Abstract
The indiscriminate use of antibiotics has contributed to the dissemination of multiresistant bacteria, which represents a public health concern. The aim of this work was to characterize 27 coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) isolated from eight wild Northeast Atlantic hakes (Merluccius merluccius, L.) and taxonomically identified as Staphylococcus epidermidis (n = 16), Staphylococcus saprophyticus (n = 4), Staphylococcus hominis (n = 3), Staphylococcus pasteuri (n = 2), Staphylococcus edaphicus (n = 1), and Staphylococcus capitis (n = 1). Biofilm formation was evaluated with a microtiter assay, antibiotic susceptibility testing was performed using the disk diffusion method, and antibiotic resistance and virulence determinants were detected by PCR. Our results showed that all staphylococci produced biofilms and that 92.6% of the isolates were resistant to at least one antibiotic, mainly penicillin (88.8%), fusidic acid (40.7%), and erythromycin (37%). The penicillin resistance gene (blaZ) was detected in 66.6% (18) of the isolates, of which 10 also carried resistance genes to macrolides and lincosamides (mphC, msr(A/B), lnuA, or vgaA), 4 to fusidic acid (fusB), and 3 to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (dfrA). At least one virulence gene (scn, hla, SCCmecIII, and/or SCCmecV) was detected in 48% of the isolates. This study suggests that wild European hake destined for human consumption could act as a vector of CoNS carrying antibiotic resistance genes and/or virulence factors.
1. Introduction
Marine fisheries are part of the primary extractive sector, comprising the maritime areas defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO, Rome, Italy) of the United Nations (New York, NY, USA), with precise delimitations for each major fishing area [1]. The importance of responsible use of fishery and aquaculture resources is now recognized. In 2020, the yield from capture fisheries amounted to 90.3 million tonnes [2]. Fish and fishery products continue to be amongst the most traded food products worldwide due to the fact that fish are a significant source of protein and minerals. The global consumption of edible fish increased at an average annual rate of 5.9% between 1960 and 2020. For 3.3 billion people, aquatic foods represent at least 20% of the average per capita intake of animal protein [2]. In the Spanish gastronomic culture, European hake (Merluccius merluccius, L.) is one of the most deeply rooted and valued white fish, with an important economic impact on the fishing sector. This fish species is mostly derived from the catches of the Spanish fishing fleet and from intra-Community trade [3]. Specifically, 62,500 tonnes of European hake were consumed in Spain in 2021 [4].
Traditionally, antibiotics have been used as therapeutic agents and, in some cases, as prophylactic treatment of bacterial ichthyopathologies. In this respect, the overuse of antibiotics has contributed to the growing and serious problem of the emergence and spread of transmissible bacterial resistance genes to many antibiotics, which is a major global problem for the treatment of infectious diseases of bacterial etiology [5], endangering veterinary and human medicine and affecting food safety and the environment [1]. The most commonly used antibiotics in aquaculture are amoxicillin, florfenicol, oxytetracycline, oxolinic acid, flumequine, enrofloxacin, and trimethoprim-sulfadiazine [6,7,8].
In the European Union (EU), and in most industrialized countries, their use as a prophylactic treatment has been expressly prohibited, and increasingly restrictive regulations on their use have been developed due to their serious adverse effects on animal and human health, food safety, and the environment [9,10,11]. In 2006, the EU banned the use of antibiotics as growth promoters due to the increasing spread of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria [12]. Additionally, Commission Regulation (EU) 37/2010 sets maximum residue limits (MRLs) on pharmacologically active substances in foodstuffs of animal origin [13]. However, the use of antibiotics is not strictly regulated in all countries, making it difficult to control the spread of bacterial resistance [14]. In 2015, a total of 8361 tonnes of antimicrobial agents were used in veterinary practices in the EU [15] and, according to a 2017 ECDC/EFSA/EMA report, tetracycline and penicillin were the most prescribed antibiotics for food-producing animals [16]. Through the consumption of food of animal origin, including fish, humans can be exposed to antibiotic residues and bacteria carrying resistance genes [17]. In 2019, five million people died globally from causes related to bacterial antimicrobial resistance, and 1.3 million people died as a direct result of antibiotic-resistant bacteria [18]. If no action is taken by 2050, these diseases could cause 10 million deaths per year, representing the leading cause of death globally [18,19]. Considering the growing concern about the risk of antibiotic resistance and its possible worsening in the future, collaboration between health authorities has been encouraged to develop strategies focused on the correct use of veterinary medicines to prevent bacterial resistance, such as the current engagement between the FAO, the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) and the World Health Organization (WHO) to address the challenge of antimicrobial resistance to human health worldwide [20].
Species of the genus Staphylococcus are recognized as pathogens responsible for several opportunistic diseases in humans and animals [21] and are the most frequent cause of biofilm-associated infections [22]. Although coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) are not classical food poisoning bacteria, a number of studies indicate that food can be considered as an important route for the transmission of antibiotic-resistant CoNS harboring multiple antibiotic resistance genes [23]. Although some species of CoNS have been described as starter cultures playing a valuable role in the fermentation and biopreservation of meat products [24], other species such as Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus are considered as emerging opportunistic pathogens [25]. Particularly, S. epidermidis is the most clinically relevant and characterized biofilm-forming microorganism [26]. Staphylococcal bacteria isolated from different origins, including humans, livestock, companion animals, and food, have largely been characterized to determine the presence of antibiotic resistance genes [27,28,29,30,31]. The most frequent mechanisms of acquired resistance in staphylococci include the acquisition of blaZ, which encodes the production of a β-lactamase enzyme (conferring resistance to penicillin); mecA, which encodes the expression of PBP2 (conferring resistance to methicillin and cephalosporins); tetK and tetL, which encode the production of efflux pumps, and tetM or tetO, which encode the elongation factor-like proteins protecting ribosomes (conferring resistance to tetracycline); aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2″)-Ia, aph(3′)-IIIa, ant(4′)-Ia, and str, which encode cytoplasmic aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes; ermA, ermB, ermC, and mphC, which are responsible for target modification, and msr(A/B), lnuA, lnuB, and vgaA, which are responsible for target protection (conferring resistance to macrolides and lincosamides); fusB, which confers target protection for fusidic acid resistance; and dfrA, dfrD, dfrG, and dfrK, which encode dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) enzymes that are not susceptible to the inhibition of trimethoprim [32].
Recently, there has been great interest in elucidating whether the spread of antibiotic-resistant staphylococci from humans and livestock reaches the marine environment and, consequently, wild fish that may act as reservoirs [33,34,35]. For this reason, and taking into consideration that European hake is one of the most consumed fish in Spain and an unexplored niche, the aim of this work was to characterize staphylococcal isolates from intestinal samples of eight hake from the Northeast Atlantic to study their resistance to antibiotics, the presence of virulence factor genes, and their capability to produce biofilms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Collection
Eight European hake (Merluccius merluccius, L.) specimens (1.0–1.5 kg approx.), caught by a Galician professional fishing skipper in the Northeast Atlantic, specifically in the sub-area 27.VIIj (Southwest of Ireland) [36], during two consecutive years (June 2021 and 2022), were used for bacterial isolation.
2.2. Sample Collection, Bacterial Isolation and Antimicrobial Activity Assays
The fish were transported in polystyrene boxes with ice under refrigeration and aseptically handled until arrival at the laboratory within 48–72 h of their capture. One gram of feces of each hake was extracted and then diluted in peptone water (Oxoid Ltd., Basingstoke, UK) and pour-plated onto De Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS, Oxoid) agar (1.5%, w/v, Scharlau, Barcelona, Spain) plates. For the collection of intestinal samples, the gut was rinsed with 10 mM phosphate buffered saline (PBS, Oxoid Ltd., Basingstoke, UK), cut, and homogenized in a stomacher with peptone water. Subsequently, samples were pour-plated onto MRS agar plates. After plate incubation at 30 °C under aerobic and anaerobic conditions for 24–72 h, a total of 286 isolates with different morphologies were selected and tested for direct antimicrobial activity, using the Stab-On-Agar Test (SOAT) [37], against several ichthyopathogens of relevance to aquaculture (i.e., Lactococcus garvieae CF00021, Lc. garvieae CLG4, Listeria monocytogenes CECT911, Listeria ivanovii CECT913, Yersinia ruckeri LMG3279, Aeromonas hydrophila CECT839, A. hydrophila CECT5734, A. hydrophila CECT5734, Aeromonas salmonicida CLFP-23, A. salmonicida CECT4237, Listonella anguillarum CECT4344, Tenacibaculum maritimum NCIMB2154, T. maritimum CECT1161, Edwardsiella tarda CECT886, and Streptococcus parauberis LMG22225). A total of 66 isolates were preselected based on their direct antimicrobial activity.
