High Prevalence of Syphilis and Syphilis/HIV Coinfection among Men Who Have Sex with Men Who Attend Meeting Places in Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Survey Design and Fieldwork
2.2. Laboratory Test
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Public Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
3.2. Factors Associated with Syphilis
3.3. Syphilis/HIV Coinfection
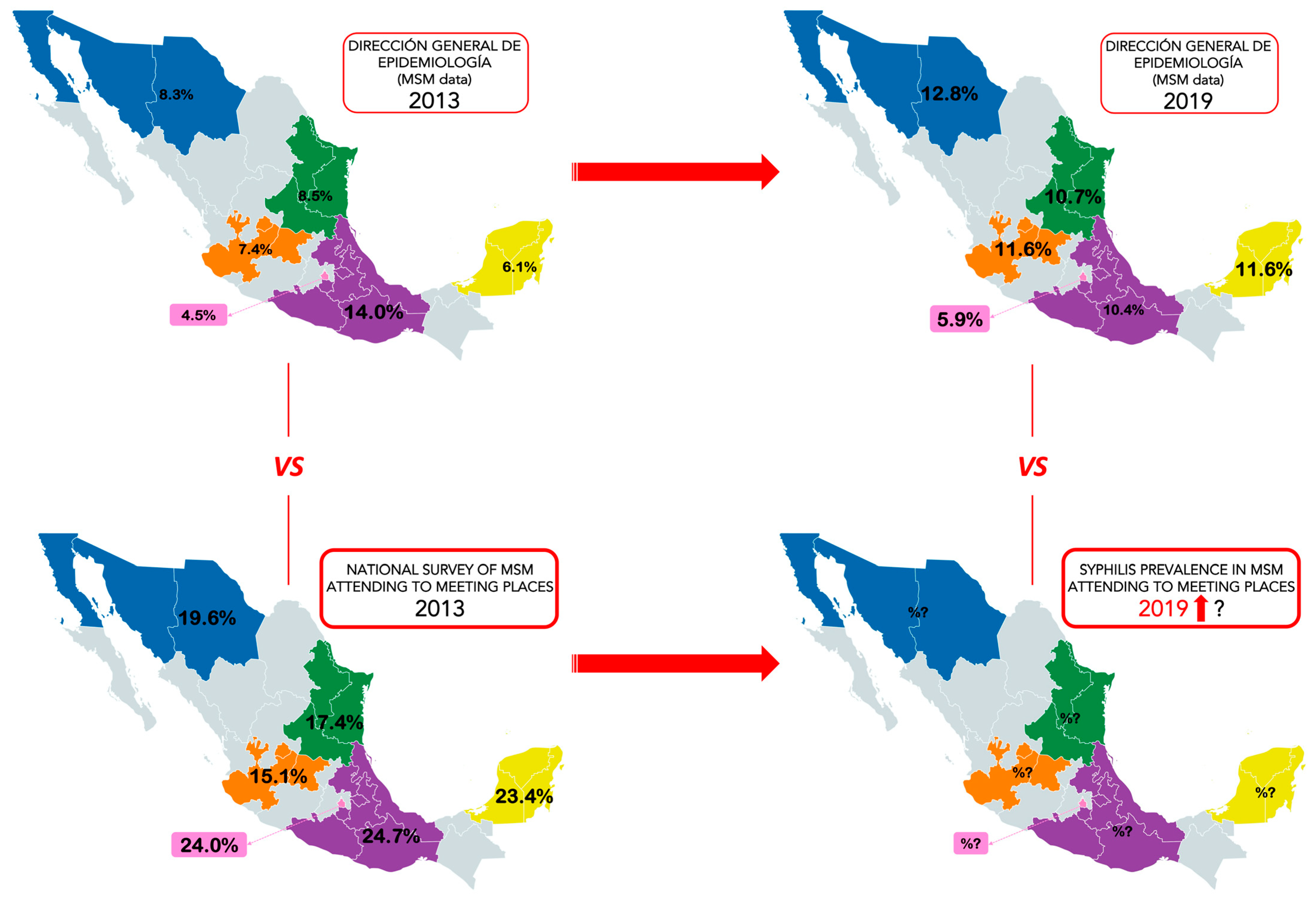
3.4. Comparison of Syphilis Prevalence among MSM: Public Data vs. National Survey in Meeting Places
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Refugio, O.N.; Klausner, J.D. Syphilis incidence in men who have sex with men with human immunodeficiency virus comorbidity and the importance of integrating sexually transmitted infection prevention into HIV care. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2018, 16, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeling, R.W.; Mabey, D.; Kamb, M.L.; Chen, X.-S.; Radolf, J.D.; Benzaken, A.S. Syphilis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2017, 3, 17073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abara, W.E.; Hess, K.L.; Neblett Fanfair, R.; Bernstein, K.T.; Paz-Bailey, G. Syphilis Trends among Men Who Have Sex with Men in the United States and Western Europe: A Systematic Review of Trend Studies Published between 2004 and 2015. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salado-Rasmussen, K. Syphilis and HIV co-infection. Epidemiology, treatment and molecular typing of Treponema pallidum. Dan. Med. J. 2015, 62, B5176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kofoed, K.; Gerstoft, J.; Mathiesen, L.R.; Benfield, T. Syphilis and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 coinfection: Influence on CD4 T-cell count, HIV-1 viral load, and treatment response. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2006, 33, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.P.F.; Wilson, D.P.; Zhang, L. HIV and syphilis co-infection increasing among men who have sex with men in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, G.; Schlaeffer, F.; Jotkowitz, A.; Riesenberg, K. Syphilis and HIV co-infection. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 20, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Arredondo, S.; Colchero, M.A.; Romero, M.; Conde-Glez, C.J.; Sosa-Rubí, S.G. Is the HIV epidemic stable among MSM in Mexico? HIV prevalence and risk behavior results from a nationally representative survey among men who have sex with men. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colchero, M.A.; Bautista-Arredondo, S.; Cortés-Ortiz, M.A.; Romero-Martinez, M.; Salas, J.; Sosa-Rubí, S.G.; Uribe, P. Impact and economic evaluations of a combination prevention programme for men who have sex with men in Mexico. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2016, 30, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resultados Principales de la Encuesta de Sero-Prevalencia en Sitios de Encuentro de Hombres que Tienen Sexo con Hombres. Available online: https://funsalud.org.mx/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Encuesta-seroprevalencia.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- HIV Ag/Ab Combo. Available online: https://www.ilexmedical.com/files/PDF/HIVAgAbCombo.