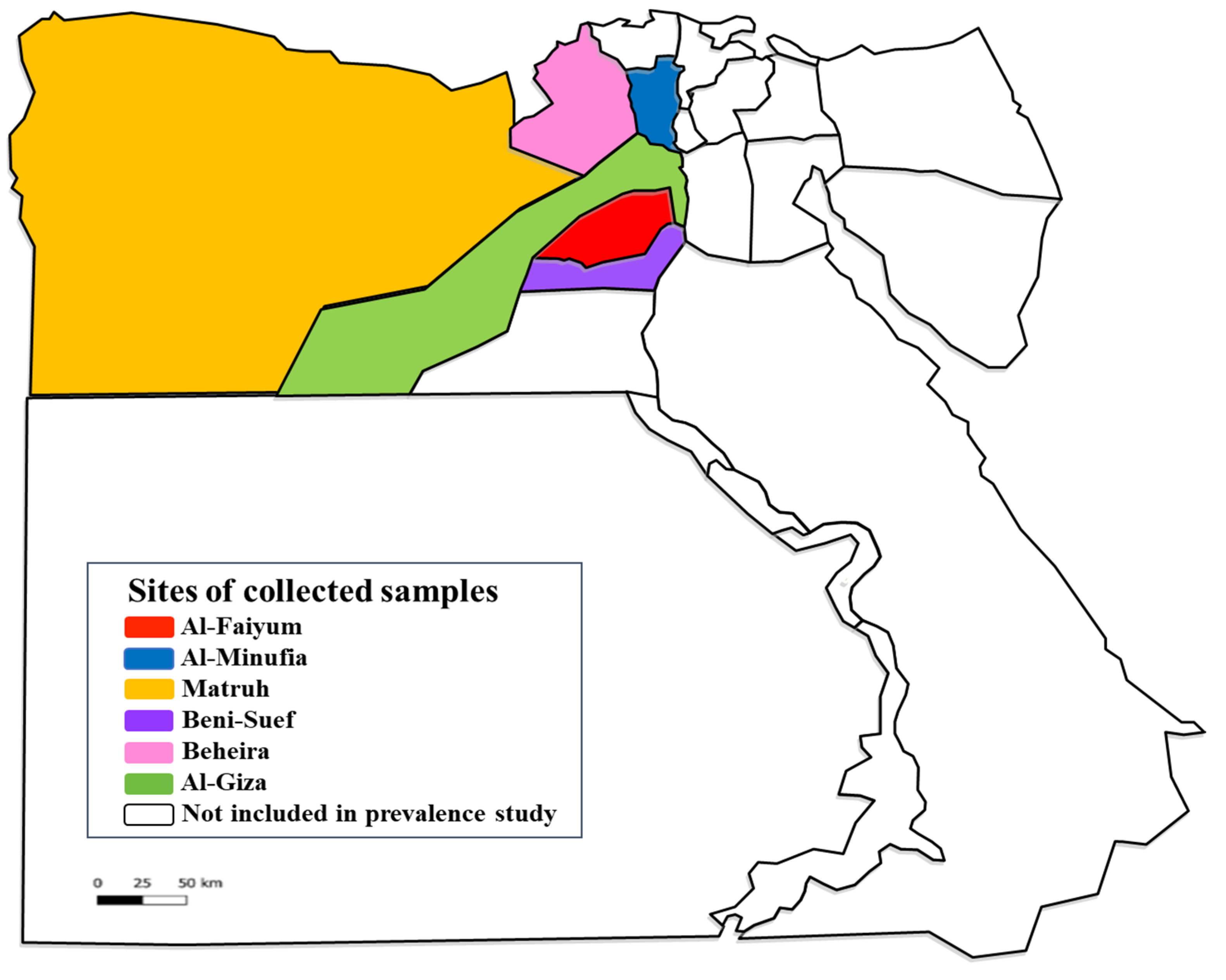
A total of 234 animal hosts (112 cattle, 38 sheep, 28 goats, 26 buffaloes, 22 donkeys, and 8 horses) were included in a cross-sectional study using a convenience sampling strategy. These animals were collected from six provinces of Egypt (AL-Faiyum, AL-Giza, Beni-Suef, Al-Minufia, Al-Beheira, and Matruh) during the period from December 2019 to March 2020 (Figure 3, Table 4). The species, sex, age, and tick infestation of each domestic animal were recorded. Moreover, 3 mL of blood per animal was collected by sterile syringe in a sterile EDTA-Vacutainer tube. All blood samples were stored at −20 °C till molecular investigation.