2.3. Taxonomic Identification of Bacterial Isolates
Total bacterial DNA from the preselected 66 isolates was extracted by using the InstaGene Matrix (BioRad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The 16S rDNA gene was amplified with the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and then sequenced. PCR amplifications were performed using 25 µL of DreamTaq Hot Start PCR Master Mix 2x (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), 0.5 µM of fD1 (5′-AGAGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′), 0.5 µM rD1 (5′-TAAGGAGGAGGTGATCCAGCC-3′), 50–100 ng of purified DNA, and 19 µL of molecular biology–grade water (Thermo Scientific) [38]. PCR mixtures were subjected to several amplification cycles, starting with an initial denaturation cycle (95 °C, 3 min), followed by 35 cycles of denaturation (95 °C, 30 s), hybridization (60 °C, 30 s), and elongation (72 °C, 1 min) and a final elongation cycle (72 °C, 5 min) in a thermal cycler (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). The resulting amplicons were then purified using the NucleoSpin® Gel and PCR Clean-up kit (Macherey-Nagel™) and sent to Eurofins Genomics (Ebersberg, Germany) for DNA sequencing. To determine their taxonomic identification, the nucleotide sequences were analyzed using the BLAST nucleotide server of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 1 February 2023). The 27 CoNS isolates (Supplementary Table S1) were selected for further characterization.
2.4. Genetic Diversity Analysis by Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus—PCR (ERIC-PCR)
In order to study the genetic diversity of the CoNS isolated from European hakes, a PCR-based typing method was carried out. In particular, ERIC-PCR analysis of the 27 CoNS isolates was performed using primers ERIC-1R (5′-ATGTAAGCTCCTGGGGGGATTCAC-3′) and ERIC-2 (5′-AAGTAAGTGACTGGGGGGTGAGCG-3′) as previously described by Araújo et al. (2015) [39]. PCRs of 50 μL were prepared with 25 μL of MyTaq Mix (Bioline Reagents, Ltd., London, UK), 0.7 µM of each primer, 50–100 ng of purified DNA, 3 μM of MgCl2, and 19 µL of molecular biology–grade water. PCR mixtures were subjected to an initial denaturation (95 °C, 1 min), 35 cycles of denaturation-annealing-elongation (95 °C, 15 s; 46 °C, 15 s; and 72 °C, 10 s), and a final elongation (72 °C, 4 min) in a thermal cycler (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). The amplification products were run at 90 V for 60 min in an electrophoresis chamber (BioRad Laboratories, Inc.), and the visualization of the bands was performed using the ChemiDoc Imaging System (BioRad Laboratories, Inc.), with HyperLadder 100 bp (Bioline Reagents, Ltd.) as a molecular weight marker. ERIC type analysis, clustering, and dendrogram construction were performed using Phoretix v.5.0 software (Nonlinear Dynamics Ltd., Newcastle upon Tyne, UK).
2.5. Biofilm Formation and Quantification Assays
Biofilm formation was tested using a microtiter assay as previously described by Oniciuc et al. (2016) [40]. The CoNS isolates were grown on tryptic soy agar (TSA, Oxoid) plates at 37 °C for 24 h. After incubation, two colonies were transferred to 3 mL tubes of tryptic soy broth (TSB, Oxoid) and incubated at 37°C with continuous shaking at 120 rpm (ES-80 Shaker-incubator, Grant Instruments, Cambridge, UK) for 16 h. Then, 200 µL of each bacterial suspension with a concentration of 1 × 106 cfu/mL was added to each well of a 96-well flat-bottom microtiter plate (Orange Scientific, Braine-l’Alleud, Belgium). In all microplates, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC25923 and TSB without bacterial inoculum were used as the positive and negative controls, respectively. The microplates were incubated at 37 °C under aerobic conditions for 24 h. All experiments were carried out in sixteen replicates. Biofilm formation was quantified using the crystal violet (CV) staining method as previously described by Peeters et al. (2008) with some modifications [41]. Briefly, after microplate incubation, the medium was removed from each well by washing the plates twice with distilled water in order to remove unattached bacterial cells. The microplates were air-dried at room temperature for 30 min. To fix the biofilms, 100 µL of methanol (VWR International) was added to each well. After 15 min, the methanol was removed, the microplates were air-dried at room temperature for 10 min, and 100 µL of CV (1%, v/v) was added to each well. After 10 min, the CV was removed, and the microplates were washed twice with distilled water to remove the excess of dye and dried with a paper. Then, to solubilize the CV, 100 µL of acetic acid (33%, v/v) was added, and the absorbance was measured at 570 nm using a BioTek ELx808U microplate reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA). To standardize the results, the biofilm of each isolate was normalized according to the results obtained with the positive control strain, S. aureus ATCC25923, assuming that it possessed a 100% biofilm-forming capability.
2.6. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
Antibiotic susceptibility testing was performed with the agar disk diffusion test according to the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) guidelines [42], except for kanamycin, for which the recommendations of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) were followed [43]. For this purpose, the isolates were grown on TSA plates (Oxoid) at 37 °C for 24 h. Afterward, a colony was transferred to 3 mL tubes of sterile saline solution (0.9%, w/v) and seeded on Mueller Hinton agar (Oxoid). Disks containing known amounts of each antibiotic were placed on the surface of the agar plates, which were then incubated at 37 °C for 16 h. For this test, a total of 14 antibiotics were used: cefoxitin (30 μg), chloramphenicol (30 μg), ciprofloxacin (5 μg), clindamycin (2 μg), erythromycin (15 μg), fusidic acid (10 μg), gentamycin (10 μg), kanamycin (30 μg), linezolid (10 μg), mupirocin (200 μg), penicillin (1 U), tetracycline (30 μg), tobramycin (10 μg), and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (1.25/23.75 μg). The susceptibility of CoNS to vancomycin was determined using a microdilution method in order to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) following the guidelines provided by EUCAST (2023) [42]. Briefly, individual colonies were suspended in a sterile glass tube containing 10 mL saline solution (0.85% NaCl) to a turbidity of 0.5 on the McFarland scale, and then, the bacterial suspensions were diluted 1000-fold in Mueller Hinton broth (Oxoid). A volume of 50 μL of the diluted bacterial suspensions was added to each microplate well containing 50 μL of Mueller Hinton broth with vancomycin (1–64 µg/mL). After incubation at 37 °C for 18 h, the MIC for vancomycin was established as the lowest antibiotic concentration inhibiting bacterial growth and interpreted according to MIC breakpoints established for CoNS by EUCAST. S. aureus ATCC25923 was used as the quality control.
2.7. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Factor Genes
Based on the antibiotic resistance phenotypes, the presence of antimicrobial resistance genes was determined by PCR. In particular, the presence of antimicrobial genes encoding transferable resistance to β-lactam antibiotics (blaZ and mecA), macrolides and lincosamides (ermA, ermB, ermC, mphC, msr(A/B), lnuA, lnuB, and vgaA), aminoglycosides (aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2′’)-Ia, aph(3′)-IIIa, ant(4′)-Ia, and str), fusidic acid (fusB), and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (dfrA, dfrD, dfrG, and dfrK) was investigated as previously described by Silva et al. (2019) [44].
In addition, all isolates were tested by PCR for the presence of virulence genes encoding toxic shock syndrome toxin (tst), exfoliative toxins (eta, etb, and etd2), and the alpha, beta, and delta hemolysins (hla, hlb, and hld, respectively). Moreover, the scn gene, which is the marker of the immune evasion cluster (IEC) system, was also investigated. When the scn gene was detected, the presence of chp, sak, sea, and sep was checked to determine the IEC group [44,45,46,47,48].
The positive and negative controls used in PCR assays belonged to the collection of bacterial strains from the Microbiology and Antibiotic Resistance Team (MicroART) of the University of Trás-os-Montes and Alto Douro [49].
2.8. Statistical Analyses
Data curation and statistical analyses were performed and graphical representations were generated using the GraphPad Prism 8 software (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) and Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Office 365). Statistical analyses were performed using an unpaired Student’s t-test to compare biofilm formation amongst the different CoNS isolates at 24 and 48 h.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the CoNS Isolated from Fecal and Intestinal Samples from European Hakes
A total of 27 out of the 66 pre-selected isolates from European hake feces and intestines were taxonomically identified as CoNS, namely, S. epidermidis (n = 16), S. saprophyticus (n = 4), S. hominis (n = 3), S. pasteuri (n = 2), S. edaphicus (n = 1), and S. capitis (n = 1) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Number of samples and frequency of the CoNS isolated from European hakes.
