Ginger Is a Potential Therapeutic for Chronic Toxoplasmosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Treatment with Ginger Extract Significantly Reduced Cyst Count in the Brains of T. gondii-Infected Mice
2.2. Treatment with Ginger Extract Protected Brain and Reduced Infection-Induced Edema and Inflammation
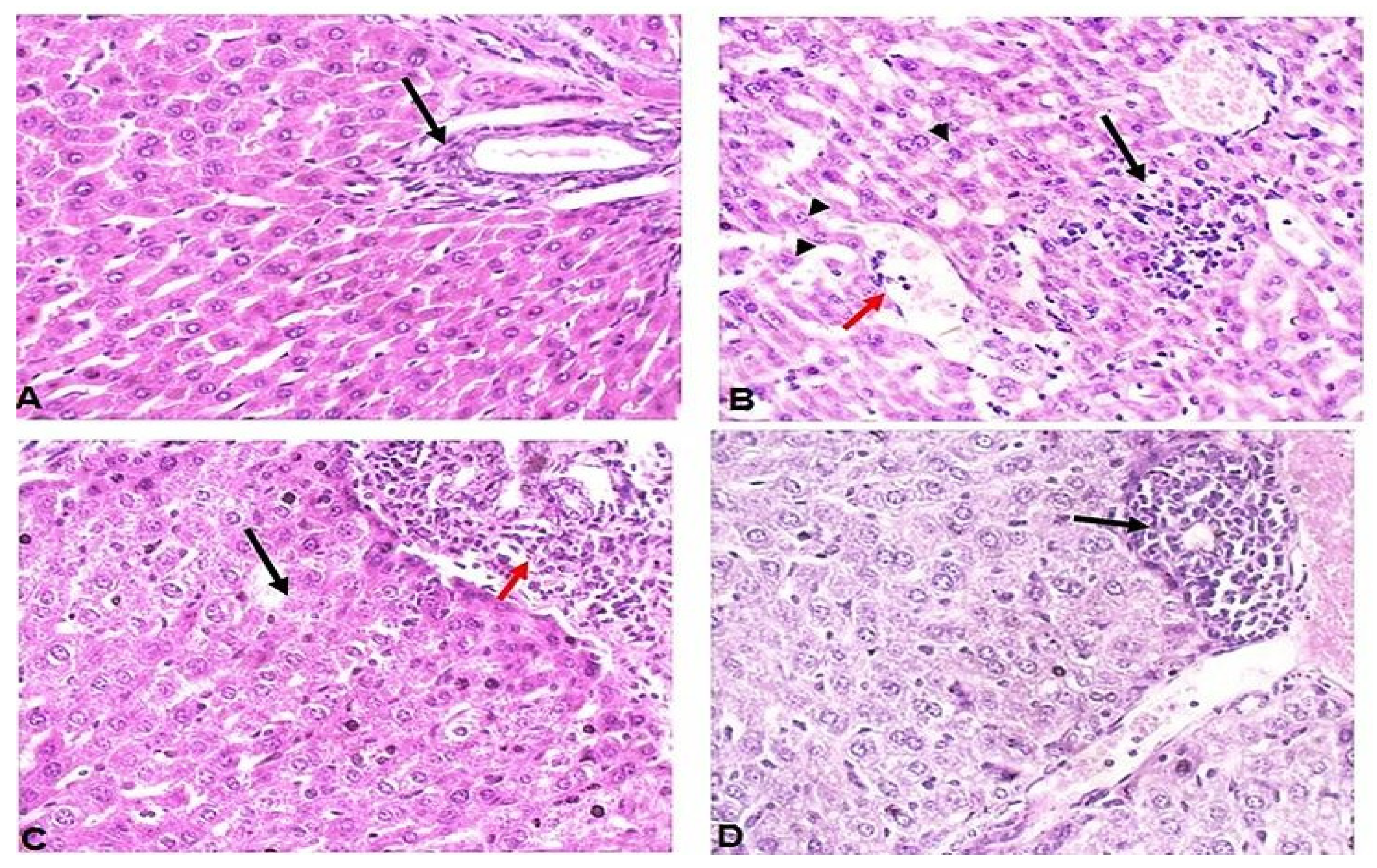
2.3. Treatment with Ginger Extract Preserved the Liver and Reduced Inflammation in T. gondii-Infected Mice
2.4. Treatment with Ginger Extract Reduced Inflammation in Lungs of T. gondii-Infected Mice
2.5. Treatment with Ginger Extract Protected Brains of T. gondii-Infected Mice from Apoptosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Extract Preparation
4.2. Animal Experiment
4.3. Evaluation of Ginger Extract Treatment Efficacy against T. gondii Infection
4.3.1. Quantification of Parasite Burden in Mice Brains
4.3.2. Histopathological Examination
Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.P. The history of Toxoplasma gondii--the first 100 years. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2008, 55, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.-D.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zhu, X.-Q. Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis and typing of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Dardé, M.-L. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-D.; Liu, H.-H.; Ma, Z.-X.; Ma, H.-Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Yang, Z.-B.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Xu, B.; Wei, F.; Liu, Q. Toxoplasma gondii infection in immunocompromised patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Riahi, S.M.; Gamble, H.R.; Fakhri, Y.; Nourollahpour Shiadeh, M.; Danesh, M.; Behniafar, H.; Paktinat, S.; Foroutan, M.; Mokdad, A.H.; et al. Global prevalence of latent toxoplasmosis in pregnant women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldursson, S.; Karanis, P. Waterborne transmission of protozoan parasites: Review of worldwide outbreaks—An update 2004-2010. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6603–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, L.R.; Ekman, C.C.J.; Andrade, H.F.d., Jr.; Luna, E.J.d.A. Human toxoplasmosis outbreaks and the agent infecting form. Findings from a systematic review. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2015, 57, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.S.; Sousa, S.; Castro, A.; da Costa, J.M.C. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in fresh vegetables and berry fruits. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lass, A.; Kontogeorgos, I.; Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Karanis, P. Investigation of Toxoplasma gondii in wastewater and surface water in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China using real-time PCR and multilocus genotyping. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, K.; Bahia-Oliveira, L.; Dixon, B.; Dumètre, A.; de Wit, L.A.; VanWormer, E.; Villena, I. Environmental transmission of Toxoplasma gondii: Oocysts in water, soil and food. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pott, H.J.; Castelo, A. Isolated cerebellar toxoplasmosis as a complication of HIV infection. Int. J. STD AIDS 2013, 24, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Ai, Q. Toxoplasmosis complicating lung cancer: A case report. Int. Med. Case Rep. J. 2015, 8, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.R.; Singh, V.; Ingale, S.; Jain, A.P. Toxoplasmosis of spinal cord in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patient presenting as paraparesis: A rare entity. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2014, 6, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KarimiPourSaryazdi, A.; Tavakoli, P.; Barati, M.; Ghaffarifar, F.; Dalir Ghaffari, A.; KarimiPourSaryazdi, Y. Anti-Toxoplasma effects of silver nanoparticles based on ginger extract: An in vitro study. J. Arch. Mil. Med. 2019, 7, e104248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, L.; Santana, P.L.; Evangelista, F.F.; Beletini, L.F.; Souza, A.H.; Mantelo, F.M.; Souza-Kaneshima, A.M.; Costa, I.N.; Falavigna-Guilherme, A.L. Rosuvastatin reduced brain parasite burden in a chronic toxoplasmosis in vivo model and influenced the neuropathological pattern of ME-49 strain. Parasitology 2020, 147, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rita, D.I.; Kiran, G.; Reshika, D.; Oliver, L.; Montoya, J.G. Treatment of toxoplasmosis: Historical perspective, animal models, and current clinical practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 31, e00057-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.B.; Szajnman, S.H. New antibacterials for the treatment of toxoplasmosis; a patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 311–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinovic, N.; Guegan, H.; Stäjner, T.; Belaz, S.; Robert-Gangneux, F. Treatment of toxoplasmosis: Current options and future perspectives. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, E.; Sarvi, S.; Hashemi Soteh, M.B.; Sharif, M.; Rahimi, M.T.; Valadan, R.; Tehrani, M.; Khalilian, A.; Montazeri, M.; Fasihi-Ramandi, M.; et al. Enhancing immune responses to a DNA vaccine encoding Toxoplasma gondii GRA14 by calcium phosphate nanoparticles as an adjuvant. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 185, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alday, P.H.; Doggett, J.S. Drugs in development for toxoplasmosis: Advances, challenges, and current status. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-M.; Gang, J.; Yun, J. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii RH strain activity of herbal extracts used in traditional medicine. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 32, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayser, O.; Masihi, K.N.; Kiderlen, A.F. Natural products and synthetic compounds as immunomodulators. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2003, 1, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, S.; Saleh-e-In, M.; Rahim, M.; Bhuiyan, M.; Huda, N.; Sultana, N.; Ahsan, M.; Ahmed, S.; Siraj, S.; Rahman, M. Quality composition and biological significance of the Bangladeshi and China ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 2283–2290. [Google Scholar]
- Mahboubi, M. Zingiber officinale Rosc. essential oil, a review on its composition and bioactivity. Clin. Phytoscience 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, L.; Bartlett, A.; Whitfield, P.J. In vitro and in vivo studies on the bioactivity of a ginger (Zingiber officinale) extract towards adult schistosomes and their egg production. J. Helminthol. 2002, 76, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazeni, M.; Nazer, A. In vitro lethal effect of Zingiber officinale R. on protoscolices of hydatid cyst from sheep liver. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 2, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Merawin, L.T.; Arifah, A.K.; Sani, R.A.; Somchit, M.N.; Zuraini, A.; Ganabadi, S.; Zakaria, Z.A. Screening of microfilaricidal effects of plant extracts against Dirofilaria immitis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 88, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- El-Melegy, M.A.; El-Saify, G.H.; Hassab-El-Nabi, S.E. Evaluation of therapeutic effect of ginger compared to flubendazole on experimental trichinelosis in mice. Egyp J Med Sci 2006, 27, 25–48. [Google Scholar]
- Montazeri, M.; Sharif, M.; Sarvi, S.; Mehrzadi, S.; Ahmadpour, E.; Daryani, A. A systematic review of in vitro and in vivo activities of anti-Toxoplasma drugs and compounds (2006–2016). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalir Ghaffari, A.; Dalimi, A. Molecular Identification of Toxoplasma gondii in the native slaughtered cattle of Tehran Province, Iran. J. Food Qual. Hazards Control. 2019, 6, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoli, A.; Barati, M.; Pirestani, M.; Dalimi, A. Screening of toxoplasmosis in cancer patients: A concern. Trop. Doct. 2019, 49, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, C.; Belfort, R.J.; Muccioli, C.; Holland, G.N.; Victora, C.G.; Horta, B.L.; Yu, F.; Nussenblatt, R.B. The effect of long-term intermittent trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole treatment on recurrences of toxoplasmic retinochoroiditis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 134, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serranti, D.; Buonsenso, D.; Valentini, P. Congenital toxoplasmosis treatment. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, E.; Schmidt, D.R. Sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine in the postnatal treatment of congenital toxoplasmosis: What are the options? Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2003, 1, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, M.; Mehrzadi, S.; Sharif, M.; Sarvi, S.; Shahdin, S.; Daryani, A. Activities of anti-Toxoplasma drugs and compounds against tissue cysts in the last three decades (1987 to 2017), a systematic review. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3045–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.H.; Jiang, M.H.; Chu, J.P. Antiparasitic effects of Zingiber officinale (ginger) extract against Toxoplasma gondii. J. Appl. Biomed. 2013, 11, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Attia, R.; Said, S.; Ibraheim, Z. Ginger and cinnamon: Can this household remedy treat giardiasis? Parasitological and histopathological studies. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2014, 9, 530–540. [Google Scholar]
- Kobo, P.; Erin, J.; Suleiman, M.M.; Aliyu, H.; Tauheed, A.; Muftau, S.; Mamman, M. Antitrypanosomal effect of methanolic extract of Zingiber officinale (ginger) on Trypanosoma brucei brucei-infected Wistar mice. Vet. World 2014, 7, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zawawy, L.A.; El-Said, D.; Mossallam, S.F.; Ramadan, H.S.; Younis, S.S. Triclosan and triclosan-loaded liposomal nanoparticles in the treatment of acute experimental toxoplasmosis. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 149, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, N.M.; Aly, E.M. Toxoplasma gondii infection can induce retinal DNA damage: An experimental study. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 7, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carleton, H.M.; Harry, M. Carleton’s Histological technique; Drury, R.A.B., Roger, A.B., Wallington, E.A., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1980; ISBN 0192613103. [Google Scholar]
- Elmi, T.; Hajialiani, F.; Asadi, M.; Orujzadeh, F.; Kalantari Hesari, A.; Rahimi Esboei, B.; Gholami, S. A study on the effect of Zingiber officinale hydroalcoholic extract on plasmodium berghei in infected mice: An experimental study. J. Rafsanjan Univ. Med. Sci. 2019, 18, 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Dincel, G.C. First description of enhanced expression of glia maturation factor-beta in experimental toxoplasmic encephalitis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincel, G.C.; Atmaca, H.T. Role of oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of Toxoplasma gondii infection. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galván-Ramírez, M.D.; Salas-Lais, A.G.; Dueñas-Jiménez, S.H.; Mendizabal-Ruiz, G.; Franco Topete, R.; Berumen-Solís, S.C.; Rodríguez Pérez, L.R.; Franco Topete, K. Kinematic locomotion changes in C57BL/6 mice infected with Toxoplasma strain ME49. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunk, T.; Inder, T.; Wang, X.; Burgner, D.; Mallard, C.; Levy, O. Infection-induced inflammation and cerebral injury in preterm infants. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drögemüller, K.; Helmuth, U.; Brunn, A.; Sakowicz-Burkiewicz, M.; Gutmann, D.H.; Mueller, W.; Deckert, M.; Schlüter, D. Astrocyte gp130 expression is critical for the control of Toxoplasma encephalitis. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, U.K.; Hassan, N.E.-H.Y.; Elhalwagy, M.E.A.; Zaki, A.R.; Abubakr, H.O.; Nagulapalli Venkata, K.C.; Jang, K.Y.; Bishayee, A. Ginger and propolis exert neuroprotective effects against monosodium glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Molecules 2017, 22, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Akabawy, G.; El-Kholy, W. Neuroprotective effect of ginger in the brain of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Ann. Anat. 2014, 196, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Breemen, R.B.; Tao, Y.; Li, W. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in ginger (Zingiber officinale). Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.C.A.; Silva, R.J.; Franco, P.S.; De Oliveira Gomes, A.; Souza, G.; Milian, I.C.B.; Ribeiro, M.; Rosini, A.M.; Guirelli, P.M.; Ramos, E.L.P.; et al. Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitors reduce Toxoplasma gondii infection and upregulate the pro-inflammatory immune response in Calomys callosus rodents and human monocyte cell line. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unno, A.; Kachi, S.; Batanova, T.A.; Ohno, T.; Elhawary, N.; Kitoh, K.; Takashima, Y. Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite-infected peripheral blood mononuclear cells are enriched in mouse lungs and liver. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 134, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Q.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Hu, R.S.; Hu, G.X.; Guo, S.L.; Zhou, C.X.; Zhu, X.Q. Hepatic metabolomics investigation in acute and chronic murine toxoplasmosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Escobar, M.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Regidor-Cerrillo, J.; Vallejo, R.; Benavides, J.; Collantes-Fernández, E.; Ortega-Mora, L.M. Isolation, genotyping, and mouse virulence characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from free ranging iberian pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, R.G.; Costa, A.d.C.L.; Sawamura, M.V.Y.; Nicodemo, A.C.; Duarte-Neto, A.N. Disseminated toxoplasmosis in a patient with advanced acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Autops. Case Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, S. Fatal disseminated toxoplasmosis in an immunocompetent cat. J. South Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2013, 84, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leal, F.E.; Cavazzana, C.L.; de Andrade, H.F., Jr.; Galisteo, A.J., Jr.; de Mendonça, J.S.; Kallas, E.G. Toxoplasma gondii pneumonia in immunocompetent subjects: Case report and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, e62–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, D.; Madan, N.; Qaqish, O.; Nagarakanti, S.; Patel, V. Pulmonary toxoplasmosis diagnosed on transbronchial lung biopsy in a mechanically ventilated patient. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2020, 2020, 9710182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desoubeaux, G.; Cabanne, É.; Franck-Martel, C.; Gombert, M.; Gyan, E.; Lissandre, S.; Renaud, M.; Monjanel, H.; Dartigeas, C.; Bailly, É.; et al. Pulmonary toxoplasmosis in immunocompromised patients with interstitial pneumonia: A single-centre prospective study assessing PCR-based diagnosis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanain, M.A.; Hassanain, N.A.; Shaapan, R.M. A model of pulmonary toxoplasmosis in rats as potential impact on immune deficient diseases. Comp. Clin. Path. 2018, 27, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yocum, G.T.; Hwang, J.J.; Mikami, M.; Danielsson, J.; Kuforiji, A.S.; Emala, C.W. Ginger and its bioactive component 6-shogaol mitigate lung inflammation in a murine asthma model. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2022, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, E.A.; Siviski, M.E.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Hoonjan, B.; Emala, C.W. Effects of ginger and its constituents on airway smooth muscle relaxation and calcium regulation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çifci, A.; Tayman, C.; Yakut, H.İ.; Halil, H.; Çakır, E.; Çakır, U.; Aydemir, S. Ginger (Zingiber officinale) prevents severe damage to the lungs due to hyperoxia and inflammation. Turkish J. Med. Sci. 2018, 48, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, A.; Huo, X.; Luo, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yu, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Lun, Z.; et al. Reactive oxygen species-triggered trophoblast apoptosis is initiated by endoplasmic reticulum stress via activation of caspase-12, CHOP, and the JNK pathway in Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 2121–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Kawase, O.; Vielemeyer, O.; Suzuki, H.; Joiner, K.A.; Xuan, X.; Nagasawa, H. Toxoplasma gondii infection induces apoptosis in noninfected macrophages: Role of nitric oxide and other soluble factors. Parasite Immunol. 2007, 29, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincel, G.C.; Atmaca, H.T. Increased expressions of ADAMTS-13 and apoptosis contribute to neuropathology during Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis in mice. Neuropathology 2016, 36, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, S.A.; Badawy, G.M. Effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale R.) on metiram-inhibited spermatogenesis and induced apoptosis in albino mice. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 131. [Google Scholar]
