Inhibition of Melanization by Kojic Acid Promotes Cell Wall Disruption of the Human Pathogenic Fungus Fonsecaea sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
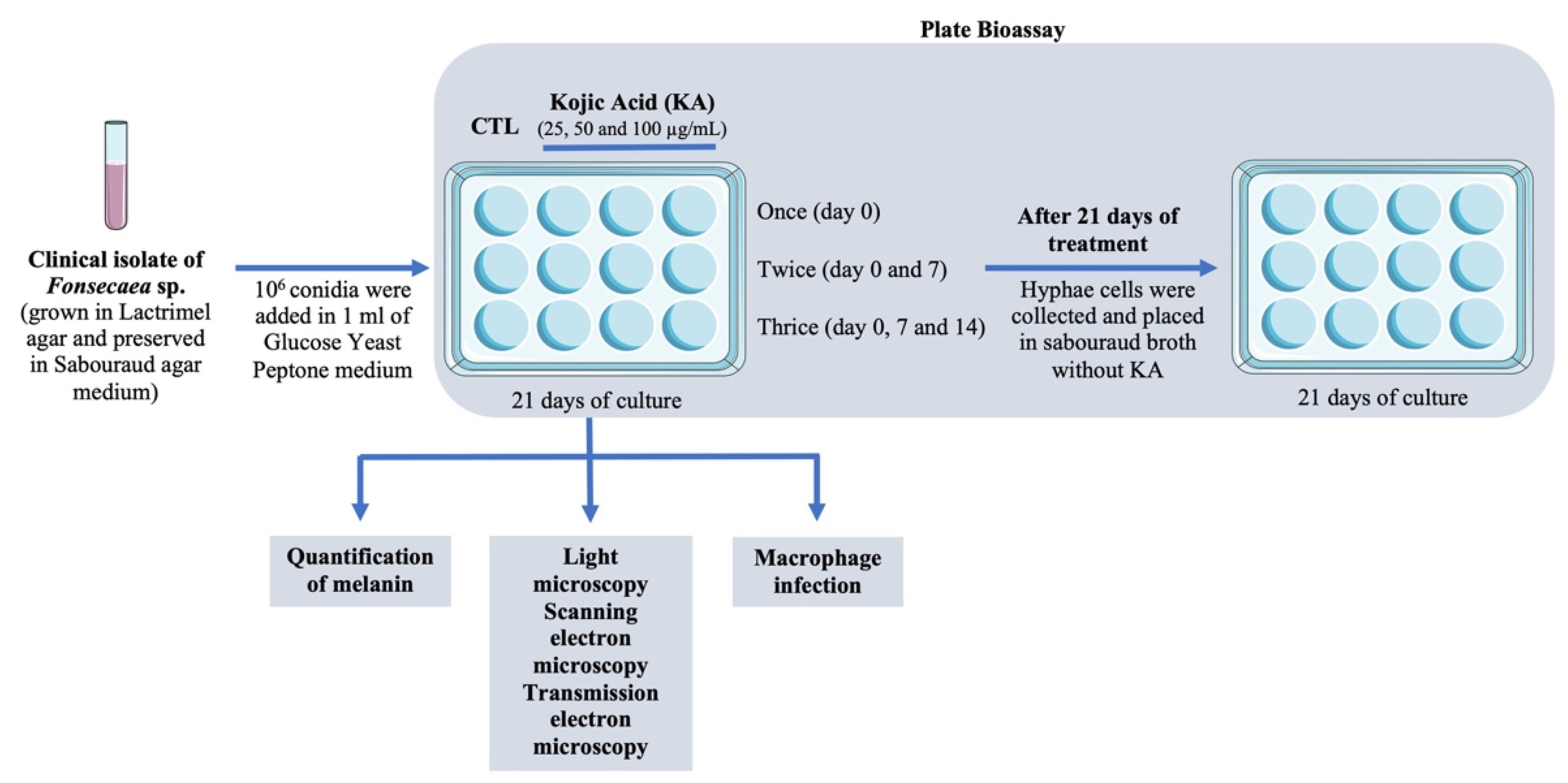
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtaining, Maintenance, and Cultivation of Clinical Isolate
2.2. Obtaining and Diluting Drugs
2.3. Plate Bioassay
2.4. Microscopy Analysis
2.5. Cytochemical Detection and Quantification of Melanin
2.6. Analysis of Vesicles in the Culture Supernatant
2.7. Cell Differentiation Analysis in KA-Treated Fungal Cultures and during Host Cell-Fungal Interactions
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of KA Action on the Melanization of Chromoblastomycosis Agent
3.2. Microscopy of Chromoblastomycosis Agent after KA Treatment
3.3. Quantification of Externalized Vesicles
3.4. TEM Analysis
3.5. Action of KA on Fungal Filamentation in Culture and During Fungus-Macrophage Interaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamza, S.H.; Mercado, P.J.; Skelton, H.G.; Smith, K.J. An Unusual Dematiaceous Fungal Infection of the Skin Caused by Fonsecaea Pedrosoi: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2003, 30, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifaz, A.; Vázquez-González, D.; Perusquía-Ortiz, A.M. Subkutane Mykosen: Chromoblastomykose, Sporotrichose Und Myzetom. JDDG J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. 2010, 8, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.W.C.L.; e Silva de Azevedo, C.d.M.P.; Vicente, V.A.; Queiroz-Telles, F.; Rodrigues, A.M.; de Hoog, G.S.; Denning, D.W.; Colombo, A.L. The Global Burden of Chromoblastomycosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, C.G.; Da Silva, J.P.; Da Silva, M.B.; Da Costa, P.F.; Salgado, U.I. Cutaneous Diffuse Chromoblastomycosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz-Telles, F.; Esterre, P.; Perez-Blanco, M.; Vitale, R.; Salgado, C.G.; Bonifaz, A. Chromoblastomycosis: An Overview of Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis and Treatment. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, A.P.; Regina, M.; Silva, R.; Fischman, O. Local Phagocytic Responses after Murine Infection with Different Forms of Fonsecaea Pedrosoi and Sclerotic Bodies Originating from an Inoculum of Conidiogenous Cells. Mycoses 2011, 54, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Duin, D.; Casadevall, A.; Nosanchuk, J.D. Melanization of Cryptococcus neoformans and Histoplasma Capsulatum Reduces Their Susceptibilities to Amphotericin B and Caspofungin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3394–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosanchuk, J.D.; Nimrichter, L.; Casadevall, A.; Rodrigues, M.L. A Role for Vesicular Transport of Macromolecules across Cell Walls in Fungal Pathogenesis. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2008, 1, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.B.; Thomaz, L.; Marques, A.F.; Svidzinski, A.E.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Casadevall, A.; Travassos, L.R.; Taborda, C.P. Resistance of Melanized Yeast Cells of Paracoccidioides Brasiliensis to Antimicrobial Oxidants and Inhibition of Phagocytosis Using Carbohydrates and Monoclonal Antibody to CD18. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2009, 104, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prates, R.A.; Fuchs, B.B.; Mizuno, K.; Naqvi, Q.; Kato, I.T.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Mylonakis, E.; Tegos, G.P.; Hamblin, M.R. Effect of Virulence Factors on the Photodynamic Inactivation of Cryptococcus neoformans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Youngchim, S.; Zamith-Miranda, D.; Nosanchuk, J.D. Fungal Melanin and the Mammalian Immune System. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakhage, A.A.; Bruns, S.; Thywissen, A.; Zipfel, P.F.; Behnsen, J. Interaction of Phagocytes with Filamentous Fungi. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erwig, L.P.; Gow, N.A.R. Interactions of Fungal Pathogens with Phagocytes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Sun, J.; Lu, S.; Qin, J.; Xi, L.; Zhang, J. Transcriptional Profiling of Macrophages Infected with Fonsecaea monophora. Mycoses 2019, 62, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Jung, H.M.; Kim, S.Y. 1,8-Dihydroxynaphthalene (DHN)-Melanin Biosynthesis Inhibitors Increase Erythritol Production in Torula Corallina, and DHN-Melanin Inhibits Erythrose Reductase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3427–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, K.; Streibel, M.; Jahn, B.; Haase, G.; Brakhage, A.A. Biosynthesis of Fungal Melanins and Their Importance for Human Pathogenic Fungi. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2003, 38, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selinheimo, E.; Autio, K.; Kruus, K.; Buchert, J. Elucidating the Mechanism of Laccase and Tyrosinase in Wheat Bread Making. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6357–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifaz, A.; Martínez-Soto, E.; Carrasco-Gerard, E.; Peniche, J. Treatment of Chromoblastomycosis with Itraconazole, Cryosurgery, and a Combination of Both. Int. J. Dermatol. 1997, 36, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Taborda, P.R.; Sanzovo, A.D. Alternate Week and Combination Itraconazole and Terbinafine Therapy for Chromoblastomycosis Caused by Fonsecaea Pedrosoi in Brazil. Med. Mycol. 2002, 40, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.G.M.; Pimentel, E.R.A.; Lacaz, C.S. Treatment of Chromomycosis by Cryosurgery with Liquid Nitrogen: 15 Years’ Experience. Int. J. Dermatol. 2003, 42, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, T.S.; Castro, L.G.M.; Nunes, R.S.; Gimenes, V.M.F.; Cury, A.E. Susceptibility of Sequential Fonsecaea Pedrosoi Isolates from Chromoblastomycosis Patients to Antifungal Agents. Mycoses 2004, 47, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, J.P.; Moreira, L.M.; Dutra de Carvalho, V.S.; dos Santos, F.V.; de Lima, C.J.; de Resende, M.A. In Vitro Photodynamic Therapy against Foncecaea pedrosoi and Cladophialophora carrionii. Mycoses 2013, 56, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, U.D.; Bortolussi, R.; Finlay, J.; McDonald, J.C.; Onyett, H.; Robinson, J.L.; Rousseau-Harsany, É.; Hui, C.P.S.; Le Saux, N.; Pickering, L.; et al. Antifungal Agents for the Treatment of Systemic Fungal Infections in Children. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 21, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.E. Current Concepts in Antifungal Pharmacology. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fávero Gimenes, V.M.; De Souza, M.D.G.; Ferreira, K.S.; Marques, S.G.; Gonçalves, A.G.; De Castro Lima Santos, D.V.; Pedroso e Silva, C.D.M.; Almeida, S.R. Cytokines and Lymphocyte Proliferation in Patients with Different Clinical Forms of Chromoblastomycosis. Microbes Infect. 2005, 7, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterre, P.; Queiroz-Telles, F. Management of Chromoblastomycosis: Novel Perspectives. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 19, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosfarizan, M.; Mohamed, M.S.; Suhaili, N.; Salleh, M.M.; Ariff, A.B. Kojic Acid: Applications and Development of Fermentation Process for Production. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 5, 24–37. [Google Scholar]