3.2. Genetic Diversity Analysis by ERIC-PCR
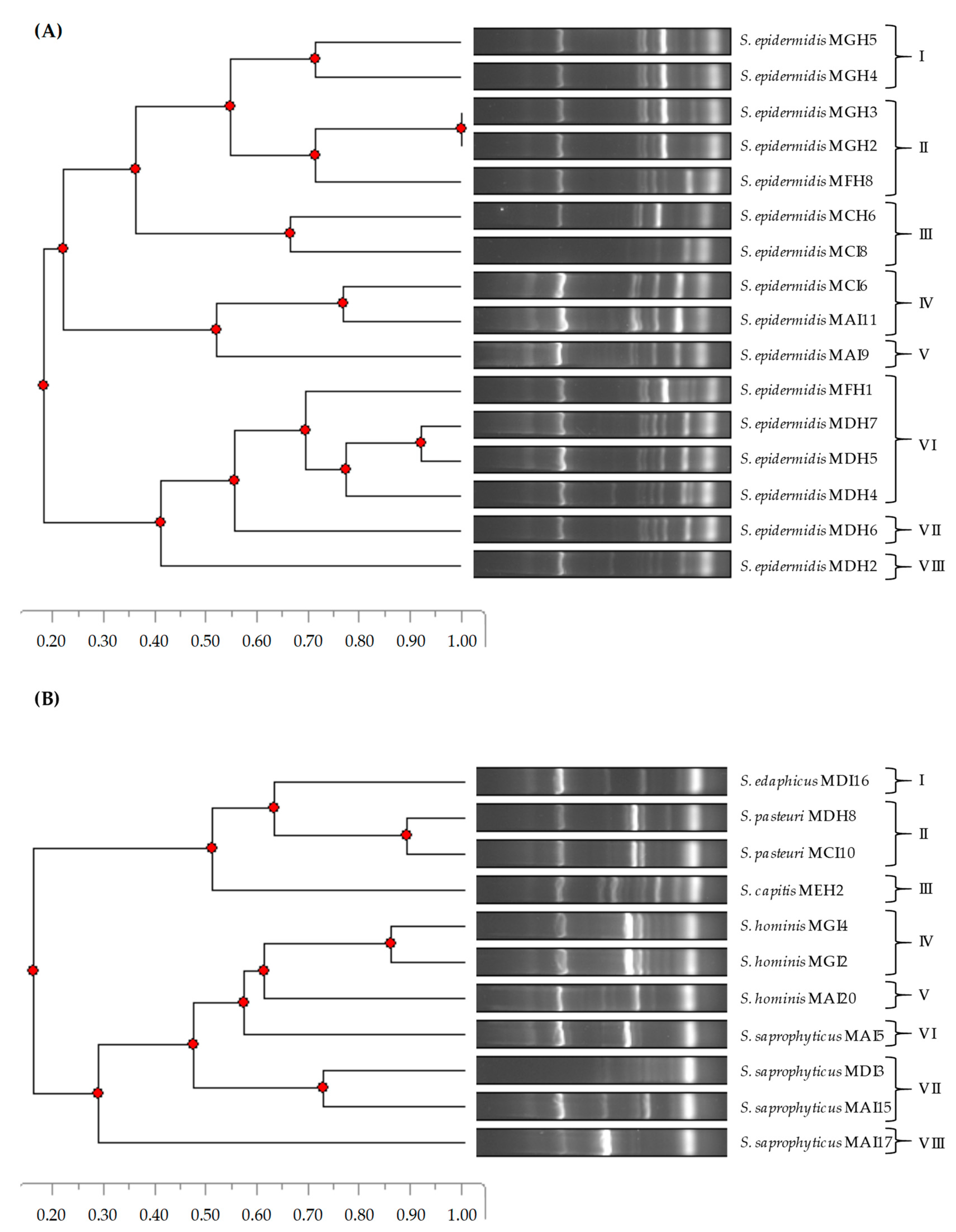
The phylogenetic relatedness of the CoNS isolates was determined using a DNA fingerprinting method, namely, ERIC-PCR (Figure 1). In the case of S. epidermidis isolates, eight ERIC-PCR patterns were detected. While patterns I and II were found in the second year (2022), patterns III–V and VII–VIII were detected in the first year (2021). Interestingly, pattern VI was found in both years. On the other hand, eight ERIC-PCR patterns were identified for the remaining CoNS species. Regarding this, the S. edaphicus, S. pasteuri, and S. capitis isolates were clustered in patterns I, II, and III, respectively. In addition, the S. saprophyticus and S. hominis isolates were grouped in patterns IV–V and VI–VIII, respectively.
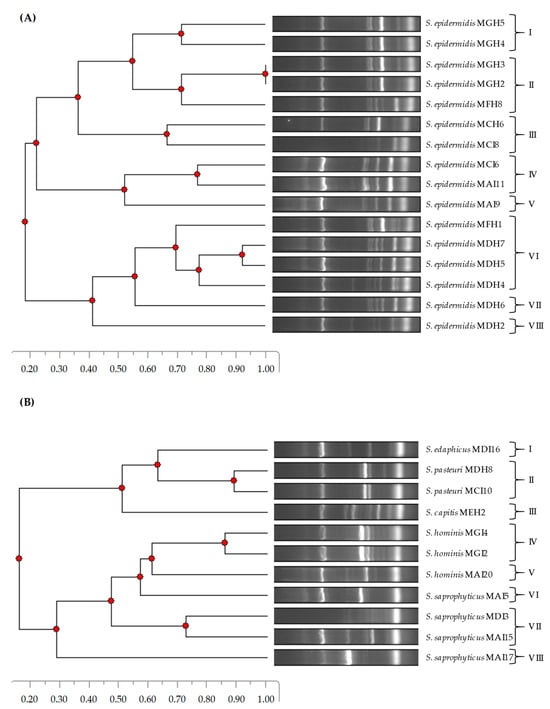
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic relatedness of S. epidermidis (A) and other CoNS species (B) isolated from European hakes based on ERIC-PCR patterns.
3.3. Biofilm Formation
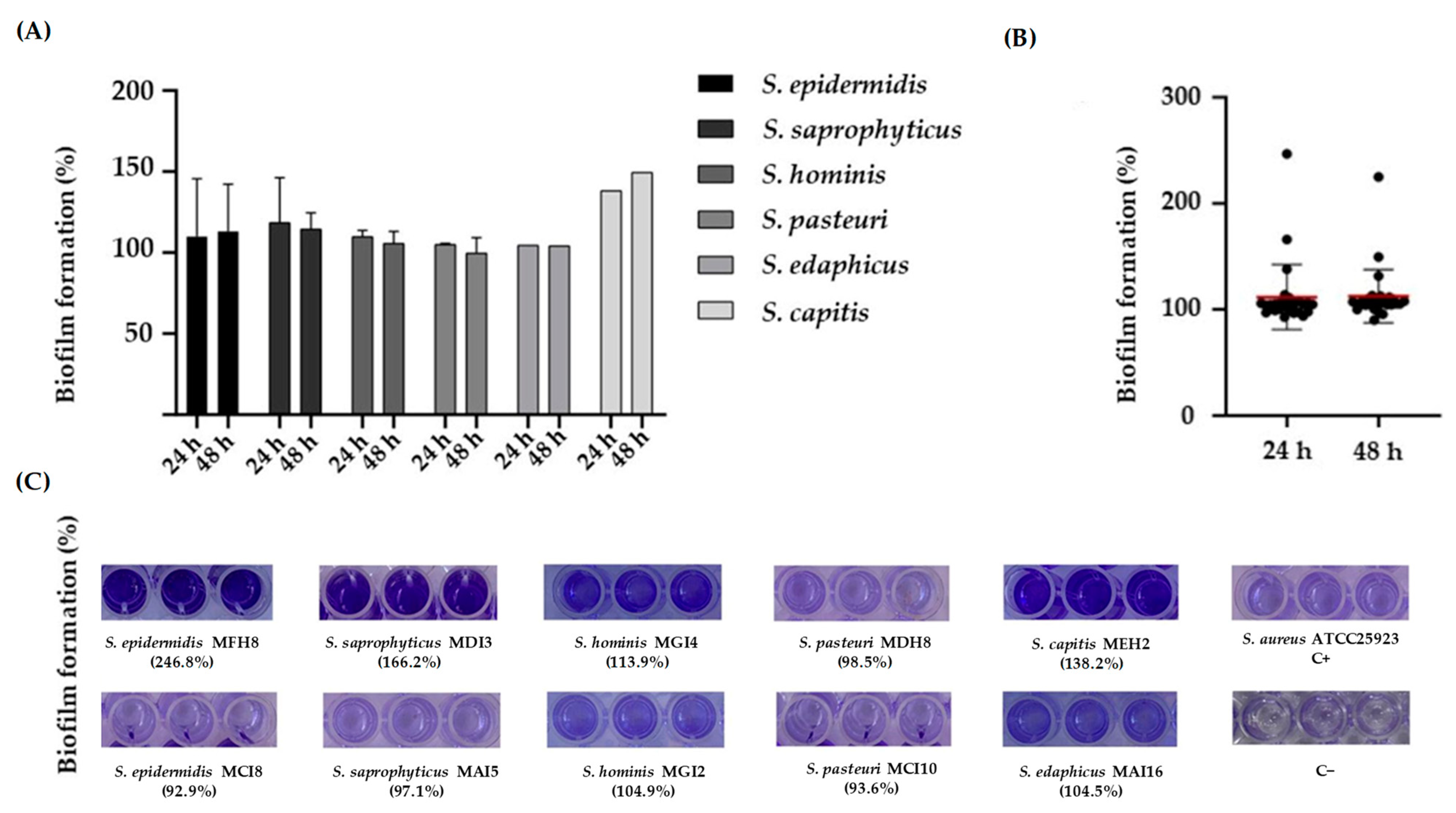
The biofilm-forming capability of the CoNS was determined using a microtiter assay [22]. In order to standardize the results, the percentage of biofilm formation for each isolate was normalized using S. aureus ATCC25923. Our results showed that all the CoNS produced biofilms (Figure 2A,C), and no statistically significant differences were found at 24 and 48 h (Figure 2B).
