Isolation and Characterization of a Viable Toxoplasma gondii from Captive Caracal (Caracal caracal)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Detection of Antibodies against T. gondii in Tissue Juice of Caracal
2.3. Isolation of Viable T. gondii from Caracal Tissues Using Bioassay in Mice
2.4. Histopathological Analysis and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification of T. gondii
2.5. Toxoplasma gondii Cell Cultivation and Genotyping
2.6. Evaluation of the Virulence of T. gondii Isolated from Caracal Using Swiss Mice
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
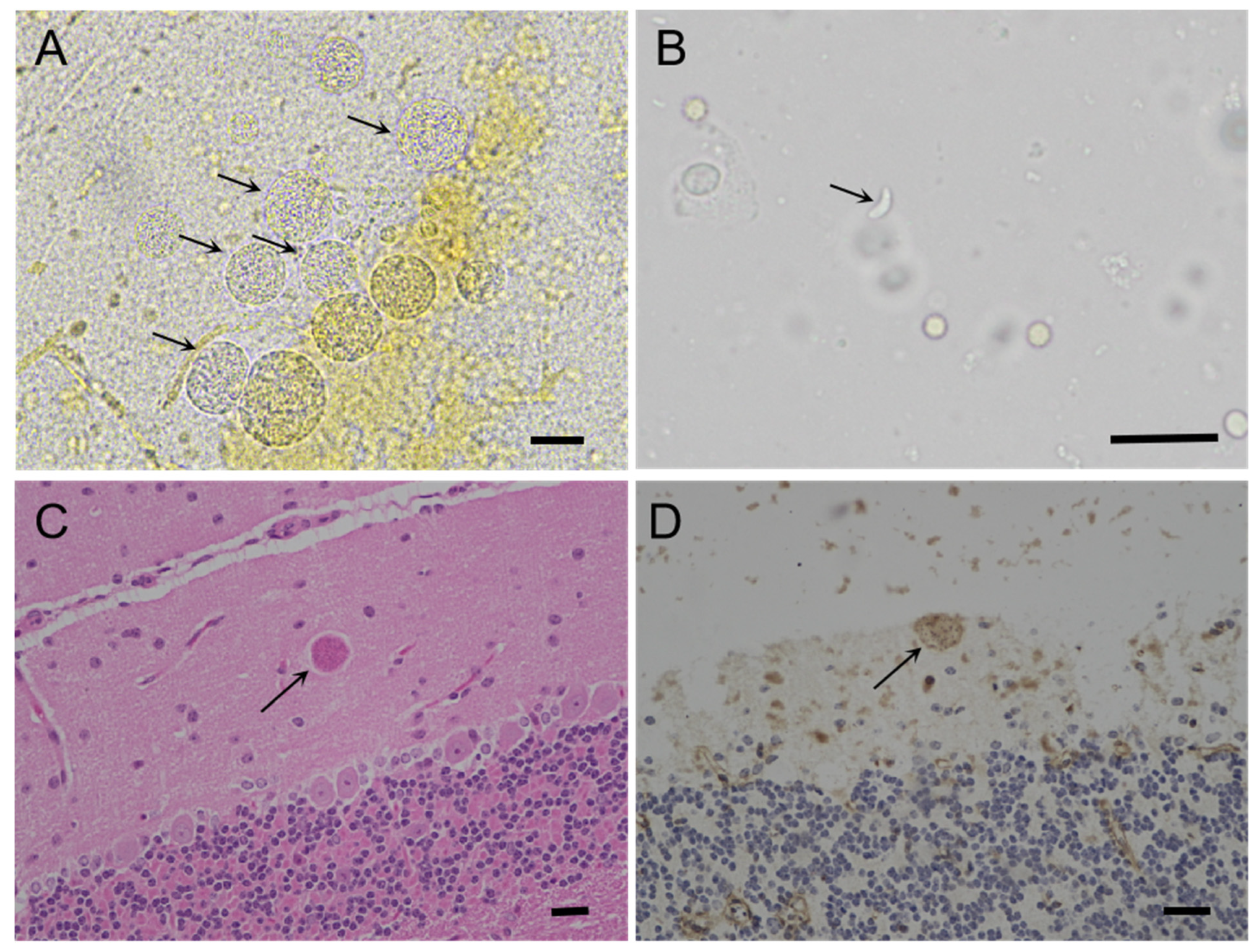
3.1. Clinical Findings, Pathology Lesions, and T. gondii Infection in Captive Caracal
3.2. Isolation of Viable T. gondii from the Tissues of the Caracal Using Bioassay in Mice
3.3. Genotyping and Virulence of TgCaracalCHn2
3.4. Morphology of TgCaracalCHn2 under Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
4. Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans; C.R.C. Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zulpo, D.L.; Sammi, A.S.; Dos Santos, J.R.; Sasse, J.P.; Martins, T.A.; Minutti, A.F.; Cardim, S.T.; de Barros, L.D.; Navarro, I.T.; Garcia, J.L. Toxoplasma gondii: A study of oocyst re-shedding in domestic cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 249, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Duration of immunity to shedding of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts by cats. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Cerqueira-Cezar, C.K.; Murata, F.H.A.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Yang, Y.R.; Su, C. All about toxoplasmosis in cats: The last decade. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 283, 109145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatam-Nahavandi, K.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Rahimi, M.T.; Pagheh, A.S.; Zarean, M.; Dezhkam, A.; Ahmadpour, E. Toxoplasma gondii infection in domestic and wild felids as public health concerns: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Gao, Y.M.; Deng, Y.; Lamberton, P.H.; Lu, D.B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in cats in mainland China. Parasit Vectors 2017, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, J.A.; Higginbotham, M.J.; Blagburn, B.L. Seroprevalence of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii in captive and free-ranging nondomestic felids in the United States. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2003, 34, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serieys, L.E.K.; Hammond-Aryee, K.; Bishop, J.; Broadfield, J.; O’Riain, M.J.; van Helden, P.D. High seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in an Urban Caracal (Caracal caracal) Population in South Africa. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 951–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seltmann, A.; Schares, G.; Aschenborn, O.H.K.; Heinrich, S.K.; Thalwitzer, S.; Wachter, B.; Czirjak, G.A. Species-specific differences in Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Besnoitia besnoiti seroprevalence in Namibian wildlife. Parasit Vectors 2020, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Rios, A.; Ortega-Pacheco, A.; Gutierrez-Blanco, E.; Acosta-Viana, K.Y.; Guzman-Marin, E.; Guiris-Andrade, M.D.; Hernandez-Cortazar, I.B.; Lopez-Alonso, R.; Cruz-Aldan, E.; Jimenez-Coello, M. Toxoplasma gondii in captive wild felids of Mexico: Its frequency and capability to eliminate Oocysts. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Pas, A.; Rajendran, C.; Kwok, O.C.; Ferreira, L.R.; Martins, J.; Hebel, C.; Hammer, S.; Su, C. Toxoplasmosis in Sand cats (Felis margarita) and other animals in the Breeding Centre for Endangered Arabian Wildlife in the United Arab Emirates and Al Wabra Wildlife Preservation, the State of Qatar. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 172, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Camps, S.; Dubey, J.P.; Saville, W.J. Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii in zoo animals in selected zoos in the midwestern United States. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Xin, S.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y. Isolation and characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from captive caracals (Caracal caracal). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 13, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Knowles, S.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.; Jiang, T.; Su, C.; Dubey, J.P. An update on Toxoplasma gondii infections in northern sea otters (Enhydra lutris kenyoni) from Washington State, USA. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 258, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwab, E.K.; Zhu, X.Q.; Majumdar, D.; Pena, H.F.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. Geographical patterns of Toxoplasma gondii genetic diversity revealed by multilocus PCR-RFLP genotyping. Parasitology 2014, 141, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C.; Ajioka, J.W.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Sibley, L.D. Genetic analyses of atypical Toxoplasma gondii strains reveal a fourth clonal lineage in North America. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Shwab, E.K.; Martin, R.M.; Gerhold, R.W.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. A partition of Toxoplasma gondii genotypes across spatial gradients and among host species, and decreased parasite diversity towards areas of human settlement in North America. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Velmurugan, G.V.; Rajendran, C.; Yabsley, M.J.; Thomas, N.J.; Beckmen, K.B.; Sinnett, D.; Ruid, D.; Hart, J.; Fair, P.A.; et al. Genetic characterisation of Toxoplasma gondii in wildlife from North America revealed widespread and high prevalence of the fourth clonal type. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Desmonts, G. Serological responses of equids fed Toxoplasma gondii oocysts. Equine. Vet. J. 1987, 19, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reischl, U.; Bretagne, S.; Kruger, D.; Ernault, P.; Costa, J.M. Comparison of two DNAtargets for the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis by real-time PCR using fluorescence resonance energy transfer hybridization probes. BMC Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Shwab, E.K.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Dubey, J.P. Moving towards an integrated approach to molecular detection and identification of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 2010, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwab, E.K.; Jiang, T.; Pena, H.F.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. The ROP18 and ROP5 gene allele types are highly predictive of virulence in mice across globally distributed strains of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Ferreira, L.R.; Martins, J.; McLeod, R. Oral oocyst-induced mouse model of toxoplasmosis: Effect of infection with Toxoplasma gondii strains of different genotypes, dose, and mouse strains (transgenic, out-bred, in-bred) on pathogenesis and mortality. Parasitology 2012, 139, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ying, Y.; Verma, S.K.; Cassinelli, A.B.; Kwok, O.C.; Liang, H.; Pradhan, A.K.; Zhu, X.Q.; Su, C.; Dubey, J.P. Isolation and genetic characterization of viable Toxoplasma gondii from tissues and feces of cats from the central region of China. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 211, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Su, R.; Li, T.; Su, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y. Isolation, genotyping and pathogenicity of a Toxoplasma gondii strain isolated from a Serval (Leptailurus serval) in China. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Dong, H.; Su, R.; Jiang, N.; Li, T.; Su, C.