Associated-Onset Symptoms and Post-COVID-19 Symptoms in Hospitalized COVID-19 Survivors Infected with Wuhan, Alpha or Delta SARS-CoV-2 Variant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parra-Lucares, A.; Segura, P.; Rojas, V.; Pumarino, C.; Saint-Pierre, G.; Toro, L. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants in the world: How could this happen? Life 2022, 12, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thye, A.Y.; Law, J.W.; Pusparajah, P.; Letchumanan, V.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern (VOCs): An Impending Global Crisis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teyssou, E.; Delagrèverie, H.; Visseaux, B.; Lambert-Niclot, S.; Brichler, S.; Ferre, V.; Marot, S.; Jary, A.; Todesco, E.; Schnuriger, A.; et al. The Delta SARS-CoV-2 variant has a higher viral load than the Beta and the historical variants in nasopharyngeal samples from newly diagnosed COVID-19 patients. J. Infect. 2021, 83, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, S.S.A.; Karim, Q.A. Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variant: A new chapter in the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 2126–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani-Sassa, C.; Iwasaki, Y.; Ichimura, N.; Nagano, K.; Takatsuki, Y.; Yuasa, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Nakajima, J.; Sonobe, K.; Nukui, Y.; et al. Viral loads and profile of the patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta, Alpha, or R.1 variants in Tokyo. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1707–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Montero, M.T.V.; Rowe, K.; Kirton, R.; Kunik, F., Jr. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentations, diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19: A review of current evidence. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 601–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struyf, T.; Deeks, J.J.; Dinnes, J.; Takwoingi, Y.; Davenport, C.; Leeflang, M.M.; Spijker, R.; Hooft, L.; Emperador, D.; Dittrich, S.; et al. Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19 disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 7, CD013665. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Ji, P.; Pang, J.; Zhong, Z.; Li, H.; He, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C. Clinical characteristics of 3062 COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1902–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoang, V.T.; Colson, P.; Levasseur, A.; Delerce, J.; Lagier, J.C.; Parola, P.; Million, M.; Fournier, P.E.; Raoult, D.; Gautret, P. Clinical outcomes in patients infected with different SARS-CoV-2 variants at one hospital during three phases of the COVID-19 epidemic in Marseille, France. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 95, 105092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lim, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, H.; Lim, J.S.; Bae, S.; Kim, J.; Jung, J.; Kim, M.J.; Chong, Y.P.; et al. Clinical and virological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant: A prospective cohort study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 1, ciac239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C. Long COVID: Current definition. Infection 2022, 50, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, J.B.; Murthy, S.; Marshall, J.C.; Relan, P.; Diaz, J.V.; WHO Clinical Case Definition Working Group on Post-COVID-19 Condition. A clinical case definition of post-COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Palacios-Ceña, D.; Gómez-Mayordomo, V.; Florencio, L.L.; Cuadrado, M.L.; Plaza-Manzano, G.; Navarro-Santana, M. Prevalence of post-COVID-19 symptoms in hospitalized and non-hospitalized COVID-19 survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Int. Med. 2021, 92, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zheng, B.; Daines, L.; Sheikh, A. Long-term sequelae of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of one-year follow-up studies on post-COVID symptoms. Pathogens 2022, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdal, C.D.; Pe, M.; Falk, R.S.; Piccinin, C.; Bottomley, A.; Arraras, J.I.; Darlington, A.S.; Hofsø, K.; Holzner, B.; Jørgensen, N.M.H.; et al. Health-related quality of life issues, including symptoms, in patients with active COVID-19 or post COVID-19; a systematic literature review. Qual. Life Res. 2021, 30, 3367–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, H.; Flower, B.; Garcia, P.J.; Ong, S.W.X.; Altmann, D.M.; Delaney, B.; Smith, N.; Elliott, P.; Cooke, G. Global surveillance, research, and collaboration needed to improve understanding and management of long COVID. Lancet 2021, 398, 2057–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinicci, M.; Nkurunziza, I.; Vellere, I. SARS-CoV-2 variants may induce different long COVID phenotypes. In Proceedings of the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID), Lisbon, Portugal, 23–26 April 2022. Abstract 000193. [Google Scholar]
- Mattiuzzi, C.; Henry, B.M.; Lippi, G. Is diffusion of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern associated with different symptoms? J. Infect. 2022, 84, 94–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, S.A.; Iddawela, S.; Pillai, K.; Choudhury, R.Y.; Harky, A. Can symptoms of anosmia and dysgeusia be diagnostic for COVID-19? Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Nocini, R.; Henry, B.M. Analysis of online search trends suggests that SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant causes different symptoms. J. Infect. 2022, 84, E76–E77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/flu-vs-covid19.htm (accessed on 23 April 2022).
- Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, M.; Ling, W.; Sui, Y.; Zhao, H.L. Obesity in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 2020, 113, 154378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, A. A paradigm for post-COVID-19 fatigue syndrome analogous to ME/CFS. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 701419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffke, M.; Freitag, H.; Rudolf, G.; Seifert, M.; Doehner, W.; Scherbakov, N.; Hanitsch, L.; Wittke, K.; Bauer, S.; Konietschke, F.; et al. Endothelial dysfunction and altered endothelial biomarkers in patients with post-COVID-19 syndrome and chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menges, D.; Ballouz, T.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Aschmann, H.E.; Domenghino, A.; Fehr, J.S.; Puhan, M.A. Burden of post-COVID-19 syndrome and implications for healthcare service planning: A population-based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, O. Long-term sequelae following previous coronavirus epidemics. Clin. Med. 2020, 21, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Boglione, L.; Meli, G.; Poletti, F.; Rostagno, R.; Moglia, R.; Cantone, M.; Esposito, M.; Scianguetta, C.; Domenicale, B.; Di, F.; et al. Pasquale Risk factors and incidence of long-COVID syndrome in hospitalized patients: Does remdesivir have a protective effect? QJM 2022, 114, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.A.; Luginbuhl, R.D.; Parker, R. Reduced incidence of long-COVID Symptoms related to administration of COVID-19 vaccines both before COVID-19 diagnosis and up to 12 weeks after. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Fuertes, F.; Iglesias-Caballero, M.; García-Pérez, J.; Monzón, S.; Jiménez, P.; Varona, S.; Cuesta, I.; Zaballos, Á.; Jiménez, M.; Checa, L.; et al. A founder effect led early SARS-CoV-2 transmission in Spain. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Wuhan | Alpha | Delta | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) * | 60.5 (15.5) | 70.0 (15.5) | 56.5 (21.0) | <0.001 |
| Female (%) | 109 (54.2%) | 108 (51.2%) | 110 (54.5%) | 0.878 |
| Weight (kg) | 75.0 (14.0) | 75.5 (16.5) | 77.0 (13.5) | 0.576 |
| Height (cm) | 168 (14) | 165 (12) | 166 (10) | 0.254 |
| Number of onset symptoms * | 2.4 (0.8) | 2.0 (1.0) | 2.5 (0.8) | <0.001 |
| Symptoms at Admission, n (%) | ||||
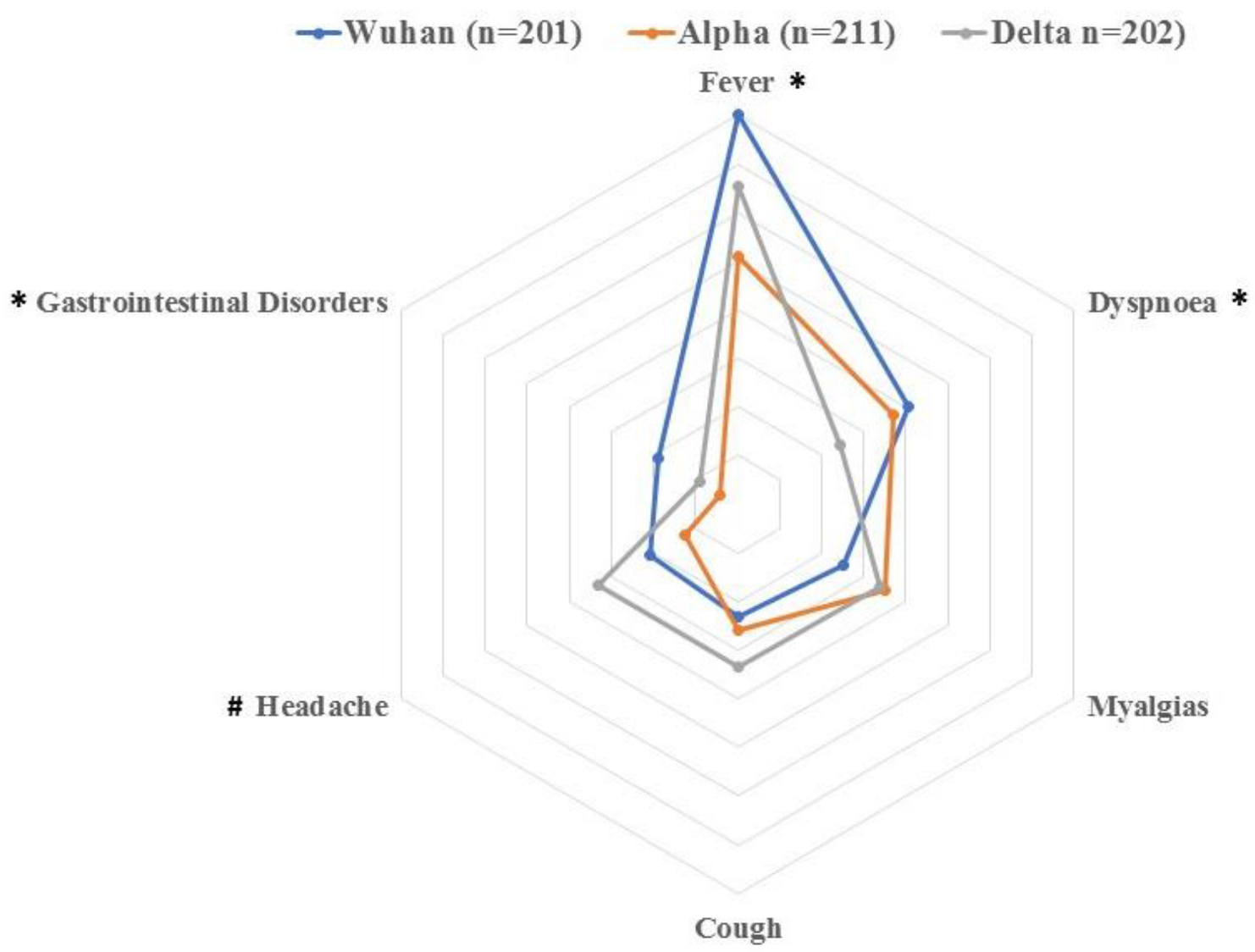
| Fever (>37.5 °C) * | 160 (79.6%) | 102 (48.3%) | 131 (64.8%) | 0.01 |
| Dyspnoea * | 81 (40.3%) | 74 (35.1%) | 49 (24.2%) | 0.015 |
| Myalgia | 50 (24.9%) | 70 (33.2%) | 68 (33.7%) | 0.199 |
| Cough | 46 (22.9%) | 52 (24.6%) | 67 (33.2%) | 0.102 |
| Headache * | 42 (20.9%) | 25 (11.85%) | 66 (32.65%) | 0.001 |
| Gastrointestinal * | 38 (18.9%) | 8 (3.4%) | 18 (8.9%) | <0.001 |
| Anosmia * | 20 (9.9%) | 5 (2.4%) | 29 (14.3%) | 0.008 |
| Ageusia * | 13 (6.4%) | 6 (2.8%) | 32 (15.8%) | 0.002 |
| Throat Pain | 10 (5.0%) | 23 (10.9%) | 33 (16.3%) | 0.109 |
| Medical Co-Morbidities | ||||
| Hypertension | 63 (31.3%) | 83 (39.3%) | 72 (35.6%) | 0.396 |
| Diabetes | 25 (12.4%) | 21 (10%) | 28 (13.9%) | 0.501 |
| Cardiovascular | 32 (15.9%) | 43 (20.4%) | 27 (13.4%) | 0.208 |
| Rheumatological | 3 (1.5%) | 1 (0.5%) | 1 (0.5%) | 0.423 |
| Asthma | 11 (5.4%) | 11 (5.2%) | 19 (9.4%) | 0.186 |
