Recent Advances in the Immunologic Method Applied to Tick-Borne Diseases in Brazil
Abstract
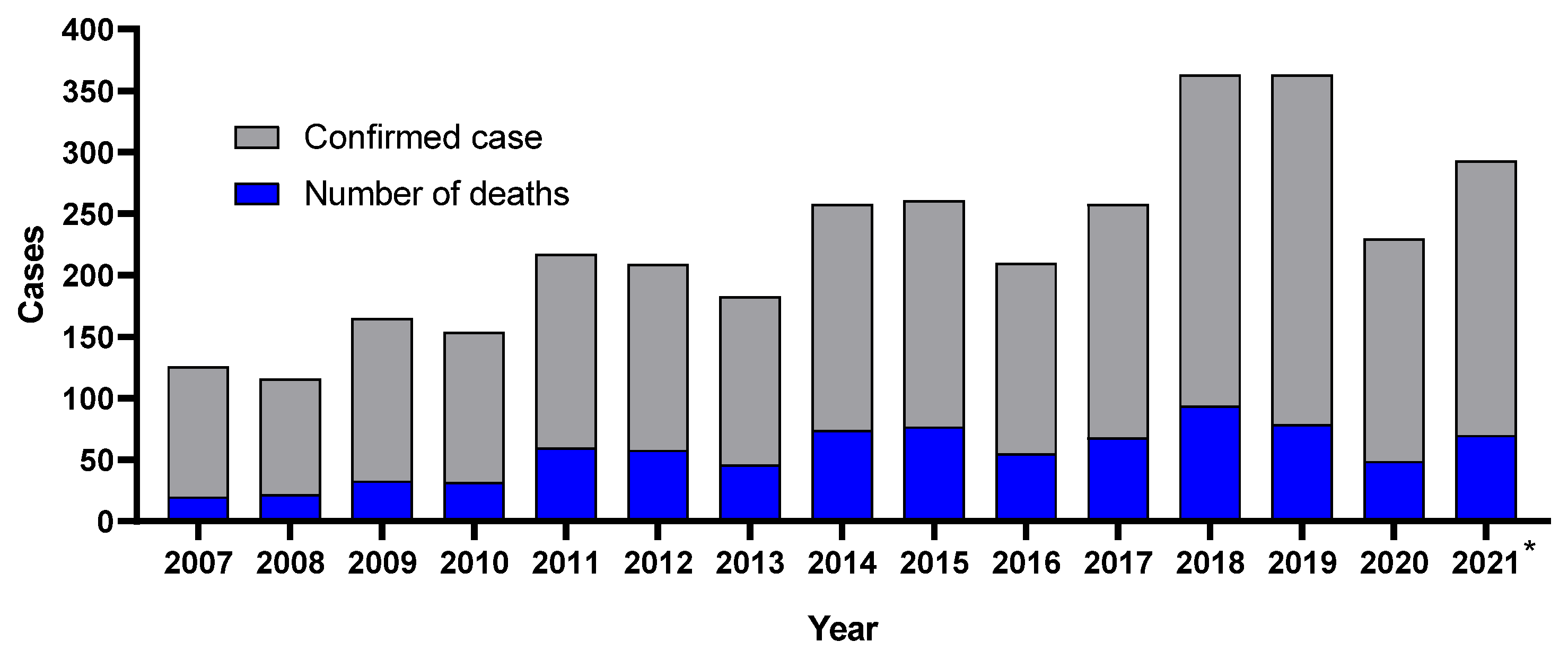
:1. Introduction
| Disease | Pathogen | Test | Method | % Sens | % Sp | % PS | Country | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VlsE1/pepC10 | ELISA IgM/IgG | 59.5–80.9 | 86.9–93.0 | USA | [53] | |||
| LD | B. burgdorferi | MarBlot® | WB IgM/IgG | 84.7/87.3 | USA | [54] | ||
| VIDAS®Lyme | EIA IgM/IgG | 83–85 | 85–88 | USA | [55] | |||
| ATBF | R. africae | Focus Diagnostics | IFA IgM/IgG | 95 | USA | [56] | ||
| RMSF | R. rickettsii | Tulip Diagnostics | WF IgM/IgG | 49 | 96 | India | [57] | |
| MSF | R.conorii | Vircell | ELISA IgM/IgG | 94/85 | 95/100 | Spain | [58] | |
| E. chaffeensis | Fuller Laboratories | IFA IgM/IgG | 1.8/7.0 | USA | [59] | |||
| HME | E. canis | Fuller Laboratories | IFA IgG | 19 | USA | [60] | ||
| E. canis | ImmunoComb | ELISA IgG | 4.33 | Spain | [17] |
| Serology-Based Methods | Disease | Sample | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | ehrlichiosis/LD | 100 mL | ↑ specificity | ↓ sensitivity | [61] |
| Immunoblotting | borreliosis (LD) | 0.5 mL | ↑ specificity | heterogeneity, ↓ sensitivity | [62] |
| IFA | rickettsiosis/ehrlichiosis | 25 µL | ↑ sensitivity | subjective | [45] |
| WFT | rickettsiosis | 0.1 mL | ↓ sensitivity/specificity | [63] | |
| Electrochemical | rickettsiosis | 20 µL | ↑ sensitivity/specificity, fast response | [64] |
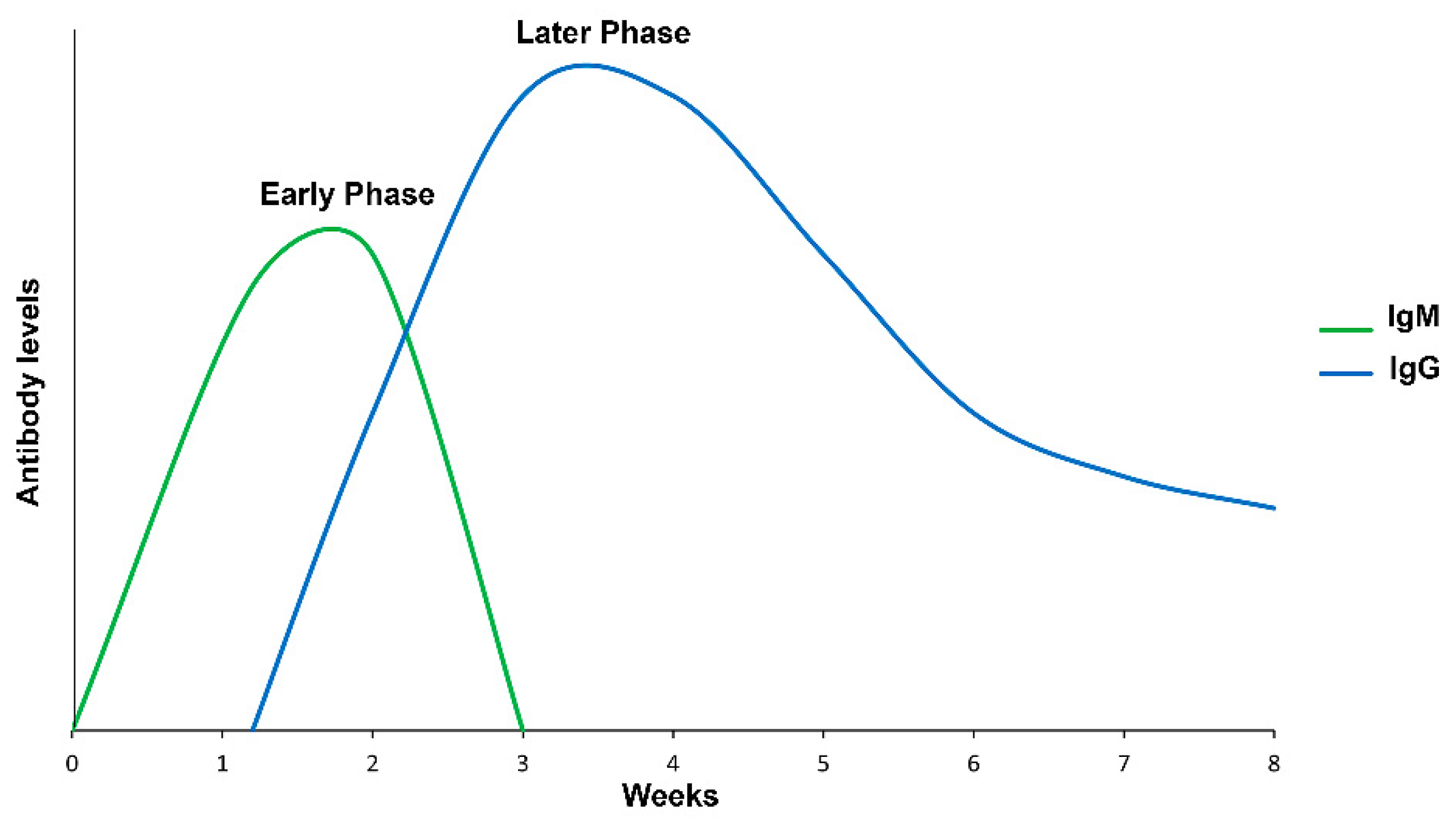
1.1. Humoral Immunity
1.1.1. Agglutination Tests
1.1.2. Immunoblotting (Western Blotting)
1.1.3. Indirect Immunofluorescent Assay
1.1.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
1.1.5. Immunosensors
1.2. Immune Disorder and Diagnostic Implication
2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Vector-Born Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/vector-borne-diseases (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Wilson, A.L.; Courtenay, O.; Kelly-Hope, L.A.; Scott, T.W.; Takken, W.; Torr, S.J.; Lindsay, S.W. The importance of vector control for the control and elimination of vector-borne diseases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mogg, M.; Wang, H.-H.; Baker, A.; DeRouen, Z.; Borski, J.; Grant, W.E. Increased Incidence of Ehrlichia chaffeensis Infections in the United States, 2012 Through 2016. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, S.L.; Banda, B.K.; Burnsides, C.L.; Stuber, A.J. Zoonosis: Update on Existing and Emerging Vector-Borne Illnesses in the USA. Curr. Emerg. Hosp. Med. Rep. 2019, 7, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, A.M.; Armstrong, P.A. Increase in Reports of Tick-Borne Rickettsial Diseases in the United States. Am. J. Nurs. 2019, 119, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, C.B.; Eisen, L.; Eisen, R.J. The Rise of Ticks and Tickborne Diseases in the United States—Introduction. J. Med. Èntomol. 2021, 58, 1487–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochlin, I.; Ninivaggi, D.V.; Benach, J.L. Malaria and Lyme Disease-the Largest Vector-Borne US Epidemics in the Last 100 Years: Success and Failure of Public Health. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouque, F.; Reeder, J.C. Impact of past and on-going changes on climate and weather on vector-borne diseases transmission: A look at the evidence. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocklöv, J.; Dubrow, R. Climate change: An enduring challenge for vector-borne disease prevention and control. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz, H.R.; Costa, F.B.; Benatti, H.R.; Ramos, V.N.; de ASerpa, M.C.; Martins, T.F.; Acosta, I.C.L.; Ramirez, D.G.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; Ramirez-Hernandez, A.; et al. Epidemiology of capybara-associated Brazilian spotted fever. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, D.A.G.; Vieira, R.F.D.C.; Vieira, T.S.W.J.; Toledo, R.D.S.; Tamekuni, K.; Dos Santos, N.J.R.; Gonçalves, D.D.; Vieira, M.L.; Biondo, A.W.; Vidotto, O. Serosurvey of Borrelia in dogs, horses, and humans exposed to ticks in a rural settlement of southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. De Parasitol. Veterinária 2016, 25, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira, G.M.B.; da Silva, I.W.G.; Evaristo, A.M.D.C.F.; Serpa, M.C.D.A.; Campos, A.N.S.; Dutra, V.; Nakazato, L.; de Aguiar, D.M.; Labruna, M.B.; Horta, M.C. Tick-Borne pathogens in dogs, wild small mammals and their ectoparasites in the semi-arid Caatinga biome, northeastern Brazil. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labruna, M.B.; Nava, S.; Marcili, A.; Barbieri, A.R.; Nunes, P.H.; Horta, M.C.; Venzal, J.M. A new argasid tick species (Acari: Argasidae) associated with the rock cavy, Kerodon rupestris Wied-Neuwied (Rodentia: Caviidae), in a semiarid region of Brazil. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Sun, W.; Yang, X.; Liu, J. Tick-Borne pathogens and the vector potential of ticks in China. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Nagar, G. Problem of ticks and Tick-Borne diseases in India with special emphasis on progress in tick control research: A review. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2014, 51, 259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, N.S.; Kostarnoy, A.V.; Kondratev, A.V.; Gancheva, P.G.; Grumov, D.A.; Gintsburg, A.L. Diagnostic Value of IgA Antibody Measurement in Tick-Borne Spotted Fever (Astrakhan Rickettsial Fever). Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01687-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugassy, L.; Amdouni-Boursier, L.; Alout, H.; Berrebi, R.; Boëte, C.; Boué, F.; Boulanger, N.; Cosson, J.-F.; Durand, T.; De Garine-Wichatitsky, M.; et al. What is the evidence that ecosystem components or functions have an impact on infectious diseases? A systematic review protocol. Environ. Évid. 2019, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, C.; De Paula, E.F.E.; Brandão, A.P.D.; Ferreira, F.; Vieira, R.; Biondo, A.W. Survey of spatial distribution of vector-borne disease in neighborhood dogs in southern Brazil. Open Vet. J. 2017, 7, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowser, N.H.; Anderson, N.E. Dogs (Canis familiaris) as Sentinels for Human Infectious Disease and Application to Canadian Populations: A Systematic Review. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calchi, A.C.; Vultão, J.G.; Alves, M.H.; Yogui, D.R.; Desbiez, A.L.J.; De Santi, M.; de Souza Santana, M.; Da Silva, T.M.V.; Werther, K.; Teixeira, M.M.G.; et al. Ehrlichia spp. and Anaplasma spp. in Xenarthra mammals from Brazil, with evidence of novel ‘Candidatus Anaplasma spp.’. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, P.G.; Pires, M.S.; da Silva, C.B.; Peckle, M.; da Costa, R.L.; Vitari, G.V.; Vilela, J.A.R.; de Abreu, A.P.M.; Massard, C.L.; Santos, H.A. Epidemiology of Ehrlichia canis in healthy dogs from the Southeastern region of the state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 159, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanikawa, A.; Labruna, M.; Costa, A.; Aguiar, D.; Justiniano, S.; Mendes, R.; Melo, A.; Alves, C.; Azevedo, S. Ehrlichia canis in dogs in a semiarid region of Northeastern Brazil: Serology, molecular detection and associated factors. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 94, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taques, I.I.G.G.; Campos, A.N.S.; Kavasaki, M.L.; De Almeida, S.L.H.; De Aguiar, D.M. Geographic Distribution of Ehrlichia canis TRP Genotypes in Brazil. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Toledo Vieira, F.; Acosta, I.C.L.; Martins, T.F.; Filho, J.M.; Krawczak, F.; Barbieri, A.R.M.; Egert, L.; Fernandesm, D.R.; Braga, F.R.; Labruna, M.B.; et al. Tick-Borne infections in dogs and horses in the state of Espírito Santo, Southeast Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 249, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, R.F.D.C.; Vieira, T.S.W.J.; Nascimento, D.D.A.G.; Martins, T.F.; Krawczak, F.S.; Labruna, M.B.; Chandrashekar, R.; Marcondes, M.; Biondo, A.W.; Vidotto, O. Serological survey of ehrlichia species in dogs, horses and humans: Zoonotic scenery in a rural settlement from southern brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2013, 55, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farias, I.F.; de Souza, E.A.R.; Serpa, M.C.D.A.; Palha, F.S.; de Oliveira, G.M.B.; Labruna, M.B.; Horta, M.C. Serological evidence of Rickettsia in horses from a semi-arid Brazilian region. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Veterinária 2021, 30, e026220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, J.D.; Silva, P.W.; Arzua, M.; Barros-Battesti, D.M.; Martins, T.F.; Silva, A.M.; Vieira, T.S.; Labruna, M.B.; Vieira, R. Records of ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) on humans and distribution of spotted-fever cases and its tick vectors in Paraná State, southern Brazil. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavov, S.N.; Christova, I.S.; Ferreira, A.R.; Rodrigues, E.S.; Bianquini, M.L.; Hespanhol, M.R.; Covas, D.T.; Kashima, S. Serological evidence of Borrelia circulation among blood donors in the São Paulo state, Brazil. Transfus. Med. 2019, 29, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonoldi, V.L.N.; Yoshinari, N.H.; de Aniz, P.A.E.A.; Pereira, R.M.R. Innate and Th1/Th17 adaptive immunity in acute and convalescent Brazilian borreliosis disease. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 25, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFee, R.B. Tick vectors and Tick-Borne illnesses overview. Dis. Mon. 2018, 64, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.L. Clinical Manifestations and Treatment of Lyme Disease. Clin. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F. Canine vector-borne diseases in Brazil. Parasites Vectors 2008, 1, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Littman, M.P.; Gerber, B.; Goldstein, R.E.; Labato, M.A.; Lappin, M.R.; Moore, G.E. ACVIM consensus update on Lyme borreliosis in dogs and cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 887–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, R.G.; Krämer, F. A review on the occurrence of companion vector-borne diseases in pet animals in Latin America. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webber, B.; Burganowski, R.; Colton, L.; Escobar, J.; Pathak, S.; Gambino-Shirley, K. Lyme disease overdiagnosis in a large healthcare system: A population-based, retrospective study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, C.B.; Scheeler, V.M.; Aucott, J.N. Lyme Disease in the Era of COVID-19: A Delayed Diagnosis and Risk for Complications. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2021, 2021, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Liu, Q. Rapid, simple, and sensitive detection of the ompB gene of spotted fever group rickettsiae by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gehrke, F.S.; Angerami, R.N.; Marrelli, M.T.; De Souza, M.E.R.; Nascimento, M.E.M.D.; Colombo, B.S.; Da Silva, L.J.; Schumaker, T.T. Molecular Characterization of Mediterranean Spotted Fever Rickettsia Isolated From a European Traveler in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. J. Travel Med. 2012, 20, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giulieri, S.; Jaton, K.; Cometta, A.; Trellu, L.T.; Greub, G. Development of a duplex real time PCR for the detection of Rickettsia spp. and typhus group rickettsia in clinical samples. FEMS Immunol. Med Microbiol. 