A Retrospective Review on Severe Malaria in Colombia, 2007–2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Malaria in Colombia in 2007–2020
2.2. Cases of Severe Malaria in Colombia 2007–2020
2.3. Risk of Malaria and SM in Colombia in 2007–2020
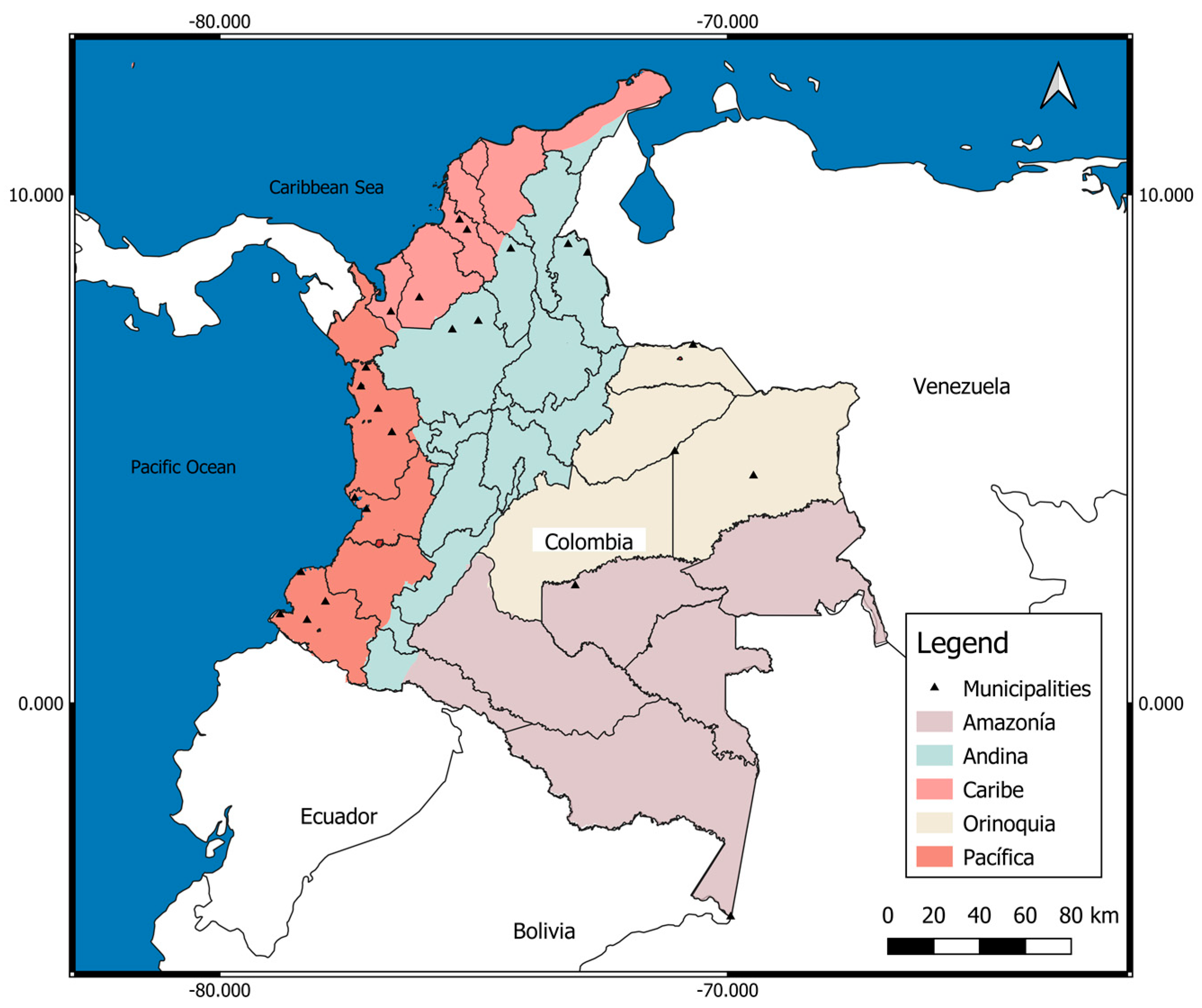
2.4. SM Risk in Colombia in 2015–2020 According to Year and Municipality
2.5. SM in 2015–2020 According to Residence Area, Ethnicity, Age, and Plasmodium Species
2.6. Organs and Systems Affected by SM in Colombia in 2015–2020
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Location, Study Type, Sample Size
4.2. Data Coverage (Sample Size)
4.3. Variables Studied
4.4. Study Participants
4.5. Bias Control
4.6. Definition of Severe Malaria Cases
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balaji, S.; Deshmukh, R.; Trivedi, V. Severe Malaria: Biology, Clinical Manifestation, Pathogenesis and Consequences. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2020, 57, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobaño, C.; Bardají, A.; Arévalo-Herrera, M.; Martínez-Espinosa, F.E.; Bôtto-Menezes, C.; Padilla, N.; Menegon, M.; Kochar, S.; Kochar, S.K.; Unger, H.; et al. Cytokine Signatures of Plasmodium Vivax Infection during Pregnancy and Delivery Outcomes. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro-Narváez, P.E.; Lopez-Perez, M.; Rengifo, L.M.; Padilla, J.; Herrera, S.; Arévalo-Herrera, M. Clinical and Epidemiological Aspects of Complicated Malaria in Colombia, 2007–2013. Malar. J. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, A.T.; Ramírez, J.F.; Martínez, S.P. A Descriptive Study of 16 Severe Plasmodium Vivax Cases from Three Municipalities of Colombia between 2009 and 2013. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de la Protección Social. Guía Protocolo Para La Vigilancia En Salud Pública de La Malaria. INS 2020. Available online: https://www.hosdenar.gov.co/images/protoc_ficha_temas_consulta/protocolos2020/Pro_Malaria.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Ministerio de Salud Colombiano. Guía para la Atención Clínica Integral del Paciente con Malaria 2010. Available online: https://www.paho.org/col/dmdocuments/CLINICA_MALARIA.PDF (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Padilla-Rodríguez, J.C.; Álvarez Uribe, G.; Montoya Araujo, R.; Chaparro Narvaez, P.; Herrera Valencia, S. Epidemiology and Control of Malaria in Colombia. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Fonseca, J. The Epidemiology of Malaria in Colombia: A Heretical View. Soc. Med. 2020, 13, 140–147. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Fonseca, J.; Cardona-Arias, J.A. Overview of Epidemiology of Malaria Associated with Pregnancy in Northwestern Colombia 1985–2020. J. Commun. Dis. 2021, 53, 140–147. [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos, A.; Chaparro-Narváez, P.; Morales-Plaza, C.D.; Alzate, A.; Padilla, J.; Arévalo, M.; Herrera, S. Malaria in Gold-Mining Areas in Colombia. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2016, 111, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, D.; Sánchez, D.Y.; Achury, G.; Díaz, F.E. Malaria En Poblaciones Con Ocupación Minera, Colombia, 2012–2018. Biomédica 2021, 41, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piraquive, C.; Angela, L.; Jiménez, D.; Patricia, D. Minería de Oro y Aumento de La Malaria: ¿qué Ocurre En Chocó? Instituto Nacional de Salud: Bogotá, Columbia, 2019; p. 4.