| COPD | 12 (6.0%) | 14 (6.6%) | 12 (5.9%) | 0.949 |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 30) * | 8 (4.0%) | 19 (9.0%) | 53 (26.2%) | <0.001 |
| Cancer * | 27 (13.4%) | 90 (42.5%) | 35 (17.3%) | <0.001 |
| Days at hospital *,# | 10 (13) | 12 (21) | 7 (8) | <0.001 |
| ICU admission | ||||
| Yes n (%) | 20 (9.9%) | 33 (15.6%) | 19 (9.4%) | 0.121 |
| Days at ICU | 13.5 (11) | 14.3 (16) | 10.5 (7) | 0.684 |
| Wuhan | Alpha | Delta | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Post-COVID-19 Symptoms * | 2.7 (1.3) | 1.8 (1.1) | 2.1 (1.5) | <0.001 |
| Post-COVID-19 Symptoms, n (%) | ||||
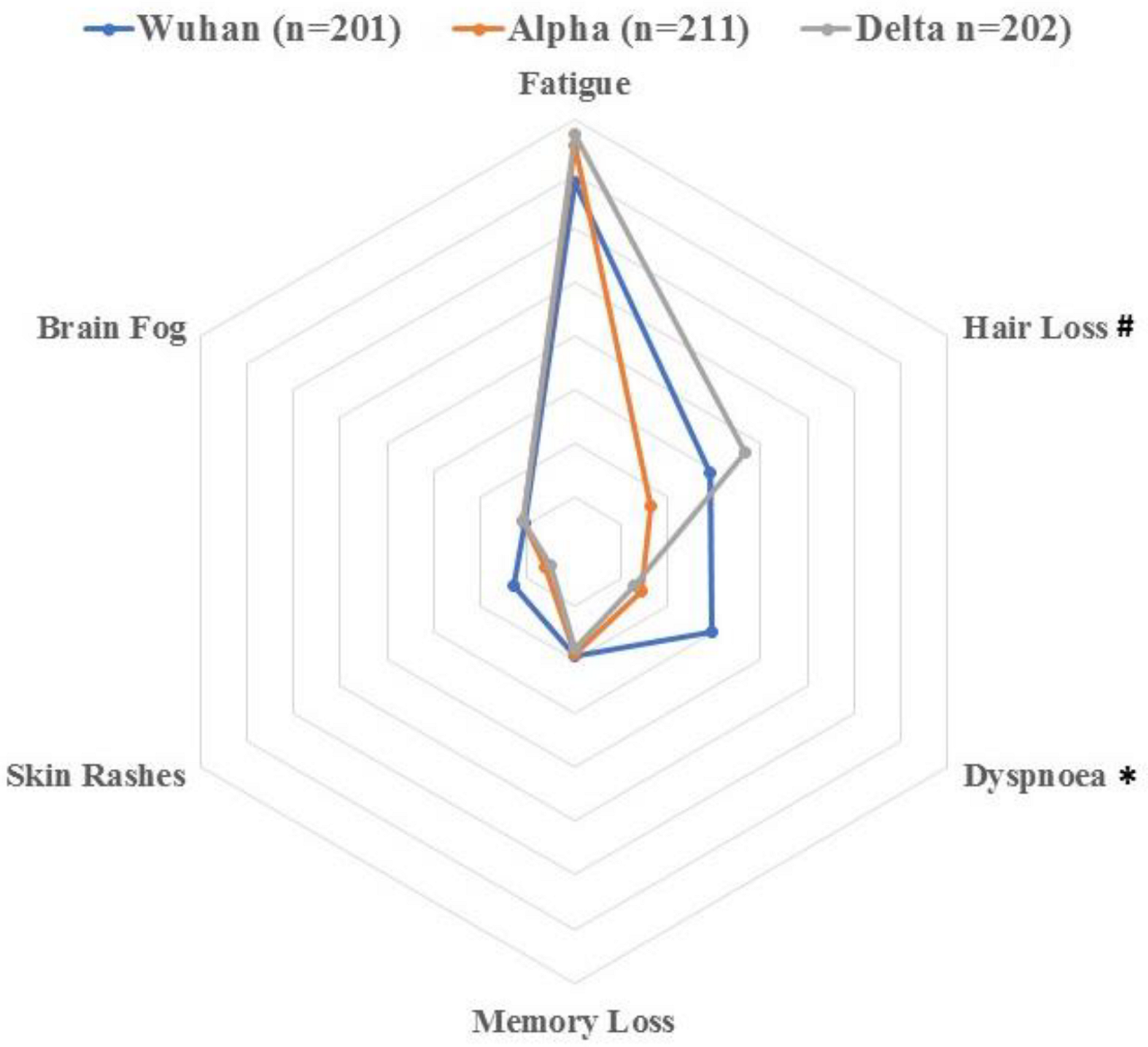
| Fatigue | 137 (68.2%) | 151 (71.5%) | 155 (76.35%) | 0.594 |
| Dyspnoea * | 59 (29.35%) | 29 (13.75%) | 26 (12.8%) | <0.001 |
| Hair loss * | 58 (28.9%) | 33 (15.7%) | 73 (36.15%) | 0.002 |
| Memory loss | 39 (19.4%) | 38 (18.0%) | 36 (17.8%) | 0.921 |
| Skin Rashes | 26 (12.9%) | 12 (5.7%) | 10 (5.0%) | 0.252 |
| Brain fog | 21 (10.4%) | 22 (10.4%) | 22 (10.9%) | 0.989 |
| Attention Disorders | 14 (7.0%) | 13 (6.1%) | 6 (3.0%) | 0.186 |
| Diarrhoea | 15 (7.4%) | 11 (5.2%) | 30 (15.0%) | 0.766 |
| Tachycardia | 3 (1.4%) | 7 (3.3%) | 8 (3.95%) | 0.323 |
| Visual Problems | 5 (2.5%) | 11 (5.2%) | 9 (4.5%) | 0.370 |
| Ageusia | 10 (5.0%) | 9 (4.2%) | 10 (5.0%) | 0.931 |
| Anosmia | 3 (1.5%) | 12 (5.7%) | 12 (6.0%) | 0.654 |
| Cough | 3 (1.5%) | 9 (4.2%) | 24 (2.1%) | 0.684 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Cancela-Cilleruelo, I.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, J.; Gómez-Mayordomo, V.; Pellicer-Valero, O.J.; Martín-Guerrero, J.D.