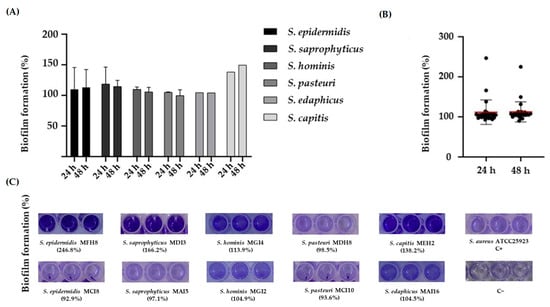
Figure 2.
(A) Percentage of biofilm formation of the CoNS evaluated in this study at 24 and 48 h. (B) Comparison of biofilm formation at 24 and 48 h. The symbols represent the mean of the biofilm formed by the individual isolates. The red lines represent the average of the biofilm mass formed by all the isolates. No significant differences in biofilm formation at 24 and 48 h were observed. (C) Representative images of crystal violet staining of biofilms formed by CoNS species at 24 h. When there is more than one isolate of each species, the images show the isolates with the highest and lowest percentages of biofilm formation. C+, positive control. C−, negative control.
3.4. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Factors
The presence of antibiotic resistance genes in the CoNS in relation to the specific phenotype of resistance as well as the presence of virulence genes is summarized in Table 2. Concerning the antibiotic resistance of CoNS, nine different resistance phenotypes were detected. The results showed that 92.6% of the isolates were resistant to at least one antibiotic. The most frequent resistances were detected to penicillin (88.8%), fusidic acid (40.7%), and erythromycin (37%). Only two isolates were considered as multiresistant (S. epidermidis MDH2 and S. epidermidis MDH5), as they were resistant to at least three classes of antimicrobial agents. Specifically, S. epidermidis MDH2 showed resistance to gentamycin, clindamycin, erythromycin, fusidic acid, cefoxitin, kanamycin, and penicillin, and S. epidermidis MDH5 to gentamycin, erythromycin, fusidic acid, kanamycin, penicillin, tobramycin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. On the other hand, no phenotypic resistance was detected for ciprofloxacin, linezolid, tetracycline, mupirocin, chloramphenicol, or vancomycin.

Table 2.
Antibiotic resistance and virulence factors of the CoNS isolated from European hakes a.
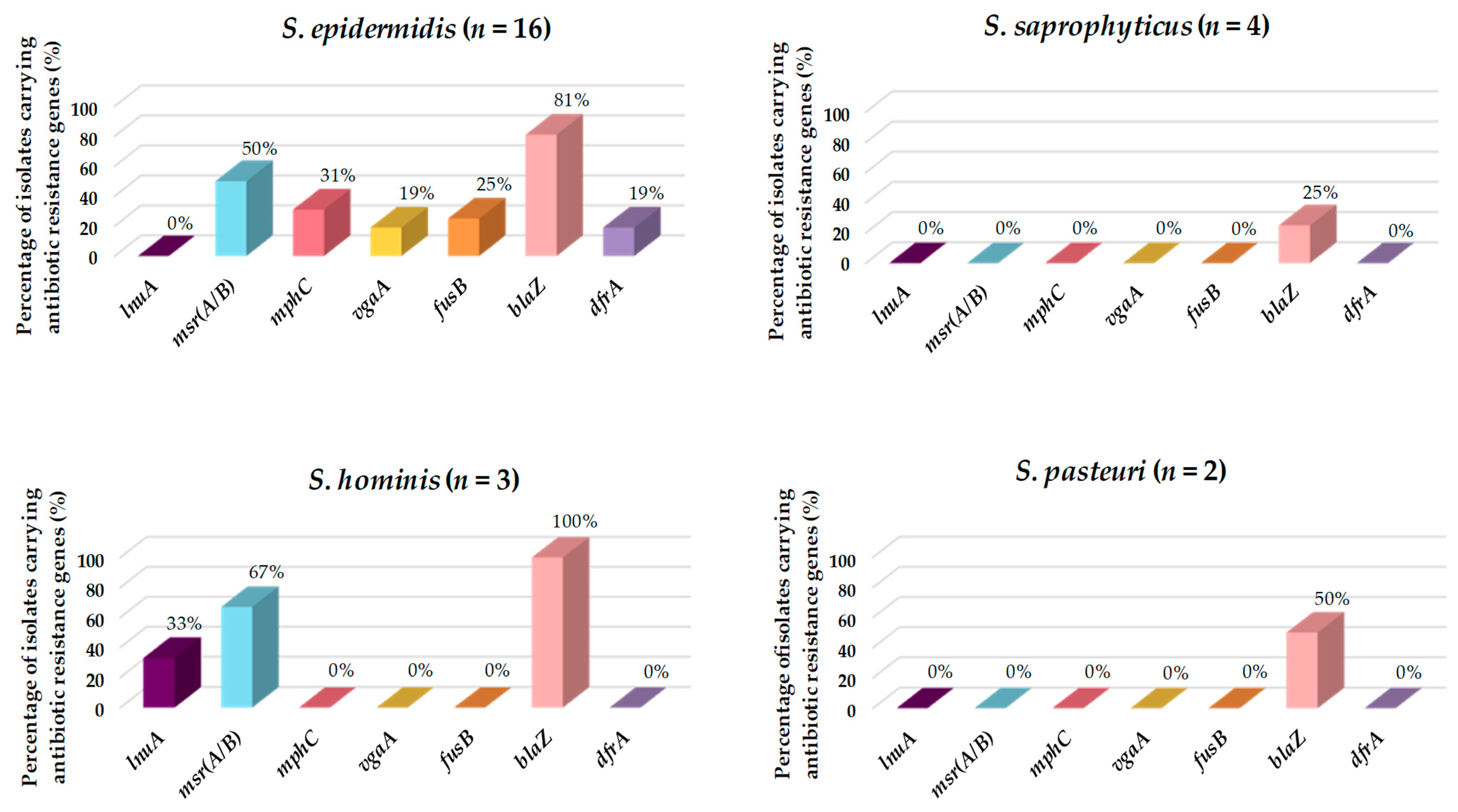
According to the antibiotic resistance genotypes, 70.4% of the CoNS harbored at least one antibiotic resistance gene. In this regard, the gene involved in the horizontal transfer of resistance to penicillin (blaZ) was identified in 18 isolates (66.7%), 10 harbored macrolide and lincosamide resistance genes (mphC, msr(A/B), lnuA, or vgaA), 4 had the fusidic acid resistance gene (fusB), and 3 carried the trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole resistance gene (dfrA). All isolates that had resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole also carried the dfrA gene. Although the phenotypic resistance to aminoglycosides was identified in three isolates (11.1%), none of them harbored aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2″)-Ia, aph(3′)-IIIa, ant(4′)-Ia, or str.
Considering the different species of Staphylococcus evaluated in this work, S. epidermidis showed the highest number of phenotypic resistances (nine out of the 14 tested antibiotics), specifically to gentamycin, clindamycin, erythromycin, fusidic acid, cefoxitin, kanamycin, penicillin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and tobramycin (Table 3). Two of the isolates (S. epidermidis MFH1 and MFH8) were susceptible to all the tested antibiotics, and only S. epidermidis MFH1 did not harbor any virulence factor gene (Table 2). All S. saprophyticus isolates (n = 4) displayed resistance to penicillin, half of them showed resistance to fusidic acid, and one isolate was resistant to kanamycin. On the other hand, all S. hominis isolates (n = 3) were resistant to penicillin, and two isolates were resistant to erythromycin. S. pasteuri isolates (n = 2) showed phenotypic resistance to penicillin only. S. edaphicus (n = 1) showed resistance to fusidic acid and penicillin, and S. capitis (n = 1) was the only species resistant to fusidic acid and not to penicillin (Table 3).

