Occurrence of Macrophomina phaseolina on Chickpea in Italy: Pathogen Identification and Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Morphological Identification
2.2. Molecular Characterization of Macrophomina phaseolina CREA OF 189.2
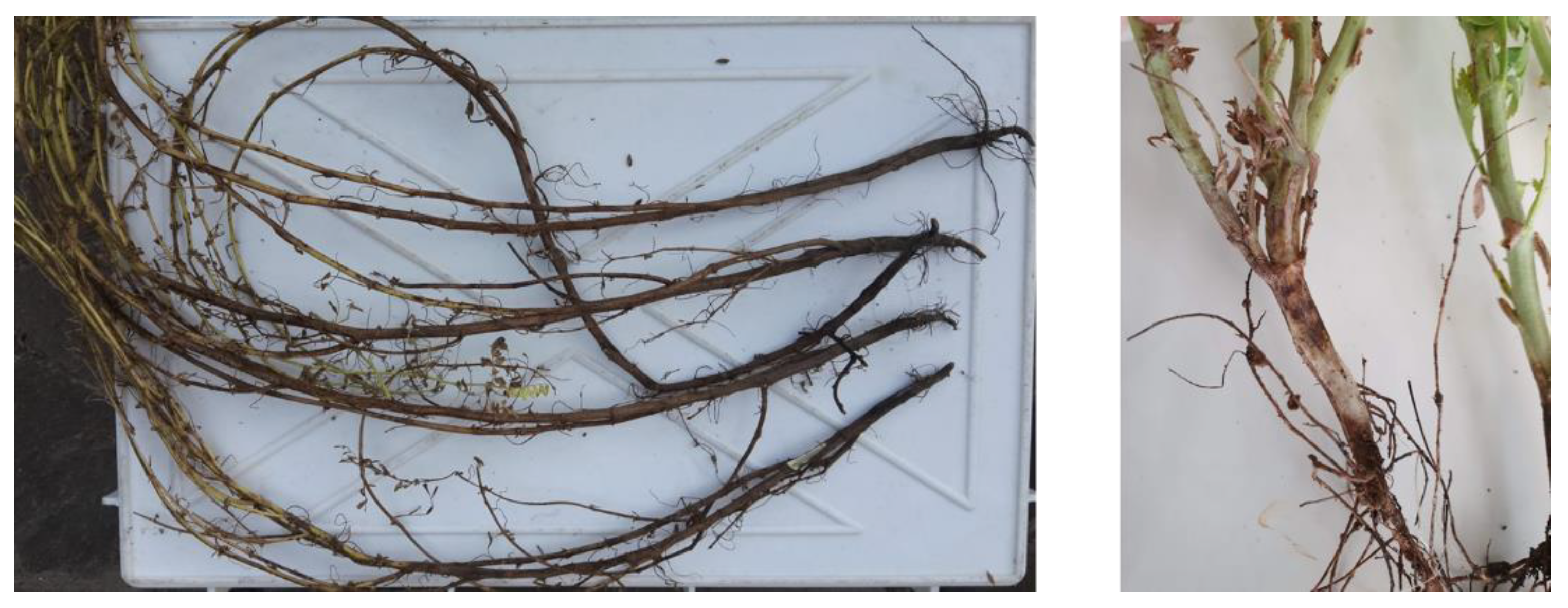
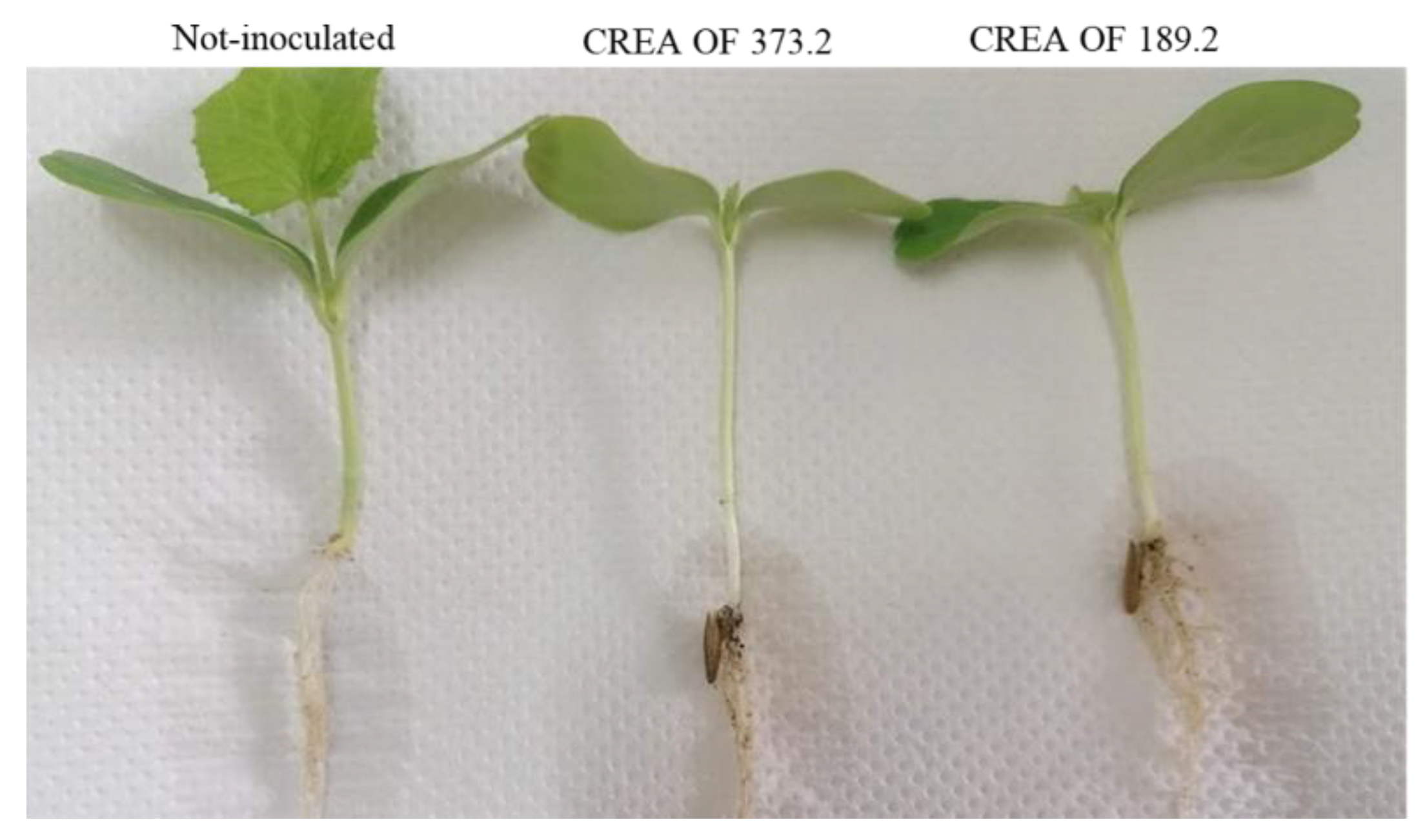
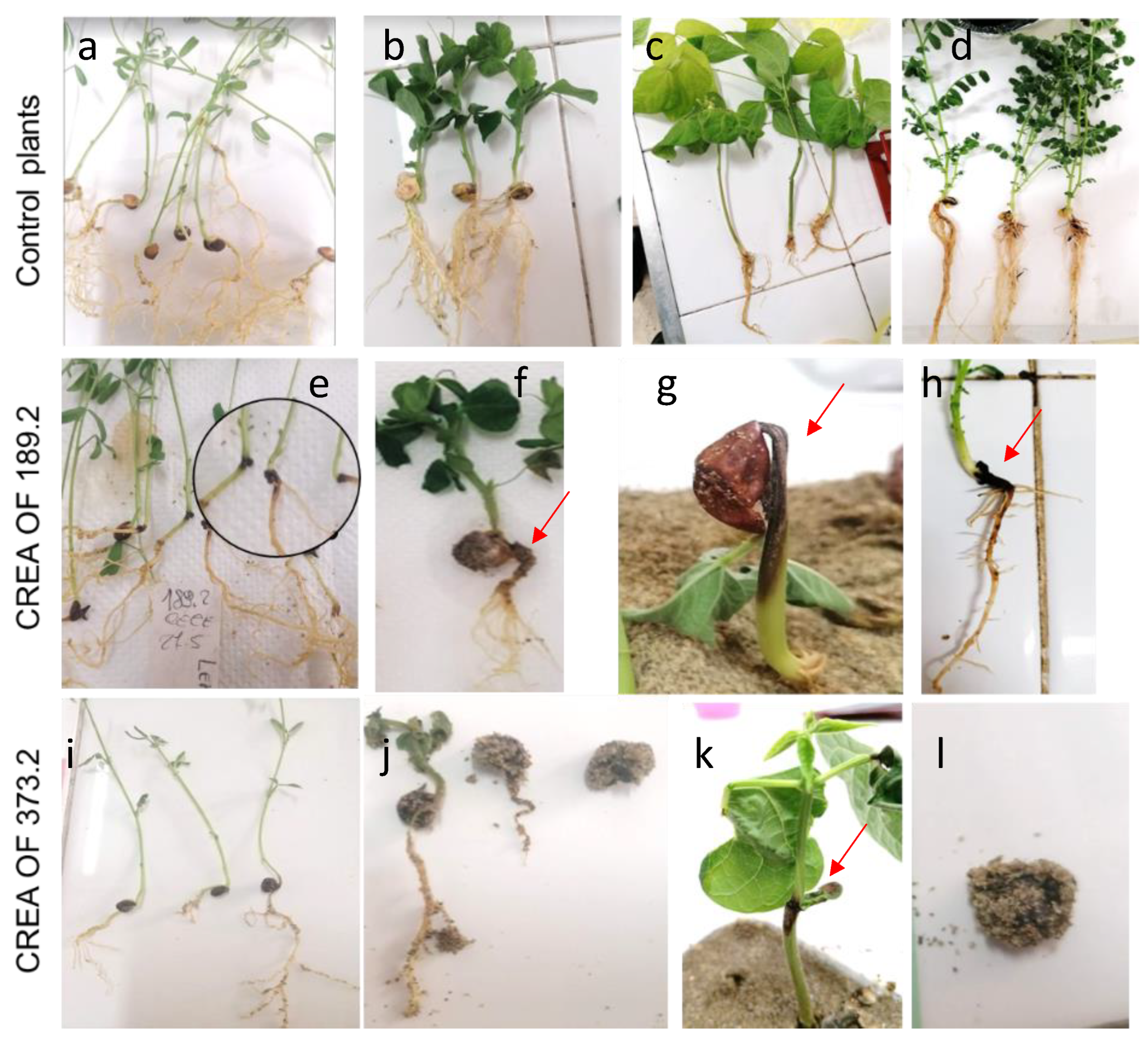
2.3. Pathogenicity of M. phaseolina CREA OF 189.2 Isolate from Chickpea
2.4. Host Range of M. phaseolina CREA OF 189.2
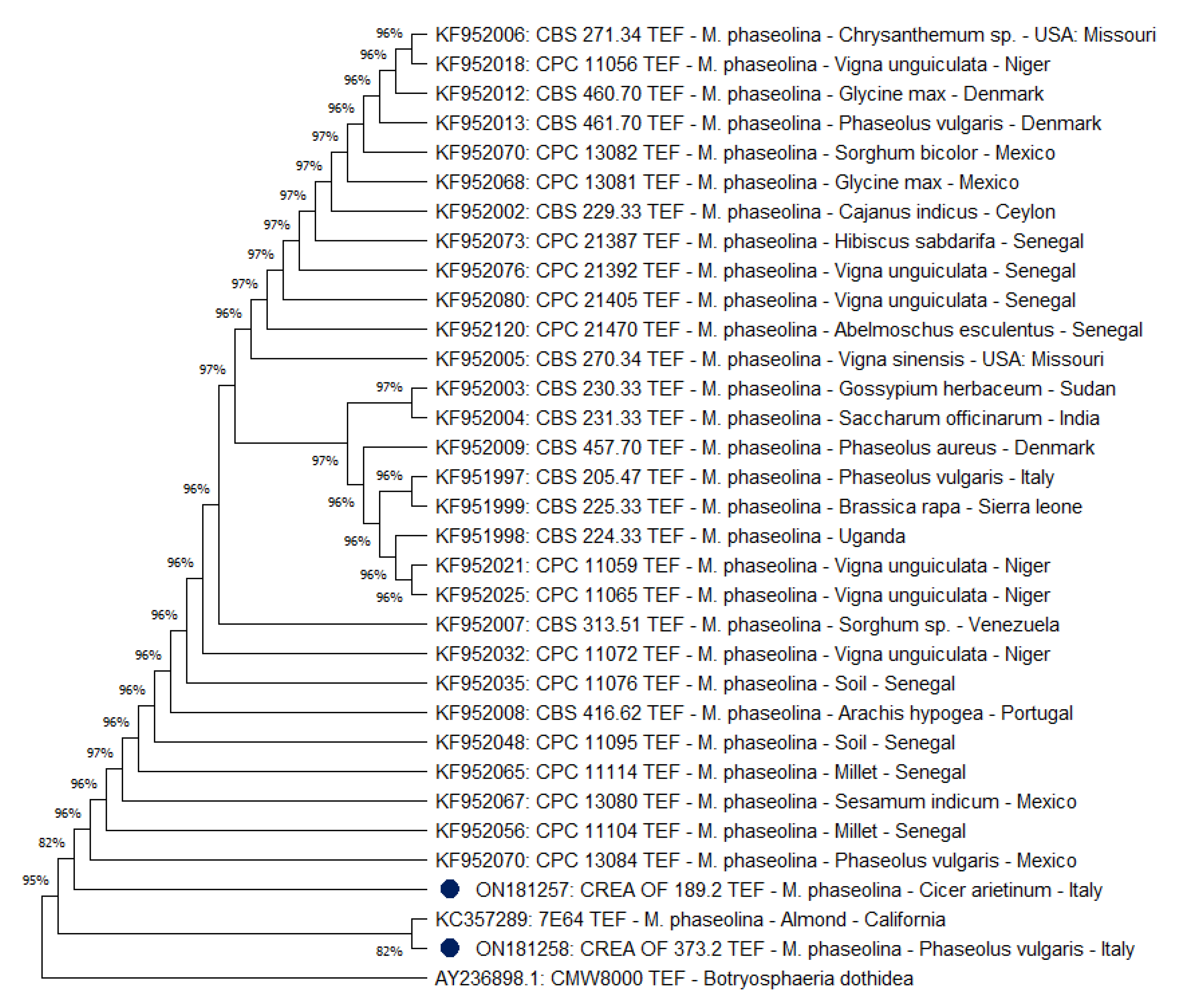
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of M. phaseolina CREA OF 189.2 Isolate
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Fungal Isolation
4.2. Morphological Characterization of M. phaseolina Isolates
4.3. Molecular Identification of M. phaseolina CREA_OF Isolates
4.4. Pathogenicity Test of M. phaseolina CREA OF 189.2 on Chickpea and Host Range
4.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of Macrophomina Phaseolina CREA_OF_189.2
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghini, R.; Hamada, E.; Angelotti, F.; Costa, L.B.; Bettiol, W. Research approaches, adaptation strategies, and knowledge gaps concerning the impacts of climate change on plant diseases. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2012, 37, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bebber, D.P. Range-Expanding Pests and Pathogens in a Warming World. Annu. Rev. Phytopatol. 2015, 53, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, A.J.L.; Alves, A.; Abdollahzadeh, J.; Slippers, B.; Wingfield, M.J.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Crous, P.W. The Botryosphaeriaceae: Genera and species known from culture. Stud. Mycol. 2013, 76, 51–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biswas, M.K.; Ali, M. A review on characterization, therapeutic approaches and pathogenesis of Macrophomina phaseolina. Artic. Plant Cell Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. 