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Interim Recommendations for the Use of the BED Capture Enzyme Immunoassay for Incidence Estimation and Surveillance. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/globalAIDS/docs/surveillance/Interim%20Recommendations%20for%20the%20use%20of%20the%20BED%20capture%20enzyme%20immunoassay%20for%20incidence%20estimation%20and%20surveillance%20Approved%20November%2021%202006%20(2).pdf (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- bioelisa Syphilis 3.0 | Werfen OEM. Available online: https://www.werfen.com/oem/bioelisa-syphilis-30 (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Lewis, B. Serodia Treponema Pallidum Particle Agglutination Test; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2001; 13p. [Google Scholar]
- Cubos Dinámicos. Available online: http://www.dgis.salud.gob.mx/contenidos/basesdedatos/BD_Cubos_gobmx.html (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Herrera-Ortiz, A.; Uribe-Salas, F.J.; Olamendi-Portugal, M.L.; García-Cisneros, S.; Conde-Glez, C.J.; Sánchez-Alemán, M.A. Trend analysis of acquired syphilis in Mexico from 2003 to 2013. Salud Publica Mex. 2015, 57, 335–342. [Google Scholar]
- Tumalán-Gil, O.D.; Ruiz-González, V.; García-Cisneros, S.; González-Rodríguez, A.; Herrera-Ortiz, A.; Olamendi-Portugal, M.; Sánchez-Alemán, M.A. High Incidence, Reinfections, and Active Syphilis in Populations Attending a Specialized HIV Clinic in Mexico, a Dynamic Cohort Study. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2023, 52, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GHO | Por Categoria | Men Who Have Sex with Men (MSM) with Active Syphilis—Data by Country. Available online: https://apps.who.int/gho/data/node.main.A1361STI?lang=es (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- de Voux, A.; Kidd, S.; Grey, J.A.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Gift, T.L.; Weinstock, H.; Bernstein, K.T. State-Specific Rates of Primary and Secondary Syphilis Among Men Who Have Sex with Men—United States, 2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, M.; Evans, J.; Davies, E.P.; Rowley, J.; Korenromp, E.L.; Clayton, T.; Taylor, M.M.; Mabey, D.; Chico, R.M. Prevalence of syphilis among men who have sex with men: A global systematic review and meta-analysis from 2000–20. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e1110–e1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Figueroa, L.A.; Uribe-Salas, F.J.; Vargas-Guadarrama, G.; González-Rodríguez, A.; Ruíz-González, V.; Medina-Islas, Y.; Hernández-Nevares, P.; Iracheta-Hernández, P. Syphilis Infection Markers Among HIV Positive Individuals in The Mexico City HIV/AIDS Program. Salud Pública México 2021, 63, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramke, J.; Palagyi, A.; Kuper, H.; Gilbert, C.E. Assessment of Response Bias Is Neglected in Cross-Sectional Blindness Prevalence Surveys: A Review of Recent Surveys in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2018, 25, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephanie. Response Bias: Definition and Examples. Statistics How To. 2015. Available online: https://www.statisticshowto.com/response-bias/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Kelly, C.A.; Soler-Hampejsek, E.; Mensch, B.S.; Hewett, P.C. Social Desirability Bias in Sexual Behavior Reporting: Evidence from an Interview Mode Experiment in Rural Malawi. Int. Perspect. Sex. Reprod. Health 2013, 39, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimonovich, M.; Pearce, A.; Thomson, H.; Keyes, K.; Katikireddi, S.V. Assessing causality in epidemiology: Revisiting Bradford Hill to incorporate developments in causal thinking. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 36, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanie. Reverse Causality: Definition, Examples. Statistics How to. 2016. Available online: https://www.statisticshowto.com/reverse-causality/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Fernandes, F.R.P.; Zanini, P.B.; Rezende, G.R.; Castro, L.S.; Bandeira, L.M.; Puga, M.A.; Tanaka, T.S.O.; Castro, L.S.; Bertolacci-Rocha, L.G.; Teles, S.A.; et al. Syphilis infection, sexual practices and bisexual behaviour among men who have sex with men and transgender women: A cross-sectional study. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2015, 91, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.-J.; Peng, B.; Liu, Z.-F.; Ye, Q.-N.; Liu, H.; Lu, X.-L.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.-J. The prevalence of HIV among MSM in China: A large-scale systematic analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.T.F.; Zhao, J.-K.; Wu, X.-B.; Gu, J.; Hao, C. Gay saunas and the risks of HIV and syphilis transmissions in China—Results of a meta-analysis. J. Sex. Med. 2013, 10, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.T.; Kamb, M.L.; Luu, M.; Ham, D.C.; Perez, F. Syphilis testing practices in the Americas. Trop. Med. Int. Health TMIH 2017, 22, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Pliego, A.; Sánchez-Alemán, M.Á.; Orbe-Orihuela, Y.C.; Medina-García, C.V.; Vergara-Ortega, D.N. Syphilis; an old foe powerfully re-emerging through the last years: A brief report. In Progress.
- Orbe-Orihuela, Y.C.; Sánchez-Alemán, M.Á.; Hernández-Pliego, A.; Medina-García, C.V.; Vergara-Ortega, D.N. Syphilis as Re-Emerging Disease, Antibiotic Resistance, and Vulnerable Population: Global Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Categories | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Mexico City | 1389 | 27.9 |
| Center | 961 | 19.3 | |
| West | 894 | 18.0 | |
| Northwest | 693 | 13.9 | |
| Northeast | 741 | 14.9 | |
| South | 299 | 6.0 | |
| Aged | ≥35 years | 869 | 17.5 |
| 30–34 years | 655 | 13.2 | |
| 25–29 years | 1126 | 22.6 | |
| 20–24 years | 1728 | 34.7 | |
| 18–19 years | 599 | 12.0 | |
| Goods | 0–3 | 579 | 11.6 |
| 4–6 | 2329 | 46.8 | |
| 7–8 | 2069 | 41.6 | |
| Occupation | Employee | 3059 | 61.5 |
| Unemployed | 307 | 6.2 | |
| Own business | 262 | 5.3 | |
| Others | 56 | 1.1 | |
| Student | 1293 | 26.0 | |
| Inhalant drugs (last 12 months) | Any time | 235 | 4.7 |
| Never | 4742 | 95.3 | |
| HIV infection | Positive | 789 | 15.9 |
| Negative | 4188 | 84.1 | |
| HIV test (last 12 months) | Yes | 2387 | 48.0 |
| No | 2590 | 52.0 | |
| Sexual intercourse (last 12 months) | Only men | 4381 | 88.0 |
| Men and women | 596 | 12.0 | |
| Rewarded sex | Yes | 1330 | 26.7 |
| No | 3647 | 73.3 | |
| Male sexual partners (last month) | Not answer | 332 | 6.7 |
| ≥6 partners | 294 | 5.9 | |