- El-Borm, H.T.; Gobara, M.S.; Badawy, G.M. Ginger extract attenuates labetalol induced apoptosis, DNA damage, histological and ultrastructural changes in the heart of rat fetuses. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.F.; Bennett, M.T. The effect of different methods and solvents on the extraction of polyphenols in ginger (Zingiber officinale. J. Teknol. 2016, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurković-Djaković, O.; Milenković, V.; Nikolić, A.; Bobić, B.; Grujić, J. Efficacy of atovaquone combined with clindamycin against murine infection with a cystogenic (Me49) strain of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouel-Nour, M.F.; El-Shewehy, D.M.M.; Hamada, S.F.; Morsy, T.A. The efficacy of three medicinal plants; garlic, ginger and mirazid and a chemical drug metronidazole against Cryptosporidium parvum: Ii-histological changes. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ridley, D.S.; Hawgood, B.C. The value of formol-ether concentration of faecal cysts and ova. J. Clin. Pathol. 1956, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, S.A.; Pohlenz, J.F. Staining of cryptosporidia by a modified Ziehl-Neelsen technique. Acta Vet. Scand. 1981, 22, 594–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, A.; Malla, N. Evaluation of Ziehl-Neelsen staining, auramine phenol staining, antigen detection enzyme linked immunosorbent assay and polymerase chain reaction, for the diagnosis of intestinal cryptosporidiosis. Trop. Parasitol. 2012, 2, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etewa, S.E.; El-Maaty, D.A.A.; Hamza, R.S.; Metwaly, A.S.; Sarhan, M.H.; Abdel-Rahman, S.A.; Fathy, G.M.; El-Shafey, M.A. Assessment of spiramycin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles treatment on acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in mice. J. Parasit. Dis. 2018, 42, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grujić, J.; Djurković-Djaković, O.; Nikolić, A.; Klun, I.; Bobić, B. Effectiveness of spiramycin in murine models of acute and chronic toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, M.E.; Abd El Hamid, A.H.; Aly, N.S.M.; Omar, G.H.; Barakat, A.M.A.; Ahmed, K.A.; Youssif, S.H.; Rashed, G.A. Efficacy of azithromycin on experimental toxoplasmosis infected mice. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-kady, A.M.; Al-Megrin, W.A.I.; Abdel-Rahman, I.A.M.; Sayed, E.; Alshehri, E.A.; Wakid, M.H.; Baakdah, F.M.; Mohamed, K.; Elshazly, H.; Alobaid, H.M.; et al. Ginger Is a Potential Therapeutic for Chronic Toxoplasmosis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070798
El-kady AM, Al-Megrin WAI, Abdel-Rahman IAM, Sayed E, Alshehri EA, Wakid MH, Baakdah FM, Mohamed K, Elshazly H, Alobaid HM, et al. Ginger Is a Potential Therapeutic for Chronic Toxoplasmosis. Pathogens. 2022; 11(7):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070798
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-kady, Asmaa M., Wafa Abdullah I. Al-Megrin, Iman A. M. Abdel-Rahman, Eman Sayed, Eman Abdullah Alshehri, Majed H. Wakid, Fadi M. Baakdah, Khalil Mohamed, Hayam Elshazly, Hussah M. Alobaid, and et al. 2022. "Ginger Is a Potential Therapeutic for Chronic Toxoplasmosis" Pathogens 11, no. 7: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070798
APA StyleEl-kady, A. M., Al-Megrin, W. A. I., Abdel-Rahman, I. A. M., Sayed, E., Alshehri, E. A., Wakid, M. H., Baakdah, F. M., Mohamed, K., Elshazly, H., Alobaid, H. M., Qahl, S. H., Elshabrawy, H. A., & Younis, S. S. (2022). Ginger Is a Potential Therapeutic for Chronic Toxoplasmosis. Pathogens, 11(7), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070798