- Padilla, J.C.; Chaparro, P.E.; Molina, K.; Arevalo-Herrera, M.; Herrera, S. Is There Malaria Transmission in Urban Settings in Colombia? Malar. J. 2015, 14, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Fonseca, J. La Región “Urabá Antioqueño-Cuencas Altas de Los Ríos Sinú y San Jorge-Bajo Cauca Antioqueño”: “Guarida” Del Paludismo Colombiano. Rev. Univ. Ind. Santander. Salud 2017, 49, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.K. Evidence and Implications of Mortality Associated with Acute Plasmodium Vivax Malaria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Acero, C.; Velasco, M.C.; Avilés-Vergara, P.A.; Ricardo-Caldera, D.M.; Alvis, E.M.; Montoya, J.R.; Acosta, M.F.Y. Liver and Kidney Dysfunction, Hypoglycemia, and Thrombocytopenia in Plasmodium Vivax Malaria Patients at a Colombian Northwest Region. Parasite Epidemiol. Control. 2021, 13, e00203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobón-Castaño, A.; Betancur, J.E.; Malaria, G. Severe Malaria in Pregnant Women Hospitalized between 2010 and 2014 in the Department of Antioquia (Colombia). Biomed. Rev. Inst. Nac. Salud 2019, 39, 354–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobón-Castaño, A.; Escobar, S.B.; Castro, C.G. Urinalysis and Clinical Correlations in Patients with P. Vivax or P. Falciparum Malaria from Colombia. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 2017, 7868535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Morales, D.A.; Montoya-Franco, E.; Sanchez-Aristizabal, V.d.P.; Machado-Alba, J.E.; Rodríguez-Morales, A.J. Severe and Benign Plasmodium Vivax Malaria in Emberá (Amerindian) Children and Adolescents from an Endemic Municipality in Western Colombia. J. Infect. Public Health 2016, 9, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, M.A.; Lopez-Perez, M.; Vallejo, A.F.; Herrera, S.; Arévalo-Herrera, M.; Escalante, A.A. Multiplicity of Infection and Disease Severity in Plasmodium Vivax. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo-Herrera, M.; Lopez-Perez, M.; Medina, L.; Moreno, A.; Gutierrez, J.B.; Herrera, S. Clinical Profile of Plasmodium Falciparum and Plasmodium Vivax Infections in Low and Unstable Malaria Transmission Settings of Colombia. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foko, L.P.K.; Arya, A.; Sharma, A.; Singh, V. Epidemiology and Clinical Outcomes of Severe Plasmodium Vivax Malaria in India. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlani, M.; Kojom, L.P.; Mishra, N.; Dogra, V.; Singh, V. Severe Vivax Malaria Trends in the Last Two Years: A Study from a Tertiary Care Centre, Delhi, India. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, R.E.; Battle, K.E.; Mendis, K.N.; Smith, D.L.; Cibulskis, R.E.; Baird, J.K.; Hay, S.I. Global Epidemiology of Plasmodium Vivax. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imirzalioglu, C.; Soydan, N.; Schaller, M.; Bretzel, R.G.; Chakraborty, T.; Domann, E. Diagnosis of Mixed Plasmodium Malariae and P. Vivax Infection in a Development Aid Volunteer by Examination of Bone-Marrow Specimens by Real-Time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2307–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, H.; Diaz-Varela, M.; Segui-Barber, J.; Roobsoong, W.; Baro, B.; Garcia-Silva, S.; Galiano, A.; Gualdrón-López, M.; Almeida, A.C.G.; Brito, M.A.M.; et al. Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Plasmodium Vivax Patients Signal Spleen Fibroblasts via NF-KB Facilitating Parasite Cytoadherence. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Correaid, J.; Yasnot-Acosta, M.F.; Tovar, N.C.; Velasco-Parejaid, M.C.; Easton, A.; Rodriguez, A. Atypical Memory B-Cells and Autoantibodies Correlate with Anemia during Plasmodium Vivax Complicated Infections. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroost, K.; Pham, T.T.; Opdenakker, G.; den Steen, P.E. van The Immunological Balance between Host and Parasite in Malaria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 208–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, J.; Hurtado, S.; Alvarez, V.H.; Arévalo, M.; Herrera, S. Characterization of Plasmodium Malariae Transmission in Four Malaria Endemic Regions in Colombia. Biomédica 2001, 21, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Camargo-Ayala, P.A.; Cubides, J.R.; Niño, C.H.; Camargo, M.; Rodríguez-Celis, C.A.; Quiñones, T.; Sánchez-Suárez, L.; Patarroyo, M.E.; Patarroyo, M.A. High Plasmodium Malariae Prevalence in an Endemic Area of the Colombian Amazon Region. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño, C.H.; Cubides, J.R.; Camargo-Ayala, P.A.; Rodríguez-Celis, C.A.; Quiñones, T.; Cortés-Castillo, M.T.; Sánchez-Suárez, L.; Sánchez, R.; Patarroyo, M.E.; Patarroyo, M.A. Plasmodium Malariae in the Colombian Amazon Region: You Don’t Diagnose What You Don’t Suspect. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.; Mendoza, N. Análisis de La Red de Diagnóstico de Malaria, 2008. Nova 2009, 7, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotepui, M.; Kotepui, K.U.; Milanez, G.D.; Masangkay, F.R. Global Prevalence and Mortality of Severe Plasmodium Malariae Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. Declaración de La Iniciativa STROBE (Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology): Directrices Para La Comunicación de Estudios Observacionales. Gac. Sanit. 2008, 22, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Malaria a | Severe Malaria a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Cases | API-aj 103 | Cases | Rate-aj 105 |
| 2007 | 110,389 | 8377 | 188 | 1427 |
| 2008 | 61,701 | 4957 | 217 | 1743 |
| 2009 | 149,999 | 12,826 | 288 | 2463 |
| 2010 | 115,884 | 10,185 | 706 | 6205 |
| 2011 | 62,716 | 5675 | 541 | 4896 |
| 2012 | 58,422 | 5337 | 324 | 2960 |
| 2013 | 60,383 | 5627 | 485 | 4519 |
| 2014 | 39,762 | 3664 | 334 | 3078 |
| 2015 | 53,254 | 4852 | 782 | 7125 |
| 2016 | 90,296 | 8135 | 1515 | 13,649 |
| 2017 | 52,954 | 4775 | 1015 | 9152 |
| 2018 | 62,141 | 5251 | 940 | 7943 |
| 2019 | 78,513 | 6559 | 1295 | 10,819 |
| 2020 | 64,536 | 5343 | 1251 | 10,356 |
| 1,060,950 | 9881 | |||
| Total malaria | ||||
| r | Slope b | |||
| Cases | −0.465 | −6.37766 × 10−5 | ||
| API 103 | −0.437 | −0.729 | ||
| Severe malaria | ||||
| Cases | 0.835 | 0.008 | ||
| Rate 105 | 0.823 | 0.906 | ||
| Municipality | Department; Region | Cases 5 y | Cases/Year | Population 2020 | Rate 105-aj |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chalán | Sucre; Costa Atlántica | 230 | 46 | 4604 | 999.13 |
| Unión Panamericana | Chocó; Cuenca del Atrato | 156 | 31 | 6982 | 446.86 |
| Orocué | Casanare; Orinoquia | 230 | 46 | 12,652 | 363.58 |
| Arauca | Arauca, Orinoquia | 1667 | 333 | 96,814 | 344.37 |
| El Retorno | Guaviare; Amazonia | 128 | 26 | 13,722 | 186.56 |
| El Tarra | Norte Santander, Andina | 186 | 37 | 21,926 | 169.66 |
| El Charco | Nariño; Costa Pacífica | 186 | 37 | 22,550 | 164.97 |
| Tiquisio | Bolívar; Bajo Magdalena | 156 | 31 | 19,034 | 163.92 |
