The Evolution of the Safety of Plasma Products from Pathogen Transmission—A Continuing Narrative
Abstract
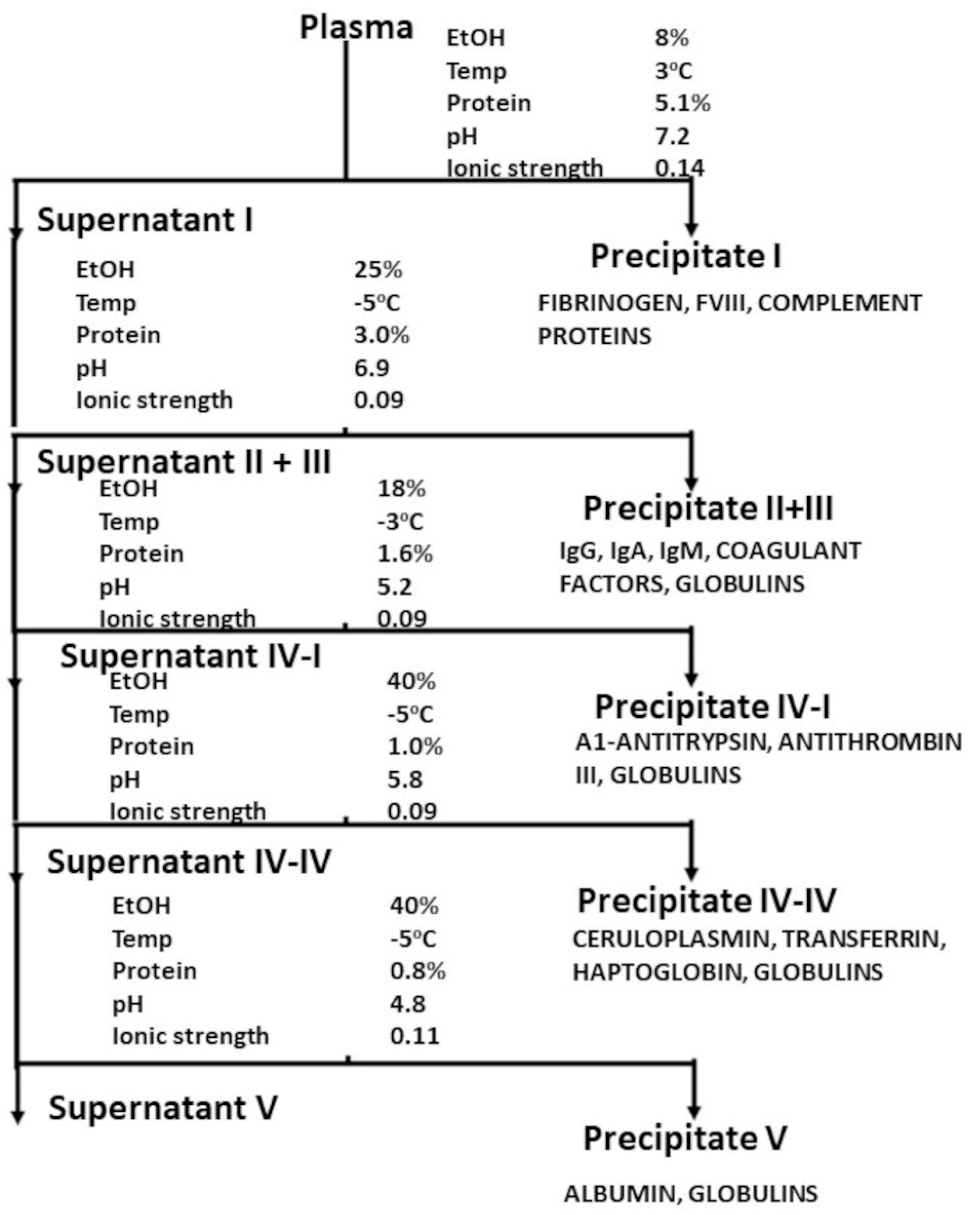
:1. Background—The Development of Plasma-Derived Pharmaceuticals
2. The (Invisible) Elephant in the (Treatment) Room—The Potential Infection by Pathogens Present in the Plasma Pools
3. Emergence of Pathogen Transmission as a Risk for Recipients of Blood and Plasma Products—The Hepatitis Story
4. The Catastrophe of AIDS
5. A Further Note on Pooling
6. The Development of Effective Measures for Assuring Plasma Product Safety
7. A Footnote—Safety from Prion Transmission
8. Development of a Cohesive Framework—The Current Landscape of Plasma Product Safety
9. Concluding Reflections
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kendrick, D.B. Blood Program in World War II; Office of the Surgeon General: Department of the Army: Washington, DC, USA, 1964; 968p. [Google Scholar]
- Eibl, M.M. History of Immunoglobulin Replacement. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2008, 28, 737–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, M.-C.; Card, R.T. Samuel Armstrong Lane’s first successful treatment of haemophilia with blood transfusion in 1840: Could this also be the first successful bypassing therapy? Haemophilia 2018, 25, e45–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bloom, A.L. Oliver Memorial Lecture 1989. The evolution and future of haemophilia therapy. Transfus. Med. Oxf. Engl. 1991, 1, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruton, J.S. Joseph S. Edwin J. Cohn and the Development of Protein Chemistry: With a Detailed Account of His Work on the Fractionation of Blood during and after World War II review. J. Hist. Med. Allied Sci. 2004, 59, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, E.J. The History of Plasma Fractionation. In Advances in Military Medicine; Little, Brown and Co.: Boston, MA, USA, 1948; pp. 364–443. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, E.J.; Strong, L.E.; Hughes, W.L.; Mulford, D.J.; Ashworth, J.N.; Melin, M.; Taylor, H.L. Preparation and Properties of Serum and Plasma Proteins. IV. A System for the Separation into Fractions of the Protein and Lipoprotein Components of Biological Tissues and Fluids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1946, 68, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, A.; Mori, F. Therapeutic Solutions of Human Albumin—The Possible Effect of Process-Induced Molecular Alterations on Clinical Efficacy and Safety. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 1292–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendrick, D. The Bovine and Human Albumin Programs. In Blood Program in World War II—Digital Collections—National Library of Medicine [Internet]. 1965; pp. 325–357. Available online: https://collections.nlm.nih.gov/catalog/nlm:nlmuid-0014773-bk (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Barnett, V.H.; Cussen, C.A. Acquired afibrinogenaemia complicating pregnancy; report of two cases of two cases of concealed accidental haemorrhage treated by human fibrinogen. Br. Med. J. 1954, 2, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruton, O.C. Agammaglobulinemia. Pediatrics 1952, 9, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnouf, T. An overview of plasma fractionation. Ann. Blood 2018, 3, 33. Available online: https://aob.amegroups.com/article/view/4496 (accessed on 2 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Mousavi Hosseini, K.; Ghasemzadeh, M. Implementation of Plasma Fractionation in Biological Medicines Production. Iran J. Biotechnol. 2016, 14, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, T.; Weinstein, M.; Tankersley, D.; Fratantoni, J.; Finlayson, J. Considerations of pool size in the manufacture of plasma derivatives. Transfusion 2003, 36, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce-Chwatt, L.J. Transfusion malaria. Bull. World Health Organ. 1974, 50, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCluskie, J.A.W. Transmission of Syphilis by Blood Transfusion. BMJ 1939, 1, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lurman, A. Eine icterusepidemic. Berl Klin Wochenschr. 