| 2–5 partners | 1269 | 25.5 | |
| 1 partner | 2184 | 43.9 | |
| Neither | 898 | 18.0 | |
| Aged at sexual debut with men | Missing | 222 | 4.5 |
| 8–10 years | 187 | 3.8 | |
| 11–15 years | 1417 | 28.5 | |
| 16–20 years | 2364 | 47.5 | |
| 21–25 years | 603 | 12.1 | |
| ≥26 years | 184 | 3.7 |
| Variables | Categories | Syphilis (%) | OR (95%CI) | ORa (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Mexico City | 24.0 | 1.8 (1.4–2.2) | 1.6 (1.3–1.9) |
| Center | 24.7 | 1.8 (1.5–2.3) | 1.9 (1.5–2.5) | |
| Northwest | 19.6 | 1.4 (1.1–1.8) | 1.2 (0.9–1.6) | |
| Northeast | 17.4 | 1.2 (0.9–1.5) | 1.1 (0.8–1.4) | |
| South | 23.4 | 1.7 (1.2–2.4) | 1.6 (1.1–2.2) | |
| West | 15.1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| Aged | ≥35 years | 28.2 | 3.0 (2.2–4.0) | 2.5 (1.8–3.5) |
| 30–34 years | 24.3 | 2.4 (1.8–3.3) | 1.9 (1.4–2.7) | |
| 25–29 years | 23.6 | 2.3 (1.8–3.1) | 2.0 (1.5–2.8) | |
| 20–24 years | 17.4 | 1.6 (1.2–2.1) | 1.4 (1.1–1.9) | |
| 18–19 years | 11.7 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| Goods | 0–3 | 25.6 | 1.4 (1.2–1.8) | 1.3 (1.1–1.7) |
| 4–6 | 21.2 | 1.1 (0.9–1.3) | 1.1 (0.9–1.3) | |
| 7–8 | 19.3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| Occupation | Employee | 22.8 | 1.7 (1.4–2.0) | 1.4 (1.1–1.7) |
| Unemployed | 19.5 | 1.4 (1.0–1.9) | 1.0 (0.7–1.5) | |
| Own business | 28.2 | 2.2 (1.6–3.1) | 1.6 (1.2–2.3) | |
| Others | 32.1 | 2.7 (1.5–4.8) | 1.9 (1.0–3.4) | |
| Student | 14.9 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| Inhalant drugs (last 12 months) | Any time | 31.1 | 1.8 (1.3–2.3) | 1.5 (1.1–2.1) |
| Never | 20.4 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| HIV infection | Positive | 36.0 | 2.5 (2.2–3.0) | 2.0 (1.7–2.4) |
| Negative | 18.1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| HIV test (last 12 months) | Yes | 23.9 | 1.4 (1.2–1.6) | 1.3 (1.1–1.5) |
| No | 18.2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| Sexual intercourse (last 12 months) | Only men | 21.6 | 1.5 (1.2–1.9) | 1.4 (1.1–1.8) |
| Men and women | 15.8 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| Rewarded sex | Yes | 25.6 | 1.4 (1.2–1.7) | 1.3 (1.1–1.5) |
| No | 19.2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| Male sexual partners (last month) | Not answer | 19.9 | 1.1 (0.8–1.5) | 1.1 (0.8–1.5) |
| ≥6 partners | 28.9 | 1.8 (1.4–2.5) | 1.4 (1.0–2.0) | |
| 2–5 partners | 23.9 | 1.4 (1.1–1.8) | 1.2 (0.9–1.5) | |
| 1 partner | 19.4 | 1.1 (0.9–1.3) | 1.0 (0.8–1.3) | |
| Neither | 18.2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| Aged at sexual debut with men | Missing | 15.8 | 0.8 (0.5–1.3) | 1.1 (0.7–2.0) |
| 8–10 years | 33.7 | 2.2 (1.3–3.5) | 2.0 (1.2–3.3) | |
| 11–15 years | 22.7 | 1.2 (0.8–1.8) | 1.4(0.9–2.1) | |
| 16–20 years | 20.1 | 1.1 (0.7–1.6) | 1.3 (0.9–2.0) | |
| 21–25 years | 18.7 | 1.0 (0.6–1.5) | 1.1 (0.7–1.6) | |
| ≥26 years | 19.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| STATUS | Syphilis (-) HIV (-) | Syphilis (+) HIV (-) | Syphilis (-) HIV (+) | Syphilis (+) HIV (+) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 3431 (68.9) | 757 (15.2) | 505 (10.2) | 284 (5.7) | ||
| Variables | Categories | |||||
| Region | Mexico City | 25.9 | 29.3 | 33.1 | 39.4 | <0.001 |
| Center | 18.3 | 22.6 | 19.0 | 23.2 | ||