2012, 64, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellati, T.J.; Barberio, D.M. Mechanisms of Dysregulated Antibody Response in Lyme Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 567252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly-Cirino, C.; Nkengasong, J.; Kettler, H.; Tongio, I.; Gay-Andrieu, F.; Escadafal, C.; Piot, P.; Peeling, R.W.; Gadde, R.; Boehme, C. Importance of diagnostics in epidemic and pandemic preparedness. BMJ Glob. Health 2019, 4, e001179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, M.D.; Dye, C.; Balasegaram, M.; Bréchot, C.; Mombouli, J.-V.; Røttingen, J.-A.; Tanner, M.; Boehme, C.C. Diagnostic preparedness for infectious disease outbreaks. Lancet 2017, 390, 2211–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezerra, M.C.F.; Melo, A.L.T.; De Aguiar, D.M.; Pacheco, R.C.; Slhessarenko, R.D.; Taques, I.I.G.G. Seropositivity for Rickettsia spp. and Ehrlichia spp. in the human population of Mato Grosso, Central-Western Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2017, 50, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- da Silva, V.S.; de Santana, M.M.; Gomes, D.L.X.; de Medeiros, E.P.; Cordeiro, M.F.; Takenami, I. Baggio-Yoshinari syndrome: A literature review. Rev. Med. 2020, 99, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, S.D.E.; da Cunha, N.C.; Almosny, N.R.P. Brazilian spotted fever with an approach in veterinary medicine and one health perspective. Vet. Med. Int. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Nordone, S.K.; Yabsley, M.J.; Lund, R.B.; McMahan, C.S.; Gettings, J.R. Quantifying the relationship between human Lyme disease and Borrelia burgdorferi exposure in domestic dogs. Geospat. Health 2019, 14, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohr, B.; Fingerle, V.; Norris, D.; Hunfeld, K.-P. Laboratory diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis: Current state of the art and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 55, 219–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinari, N.H.; Mantovani, E.; Bonoldi, V.L.N.; Marangoni, R.G.; Gauditano, G. Doença de Lyme-símile brasileira ou síndrome Baggioyoshinari: Zoonose exótica e emergente transmitida por carrapatos. Rev. Assoc. Médica Bras. 2010, 56, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miziara, C.S.M.G.; Serrano, V.A.G.; Yoshinari, N. Passage of Borrelia burgdorferi through diverse Ixodid hard ticks causes distinct diseases: Lyme borreliosis and Baggio-Yoshinari syndrome. Clinics 2018, 73, e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torina, A.; Blanda, V.; Villari, S.; Piazza, A.; La Russa, F.; Grippi, F.; La Manna, M.P.; Di Liberto, D.; De La Fuente, J.; Sireci, G. Immune response to Tick-Borne hemoparasites: Host adaptive immune response mechanisms as potential targets for therapies and vaccines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.T.; Satjanadumrong, J.; Hughes, T.; Stenos, J.; Blacksell, S.D. Diagnosis of spotted fever group Rickettsia infections: The Asian perspective. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Springer, A.; Glass, A.; Probst, J.; Strube, C. Tick-Borne zoonoses and commonly used diagnostic methods in human and veterinary medicine. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 4075–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baarsma, M.E.; Vrijlandt, A.; Ursinus, J.; Zaaijer, H.L.; Jurriaans, S.; van Dam, A.P.; Hovius, J.W. Diagnostic performance of the ZEUS Borrelia VlsE1/pepC10 assay in European LB patients: A case–control study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 41, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnicker, M.J.; Jespersen, D.J.; Harring, J.A.; Rollins, L.O.; Bryant, S.C.; Beito, E.M. Evaluation of Two Commercial Systems for Automated Processing, Reading, and Interpretation of Lyme Borreliosis Western Blots. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 2216–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molins, C.R.; Delorey, M.J.; Replogle, A.; Sexton, C.; Schriefer, M.E. Evaluation of bioMérieux’s Dissociated Vidas Lyme IgM II and IgG II as a First-Tier Diagnostic Assay for Lyme Disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ocias, L.F.; Jensen, B.B.; Villumsen, S.; Lebech, A.