1885, 22, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, P.R.; Bienek, C. Fractionated Products. In Transfusion Microbiology [Internet]; Regan, F.A.M., Barbara, J.A.J., Contreras, M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 259–304. Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/transfusion-microbiology/fractionated-products/A3F5C27C822FADCA41D4FA78184744D4 (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Beeson, P.B. Jaundice occurring one to four months after transfusion of blood or plasma: Report of seven cases. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1943, 121, 1332–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinberg, I.H.; Kinney, T.D.; Janeway, C.A. homologous serum jaundice: A Problem in the Operation of Blood Banks. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1947, 134, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gellis, S.S.; Neefe, J.R.; Stokes, J.; Strong, L.E.; Janeway, C.A.; Scatchard, G. Chemical, clinical, and immunological studies on the products of human plasma fractionation. Xxxvi. Inactivation of the virus of homologous serum hepatitis in solutions of normal human serum albumin by means of heat. J. Clin. Investig. 1948, 27, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, R.; Diefenbach, W.C.; Geller, H.; Leone, N.C.; Ratner, F. The problem of reducing the danger of serum; hepatitis from blood and blood products. N. Y. State J. Med. 1955, 55, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle, J.H.; Barker, L.F.; Thiel, J.; Gerety, R.J. Hepatitis B virus and hepatitis B surface antigen in human albumin products. Transfusion 1976, 16, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, L.H.; Busch, M.P. History of posttransfusion hepatitis. Clin. Chem. 1997, 43, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeler, R.A.; Mufson, M.A. Development and Persistence of Antibody to Hepatitis-Associated (Australia) Antigen in Patients with Hemophilia. J. Infect. Dis. 1971, 123, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.E.; Grizzle, J.E.; Ii, J.A.B. 347. Note: Estimation of the Probability of Post Transfusion Hepatitis in Hemophilia Treatment. Biometrics 1973, 29, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domen, R.E. Paid-versus-volunteer blood donation in the united states: A historical review. Transfus. Med. Rev. 1995, 9, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, Q.-L.; Kuo, G.; Weiner, A.J.; Overby, L.R.; Bradley, D.W.; Houghton, M. Isolation of a cDNA cLone Derived from a Blood-Borne Non-A, Non-B Viral Hepatitis Genome. Science 1989, 244, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fletcher, M.L.; Trowell, J.M.; Craske, J.; Pavier, K.; Rizza, C.R. Non-A non-B hepatitis after transfusion of factor VIII in infrequently treated patients. BMJ 1983, 287, 1754–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rickard, K.; Dority, P.; Campbell, J.; Batey, R.; Johnson, S.; Hodgson, J. Hepatitis and Haemophilia Therapy in Australia. Lancet 1982, 320, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isfordink, C.J.; van Erpecum, K.J.; van der Valk, M.; Mauser-Bunschoten, E.P.; Makris, M. Viral hepatitis in haemophilia: Historical perspective and current management. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 195, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveton, L.B.; Harold CSox, J.; Stoto, M.A. History of the Controversy [Internet]. HIV And The Blood Supply: An Analysis of Crisis Decisionmaking; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1995. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK232419/ (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Evatt, B.L. The tragic history of AIDS in the hemophilia population, 1982–1984. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2006, 4, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.; Young, M.; Samson, S.; Mosley, J.; Ward, J.; Perkins, H. Risk of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) transmission by blood transfusions before the implementation of HIV-1 antibody screening. The Transfusion Safety Study Group. Transfusion 1991, 31, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, J.W.; Evatt, B.L.; Lawrence, D.N. Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome: The Past as Prologue. Ann. Intern. Med. 1983, 98, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucie, J.M.; Richardson, L.C.; Evatt, B.L.; Linden, J.V.; Ewenstein, B.M.; Stein, S.F.; Leissinger, C.; Manco-Johnson, M.; Sexauer, C.L.; for the Hemophilia Surveillance System Project Investigators. Risk factors for infection with HBV and HCV in a largecohort of hemophiliac males. Transfusion 2001, 41, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, S.A.; Ulstrup, J.; Skaug, K.; Frøland, S.S.; Glomstein, A.; Rollag, H. HIV infection in Norwegian haemophiliacs: The prevalence of antibodies against HIV in haemophiliacs treated with lyophilized cryoprecipitate from volunteer donors. Eur. J. Haematol. 2009, 39, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollag, H.; Evesen, S.A.; Fröland, S.S.; Glomstein, A. Prevalence of antibodies against hepatitis C virus in Norwegians with congenital coagulation factor defects treated with plasma products from small pools. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1990, 9, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollag, H.; Patou, G.; Pattison, J.R.; Degré, M.; Evensen, S.A.; Fröland, S.S.; Glomstein, A. Prevalence of antibodies against parvovirus B19 in Norwegians with congenital coagulation factor defects treated with plasma products from small donor pools. Scand J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 23, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haemophilia Study Group. Haemophilia, HIV Infection, and Blood Transfusion in Belgium. Acta Clin. Belg. 1988, 43, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauser-Bunschoten, E.P.; Roosendaal, G.; Berg, H.M.V.D.; Bresters, D.; van Drimmelen, A.A.J.; Cuypers, H.T.M.; Lelie, P.N.; Reesink, H.W.; Der Van Poel, C.L. Hepatitis C infection and viremia in Dutch Hemophilia patients. J. Med. Virol. 1995, 45, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wolock, T.M.; Carter, A.; Nguyen, G.; Kyu, H.H.; Gakidou, E.; Hay, S.I.; Mills, E.J.; Trickey, A.; Msemburi, W.; et al. Estimates of global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and mortality of HIV, 1980–2015: The Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet HIV 2016, 3, e361–e387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, T.S. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Diagnostic Testing: 30 Years of Evolution. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berntorp, E. History of prophylaxis. Haemophilia 2013, 19, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, E.; Epstein, J. NAT screening of blood and plasma donations: Evolution of technology and regulatory policy*. Transfusion 2002, 42, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, A. Plasma for fractionation: Safety and quality issues. Haemophilia 2004, 10, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, P.R. Plasma Fractionation. In Transfusion Medicine: Quo Vadis? What Has Been Achieved, What Is to Be Expected: Proceedings of the jubilee Twenty-Fifth International Symposium on Blood Transfusion, Groningen, 2000; Sibinga, C.T.h.S., Cash, J.D., Eds.; Organized by the Sanquin Division Blood Bank Noord Nederland [Internet]; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 87–101, (Developments in Hematology and Immunology). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimburger, N.; Schwinn, H.; Gratz, P.; Lüben, G.; Kumpe, G.; Herchenhan, B. Factor VIII concentrate, highly purified and heated in solution (author’s transl). Arzneimittelforschung 1981, 31, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heimburger, N.; E Karges, H.; Weidmann, E. Virus safety of pasteurized factor VIII and factor IX concentrates: Study in virgin patients. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1987, 67, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rouzioux, C.; Chamaret, S.; Montagnier, L.; Carnelli, V.; Rolland, G.; Mannucci, P. Absence of antibodies to aids virus in haemophiliacs treated with heat-treated factor viii concentrate. Lancet 1985, 325, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Carnelli, V.; Gazengel, C.; Mannucci, P.; Savidge, G.; Schimpf, K. Transmission Of Non-A, Non-B Hepatitis By Heat-Treated Factor Viii Concentrate. Lancet 1985, 326, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.K.; Winkelman, L.; A Feldman, P. Interim results of surveillance for NANBH in patients receiving heated concentrates produced in England. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1987, 67, 323–325. [Google Scholar]
- Winkelmana, L.; Owena, N.E.; Evans, D.R.; Evans, H.; Haddon, M.E.; Smitha, J.K.; Prince, P.J.; Williams, J.D.; Lane, R.S. Severely Heated Therapeutic Factor VIII Concentrate of High Specific Activity. Vox Sang. 1989, 57, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, B.; Wiebe, M.E.; Lippin, A.; Stryker, M.H. Inactivation of viruses in labile blood derivatives. I. Disruption of lipid-enveloped viruses by tri(n-butyl)phosphate detergent combinations. Transfusion 1985, 25, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, B.; Prince, A.M.; Horowitz, M.S.; Watklevicz, C. Viral safety of solvent-detergent treated blood products. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1993, 81, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway, C.A. Use of Concentrated Human Serum gamma-Globulin in the Prevention and Attenuation of Measles. Bull. N. Y. Acad. Med. 1945, 21, 202–222. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, R.; Ratner, F. Safety of Immune Serum Globulin with Respect to Homologous Serum Hepatitis. Exp. Biol. Med. 1953, 83, 554–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockburn, W.C.; Harrington, J.A.; Zeitlin, R.A.; Morris, D.; Camps, F.E. Homologous serum hepatitis and measles prophylaxis; a report to the Medical Research Council. Br. Med. J. 1951, 2, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petrilli, F.L.; Crovari, P.; De Flora, S. Hepatitis B in Subjects Treated with a Drug Containing Immunoglobulins. J. Infect. Dis. 1977, 135, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabor, E.; Gerety, R. Transmission of Hepatitis B by Immune Serum Globulin. Lancet 1979, 314, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, S.; Roggendorf, M.; Dürkop, J.; Wiese, M.; Lorbeer, B.; Deinhardt, F. Long-term persistence of hepatitis C virus antibodies in a single source outbreak. J. Hepatol. 1991, 13, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny-Walsh, E. Clinical Outcomes after Hepatitis C Infection from Contaminated Anti-D Immune Globulin. New Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, P.L. The viral safety of intravenous immune globulin. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1996, 104 (Suppl. 1), 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, A.; Quinti, I. Manufacture of Immunoglobulin Products for Patients with Primary Antibody Deficiencies – The Effect of Processing Conditions on Product Safety and Efficacy. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yei, S.; Yu, M.; Tankersley, D.L. Partitioning of hepatitis C virus during Cohn-Oncley fractionation of plasma. Transfusion 1992, 32, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Mason, B.; Tankersley, D. Detection and characterization of hepatitis C virus RNA in immune globulins. Transfusion 1994, 34, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-Y.W.; Mason, B.L.; Guo, Z.P.; Tankersley, D.L. Safety of intravenous immunoglobulin with regard to hepatitis c virus. Clin. Ther. 1996, 18 (Suppl. B), 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.y.W.; Bartosch, B.; Zhang, P.; Guo, Z.p.; Renzi, P.M.; Shen, L.m.; Granier, C.; Feinstone, S.; Cosset, F.