| Northwest | 14.3 | 13.3 | 13.3 | 12.3 | ||
| Northeast | 15.8 | 13.5 | 13.7 | 9.5 | ||
| South | 5.5 | 6.9 | 7.7 | 6.3 | ||
| West | 20.2 | 14.4 | 13.3 | 9.2 | ||
| Aged | ≥35 years | 14.9 | 21.5 | 22.2 | 28.9 | <0.001 |
| 30–34 years | 12.0 | 13.5 | 16.8 | 20.1 | ||
| 25–29 years | 21.7 | 24.7 | 22.8 | 27.8 | ||
| 20–24 years | 37.0 | 32.5 | 30.9 | 19.4 | ||
| 18–19 years | 14.3 | 7.8 | 7.3 | 3.9 | ||
| Goods | 0–3 | 10.7 | 14.0 | 12.7 | 14.8 | 0.017 |
| 4–6 | 46.4 | 48.5 | 48.1 | 44.7 | ||
| 7–8 | 42.9 | 37.5 | 39.2 | 40.5 | ||
| Occupation | Employed | 59.8 | 67.1 | 61.4 | 66.2 | <0.001 |
| Unemployed | 5.7 | 5.7 | 10.1 | 6.0 | ||
| Own business | 4.7 | 6.3 | 5.1 | 9.2 | ||
| Others | 0.8 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.1 | ||
| Student | 28.9 | 18.9 | 21.6 | 7.6 | ||
| Inhalable drugs (last 12 months) | Yes | 3.8 | 6.7 | 6.3 | 7.7 | <0.001 |
| No | 96.2 | 93.3 | 93.7 | 92.3 | ||
| HIV test (last 12 months) | Yes | 45.4 | 53.0 | 51.7 | 59.5 | <0.001 |
| No | 54.6 | 47.0 | 48.3 | 40.5 | ||
| Sexual intercourse (last 12 months) | Only men | 86.6 | 89.6 | 91.7 | 94.7 | <0.001 |
| Men and women | 13.4 | 10.4 | 8.3 | 5.3 | ||
| Rewarded sex | Yes | 24.2 | 30.3 | 31.9 | 39.1 | <0.001 |
| No | 75.8 | 69.7 | 68.1 | 60.9 | ||
| Male sexual partners (last month) | Not answer | 6.6 | 5.8 | 7.9 | 7.7 | <0.001 |
| ≥6 partners | 5.2 | 8.2 | 6.3 | 8.1 | ||
| 2–5 partners | 24.1 | 28.1 | 27.7 | 31.7 | ||
| One partner | 45.1 | 42.5 | 41.8 | 35.9 | ||
| Neither | 19.0 | 15.3 | 16.2 | 16.5 | ||
| Aged at sexual debut with men | Missing | 5.0 | 3.0 | 3.2 | 4.2 | <0.001 |
| 8–10 years | 2.9 | 5.2 | 5.1 | 8.5 | ||
| 11–15 years | 27.3 | 29.6 | 31.7 | 34.2 | ||
| 16–20 years | 48.2 | 47.0 | 46.7 | 41.5 | ||
| 21–25 years | 12.7 | 11.2 | 10.7 | 9.9 | ||
| ≥26 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 2.6 | 1.8 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vergara-Ortega, D.N.; Tapia-Maltos, A.; Herrera-Ortíz, A.; García-Cisneros, S.; Olamendi-Portugal, M.; Sánchez-Alemán, M.Á. High Prevalence of Syphilis and Syphilis/HIV Coinfection among Men Who Have Sex with Men Who Attend Meeting Places in Mexico. Pathogens 2023, 12, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030356
Vergara-Ortega DN, Tapia-Maltos A, Herrera-Ortíz A, García-Cisneros S, Olamendi-Portugal M, Sánchez-Alemán MÁ. High Prevalence of Syphilis and Syphilis/HIV Coinfection among Men Who Have Sex with Men Who Attend Meeting Places in Mexico. Pathogens. 2023; 12(3):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030356
Chicago/Turabian StyleVergara-Ortega, Dayana Nicté, Andrés Tapia-Maltos, Antonia Herrera-Ortíz, Santa García-Cisneros, María Olamendi-Portugal, and Miguel Ángel Sánchez-Alemán. 2023. "High Prevalence of Syphilis and Syphilis/HIV Coinfection among Men Who Have Sex with Men Who Attend Meeting Places in Mexico" Pathogens 12, no. 3: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030356
APA StyleVergara-Ortega, D. N., Tapia-Maltos, A., Herrera-Ortíz, A., García-Cisneros, S., Olamendi-Portugal, M., & Sánchez-Alemán, M. Á. (2023). High Prevalence of Syphilis and Syphilis/HIV Coinfection among Men Who Have Sex with Men Who Attend Meeting Places in Mexico. Pathogens, 12(3), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030356










