HPV16 Impacts NHERF2 Expression in Oropharyngeal Cancers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Samples
2.2. DNA Isolation and Genotyping
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
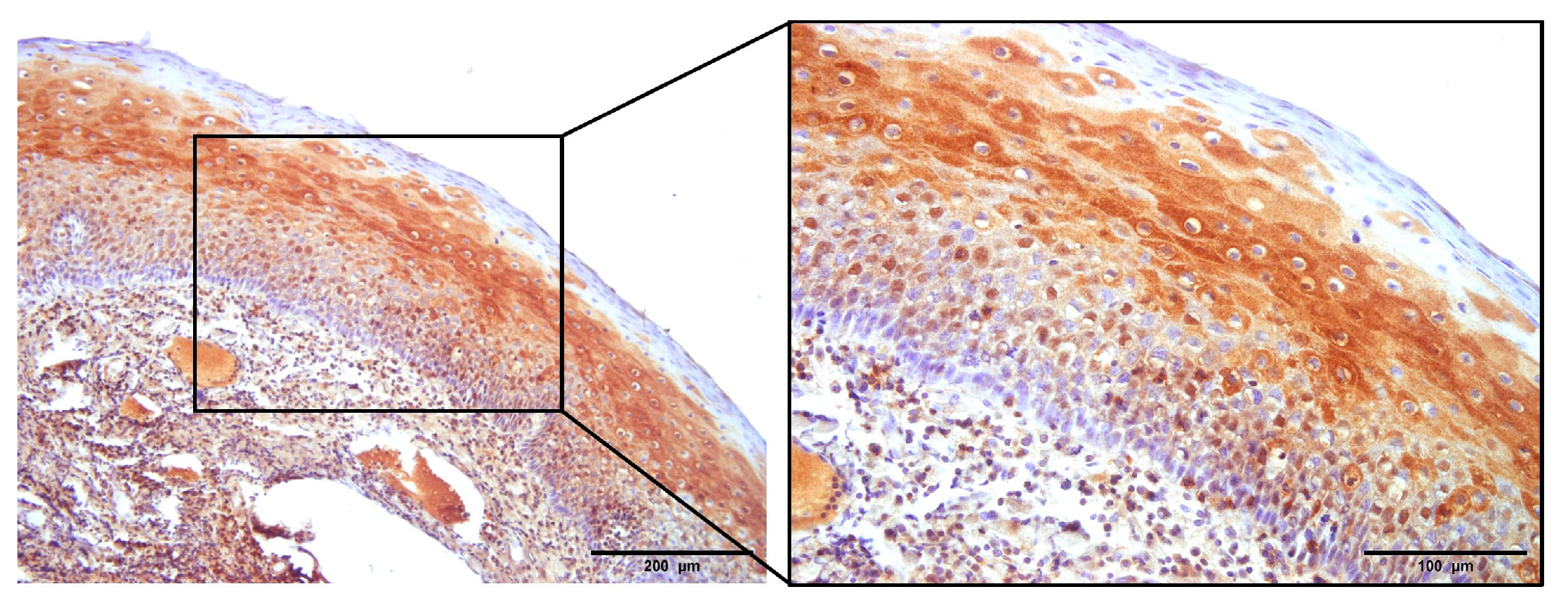
3.1. The Expression of p16
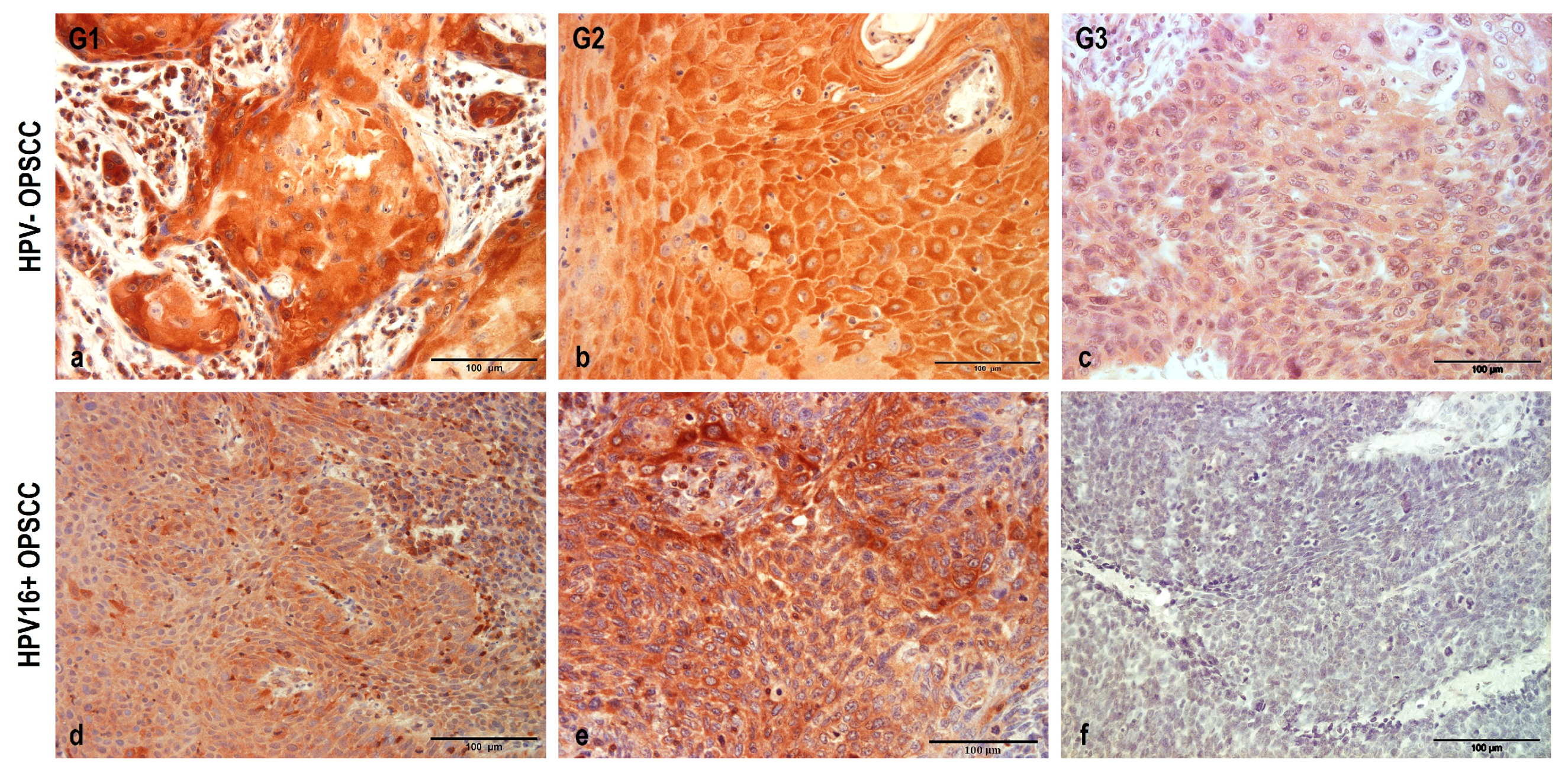
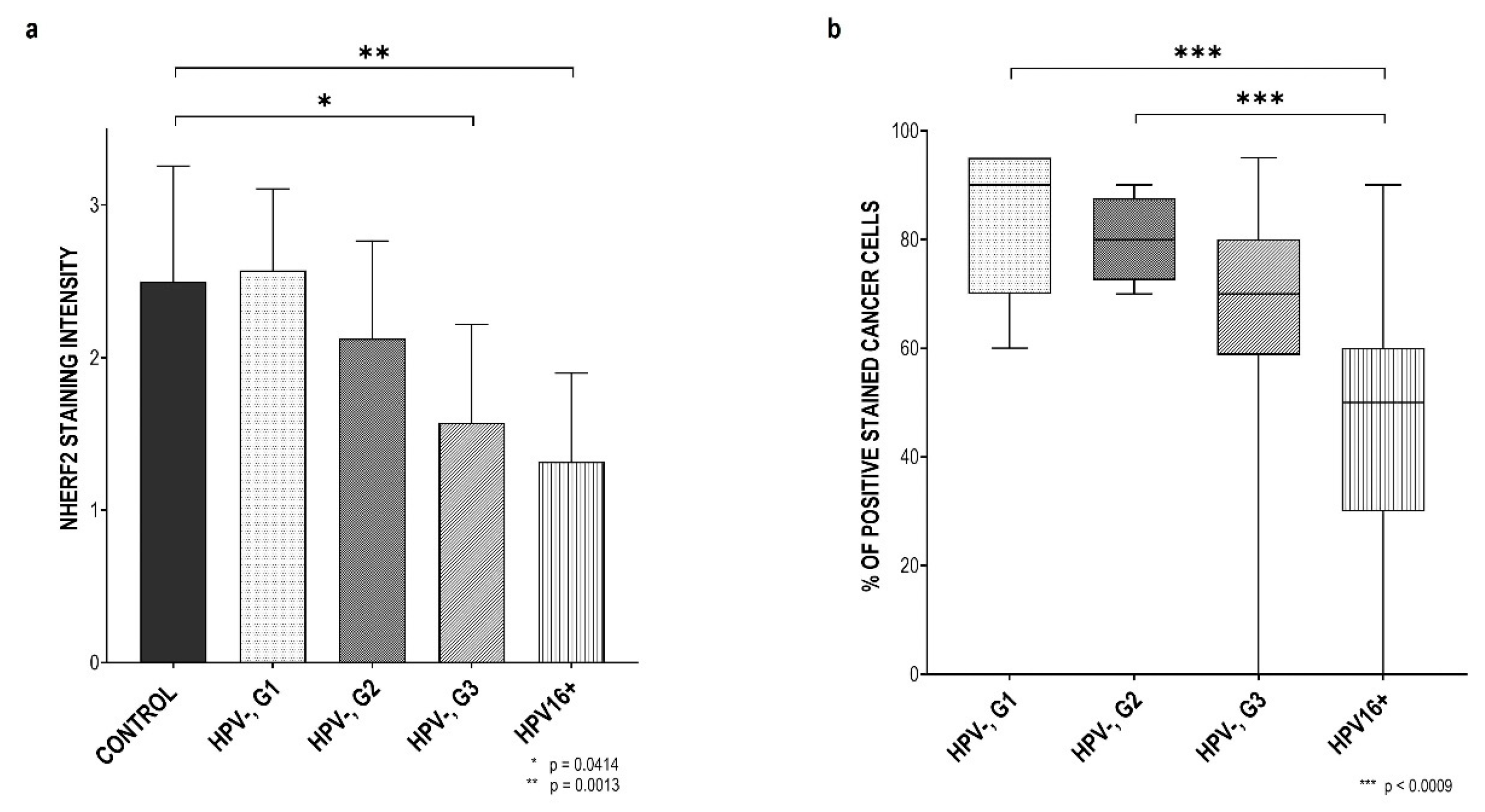
3.2. NHERF2 Expression Intensity and Score Are Dependent on Tumor Grade and HPV16 Positivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, J.D.; Burtness, B.; Le, Q.T.; Ferris, R.L. The Changing Therapeutic Landscape of Head and Neck Cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC (Ed.) Human Papillomaviruses. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2007; Volume 90, ISBN 978-92-832-1290-4. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, S.I.; Westra, W.H. Molecular Pathology of Head and Neck Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2009, 4, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, M.; Liu, J.; Masterson, L.; Fenton, T.R. HPV-Associated Oropharyngeal Cancer: Epidemiology, Molecular Biology and Clinical Management. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 306–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, H.; Beech, T.; Nicholson, T.; El-Hariry, I.; McConkey, C.; Paleri, V.; Roberts, S. Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus in Oropharyngeal and Nonoropharyngeal Head and Neck Cancer-Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Trends by Time and Region. Head Neck 2013, 35, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huibregtse, J.M.; Scheffner, M.; Howley, P.M. A Cellular Protein Mediates Association of P53 with the E6 Oncoprotein of Human Papillomavirus Types 16 or 18. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 4129–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, M.S.; Edmonds, C.; Fisher, C.; Schiller, J.T.; Lowy, D.R.; Vousden, K.H. The Region of the HPV E7 Oncoprotein Homologous to Adenovirus E1a and Sv40 Large T Antigen Contains Separate Domains for Rb Binding and Casein Kinase II Phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galati, L.; Chiocca, S.; Duca, D.; Tagliabue, M.; Simoens, C.; Gheit, T.; Arbyn, M.; Tommasino, M. HPV and Head and Neck Cancers: Towards Early Diagnosis and Prevention. Tumour Virus Res. 2022, 14, 200245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pešut, E.; Đukić, A.; Lulić, L.; Skelin, J.; Šimić, I.; Milutin Gašperov, N.; Tomaić, V.; Sabol, I.; Grce, M. Human Papillomaviruses-Associated Cancers: An Update of Current Knowledge. Viruses 2021, 13, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, H.