-M.; Skarphedinsson, S.; Dessau, R.B.; Krogfelt, K.A. Rickettsioses in Denmark: A retrospective survey of clinical features and travel history. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, N.B.; Rathi, A.N.; Goodman, M.H.; Aghai, Z.H. Rickettsial diseases in central India: Proposed clinical scoring system for early detection of spotted fever. Indian Pediatr. 2011, 48, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, S.; Ambroise, S.; Gunasekaran, D.; Hanifah, M.; Sangeetha, B.; Pradeep, J.; Sarangapani, K. Serological evidence of spotted fever group rickettsiosis in and around Puducherry, south India—A three years study. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2018, 55, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawełczyk, A.; Bednarska, M.; Kowalska, J.D.; Uszyńska-Kałuża, B.; Radkowski, M.; Welc-Falęciak, R. Seroprevalence of six pathogens transmitted by the Ixodes ricinus ticks in asymptomatic individuals with HIV infection and in blood donors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, M.J.; Black, K.E.; Lanza-Perea, M.; Sharma, B.; Gibson, K.; Stone, D.M.; George, A.; Nair, A.D.S.; Ganta, R.R. Initial development and preliminary evaluation of a multiplex bead assay to detect antibodies to Ehrlichia canis, Anaplasma platys, and Ehrlichia chaffeensis outer membrane peptides in naturally infected dogs from Grenada, West Indies. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2016, 29, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydin, S. A short history, principles, and types of ELISA, and our laboratory experience with peptide/protein analyses using ELISA. Peptides 2015, 72, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Xu, P.; Gallagher, S. Immunoblotting and Immunodetection. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2017, 74, 6.2.1–6.2.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondakova, A.N.; Vinogradov, E.; Lindner, B.; A Knirel, Y.; Amano, K.-I. Structural studies on the lipopolysaccharide core of Proteus OX strains used in Weil–Felix test: A mass spectrometric approach. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 2697–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prado, I.C.; Chino, M.E.T.A.; Dos Santos, A.L.; Souza, A.L.A.; Pinho, L.G.; Lemos, E.R.S.; De-Simone, S.G. Development of an electrochemical immunosensor for the diagnostic testing of spotted fever using synthetic peptides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoolo, L.; Djokic, V.; Rocha, S.C.; Parveen, N. Pathogenesis of Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti in TLR4-Competent and TLR4 -dysfunctional C3H mice. Cell. Microbiol. 2021, 23, e13350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukata, M.; Vamadevan, A.S.; Abreu, M.T. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and Nod-like receptors (NLRs) in inflammatory disorders. Semin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, H.M.; Behravesh, C.B.; Bradley, K.K.; Dahlgren, F.S.; Drexler, N.A.; Dumler, J.S.; Folk, S.M.; Kato, C.Y.; Lash, R.R.; Levin, M.L.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Tickborne Rickettsial Diseases: Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and Other Spotted Fever Group Rickettsioses, Ehrlichioses, and Anaplasmosis—United States. MMWR. Recomm. Rep. 2016, 65, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, E.; Lin, Y.-P.; Cady, N.C. Recent Strategies for the Diagnosis of Early Lyme Disease. Sci. Prog. 2018, 101, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewmongkol, S.; Suwan, E.; Sirinarumitr, T.; Jittapalapong, S.; Fenwick, S.G.; Kaewmongkol, G. Detection of specific IgM and IgG antibodies in acute canine monocytic ehrlichiosis that recognize recombinant gp36 antigens. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, N.; Weisel, F.; Smita, S.; Joachim, S.; Kader, M.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Clouser, C.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; Chikina, M.; Vigneault, F.; et al. Liver Is a Generative Site for the B Cell Response to Ehrlichia muris. Immunity 2019, 51, 1088–1101.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesewski, E.; Johnson, B.N. Electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.; Jones, D.D.; Chatterjee, M.; McLaughlin, M.; MacNamara, K.; Winslow, G.M. Impaired Germinal Center Responses and Suppression of Local IgG Production during Intracellular Bacterial Infection. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5085–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortega-Vinuesa, J.L.; Bastos-González, D. A review of Fctors Afecting the Prformances of Ltex Aglutination Tsts. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2001, 12, 379–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalish, R.A.; McHugh, G.; Granquist, J.; Shea, B.; Ruthazer, R.; Steere, A.C. Persistence of Immunoglobulin M or Immunoglobulin G Antibody Responses to Borrelia burgdorferi 10–20 Years after Active Lyme Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- E Hechemy, K.; Anacker, R.L.; Philip, R.N.; Kleeman, K.T.; MacCormack, J.N.; Sasowski, S.J.; E Michaelson, E. Detection of Rocky Mountain Sotted Fver Atibodies by a Laex Aglutination Tst. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 12, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trevethan, R. Sensitivity, Specificity, and Predictive Values: Foundations, Pliabilities, and Pitfalls in Research and Practice. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmar, M.; Soleimani, M.; Oreizi, F.; Piazak, N.; Hossini, S.M.; Saghiri, R.; Zamani, Z. Purification of Periplasmic Flagellar Antigen from Borrelia microtti. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, L.; Anda, P.; Rodríguez, I.; Hechemy, K.E.; Raoult, D.; Casal, J. Evaluation of a latex agglutination test for Rickettsia conorii antibodies in seropositive patients. J. Med. Microbiol. 1989, 28, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kularatne, S.; Gawarammana, I. Validity of the Weil-Felix test in the diagnosis of acute rickettsial infections in Sri Lanka. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 423–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, K.A. An analysis of critical factors for quantitative immunoblotting. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, rs2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seriburi, V.; Ndukwe, N.; Chang, Z.; Cox, M.; Wormser, G. High frequency of false positive IgM immunoblots for Borrelia burgdorferi in Clinical Practice. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waddell, L.A.; Greig, J.; Mascarenhas, M.; Harding, S.; Lindsay, R.; Ogden, N. The Accuracy of Diagnostic Tests for Lyme Disease in Humans, A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of North American Research. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qurollo, B.A.; Stillman, B.A.; Beall, M.J.; Foster, P.; Hegarty, B.C.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Chandrashekar, R. Comparison of Anaplasma and Ehrlichia species–specific peptide ELISAs with whole organism–based immunofluorescent assays for serologic diagnosis of anaplasmosis and ehrlichiosis in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2021, 82, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrus, S.; Alleman, A.; Bark, H.; Mahan, S.M.; Waner, T. Comparison of three enzyme-linked immunosorbant assays with the indirect immunofluorescent antibody test for the diagnosis of canine infection with Ehrlichia canis. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 86, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, T.P.; Hanscom, J.L.; Hegarty, B.C.; Groat, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Comparison of an indirect immunofluorescence assay, western blot analysis, and a commercially available ELISA for detection of Ehrlichia canis antibodies in canine sera. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stradiotto, N.; Yamanaka, H.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Electrochemical sensors: A powerful tool in analytical chemistry. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2003, 14, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kouzmitcheva, G.A.; Petrenko, V.A.; Smith, G.P. Identifying Diagnostic Peptides for Lyme Disease through Epitope Discovery. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lokida, D.; Sudarmono, P.; Kosasih, H.; Butar-Butar, D.P.; Salim, G.; Antonjaya, U.; Sari, R.A.; Aman, A.T.; Parwati, I.; Arif, M.; et al. Comparison of Commercial Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Immunofluorescence Assay for Diagnosis of AcuteRickettsia typhiInfections. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanholo, P.V.; Razzino, C.A.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Prado, T.M.; Machado, S.A.; Sgobbi, L.F. Biomimetic electrochemical sensors: New horizons and challenges in biosensing applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 185, 113242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolotsky, A.; Butler, D.; Dong, C.; Gerace, K.; Glavin, N.R.; Muratore, C.; Robinson, J.A.; Ebrahimi, A. Two-Dimensional Materials in Biosensing and Healthcare: From In Vitro Diagnostics to Optogenetics and Beyond. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9781–9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Ye, K.; Jia, Z.; Xue, T.; Nie, A.; Xiang, J.; Mu, C.; Wang, B.; Wen, F.; Zhai, K.; et al. High-sensitivity and versatile plasmonic biosensor based on grain boundaries in polycrystalline 1LWS2 films. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 194, 113596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khristunova, Y.; Korotkova, E.; Kratochvil, B.; Barek, J.; Dorozhko, E.; Vyskocil, V.; Plotnikov, E.; Voronova, O.; Sidelnikov, V. Preparation and Investigation of Silver Nanoparticle–Antibody Bioconjugates for Electrochemical Immunoassay of Tick-Borne Encephalitis. Sensors 2019, 19, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ivanov, A.S.; Nikolaev, K.G.; Stekolshchikova, A.A.; Tesfatsion, W.T.; Yurchenko, S.O.; Novoselov, K.S.; Andreeva, D.V.; Rubtsova, M.Y.; Vorovitch, M.F.; Ishmukhametov, A.A.; et al. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Electrochemical Detection by Multilayer Perceptron on Liquid–Metal Interface. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 7352–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porwancher, R.B.; Hagerty, C.G.; Fan, J.; Landsberg, L.; Johnson, B.J.B.; Kopnitsky, M.; Steere, A.C.; Kulas, K.; Wong, S.J. Multiplex Immunoassay for Lyme Disease Using VlsE1-IgG and pepC10-IgM Antibodies: Improving Test Performance through Bioinformatics. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Branda, J.; A Body, B.; Boyle, J.; Branson, B.M.; Dattwyler, R.J.; Fikrig, E.; Gerald, N.J.; Gomes-Solecki, M.; Kintrup, M.; Ledizet, M.; et al. Advances in Serodiagnostic Testing for Lyme Disease Are at Hand. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 66, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosel, M.R.; Carolan, H.E.; Rebman, A.W.; Castro, S.; Massire, C.; Ecker, D.J.; Soloski, M.J.; Aucott, J.N.; Eshoo, M.W. Molecular testing of serial blood specimens from patients with early Lyme disease during treatment reveals changing coinfection with mixtures of Borrelia burgdorfer genotypes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00237-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arumugam, S.; Nayak, S.; Williams, T.; Maria, F.S.D.S.; Guedes, M.S.; Chaves, R.C.; Linder, V.; Marques, A.R.; Horn, E.J.; Wong, S.J.; et al. A Multiplexed Serologic Test for Diagnosis of Lyme Disease for Point-of-Care Use. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01142-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunev, S.S.; Hastey, C.J.; Hodzic, E.; Feng, S.; Barthold, S.W.; Baumgarth, N. Lymphoadenopathy during Lyme Borreliosis Is Caused by Spirochete Migration-Induced Specific B Cell Activation. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hastey, C.J.; Ochoa, J.; Olsen, K.J.; Barthold, S.W.; Baumgarth, N. MyD88- and TRIF-Independent Induction of Type I Interferon Drives Naive B Cell Accumulation but Not Loss of Lymph Node Architecture in Lyme Disease. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 1548–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hastey, C.J.; Elsner, R.A.; Barthold, S.W.; Baumgarth, N. Delays and Diversions Mark the Development of B Cell Responses to Borrelia burgdorferi Infection. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5612–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsner, R.A.; Hastey, C.J.; Olsen, K.J.; Baumgarth, N. Suppressionof long-lived humoral immunity following Borrelia burgdorferi infection. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsner, R.A.; Hastey, C.J.; Baumgarth, N. CD4+ T Cells Promote Antibody Production but Not Sustained Affinity Maturation during Borrelia burgdorferi Infection. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaya, E.; Fernández-Brime, S.; Vargas, R.; Lachlan, R.F.; Gueidan, C.; Ramírez-Mejía, M.; Lutzoni, F. The adaptive radiation of lichen-forming Teloschistaceae is associated with sunscreening pigments and a bark-to-rock substrate shift. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11600–11605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, A.R. Laboratory diagnosis of Lyme disease: Advances and challenges. Infect. Dis. Clin. 2015, 29, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabb, J.S.; Rapoport, E.; Han, I.; Lombardi, J.; Green, O. An antigen-targeting assay for Lyme disease: Combining aptamers and SERS to detect the OspA protein. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 41, 102528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehoe, E.R.; Fitzgerald, B.L.; Graham, B.; Islam, M.N.; Sharma, K.; Wormser, G.P.; Belisle, J.T.; Kirby, M.J. Biomarker selection and a prospective metabolite-based machine learning diagnostic for lyme disease. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutras, B.L.; Lochhead, R.B.; Kloos, Z.A.; Biboy, J.; Strle, K.; Booth, C.J.; Govers, S.K.; Gray, J.; Schumann, P.; Vollmer, W.; et al. Borrelia burgdorferi peptidoglycan is a persistent antigen inpatients with Lyme arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13498–13507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Carneiro, F.R.G.; Durans, A.M.; Gomes, L.R.; Morel, C.M.; Provance, D.W.; De-Simone, S.G. Performance assessment of a multi-epitope chimeric antigen for the serological diagnosis of acute Mayaro fever. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcon-Chino, M.E.T.; De-Simone, S.G. Recent Advances in the Immunologic Method Applied to Tick-Borne Diseases in Brazil. Pathogens 2022, 11, 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080870
Alcon-Chino MET, De-Simone SG. Recent Advances in the Immunologic Method Applied to Tick-Borne Diseases in Brazil. Pathogens. 2022; 11(8):870. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080870
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcon-Chino, Mônica E. T., and Salvatore G. De-Simone. 2022. "Recent Advances in the Immunologic Method Applied to Tick-Borne Diseases in Brazil" Pathogens 11, no. 8: 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080870
APA StyleAlcon-Chino, M. E. T., & De-Simone, S. G. (2022). Recent Advances in the Immunologic Method Applied to Tick-Borne Diseases in Brazil. Pathogens, 11(8), 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080870