| Litoral San Juan | Chocó; Costa Pacífica | 186 | 37 | 22,890 | 162.52 |
| Bojayá | Chocó; Cuenca del Atrato | 100 | 20 | 12,326 | 162.26 |
| Sucre | Sucre; Costa Atlántica | 198 | 40 | 30,814 | 128.51 |
| Alto Baudó | Chocó; Costa Pacífica | 128 | 26 | 28,293 | 90.48 |
| Ituango | Antioquia; Zona Andina | 111 | 22 | 27,789 | 79.89 |
| Istmina | Chocó; Cuenca del Atrato | 111 | 22 | 30,806 | 72.06 |
| El Bagre | Antioquia; Bajo Cauca | 186 | 37 | 53,846 | 69.09 |
| Leticia | Amazonas; Amazonia | 1667 | 333 | 505,334 | 65.98 |
| Timbío | Cauca; Costa Pacífica | 116 | 23 | 36,287 | 63.93 |
| Barbacoas | Nariño; Costa Pacífica | 152 | 30 | 56,526 | 53.78 |
| Tibú | Norte Santander; Catatumbo | 156 | 31 | 58,721 | 53.13 |
| Cumaribo | Vichada; Amazonia | 198 | 40 | 78,863 | 50.21 |
| Chigorodó | Antioquia; Urabá | 127 | 25 | 59,836 | 42.45 |
| Tumaco | Nariño, Costa Pacífica | 493 | 99 | 257,052 | 38.36 |
| Tierralta | Córdoba; Cuenca alta Sinú | 116 | 23 | 95,177 | 24.38 |
| Buenaventura | Valle Cauca, Costa Pacífica | 298 | 60 | 311,827 | 19.11 |
| Organ or System | Code of O–S | Organ–System Affected | n | % | Ac-% | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single organ or system | 1 | Hematologic | 3922 | 54.9 | 54.9 | 1 organ or system: 6114 cases; 86% |
| 2 | Liver | 651 | 9.1 | 64 | ||
| 3 | Renal | 304 | 4.3 | 68.3 | ||
| 4 | Pulmonary | 134 | 1.9 | 70.1 | ||
| 5 | Cerebral | 113 | 1.6 | 71.7 | ||
| 6 | Other (no 1 to 5) | 990 | 13.9 | 85.6 | ||
| Hematic | 7 | Hematic–Hepatic | 351 | 4.9 | 90.5 | 2 organs or systems: 12% |
| 8 | Hematic–Renal | 89 | 1.2 | 91.7 | ||
| 9 | Hematic–Pulmonary | 42 | 0.6 | 92.3 | ||
| 10 | Hematic–Cerebral | 24 | 0.3 | 92.7 | ||
| 11 | Hematic–Other | 180 | 2.5 | 95.2 | ||
| Hepatic | 12 | Hepatic–Renal | 82 | 1.1 | 96.3 | |
| 13 | Hepatic–Pulmonary | 11 | 0.2 | 96.5 | ||
| 14 | Hepatic–Cerebral | 8 | 0.1 | 96.6 | ||
| 15 | Hepatic–Other | 31 | 0.4 | 97 | ||
| Renal | 16 | Renal–Pulmonary | 8 | 0.1 | 97.1 | |
| 17 | Renal–Cerebral | 10 | 0.1 | 97.3 | ||
| 18 | Renal–Other | 12 | 0.2 | 97.4 | ||
| Pulmonary | 19 | Pneumo–Cerebral | 11 | 0.2 | 97.6 | |
| 20 | Pneumo–Other | 11 | 0.2 | 97.7 | ||
| Cerebral | 21 | Cerebral–Other | 6 | 0.1 | 97.8 | |
| 3 O–S | 22 | Hematic–Hepatic–Renal | 103 | 1.4 | 99.3 | 3 organs or systems: 2% |
| 23 | Hematic–Renal–Pulmonary | 11 | 0.2 | 99.4 | ||
| 24 | Renal–Pneumo–Cerebral | 2 | 0 | 99.5 | ||
| 4 O–S | 25 | Hematic–Hepato–Reno–Pulmonary | 10 | 0.1 | 99.6 | --- |
| 26 | Hepato–Renal–Pneumo–Cerebral | 5 | 0.1 | 99.7 | ||
| 5 O–S | 27 | Hemato–Hepato–Renal–Pneumo– Cerebral | 24 | 0.3 | 100 | --- |
| Total | 7145 | 100 | --- | --- |
| O–S | Plasmodium | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. vivax | P. falciparum | P. malariae | Pv + Pf | Total | p(X2–Pearson) | ||
| (n = 4117) | (n = 2758) | (n = 43) | (n = 227) | (n = 7145) | |||
| Hematic | Yes | 2980 | 1707 | 28 | 147 | 4862 | 0.001 |
| No | 1137 | 1051 | 15 | 80 | 2283 | ||
| Hepatic | Yes | 773 | 563 | 12 | 46 | 1394 | 0.182 |
| No | 3344 | 2195 | 31 | 181 | 5751 | ||
| Renal | Yes | 282 | 294 | 3 | 18 | 597 | 0.001 |
| No | 3835 | 2464 | 40 | 209 | 6548 | ||
| Pulmonary | Yes | 178 | 101 | 5 | 11 | 295 | 0.040 |
| No | 3939 | 2657 | 38 | 216 | 6850 | ||
| Cerebral | Yes | 103 | 126 | 2 | 11 | 242 | 0.001 |
| No | 4014 | 2632 | 41 | 216 | 6903 | ||
| Other | Yes | 657 | 599 | 10 | 49 | 1315 | 0.001 |
| No | 3449 | 2155 | 32 | 178 | 5814 | ||