-U.; Burk, R.D.; Chen, Z.; van Doorslaer, K.; zur Hausen, H.; de Villiers, E.-M. Classification of Papillomaviruses (PVs) Based on 189 PV Types and Proposal of Taxonomic Amendments. Virology 2010, 401, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvard, V.; Baan, R.; Straif, K.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; Ghissassi, F.E.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. A Review of Human Carcinogens—Part B: Biological Agents. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre-Garau, X.; Harlé, A. Pathology of HPV-Associated Head and Neck Carcinomas: Recent Data and Perspectives for the Development of Specific Tumor Markers. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 528957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Narayan, N.; Pim, D.; Tomaić, V.; Massimi, P.; Nagasaka, K.; Kranjec, C.; Gammoh, N.; Banks, L. Human Papillomaviruses, Cervical Cancer and Cell Polarity. Oncogene 2008, 27, 7018–7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrefaey, S.; Massaro, M.A.; Chiocca, S.; Chiesa, F.; Ansarin, M. HPV in Oropharyngeal Cancer: The Basics to Know in Clinical Practice. ACTA Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2014, 34, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Best, S.R.; Niparko, K.J.; Pai, S.I. Biology of Human Papillomavirus Infection and Immune Therapy for HPV-Related Head and Neck Cancers. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 2012, 45, 807–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorbar, J.; Jenkins, D.; Stoler, M.H.; Bergeron, C. Biology of the Human Papillomavirus Life Cycle: The Basis for Understanding the Pathology of PreCancer and Cancer. In Human Papillomavirus; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 67–83. ISBN 978-0-12-814457-2. [Google Scholar]
- Harden, M.E.; Munger, K. Human Papillomavirus Molecular Biology. Mutat. Res. Mutat. Res. 2017, 772, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zur Hausen, H. Papillomaviruses and Cancer: From Basic Studies to Clinical Application. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Mima, M.; Imamoto, S.; Mizokami, H.; Kondo, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Misawa, K.; Hanazawa, T.; Kaneda, A. DNA Methylation and HPV-Associated Head and Neck Cancer. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorbar, J.; Quint, W.; Banks, L.; Bravo, I.G.; Stoler, M.; Broker, T.R.; Stanley, M.A. The Biology and Life-Cycle of Human Papillomaviruses. Vaccine 2012, 30, F55–F70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingelhutz, A.J.; Roman, A. Cellular Transformation by Human Papillomaviruses: Lessons Learned by Comparing High- and Low-Risk Viruses. Virology 2012, 424, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đukić, A.; Lulić, L.; Thomas, M.; Skelin, J.; Bennett Saidu, N.E.; Grce, M.; Banks, L.; Tomaić, V. HPV Oncoproteins and the Ubiquitin Proteasome System: A Signature of Malignancy? Pathogens 2020, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, K.; Zhou, X.; Hayakawa, H.; Cho, J.-Y.; Libermann, T.A.; Jin, J.; Wade Harper, J.; Munger, K. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E7 Oncoprotein Associates with the Cullin 2 Ubiquitin Ligase Complex, Which Contributes to Degradation of the Retinoblastoma Tumor Suppressor. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9737–9747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, M.S.; Mack, D.H.; Finicle, A.B.; Crook, T.; Vousden, K.H.; Laimins, L.A. Human Papillomavirus E6 Proteins Bind P53 in Vivo and Abrogate P53-Mediated Repression of Transcription. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3045–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganti, K.; Broniarczyk, J.; Manoubi, W.; Massimi, P.; Mittal, S.; Pim, D.; Szalmas, A.; Thatte, J.; Thomas, M.; Tomaić, V.; et al. The Human Papillomavirus E6 PDZ Binding Motif: From Life Cycle to Malignancy. Viruses 2015, 7, 3530–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Banks, L. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7 Oncoprotein-Induced Cell Transformation. Mutat. Res. Mutat. Res. 2017, 772, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pim, D.; Bergant, M.; Boon, S.S.; Ganti, K.; Kranjec, C.; Massimi, P.; Subbaiah, V.K.; Thomas, M.; Tomaić, V.; Banks, L. Human Papillomaviruses and the Specificity of PDZ Domain Targeting: HPV PDZ Interactions. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 3530–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardi, R.; Rubino, R.; Scalise, M.; Gheit, T.; Shahzad, N.; Thomas, M.; Banks, L.; Indiveri, C.; Sylla, B.S.; Cardone, R.A.; et al. E6 and E7 from Human Papillomavirus Type 16 Cooperate To Target the PDZ Protein Na/H Exchange Regulatory Factor 1. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8208–8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drews, C.M.; Case, S.; Vande Pol, S.B. E6 Proteins from High-Risk HPV, Low-Risk HPV, and Animal Papillomaviruses Activate the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway through E6AP-Dependent Degradation of NHERF1. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponaro, C.; Galati, L.; Gheit, T.; Pappagallo, S.A.; Zambetti, M.; Zito, F.A.; Cardone, R.A.; Reshkin, S.J.; Tommasino, M. Alteration of Na/H Exchange Regulatory Factor-1 Protein Levels in Anogenital Lesions Positive for Mucosal High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Type 16. Virology 2022, 576, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voltz, J.W.; Weinman, E.J.; Shenolikar, S. Expanding the Role of NHERF, a PDZ-Domain Containing Protein Adapter, to Growth Regulation. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6309–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Wang, E.; Dutta, S.K.; Vohra, P.K.; E, G.; Prakash, Y.S.; Mukhopadhyay, D. NHERF-2 Maintains Endothelial Homeostasis. Blood 2012, 119, 4798–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alao, J.P. The Regulation of Cyclin D1 Degradation: Roles in Cancer Development and the Potential for Therapeutic Invention. Mol. Cancer 2007, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, I.M.; Hengst, L.; Slingerland, J.M. The Cdk Inhibitor P27 in Human Cancer: Prognostic Potential and Relevance to Anticancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidu, N.E.B.; Filić, V.; Thomas, M.; Sarabia-Vega, V.; Đukić, A.; Miljković, F.; Banks, L.; Tomaić, V. PDZ Domain-Containing Protein NHERF-2 Is a Novel Target of Human Papillomavirus 16 (HPV-16) and HPV-18. J. Virol. 2019, 94, e00663-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zito Marino, F.; Ronchi, A.; Stilo, M.; Cozzolino, I.; La Mantia, E.; Colacurci, N.; Colella, G.; Franco, R. Multiplex HPV RNA in Situ Hybridization/P16 Immunohistochemistry: A Novel Approach to Detect Papillomavirus in HPV-Related Cancers. A Novel Multiplex ISH/IHC Assay to Detect HPV. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2020, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dok, R.; Nuyts, S. HPV Positive Head and Neck Cancers: Molecular Pathogenesis and Evolving Treatment Strategies. Cancers 2016, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lulić, L.; Jakovčević, A.; Manojlović, L.; Dediol, E.; Banks, L.; Tomaić, V. Human DLG1 and SCRIB Are Distinctly Regulated Independently of HPV-16 during the Progression of Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas: A Preliminary Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesnikova, I.; Lidang, M.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; Koch, J. Rapid, Sensitive, Type Specific PCR Detection of the E7 Region of Human Papillomavirus Type 16 and 18 from Paraffin Embedded Sections of Cervical Carcinoma. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2010, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijders, P.J.F.; van den Brule, A.J.C.; Schrijnemakers, H.F.J.; Snow, G.; Meijer, C.J.L.M.; Walboomers, J.M.M. The Use of General Primers in the Polymerase Chain Reaction Permits the Detection of a Broad Spectrum of Human Papillomavirus Genotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanjose, S.; Quint, W.G.; Alemany, L.; Geraets, D.T.; Klaustermeier, J.E.; Lloveras, B.; Tous, S.; Felix, A.; Bravo, L.E.; Shin, H.-R.; et al. Human Papillomavirus Genotype Attribution in Invasive Cervical Cancer: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Worldwide Study. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milutin-Ga, N. Retrospective Study of the Prevalence of High-Risk Human Papillomaviruses among Croatian Women. Coll. Antropol. 2007, 31, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Baay, M.F.; Quint, W.G.; Koudstaal, J.; Hollema, H.; Duk, J.M.; Burger, M.P.; Stolz, E.; Herbrink, P. Comprehensive Study of Several General and Type-Specific Primer Pairs for Detection of Human Papillomavirus DNA by PCR in Paraffin-Embedded Cervical Carcinomas. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, B.; Hafkamp, H.C.; Haesevoets, A.; Manni, J.J.; Slootweg, P.J.; Weissenborn, S.J.; Klussmann, J.P.; Speel, E.-J.M. P16INK4A Overexpression Is Frequently Detected in Tumour-Free Tonsil Tissue without Association with HPV: Tumour-Free Tonsils, P16INK4A and HPV. Histopathology 2010, 56, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golusiński, P.; Pazdrowski, J.; Szewczyk, M.; Misiołek, M.; Pietruszewska, W.; Klatka, J.; Okła, S.; Kaźmierczak, H.; Marszałek, A.; Filas, V.; et al. Is Immunohistochemical Evaluation of P16 in Oropharyngeal Cancer Enough to Predict the HPV Positivity? Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2017, 22, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blitzer, G.C.; Smith, M.A.; Harris, S.L.; Kimple, R.J. Review of the Clinical and Biologic Aspects of Human Papillomavirus-Positive Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Head and Neck. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 88, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, M.E.; Chiocca, S. Human Papillomavirus as a Driver of Head and Neck Cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S. HPV-Related Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oropharynx: A Review. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 73, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martel, C.; Plummer, M.; Vignat, J.; Franceschi, S. Worldwide Burden of Cancer Attributable to HPV by Site, Country and HPV Type: Worldwide Burden of Cancer Attributable to HPV. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, A.A. Human Papillomaviruses: Diversity, Infection and Host Interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Du, G.; Yu, Z.; Si, Y.; Martin, T.A.; He, J.; Cheng, S.; Jiang, W.G. A Novel NHERF1 Mutation in Human Breast Cancer and Effects on Malignant Progression. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audagnotto, M.; Dal Peraro, M. Protein Post-Translational Modifications: In Silico Prediction Tools and Molecular Modeling. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, M.-M.; Morales, F.; Molina, J.; Hayashi, Y. Roles of NHERF1/EBP50 in Cancer. Curr. Mol. Med. 2008, 8, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Zhao, L.; Grigoryan, G.; Shim, H.; He, P.; Yun, C.C. Deletion of Na+/H+ Exchanger Regulatory Factor 2 Represses Colon Cancer Progress by Suppression of Stat3 and CD24. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G586–G598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Glaunsinger, B.; Pim, D.; Javier, R.; Banks, L. HPV E6 and MAGUK Protein Interactions: Determination of the Molecular Basis for Speci®c Protein Recognition and Degradation. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5431–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Massimi, P.; Navarro, C.; Borg, J.-P.; Banks, L. The HScrib/Dlg Apico-Basal Control Complex Is Differentially Targeted by HPV-16 and HPV-18 E6 Proteins. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6222–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lulić, L.; Jakovčević, A.; Kovačić, I.; Manojlović, L.; Dediol, E.; Skelin, J.; Tomaić, V. HPV16 Impacts NHERF2 Expression in Oropharyngeal Cancers. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081013
Lulić L, Jakovčević A, Kovačić I, Manojlović L, Dediol E, Skelin J, Tomaić V. HPV16 Impacts NHERF2 Expression in Oropharyngeal Cancers. Pathogens. 2023; 12(8):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081013
Chicago/Turabian StyleLulić, Lucija, Antonia Jakovčević, Iva Kovačić, Luka Manojlović, Emil Dediol, Josipa Skelin, and Vjekoslav Tomaić. 2023. "HPV16 Impacts NHERF2 Expression in Oropharyngeal Cancers" Pathogens 12, no. 8: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081013
APA StyleLulić, L., Jakovčević, A., Kovačić, I., Manojlović, L., Dediol, E., Skelin, J., & Tomaić, V. (2023). HPV16 Impacts NHERF2 Expression in Oropharyngeal Cancers. Pathogens, 12(8), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081013