-L.; Purcell, R. Neutralizing antibodies to hepatitis C virus (HCV) in immune globulins derived from anti-HCV-positive plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7705–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lane, R. NON-A, non-B Hepatitis from Intravenous Immunoglobulin. Lancet 1983, 322, 974–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeArmond, S.J. Overview of the transmissible spongiform encephalopathies: Prion protein disorders. Br. Med Bull. 1993, 49, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Rohwer, R.G.; Dunstan, B.C.; MacAuley, C.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Drohan, W.N. The distribution of infectivity in blood components and plasma derivatives in experimental models of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy. Transfusion 1998, 38, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregori, L.; Maring, J.-A.; MacAuley, C.; Dunston, B.; Rentsch, M.; Kempf, C.; Rohwer, R. Partitioning of TSE infectivity during ethanol fractionation of human plasma. Biologicals 2004, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, J.; Wikman, A.; Pedersen, O.B.; Nielsen, K.R.; Rostgaard, K.; Hjalgrim, H.; Edgren, G. No evidence of transfusion transmitted sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Results from a bi-national cohort study. Transfusion 2020, 60, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, F.; Foster, J.; Chong, A.; Hunter, N.; Bostock, C. Transmission of BSE by blood transfusion in sheep. Lancet 2000, 356, 999–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urwin, P.J.M.; Mackenzie, J.M.; Llewelyn, C.A.; Will, R.G.; Hewitt, P.E. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and blood transfusion: Updated results of the UK Transfusion Medicine Epidemiology Review Study. Vox Sang. 2015, 110, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.C.; Stenland, C.J.; Miller, J.L.; Cai, K.; Ford, E.K.; Gilligan, K.J.; Hartwell, R.C.; Terry, J.C.; Rubenstein, R.; Fournel, M.; et al. A direct relationship between the partitioning of the pathogenic prion protein and transmissible spongiform encephalopathy infectivity during the purification of plasma proteins. Transfusion 2001, 41, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peden, A.; McCardle, L.; Head, M.; Love, S.; Ward, H.J.T.; Cousens, S.N.; Keeling, D.; Millar, C.M.; Hill, F.G.H.; Ironside, J.W. Variant CJD infection in the spleen of a neurologically asymptomatic UK adult patient with haemophilia. Haemophilia 2010, 16, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EEl-Shanawany, T.; Jolles, S.; Unsworth, D.J.; Williams, P. A recipient of immunoglobulin from a donor who developed vCJD. Vox Sang. 2009, 96, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UK Department of Health and Social Care. Ban Lifted to Allow UK Blood Plasma to Be Used for Life-Saving Treatments [Internet]. GOV.UK. 2021. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/ban-lifted-to-allow-uk-blood-plasma-to-be-used-for-life-saving-treatments (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Recommendations To Reduce the Possible Risk of Transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease and Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease by Blood and Blood Components [Internet]. Federal Register, Volume 87 Issue 100 (Tuesday, May 24, 2022); 2022. Available online: https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2022-05-24/html/2022-11119.htm (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Seed, C.R.; Hewitt, P.E.; Dodd, R.Y.; Houston, F.; Cervenakova, L. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and blood transfusion safety. Vox Sang. 2018, 113, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, J.E. Emerging Infectious Agents and Blood Safety in Latin America. Front. Med. 2018, 5. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2018.00071/full (accessed on 2 February 2023). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrugia, A. Globalisation and blood safety. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, G.M. Emerging and Re-Emerging Viral Diseases: The Case of Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19). Int. J. Virol. AIDS 2020, 7. Available online: https://www.clinmedjournals.org/articles/ijva/international-journal-of-virology-and-aids-ijva-7-067.php?jid=ijva (accessed on 18 January 2023).