| O–S | Presence of O–S | Place of Residence (n; %) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MH (n = 3053; 43) | RN (n = 1032; 14) | RD (n = 3060; 43) | Total (n = 7145; 100) | (X2–Pearson) | ||
| Hematic | Yes | 2079; 43 | 635; 13 | 2148; 44 | 4862; 100 | 0.001 |
| No | 974 | 397 | 912 | 2283 | ||
| Hepatic | Yes | 655; 47 | 197; 6 | 542; 47 | 1394; 100 | 0.001 |
| No | 2398 | 835 | 2518 | 5751 | ||
| Renal | Yes | 288; 48 | 93; 16 | 216; 36 | 597; 100 | 0.003 |
| No | 2765 | 939 | 2844 | 6548 | ||
| Pulmonary | Yes | 118; 40 | 52; 18 | 125; 42 | 295 | 0.258 |
| No | 2935 | 980 | 2935 | 6850 | ||
| Cerebral | Yes | 118; 49 | 41; 17 | 83; 34 | 242 | 0.024 |
| No | 2935 | 991 | 2977 | 6903 | ||
| Criteria | WHO, Defined before 2010 | MoH, Defined after 2010 |
|---|---|---|
| Cerebral malaria | Impaired consciousness or coma (Blantyre score < 3 or Glasgow score < 9); unconsciousness with the possibility of waking up | Impaired consciousness or coma (Blantyre score < 3 or Glasgow score < 9); unconsciousness with the possibility of waking up |
| Renal dysfunction | Serum creatinine > 3.0 mg/dL and/or urine vol < 400 mL in 24 h (adults) or <12 mL/kg of body weight in 24 h (children) | Serum creatinine > 1.5 mg/dL |
| Hepatic dysfunction | Serum bilirubin > 3 mg/dL and altered liver function tests | Serum bilirubin > 1.5 mg/dL or aminotransferases > 40 U/L |
| Respiratory distress | Increased respiratory rate at admission, presence of abnormal lung sounds or pulmonary edema (X-rays) | Increased respiratory rate at admission, presence of abnormal lung sounds or pulmonary edema (X-rays) |
| Circulatory collapse or shock | SBP < 70 mm Hg in adults or <50 mm Hg in children (3–5 years) | SBP < 80 mm Hg in adults |
| Hyperemesis | >5 episodes in 24 h | Not applicable |
| Hyperpyrexia | Axillary temperature > 39.5 °C | Not applicable |
| Hypoglycemia | Blood glucose level < 40 mg/dL | Blood glucose level < 60 mg/dL |
| Severe anemia | Hemoglobin < 5 g/dL or hematocrit < 15% | Hemoglobin < 7 g/dL |
| DIC | Abnormal bleeding in the presence of laboratory evidence of DIC | Abnormal bleeding in the presence of laboratory evidence of DIC |
| Acidemia/acidosis and hyperlactemia | Acidemia/acidosis (clinical signs) | Plasmatic bicarbonate < 15 mmol/L or base excess > −10; acidemia pH < 7.35; lactate acid > 5 mmol/L |
| Hemoglobinuria | Macroscopic hemoglobinuria | Macroscopic hemoglobinuria and positive urine dipstick |
| Hyperparasitemia | >100,000 asexual parasites/μL of P. falciparum or in mixed infection with P. vivax and schizontemia | >50,000 asexual parasites/μL |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carmona-Fonseca, J.; Olivera, M.J.; Yasnot-Acosta, M.F. A Retrospective Review on Severe Malaria in Colombia, 2007–2020. Pathogens 2022, 11, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080893
Carmona-Fonseca J, Olivera MJ, Yasnot-Acosta MF. A Retrospective Review on Severe Malaria in Colombia, 2007–2020. Pathogens. 2022; 11(8):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080893
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarmona-Fonseca, Jaime, Mario J. Olivera, and María F. Yasnot-Acosta. 2022. "A Retrospective Review on Severe Malaria in Colombia, 2007–2020" Pathogens 11, no. 8: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080893
APA StyleCarmona-Fonseca, J., Olivera, M. J., & Yasnot-Acosta, M. F. (2022). A Retrospective Review on Severe Malaria in Colombia, 2007–2020. Pathogens, 11(8), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080893