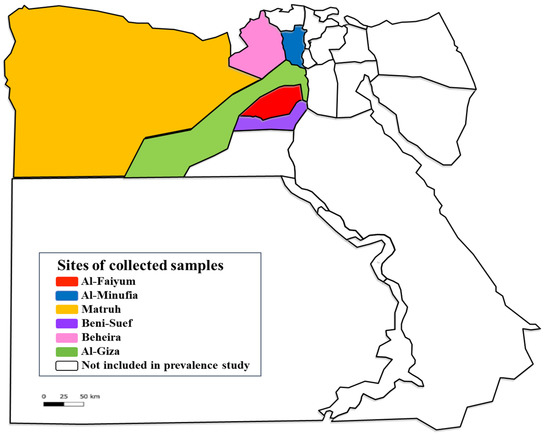
Figure 3.
Map of Egypt presenting the provinces where the studied animals and their ticks were collected. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Governorates_of_Egypt (accessed on 27 May 2022) and the picture has CC BY-SA 3.0.

Table 4.
Data of the studied animals.
4.2. Ticks
From the examined animals, a total of 95 ticks were collected in Eppendorf tubes containing 70% ethanol. Each Eppendorf tube was assigned to one animal host and then transferred to the laboratory for morphological identification according to the keys of Estrada-Pena and his colleagues [57]. All ticks were processed for molecular screening.
4.3. Molecular Investigation
4.3.1. DNA Extraction
DNA was extracted from 300 µL of each blood sample using a Genomic DNA isolation Kit (Blood; GeneDireX, Taiwan, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. In addition, ticks were individually dipped twice in distilled water and then dried with sterile filter paper [58]. Cleaned ticks were cut longitudinally into two parts; one half was sliced up into small pieces, and another half was stored at −20 °C as a backup. Each sliced tick half was added into a sterile 1.5-mL Eppendorf containing 400 µL of lysis buffer and 10 µL of proteinase K (40 mg/µL; SimplyTM, Taiwan, China) and incubated overnight at 65 °C. After centrifugation, the supernatant was transferred into a sterile 1.5-mL Eppendorf tube and directed to DNA extraction using a Tissue Genomic DNA isolation Kit (Tissue; GeneDireX, Taiwan, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The extracted DNA from each blood and tick sample was stored at −20 °C until PCR pathogen screening.
4.3.2. Screening of Pathogens DNA by Standard PCR
The primers were used targeting 969 bp of the conserved region of encoding ribosomal 18S and 500 bp of 16S RNA genes to detect Piroplasma [2] and Anaplasmataceae DNA [59], respectively (Table 5). PCR assays were performed using One PCR master mix™ (GeneDireX, Taiwan, China) in an automated BIO-RAD Thermal Cycler (BIO-RAD, Singapore). PCR conditions of the Piroplasma and Anaplasmataceae amplification were applied according to previously published methods by Dahmana and his colleagues [2] and Cardoso and his colleagues [59], respectively (Table 5). In addition, we used genus-specific primers for amplifying and sequencing Theileria sp. and Babesia sp. [60,61] (Table 5). Positive controls were T. annulata (MN625888), B. bigemina (MN625890), and A. marginale (MN625935) DNA extracted from cattle for PCR assays of Piroplasma and Anaplasmataceae, respectively, whereas distilled water was used as a negative control. Then, 1.5% agar gel stained with Red Safe electrophoresis was performed to check the amplification and then visualized by UV transilluminator. Moreover, a 100 bp DNA Ladder (GeneDireX, Taiwan, China) was used to assess the size of PCR products. A PCR Clean-Up and Gel Extraction Kit (GeneDireX, Taiwan, China) was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions to purify the PCR products of the positive samples.

Table 5.
Oligonucleotide sequences of primers used for PCR and sequencing.
4.3.3. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analyses
The purified PCR products were sequenced at the Macrogene Lab Technology, Korea. ChromasPro software (ChromasPro 1.7, Technelysium Pty Ltd., Tewantin, Australia) assembled and corrected the obtained sequences. The corrected sequences of Piroplasma or Anaplasmataceae were submitted to GenBank and then compared with those available in the GenBank database by NCBI BLASTn (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 12 December 2021). MEGA software version X was used for multiple alignments of the obtained sequences and sequences of validated species already available in GenBank. Then, maximum-likelihood phylogenetic trees were constructed with 1000 bootstrap replications [62,63].