2018, 19, 72–84. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, D.F.; Rossman, A.Y. Fungal Databases, U.S. National Fungus Collections, ARS, USDA. Available online: https://nt.ars-grin.gov/fungaldatabases/ (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- Gupta, G.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Ramteke, R. Biology, Epidemiology and Management of the Pathogenic Fungus Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) Goid with Special Reference to Charcoal Rot of Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill). J. Phytopathol. 2012, 160, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.K.; Gawande, S.P. Diseases of jute and allied fibre crops and their management. J. Mycopathol. Res. 2016, 54, 321–337. [Google Scholar]
- Indra, N.; Subbiah, G. Management of blackgram root rot caused by Macrophomina phaseolina by antagonistic microorganisms. Madras Agric. J. 2003, 90, 490–494. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Zhu, Z.D.; Duan, C.X.; Wang, X.M.; Li, H.J. First Report of Charcoal Rot Caused by Macrophomina phaseolina on Mungbean in China. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, R.E.; Wadl, P.A.; Wang, X.; Johnson, D.H.; Rinehart, T.A.; Abbas, H.K.; Shier, T.; Trigiano, R.N. Microsatellites from the charcoal rot fungus (Macrophomina phaseolina). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 946–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarr, M.P.; Ndiaye, M.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Crous, P.W. Genetic diversity in Macrophomina phaseolina, the causal agent of charcoal rot. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2014, 53, 250–268. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, R.E.; Brock, J.H. First Report of Macrophomina phaseolina on Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) in Georgia. Plant Dis. 2007, 83, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.; Budak, H. First Report of Charcoal Rot Caused by Macrophomina phaseolina in Sunflower in Turkey. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerin, D.; Dongiovanni, C.; De Miccolis Angelini, R.M.; Pollastro, S.; Faretra, F. First Report of Macrophomina phaseolina Causing Crown and Root Rot on Strawberry in Italy. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, C.; Adkins, S.; Turechek, W.W.; Patel, P.C.; Rosskopf, E.N. First Report of Macrophomina phaseolina, Fusarium brachygibbosum, and Lasiodiplodia theobromae Causing Fungal Watermelon Vine Decline in Southwest and West-Central Florida. Plant Health Prog. 2021, 22, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlicskó, S.; Kovács, J.; Horváth, J.; Kazinczi, G. Experiments on the Resistance or Pepper Cultivars to Macrophomina phaseolina. Int. J. Hortic. Sci. 2000, 6, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Basandrai, A.K. Will Macrophomina phaseolina spread in legumes due to climate change? A critical review of current knowledge. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2021, 128, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltivazioni. Available online: http://dati.istat.it/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=DCSP_COLTIVAZIONI (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Marquez, N.; Giachero, M.L.; Declerck, S.; Ducasse, D.A. Macrophomina phaseolina: General Characteristics of Pathogenicity and Methods of Control. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 634397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abawi, G.S.; Pastor-Corrales, M.A. Charcoal rot screening procedure and virulence of Macrophomina phaseolina isolates on dry edible beans. Turrialba 1989, 39, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Salgado, S.J.; Romero-Arenas, O.; Morales-Mora, L.A.; Luna-Cruz, A.; Rivera-Tapia, J.A.; Silva-Rojas, H.V.; Andrade-Hoyos, P. First Report of Macrophomina phaseolina Causing Charcoal Rot of Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) in Mexico. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, S.T.; Stanghellini, H.; Burkhardt, A. First report of macrophomina crown rot caused by Macrophomina phaseolina on Basil in the United States. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokor, P. Macrophomina phaseolina causing a charcoal rot of sunflower through Slovakia. Biologia 2007, 62, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.M.; Lima, G.S.; Barros, A.P.O.; Machado, A.R.; Souza-Motta, C.M.; Correia, K.C.; Michereff, S.J. Novel specific primers for rapid identification of Macrophomina species. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 156, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis Machado, A.; Batista Pinho, D.; José Soares, D.; Angelo Medeiros Gomes, A.; Liparini Pereira, O. Bayesian analyses of five gene regions reveal a new phylogenetic species of Macrophomina associated with charcoal rot on oilseed crops in Brazil. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 153, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.; Shivas, R.G.; Adorada, D.L.; Barbetti, M.J.; Bithell, S.L.; Kelly, L.A.; Moore, N.; Sparks, A.H.; Tan, Y.P.; Thomas, G.; et al. Hidden diversity of Macrophomina associated with broadacre and horticultural crops in Australia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 161, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tančić Živanov, S.; Dedić, B.; Dimitrijević, A.; Dušanić, N.; Jocić, S.; Miklič, V.; Kovačević, B.; Miladinović, D. Analysis of genetic diversity among Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) Goid. isolates from Euro-Asian countries. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2019, 126, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, U.; Mukhtar, T. Morphological and pathogenic variability among Macrophomina phaseolina isolates associated with mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) Wilczek from Pakistan. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 950175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abed-Ashtiani, F.; Narmani, A.; Arzanlou, M. Macrophomina phaseolina associated with grapevine decline in Iran. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2018, 57, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhran, L.; Ahir, R.R.; Choudhary, M.; Choudhary, S. Isolation, purification, identification and pathogenicity of Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) goid caused dry root rot of chickpea. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 3314–3317. [Google Scholar]
- Sukanya, R.; Jayalakshmi, S.K. Response of inoculation technique to seed and seedling infection by M. Phaseolina in sorghum. Adv. Plants Agric. Res. 2017, 6, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, C.G.; Muniz, M.F.B.; Mezzomo, R.; Reiniger, L.R.S. Lasiodiplodia theobromae associated with seeds of Pinus spp. originated from the northwest of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Sci. For. 2015, 43, 639–646. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egel, D.S.; Guan, W.; Creswell, T.; Bonkowski, J. First Report of Macrophomina Phaseolina Causing Charcoal Rot of Cucumber in Indiana. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Morgan, D.; Beede, R.H.; Michailides, T.J. First Report of Lasiodiplodia theobromae Associated with Stem Canker of Almond in California. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türkkan, M.; Benli, H.İ.; Yılmaz, Ö.; Özer, G.; Yaman, M.; Şahin, N.; Erper, I. First report of charcoal rot caused by Macrophomina phaseolina on kiwifruit in Turkey. J. Plant Pathol. 2004, 102, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erper, I.; Turkkan, M.; Bobushova, S.; Ozer, G. First report of charcoal rot caused by Macrophomina phaseolina on common bean in Kyrgyzstan. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 103, 1025–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



