Clonal Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant and Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Clonal Complex in a Chinese Hospital
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Collection
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. Whole Genome Sequencing, De Novo Assembly, and Annotation
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Data Availability
3. Results
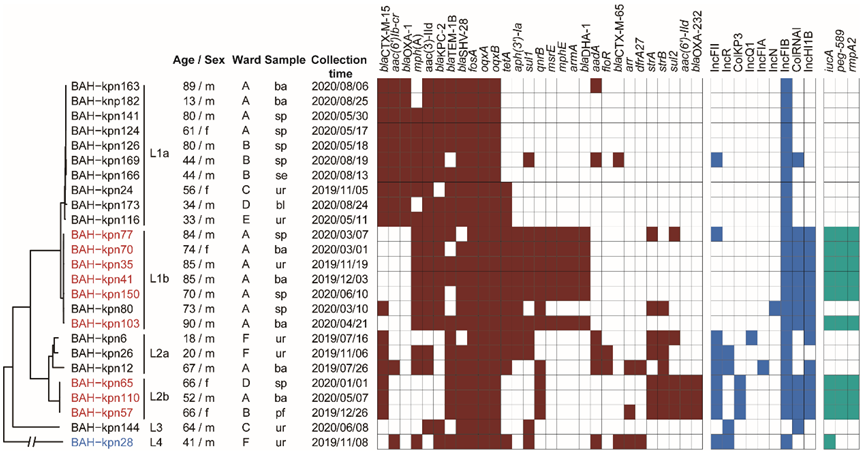
3.1. Sources of CC15 K. pneumoniae Isolates and Their Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles
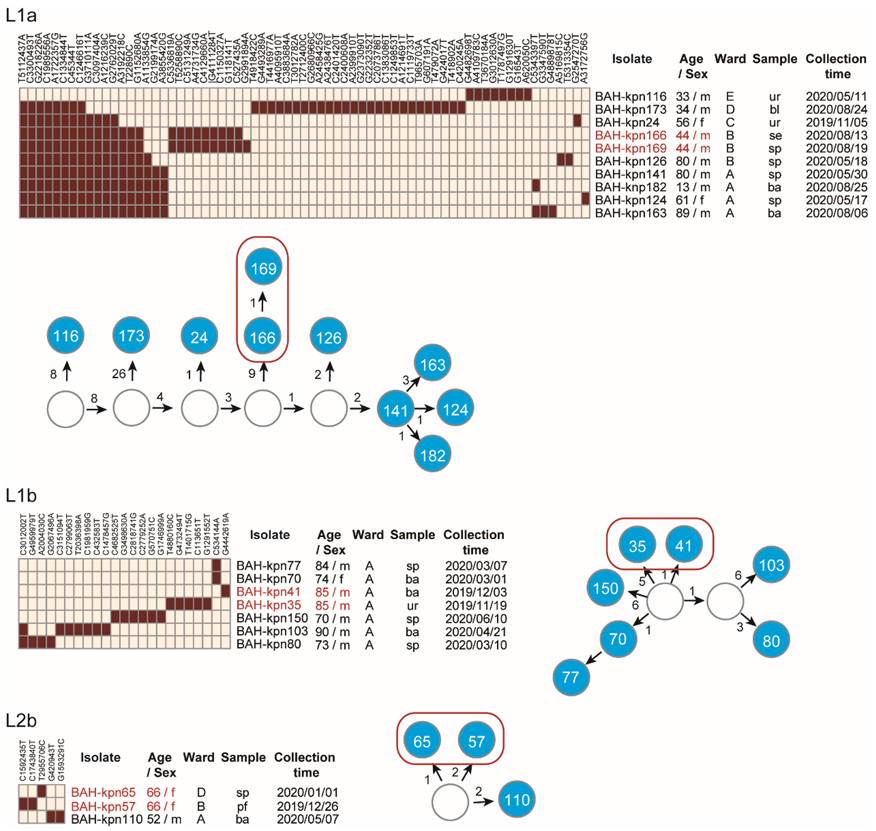
3.2. Phylogenetic Relationships of CC15 K. pneumoniae in Our Hospital
3.3. Nosocomial Reservation and Transmission of CC15 Lineages
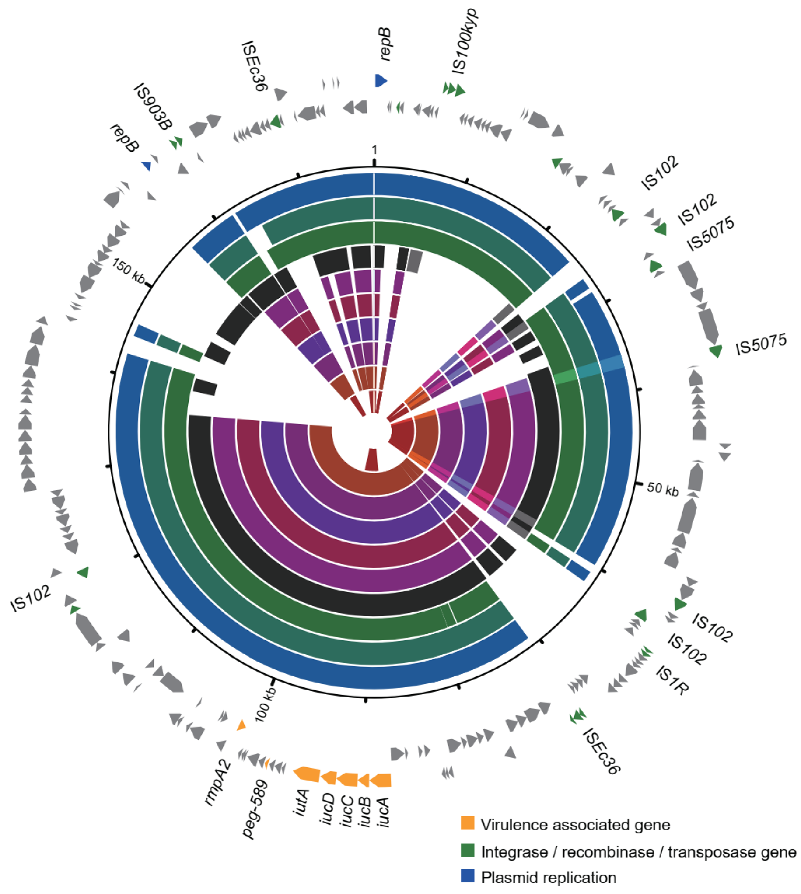
3.4. Prevalence of Virulence Genes, Resistance Genes, and Plasmid Types
3.5. Varied Virulence Plasmid in Different CC15 Lineages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. Klebsiella pneumoniae as a key trafficker of drug resistance genes from environmental to clinically important bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Earley, M.; Chen, L.; Hanson, B.M.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Salcedo, S.; Cober, E.; Li, L.; Kanj, S.S. Clinical outcomes and bacterial characteristics of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae complex among patients from different global regions (CRACKLE-2): A prospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duin, D.; Arias, C.A.; Komarow, L.; Chen, L.; Hanson, B.M.; Weston, G.; Cober, E.; Garner, O.B.; Jacob, J.T.; Satlin, M.J. Molecular and clinical epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in the USA (CRACKLE-2): A prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Du, P.; Xiao, N.; Ji, F.; Russo, T.A.; Guo, J. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae is emerging as an increasingly prevalent K. pneumoniae pathotype responsible for nosocomial and healthcare-associated infections in Beijing, China. Virulence 2020, 11, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Dong, N.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, D.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Chan, E.W.; Shu, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R. A fatal outbreak of ST11 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Chinese hospital: A molecular epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-C.; Lu, M.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Hypervirulence and carbapenem resistance: Two distinct evolutionary directions that led high-risk Klebsiella pneumoniae clones to epidemic success. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Ouyang, P.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Network CC-RE: Evolution of hypervirulence in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in China: A multicentre, molecular epidemiological analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 75, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnin, R.A.; Jousset, A.B.; Chiarelli, A.; Emeraud, C.; Glaser, P.; Naas, T.; Dortet, L. Emergence of New Non-Clonal Group 258 High-Risk Clones among Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producing K. pneumoniae Isolates, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Lam, M.M.; Holt, K.E. Population genomics of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data; Babraham Institute: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Watts, S.C.