Table 3.
Prevalence (%) of phenotypic antibiotic resistances in the CoNS isolated from European hakes.
Of all the CoNS isolated and characterized in this study, S. epidermidis was the species harboring the most different resistance genes (msr(A/B), vgaA, fusB, blaZ, mphC, and dfrA), followed by S. hominis (msr(A/B), blaZ, and lnuA), S. pasteuri (blaZ), and S. saprophyticus (blaZ) (Figure 3). However, S. edaphicus and S. capitis did not harbor any antibiotic resistance genes.
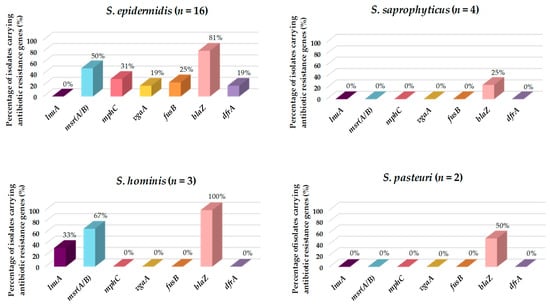
Figure 3.
Prevalence (%) of antibiotic resistance genes in the CoNS isolated from European hakes. CoNS species lacking antibiotic resistance genes are not represented.
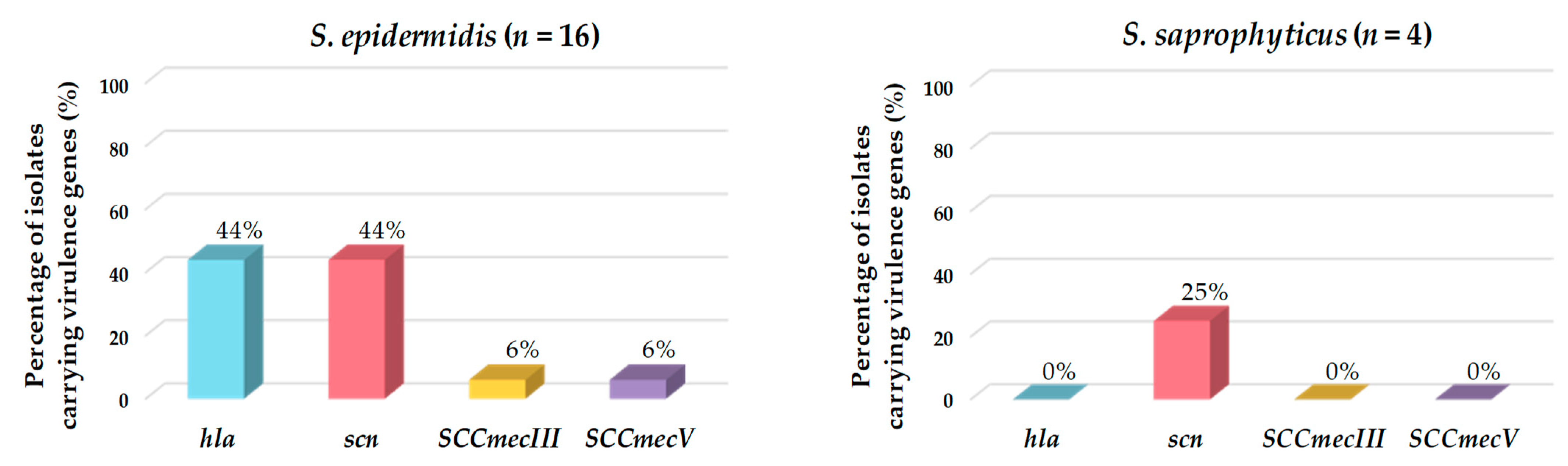
Of the total CoNS isolates, 48% harbored at least one virulence factor gene. The most frequently detected genes encoding virulence factors were the marker of the IEC system (scn) and the hemolysin alpha (hla) genes. Of the eight isolates carrying the scn gene, seven belonged to the species S. epidermidis, and one to S. saprophyticus. All isolates carrying hla, SCCmecIII, or SCCmecV were identified as S. epidermidis (Table 2 and Figure 4).
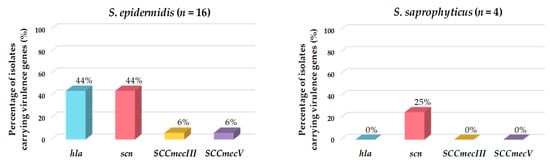
Figure 4.
Prevalence (%) of genes encoding virulence factors detected in the CoNS isolated from European hakes. CoNS species lacking virulence genes are not represented.
4. Discussion
Several studies have shown that wastewater treatment does not completely eliminate bacteria, which means that they may reach natural aquatic environments and, subsequently, could be disseminated to animals living in these ecosystems [50,51,52]. As a result, fish and other aquatic animals may act as reservoirs of human pathogenic bacteria of relevance to public health and food safety carrying virulence and antibiotic resistance genes [28,53]. Recent studies have identified antibiotic-resistant and virulent strains of Staphylococcus spp. in samples recovered from wastewater treatment plants, supporting the hypothesis that these facilities are one of the main reservoirs of pathogens contributing to their dissemination to aquatic ecosystems [29,51]. Moreover, some studies have described that many cultured fish species are affected by staphylococcal infections worldwide, mostly caused by S. epidermidis, S. aureus, S. hominis, or S. capitis [54,55,56]. In this study, CoNS were isolated from fecal and intestinal samples from eight European hake specimens recovered from the Northeast Atlantic, suggesting that the dissemination of staphylococci in the marine environment should not be underestimated. These CoNS isolates were characterized in order to study their capability to form biofilms and to evaluate the presence of genetic determinants conferring antibiotic resistance and virulence.
Molecular fingerprinting methods, such as ERIC-PCR, have widely and successfully been used for bacterial typing and epidemiological studies to determine the genetic relatedness between isolates from various sources, in particular, for S. aureus [57], S. epidermidis, S. hominis, S. capitis [58], and other Gram-positive bacteria [39,59]. In this respect, the ERIC-PCR technique represents a valid, fast, and simple strategy for the molecular fingerprinting of isolates. Herein, we show that ERIC-PCR allowed us to differentiate and cluster S. epidermidis isolates and to distinguish amongst CoNS species. To the best of our knowledge, this study represents the first description of the use of ERIC-PCR to assess the genetic relatedness in the species S. edaphicus and S. pasteuri.
Staphylococci, especially CoNS, are generally recognized as the most frequent microorganisms producing biofilm-associated infections [26,60]. All the CoNS isolated from hake feces and intestines showed the ability to form biofilms as previously described for other staphylococci isolated from fish [61,62]. The capability of these microorganisms to produce biofilms in aquatic environment facilitates the exchange of mobile genetic elements amongst aquatic bacteria [50], representing a public health hazard [63,64,65]. Additionally, biofilms facilitate the persistence of pathogenic bacteria in the host and make them resistant to antibiotic treatment [60]. In this respect, S. epidermidis is one of the main CoNS species causing nosocomial infections, especially due to its capacity to form biofilms on medical devices in comparison to other biofilm-producing Staphylococcus spp. [66]. Similarly, our results showed that S. epidermidis harbored the most virulence factor and antibiotic resistance genes. Different studies on the complete genome of this species have concluded that S. epidermidis and S. aureus share some genes involved in pathogenicity, suggesting the existence of horizontal gene transfer between these species [67]. For this reason, some virulence factors specific to S. aureus were evaluated in our study. In this respect, SCCmecIII and SCCmecV were detected in two isolates of S. epidermidis (S. epidermidis MFH8 and S. epidermidis MAI9, respectively). It has been reported that methicillin-resistant staphylococci arise due to the acquisition and insertion of the SCCmec element in the chromosome of susceptible strains [68]. Interestingly, only one isolate of this species, S. epidermidis MFH1, did not harbor any gene encoding antibiotic resistance or virulence factors.
In addition to S. epidermidis, all species studied in this work are potentially pathogenic to both animals and humans. Regarding S. saprophyticus, it has been reported that this commensal CoNS has an unusual ability to attach to urothelial cells and produce urease, causing urinary tract infections [69,70,71]. Our results showed that the highest percentages in biofilm-forming isolates were found in this species. However, only one of the four S. saprophyticus isolates harbored a virulence factor gene, namely, scn. In this regard, other studies have also described the absence of virulence factors in S. saprophyticus [72,73].