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Significant differences in the prevalence rates with Piroplasma and Anaplasmataceae and their risk factors such as animal species, sex, age, and tick infestation were calculated by the χ2 test using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) at p < 0.05.
5. Conclusions
Piroplasm is still a dangerous bovine hemopathogen in Egypt, and its negative effects may increase, especially when its tick vector R. annulatus is found. The Anaplasmataceae prevalence rate in subclinical and carrier animals was high and needs more attention to reduce its effect on animal production. The findings of this study will provide baseline data on TBD epidemiology and tick vector management patterns, which will aid the government in establishing policies that could improve animal health security and the economy of the country. Further studies are recommended on large scales of animals and their associated arthropods (ticks, lice, and sucking flies) using species-specific primers for the detection of co-infections and novel emerging and re-emerging species and/or genotypes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, S.A.-S. and H.H.A.M.A.; methodology, H.H.A.M.A., S.A.-S., M.K.E., B.S.M.E. and M.R.H.; software, H.H.A.M.A. and S.A.-S.; Validation, H.H.A.M.A., S.A.-S. and M.K.E.; formal analysis and investigation, H.H.A.M.A., S.A.-S., M.K.E., B.S.M.E. and M.R.H.; resources, S.A.-S., M.K.E., M.R.H., M.S.M., A.G.H. and E.H.A.-R.; data curation, S.A.-S. and H.H.A.M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, H.H.A.M.A. and M.K.E.; writing—review and editing, S.A.-S. and A.G.H.; visualisation, H.H.A.M.A., S.A.-S., M.K.E., B.S.M.E. and M.R.H.; supervision, S.A.-S., M.S.M., A.G.H. and E.H.A.-R.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Research Centre of Egypt under registration numbers 12070104 and 12050508.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Medical and Veterinary Research Ethics Committee (No. 19147) at the National Research Centre, Egypt.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
References
- AL-Hosary, A.; Răileanu, C.; Tauchmann, O.; Fischer, S.; Nijhof, M.A.; Silaghi, C. Epidemiology and genotyping of An aplasma marginale and co-infection with piroplasms and other Anaplasmataceae in cattle and buffaloes from Egypt. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahmana, H.; Amanzougaghene, N.; Davoust, B.; Carette, O.; Normand, T.; Demoncheaux, J.P.; Mulot, B.; Fabrizy, B.; Scandola, P.; Chik, M.; et al. Great diversity of Piroplasmida in Equidae in Africa and Europe, including potential new species. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2019, 18, e100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Hosary, A.; Ahmed, L.; Ahmed, J.; Nijhof, A.; Clausen, P. Epidemiological study on tropical theileriosis (Theileria annulata infection) in the Egyptian Oases with special reference to the molecular characterization of Theileria spp. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.H.; Amanzougaghene, N.; Dahmana, H.; Louni, M.; Raoult, D.; Mediannikov, O. Multiple vector-borne pathogens of domestic animals in Egypt. PLoS Neg. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C. Tropical theileriosis. In Foreign Animal Diseases, 7th ed.; Brown, C., Torres, A., Eds.; Boca Publications: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 401–404. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, R.P.; Odongo, D.O.; Mann, D.J.; Pearson, T.W.; Sugimoto, C.; Haines, L.R.; Glass, E.; Jensen, K.; Seitzer, U.; Ahmed, J.S.; et al. Theileria. In Genome Mapping and Genomics in Animal–Associated Microbes; Nene, V., Kole, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 191–231. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgic, H.B.; Karagenc, T.; Shiels, B.; Tait, A.; Eren, H.; Weir, W. Evaluation of cytochrome b as a sensitive target for PCR based detection of T. annulata carrier animals. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 174, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, J.; Shams, S.; Din, I.U.; Ayaz, S.; Khan, A.; Nasreen, N.; Khan, H.; Khan, M.A.; Senbill, H. Molecular epidemiology and associated risk factors of Anaplasma marginale and Theileria annulata in cattle from North-western Pakistan. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 279, 109044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupin, R.C.; Guizelini, C.C.; Lemos, R.A.A.; Martins, T.B.; Borges, F.A.; Borges, F.G.L.; Gomes, D.C. Retrospective study of epidemiological, clinical and pathological findings of bovine babesiosis in Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil (1995–2017). Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ola-Fadunsin, S.D.; Sharma, R.S.K.; Abdullah, D.A.; Gimba, F.I.; Abdullah, F.F.J.; Sani, R.A. The molecular prevalence, distribution and risk factors associated with Babesia bigemina infection in Peninsular Malaysia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tembue, A.A.M.; Silva, F.J.M.; Silva, J.B.; Santos, T.M.; Santos, H.A.; Soares, C.O.; Fonseca, A.H. Risk factors associated with the frequency of antibodies against Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in cattle in southern Mozambique. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2011, 31, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhariri, M.D.; Elhelw, R.A.; Hamza, D.A.; Soliman, D.E. Molecular detection of Anaplasma marginale in the Egyptian water bufaloes (Bubuloes bubalis) based on major surface protein 1α. J. Egyp. Soc. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocan, K.M.; de la Fuente, J.; Blouin, E.F. Characterization of the tick–pathogen– host interface of the tick–borne rickettsia Anaplasma marginale. In Ticks: Biology, Diseases and Control; Bowman, A.S., Nuttall, P.A., Eds.; Cambridge Univesity Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 325–343. [Google Scholar]
- Aubry, P.; Geale, D.W. A review of bovine anaplasmosis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2011, 58, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelsson, J.; Ramabu, S.S.; Lysholm, S.; Aspán, A.; Wensman, J.J. Anaplasma ovis infection in goat flocks around Gaborone, Botswana. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 29, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medley, G.F.; Perry, B.D.; Young, A.S. Preliminary analysis of the transmission dynamics of Theileria parva in eastern Africa. Parasitology 1993, 106, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, J.A.; Reddy, G.R.; Chieves, L.; Courtney, C.H.; Littell, R.; Livengood, J.R. Monitoring Babesia bovis infections in cattle by using PCR-based tests. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 2748–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, S.A.E.; AbouLaila, M.; ElKhatam, A.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Rizk, M.A. An epidemiological survey of Theileria equi parasite in donkeys (Equus asinus) in Egypt. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 21, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampersad, J.; Cesar, E.; Campbell, M.D.; Samlal, M.; Ammons, D. A field PCR for the routine detection of Babesia equi in horses. J. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 114, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, R.; Rangel-Rivas, A.; Escalona, A.; Jordan, L.S.; Gonzatti, M.I.; Aso, P.M.; Perrone, T.; Silva-Iturriza, A.; Mijares, A. Detection of Theileria equi and Babesia caballi infections in Venezuelan horses using competitive-inhibition ELISA and PCR. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buling, A.; Criado-Fornelio, A.; Asenzo, G.; Benitez, D.; Barba-Carretero, J.C.; Florin-Christensen, M. A quantitative PCR assay for the detection and quantification of Babesia bovis and B. bigemina. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 147, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsify, A.; Sivakumar, T.; Nayel, M.; Salama, A.; Elkhtam, A.; Rizk, M.; Mosaab, O.; Sultan, K.; Elsayed, S.; Igarashi, I.; et al. An epidemiological survey of bovine Babesia and Theileria parasites in cattle, buffaloes, and sheep in Egypt. Parasitol. Int. 2014, 64, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeddine, R.; Diarra, A.Z.; Laroche, M.; Mediannikov, O.; Righi, S.; Benakhla, A.; Dahmana, H.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Molecular identification of protozoal and bacterial organisms in domestic animals and their infesting ticks from northeastern Algeria. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ashker, M.; Hotzel, H.; Gwida, M.; El-Beskawy, M.; Silaghi, C.; Tomaso, H. Molecular biological identification of Babesia, Theileria, and Anaplasma species in cattle in Egypt using PCR assays, gene sequence analysis and a novel DNA microarray. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 207, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soosaraei, M.; Haghi, M.M.; Etemadifar, F.; Fakhar, M.; Teshnizi, S.H.; Asfaram, S.; Esboei, B.R. Status of Anaplasma spp. infection in domestic ruminants from Iran: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Parasit. Epidemiol. Control. 2020, 11, e00173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocan, K.M.; de la Fuente, J.; Blouin, E.F.; Coetzee, J.F.; Ewing, S.A. The natural history of Anaplasma marginale. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizk, M.A.; Salama, A.; El-Sayed, S.A.; Elsify, A.; El-Ashkar, M.; Ibrahim, H.; Youssef, M.; El-Khodery, S. Animal level risk factors associated with Babesia and Theileria infections in cattle in Egypt. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, O.; El-Adawy, H.; Melzer, F.; Roesler, U.; Neubauer, H.; Mertens-Scholz, K. Seroprevalence and Molecular Detection of Bovine Anaplasmosis in Egypt. Pathogens 2020, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CAPMAS. Animal Diseases. Available online: https://www.capmas.gov.eg/ (accessed on 17 June 2019).