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. A genomic surveillance framework and genotyping tool for Klebsiella pneumoniae and its related species complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Yao, Z.; Sun, L.; Shen, Y.; Jin, Q. VFDB: A reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D325–D328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siguier, P.; Perochon, J.; Lestrade, L.; Mahillon, J.; Chandler, M. ISfinder: The reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Hasman, H. PlasmidFinder and In Silico pMLST: Identification and Typing of Plasmid Replicons in Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS). Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2075, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Madden, T. The BLAST sequence analysis tool. In The NCBI Handbook [Internet], 2nd ed.; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Croucher, N.J.; Page, A.J.; Connor, T.R.; Delaney, A.J.; Keane, J.A.; Bentley, S.D.; Parkhill, J.; Harris, S.R. Rapid phylogenetic analysis of large samples of recombinant bacterial whole genome sequences using Gubbins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, P.; Jin, C.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: Data from a Longitudinal Large-scale CRE Study in China (2012–2016). Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2018, 67 (Suppl. S2), S196–S205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, C.A.M.; Pereira, P.S.; Rocha-de-Souza, C.M.; Silveira, M.C.; Carvalho-Assef, A.P.D.; Asensi, M.D. Population Structure of KPC-2-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Surveillance Rectal Swabs in Brazil. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00001-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, C.M.; Braxton, J.R.; Rodriguez-Osorio, C.A.; Zagieboylo, A.P.; Li, L.; Pironti, A.; Manson, A.L.; Nair, A.V.; Benson, M.; Cummins, K. Adaptive evolution of virulence and persistence in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choby, J.E.; Howard-Anderson, J.; Weiss, D.S. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae—Clinical and molecular perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Dong, N.; Chan, E.W.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Carbapenem Resistance-Encoding and Virulence-Encoding Conjugative Plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 29, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Liu, C.; Fan, S.; Baker, S.; Guo, J. The Role of Plasmid and Resistance Gene Acquisition in the Emergence of ST23 Multi-Drug Resistant, Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0192921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, N.