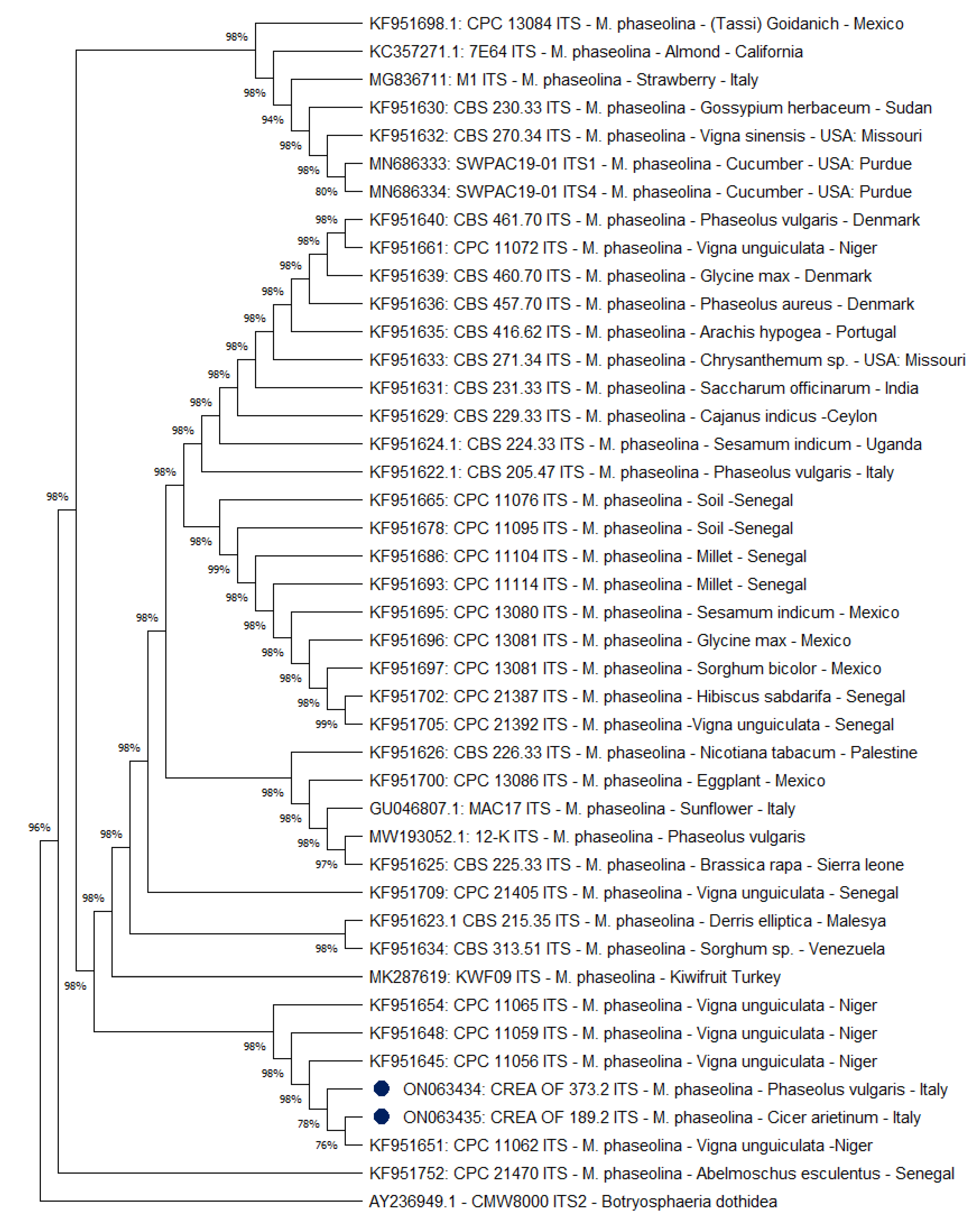


| Species | Isolate | Host | Location | Accession Number | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | Tef 1-α | |||||
| M. phaseolina | Purdue_SWPAC19-01 | Cucumis sativus L. | Indiana, USA | MN686333 | - | [35] |
| M. phaseolina | Purdue_SWPAC19-01 | Cucumis sativus L. | Indiana, USA | MN686334 | - | [35] |
| M. phaseolina | M1 | Fragaria × ananassa | Italy | MG836711 | - | [14] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 13084 | Phaseolus vulgaris | Mexico | KF951698.1 | KF952070 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | 7E64 | Prunus dulcis | California, USA | KC357271.1 | KC357289 | [36] |
| M. phaseolina | KWF09 | Actinidia deliciosa | Turkey | MK287619 | - | [37] |
| M. phaseolina | 12-K | Phaseolus vulgaris | Kyrgyzstan | MW193052.1 | - | [38] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC13086 | Solanum melongena | Mexico | KF951700 | - | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | MAC17 | Helianthus annuus | Italy | GU046807.1 | - | Present work |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 205.47 | Phaseolus vulgaris | Italy | KF951622.1 | KF951997 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 215.35 | Derris elliptica | Malesya | KF951623.1 | - | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 224.33 | Sesamum indicum | Uganda | KF951624.1 | KF951998 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 225.33 | Brassica rapa | Sierra Leone | KF951625 | KF951999 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 226.33 | Nicotiana tabacum | Palestine | KF951626 | - | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 229.33 | Cajanus indicus | Sri Lanka | KF951629 | KF952002 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 230.33 | Gossypium herbaceum | Sudan | KF951630 | KF952003 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 231.33 | Saccharum officinarum | India | KF951631 | KF952004 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 270.34 | Vigna sinensis | Missouri, USA | KF951632 | KF952005 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 271.34 | Chrysantemum sp. | Missouri, USA | KF951633 | KF952006 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 313.51 | Sorghum sp. | Venezuela | KF951634 | KF952007 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 460.70 | Glycine max | Denmark | KF951639 | - | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 416.62 | Arachis hypogaea | Portugal | KF951635 | KF952008 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 457.70 | Phaseolus aureus | Denmark | KF951636 | KF952009 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 460.70 | Glycine max | Denmark | KF951639 | KF952012 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CBS 461.70 | Phaseolus vulgaris | Denmark | KF951640 | KF952013 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 11056 | Vigna unguiculata | Niger | KF951645 | KF952018 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 11059 | Vigna unguiculata | Niger | KF951648 | KF952021 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 11062 | Vigna unguiculata | Niger | KF951651 | KF952025 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 11065 | Vigna unguiculata | Niger | KF951654 | KF952032 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 11072 | Vigna unguiculata | Niger | KF951661 | KF952035 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 11076 | Soil | Senegal | KF951665 | KF952048 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 11095 | Soil | Senegal | KF951678 | KF952056 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 11104 | Panicum miliaceum | Senegal | KF951686 | KF952065 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 11114 | Panicum miliaceum | Senegal | KF951693 | KF952067 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 13080 | Sesamum indicum | Mexico | KF951695 | KF952068 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 13081 | Glycine max | Mexico | KF951696 | KF952070 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 13082 | Sorghum bicolor | Mexico | KF951697 | KF952073 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 21387 | Hibiscus sabdarifa | Senegal | KF951702 | KF952076 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 21392 | Vigna unguiculata | Senegal | KF951705 | KF952080 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CPC 21405 | Vigna unguiculata | Senegal | KF951709 | KF952120 | [11] |
| M. phaseolina | CREA OF 189.2 | Cicer arietinum | Italy | ON063435 | ON181257 | Present work |
| M. phaseolina | CREA OF 373.2 | Phaseolus vulgaris | Italy | ON063434 | ON181258 | Present work |
| B. dothidea | CMW8000 | Prunus sp. | Switzerland | AY236949.1 | AY236898.1 | [11] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dell’Olmo, E.; Tripodi, P.; Zaccardelli, M.; Sigillo, L. Occurrence of Macrophomina phaseolina on Chickpea in Italy: Pathogen Identification and Characterization. Pathogens 2022, 11, 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080842
Dell’Olmo E, Tripodi P, Zaccardelli M, Sigillo L. Occurrence of Macrophomina phaseolina on Chickpea in Italy: Pathogen Identification and Characterization. Pathogens. 2022; 11(8):842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080842
Chicago/Turabian StyleDell’Olmo, Eliana, Pasquale Tripodi, Massimo Zaccardelli, and Loredana Sigillo. 2022. "Occurrence of Macrophomina phaseolina on Chickpea in Italy: Pathogen Identification and Characterization" Pathogens 11, no. 8: 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080842
APA StyleDell’Olmo, E., Tripodi, P., Zaccardelli, M., & Sigillo, L. (2022). Occurrence of Macrophomina phaseolina on Chickpea in Italy: Pathogen Identification and Characterization. Pathogens, 11(8), 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080842