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Torres-Macho, J. Associated-Onset Symptoms and Post-COVID-19 Symptoms in Hospitalized COVID-19 Survivors Infected with Wuhan, Alpha or Delta SARS-CoV-2 Variant. Pathogens 2022, 11, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070725
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Cancela-Cilleruelo I, Rodríguez-Jiménez J, Gómez-Mayordomo V, Pellicer-Valero OJ, Martín-Guerrero JD, Hernández-Barrera V, Arendt-Nielsen L, Torres-Macho J. Associated-Onset Symptoms and Post-COVID-19 Symptoms in Hospitalized COVID-19 Survivors Infected with Wuhan, Alpha or Delta SARS-CoV-2 Variant. Pathogens. 2022; 11(7):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070725
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-de-las-Peñas, César, Ignacio Cancela-Cilleruelo, Jorge Rodríguez-Jiménez, Victor Gómez-Mayordomo, Oscar J. Pellicer-Valero, José D. Martín-Guerrero, Valentín Hernández-Barrera, Lars Arendt-Nielsen, and Juan Torres-Macho. 2022. "Associated-Onset Symptoms and Post-COVID-19 Symptoms in Hospitalized COVID-19 Survivors Infected with Wuhan, Alpha or Delta SARS-CoV-2 Variant" Pathogens 11, no. 7: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070725
APA StyleFernández-de-las-Peñas, C., Cancela-Cilleruelo, I., Rodríguez-Jiménez, J., Gómez-Mayordomo, V., Pellicer-Valero, O. J., Martín-Guerrero, J. D., Hernández-Barrera, V., Arendt-Nielsen, L., & Torres-Macho, J. (2022). Associated-Onset Symptoms and Post-COVID-19 Symptoms in Hospitalized COVID-19 Survivors Infected with Wuhan, Alpha or Delta SARS-CoV-2 Variant. Pathogens, 11(7), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070725