- Rukachaisirikul, V.; Kaeobamrung, J.; Panwiriyarat, W.; Saitai, P.; Sukpondma, Y.; Phongpaichit, S.; Sakayaroj, J. A New Pyrone Derivative from the Endophytic Fungus Penicillium Paxilli PSU-A71. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 1383–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagianni, M. Fungal Morphology and Metabolite Production in Submerged Mycelial Processes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2004, 22, 189–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.S. An Updated Review of Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 2440–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R. From Miso, Saké and Shoyu to Cosmetics: A Century of Science for Kojic Acid. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 1046–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chusiri, Y.; Wongpoomchai, R.; Kakehashi, A.; Wei, M.; Wanibuchi, H.; Vinitketkumnuan, U.; Fukushima, S. Non-Genotoxic Mode of Action and Possible Threshold for Hepatocarcinogenicity of Kojic Acid in F344 Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chee, H.Y.; Lee, E.H. Fungistatic Activity of Kojic Acid Against Human Pathogenic Fungi and Inhibition of Melanin-Production in Cryptococcus neoformans. Microbiology 2003, 31, 248–250. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, A.P.D.; Carvalho, A.S.C.; Santos, A.S.; Alves, C.N.; do Nascimento, J.L.M.; Silva, E.O. Kojic Acid, a Secondary Metabolite from Aspergillus Sp., Acts as an Inducer of Macrophage Activation. Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, Y.; Akamatsu, H. Kojic Acid Scavenges Free Radicals While Potentiating Leukocyte Functions Including Free Radical Generation. Inflammation 1991, 15, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, J.P.; Rodrigues, A.P.D.; Farias, L.H.S.; Frade, P.C.R.; Da Silva, B.J.M.; Do Nascimento, J.L.M.; Silva, E.O. Biological Effects of Kojic Acid on Human Monocytes in Vitro. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Hirai, Y.; Hirai, H.; Hoffmann, K.F. Schistosome Egg Production Is Dependent upon the Activities of Two Developmentally Regulated Tyrosinases. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.P.D.; Farias, L.H.S.; Carvalho, A.S.C.; Santos, A.S.; Do Nascimento, J.L.M.; Silva, E.O. A Novel Function for Kojic Acid, a Secondary Metabolite from Aspergillus Fungi, as Antileishmanial Agent. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Campbell, B.C.; Chan, K.L.; Mahoney, N.; Haff, R.P. Synergism of Antifungal Activity between Mitochondrial Respiration Inhibitors and Kojic Acid. Molecules 2013, 18, 1564–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, R.W. Permanent Stained Mycological Preparations Obtained by Slide Culture. Mycologia 1950, 42, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, R.; Sugita, T.; Jacobson, E.S.; Shinoda, T. Effects of Melanin upon Susceptibility of Cryptococcus to Antifungals. Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 47, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youngchim, S.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Pornsuwan, S.; Kajiwara, S.; Vanittanakom, N. The Role of L-DOPA on Melanization and Mycelial Production in Malassezia Furfur. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.L.; Nimrichter, L.; Oliveira, D.L.; Frases, S.; Miranda, K.; Zaragoza, O.; Alvarez, M.; Nakouzi, A.; Feldmesser, M.; Casadevall, A. Vesicular Polysaccharide Export in Cryptococcus neoformans Is a Eukaryotic Solution to the Problem of Fungal Trans-Cell Wall Transport. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, K.L.; Proia, A.D.; Puri, P.K. Fontana-Masson Stain in Fungal Infections. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, T.; Kondoh, H.; Hiratsuka, J.; Mishima, Y. Enhanced Melanogenesis Induced by Tyrosinase Gene-Transfer Increases Boron-Uptake and Killing Effect of Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Amelanotic Melanoma. Pigment Cell Res. 1998, 11, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revankar, S.G.; Sutton, D.A. Melanized Fungi in Human Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 884–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenman, H.C.; Frases, S.; Nicola, A.M.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Casadevall, A. Vesicle-Associated Melanization in Cryptococcus neoformans. Microbiology 2009, 155, 3860–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, R.; Jiang, Z.; Friedman, M.; Dadachova, E. The Effects of Gamma Radiation, UV and Visible Light on ATP Levels in Yeast Cells Depend on Cellular Melanization. Fungal Biol. 2011, 115, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajo, A.; Bryan, R.A.; Friedman, M.; Burger, R.M.; Levitsky, Y.; Casadevall, A.; Magliozzo, R.S.; Dadachova, E. Protection of Melanized Cryptococcus neoformans from Lethal Dose Gamma Irradiation Involves Changes in Melanin’s Chemical Structure and Paramagnetism. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Jang, J.Y.; Jeon, S.J.; Lee, H.W.; Bae, C.H.; Yeo, J.H.; Lee, H.B.; Kim, I.S.; Park, H.W.; Kim, J.C. Nematicidal Activity of Kojic Acid Produced by Aspergillus oryzae against Meloidogyne incognita. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, C.; Kang, X.; Xie, Q. Effective Immobilization of Tyrosinase via Enzyme Catalytic Polymerization of L-DOPA for Highly Sensitive Phenol and Atrazine Sensing. Talanta 2016, 160, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, G.; Penalva, M.A.; Riquelme, M.; Wösten, H.A.; Harris, S.D. Cell Biology of Hyphal Growth. In The Fungal Kingdom; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 231–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.A.; Gómez, B.L.; Mora-Montes, H.M.; Mackenzie, K.S.; Munro, C.A.; Brown, A.J.P.; Gow, N.A.R.; Kibbler, C.C.; Odds, F.C. Melanin Externalization in Candida albicans Depends on Cell Wall Chitin Structures. Eukaryot. Cell 2010, 9, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Free, S.J. Fungal Cell Wall Organization and Biosynthesis. In Advances in Genetics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 81, pp. 33–82. ISBN 9780124076778. [Google Scholar]
- Franzen, A.J.; Cunha, M.M.L.; Batista, E.J.O.; Seabra, S.H.; Souza, W.D.E.; Rozental, S. Effects of Tricyclazole (5-Methyl-1,2,4-Triazol[3,4] Benzothiazole), a Specific DHN–Melanin Inhibitor, on the Morphology of Fonsecaea pedrosoi conidia and Sclerotic Cells. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2006, 69, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, R.; Lucentini, C.G.; Franco, M.E.E.; Petroselli, G.; Rosso, J.A.; Erra-Balsells, R.; Balatti, P.A.; Saparrat, M.C.N. Identification of an Intermediate for 1,8-Dihydroxynaphthalene-Melanin Synthesis in a Race-2 Isolate of Fulvia fulva (Syn. Cladosporium fulvum). Heliyon 2018, 4, e01036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Medeiros Nóbrega, Y.K.; Lozano, V.F.; de Araújo, T.S.; de Carvalho, D.D.; Bocca, A.L. The Cell Wall Fraction from Fonsecaea pedrosoi Stimulates Production of Different Profiles of Cytokines and Nitric Oxide by Murine Peritoneal Cells in Vitro. Mycopathologia 2010, 170, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, S.M.; Free, S.J. The Structure and Synthesis of the Fungal Cell Wall. BioEssays 2006, 28, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkowska-Kuleta, J.; Kozik, A. Cell Wall Proteome of Pathogenic Fungi. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.M.; Franzen, A.J.; Seabra, S.H.; Herbst, M.H.; Vugman, N.V.; Borba, L.P.; De Souza, W.; Rozental, S. Melanin in Fonsecaea Pedrosoi: A Trap for Oxidative Radicals. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.R.; Silva, J.R.A.; De Tássia Carvalho Cardoso, É.; Silva, E.O.; Lameira, J.; Do Nascimento, J.L.M.; Do Socorro Barros Brasil, D.; Alves, C.N. Combined Kinetic Studies and Computational Analysis on Kojic Acid Analogs as Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2014, 19, 9591–9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, E.M.; Canavieira, L.M.; Cardoso, É.T.C.; Silva, E.O.; Lameira, J.; Nascimento, J.L.M.; Eifler-Lima, V.L.; Macchi, B.M.; Sriram, D.; Bernhardt, P.V.; et al. Inhibition of Tyrosinase by 4H-Chromene Analogs: Synthesis, Kinetic Studies, and Computational Analysis. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 90, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, N.T.; Duah, K.; Larsen, B.; Wong, C.J.; Gingras, A.C.; O’Meara, T.R.; Robbins, N.; Veri, A.O.; Whitesell, L.; Cowen, L.E. The Macrophage-Derived Protein PTMA Induces Filamentation of the Human Fungal Pathogen Candida Albicans. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, J.M.; Alonso, M.F.; Childers, D.S.; Walls, C.A.; Mackenzie, K.; Pradhan, A.; Lewis, L.E.; Louw, J.; Avelar, G.M.; Larcombe, D.E.; et al. Immune Cells Fold and Damage Fungal Hyphae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020484118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wei, L.; Guo, T.; Tan, W. Detection of DOPA-Melanin in the Dimorphic Fungal Pathogen Penicillium marneffei and Its Effect on Macrophage Phagocytosis in Vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacelli, C.; Bryan, R.A.; Onofri, S.; Selbmann, L.; Shuryak, I.; Dadachova, E. Melanin Is Effective in Protecting Fast and Slow Growing Fungi from Various Types of Ionizing Radiation. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1612–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, C.M.; de Oliveira, H.C.; de Melo, W.d.C.M.A.; da Silva, J.d.F.; Assato, P.A.; Scorzoni, L.; Rossi, S.A.; de Paula e Silva, A.C.A.; Mendes-Giannini, M.J.S.; Fusco-Almeida, A.M. Anti-Immune Strategies of Pathogenic Fungi. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, J.A.L.; Moraes, L.S.d.; Sena, C.B.C.d.; Nascimento, J.L.M.d.; Rodrigues, A.P.D.; Silva, S.H.M.d.; Silva, E.O. Inhibition of Melanization by Kojic Acid Promotes Cell Wall Disruption of the Human Pathogenic Fungus Fonsecaea sp. Pathogens 2022, 11, 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080925
Pereira JAL, Moraes LSd, Sena CBCd, Nascimento JLMd, Rodrigues APD, Silva SHMd, Silva EO. Inhibition of Melanization by Kojic Acid Promotes Cell Wall Disruption of the Human Pathogenic Fungus Fonsecaea sp. Pathogens. 2022; 11(8):925. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080925
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Jorge Augusto Leão, Lienne Silveira de Moraes, Chubert Bernardo Castro de Sena, José Luiz Martins do Nascimento, Ana Paula D. Rodrigues, Silvia Helena Marques da Silva, and Edilene O. Silva. 2022. "Inhibition of Melanization by Kojic Acid Promotes Cell Wall Disruption of the Human Pathogenic Fungus Fonsecaea sp." Pathogens 11, no. 8: 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080925
APA StylePereira, J. A. L., Moraes, L. S. d., Sena, C. B. C. d., Nascimento, J. L. M. d., Rodrigues, A. P. D., Silva, S. H. M. d., & Silva, E. O. (2022). Inhibition of Melanization by Kojic Acid Promotes Cell Wall Disruption of the Human Pathogenic Fungus Fonsecaea sp. Pathogens, 11(8), 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080925