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Adjou Moumouni, P.F.; Mohamed-Geba, K.; Sheir, S.K.; Hashem, I.S.; Cao, S.; Terkawi, M.A.; Kamyingkird, K.; Nishikawa, Y.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Molecular and serological prevalence of Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis in cattle and water buffalos under small-scale dairy farming in Beheira and Faiyum Provinces, Egypt. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 198, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayel, M.; El-Dakhly, K.M.; Aboulaila, M.; Elsify, A.; Hassan, H.; Ibrahim, E.; Salama, A.; Yanai, T. The use of different diagnostic tools for Babesia and Theileria parasites in cattle in Menofia, Egypt. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, E.M. Studies on Some Blood Parasites Infecting Farm Animals in Gharbia Governorate. Ph.D. Thesis, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- El-Fayomy, A.O.; Ghoneim, A.M.; Abu-Samak, O.A.; Khidr, A.A. Contribution of Babesia to the illness of cows in Port Said Governorate, Egypt. Glob. Vet. 2013, 11, 118–222. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Hosary, A.; Răileanu, C.; Tauchmann, O.; Fischer, S.; Nijhof, M.A.; Silaghi, C. Tick species identification and molecular detection of tick-borne pathogens in blood and ticks collected from cattle in Egypt. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumwebaze, M.A.; Lee, S.H.; Adjou Moumouni, P.F.; Mohammed-Geba, K.; Sheir, S.K.; Galal-Khallaf, A.; Abd El Latif, H.M.; Morsi, D.S.; Bishr, N.M.; Galon, E.M.; et al. First detection of Anaplasma ovis in sheep and Anaplasma platys-like variants from cattle in Menoufia governorate, Egypt. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 78, 102150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, E.E.; Hegazy, N.A.M.; El-Deeb, W.; El-Khatib, R.M. Epidemiological and biochemical studies on bovine anaplamosis in Dakahliaand Demiatta Governorates in Egypt. Bull. Anim. Health Prod. Afr. 2009, 57, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Abo El Fadl, E.A.; El-Ashker, M.; Suganuma, K.; Kayano, M. Discriminant analysis for the prediction and classification of tick-borne infections in some dairy cattle herds at Dakahlia Governorate, Egypt. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 65, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Fereig, R.M.; Mohamed, S.G.A.; Mahmoud, H.; AbouLaila, M.R.; Guswanto, A.; Nguyen, T.T.; Mohamed, A.A.; Inoue, N.; Igarashi, I.; Nishikawa, Y. Seroprevalence of Babesia bovis, B. bigemina, Trypanosoma evansi, and Anaplasma marginale antibodies in cattle in southern Egypt. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, M.E.I.; Ali, A.F.; el Hamied, O.A. Epidemiological Studies, Molecular Diagnosis of Anaplasma marginale in Cattle and Biochemical Changes Associated with it in Kaliobia Governorate. Am. J. Infect. Dis. Microbiol. 2013, 1, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, H.H.A.M.; Aboelsoued, D.; Farag, K.T.; Abdel Megeed, N.K.; Abdel-Shafy, S.; Parola, P.; Raoult, D.; Mediannikov, O. Molecular characterization of some equine vector-borne diseases and associated arthropods in Egypt. Acta Trop. 2022, 227, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, A.; Attia, K.A.; Alsubki, R.A.; Albohairy, F.; Kimiko, I.; Ben Said, M. The first study on the seroprevalence of Anaplasma spp. in small ruminants and assessment of associated risk factors in North Egypt. Vet. World 2022, 15, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussaadoun, M.A.; Gharbi, M.; Sayeh, L.; Soudani, M.C.; Darghouth, M.A. Epidemiological situation of bovine tropical theileriosis (Theileria annulata infection) in the Northwest Tunisia. J. Adv. Parasitol. 2015, 2, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, I.C.B.; Capuno, L.X.B., Jr.; Collera, P.D.; Cabralda, A.P.D.; De Ramos, K.A.S.; Bernardo, J.M.G.; Divina, B.P.; Masatani, T.; Tanaka, T.; Galay, R.L. Molecular Detection and Characterization of Babesia and Theileria in Cattle and Water Buffaloes from Southern Luzon, Philippines. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjou Moumouni, P.F.; Minoungou, G.L.B.; Dovonou, C.E.; Galon, E.M.; Efstratiou, A.; Tumwebaze, M.A.; Byamukama, B.; Vudriko, P.; Umemiya-Shirafuji, R.; Suzuki, H.; et al. A Survey of Tick Infestation and Tick-Borne Piroplasm Infection of Cattle in Oudalan and Séno Provinces, Northern Burkina Faso. Pathogens 2022, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, M.B.; Attia, K.A.; Alsubki, R.A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Kimiko, I.; Selim, A. Molecular epidemiological survey, genetic characterization and phylogenetic analysis of Anaplasma ovis infecting sheep in Northern Egypt. Acta Trop. 2022, 229, 106370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkahia, H.; Ben Said, M.; El Hamdi, S.; Yahiaoui, M.; Gharbi, M.; Daaloul-Jedidi, M.; Mhadhbi, M.; Jedidi, M.; Darghouth, M.A.; Klabi, I.; et al. First molecular identification and genetic characterization of Anaplasma ovis in sheep from Tunisia. Small Rumin. Res. 2014, 121, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmani, M.; Davoust, B.; Sambou, M.; Bassene, H.; Scandola, P.; Ameur, T.; Raoult, D.; Fenollar, F.; Mediannikov, O. Molecular investigation and phylogeny of species of the Anaplasmataceae infecting animals and ticks in Senegal. Parasit. Vectors. 2019, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.S.; Dyary, O.H. Molecular characterization and phylogenic analysis of Anaplasma spp. in small ruminants from Sulaymaniyah governorate, Iraq. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 36, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, A.; Kaewlamuna, W.; Narapakdeesakula, D.; Pooferya, J.; Kaewthamasorna, M. Molecular detection and characterization of tick-borne parasites in goats and ticks from Thailand. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Faruque, M.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Chowdhury, M.Y.E. Epidemiology and molecular detection of Anaplasma spp. in goats from Chattogram district, Bangladesh. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.H.L.; Tiawsirisup, S.; Kaewthamasorn, M. Molecular detection and genetic characterization of Anaplasma marginale and Anaplasma platys-like (Rickettsiales: Anaplasmataceae) in water buffalo from eight provinces of Thailand. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bursakov, S.A.; Kovalchuk, S.N. Co-infection with tick-borne disease agents in cattle in Russia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abanda, B.; Paguem, A.; Abdoulmoumini, M.; Kingsley, T.M.; Renz, A.; Eisenbarth, A. Molecular identification and prevalence of tick-borne pathogens in zebu and taurine cattle in North Cameroon. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Tian, J.; Pan, X.; Qin, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Guo, W.; Li, K. Identification of Rickettsia spp., Anaplasma spp., and an Ehrlichia canis-like agent in Rhipicephalus microplus from Southwest and South-Central China. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkun, Ö. Comprehensive screening of tick-borne microorganisms indicates that a great variety of pathogens are circulating between hard ticks (Ixodoidea: Ixodidae) and domestic ruminants in natural foci of Anatolia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 102027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafar, A.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Galon, C.; Obregon, D.; Gasser, R.B.; Moutailler, S.; Jabber, A. Bovine ticks harbour a diverse array of microorganisms in Pakistan. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Pena, A.; Bouattour, A.; Camicas, J.L.; Walker, A.R. Ticks of Domestic Animals in the Mediterranean Region. A guide to Identification of Species; University of Zaragoza: Zaragoza, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kumsa, B.; Laroche, M.; Almeras, L.; Mediannikov, O.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Morphological, molecular and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry identification of ixodid 688 tick species collected in Oromia, Ethiopia. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4199–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, L.; Oliveira, A.C.; Granada, S.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Gilad, M.; Lopes, A.P.; Sousa, S.R.; Vilhena, H.; Baneth, G. Molecular investigation of tick-borne pathogens in dogs from Luanda, Angola. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qablan, M.A.; Oborník, M.; Petrželková, K.J.; Sloboda, M.; Shudiefat, M.F.; Hořín, P.; Lukeš, J.; Modrý, D. Infections by Babesia caballi and Theileria equi in Jordanian equids: Epidemiology and genetic diversity. Parasitology 2013, 140, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naga, T.R.A.; Barghash, S.M. Blood Parasites in Camels (Camelus dromedarius) in Northern West Coast of Egypt. J. Bacteriol. Parasitol. 2016, 7, 258. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.; Biosciences, I.; Carlsbad, C. BioEdit: An important software for molecular biology. GERF Bull. Biosci. 2011, 2, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).