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Lu, S.; Zhang, G.; Song, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhong, J. The human gut serves as a reservoir of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2114739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Isolate | AMK * | CIP | IPM | LEV | TOB | AMP | SAM | ATM | FEP | CTT | CAZ | CRO | TZP | SXT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAH-kpn163 | S ** | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn182 | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn141 | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn124 | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn126 | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn169 | S | R | R | R | I | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn166 | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn24 | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn173 | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn116 | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn77 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn70 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn35 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn41 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn150 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | I | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn80 | S | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| BAH-kpn103 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn6 | S | R | S | R | I | R | R | R | S | S | R | R | S | R |
| BAH-kpn26 | S | R | S | R | I | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | S | R |
| BAH-kpn12 | S | R | S | R | I | R | R | S | S | S | S | R | S | R |
| BAH-kpn65 | S | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn110 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| BAH-kpn57 | 4 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | R |
| BAH-kpn144 | S | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | R | I | R | R | R | S |
| BAH-kpn28 | S | R | S | S | I | R | R | R | S | S | R | R | S | R |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Hua, M.; Wang, J.; Xing, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Du, P. Clonal Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant and Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Clonal Complex in a Chinese Hospital. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101202
Wang Y, Hua M, Wang J, Xing W, Chen J, Liu J, Du P. Clonal Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant and Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Clonal Complex in a Chinese Hospital. Pathogens. 2022; 11(10):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101202
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi, Mingxi Hua, Jingqiao Wang, Wen Xing, Jiatian Chen, Jingyuan Liu, and Pengcheng Du. 2022. "Clonal Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant and Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Clonal Complex in a Chinese Hospital" Pathogens 11, no. 10: 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101202
APA StyleWang, Y., Hua, M., Wang, J., Xing, W., Chen, J., Liu, J., & Du, P. (2022). Clonal Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant and Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Clonal Complex in a Chinese Hospital. Pathogens, 11(10), 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101202