S. capitis is also a CoNS classified as a human pathogen and involved in infective endocarditis [67], prosthetic joint infections [74], and neonatal sepsis [75]. This species encodes important virulence factors required for biofilm formation, persistence, and immune evasion [76,77,78]. Contrary to these studies, the S. capitis isolate from European hake characterized in our work did not harbor any virulence factor genes. With respect to S. hominis, it has been recognized as a potentially opportunistic pathogen and may cause bloodstream infections, endocarditis, peritonitis, osteomyelitis, bone, and joint infections [76,79,80,81]. However, the pathogenicity mechanisms of this microorganism have not yet been identified [82]. It should be noted that the S. hominis isolates characterized in our study lacked virulence factor genes.
In the case of S. pasteuri, it is commonly found in food as well as in the air and on surfaces [83]. Clinically, it has been identified in the gastrointestinal microbiota of children with active celiac disease [84]. In our study, S. pasteuri showed resistance to penicillin but did not carry virulence factor genes. Similarly, the only isolate of the species S. edaphicus identified in our study showed phenotypic resistance to penicillin and fusidic acid, but no virulence factor genes were found. In this context, Pantůček et al. (2018) described that S. edaphicus isolated in Antarctica had penicillin resistance genes, suggesting that this species may act not only as a reservoir of antibiotic resistance in a natural environment but also as a potential source for the spread of antibiotic resistance genes [85].
The uncontrolled use of antibiotics over recent years has led to the emergence of multiresistant Staphylococcus spp. strains due to mutations in genes encoding target proteins and, more importantly, through the acquisition and accumulation of genes conferring antibiotic resistance [32]. Studies indicating that food chains are pathways for the transmission of antimicrobial resistance from animals to humans have shown that a high abundance of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes have been detected in food of animal origin, including fish [86,87,88]. In this study, 92.6% of the CoNS isolates were resistant to at least one antibiotic, and only two multiresistant isolates were identified (S. epidermidis MDH2 and S. epidermidis MDH5). Staphylococcus spp. are frequently resistant to penicillin, followed by fusidic acid [89,90]. This is consistent with our results, in which the most frequent resistances were to penicillin (88.8%) and fusidic acid (40.7%). This can be explained by the data provided in the 2017 ECDC/EFSA/EMA report, in which it was stated that penicillin is one of the most prescribed antibiotics for food-producing animals [91]. Staphylococcus spp. exhibit different mechanisms of resistance to β-lactams, such as modified penicillin-binding proteins, production of β-lactamase enzymes, and tolerance phenomena [92]. The most important mechanism is the production of a β-lactamase enzyme, encoded by blaZ and controlled by the BlaZ-BlaR1-BlaI system. The genes blaZ and those encoding its repressor BlaI and the signal transducer-sensor protein BlaR1 are clustered either on a plasmid or on the bacterial chromosome. In the absence of β-lactam exposure, the DNA repressor BlaI represses blaZ expression. However, the detection of β-lactam molecules by BlaR1 initiates a signaling cascade that inhibits the repression of blaZ [93,94,95]. In this regard, blaZ was detected in 18 out of the 27 CoNS characterized in our work and was the most frequently detected antibiotic resistance gene. In addition, 10 of these isolates harbored macrolide and lincosamide resistance genes (i.e., mphC, msr(A/B), lnuA, or vgaA). The acquisition of resistance to macrolides and lincosamides is mainly due to the following: (i) target-site modification by methylation or mutation that prevents the binding of the antibiotic to its ribosomal target, (ii) efflux of the antibiotic, and (iii) antibiotic inactivation [96]. On the other hand, all the CoNS isolates tested in our study showing trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole resistance also carried dfrA. This is of great interest since this gene is strongly associated with mobile genetic elements such as plasmids and integrons, increasing the dissemination of sulfonamide resistance in aquatic environments [97]. Interestingly, all the CoNS characterized in our study were susceptible to chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, linezolid, mupirocin, tetracycline, and vancomycin. Similarly, another study reported that linezolid was effective against CoNS of clinical origin in over 98% of cases [98]. On the contrary, there are recent studies showing concern about resistance to chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, and mupirocin in CoNS of clinical origin [99,100,101].
5. Conclusions
Our findings show that antibiotic-resistant CoNS harboring virulence factors are present in marine fish, such as European hakes. Specifically, our study reveals a high distribution of biofilm-producing CoNS carrying genes conferring resistance to penicillin (blaZ), macrolides and lincosamides (mphC, msr(A/B), lnuA, or vgaA), fusidic acid (fusB), and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (dfrA) as well as genes encoding virulence traits, namely, scn, hla, SCCmecIII, and SCCmecV. Strikingly, only one out of the 27 CoNS isolates (S. epidermidis MFH1) was susceptible to all tested antibiotics and lacked virulence factors. Based on our results, the European hakes analyzed in this study, belonging to batches marketed for human consumption, could act as vectors of propagation in the aquatic environment of multiresistant and virulent CoNS potentially pathogenic to animals and humans.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens12121447/s1; Table S1: Direct antimicrobial activity of the CoNS isolated from European hakes against fish pathogens using the Stab-On-Agar Test (SOAT).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M.C., P.P. and E.M.-A.; methodology, L.D.-F., V.S., D.C., E.M.-A. and J.F.; software, L.D.-F., V.S., R.d.C. and D.C.; validation, P.P., G.I., J.F. and J.B.; formal analysis, L.D.-F., V.S., R.d.C. and J.F.; investigation, L.D.-F., E.M.-A. and D.C.; resources, J.B., P.P., G.I., P.E.H. and L.M.C.; data curation, L.D.-F.; writing—original draft preparation, L.D.-F.; writing—review and editing, E.M.-A., L.M.C. and P.P.; visualization, L.D.-F. and E.M.-A.; supervision, L.M.C., E.M.-A. and P.P.; project administration, L.M.C., P.E.H., E.M.-A. and J.B.; funding acquisition, L.M.C., J.B. and P.E.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades (MCIU, Spain, Projects RTI2018-094907-B-I00 and PID2019-104808RA-I00), and Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT, Portugal, UIDB/50006/2020, UIDP/50006/2020, UIDB/CVT/00772/2020, and LA/P/0059/2020). L.D.F. was supported by the Programa Investigo (Ministerio de Trabajo y Economía Social, MITES, Spain), funded by the EU (NextGenerationEU). V.S. was supported by a PhD grant (SFRH/BD/137947/2018FCT) from FCT (Portugal). D.C. was supported by a contract from the project RTI2018-094907-B-I00 (MCIU, Spain). J.F. was supported by a FEI16/54 contract from the Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM, Spain) and held a predoctoral contract from the UCM. JB was supported by the Programa Atracción de Talento (2018-T1/BIO-10158) from the Comunidad de Madrid (Spain).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge I. Ruiz Zarzuela (Facultad de Veterinaria, Universidad de Zaragoza, Spain) and C. Michel (INRA, Jouy-en-Josas, France) for providing some of the fish pathogens.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The FAO Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance 2016–2020. 2016. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i5996s/i5996s.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/cc0461es (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Ministerio de Agricultura, Alimentación y Medio Ambiente (MAPA). El Mercado de la Merluza en España. El mercado de la Merluza en España. 2016. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/pesca/temas/mercados-economia-pesquera/informemerluzaabril2016_tcm30-291641.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación (MAPA). Estadísticas Pesqueras: Pesca Marítima. 2022. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/estadistica/temas/estadisticas-pesqueras/pesca-maritima/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Antimicrobial Resistance. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 17 September 2023).