- Giménez-Richarte, Á.; de Salazar, M.I.O.; Giménez-Richarte, M.-P.; Collado, M.; Fernández, P.L.; Clavijo, C.; Navarro, L.; Arbona, C.; Marco, P.; Ramos-Rincon, J.-M. Transfusion-transmitted arboviruses: Update and systematic review. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreil, T.R.; Berting, A.; Kistner, O.; Kindermann, J. West Nile virus and the safety of plasma derivatives: Verification of high safety margins, and the validity of predictions based on model virus data. Transfusion 2003, 43, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leydold, S.M.; Farcet, M.R.; Kindermann, J.; Modrof, J.; Pölsler, G.; Berting, A.; Howard, M.K.; Barrett, P.N.; Kreil, T.R. Chikungunya virus and the safety of plasma products. Transfusion 2012, 52, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcet, M.R.; Lackner, C.; Antoine, G.; Rabel, P.O.; Wieser, A.; Flicker, A.; Unger, U.; Modrof, J.; Kreil, T.R. Hepatitis E virus and the safety of plasma products: Investigations into the reduction capacity of manufacturing processes. Transfusion 2015, 56, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Transfusion-related transmission of yellow fever vaccine virus--California, 2009. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2010, 59, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Himmelsbach, K.; Mueller, S.; Kress, J.; Fiedler, S.A.; Miskey, C.; Ivics, Z.; Patek, A.; Chudy, M. Second hepatitis C virus transmission by blood components since introduction of mandatory NAT screening in Germany. Transfusion 2022, 63, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Korn, K.; Nübling, M.; Chudy, M.; Kress, J.; Horst, H.; Geusendam, G.; Hennig, H.; Sireis, W.; Rabenau, H.; et al. First transmission of human immunodeficiency virus Type 1 by a cellular blood product after mandatory nucleic acid screening in Germany. Transfusion 2009, 49. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19453990/ (accessed on 18 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, A. The mantra of blood safety: Time for a new tune? Vox Sang. 2004, 86, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turecek, P.L.; Hibbett, D.; Kreil, T.R. Plasma procurement and plasma product safety in light of the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspective of the plasma industry. Vox Sang. 2022, 117, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrie, E.A.; Rutter, S.J.; Snyder, E.L. Pathogen Reduction: The State of the Science in 2019. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 749–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Study HIV Transmission Through Blood and Blood Products; Leveton, L.B.; Harold CSox, J.; Stoto, M.A. Executive Summary [Internet]. HIV And The Blood Supply: An Analysis Of Crisis Decisionmaking; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1995. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK232406/ (accessed on 18 January 2023).
- Murphy, W.G. Disease Transmission by Blood Products: Past, Present and Future. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2002, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Kingdom Government. Homepage | Infected Blood Inquiry [Internet]. 2023. Available online: https://www.infectedbloodinquiry.org.uk/ (accessed on 19 January 2023).
 ) and HIV-1 (
) and HIV-1 ( ). The proportion was zero for HIV after 1984, for HCV after 1992, and for HBV after 1993. From Soucie et al. 2001, used with permission.
). The proportion was zero for HIV after 1984, for HCV after 1992, and for HBV after 1993. From Soucie et al. 2001, used with permission.
 ) and HIV-1 (
) and HIV-1 ( ). The proportion was zero for HIV after 1984, for HCV after 1992, and for HBV after 1993. From Soucie et al. 2001, used with permission.
). The proportion was zero for HIV after 1984, for HCV after 1992, and for HBV after 1993. From Soucie et al. 2001, used with permission.
| Manufacturing Scale (Number of Donors) | Number of Independent Infusions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 100 | |
| Prevalence of agent = 5 × 10−5 | |||
| 60,000 | 11% | 70% | 100% |
| 25,000 | 2% | 18% | 86% |
| 1000 | 0.2% | 2% | 18% |
| Prevalence of agent = 5 × 10−4 | |||
| 60,000 | 70% | 100% | 100% |
| 25,000 | 39% | 99% | 100% |
| 1000 | 2% | 18% | 86% |
| Prevalence of agent = 5 × 10−3 | |||
| 60,000 | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| 25,000 | 99% | 100% | 100% |
| 1000 | 18% | 86% | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farrugia, A. The Evolution of the Safety of Plasma Products from Pathogen Transmission—A Continuing Narrative. Pathogens 2023, 12, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020318
Farrugia A. The Evolution of the Safety of Plasma Products from Pathogen Transmission—A Continuing Narrative. Pathogens. 2023; 12(2):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020318
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarrugia, Albert. 2023. "The Evolution of the Safety of Plasma Products from Pathogen Transmission—A Continuing Narrative" Pathogens 12, no. 2: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020318
APA StyleFarrugia, A. (2023). The Evolution of the Safety of Plasma Products from Pathogen Transmission—A Continuing Narrative. Pathogens, 12(2), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020318