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, L. Direct evidence of an extra-intestinal cycle of Toxoplasma gondii in tigers (Panthera tigris) by isolation of viable strains. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Yang, L.; Zhu, N.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Additional evidence of tigers (Panthera tigris altaica) as intermediate hosts for Toxoplasma gondii through the isolation of viable strains. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 19, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Su, R.; Lu, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Jian, F.; Yang, Y. Prevalence, risk factors, and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii in food animals and humans (2000–2017) from China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, H.; Xin, S.; Jiang, N. Comparative immunological response and pathobiology of mice inoculated with Toxoplasma gondii isolated from different hosts. J. Parasitol. 2021, 107, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lindsay, D.S.; Speer, C.A. Structures of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites, bradyzoites, and sporozoites and biology and development of tissue cysts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Crutchley, C. Toxoplasmosis in wallabies (Macropus rufogriseus and Macropus eugenii): Blindness, treatment with atovaquone, and isolation of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, A.C.; Elbadawi, L.I.; DeSalvo, T.; Straily, A.; Ajzenberg, D.; Letzer, D.; Moldenhauer, E.; Handly, T.L.; Hill, D.; Darde, M.L.; et al. Toxoplasmosis outbreak associated with Toxoplasma gondii-contaminated venison-high attack rate, unusual clinical presentation, and atypical genotype. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Prowell, M. Ante-mortem diagnosis, diarrhea, oocyst shedding, treatment, isolation, and genetic typing of Toxoplasma gondii associated with clinical toxoplasmosis in a naturally infected cat. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Cerqueira-Cezar, C.K.; Murata, F.H.A.; Verma, S.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Pedersen, K.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Su, C. Genotyping of viable Toxoplasma gondii from the first national survey of feral swine revealed evidence for sylvatic transmission cycle, and presence of highly virulent parasite genotypes. Parasitology 2020, 147, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Cerqueira-Cezar, C.K.; Murata, F.H.A.; Verma, S.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Pedersen, K.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Su, C. White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) are a reservoir of a diversity of Toxoplasma gondii strains in the USA and pose a risk to consumers of undercooked venison. Parasitology 2020, 147, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Choudhary, S.; Ferreira, L.R.; Kwok, O.C.; Butler, E.; Carstensen, M.; Yu, L.; Su, C. Isolation and RFLP genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii from the gray wolf (Canis lupus). Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 197, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Verma, S.K.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Cassinelli, A.B.; Kwok, O.C.; Van Why, K.; Su, C.; Humphreys, J.G. Isolation and genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from black bears (Ursus americanus), bobcats (Lynx rufus), and feral cats (Felis catus) from Pennsylvania. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2015, 62, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Sweeny, A.R.; Lovallo, M.J.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Kwok, O.C.; Jiang, T.; Su, C.; Grigg, M.E.; Dubey, J.P. Seroprevalence, isolation and co-infection of multiple Toxoplasma gondii strains in individual bobcats (Lynx rufus) from Mississippi, USA. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Van Why, K.; Verma, S.K.; Choudhary, S.; Kwok, O.C.; Khan, A.; Behinke, M.S.; Sibley, L.D.; Ferreira, L.R.; Oliveira, S.; et al. Genotyping Toxoplasma gondii from wildlife in Pennsylvania and identification of natural recombinants virulent to mice. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 200, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Carstensen, M.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Moore, S.A.; Jiang, T.; Su, C.; Dubey, J.P. Seroprevalence, isolation, first genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii, and possible congenital transmission in wild moose from Minnesota, USA. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, K.; VanWormer, E.; Packham, A.; Dodd, E.; Conrad, P.A.; Miller, M. Type X strains of Toxoplasma gondii are virulent for southern sea otters (Enhydra lutris nereis) and present in felids from nearby watersheds. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2019, 286, 20191334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanWormer, E.; Miller, M.A.; Conrad, P.A.; Grigg, M.E.; Rejmanek, D.; Carpenter, T.E.; Mazet, J.A. Using molecular epidemiology to track Toxoplasma gondii from terrestrial carnivores to marine hosts: Implications for public health and conservation. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Xin, S.; Zhang, L. Toxoplasma gondii infection in white spoonbills (Platalea leucorodia) from Henan Province, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2619–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, T.; Marcet, P.L.; Graham, D.H.; Dahl, E.R.; Dubey, J.P. Globalization and the population structure of Toxoplasma gondii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11423–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Caracal ID | Date Received | Sex, Age | Clinical Signs | Cause of Death | MAT Titers a | Swiss Mouse Bioassay b | T. gondii-Positive Tissues via PCR c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case #3 (TgCaracalCHn2) | 8 June 2022 | Male, Adult | Obesity, diarrhea | Cardiac insufficiency, pulmonary edema, hepatic failure, renal insufficiency. | Myocardium fluid: 1:1600 Hydropericardium: 1:800 Ascitic fluid: 1:3200. | 5/5 | Heart, lungs, kidney, skeletal muscles, diaphragm, tongue, stomach, jejunum, ileum, colon, rectum. |
| No. of Tachyzoites | No. of T. gondii Infection Mice/No. of Inoculation Mice (%) | Days of Survival/No. of T. gondii-Infected Mice | No. of Brain Cysts |
|---|---|---|---|
| 106 | 5/5 (100%) | ≥60/5 | 620 ± 128 |
| 105 | 5/5 (100%) | 16/1, ≥60/4 | 94 ± 50 |
| 104 | 5/5 (100%) | 54/1, ≥60/4 | 276 ± 89 |
| 103 | 5/5 (100%) | ≥60/5 | 164 ± 56 |
| 102 | 5/5 (100%) | ≥60/5 | 86 ± 46 |
| 101 | 2/5 (40%) | 20/1, ≥60/1 | 162 ± 162 |
| 100 | 1/5 (20%) | ≥60/1 | 18 ± 18 |
| <1 | 0/5 (0) | ≥60/5 | 0 |
| Negative control | 0/5 (0) | ≥60/5 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, H.; Mao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, N.; Liang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Isolation and Characterization of a Viable Toxoplasma gondii from Captive Caracal (Caracal caracal). Pathogens 2023, 12, 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121412
Ren H, Mao G, Zhang Y, Zhu N, Liang Q, Jiang Y, Yang Y. Isolation and Characterization of a Viable Toxoplasma gondii from Captive Caracal (Caracal caracal). Pathogens. 2023; 12(12):1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121412
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Hongjie, Gaohui Mao, Yan Zhang, Niuping Zhu, Qunchao Liang, Yibao Jiang, and Yurong Yang. 2023. "Isolation and Characterization of a Viable Toxoplasma gondii from Captive Caracal (Caracal caracal)" Pathogens 12, no. 12: 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121412
APA StyleRen, H., Mao, G., Zhang, Y., Zhu, N., Liang, Q., Jiang, Y., & Yang, Y. (2023). Isolation and Characterization of a Viable Toxoplasma gondii from Captive Caracal (Caracal caracal). Pathogens, 12(12), 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121412