- Schar, D.; Klein, E.Y.; Laxminarayan, R.; Gilbert, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global trends in antimicrobial use in aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Rheman, S.; Debnath, N.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Akhtar, Z.; Ghosh, S.; Parveen, S.; Islam, K.; Islam, A.; Rashid, M.; et al. Antibiotics usage practices in aquaculture in Bangladesh and their associate factors. One Health 2022, 15, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; MacKinnon, B.; Karunasagar, I.; Fridman, S.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Brun, E.; Le Groumellec, M.; Li, A.; Surachetpong, W.; Karunasagar, I.; et al. Reviews of alternatives to antibiotic use in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1421–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, F.C. Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: A growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoirdt, T.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P. Alternatives to antibiotics for the control of bacterial disease in aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Gómez-Sala, B.; Araújo, C.; Campanero, C.; del Campo, R.; Hernández, P.E.; Herranz, C.; Cintas, L.M. Antimicrobial activity, antibiotic susceptibility and virulence factors of lactic acid bacteria of aquatic origin intended for use as probiotics in aquaculture. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadón, A. The EU ban of antibiotics as feed additives: Alternatives and consumer safety. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 29, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (UE). No. 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on Pharmacologically Active Substances and Their Classification as Regards Maximum Residue Limits in Foodstuffs of Animal Origin. DOUE. No 15, of 20 January 2010. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/doc.php?id=DOUE-L-2010-80044 (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Santos, L.; Ramos, F. Antimicrobial resistance in aquaclture: Current knowledge and alternatives to tackle the problem. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2018, 52, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravningen, K.; Sorum, H.; Horsberg, T.E. The future of therapeutic agents in aquaculture. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2009, 38, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Understanding Antimicrobial Resistances in Aquaculture. Asian Fisheries Society. 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org/publications/card/en/c/CB2601EN/ (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Price, L.B.; Stegger, M.; Hasman, H.; Aziz, M.; Larsen, J.; Andersen, P.S.; Pearson, T.; Waters, A.E.; Foster, J.T.; Schupp, J.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus CC398: Host adaptation and emergence of methicillin resistance in livestock. mBio 2012, 3, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: Final report and recommendations. Rev. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 1–84. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjElreVvIyDAxVskVYBHUb6C4oQFnoECAoQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Famr-review.org%2Fsites%2Fdefault%2Ffiles%2F160518_Final%2520paper_with%2520cover.pdf&usg=AOvVaw0kDaiLbLr8dtJAJDnpiBEF&opi=89978449 (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Food and Agriculture Organization-World Organization for Animal Health-World Health Organization (FAO-OIE-WHO). The Tripartite’s Commitment Providing Multi-Sectoral, Collaborative Leadership in Addressing Health Challenges; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chessa, D.; Ganau, G.; Mazzarello, V. An overview of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus with a focus on developing countries. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2015, 9, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Almeida, L.; Gaio, V.; Cerca, N.; Manageiro, V.; Caniça, M.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Biofilm formation of multidrug-resistant MRSA strains isolated from different types of human infections. Pathogens 2021, 10, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W.; Zadernowska, A.; Nalepa, B.; Sierpińska, M.; Łaniewska-Trokenheim, Ł. Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) isolated from ready-to-eat food of animal origin—Phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic resistance. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søndergaard, A.; Stahnke, L. Growth and aroma production by Staphylococcus xylosus, S. carnosus and S. equorum—A comparative study in model systems. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 75, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piette, A.; Verschraegen, G. Role of coagulase-negative staphylococci in human disease. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcal biofilms. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 322, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Sanz, E.; Ceballos, S.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Clonally diverse methicillin and multidrug resistant coagulase negative staphylococci are ubiquitous and pose transfer ability between pets and their owners. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiyapuri, M.; Joseph, T.C.; Rao, B.M.; Lalitha, K.V.; Prasad, M.M. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in seafood: Prevalence, laboratory detection, clonal nature, and control in seafood chain. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieliński, W.; Korzeniewska, E.; Harnisz, M.; Drzymała, J.; Felis, E.; Bajkacz, S. Wastewater treatment plants as a reservoir of integrase and antibiotic resistance genes—An epidemiological threat to workers and environment. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukułowicz, A.; Steinka, I.; Siwek, A. Presence of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in fish and seafood originating from points of sale in the Tri-City Area (Poland). J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, S.A.; Smith, J.T.; Mydosh, J.L.; Ball, J.; Needle, D.B.; Gibson, R.; Andam, C.P. Shared antibiotic resistance and virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus from diverse animal hosts. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.J. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol. 2017, 41, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fri, J.; Njom, H.A.; Ateba, C.N.; Ndip, R.N. Antibiotic resistance and virulence gene characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from healthy edible marine fish. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 9803903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuszewska, M.; Dabrowska, A.; Murray, G.G.R.; Kett, S.M.; Vick, A.J.A.; Banister, S.C.; Munoz, L.P.; Cunningham, P.; Welch, J.J.; Holmes, M.A.; et al. Absence of Staphylococcus aureus in wild populations of fish supports a spillover hypothesis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0485822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uniacke-Lowe, S.; Collins, F.W.J.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. Bioactivity Screening and Genomic Analysis Reveals Deep-Sea Fish Microbiome Isolates as Sources of Novel Antimicrobials. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commercial Designations. Fishing Zones. Available online: https://fish-commercial-names.ec.europa.eu/fish-names/fishing-areas_es (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Cintas, L.M.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Fernández, M.F.; Sletten, K.; Nes, I.F.; Hernández, P.E.; Holo, H. Isolation and characterization of pediocin L50, a new bacteriocin from Pediococcus acidilactici with a broad inhibitory spectrum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 2643–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrès, E.; Sohier, D.; Leroi, F.; Pilet, M.F.; Prévost, H.; Joffraud, J.J.; Dousset, X. Study of the bacterial ecosystem in tropical cooked and peeled shrimps using a polyphasic approach. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 131, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, C.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Ramírez, M.; Poeta, P.; Igrejas, G.; Hernández, P.E.; Herranz, C.; Cintas, L.M. Safety assessment, genetic relatedness and bacteriocin activity of potential probiotic Lactococcus lactis strains from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) and rearing environment. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oniciuc, E.-A.; Cerca, N.; Nicolau, A.I. Compositional Analysis of Biofilms Formed by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from food sources. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, E.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Comparison of multiple methods for quantification of microbial biofilms grown in microtiter plates. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 72, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters; Version 13.1. 2023. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_13.1_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; Approved Standard—Second Edition; document M31-A2; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2002; ISBN 1-56238-461-9. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, V.; Almeida, F.; Silva, A.; Correia, S.; Carvalho, J.A.; Castro, A.P.; Ferreira, E.; Manageiro, V.; Caniça, M.; Igrejas, G.; et al. First report of linezolid-resistant cfr-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in humans in Portugal. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 17, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, G.; Piémont, Y.; Godail-Gamot, F.; Bes, M.; Peter, M.O.; Gauduchon, V.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J. Involvement of panton-valentine leukocidin-producing Staphylococcus aureus in primary skin infections and pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarraud, S.; Mougel, C.; Thioulouse, J.; Lina, G.; Meugnier, H.; Forey, F.; Nesme, X.; Etienne, J.; Vandenesch, F. Relationships between Staphylococcus aureus genetic background, virulence factors, agr groups (alleles), and human disease. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wamel, W.J.B.; Rooijakkers, S.H.M.; Ruyken, M.; van Kessel, K.P.M.; van Strijp, J.A.G. The innate immune modulators staphylococcal complement inhibitor and chemotaxis inhibitory protein of Staphylococcus aureus are located on beta-hemolysin-converting bacteriophages. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Liu, Y.; Lv, J.; Qi, X.; Lu, C.; Ding, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, L. Antimicrobial susceptibility, virulence determinant carriage and molecular characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolates associated with skin and soft tissue infections. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 19, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Vieira-Pinto, M.; Saraiva, C.; Manageiro, V.; Reis, L.; Ferreira, E.; Caniça, M.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Prevalence and characteristics of multidrug-resistant livestock-associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LA-MRSA) CC398 isolated from quails (Coturnix coturnix japonica) slaughtered for human consumption. Animals 2021, 11, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proia, L.; von Schiller, D.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Sabater, S.; Borrego, C.M.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Balcázar, J.L. Occurrence and persistence of antibiotic resistance genes in river biofilms after wastewater inputs in small rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Almeida, F.; Carvalho, J.A.; Castro, A.P.; Ferreira, E.; Manageiro, V.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Caniça, M.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Emergence of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus EMRSA-15 clone as the predominant cause of diabetic foot ulcer infections in Portugal. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 39, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marutescu, L.G.; Popa, M.; Gheorghe-Barbu, I.; Rodríguez-Molina, D.; Berglund, F.; Blaak, H.; Flach, C.-F.; Kemper, M.A.; Spießberger, B.; Wengenroth, L.; et al. Wastewater treatment plants, an “escape gate” for ESCAPE pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1193907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, P.; Lozano, C.; Benito, D.; Estepa, V.; Tenorio, C.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Characterization of staphylococci in urban wastewater treatment plants in Spain, with detection of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, F.; Picard, F.J.; Ke, D.; Paradis, S.; Roy, P.H.; Ouellette, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Development of a PCR assay for identification of staphylococci at genus and species levels. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regecová, I.; Pipová, M.; Jevinová, P.; Marušková, K.; Kmeť, V.; Popelka, P. Species identification and antimicrobial resistance of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from the meat of sea fish. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, M898–M902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canak, O.; Timur, G. An initial survey on the occurrence of staphylococcal infections in Turkish marine aquaculture (2013–1014). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2020, 36, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, B.M.; Chen, J.S.; Lin, I.C.; Hsu, G.J.; Koner, S.; Hussain, B.; Huang, S.W.; Tsai, H.C. Molecular and anti-microbial Resistance (AMR) profiling of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from hospital and long-term care facilities (LTCF) environment. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Aziz, A. ERIC-PCR fingerprint profiling and genetic diversity of coagulase negative Staphylococcus in Malaysia. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2020, 16, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feito, J.; Araújo, C.; Gómez-Sala, B.; Contente, D.; Campanero, C.; Arbulu, S.; Saralegui, C.; Peña, N.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Borrero, J.; et al. Antimicrobial activity, molecular typing and in vitro safety assessment of Lactococcus garvieae isolates from healthy cultured rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) and rearing environment. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 162, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Tiwari, M.; Donelli, G.; Tiwari, V. Strategies for combating bacterial biofilms: A focus on anti-biofilm agents and their mechanisms of action. Virulence 2018, 9, 522–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, T.M.A.; Oliveira, A.P.D.; Miyasato, I.F.; Santos, T.M.B.; Dias, F.S. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from tilapia and utensils used in the commercialization of tilapia in the street markets of a semi-arid Brazilian municipality. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2019, 18, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.; Sivaraman, G.K.; Mothadaka, M.P. Multidrug-resistant phenotypes among biofilm-producing staphylococcal isolates from farm-raised fish: A molecular scrutiny. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feazel, L.M.; Baumgartner, L.K.; Peterson, K.L.; Frank, D.N.; Harris, J.K.; Pace, N.R. Opportunistic pathogens enriched in showerhead biofilms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16393–16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzer, M.; Witt, N.; Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. Faecal indicator bacteria in river biofilms. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingender, J.; Flemming, H.-C. Biofilms in drinking water and their role as reservoir for pathogens. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisplinghoff, H.; Bischoff, T.; Tallent, S.M.; Seifert, H.; Wenzel, R.P.; Edmond, M.B. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: Analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argemi, X.; Hansmann, Y.; Prola, K.; Prévost, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci pathogenomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Working Group on the Classification of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome Elements (IWG-SCC). Classification of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec): Guidelines for reporting novel SCCmec elements. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4961–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, R.; Colodner, R.; Kunin, C.M. Who are you: Staphylococcus saprophyticus? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, H.; Takahashi, S.; Ishikawa, K.; Yasuda, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Wada, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Hamasuna, R.; Minamitani, S.; Matsumoto, T.; et al. Second nationwide surveillance of bacterial pathogens in patients with acute uncomplicated cystitis conducted by Japanese Surveillance Committee from 2015 to 2016: Antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. J. Infect. Chemother. 2019, 25, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.U.; Barata, M.; Fraqueza, M.J.; Worning, P.; Bartels, M.D.; Goncalves, L.; Paixão, P.; Goncalves, E.; Toscano, C.; Empel, J.; et al. Staphylococcus saprophyticus from clinical and environmental origins have distinct biofilm composition. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 663768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Virulence factors of the coagulase-negative staphylococci. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 841–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, M.; Yamashita, A.; Hirakawa, H.; Kumano, M.; Morikawa, K.; Higashide, M.; Maruyama, A.; Inose, Y.; Matoba, K.; Toh, H.; et al. Whole genome sequence of Staphylococcus saprophyticus reveals the pathogenesis of uncomplicated urinary tract infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13272–13277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tevell, S.; Hellmark, B.; Nilsdotter-Augustinsson, Å.; Söderquist, B. Staphylococcus capitis isolated from prosthetic joint infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, F.; Butin, M. Staphylococcus capitis and NRCS-A clone: The story of an unrecognized pathogen in neonatal intensive care units. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, D.R.; Jiang, J.-H.; Hassan, K.A.; Elbourne, L.D.H.; Tuck, K.L.; Paulsen, I.T.; Peleg, A.Y. Insights on virulence from Staphylococcus capitis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, C.E.; Bengtsson, R.J.; Horsburgh, M.J. Comparative genomics of Staphylococcus capitis reveals species determinants. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1005949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Azevedo, P.A.; Trancesi, R.; Sales, T.; Monteiro, J.; Gales, A.C.; Pignatari, A.C. Outbreak of Staphylococcus hominis subsp. novobiosepticus bloodstream infections in São Paulo city, Brazil. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 256–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorlozano, A.; Gutierrez, J.; Martinez, T.; Yuste, M.E.; Perez-Lopez, J.A.; Vindel, A.; Guillen, J.; Boquete, T. Detection of new mutations conferring resistance to linezolid in glycopeptide-intermediate susceptibility Staphylococcus hominis subspecies hominis circulating in an intensive care unit. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz de Gopegui, E.; Iuliana Marinescu, C.; Diaz, P.; Socias, A.; Garau, M. Nosocomial spread of linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus hominis in two hospitals in Majorca. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2011, 29, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczuka, E.; Krzymińska, S.; Bogucka, N.; Kaznowski, A. Multifactorial mechanisms of the pathogenesis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus hominis isolated from bloodstream infections. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoiemma, P.P.; Kalainov, D.M.; Mehta, M.P.; Bolon, M.K. An unusual case of Staphylococcus pasteuri osteomyelitis. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2020, 12, 8523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, E.; Donat, E.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Fernández-Murga, M.L.; Sanz, Y. Duodenal-mucosal bacteria associated with celiac disease in children. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5472–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantůček, R.; Sedláček, I.; Indráková, A.; Vrbovská, V.; Mašlaňová, I.; Kovařovic, V.; Švec, P.; Králová, S.; Krištofová, L.; Kekláková, J.; et al. Staphylococcus edaphicus sp. nov., isolated in Antarctica, harbors the mecC gene and genomic islands with a suspected role in adaptation to extreme environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01746-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Alcântara Rodrigues, I.; Ferrari, R.G.; Panzenhagen, P.H.N.; Mano, S.B.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Antimicrobial resistance genes in bacteria from animal-based foods. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 112, 143–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Q.E.; Zhou, X.; Wang, F.; Muurinen, J.; Virta, M.P.; Brandt, K.K.; Zhu, Y. Antibiotic resistome in the livestock and aquaculture industries: Status and solutions. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. 2021, 51, 2159–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Kong, L.; Gao, H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, X. A review of current bacterial resistance to antibiotics in food animals. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 822689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikwap, K.; Gertzell, E.; Hansson, I.; Dahlin, L.; Selling, K.; Magnusson, U.; Dione, M.; Jacobson, M. The presence of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus spp. and Escherichia coli in smallholder pig farms in Uganda. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, L.K.L.; Rodrigues, C.A.; Filho, A.R.G.; Coelho, C.J.; Goes, V.; Estrela, M.; de Souza, P.; Avelino, M.A.G.; Vieira, J.D.G.; Carneiro, L. Staphylococcus spp. causatives of infections and carrier of blaZ, femA, and mecA genes associated with resistance. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC); European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Medicines Agency (EMA). ECDC/EFSA/EMA Second Joint Report on the Integrated Analysis of the Consumption of Antimicrobial Agents and Occurrence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Humans and Food-Producing Animals. EFSA J. 2017, 15, 4872. [Google Scholar]
- Fishovitz, J.; Hermoso, J.A.; Chang, M.; Mobashery, S. Penicillin-binding protein 2a of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, M.T.; Feil, E.J.; Lindsay, J.A.; Peacock, S.J.; Day, N.P.J.; Enright, M.C.; Foster, T.J.; Moore, C.E.; Hurst, L.; Atkin, R.; et al. Complete genomes of two clinical Staphylococcus aureus strains: Evidence for the rapid evolution of virulence and drug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9786–9791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llarrull, L.I.; Mobashery, S. Dissection of events in the resistance to β-lactam antibiotics mediated by the protein BlaR1 from Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 4642–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pence, M.A.; Haste, N.M.; Meharena, H.S.; Olson, J.; Gallo, R.L.; Nizet, V.; Kristian, S.A. Beta-Lactamase Repressor BlaI Modulates Staphylococcus aureus cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide resistance and virulence. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, R. Mechanisms of resistance to macrolides and lincosamides: Nature of the resistance elements and their clinical implications. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vásquez-Ponce, F.; Higuera-Llantén, S.; Parás-Silva, J.; Gamboa-Acuña, N.; Cortés, J.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; Ugalde, J.A.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Olivares-Pacheco, J. Genetic characterization of clinically relevant class 1 integrons carried by multidrug resistant bacteria (MDRB) isolated from the gut microbiota of highly antibiotic treated Salmo salar. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 29, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Kelesidis, T.; Tsiodras, S.; Hindler, J.; Humphries, R.M. The emerging problem of linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Miao, X.; Zheng, Y.D.; Liu, J.; He, Q.-Y.; Ge, R.; Sun, X. Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus displays enhanced resistance and virulence in iron-restricted conditions. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, E.E.; Boswihi, S.S.; Mathew, B.; Noronha, B.; Verghese, T. Resurgence of chloramphenicol resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus due to the acquisition of a variant florfenicol exporter (fexAv)-mediated chloramphenicol resistance in Kuwait hospitals. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, S.; Mohammadi, A.; Hajikhani, B.; Abiri, P.; Fazeli, M.; Nasiri, M.J.; Dadashi, M.; Goudarzi, M.; Haghighi, M. Mupirocin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Iran: A biofilm production and genetic characteristics. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7408029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).